
Orthopedic operations
We should treat patient, not X-ray; our aim is to restore the function.
Preparations:
1-Planning: preop. measurement by: X-ray, 3D CT, MRI, transparent
template, paper cut-out or artificial bones; now, 3D computer-assisted surgery:
it helps reviewing the procedure on 3D image & it's results preoperatively.
2-Equipments: drill, osteotome, saw, chisel, gouge, plate &screws &
special instruments for certain operations(like joint replacement).
3-Intra-operative radiography: to check reduction & implant position using
X-ray cassettes or image intensifier & fluoroscopy giving real-time
X-ray pictures or even 3D reconstruction & MRI pictures.
4- Magnification: either using loupes (2-6 times) or
operating microscope for nerve or small vessels repair.
5-Blood-less field: for rapid &accurate operation, a tourniquet can be
used: either pneumatic cuff or rubber (Esmarch's) bandage.
Exsanguinations: means squeezing blood from distal to
proximal. The maximum tourniquet pressure is 150mmHg
above systolic blood pressure. The max. time is 3 hours.
6- Skin preparation:
*skin shaving (if necessary) should be in the theater.
Skin cleaning: by soap or cleansing agents(based on
alcohol, iodine or chlorhexidine) especially in open trauma.
Drapes: the best is plastic adhesive drapes.
7- Gown, gloves &masks:
Gowns: should be made of occlusive materials.
Gloves: use one or even better 2 pairs.
Masks: face-mask is to protect the wound from droplets of
nearby personnel.
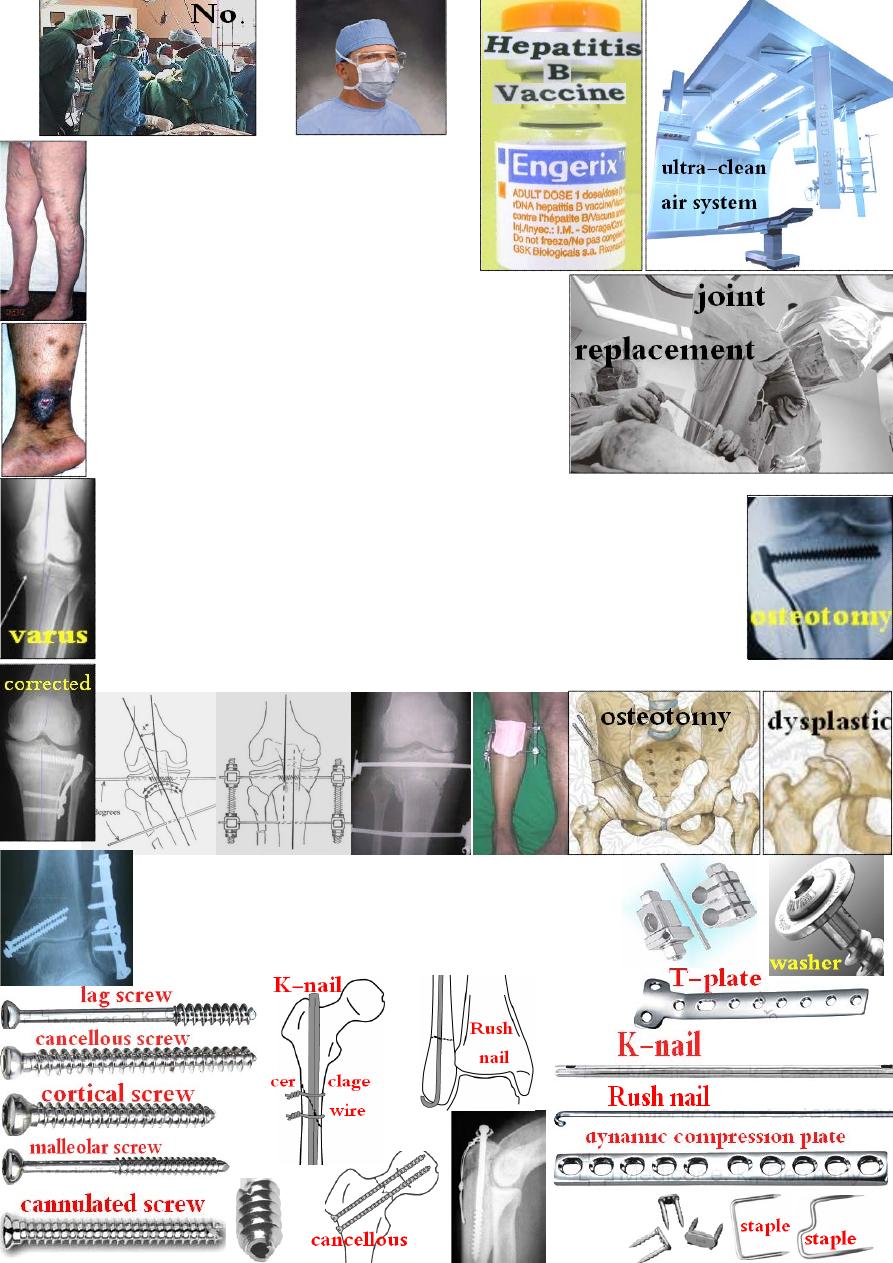
8-Measures to reduce the risk of infection:
by: a- Ultra-clean air system;
b- Reduce time of operation;
c-
↓ number of people in the theatre;
d- Pre-, intra- &post-operative AB.
