
|
P a g e
1 |
Embryology
Lec: 12 Prof Dr. Al-Hubaity
Development of Limbs
During embryonic development, the intra-embryonic mesoderm
differentiates into:
1- Paraxial part which gives 42-44 somites, each somites will divide
into:
Ventrolateral Part called sclerotome.
Dorsolateral part called dermatomyotome.
2- Intermediate mesoderm (nephrogenic cord).
3- Lateral plate mesoderm.
Development of limbs start as limb buds on the venterolateral body wall
near the end of the 4
th
week (from mesenchymal cells in the lateral plate
mesoderm)
The buds of upper limbs appears at 27 days
The buds of lower limbs appears at 29 days
Each bud at first is in fact a core of mesenchyme covered by ectoderm
The buds elongate by proliferate of mesenchymal cells & becomes
flattened so that pre-axial & post-axial surfaces appears.
The buds of upper limbs seen opposite the caudal cervical segments,
while that of lower limbs opposite lumbar & sacral segment and gain
innervations from these areas (brachial & lumbosacral plexus
respectively).

|
P a g e
2 |
Rotation of limb buds occurs as follows:
1- Buds of upper limbs rotates laterally so that the thumb is directed
laterally.
2- Buds of lower limbs rotates medially so that the hallux is directed
medially
Digital rays appear in the hand plate to form the fingers by the end of 6
th
week, and toes in the foot plate during 7
th
week. The notches between
digital rays appear due to tissue breakdown
Formation of the limb's bones
A. Chondrification centers (from hayaline cartilage) appears late in 5
th
week, thus by the end of 6
th
week Limb skeleton is cartilaginous.
B. At 7
th
week (upper limb) and 8
th
week (lower limb), ossification
centers in the middle of the cartilage appears to form the bones of
the limbs.
Primary ossification centers in the long bones seen by the end of
the 12
th
week of intrauterine life, while in the carpal bones starts at
one year age (i.e after birth).
Muscles of the limbs
Notes: -
1- The mesenchyme gives: a- Bones. b- Ligaments. c- Blood
vessels.
2- The dermamyotome gives: a- Dermatome. b- Myotome.
Thus muscles development starts from myotome where it gives rise to
myoblasts which fused together forming muscle fibers showing striation.
Each myotome gives:-
1- Hypomere migrates to ventral aspect of body & innervates by the
ventral ramus.
2- Epimere migrates to dorsum & innervates by the dorsal ramus.

