GLYCOGEN SYNTHESIS
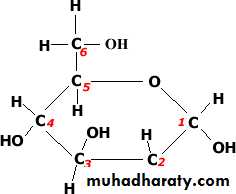
CH2OHO
mutase
Glucose-6-p glucose-1-pUDP-glu pyrophosphrylase
glucose-1-p + UTP UDP-glucoseUDP-glucose gives it’s glucose to α-1,4 chain of glycogen until the number of glucose attached to α-1,4 chain reaches 12 molecules.
This process is catalysed by Gycogen Synthetase enzyme, which is stimulated by insulin.
This enzyme is inhibited when the chain reaches 12 molecules, while the Branching enzyme is activated, so as the glucose residues will attach to α-1,6 chain untill 8 molecules are reached, so that Glycogen synthetase is reactivated glucose will be added to the α-1,4 chain again.
Branching
Glycogene synthetaseGLYCOGENE BREAKDOWN(Glycogenolysis)
Phosphorylase enzyme, which is inactive form is activated by: AdrenalineNoradrenaline
Growth hormone
Glucagone
This enzyme phosphorylate glucose molecules at the end of α-1,4 chain, converting it to glucose-1-p, and splitting it from the chain.
mutase glucose-6-phosphatase
glucose-1-p glucose-6-p glucoseuntill reaching near α-1,6 linking, where Phosphorylase enzyme is inactivated, and the Debranching enzyme is activated, which remove glucose from α-1,6 chain and attaches it to α-1,4 chain so that phosphorylase is activated again, and so on.