*
Cardiovascular
system
lecture two
Dr. Noor Jawad
3/10/2019

Objective:
1. Anatomy and Functions of heart valves?
2. Intrinsic Control of Heart beat
3. Heart sounds and murmurs

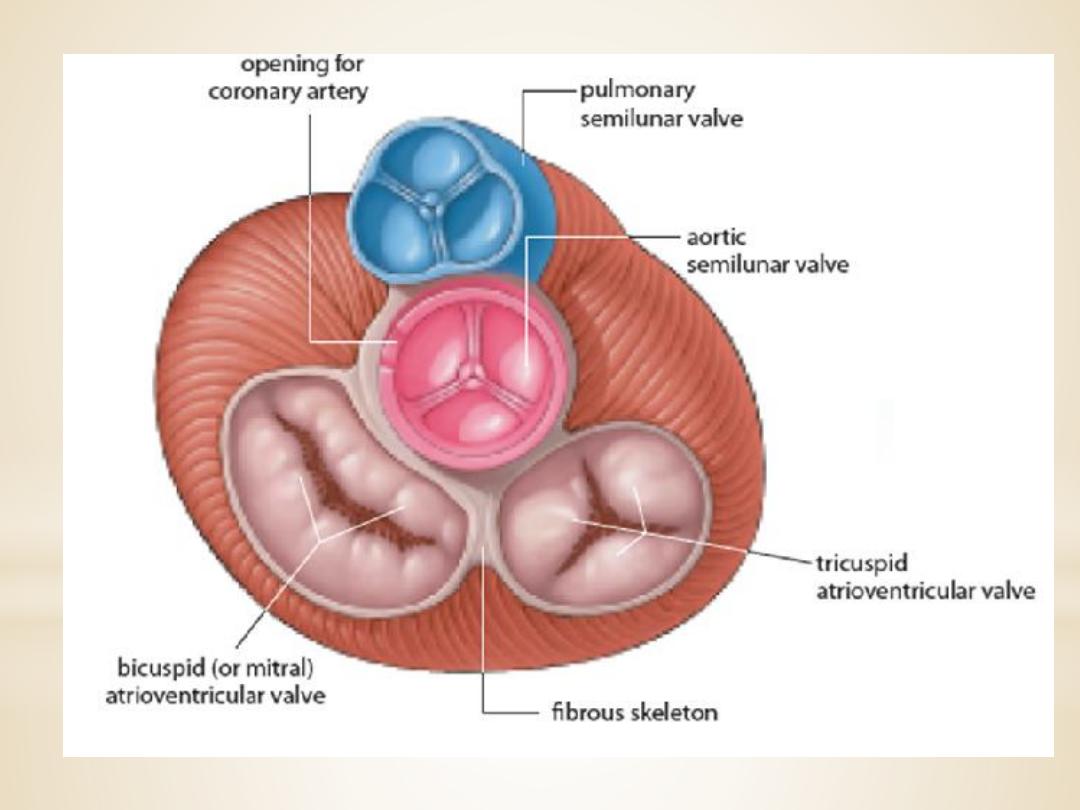
Heart valves
For the heart to function effectively, blood flow
must occur in a one-way direction, moving
forward through the chambers of the right heart
to the lungs and then through the chambers of the
left heart to the systemic circulation.

