War injuries
(Ballistic injuries)
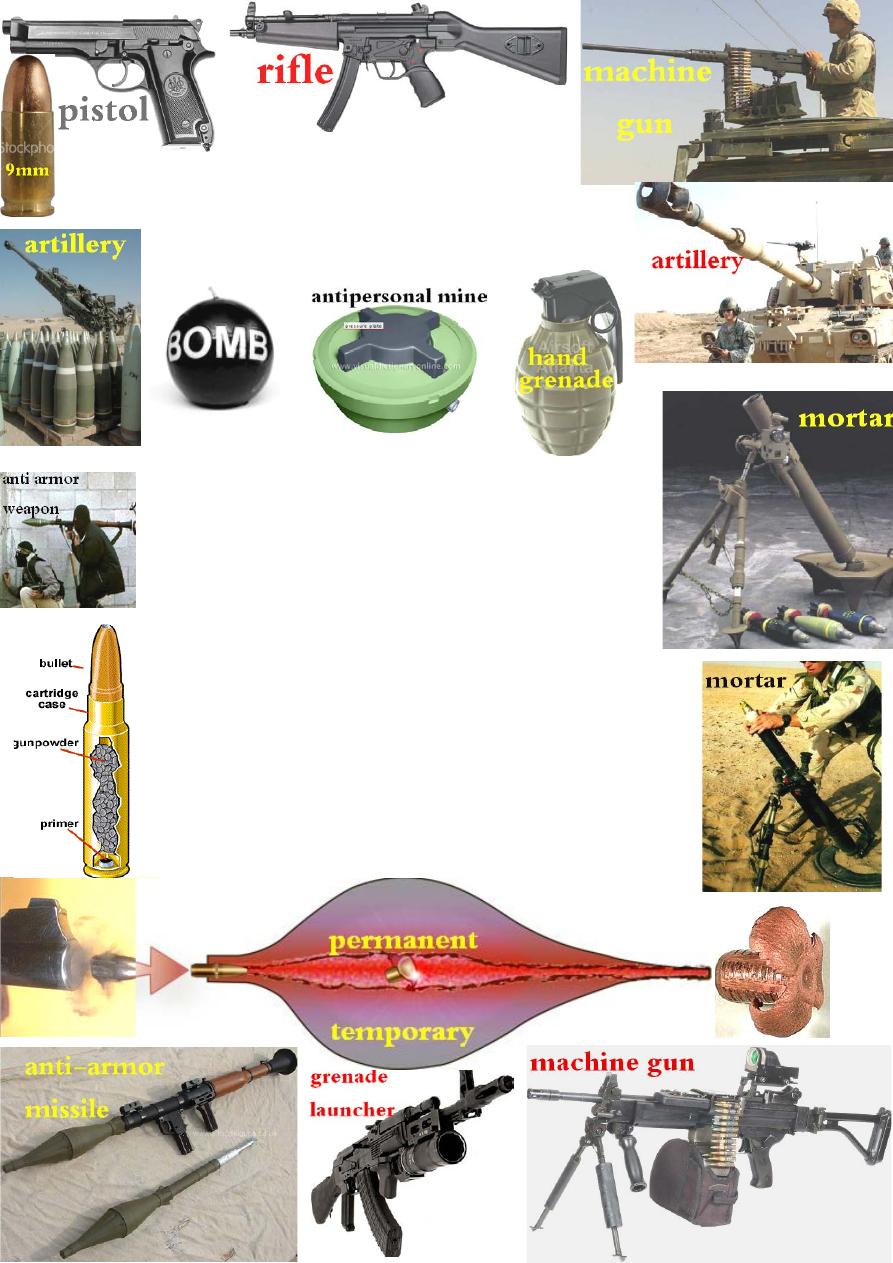
Weapons are divided into:
1-Small arms: like pistols, rifles and machine guns.
2-Explosive munitions: like artillery, grenades, hand grenades,
mortar, bomb, mine & anti-armor weapons.
