Embryology
Lec: 6 Prof Dr. Al-Hubaity
Embryonic period
The shape of the embryo changes greatly during embryonic period, so that
by the end of the 8th week (2nd month) all the main external features of the
body can be seen, include:
1. The limbs, face, nose and eyes are formed.
2. The two otic placodes are seen as thickening of the surface ectoderm,
this will give origin to the internal ear.
3. The two optic vesicles can be seen through the overlying ectoderm.
4. The Crown-Rump length (in sitting position) by the end of the 8th
week is 28-30 mm.
Somite stage: is the period which starts from day twenty till the end of day
30-31 most of the somites are seen. At the day 20 the first pair of somites
appears, then after that 3 pairs are added each day where it becomes 30-31
pairs by the end of the first month. After the 30 day newly formed somites
are added but slower than that formed at days 20-30 , the total number of
somites by the end of the fifth week (35 days) is 42-44 pairs (4 occipital , 8
cervical , 12 thoracic , 5 lumber , 5 sacral and 8-10 pairs are coccygeal).
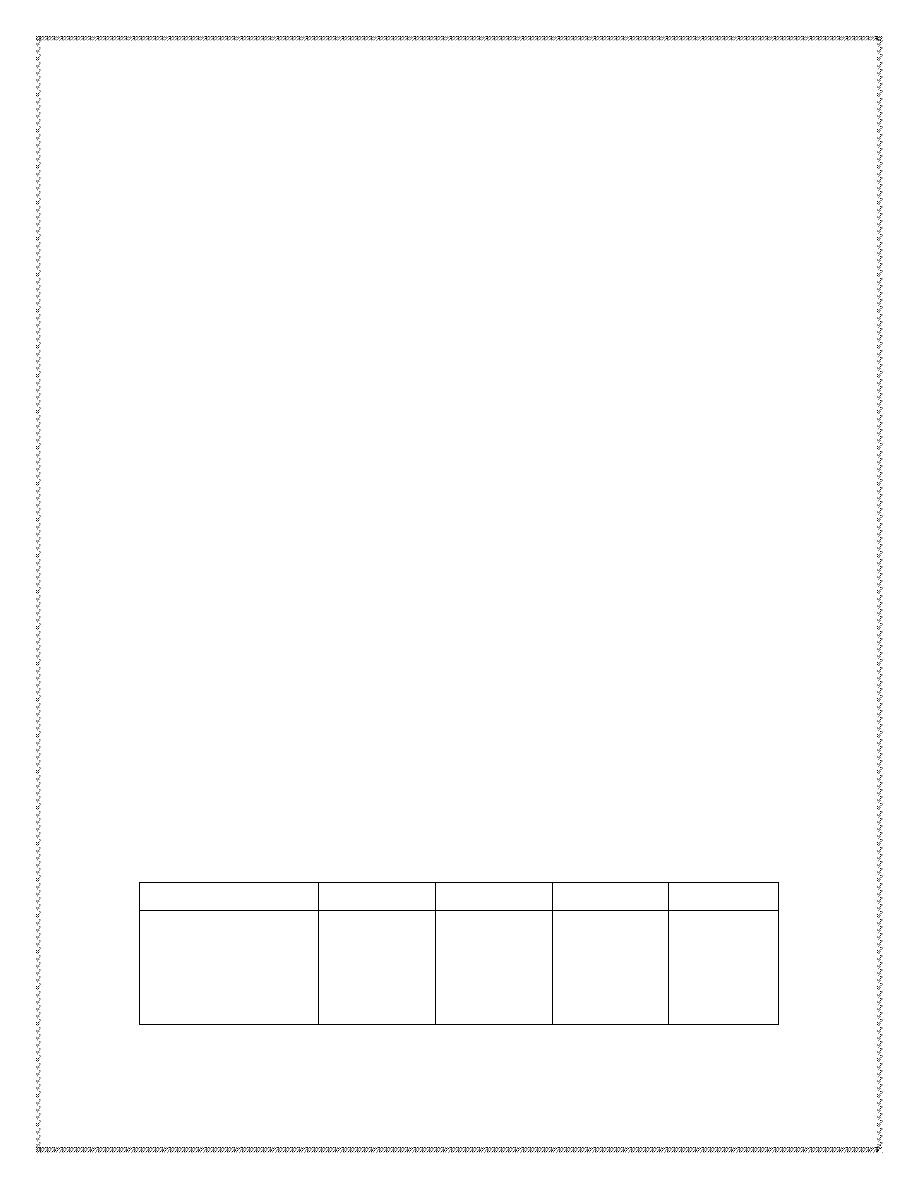
Note: The age of the embryo can be assed between days 20-35 from the
number of somites .
8
7
6
5
Age in weeks
28 - 30
17 - 22
10 - 14
5 - 8
crown-rump length
(C-R) in mm

All the following systems appear during somite stage:
1- Pharyngeal arches, pouches and clefts.
2- The digestive system.
3- The cardiovascular system.
4- The respiratory system.
5- The urogenital system.
Embryonic period
Is the period of organogenesis, where each of the 3 layers of trilaminal disc
gives rise to a number of tissues and organs and it extends from 4th – 8th
weeks.
