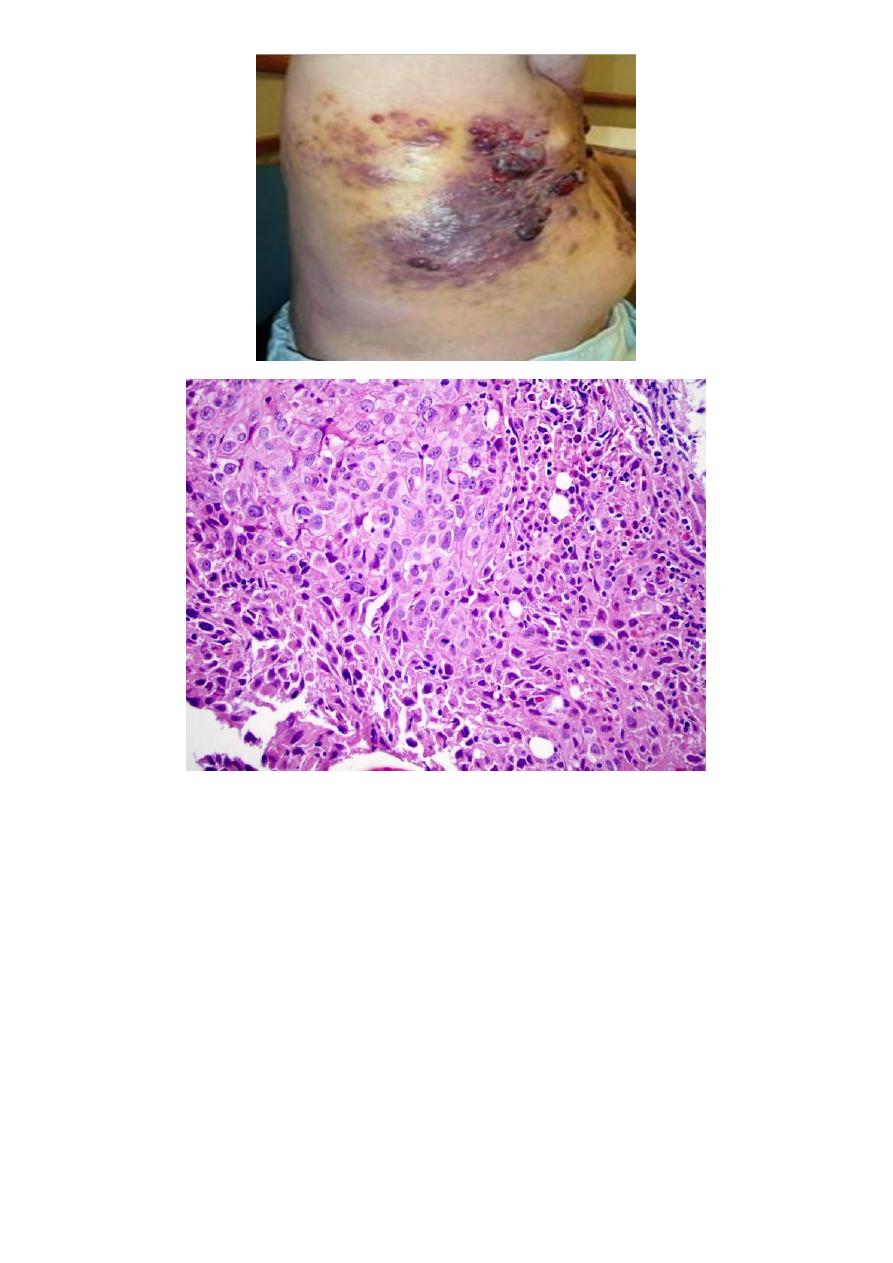
Vasculitis:
-
The term vasculitis is applied to any inflammatory involvement of an
artery, vein or venule, it's caused by infection, irradiation, mechanical
trauma and arthus reaction
But systemic necrotizing vasculitis which induced by immune
complexes, these complexes found accumulate in vessel walls by
deposition from circulation, by in situ formation or by combination of
these mechanism.
The classification of systemic vasculitis depend on the size of the
involved blood vessels, the anatomic site, the histologic characteristics
of the lesion and the clinical manifestations.
So the most common types of vasculitis.
1- Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN)
characterized by transmural acute necrotizing inflammation of
medium to small artiers, any organ or tissue of the body may be
affected except lungs and aorta with its primary branches..
2- Wegener's granulomatosis
this type of vasculiltis is necrotizing or granulomatous,
predominantly in the lungs but possibly elsewhere.
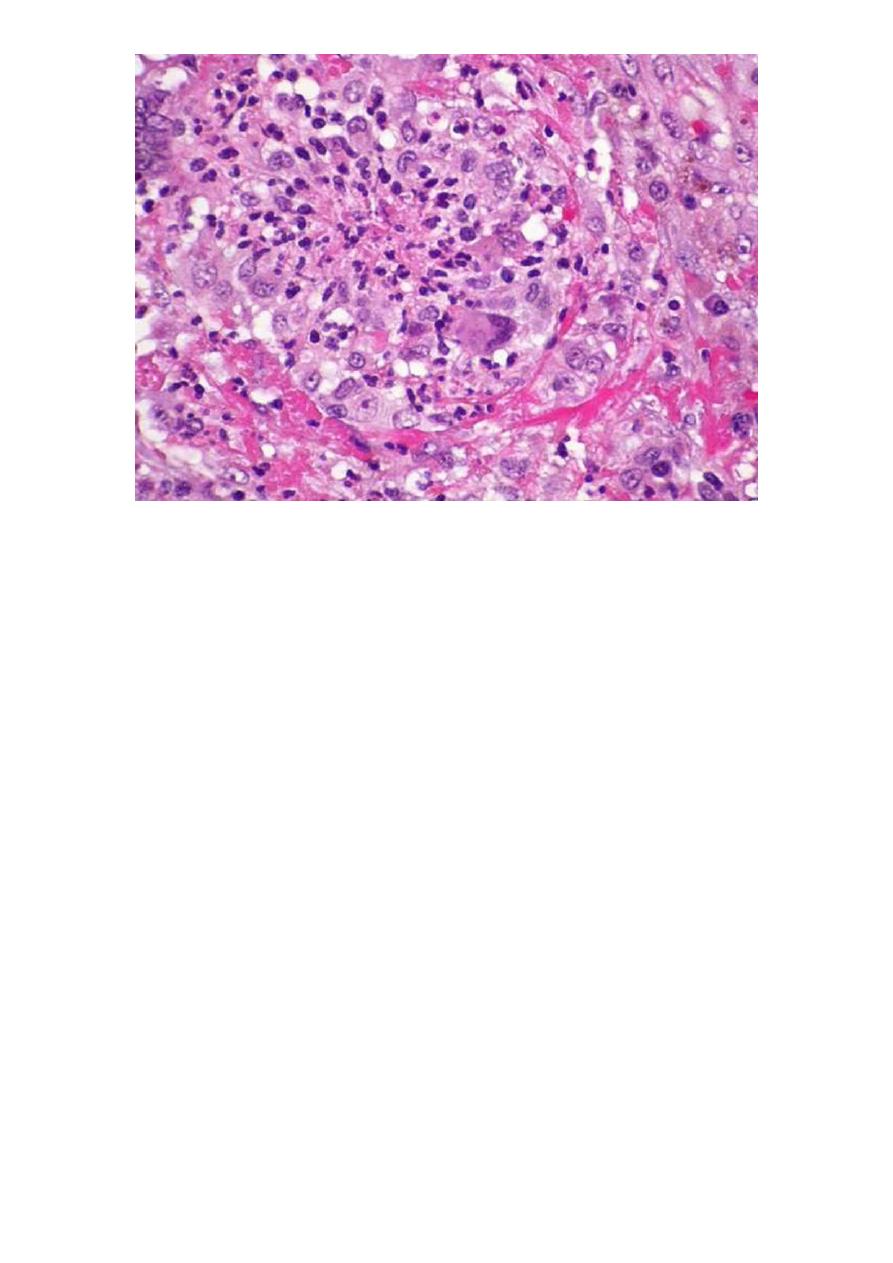
3- Microscopic polyangitis.
This type of necrotizing vasculitis generally affects smaller vessels
than PAN (arterioles, capillaries and venules).
4- Temporal( giant cell, cranial ) arteritis.
vasculitis involve larger arteries in the head especially the branches
of the carotid artery as temporal artery and ophthalmic artery.