This unidirectional flow is provided by the heart’s
valves:
1.The atrioventricular (AV) valves
control the flow
of blood between the atria and the ventricles . The
thin edges of the AV valves form cusps, two on the
left side of the heart (i.e., bicuspid or mitral valve)
and three on the right side (i.e., tricuspid valve).
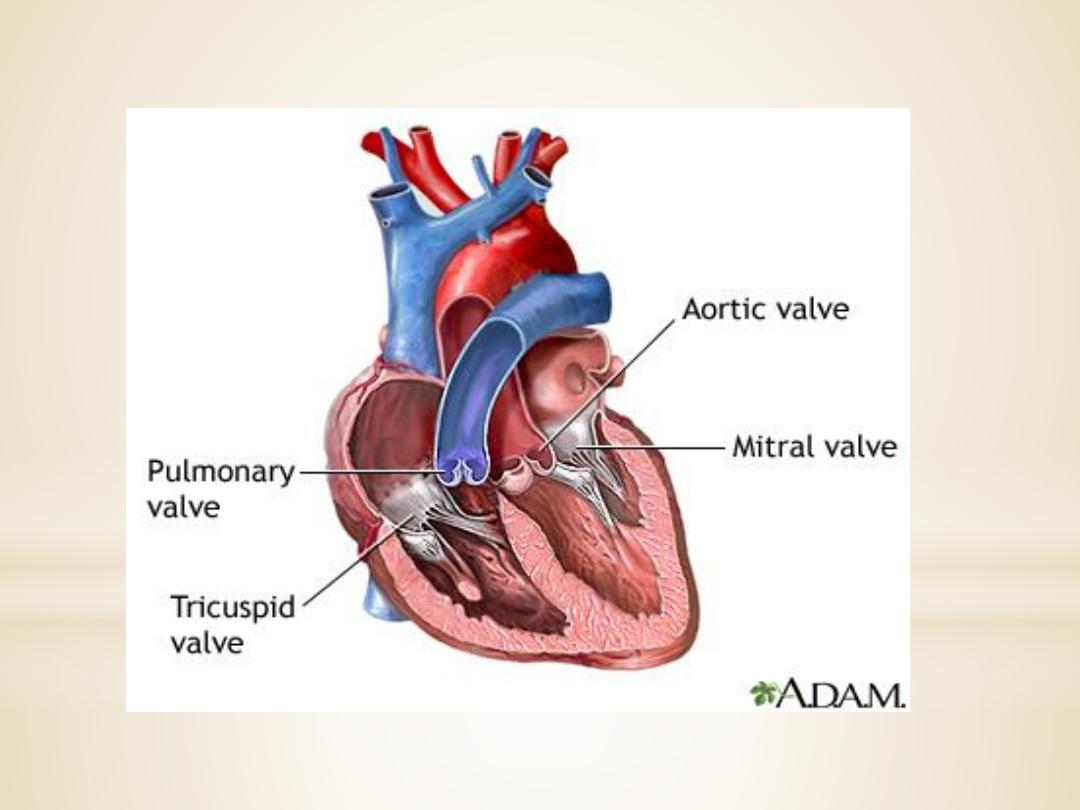