Small arm injuries
:
is common in civil practice(peace time).
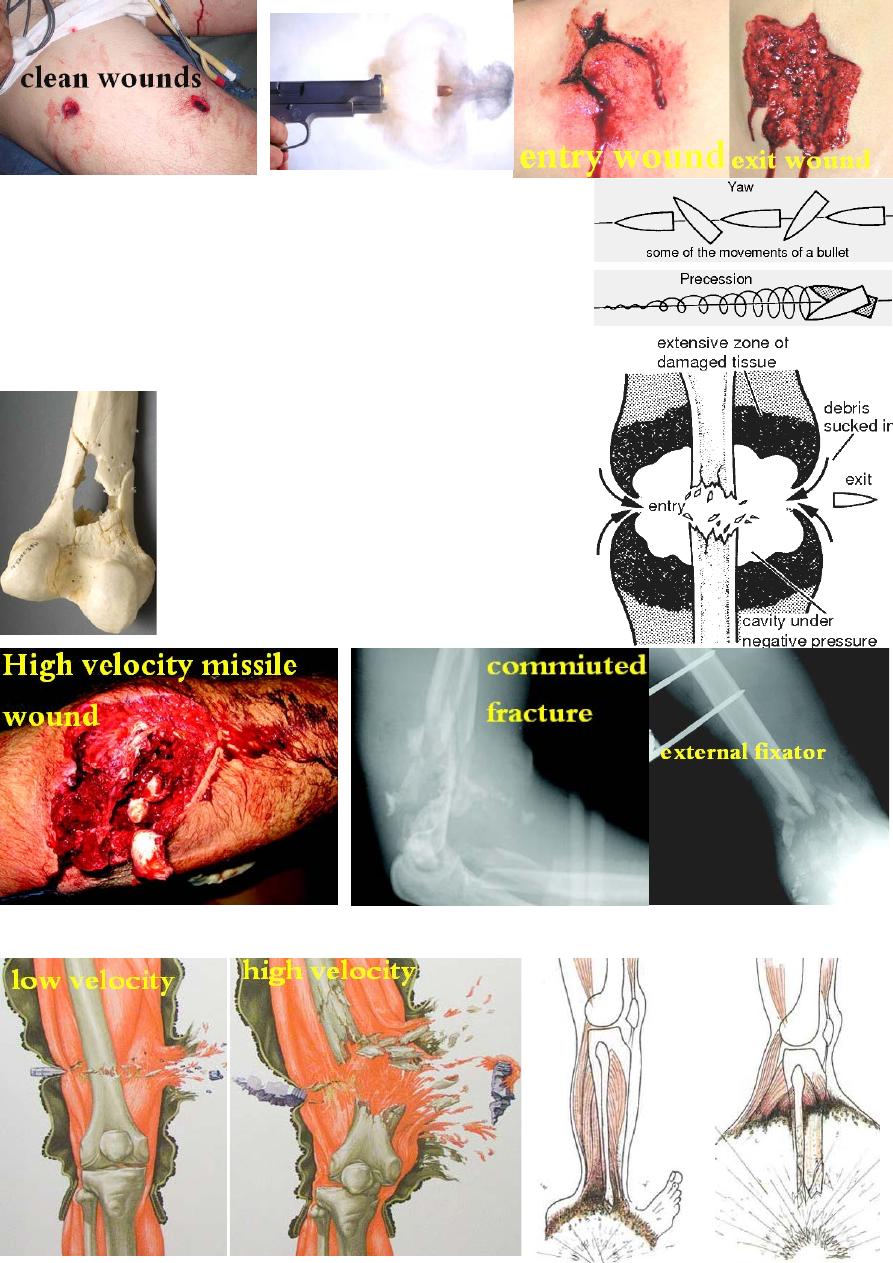
Pathophysiology: the injury is caused by transfer of
energy of the moving projectile to the body, it depend on:
1-Projectile factors:
mass, speed, nature(bullet, shrapnel or shell), composition
(fragmentatiom) &stability(tilt, rotation).