9- Surgeon protection:
Hepatitis-
B→ vaccine.
Hepatitis-
C &HIV→ use mechanical protection by:
a- protective clothing; b- gloves; c- eye protection.
10-Thromboprophylaxis:
to ↓ the risk of DVT,
pulmonary embolism &chronic venous insufficiency in
high risk group like: old age, obese &those with history
of previous thrombosis.
Operations on bones:
Osteotomy: is surgical division of bone to: correct a deformity, change the
shape of bone or to ↓ pain in OA by redirecting the load across a joint.
The site is near the deformity; the amount of correction should be measured
carefully; the method is either closing or open wedge osteotomy & the
fixation can be achieved by casting, internal or external fixation.
Comp.: 1- general complications; 2- under or over correction;
3- nerve injury; 4- compartment syndrome; 5- non-union.
Bone fixation: can be done by: screws, Kirschner-wire,
malleable wire, staples, plate &screws, intramedullary nail,
external fixator or a combination of them.
*all these will loose or break unless bone union occurs.
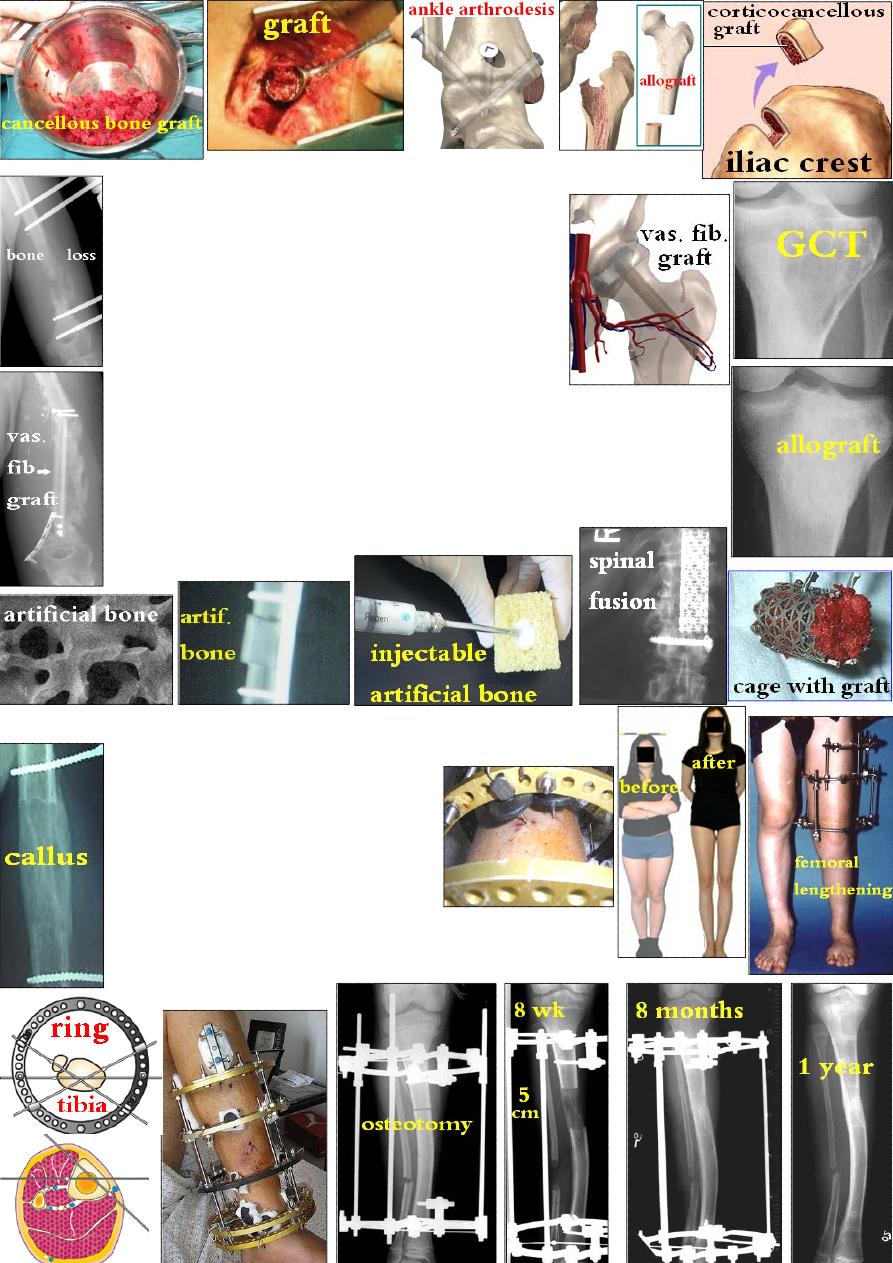
Bone graft: needs clean vascular bed for incorporation. It acts by:
1- Osteoinduction: stimulation of osteogenesis by
bone morphogenetic protein(BMP) in the graft