The AV valves are supported by the
papillary muscles, which project from the
wall of the ventricles, and the chordae
tendineae, which attach to the valve.
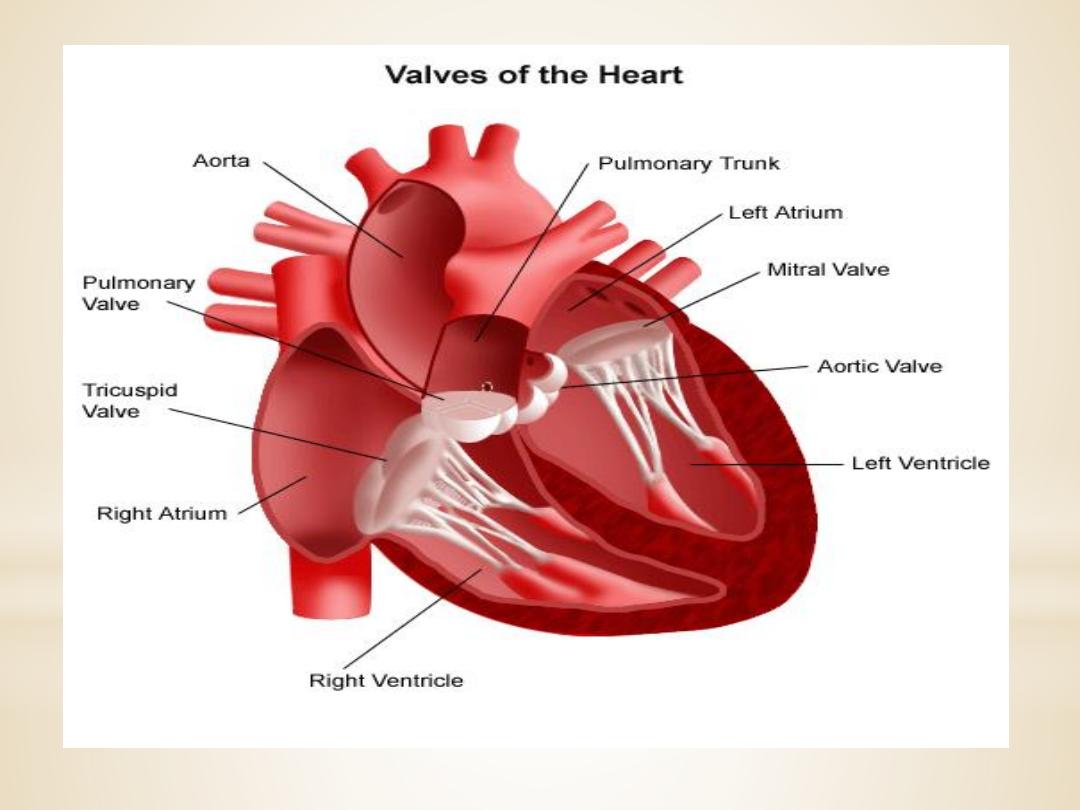
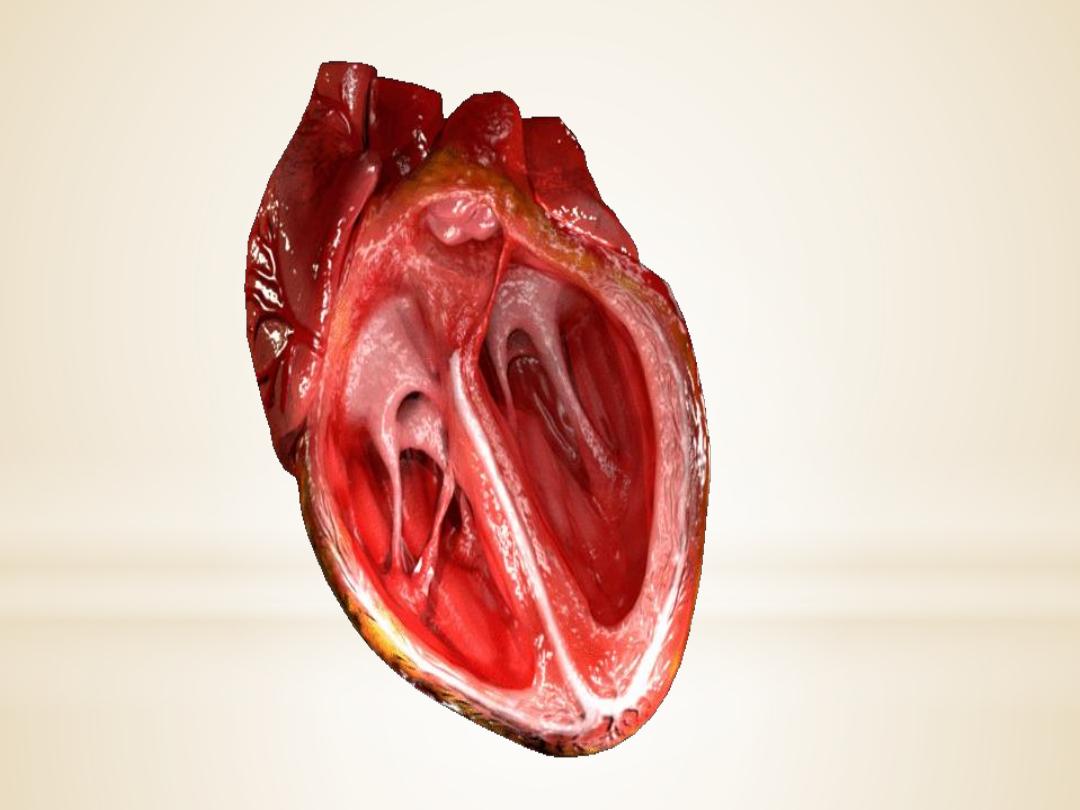