2-Anatomical factors: density &elasticity of the injured tissue.
Small arms (both high velocity missile >600m/s and low
velocity missile < 600m/s): cause two areas of tissue injury:
1-permanent cavity: is a localized area of cell necrosis
caused by direct injury of the missile along it's path.
2-temporary cavity: is a transient lateral displacement of tissue
surrounding the permanent cavity. Elastic tissues(skin, muscles
&vessels) are pushed aside, then rebound, usually need no
excision if their blood supply is intact. While, inelastic tissue,
like bone, may fracture in this area.
Treatment:
І-Emergency Ŗ: 1-stop bleeding &general resuscitation;
2-cover with sterile dressing;
3-start AB &anti tetanus.
П- Definitive treatment:
soft tissue injury:
Low velocity missile injury(pistol): there is little tissue
destruction and cavitations. So, superficial debridement
is enough provided the entry and exit wounds are clean.
High velocity missile injury(rifle): there is marked
tissue destruction &cavitation, which should be
cleaned by thorough debridement &excision of
all dead tissue leaving the wound open for daily
dressing till become clean before closure.
Bone injury: any associated # should be stabilized
using either traction, splintage or external fixation
(definitive fixation or temporary external fixation
for few weeks then internal fixation).
Anti-personal mine injury
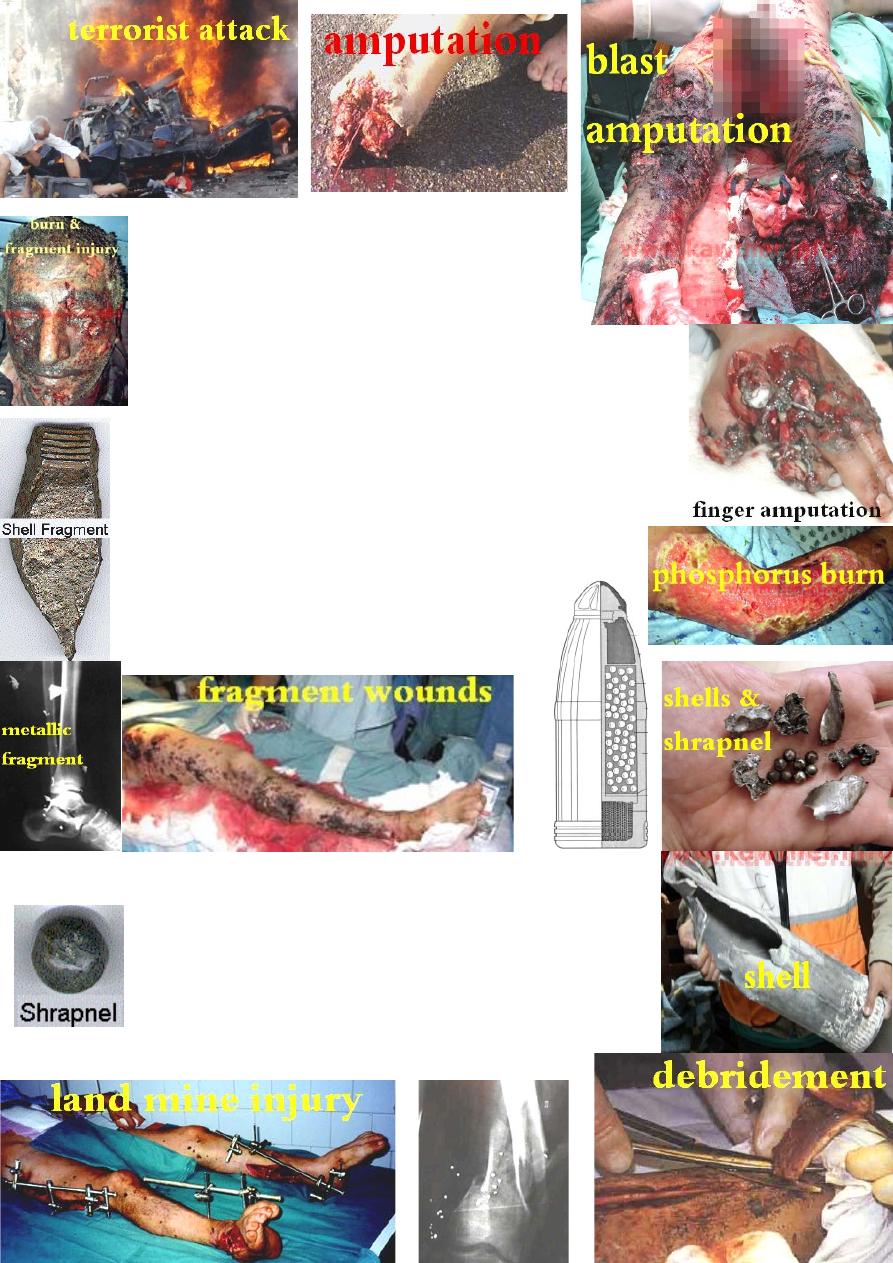
Explosive munitions injuries: common in war time
&terrorist attacks. They cause blast injuries which
