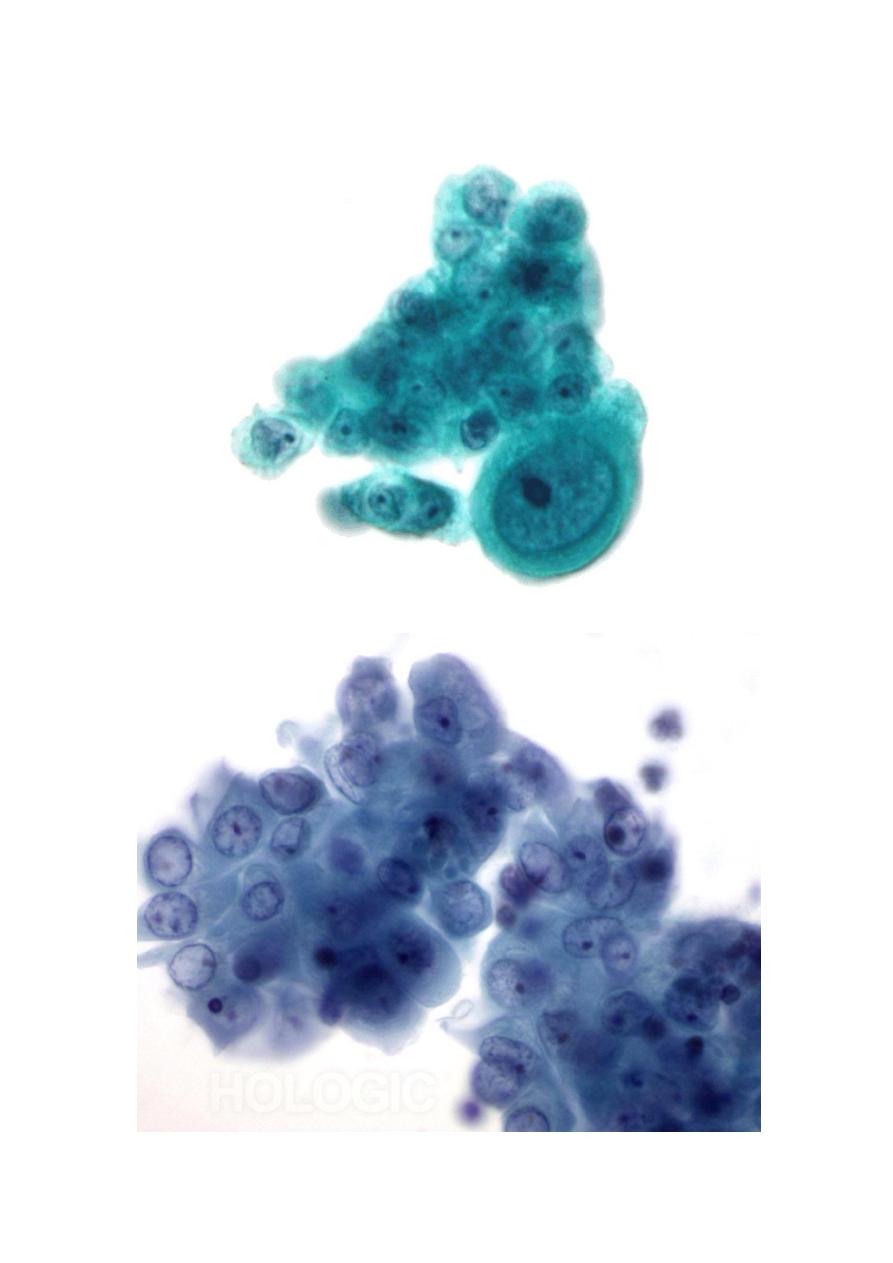
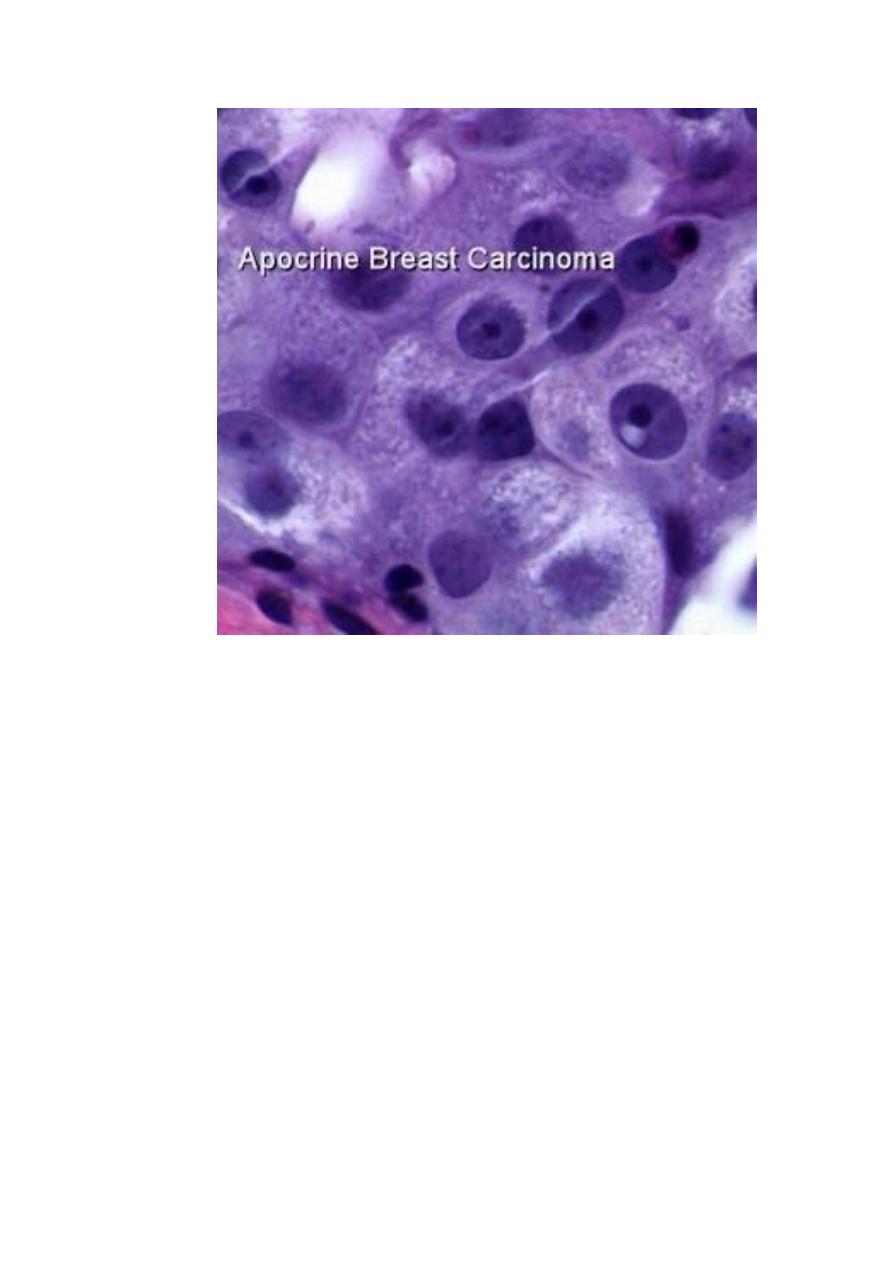
. Cytological method
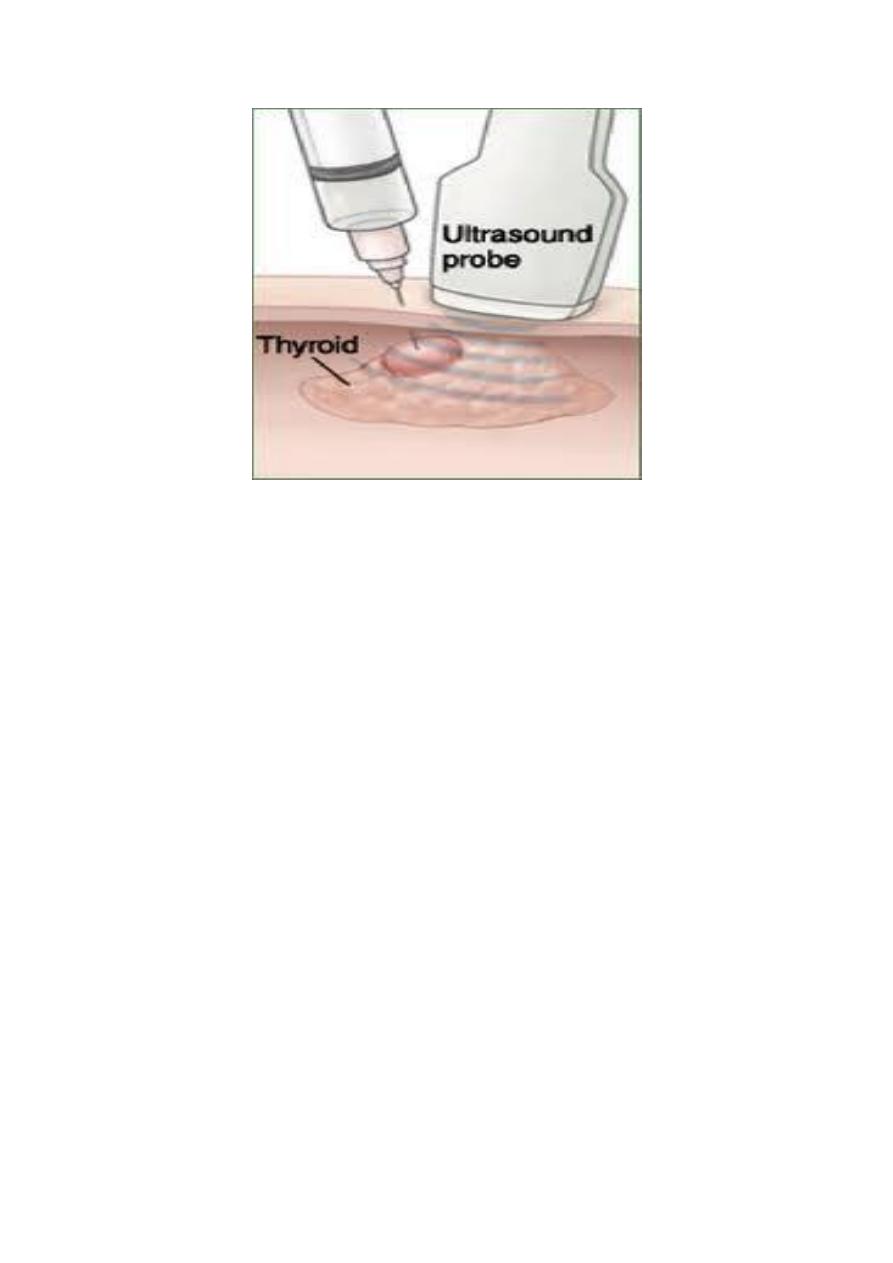
1-Fine needle aspiration is now widely used as a diagnostic
procedure for palpable masses (e.g., breast, lymph nodes, soft
tissue masses). Ultrasound or CT scan guided FNA (and/or true
cut needle biopsy) is also being increasingly used for deep-
seated masses as Lung, liver, kidney, retroperitoneum, etc.
