
1
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
Lecture 8 - Neurophysioloy Dr. Noor
2
nd
stage 2020
Limbic System
Objective:
1.
Functional Anatomy of the Limbic System?
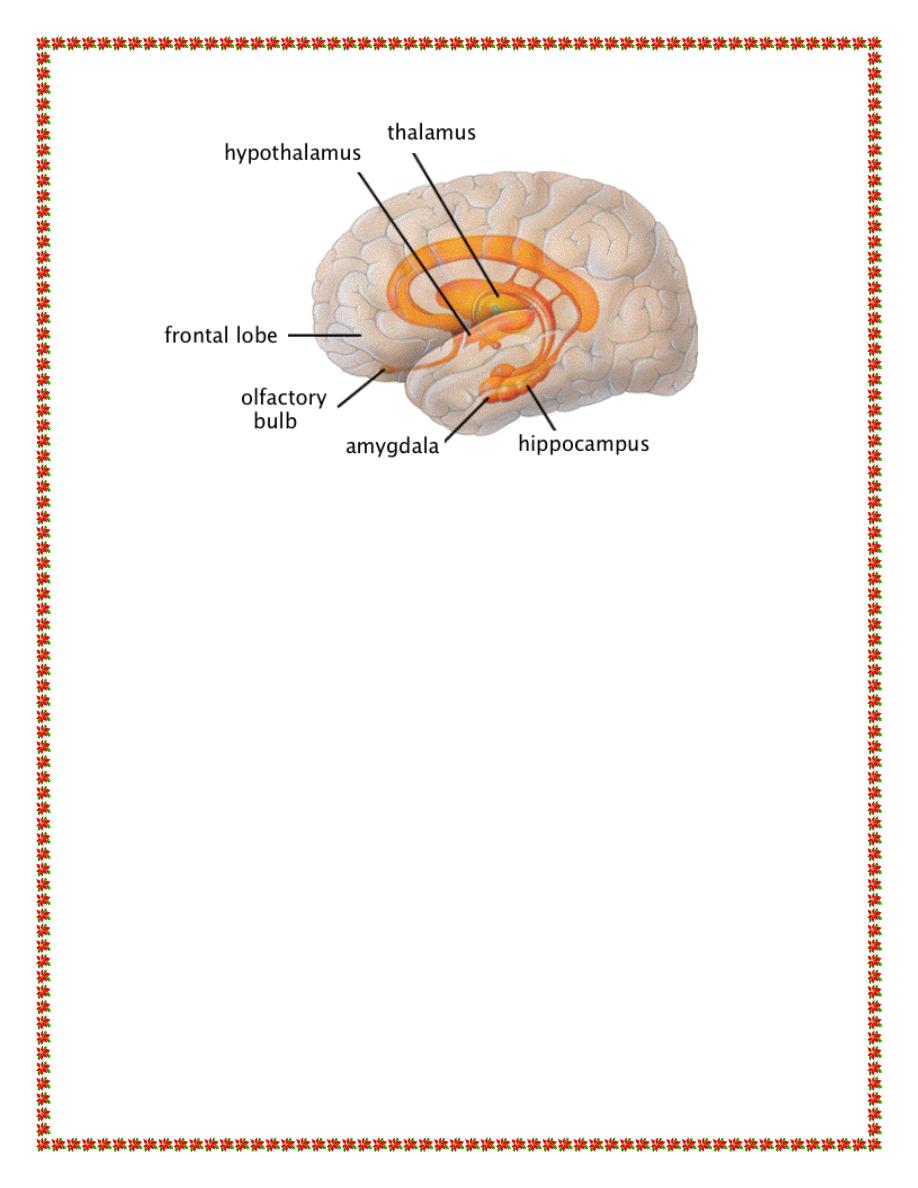
The limbic system is a complex set of structures that lies on both
sides of the thalamus, just under the cerebrum. It includes the
hypothalamus, the hippocampus, the amygdala, and several other
nearby areas. The word “limbic” means “border.” Originally, the
term “limbic” was used to describe the border structures around the
basal regions of the cerebrum, term limbic system has been
expanded to mean the entire neuronal circuitry that controls
emotional behavior and motivational drives.
2
A major Part of the limbic system is the hypothalamus, with its
related structures. In addition to their roles in behavioral control,
these areas control many internal conditions of the body, such as
body temperature, osmolality of the body fluids, and the drives to
eat and drink and to control body weight. These internal functions
are collectively called vegetative functions of the brain, and their
control is closely related to behavior.
Functional Anatomy of the Limbic System
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is a small part of the brain located just below the
thalamus on both sides of the third ventricle. (The ventricles are
areas within the cerebrum that are filled with cerebrospinal fluid,
and connect to the fluid in the spine.) It sits just inside the two

3
tracts of the optic nerve, and just above (and intimately connected
with) the pituitary gland.
The hypothalamus is one of the busiest parts of the brain, and is
mainly concerned with homeostasis. Homeostasis is the process of
returning something to some “set point.” It works like a
thermostat: When your room gets too cold, the thermostat conveys
that information to the furnace and turns it on. As your room
warms up and the temperature gets beyond a certain point, it sends
a signal that tells the furnace to turn off.
The hypothalamus is responsible for regulating your hunger, thirst,
response to pain, levels of pleasure, sexual satisfaction, anger and
aggressive behavior, and more. It also regulates the functioning of
the autonomic nervous system , which in turn means it regulates
things like pulse, blood pressure, breathing, and arousal in response
to emotional circumstances.
