The try-in appointment
After the preliminary arrangement of the artificial teeth on the occlusion rims, it is essential that the accuracy of the jaw relation records made with the occlusion rims be tested, perfected if incorrect, and then verified to be correct.The try-in appointment
• The maxillary & mandibular trial dentures are placed in the mouth
• Labial frenum checked to see that it is absolutely free, so relation of the lip to the teeth can be observed• Observation of centric occlusion is made
• VDR & VDO must be evaluated by
Amount of inter occlusal distance when the mandible is in rest position
Phonetics & esthetics
Facial dimensions & facial expression
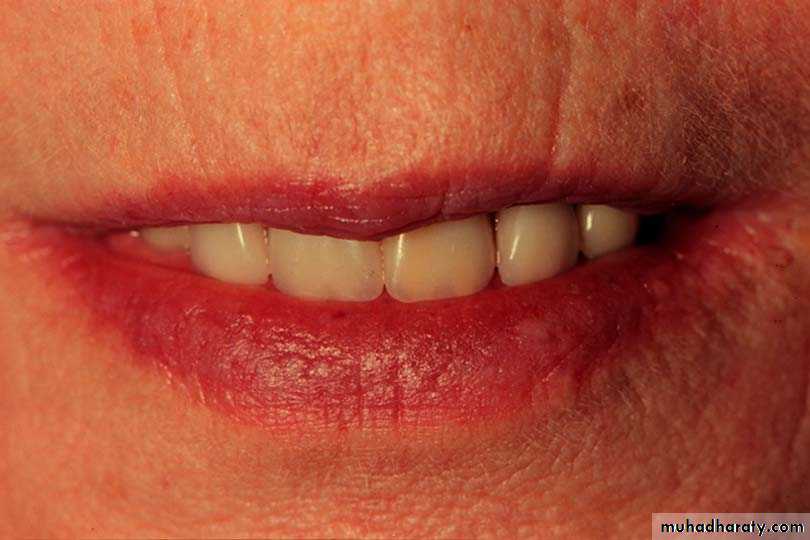
Lip length in relation to the teeth
Closest speaking space
Verifying the vertical dimension
Observation of intercuspation ( mandible pulled back by the patient & closure stopped at first tooth contact)Any error in centric relation will be apparent when the teeth slide over each other
