RESPIRATORY
DISTRESS
SYNDROME
(R.D.S.) :
Preterm infants have pulmonary immaturity which results
in surfactant deficiency.
Surfactant(produced by alveolar type 2 cells)lowers the
surface tension of the alveolar membrane. Without surfactant
the alveoli collapse at the end of each expiration. This in turn
leads to respiratory failure in the neonate.

The risk of R.D.S. is inversely correlated with
gestational age. Nearly all infants born before 28
weeks of pregnancy develop R.D.S. Those babies
have difficulty achieving adequate functional residual
capacity and maintaining alveolar aireation.
Risk
factors
for RDS include:
1. Previous sibling with RDS.
2. Maternal D.M.
3. Cesarean section(C.S.).
4. Rapid labor.
5. Multiple pregnancy.

INCIDENCE OF RDS DECREASES WITH :
a. Use of antenatal steroids.
!
b. Maternal hypertension. c.
Prolonged rupture of membranes.
SYNTHESIS OF SURFACTANT DEPENDS ON:
a. Normal temperature.
b. Normal PH.
c. Normal lung perfusion.

SURFACTANT
CONTAINS
:
1
.
Phosphatidyl choline(Lecithin) which
constitutes 60% of surfactant.
2.
Phosphatidyl
glycerol
.
3.
Phosphatidyl
inositol
.
SURFACTANT IS USED AS PROHYLAXIS AND AS RESCUE
TREATMENT FOR R.D.S.

S U R FA C TA N T
D E F IC IE N C Y
L E A D S
T O
:
!
a. Alveolar
collapse
and hypoventilation
with CO2 retention.
!
b. Reduced
lung
volume
and
compliance
with increased dead space.
c. Ventilation /
perfusion
mismatch
.
d. Pulmonary
hypertension
.
e.
Right to left (R-L)
shunt
.