The hypothalamus receives inputs from a number of sources. From
the vagus nerve, it gets information about blood pressure and the
distension of the gut (that is, how full your stomach is). From the
reticular formation in the brainstem, it gets information about skin
temperature. From the optic nerve, it gets information about light
and darkness. From unusual neurons lining the ventricles, it gets
information about the contents of the cerebrospinal fluid, including

4
toxins that lead to vomiting. And from the other parts of the limbic
system and the olfactory (smell) nerves, it gets information that
helps regulate eating and sexuality. The hypothalamus also has
some receptors of its own, that provide information about ion
balance and temperature of the blood.
The other way the hypothalamus controls things is via the pituitary
gland. It is neurally and chemically connected to the pituitary,
which in turn pumps hormones called releasing factors into the
bloodstream. As you know, the pituitary is the so-called “master
gland,” and these hormones are vitally important in regulating
growth and metabolism.
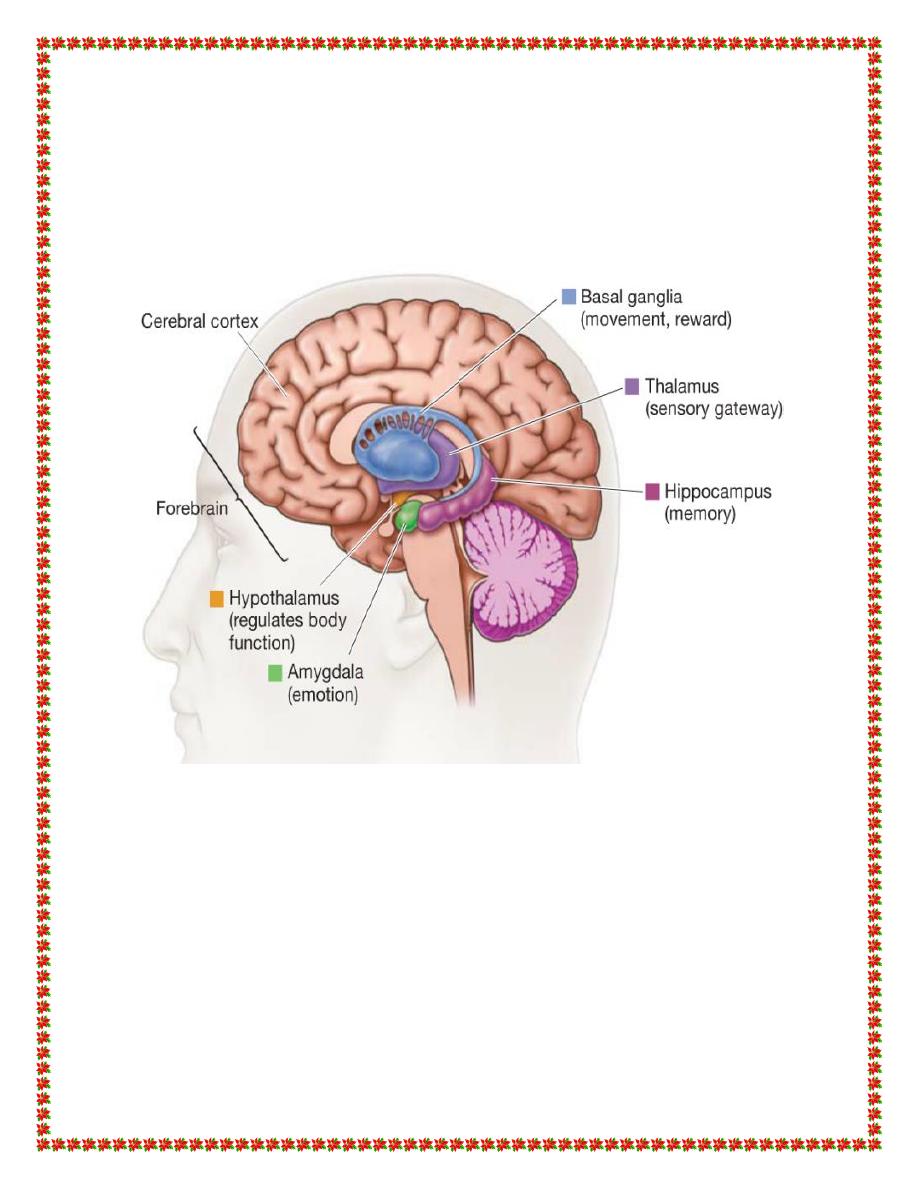
Hippocampus
The hippocampus consists of two “horns” that curve back from the
amygdala. It appears to be very important in converting things that
are “in your mind” at the moment (in short-term memory) into
things that you will remember for the long run (long-term
memory).
If the hippocampus is damaged, a person cannot build new
memories, and lives instead in a strange world where everything
they experience just fades away, even while older memories from
the time before the damage are untouched! .
5
As in other limbic structures, stimulation of different areas in the
hippocampus can cause almost any of the different behavioral
patterns such as pleasure, rage, passivity, or excess sex drive.
Another feature of the hippocampus is that it can become
hyperexcitable. For instance, weak electrical stimuli can cause focal
epileptic seizures in small areas of the hippocampi. These often
persist for many seconds after the stimulation is over, suggesting
6
that the hippocampi can perhaps give off prolonged output signals
even under normal functioning conditions.
Amygdala
The amygdalas are two almond-shaped masses of neurons on either
side of the thalamus at the lower end of the hippocampus. When it
is stimulated electrically, animals respond with aggression. And if
the amygdala is removed, animals get very tame and no longer
respond to things that would have caused rage before. But there is
more to it than just anger: When removed, animals also become
indifferent to stimuli that would have otherwise have caused fear
and even sexual responses
.
physiology,
References : Guyton and Hall textbook of medical
thirteen edition
