ORTHOPAEDIC DIAGNOSIS
Ortho = straight
Paedic = child
Orthopedics is concerned with bones, joints,
muscles, tendons and nerves.
Diseases affecting these structures could be:
1- Congenital or developmental.
2- Infection or inflammation.
3- Arthritis or rheumatic disorders.
4- Metabolic or endocrine.
5- Tumors or lesions that mimic them.
6- Sensory disturbance & / or muscle weakness.
7- injury or mechanical disorders.
Diagnosis depends on getting information from history,
physical examination, imaging and special investigations.
History: Is very important.
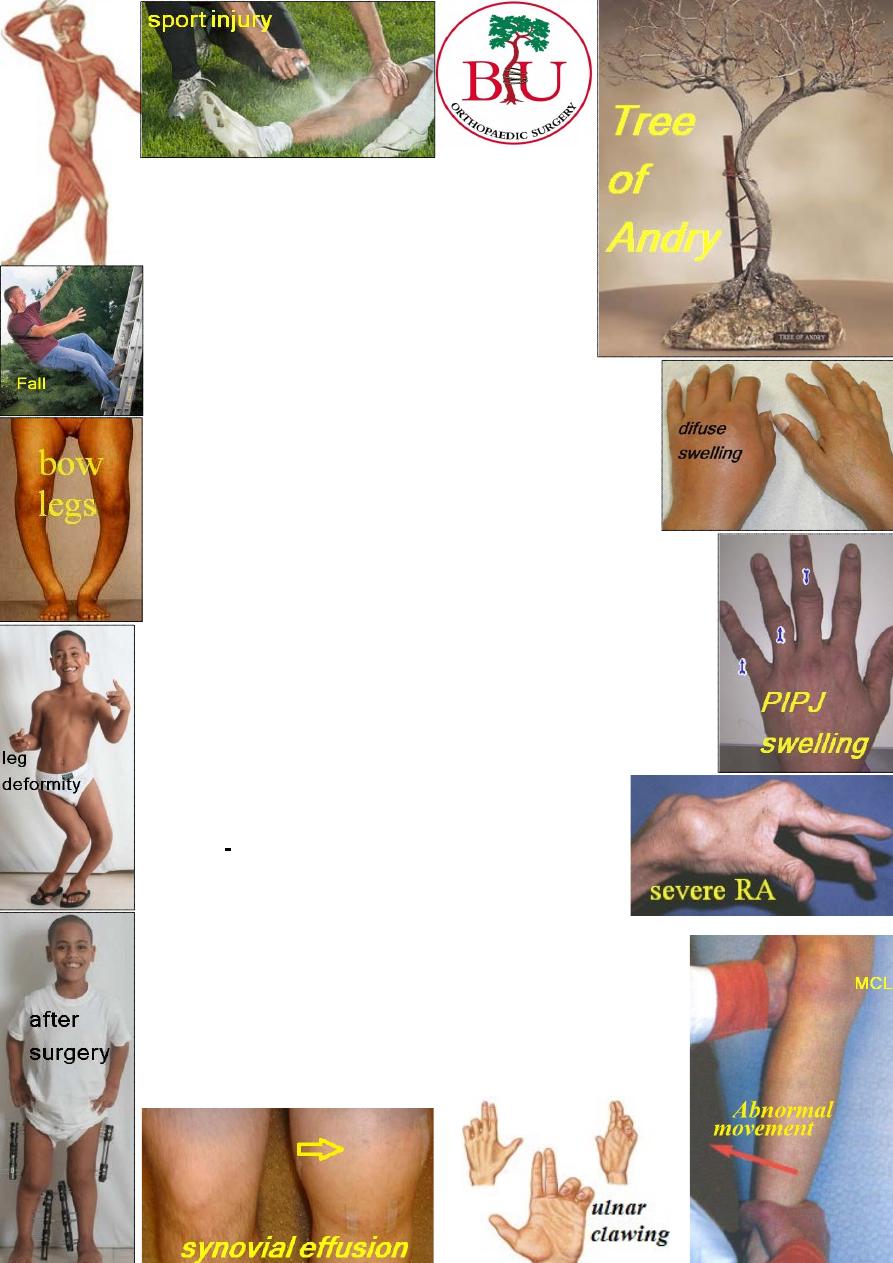
Ask about: injury, pain, stiffness, swelling, deformity,
instability, weakness, change in sensation and loss of
function. You have to know each symptom whether started
suddenly or gradually; how it has progressed; what makes
it worse; what makes it better. Also ask about past history
(previous disease or injury), family history, work
of the patient and general health.