2.The aortic and pulmonic valves
control the
movement of blood out of the ventricles. Because of
their half moon shape, they often are referred to as
the semilunar valves. The semilunar valves have
three little teacup-shaped leaflets. These cuplike
structures collect the retrograde, or backward, flow
of blood that occurs toward the end of systole,
enhancing closure.

Intrinsic Control of Heart beat
The rhythmical contraction of the heart is due to the
intrinsic conduction system of the heart, which
consist of:
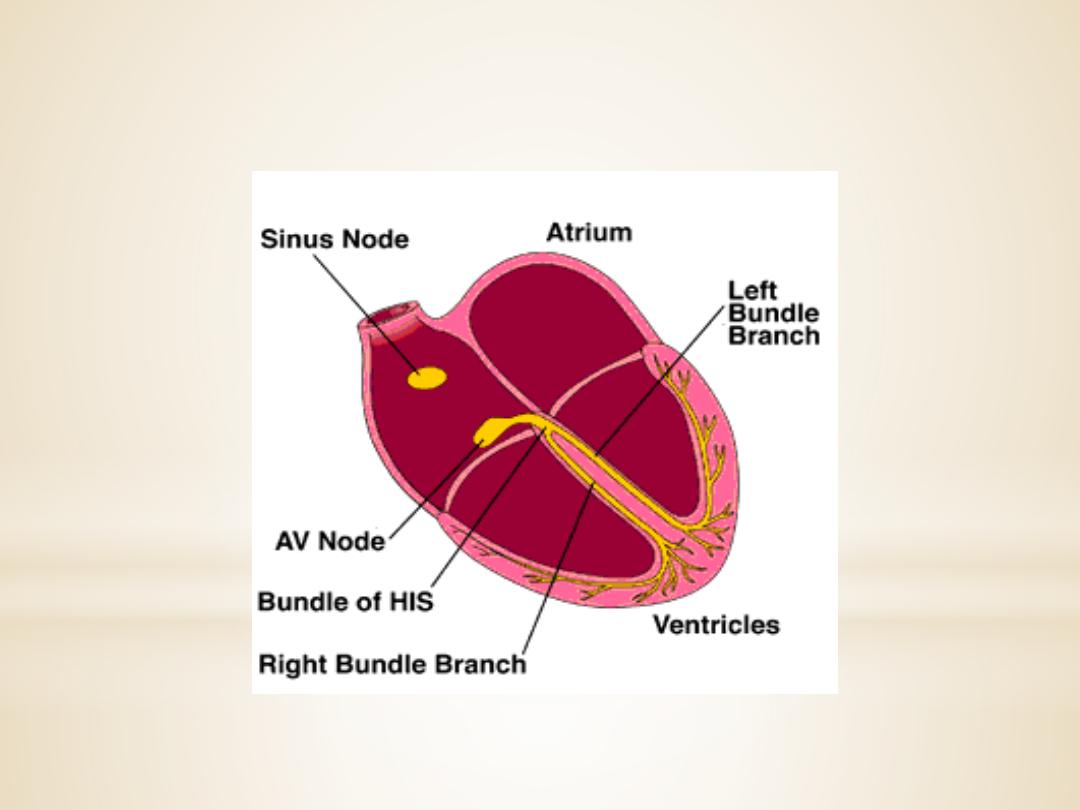
1. SA (sinoatrial) node
The sinoatrial (SA) node is the normal pacemaker of
the heart and the origin of each normal heartbeat.