5- Kawasaki's disease.
This type of vasculitis occur in skin, ocular, oral mucosa and coronary
artery, it characterized by occurance as acute febrile illness of infancy
and early childhood
6- Thromboangitis obliterans (Buerger's disease).
The wall of involved blood vessel usually acute and chronic inflamed
accompanied by thrombosis, the thrombosis characteristically contain
small microabscesses.
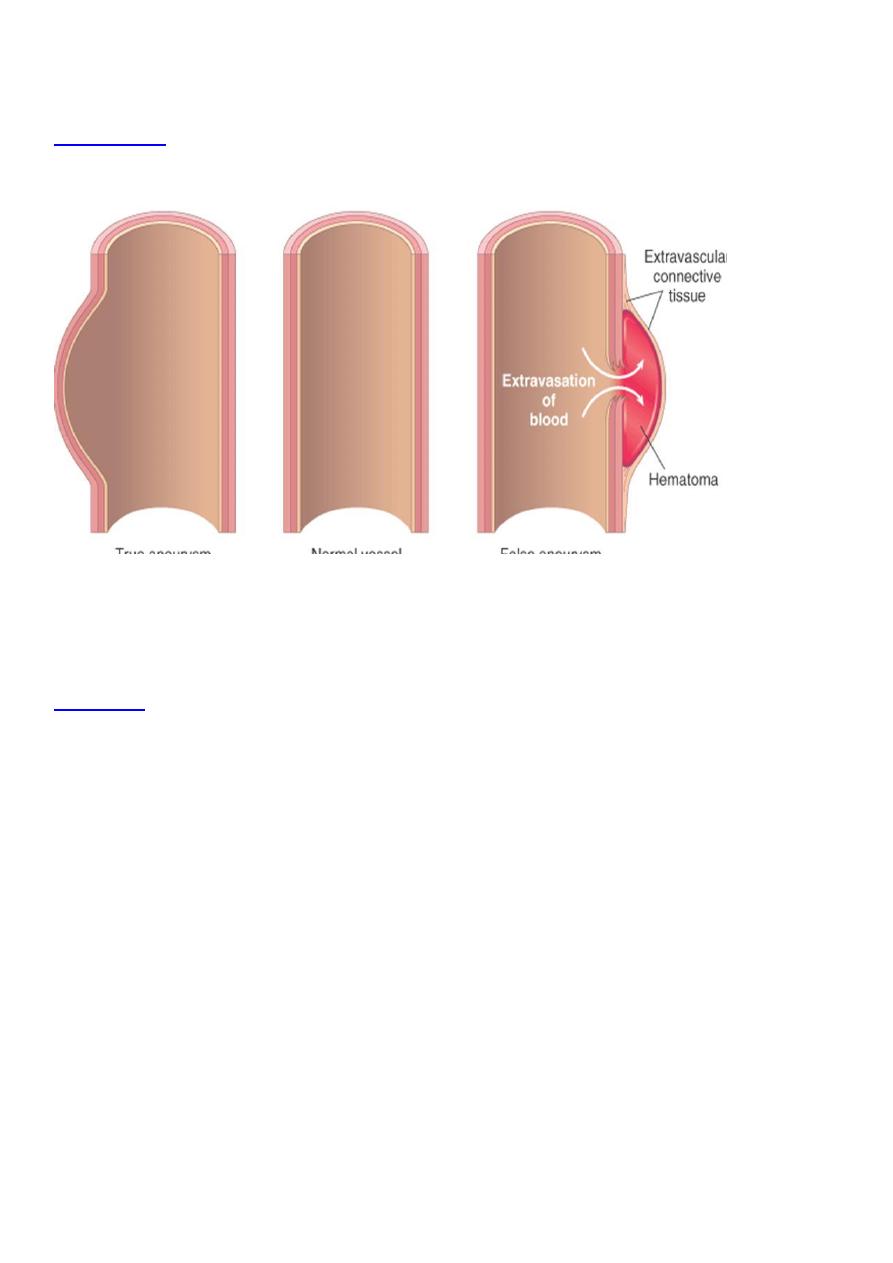
Aneurysm:
Aneurysms are congenital or acquired dilations of blood
-
:
Definition
vessels or the heart .