:
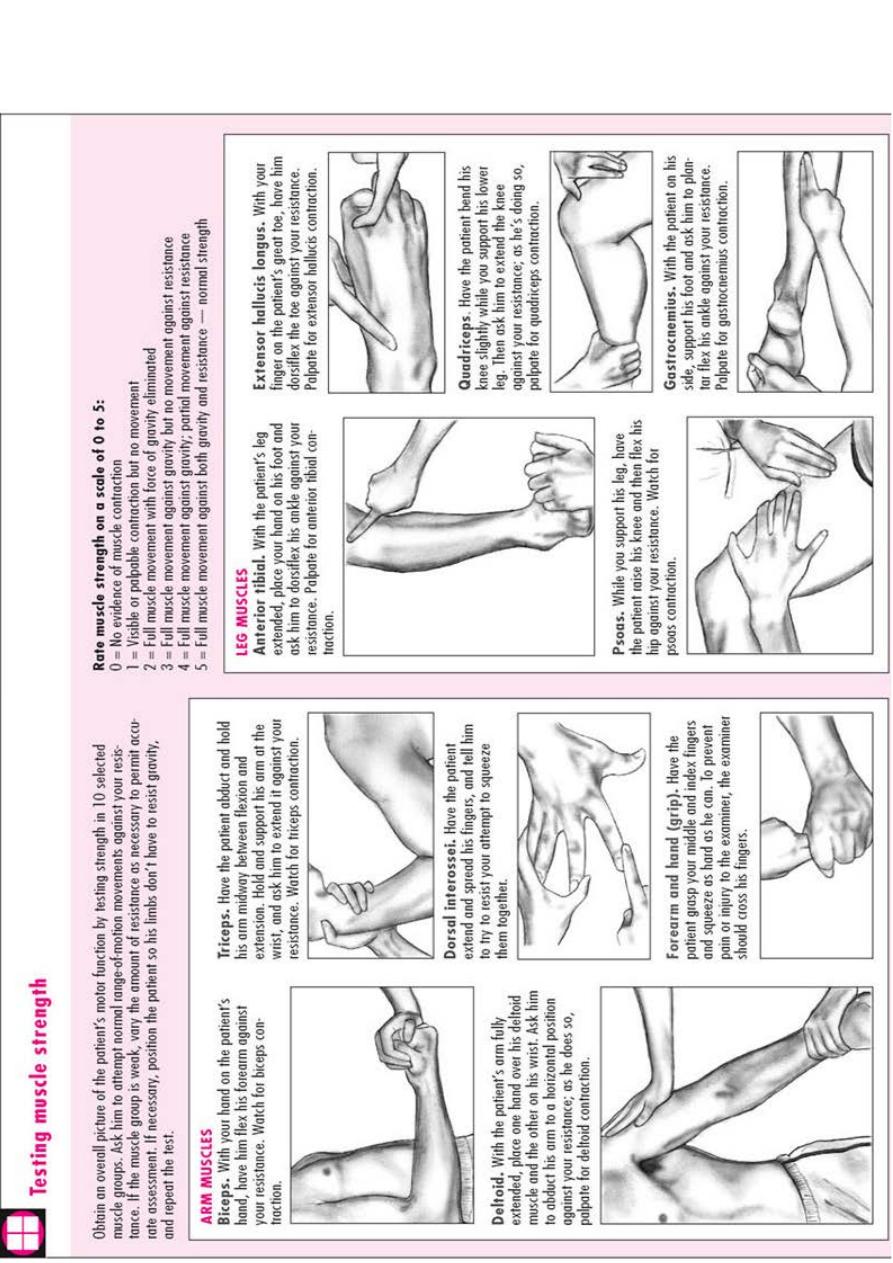
examination
Physical
The patient should be subjected to general exam.,
then gait exam., then exam. of the affected part :
1-Look: examine the skin, the shape and the position.
2-Feel: feel the skin, soft tissue, pulse, bone and joint,
synovium, fluid in the joint and the site of tenderness.
3-Move: ask the patient to do active movements, then you
do passive movement, then test for abnormal movement.
Neurological exam.: look at general appearance, then
motor (tone, power and reflexes) & sensory function.