The SA node is a collection of specialized
myocytes near the site where the superior
vena cava enters in the wall of the right
atrium.The
depolarization
begins
in
the
sinoatrial node (SA node), spread rapidly
throughout the atria via gap junctions between
adjacent myocytes
.
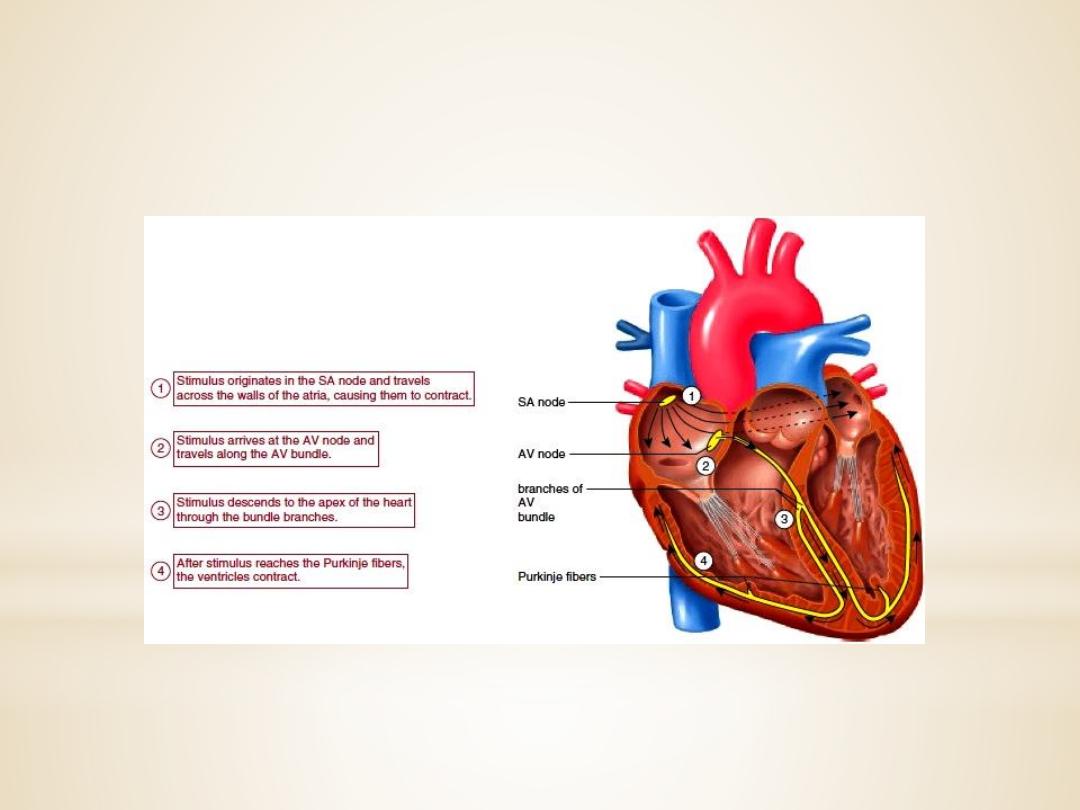