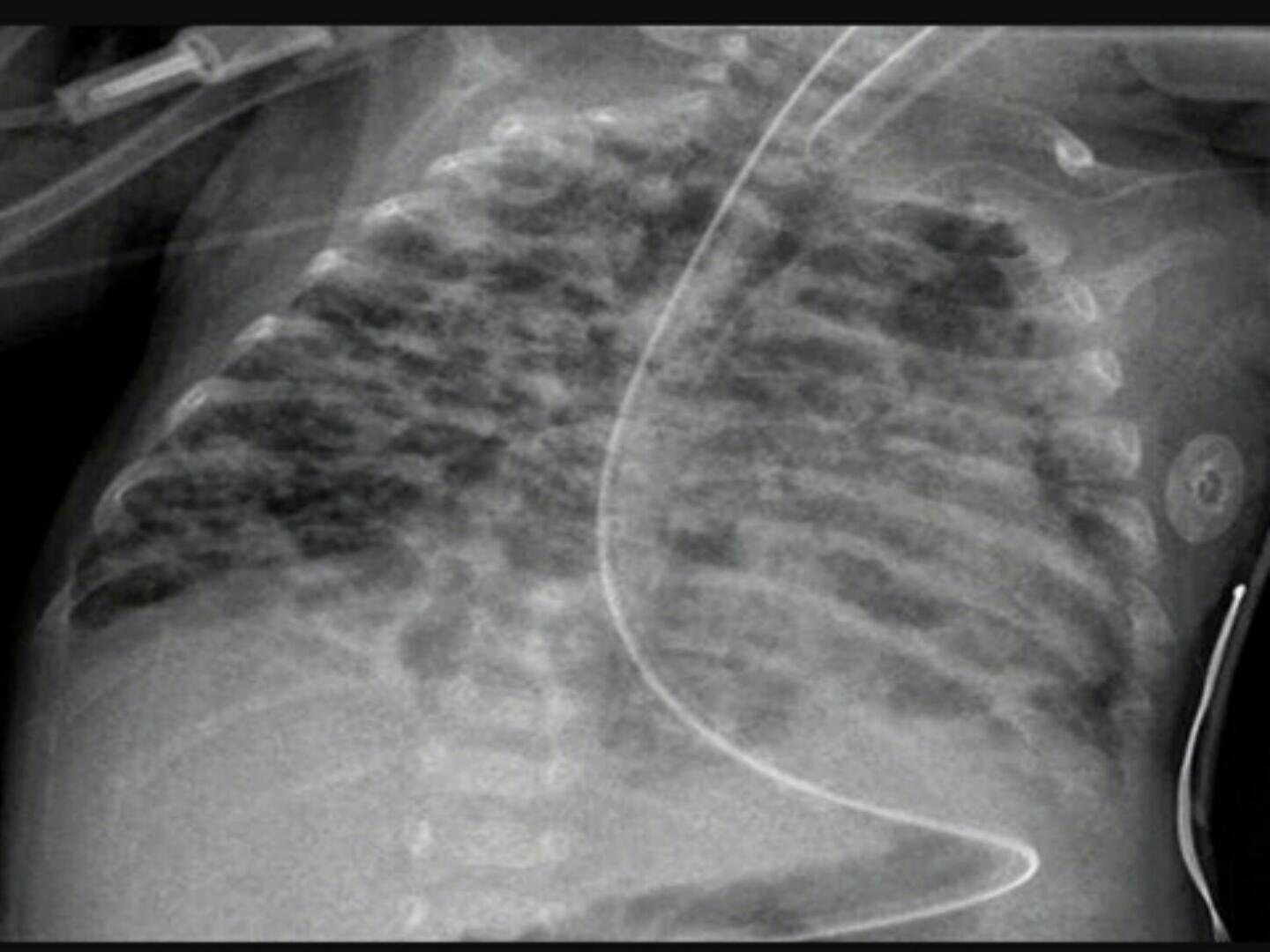
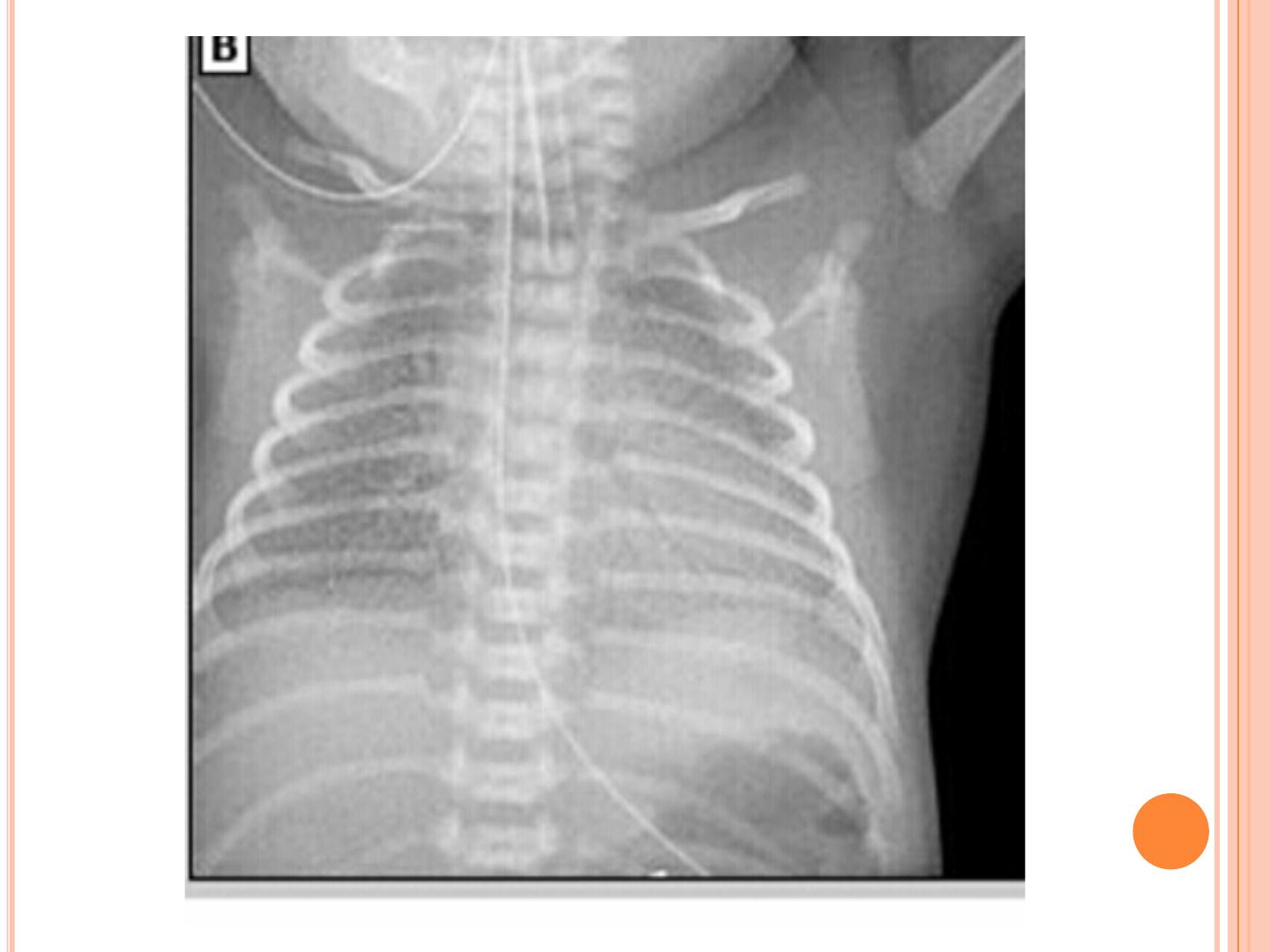
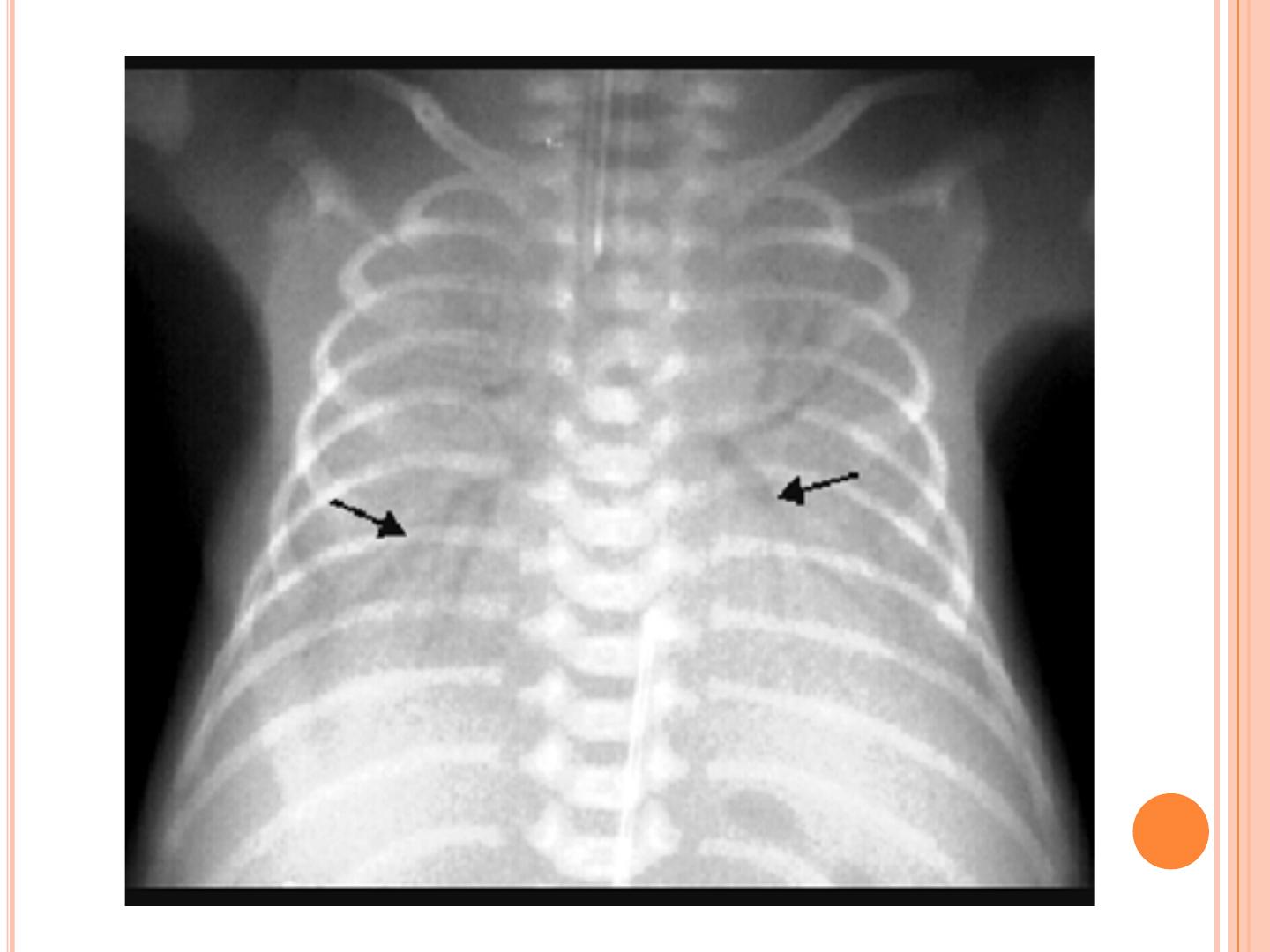
CLINICAL
PRESENTATION:
1. Tachypnea (respiratory rate > 60/min.).
2. Grunting.
!
3. Sternal, intercostals, subcostal retractions. 4.
Cyanosis in room air.
5. Oliguria.
6. Mixed respiratory and metabolic acidosis.
Grunting: is a short, low pitched sound heard when the
infant expires with a partially closed glottis.
It can conserve lung volume and keep the alveoli opened.
Grunting indicates a parenchymal disease and poor lung
compliance.





