1
Induction of Labor
Definition
: Artificial TOP after fetal viability initiating labor process .
Incidence
: About 5 – 8% of all pregnancies end by induction .
Indications :
I- Maternal :
1. Medical disorders :
a. PIH :
* Eclampsia .
* Eminent eclampsia if not improvement for 24 hrs .
* Severe pre-eclampsia if no improvement for 1 week .
* At the end of 37 Ws in mild pre-eclampsia if no improvement for 3 Ws .
b. Deteriorating renal functions in cases with renal diseases , chronic
hypertension or Diabetes .
c. Progressive retinopathy specially in diabetic cases .
d. Deteriorated cardiac reserve in cases with cardiac diseases .
e. Chorea gravidarum and icterus gravidarum .
2. APH :
a. Concealed and combined types of accidental Hge .
b. Placenta previa with mild to moderate bleeding after 37 Ws.
3. Polyhydramnios Causing severe respiratory embarrassment .
4. Malignancies needing immediate therapy after fetal viability .
5. Some
maternal infections with deteriorating
general conditions as pyelonephritis
and TB .
II- Fetal :
1. IUFD if no spontaneous labor for 4 Ws or signs of infection or signs of
DIC or maternal anxiety .
2. IUGR if there is deteriorating in utero conditions .
3. Fetal congenital anomalies in the fetus after counseling of the parents .
4. Fetus of diabetic mother due to unexplained IUFD in the last month .
2
5. Some cases with Rh incompatibility with deteriorating fetal conditions
with no facilities of intrauterine exchange transfusion .
6. PROM after 36 Ws if no spontaneous labor for 12-2 hrs .
7. History of precipitate labor .
Factors Determining Success of Induction :
1. Age of pregnancy : The nearer the age of term the more the success .
2. Prienduction uterine activity : The more the active the uterus the more the
success .
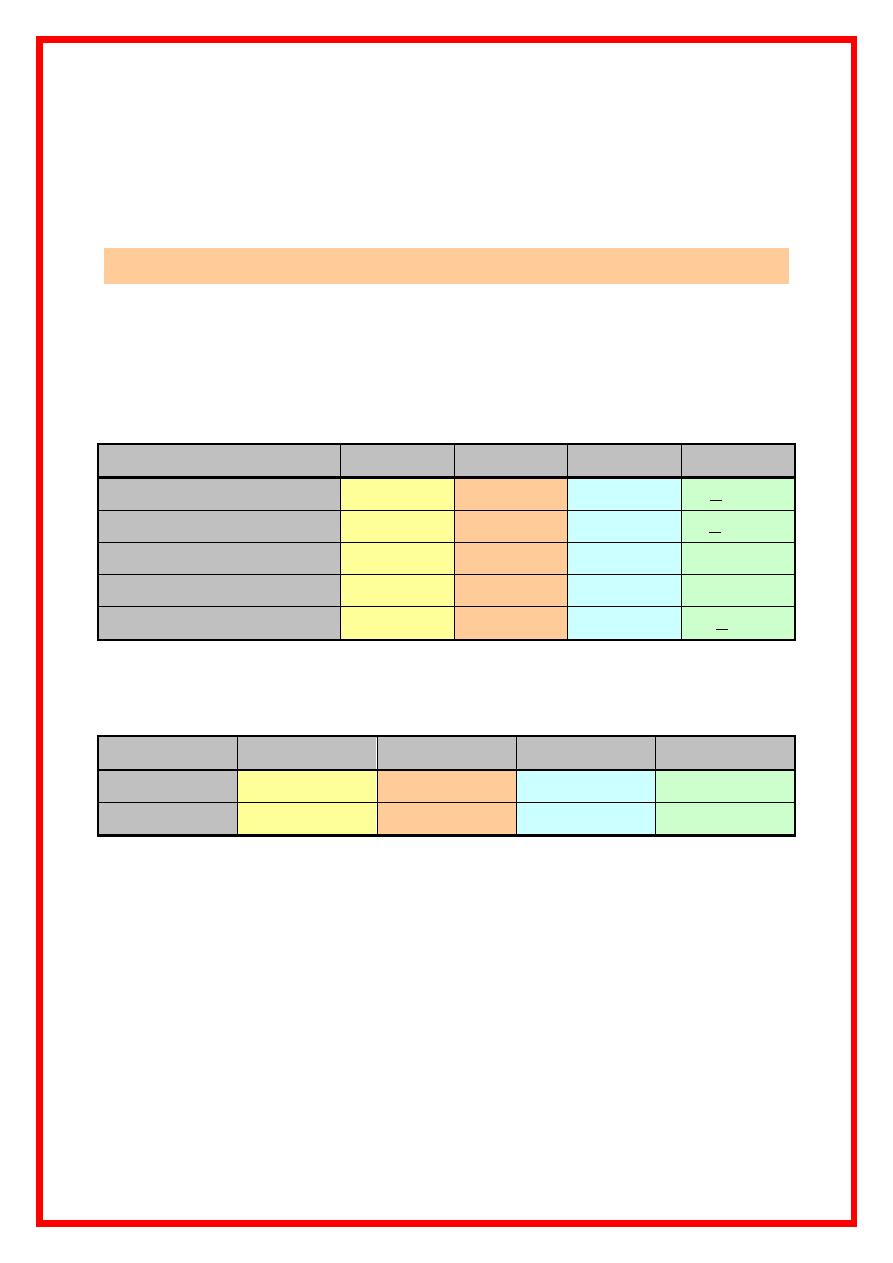
3. Bishop score :
* The higher the score , the more the success .
Item
0
1
2
3
Cervical effacement
0-30%
40-50%
60-70%