|
P a g e
3 |
Limbs Rotation
1- Upper limbs rotate laterally 90 so that the elbow becomes directed
posteriorly & the extensor muscles lie on lateral and posterior
aspects of the limbs.
2- Lower limbs rotate medially 90 so that the knee is directed
ventrally (anteriorly) & the extensor muscles on anterior aspect.
Note: Synovial joints start at the beginning of the fetal life (i.e after 9
weeks).
Innervation
Motor axons (from the spinal cord) reach the bud at 5
th
week and grow
into the dorsal & ventral muscles masses. Then sensory fibers enter after
motor axons.
A dermatome :-
is an area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve & it
is spinal ganglion ,, during 5
th
peripheral nerves grow from limb plexuses
into the mesenchyme of the limbs buds & is distributed in segmental both
dorsal & ventral surfaces of the limbs.
Blood Supply
Come from branches of intersegmental arteries coming from dorsal aorta,
vascular patern changes as the limbs developed as a result of vessels
sprouting from existing vessels.
|
P a g e
4 |
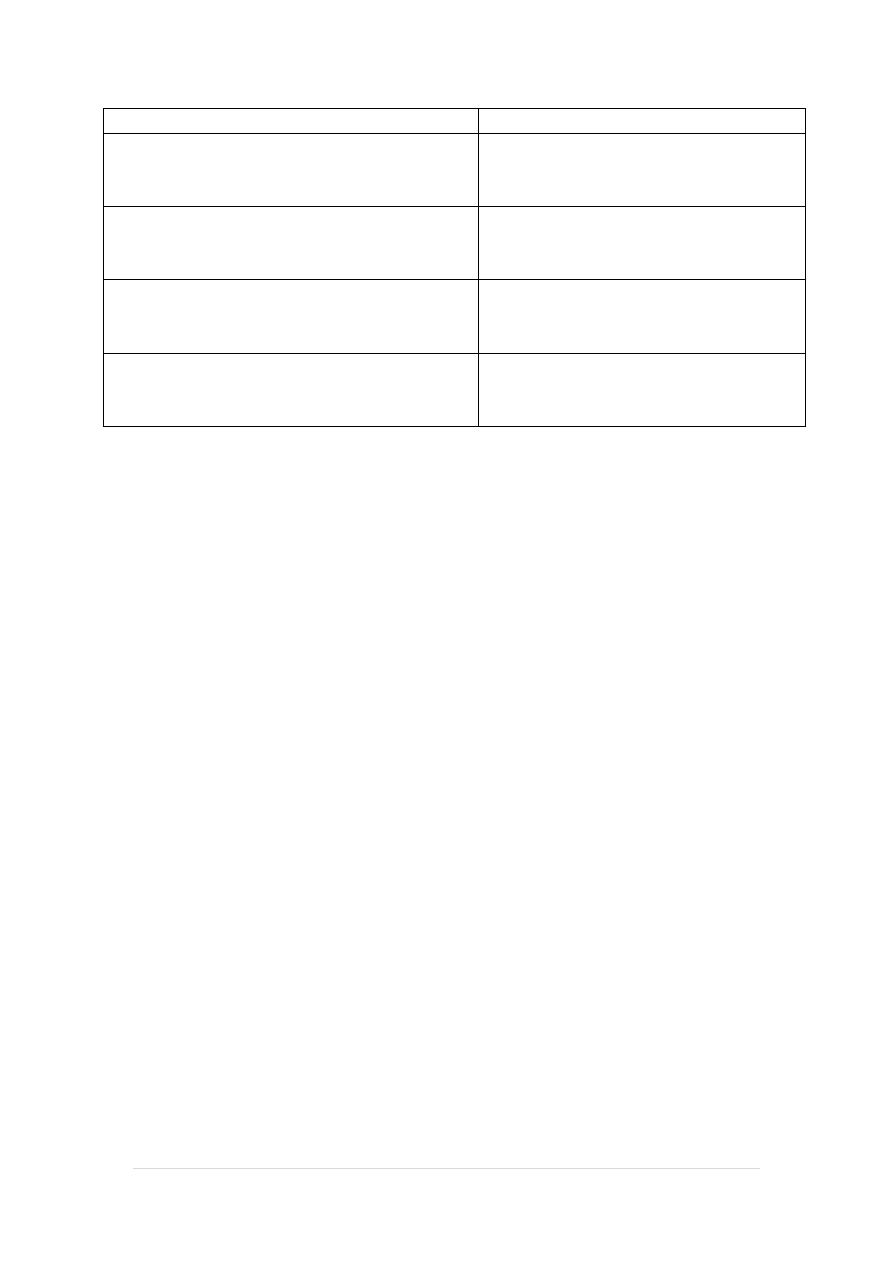
Upper limbs
Lower limbs
1. Buds appears by the end of the 4
th
week.
1. Appears at mid or late 5
th
week
2. Constrictions for future joints
appear during late 6
th
week.
2. Appears at the middle of 7
th
week.
3. Ossification starts at 7
th
week.
3. Starts at the beginning of 8
th
week.
4. Musculature appears during 8
th
week.
4. Appears at beginning of 9
weeks.
Upper limb buds paddle flipper like at 32 days (5
th
week).
Hand plate is formed at 35 days.
Digital rays in hand plate at 42-44 days.
Limbs bending at elbow, fingers are short & webbed at day 46-48.
Fingers are distinct and are separated at 54-56.
Those for the lower limbs about 2-3 days later for each event.
Anomalies of the limbs:
The most critical period of limb development is between 24-36 days post
fertilization, thus any teratogenic drug as for e.g thalidomide (used 1957-
1962) is the best example it is a potent teratogen which lead to limb
defect.
A teratogen gives before 33 days causes severe anomalies as Amelia, if
given after 34-36 its effect appear on digits as absence or hypoplasia.

|
P a g e
5 |
Main anomalies if limbs are:
1- Amelia (complete absence of limbs). Meromelia represented by
rudimentary stumps due to thalidomide.
2- Cleft hand and foot as lobster claw deformity
3- Brachyactyly = shortness of digits
4- Polydactyly = supernumery digits.
5- Syndactyly, incidence 1/2200 (cutaneous or osseous)
6- Congenital club foot, incidence 1/1000 is known as talipes
equinorans.
7- Congenital dislocated hip, incidence 1/1500, more in female than
in male, starts after birth due to:
a) Abnormal development of acetabulum.
b) Joint laxity.
