APNEA:
•
Definition:
•
Cessation of breathing for more than
20 seconds, or for any duration if
associated with bradycardia or
cyanosis.
•
Periodic breathing
: series
of respiratory pauses of 15
seconds occuring at least 3
times/minute, there is no bradycardia
or cyanosis.
TYPES OF APNEA:
•
Central :
due to cessation of motor
stimuli from the brain stem. Chest
wall motions are absent.
•
Obstructive :
absence of airflow with
aggressive chest wall motion.
•
Mixed :
is the commonest type.

CAUSES OF APNEA:
•
Hypoxia.
•
Sepsis.
•
Metabolic disorders.
•
CNS disorders.
•
Circulatory e.g. hypotension, heart
failure, anemia, polycythemia.
•
Hyperthermia, Hypothermia.
•
Excessive pharyngeal suctioning.
•
Over dose of anticonvulsants e.g.
Diazepam, Phenobarbiton.
•
Apnea of prematurity.
So the diagnosis of apnea requires
investigations of the above causes by
appropriate tests.
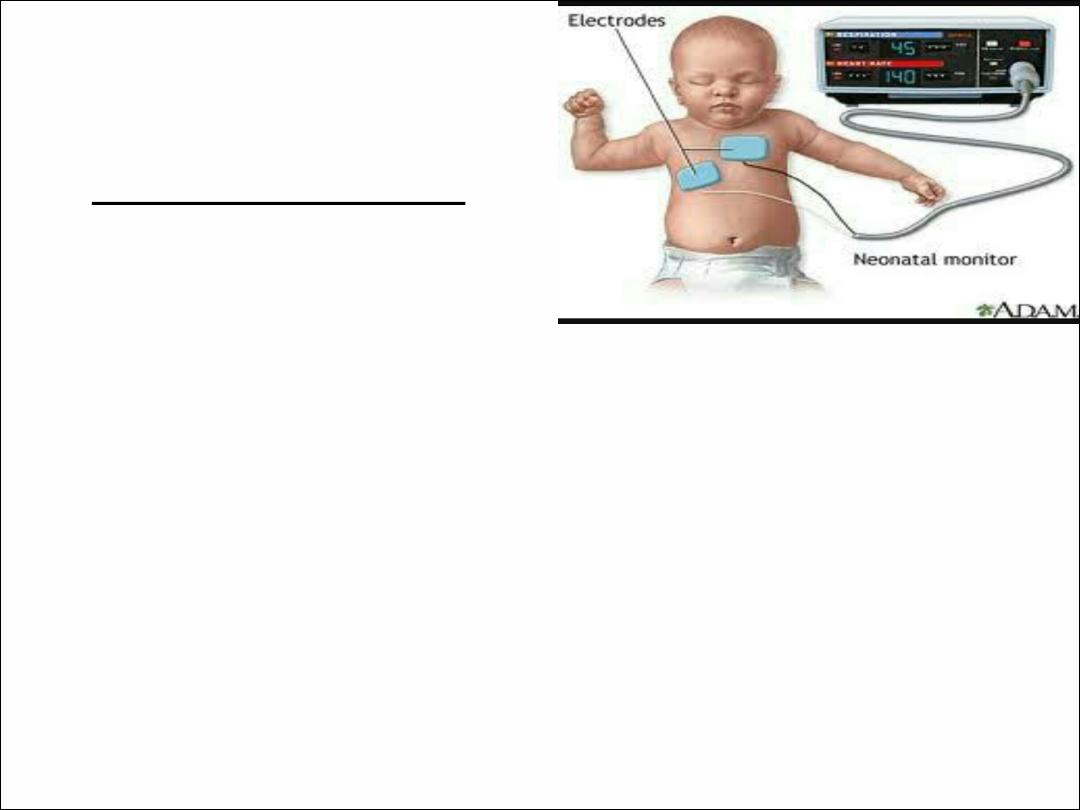
TREATMENT
:
•
1. Apnea monitors.
•
2. Repeated stimulation.
•
3. Intermittent bag&mask.
•
4. C.P.A.P. is useful in
obstructive and mixed apnea but
not useful in central apnea.

•
5. Theophylline(5-7mg/kg loading,
then 1-2mg/kg/6-12hr.oral or i.v.) is
useful in all types of apnea.
It sensitizes the respiratory center to
hypercapnia & it stimulates the
diaphragm, but it decreases cerebral
blood flow.
•
6. Caffaine citrate, Doxapram.

APNEA OF PREMATURITY:
•
Immaturity of respiratory centers or
chemoreceptors in premature babies
may cause irregular stimulation of
breathing.
•
CENTRAL RECEPTORS respond to
hypercapnia and acidosis.
•
CHEMORECEPTORS (carotid and aortic
bodies) respond to hypoxia.