Cause of weakness in vessel wall either :
-
:
Etiology
1- Congenital defect e.g. intracranial arteries as saccular Berry
aneurysm.
2- Local infection (mycotic aneurysm or due to syphilis).
3- Trauma (traumatic aneurysm).
4- Systemic disease such as occur in aorta due to atherosclerosis and
cystic medial necrosis.
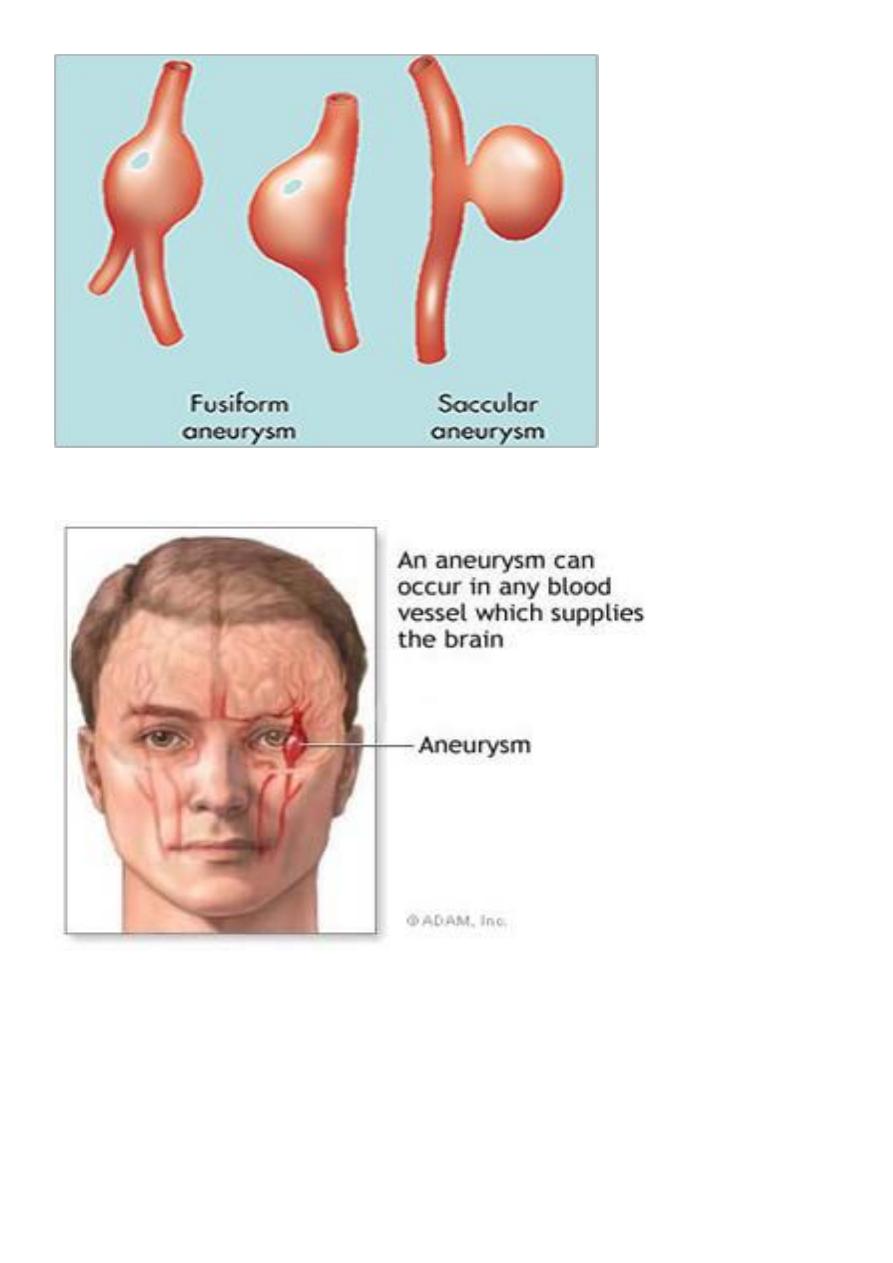
Atherosclerotic aneurysm:-
Which's usually occur in the abdominal aorta below renal arteries, its
etiology occur due to genetic defects in connective tissue component
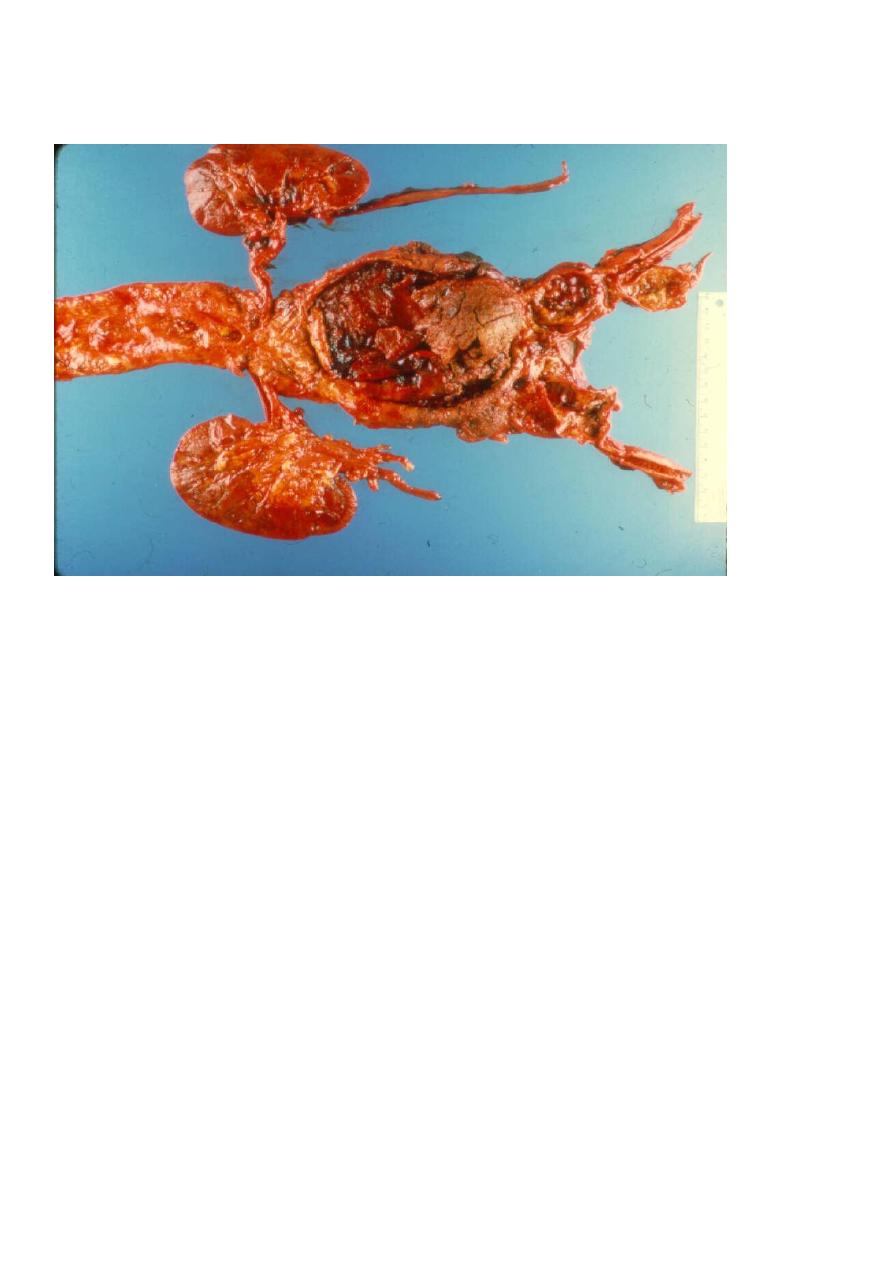

for strength of blood vessels in atherosclerotic and hypertensive which
will cause weakness of aortic wall.
Aortic dissection:
-
Definition:- dissection of blood along the laminar planes of the media
along with formation of a blood-filled channel within the aortic wall,
such a channel often ruptures, causing massive hemorrhage, it's
unusual to occur in severe atherosclerosis.

Venous disorders:
-
(I) Varicose veins:-
Are abnormally dilated tortuous veins, this condition caused by
increase in intraluminal pressure and loss of support of vessel wall.