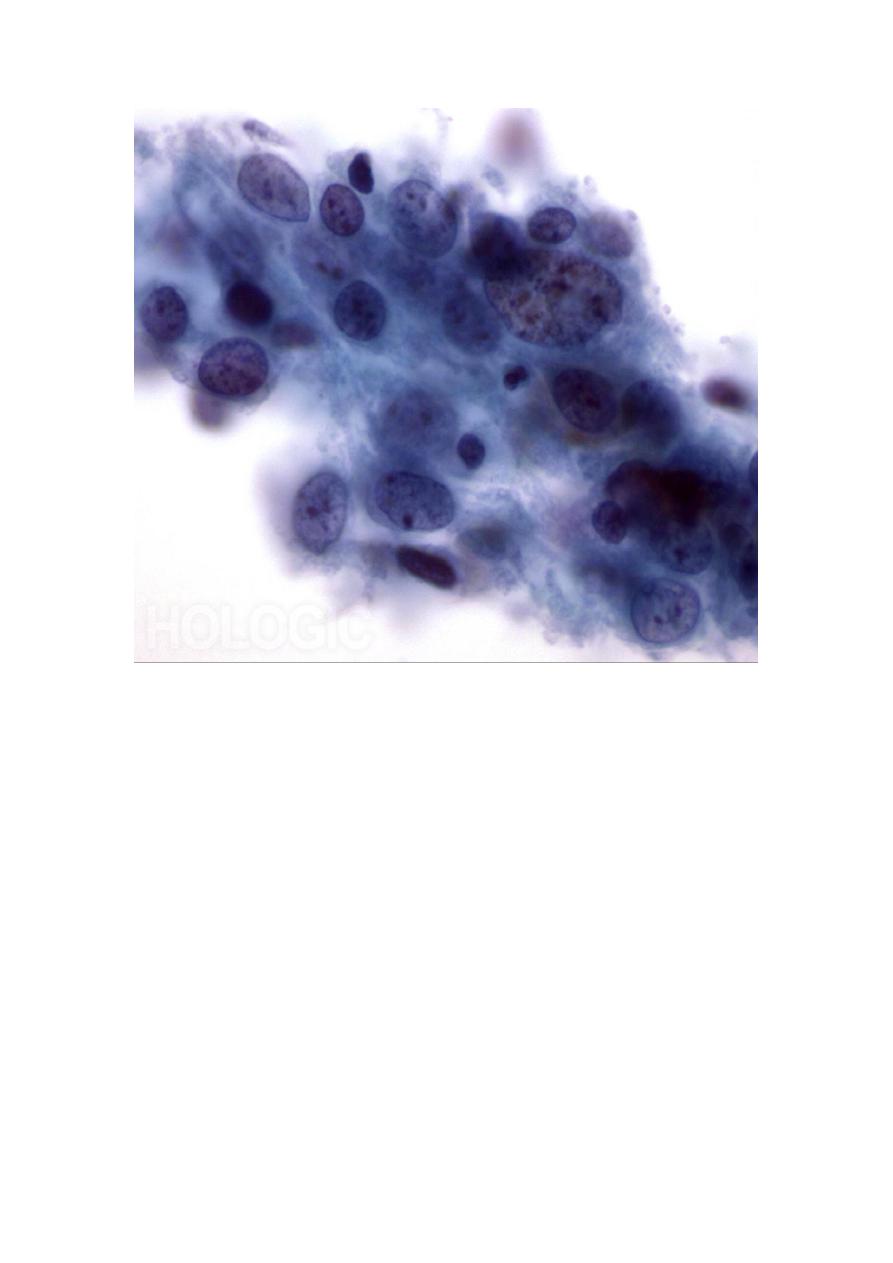
2-Exfoliative cytology e.g., from cervix, urine, sputum, and body
fluids has been widely used for diagnosis. It is particularly
useful to detect and follow up preinvasive malignancy in the
cervix early diagnosis.
3-Brush cytology techniques has been useful in endoscopic
procedures .
Cytological diagnosis depends on the identification of features
of anaplasia in cells and masses exfoliated, aspirated or
brushed
.