are divided into 4 types:
1-Primary blast (wave)injury: caused by the direct
effect of blast over pressure on the tissue leading to :
a-complete or incomplete amputation (usually irreparable).
b- injury to any gas containing organs like lungs, tympanic
membrane and bowel.
2-Secondary blast injury: is the penetrating injuries caused by
the weapon shell & shrapnel (primary fragment injuries) &the
fragments resulting from explosion(secondary fragment injuries).
3-Tertiary blast injuries: caused by displacement of the body by
shock wave striking other objects that may cause #.
4-Quaternary blast injuries: are injuries resulting from
building collapse &fire like burn &toxic chemicals
poisoning.
The most common pattern of injury seen in is
multiple small fragment wounds of the extremities.
Treatment: ( Treat the wound, not the weapon.)
Start with: history, physical exam., radiological evaluation
&classification of wounds & # (Gustillo's system), then either:
non-operative(ra
re) or usually operative Ŗ which includes:
1-AT prophylaxis, 2-AB., 3-Wound irrigation &meticulous
debridement (usually 2
nd
, 3
rd
look debridement).
4-Fracture stabilization which is critical for wound healing
&to ↓ the risk of infection.
5-definitive wound cover.
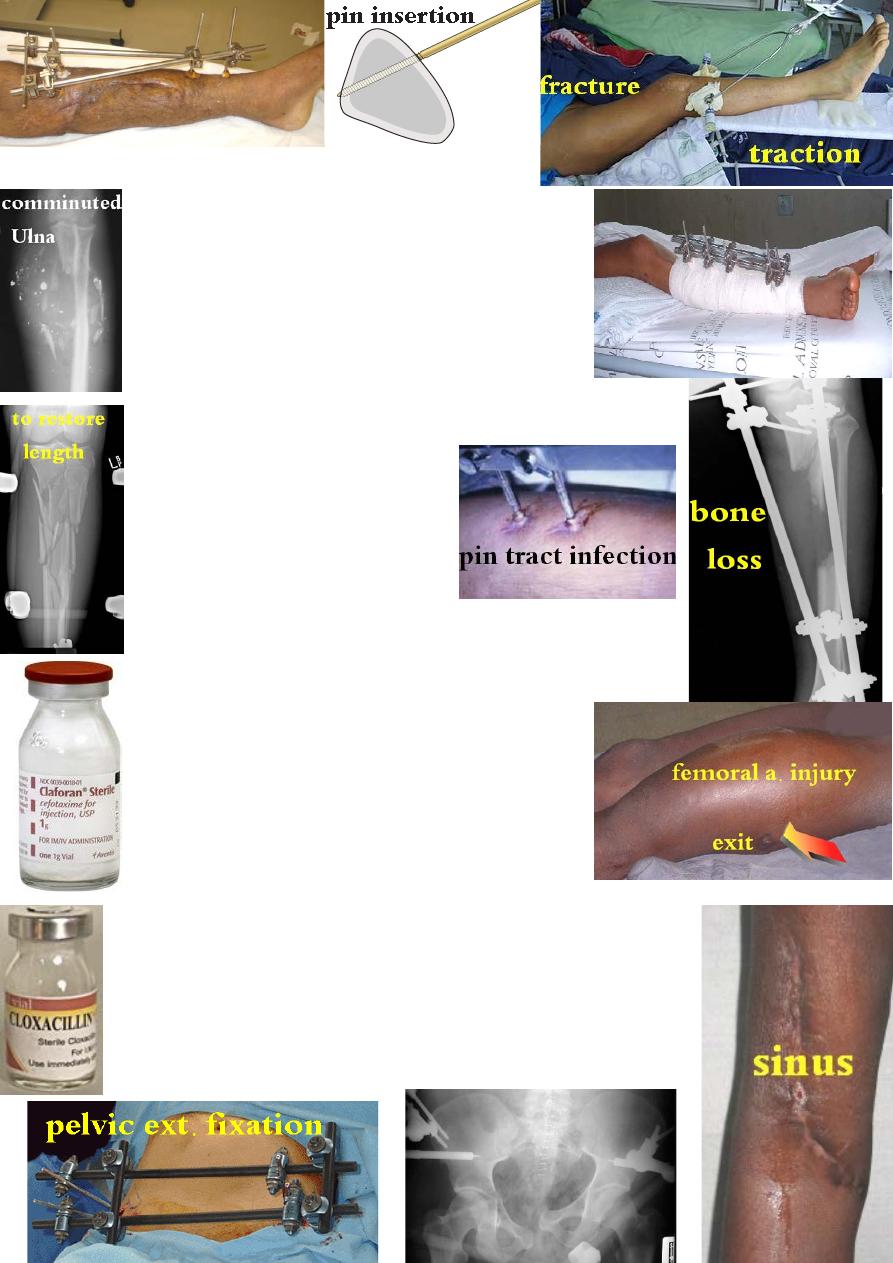
Fracture stabilization:
1-Traction: has limited use nowadays.
2-Splitage: used for closed # and for low energy
open # of the leg, ankle & upper limb(
G І & П).
3-External fixation: is the method of choice for