> 80%
Cervical dilatation
0 cm
1 – 2
3 – 4
> 5 cm
Cervical consistency
Firm
Mid
Soft
-------
Cervical position .
Posterior
Mid
Central
-------
Station
-3
-2
-1or 0
> + 1
* Score > 8 is usually successful ( > 6 is also described ) .
* A modification of Bishop score is described replacing the cervical effacement
percent with cervical length as following :
0
1
2
3
0 – 30 %
40 – 50
60 – 70
80 or more
Old
3 cm
2 cm
1 cm
0 = 100 %
New
4. Maternal disease : Diabetics and anemic are less responsive while cases
with PIH are more responsive ( due to relative uterine ischemia )
5. Maternal age : The older the mother the less the success .
6. Parity : The higher the parity , the less the success .
7. Method of induction :
PGs are the most successful methods specially in low score cases .
PGs , Oxytocin and AROM are more effective than the other methods .
3
Methods of Induction :
I- PGs :
* PGs are local hormones derived of the fatty acid arachidonic acid through the
action of the cyclo-oxygenase enzyme system .
* PGs have wide range of action allover the body as regulation of temperature ,
respiration , and genital functions. On the uterus , OGE
2
is vasodilator and
stimulant of contractions while PGF
2a
cause VC and stimulant for
contraction . The former is the used one specially with alive fetus .
* Mechanisms of action :
1. Ripening of the cervix by :
a. Breakdown and rearrangement of the collagen fibers .
b. Alteration of the hyaluronic acid content .
2. Stimulation of uterine activity ( ecbolic ) by increasing tone , intensity and
frequency of contractions . This done by increasing intracellular free Ca
++
.
PGE
2
is 10 times potent than PGF
2a
.
Selection of cases : Bishop score 4 or less .
Doses and administration :
1. Intravaginal ( most commonly used route ) :
a. PGE2 vaginal tablet ( Prostin E
2
containing 3-5 mg dinoprostone ) .
b. PGE1 analog (
Misoprostol, cytotec
): 25 ug every 3-6 hours (ACOG, 1999) .