In experienced hands, false positive diagnoses are uncommon,
but false negative results occur due to sampling errors
Whenever possible cytological diagnosis of cancer should be
confirmed by histopathological study of biopsy or frozen
section as in breast masses
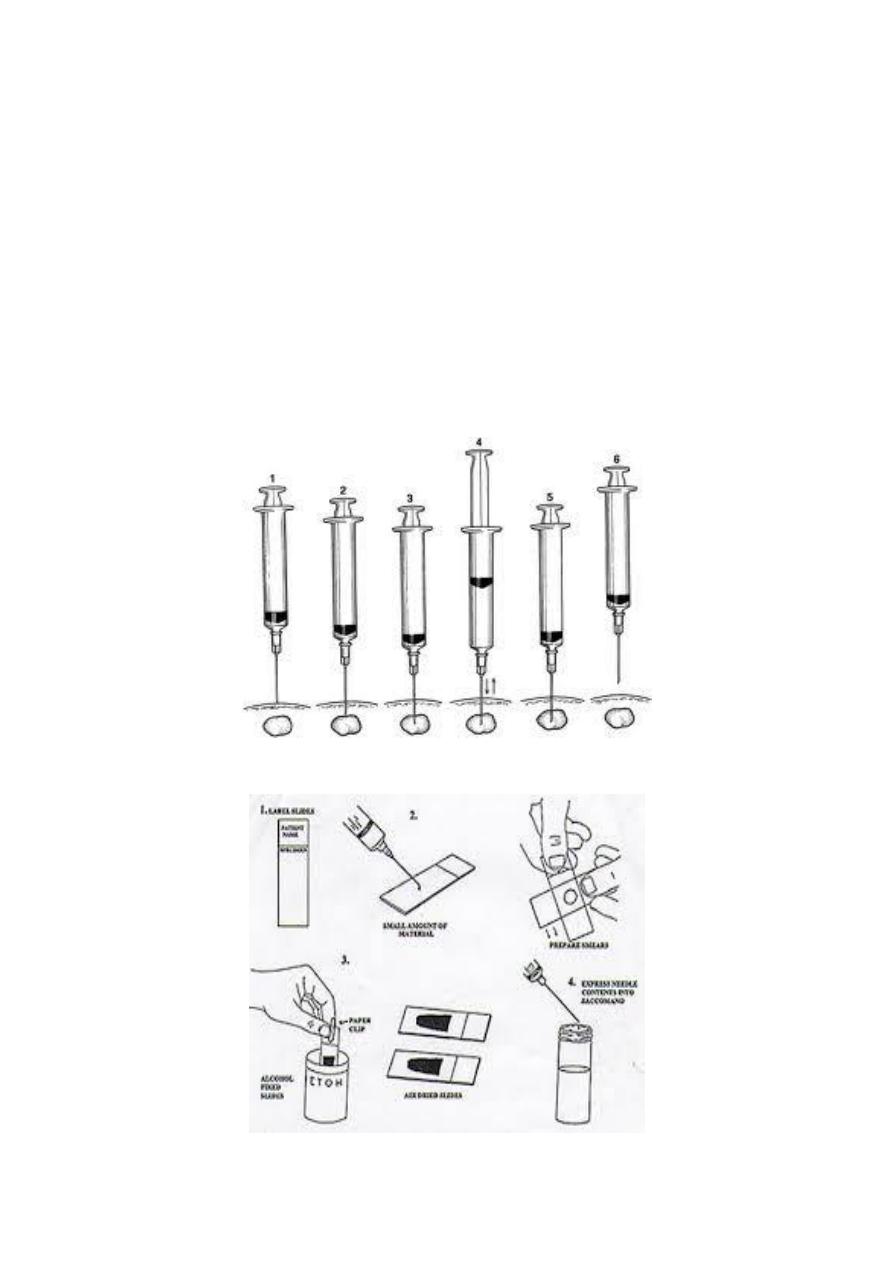
Fine Needle Aspiration:
Fine needle aspiration is a type of biopsy procedure. In fine
needle aspiration, a thin needle is inserted into an area of
abnormal-appearing tissue or body fluid
As with other types of biopsies, the sample collected during
fine needle aspiration can help make a diagnosis or rule out
conditions such as cancer
Fine needle aspiration is generally considered a safe procedure,
rapid, low cost and used for the differential diagnosis
between benign and malignant lesions Complications are
infrequent.
A lump may be felt during a doctor's examination. Or it may be
discovered on an imaging test such as : CT scan, mammogram,
and ultrasound.