(II) Phlebothrombosis and thrombophlebitis:-
These 2 names for same condition characterized by thrombus
formation in deep veins of lower extremities, this condition is silent
clinically but its complication is more serious by giving rise to emboli
that travel to the lung to produce pulmonary embolism and infarction
which will cause death when it's massive.
Lymphatic disorder:
-
The lymphatic disorders are divided into 2 categories:-
1- Primary diseases which are uncommon.
2- Secondary processes result from inflammation or cancer to give rise
2 lymphatic diseases→ lymphangitis and lymphedema.
Vascular tumors
:
It's divided into benign and malignant vascular tumor with
intermediate grade between the two.
Benign tumors:
-
The most common benign tumor of blood vessel is hemangioma
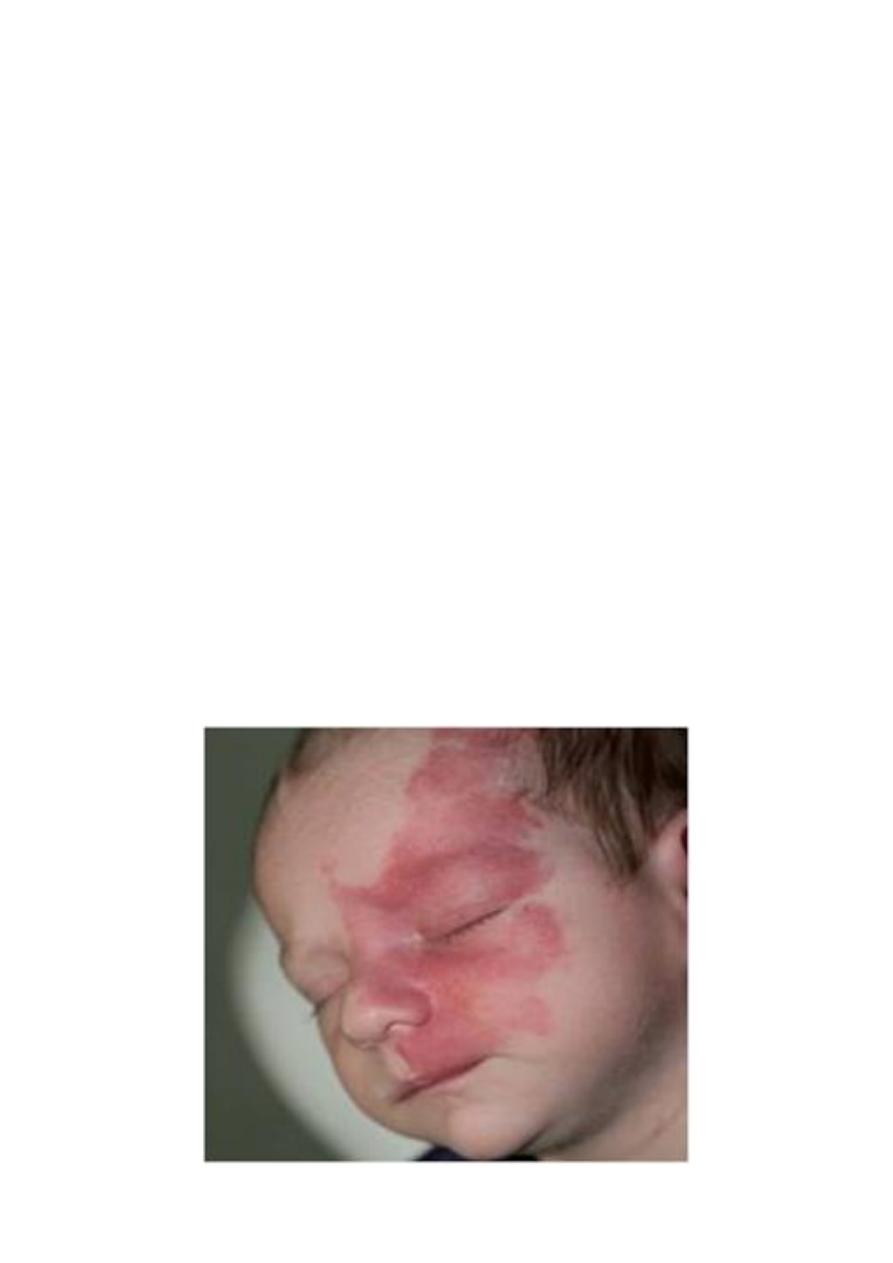
Capillary hemangioma:-
It's also occur in skin, subcutaneous tissue or mucous membrane of
oral cavity and lips, occasionally the hemangioma takes the form of
large, flat, map-like discoloration that cover large areas of face or
upper parts of body producing port wine stain.