2.Atrioventricular Node(A-V node)
The atrioventricular (AV) node is the only
electrical communication between the atria and the
ventricles. It is characterized by very slow
electrical
conduction,
ensuring
that
atrial
contraction is completed before the ventricles are
activated. The AV node is continuous with
the
atrioventricular bundle (bundle of His).
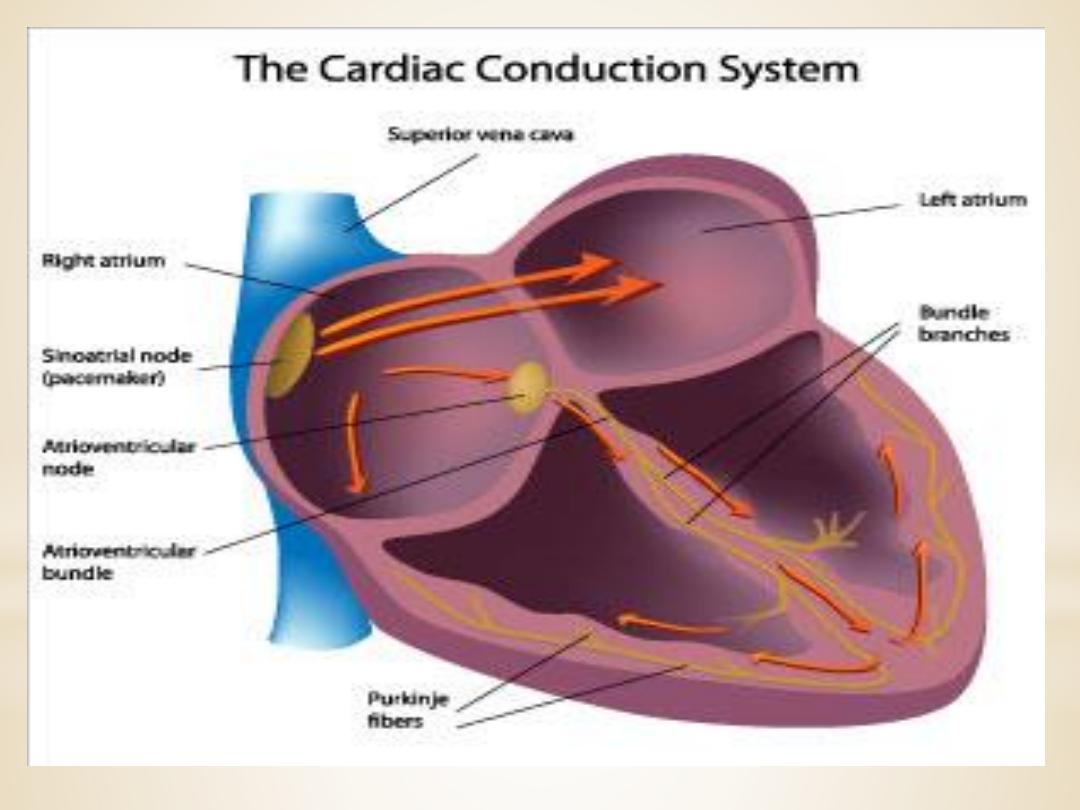

3.Atrioventricular bundle (bundle of His)
The AV bundle carry
signals from atrium to the
ventricles, in the ventricles the AV bundle divide into
right and left bundle branch, these branches then
divide into an extensive network of Purkinje fibers.
4. Purkinje fibers
Specialized conducting
fibers
that
transmit
electrical signals very rapidly to all parts of the
ventricular myocardium.
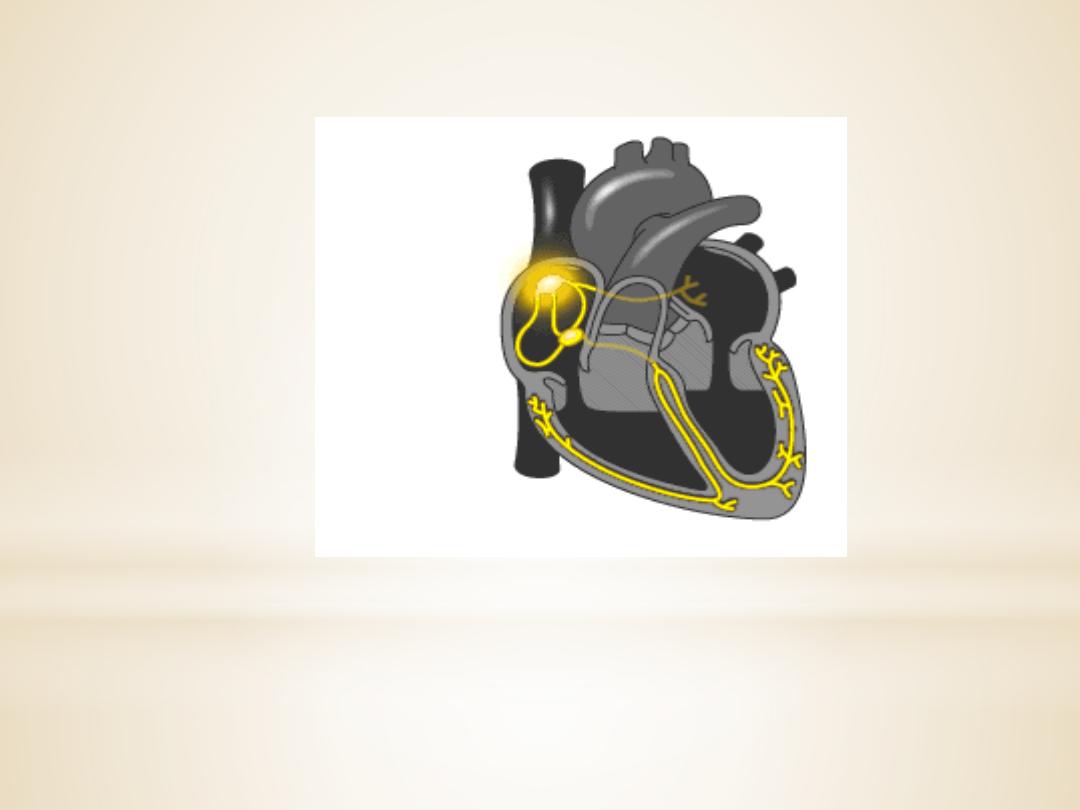