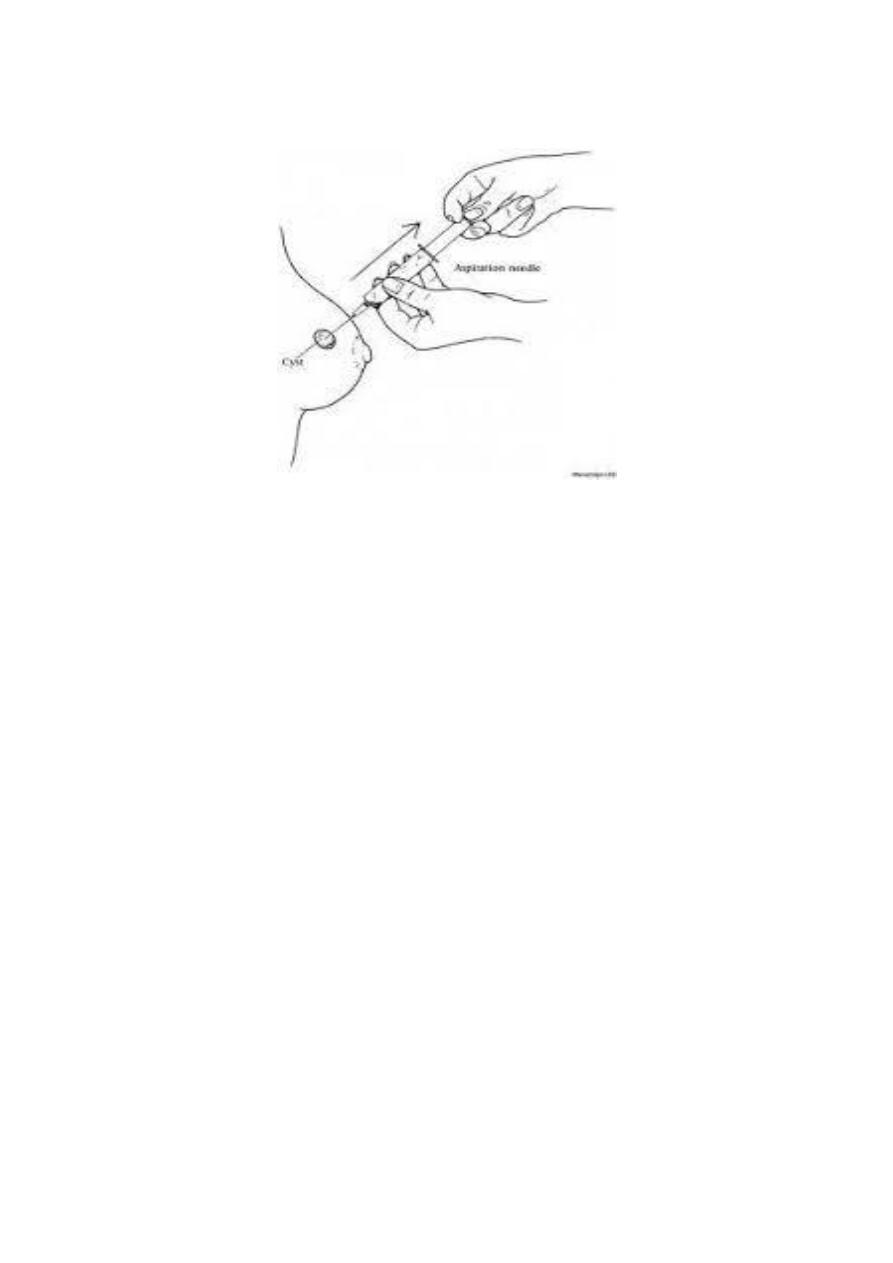
Doctors may recommend fine needle aspiration for areas such
1-cysts fluid-filled lump, and this used as diagnostic for nature
of cyst and therapeutic as in thyroid colloid cyst.
2-nodules or masses solid lumps.
3-enlarged lymph nodes.
Common complications include bruising and soreness. There is
a risk, because the biopsy is very small (only a few cells), that
the problematic cells will be missed, resulting in a false
negative result. There is also a risk that the cells taken will not
enable a definitive diagnosis.