Higher doses has significantly higher side effects ( tachyarrhythmias ,
fetal distress , meconium aspiration ) .
2. Intracervical : PGE
2
gel ( 0.5 mg PGE
2
) .
3. Oral route ( after amniotomy ) : PGE
2
0.5 in 100 ml water .
4. Extraovular route : Mainly in inducing preterm labor when the baby is
dead . Infusion of PGE
2
through a catheter introduced through the cervical
canal to the extra-amniotic space .
5. IV drip :
* PGE
2
( 1mg/ampule ) .
* Although very effective , this route is rarely used due to its systemic side
effects ( nausea , vomiting , diarrhea , bronchoconstriction in predisposed
cases and local venous reaction .
4
* Side effects :
1. Uterine hyperactivity ending in rupture uterus ( usually reversible by
terbutaline 250 ug SC ) .
2. Nausea , vomiting and diarrhea .
3. Hypotension and bradycardia .
4. Bronchospasm .
5. Fetal distress and low Apgar score .
6. Hyperthermia .
* C/I of PGs :
1. All C/I for use of ecbolics ( see abnormal uterine action ) .
2. Hypersensitivity to dinoprostone .
3. Acute PID .
4. Active cardiac , pulmonary renal or hepatic disorder .
5. Epilepsy
6. Glaucoma .
7. Bronchial asthma .
8. Rupture of membranes or APH ( inactivate the drug ) .
9. Allergy to PGs .
10. Active bleeding .
II- Oxytocin :
* It is a posterior pituitary neurohormone formed in the neuronal cells of the
paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus .
* Actions :
1. Stimulation of uterine activity . It causes increased uterine tone , intensity and
frequency of contractions . The effect of oxytocin is mainly dependent on the
amount of its receptors which is developed by estrogen . So the effect of
oxytocin is mainly late in pregnancy ( little effect in 2
nd
trimesteric
pregnancy ) . Oxytocin causes increases concentration of free Ca
++
in
myometrial cells .
2. Causes contraction of the myoepithelial cells of the lactiferous system leading
to milk letting postnatally .
3. Ripening of the cervix through release of endogenous PGs .
5
4. ADH like action leading to water retention .
5. Hypotension and reflex tachycardia .
* Types of oxytocins :
1. The crude extract of posterior pituitary is the 1
st
introduced preparation but
obsolete now due to the frequent coronary spasm noticed with its use and the
availability of purified preparation .
2. Purified natural oxytocin .
3. Synthetic oxytocin ( syntocinon , 1955 ) .
4. Combined oxytocin + Ergometrine ( syntometrine ) which is used active
management of 3
rd
stage .
* Routes of administration :
1. I.V drip is the most effective and most commonly used method (1/2 life = 5
minutes ) .
2. I.M and SC used mainly in treating post partum hemorrhage but not suitable
for induction of labor due to :
a. Unpredictable response .
b. Inability to withdraw rapidly .
c. Inability to control the dose precisely .
3. Nasal spray is mainly used for induction of lactation but not suitable for
induction due to irregular rate of absorption .
N.B
. : Oxytocin is not given orally as it is destroyed by saliva and gastric
secretions .
* Dose :
- Starting by as low as 0.5 mIU/min ( up to 6 mIU/min is described ) to be
increased by 1 – 6 mIU/ 15 – 60 min till attaining normal uterine action
( starting dosage is chosen according to the obstetric situation ) with a
maximum dose is 42 – 45 mIU/min . As labor advance , the dose is readjusted
according to the uterine activity ( keep uterine contractions at 3/10 min each
last for 60 sec ) . The drug is better to be diluted in saline or Ringer solution
to resist the ADH like action .
6
- In general , the high dose regimens are more effective but with more risk of
uterine hyperstimulation . However , because the short 1/2 life of the drug ,
this side effect is not a significant problem and is easily treated by stopping
the drug and decreasing the dose .