matrix &by the living surface bone cells on the graft.
2- Osteoconduction: mean the graft fill a bone defect
& act as a scaffold on which new bone can form.
Indications: 1- nonunion; 2- bone loss due to
trauma or tumor; 3- arthrodesis.
Types: the autogenous cancellous graft is the most commonly used graft.
1-Autograft: from patient himself e.g. cancellous (from ilium, upper
tibia, lower radius), cortical (iliac crest) or vascularized graft with it's
blood vessels (fibula, iliac crest, radius).
2-Allograft: from other alive or dead person (can be stored in bone bank).
3-Xenograft: from cows or pigs.
4-Artificial bone.
Ilizarov method: is depending on tension-stress principle:
new tissue will be formed by gradual tension.
The advantages of Ilizarov method are:
1-minimally invasive(percutaneous);
2-restore function early;
3-can elongate the bone;
4-can correct any deformity.
Applications:
1-Callotasis(callus distraction): by performing a careful #
(coticotomy
)→ wait 10days→ start callus distraction by
external frame 1mm/day→ when reach the required length→ wait +
dynamization→ remove it.
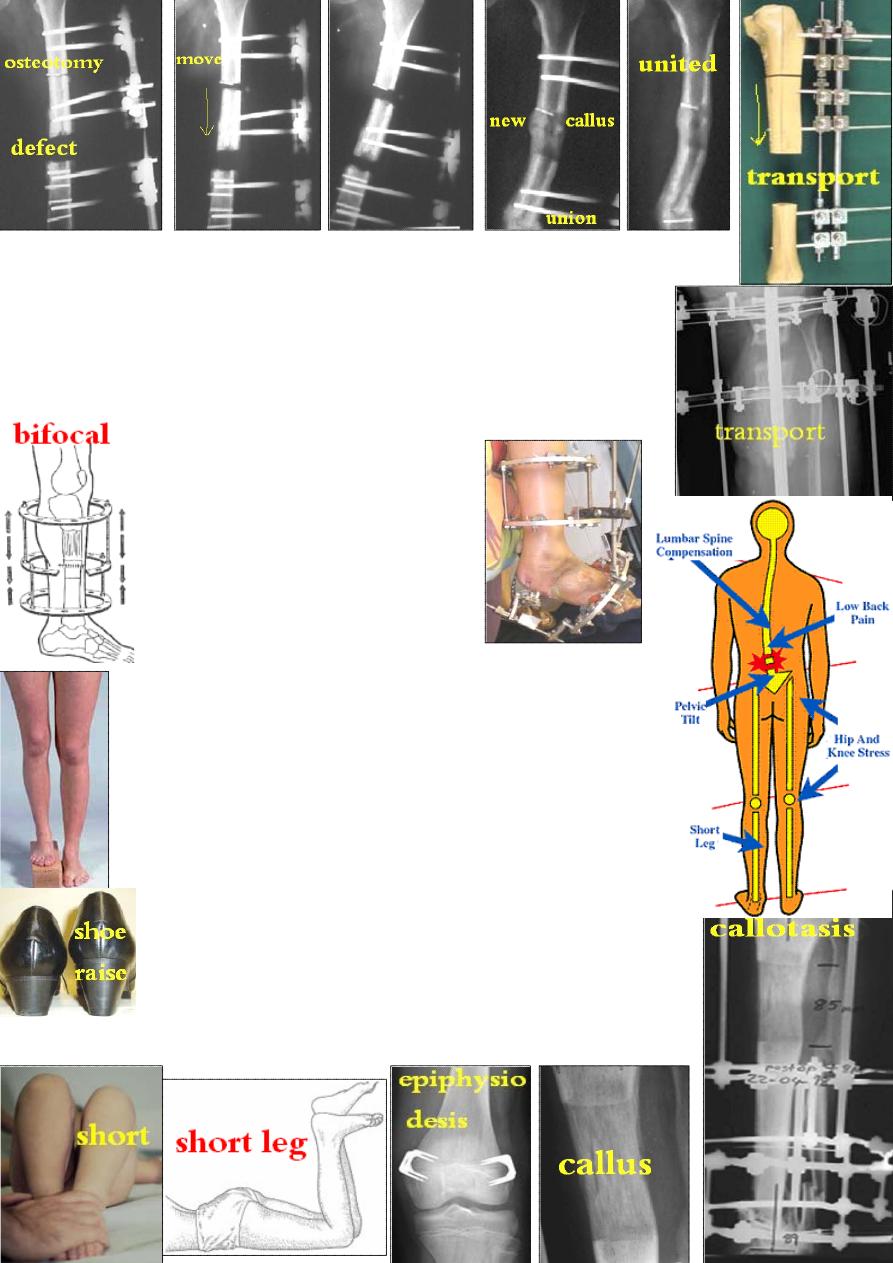
2-Chondrodiastasis: the same but the growth plate is distracted.
No osteotomy is needed & the distraction rate is slower(0.5mm/day).
*Both are used for bone lengthening &to fill a bone defect.
3-Bone transport: used to fill a bone defect: create
a corticotomy→ move the bone segment through the
defect to reach the other end till union using external fixator.
Bifocal compression-distraction: the defect is closed by bringing
bone ends together then corticotomy at a
different level &callotasis to restore length.
4-Correcting bone deformity
(>30˚)
&soft tissue contracture like
intractable club-foot deformity.
Leg length equalization:
Causes of leg length inequality:1-congenital anomaly; 2-mal
united # &bone loss; 3-physal injury; 4-infection; 5-paralysis.
A short limb may causes: limping, pelvic tilt,
compensatory scoliosis &backache.
If the shortening is < 2.5cm, it will be compensated &needs
no
Ŗ. If > 2.5 cm, it can be treated either by:
1-Shortening the longer leg:
in adult: excise segment of bone(<7.5cm from femur).
In children: epiphysiodesis (growth plate stapling).
2-Lengthening the shorter leg:
if <5cm → use shoe raise.
if >5cm → bone lengthening(callotasis or chondrodiastasis).
Comp.: 1-neurovascular injury; 2-joint contracture;
3-in children: over or under correction & angular deformity.
*bilateral leg lengthening can increase stature in short persons.