Verifying centric relation
Once an error is detected, observation of esthetic is made
Anterior teeth should support the lip properly, the vertical over lap of anterior teeth must be correctThe posterior teeth are removed from lower occlusion rim, then CR is recorded, mounted, new arrangement is done
Verifying centric relation
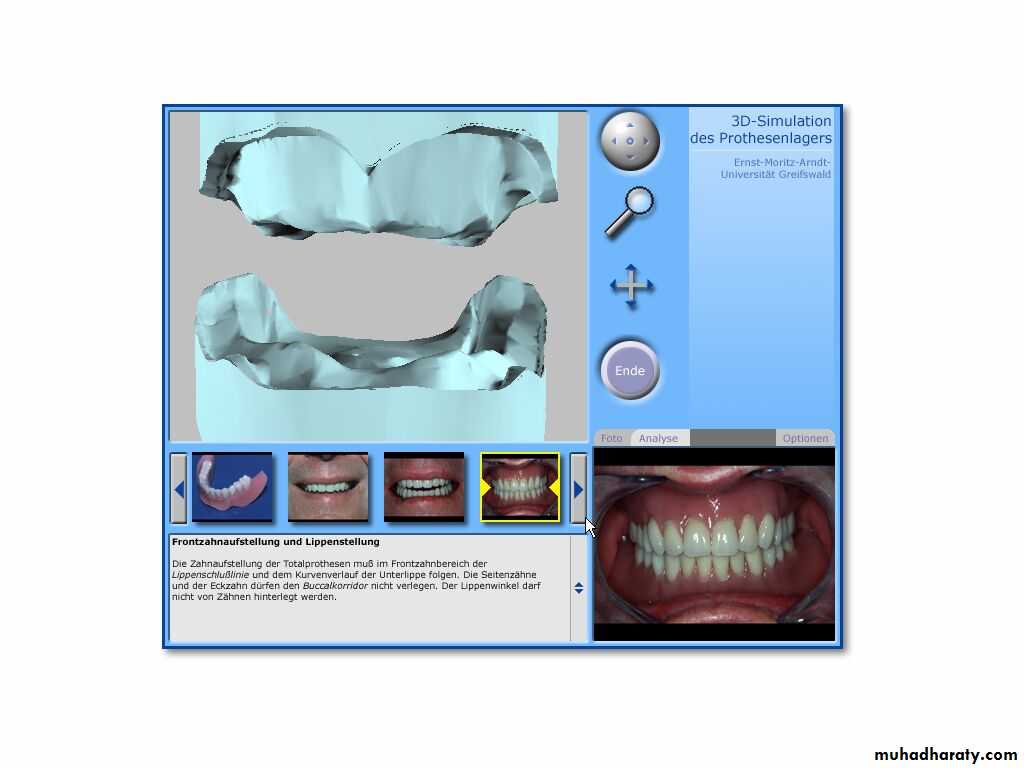
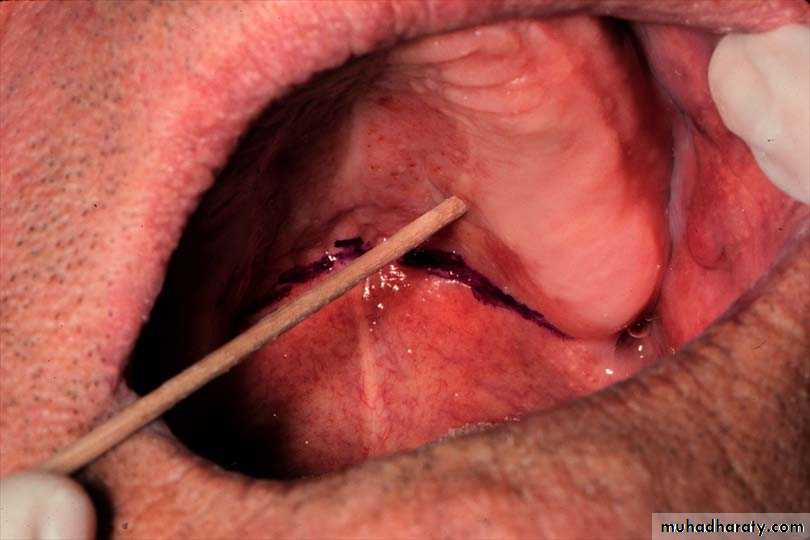
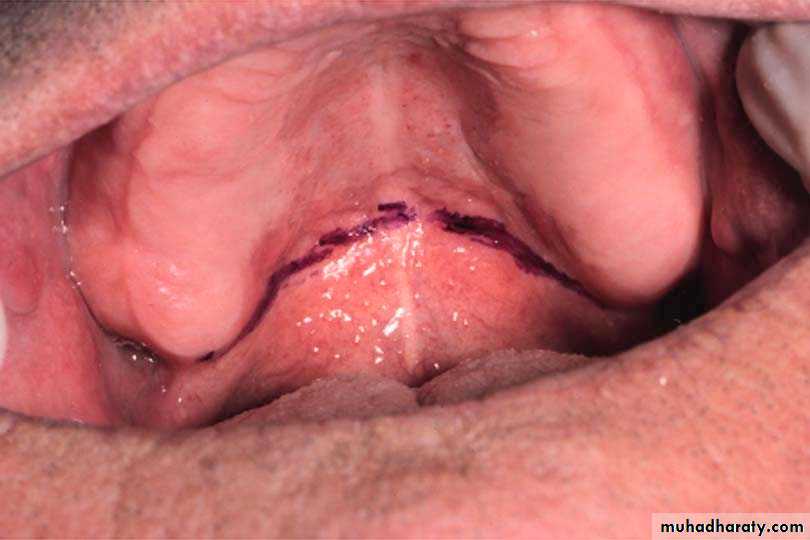
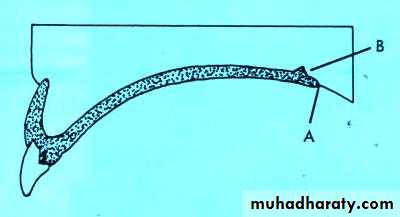
The locations of right & left pterygomaxillary (hamular) notches are marked with an indelible pencilThe foveae palatinae is detected ( blow through the nose)
The vibrating line is marked with indelible pencil ( patient say “ah”)
Establishing the posterior palatal seal
Its an imaginary line drawn across the palate that marks the beginning of motion in the soft palate, when the individual says “ah”.