Derivatives of ectoderm:
1. Neuro-ectoderm which gives rise to the C.N.S., P.N.S. and autonomic.
2. Sensory epithelium of the ear, nose and eye.
3. Epidermis of skin with hair and nails.
4. The pituitary gland and medulla of adrenal gland.
5. Enamel of the teeth.
6. The breast and sweat glands.
7. The epithelium of the anterior part of the oral cavity and lower part of
the anal canal.
The Derivatives of mesoderm:
1. The dermis of skin and C.T.
2. Muscles of trunk and skeleton (except the skull).
1+2 form the paraxial mesoderm which become segmented from day 20 into
somites. At day 20 the first pair of somites appears, then 3 pairs are added
daily till day 35 where it becomes 42-44 somites.
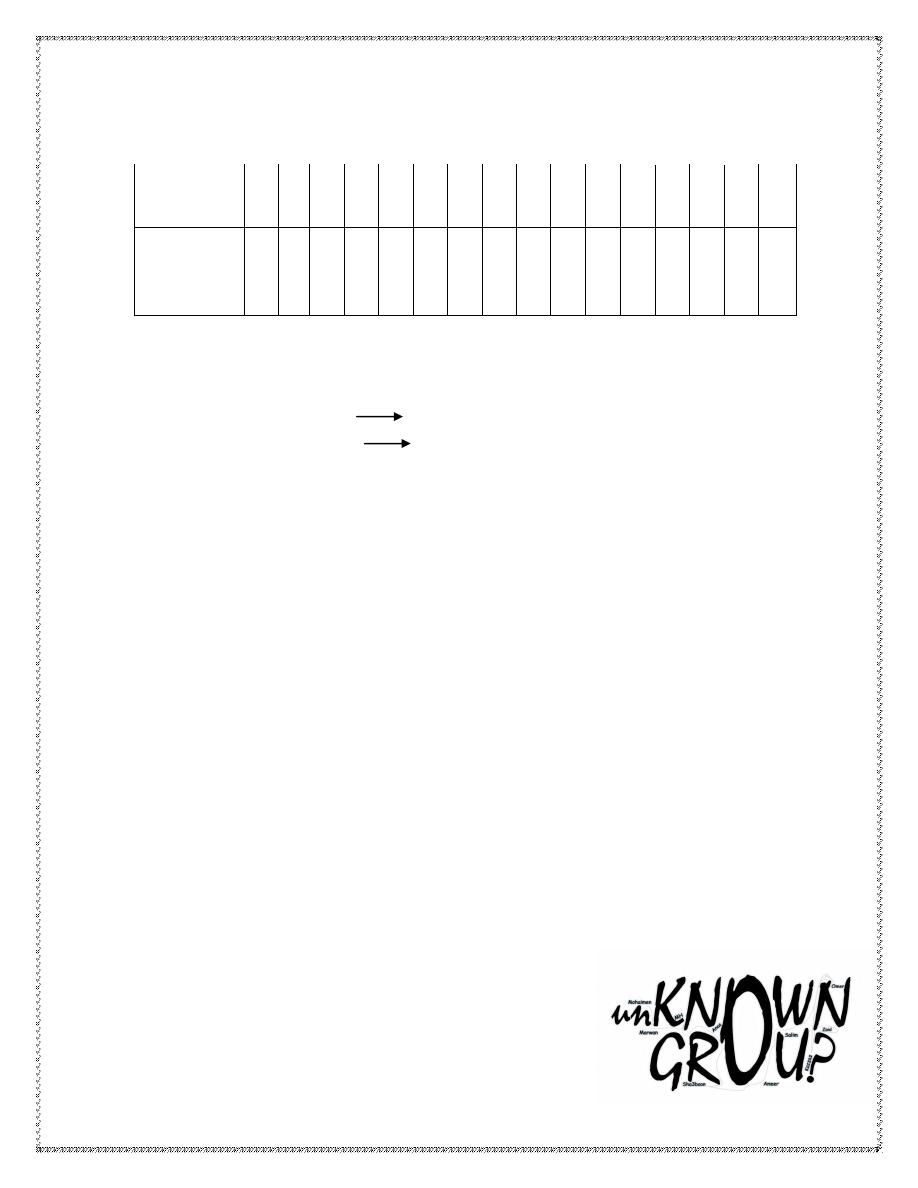
Total number of somites is 42-44 and arranged as follows: 4 occipital, 8
cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral and 8-10 coccygeal.
Age in
20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34. 35
days
Number
1 4 7 10 13 16 19 22 25 28 31 34 37 40 43 44
of
somites
Each somites differentiates into 2 parts:
A. Inner medial Sclerotome to form vertebrae and bones.
B. Outer lateral Dermomyotome which gives muscles and
strip of skin.
3. The intermediate mesoderm known as nephrogenic cords gives rise to
the urogenital system Including gonads ducts and accessory glands.
4. Lateral plate mesoderm will give:
1. C.T. + muscles of the viscera + limbs.
2. Blood + lymph cells.
3. Cardiovascular system
4. The lymphatic system
5. The spleen
6. The adrenal cortex
The Derivatives of the endoderm are:
1. The epithelium of gastro-intestinal tract including the liver and
pancreas.
2. Thyroid, parathyroid and tonsils.
3. The tympanic cavity and pharyngotympanic
tube. .
4. Epithelial lining of the pharynx.
5. Epithelial lining of trachea, bronchi and lungs.