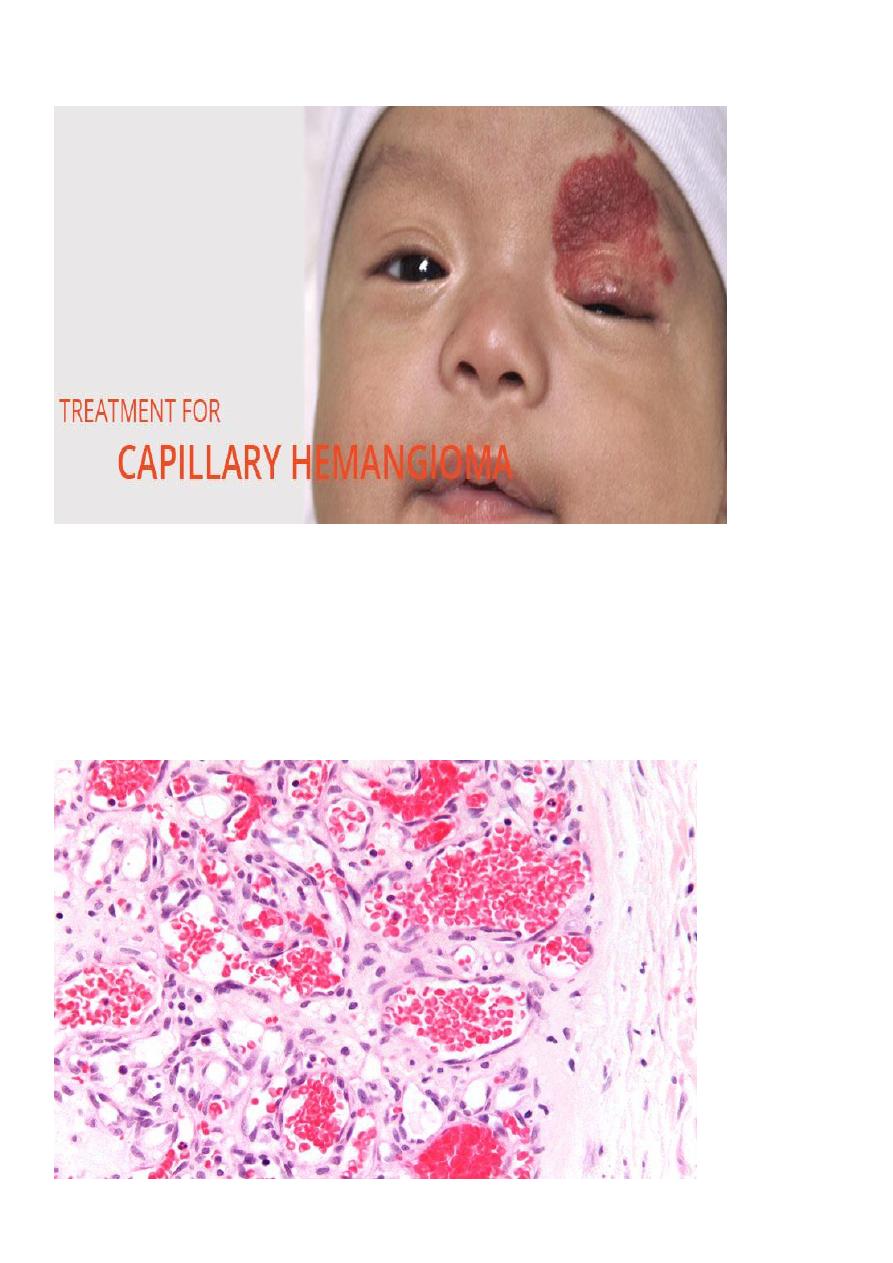
Microscopically
, it consists of uncapsulated closely packed capillaries
separated by a scant connective tissue stroma, the endothelium is
usually plumpy but no a typia present. The channels filled by fluid or
thrombosed blood .