Extends from one hamular notch to the other.
It passes about 2mm in front of the fovea palatina.
This line should lie on the soft palate.
Distal end of the denture must cover the tuberosities and extend into hamular notches. It should end 1-2mm posterior to the vibrating line.
The trial denture base is inserted so the indilible pencil line will be transferred from the soft palate to trial denture base, & the excess base plate is reduced to this line
The width of posterior palatal seal 1.5 mm, & 1-1.5 mm high. Why?
Establishing the posterior palatal seal
Proper selection of anterior teeth size, form, & color
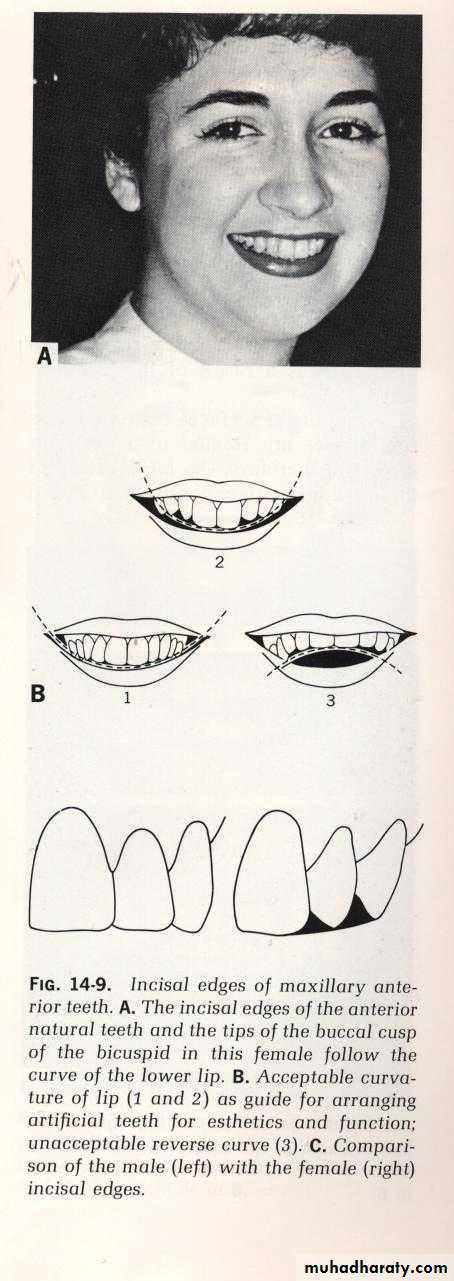
Proper vertical orientation of anterior teeth, lower anterior teeth with the level of the lip, & the upper anterior teeth 1-2 mm of incisal edge below the upper lipFacial & functional harmony with anterior teeth
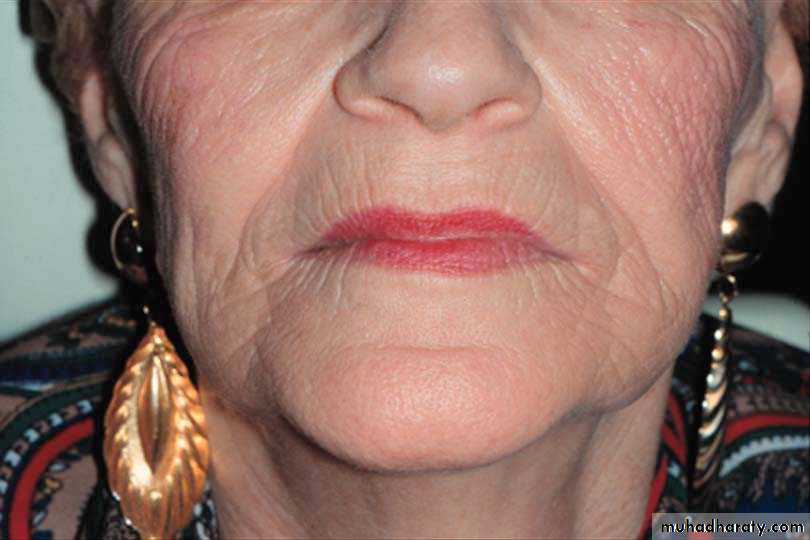