- The drug should be discontinued if uterine contractions become > 5 in 10 min
( 7 in 15 minutes ) or last for > 60 – 90 seconds or nonreassuring fetal heart
rate pattern .
* Complications :
1. Fetal distress due to abnormal tetanic uterine contractions .
2. Increased risk of rupture uterus if thee is any form of obstruction or in grand
multipara .
3. Increased incidence of premature separation of the placenta .
4. Increased incidence of contraction ring .
5. Increased risk for amniotic fluid embolism specially if given on unruptured
membranes . So , it should be given after rupture of membranes .
6. Increased risk of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia due to inhibition of hepatic
conjugation and due to inducing hemolysis .
7. Increased risk for water intoxication after prolonged use , use of large amount
of fluid specially on diluting the drug in glucose .
* C/I : See abnormal uterine action .
N.B
: Clinical uses of oxytocin :
1. Augmentation of labor .
2. Active management of 3
rd
stage of labor .
3. In preventing post partum hemorrhage when ergometrine is not available or C/I .
4. In treatment of post partum hemorrhage .
5. Induction of labor and some times of late 2
nd
trimester abortion .
6. Performing CST .
7. In stimulating milk letting .
7
III- Artificial rupture of membranes :
It is an effective method in selected cases and in some cases it is sufficient
alone to effect labor .
AROM causes stimulation of uterine action through :
1. Increased production of endogenous PGs ( see PROM ) .
2. Cause impaction of the head thus stretching the LUS Ferguson reflex.
* Prerequisites :
1. Vertex presentation with well coapted head on the cervix .
2. Ripped cervix .
3. No C/I for vaginal delivery .
* Types :
1. Forewater rupture : Through rupturing the bag of forewater after stripping of
the membranes from the LUS . It is the commonly done method as it is the
easiest but it abolishes the effect of the intact forewater bag as a cervical
dilator ( the best cervical dilator is an intact bag of forewater but its
forerunner of rival is a well flexed head ) .
2. Hind water rupture : Using Drew smythe catheter passed extraovular above
the fetal head to puncture the hind water bag . This method has less incidence
of cord prolapse , results in controlled drainage of liquor making it ideal in
cases with hydramnios and leaves an intact forewater bag . However it has a
higher incidence of injury of the uterine wall or the placenta .
* Timing :
1. Early : At 1-2 cm cervical dilatation .
2. Late : At 5 cm cervical dilatation .
* Methods :
1. Blind amniotomy using or toothed forceps kocher clamp .
2. Under vision through illuminated amnioscope using the amniotomy hook .
* Complications :
1. Cord prolapse .
2. IAI .
3. Drainage of liquor with dary labor .
8
4. APH due to placental injury or premature separation .
5. Injury of fetal scalp .
* C/I :
1. Non vertex presentation .
2. High head ( expect in stabilizing amniotomy )
3. Lower genital infection .
4. Cord presentation .
5. Concealed accidental He except after start of uterine contractions .
6. IUFD for fear of infection .
7. Prematurity .
8. Non ripped cervix or Bishop score 5 or less .
IV- Other methods :
1. Stripping of the membranes : Through digital separation of the
membranes from the lower uterine segment that produces endogenous
PGs ( 2/3 of cases will start labor within 72 hours ) . It appears effective ,
safe ( no increased risk of PROM or infection ) .
2. Extra-amniotic insertion of Foly's catheter and inflating the balloon with
30 cc fluid with or without saline infusion : Was found to be associated
with significant improvement of Bishop score and shortening of duration
of labour ( similar or even better than PGs ) .
3. Hygroscopic cervical dilators ( Laminaria , lamicel and dilapan ) : Are
Also associated with accelerated cervical ripening similar to PGs , balloon
and extra-amniotic saline infusion .
4. Breast and uterine massage .
5. How vaginal douche or tampon .
6. Castor oil + Enema + Hot bath .
7. Quinine HCL orally .