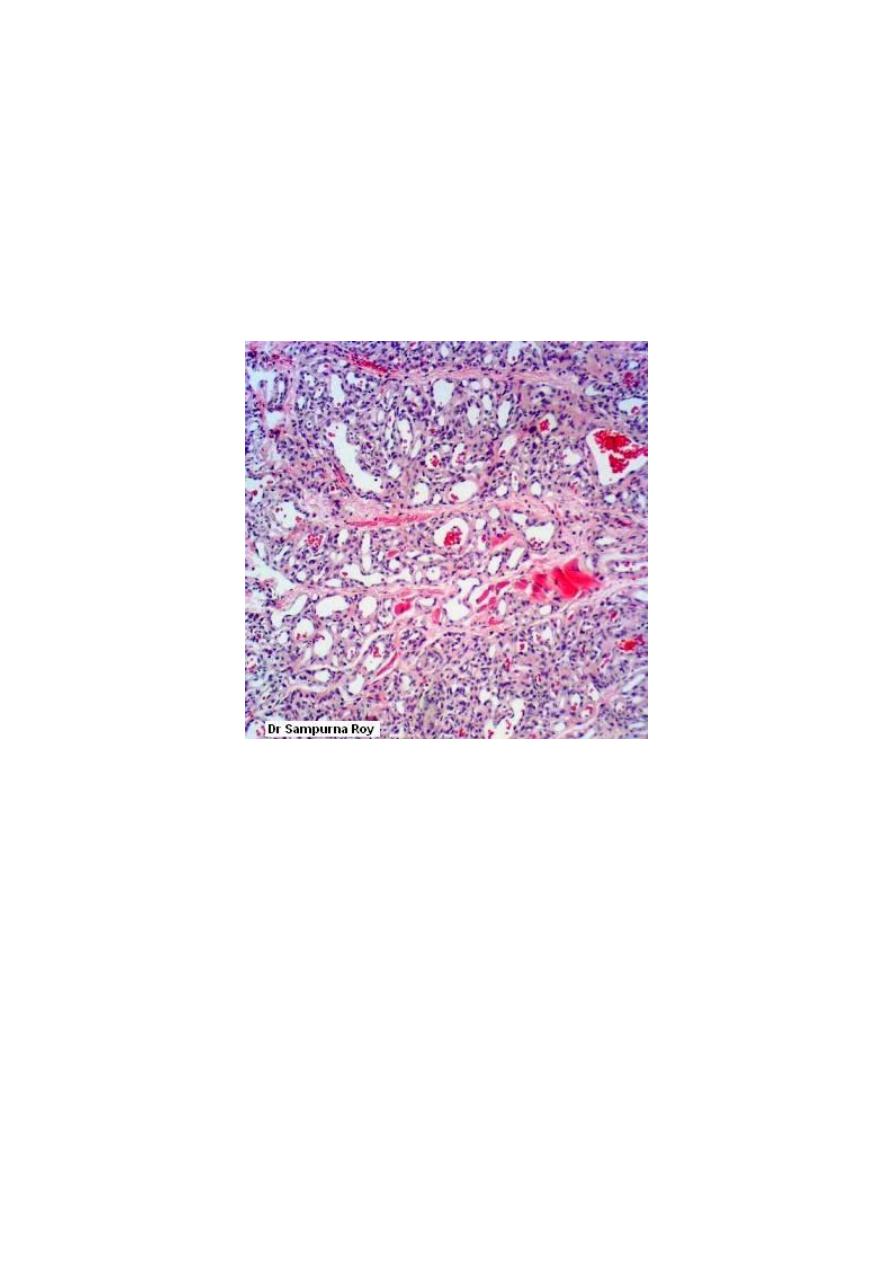
Hemangioendothelioma:-
It represents the intermediate grade between benign hemangioma
and malignant anaplastic angiosarcoma.
Microscopically
: consist of vascular channels with masses consist of
proliferating well-differntiated endothelial cells.
Angiosarcoma:
-
Microscopically
appear as masses of anaplastic cells with few poorly
formed vascular channels or may be not seen and in this case, it cannot
be differentiated from other malignant soft tissue tumor as
fibrosarcoma or leiomyosarcoma only by immunohistochemical study.