Proper horizontal orientation of anterior teeth results in normal tone of the skin of lips, vermilion borders become visible, the corners of the mouth assume normal contour, & many of the small vertical lines above the vermilion are reduced or eliminated
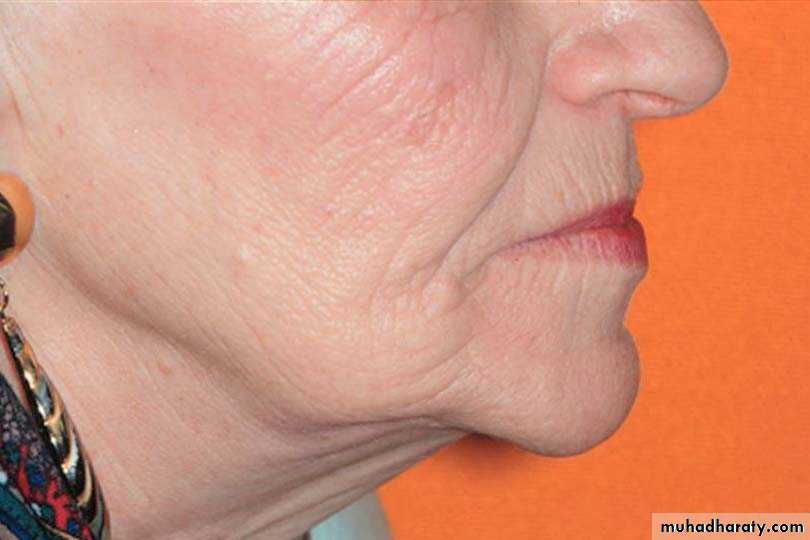
Nasolabial Angle
Angle between columella of nose & philtrum of lip
Normally, approximately 90° as viewed in profile
Labial inclination of anterior teeth often parallels the profile line of the lower third of the face
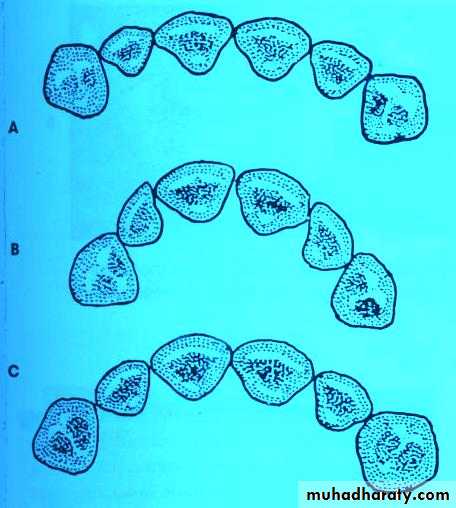
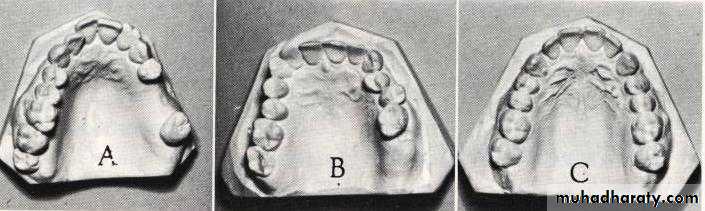
The arch form of the artificial anterior teeth should be similar in shape to the arch form of residual ridge, & the palatal vault form
Harmony of the teeth with the smiling line
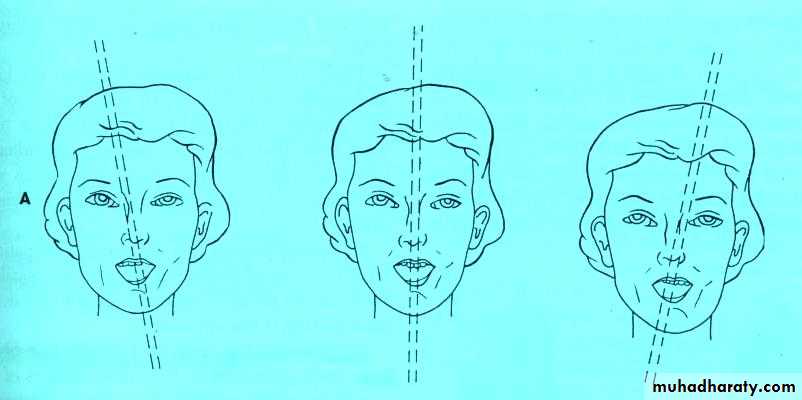
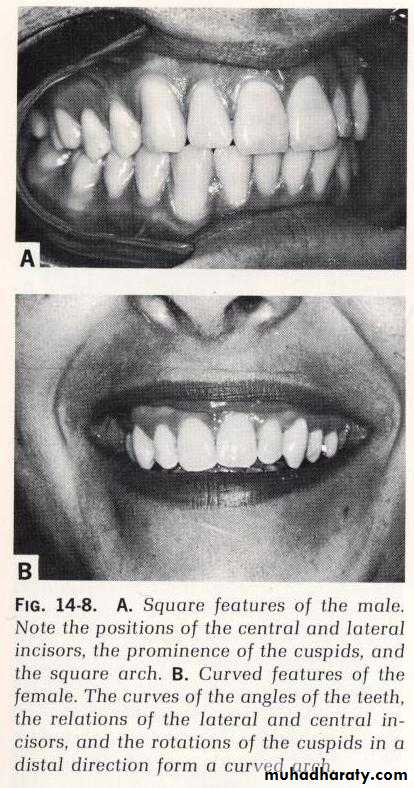
The long axes of central incisors should be parallel to the long axis of the faceHarmony with sex, age, & personality of the patient
Femininity = curved surfaces, round angles, & prominent smiling line alignmentMasculinity = boldness, square surfaces, straight incisal line of teeth
Aging = worn incisal edges, erosion, & spaces between the teeth
Lisping
Non-uniform overjet of the anterior teethDiastemas between teeth
Palatal contours
Diamond-shaped openings between incisors
Sibilant Sounds
‘S’, ‘Z’‘T’ ‘CH’ ‘SH’:(‘Sixty-six’, ‘Mississippi’)Incisors should approach end to end relationship
Fricative Sounds
F, V, ‘Fifty-Five’
Ask patient to count from ‘50 to 60’
Maxillary incisal edges should just touch the posterior one third of the lower lip
Denture base contours
Affect phonetics, comfort and retentionShould not be slightly convex in shape
Ensure that the denture base is not unduly thick or thin
Excess bulk will impair comfort
Base that is too thin will be weakened
Convex
Concave