PREVENTION
OF
RDS
:
a. Good
antenatal
care
.
!
b. Good
selection
and
timing
of
C.S
.
!
c. Betamethasone(antenatal)
.
d.
Surfactant
replacement
.
.

ANTENATAL
STEROID
S:
When given to mothers suspected to get preterm
delivery (at 24-34 wk.) 1-2 days before delivery can
induce fetal surfactant production.
Betamethasone
(2 i.m. doses) is superior to
Dexamethasone
(4 i.m. or i.v.doses) which can
cause periventricular leukomalacia.

SURFACTANT
R E P L A C E M E N T
:
Given by trained physicians in qualified centers
3-4 ml/kg as 2 doses 12 hours apart via endotracheal tube.
Surfactant reduces the incidence and severity of major
complications of prematurity (R.D.S., I.V.H., N.E.C., P.D.A.,
B.P.D.), and also reduces NOSOCOMIAL INFECTIONS &
MORTALITY.
TYPES OF SURFACTANT:
a. Natural (bovine or porcine) is preferred.
b. Synthetic.
COMPLICATIONS OF SURFACTANT:
1. Blockage of endotracheal tube.
2. Hypoxia(transient).
3. Hypotension.

TREATMENT
OF
R.D.S
. :
!
1.
Avoid
doing
elective
C.S
.
for
low
risk
fetuses before 39 wk.
because surfactant
secretion generally increases during labor.
2.Early
treatment
with
surfactant
(within 20-30 min. after birth) will greatly
reduce the duration of mechanical ventilation
and the incidence of B.P.D.
3.Admission
to
the
N.I.C.U
. for optimal
supportive care which include the followings :

a. Maintain
temp
. at
36.5-37.5 at all times.
b. Correct
hypoxia
by O2( 85-93% ).
c. Correct
acid
–
base
abnormalities
.
d. Nutrition (20ml/kg/day of breast milk),T.P.N.
e. Antibiotic(Ampicillin & Gentamicin)because it is difficult to
differentiate R.D.S. from G.B.S. pneumonia.
!
f. Inhaled
nitrous
oxide (improves gas exchange).
!
g. Assisted
ventilation.
h. i.v. fluid (10%dextrose)70ml/Kg/day, electrolytes added
after 2 days.
f. Management of P.D.A.

CAUSES
OF
SUDDEN
DETERIORATION
OF
RDS WHILE
ON
SPONTANEOUS
BREATHING
:
!
1. Pneumothorax. 2.
Periventricular
hemorrhage. 3.
Infection. 4.
Aspiration. 5.
Apnea.

C O M P L IC AT IO N S
O F
R D S
:
1. Air leak .
2. P.D.A .
3. Periventricular hemorrhage .
4. Pneumonia .
!
5. Complications of mechanical ventilation.
6. Long term sequelae e.g. R.O.P. & B.P.D.