high energy open # (G П & Ш). It ↓ the systemic
effect of injury in multiply
injured patients by ↓
hemorrhage &↓ the release of inflammatory mediators.
External fixator can be used as a temporary fracture
stabilizer for 2 weeks then change (when the wound
become clean and the risk of infection negligible) to
internal fixation; or as a definitive fixation till # healing.
Indications of external fixation:
1- open fractures of the lower limb.
2- impending open fracture.
3- # associated with vascular injury.
4- fracture with significant bone loss.
5- to restore length and alignment.
6- pelvis fracture.
7- closed # that are difficult to splint during long transport.
Complications of external fixation:
1-joint stiffness,
2-pin tract infection, 3-pin placed into # site.
4-pin placed into the joint,
5-pin placed too shallow.
6-pin placed too deep causing neurovascular injury.
7-pin fracture in side the bone.
Prevention of war wound infection:
1-aggressive wound care.
2-early & enough AB.
3-fracture stabilization.
Retained missile: not all missiles, remaining in the body, could or
should be removed. Many of them are small, innocent &inaccessible
and attempting removal is risky because damage to nearby structures
may happen during operation more than the missile caused.
Indications of missile removal:
1-persistent pain, 2-discharging sinus, 3-arterio-venous complication.
4-delayed nerve palsy, 5-limitation of joint movement,
6-local &systemic effects according to chemical nature of the missile.
7-patient fear of malignancy.