Extrinsic Innervations of the Heart
The excitatory and conductive system of the heart
receive innervations from both division of
autonomic nervous system. Although the basic heart
rate is set by the intrinsic conduction system, fibers
of the autonomic nervous system can modify the
heart beat :

1. The sympathetic nervous system (the
“accelerator”) increases both the rate and
the force of heartbeat.
2.parasympathetic slows the heart rate and
force of contraction.

*
heart sounds and Murmurs
*
Normally, there are two audible heart sounds.
The first S1 (“lub”) is associated with closure of
the AV valves. The second S2 (“dup”) is
associated with closure of the semilunar valves.
Two additional heart sounds can be recorded :

The third heart sound(S3), is a soft, low-pitched sound
heard about one-third of the way through diastole. It
coincides with the period of rapid ventricular filling.
The third heart sound is normal in children but is not
heard in normal adults; in middle-aged or older adults,
the presence of S3 indicates
volume overload
, as in
congestive heart failure
or
advanced mitral or tricuspid
regurgitation.

The fourth heart sound(S4),the fourth sound can
sometimes be heard immediately before the first
sound. The sound is caused by the atrium
contracting against, and trying to fill, a stiffened
ventricle. The fourth heart sound (S4) is not audible
in normal adults, it may be heard in ventricular
hypertrophy,
where
ventricular
compliance
is
decreased.

Other abnormal heart sounds include clicking,
caused by abnormal movement of one of the
valves, and murmurs, caused by the “whoosh” of
blood leaking through an incompletely closed or
excessively narrowed (stenotic) valve.

Heart murmurs
are
produced when
across one
of the
that are loud enough to be heard with
a
Murmurs due to valve lesions may be heard
during systole and called systolic murmur or
heard during diastole and called diastolic murmur:

• aortic or pulmonary stenosis causes systolic
murmur.
• mitral or tricuspid insufficiency causes systolic
murmur.
• Aortic or pulmonary insufficiency causes
diastolic murmur.
• mitral or tricuspid stenosis causes diastolic
murmur.


The closure of which two valves
produces the S1 heart sound?
• SAVE
•A. Aortic and mitral valves
B. Aortic and pulmonic valves
C .Mitral and tricuspid valves
D. Tricuspid and pulmonic valves

The epicardium:
A) is also known as the parietal pericardium.
B) is a layer of cardiac muscle.
C) is the visceral pericardium.
D) lines the heart chambers.
E) is the pacemaker of the heart.