Operation on joints:
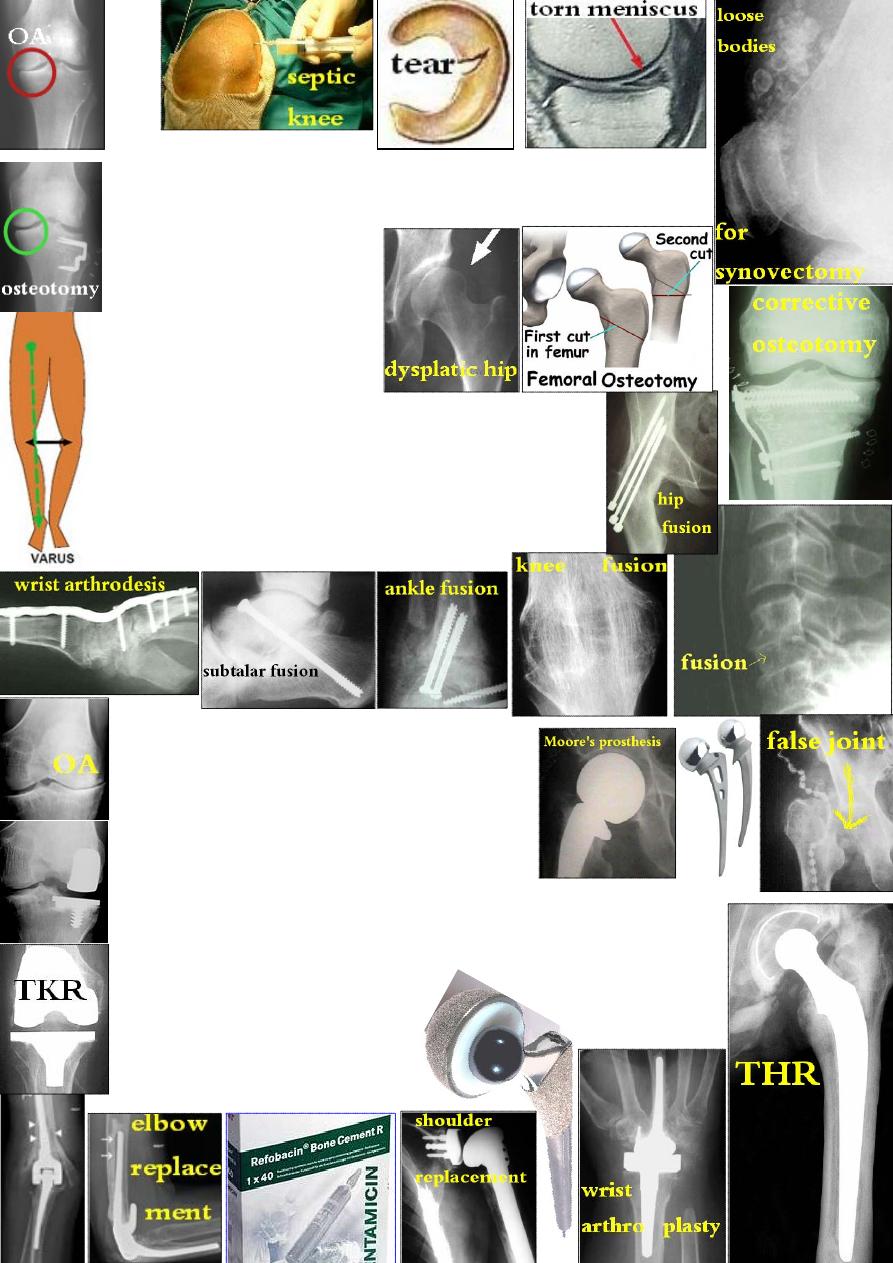
Arthrotomy: is surgical opening of a joint. The indications are:
1-drain an abscess; 2-synovial biopsy; 3-synovectomy; 4-remove
a loose body or damaged structure like torn meniscus.
Re-alignment osteotomy:
Indications:
1-early OA of hip &knee joints.
2-for dysplastic hip in DDH.
Arthrodesis: is surgical fusion of a joint.
Indications: for painful &/or unstable joint where
movement can be sacrificed e.g. ankle, wrist, spine &
sometime the knee &shoulder but rarely the hip.
Method: remove the articular cartilage→ appose the bone
ends &fix with internal or external fixation plus bone graft.
Comp.: 1-undesired position; 2-nonunion.
Arthroplasty: is surgical refashioning of
a joint to relieve pain &preserve movement.
Types: 1-Excisional arthroplasty: excise enough
bone to create a gap making a false joint.
2-Partial joint replacement: excise one articular
surface like Moore's prosthesis for femoral neck #.
Or one compartment is replaced like medial or lateral knee compartment.
3-Total joint replacement: both articular surfaces are replaced by
prosthetic implant: the convex part is metal while the concave is
polyethylene. Fixation is either by bone cement or cementless press-fit.
Microsurgery: the indications are:
1-repair of nerve or vessel;
2- toe transfer for amputated thumb;
3-bone graft with vascular pedicle;
4-replantation: of severed limb or digit.