Imaging
:
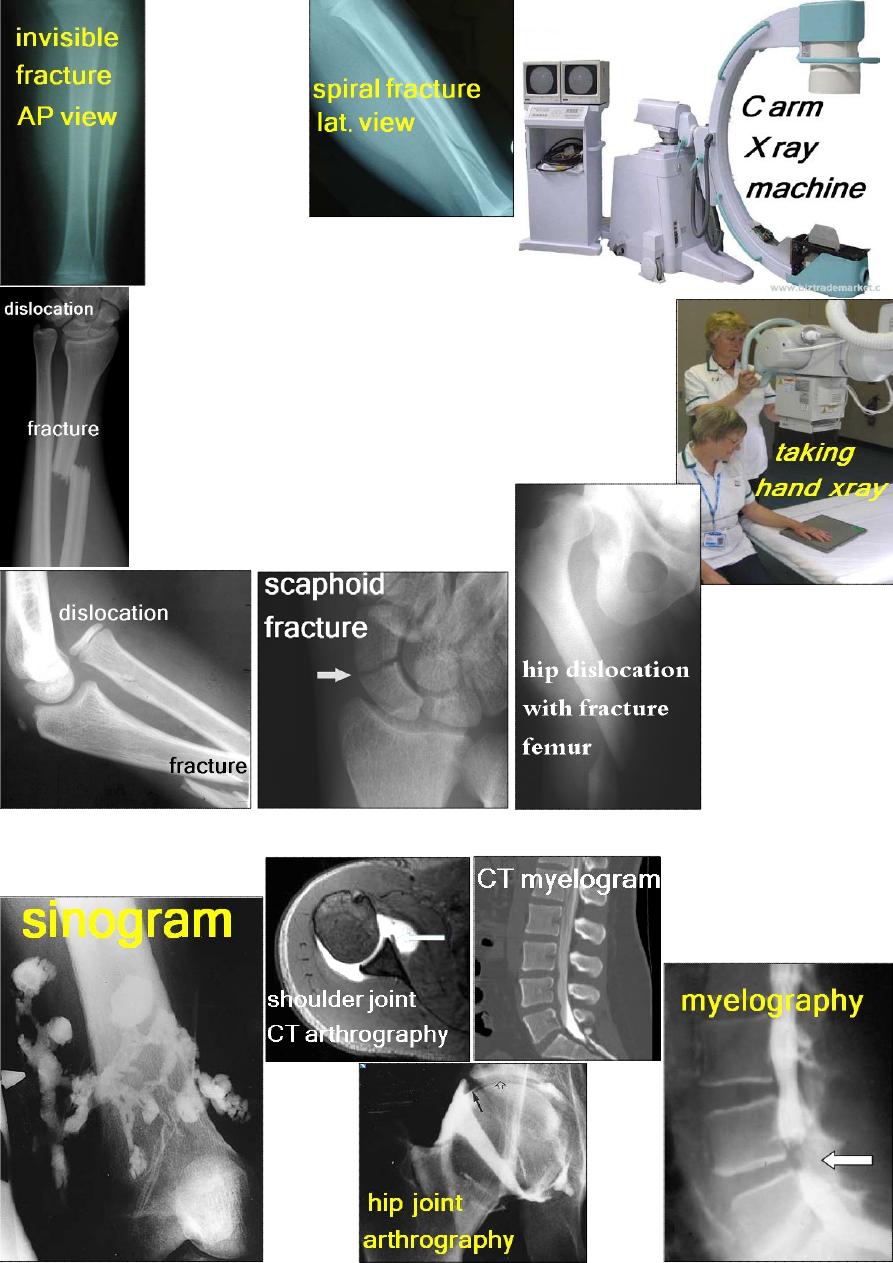
I- Plain X-ray:
For accurate diagnosis, it is better to
apply the: Rule of 2:
1- Two views: some fractures or dislocations cannot be
seen in one view, so take at least AP and Lateral views.
2- Two joints: one above and one below e.g. displaced
fracture of the ulna may be associated with radial head
dislocation which if not x-rayed, would be missed.
3- Two limbs: for comparison especially in children.
4- Two injuries: e.g. fracture of calcaneum may
be associated with spine fracture.
5- Two occasions: e.g. scaphoid # may
need 2 weeks to be visible on x-ray.
П- X-ray using contrast media: sinography, arthrography &myelography.
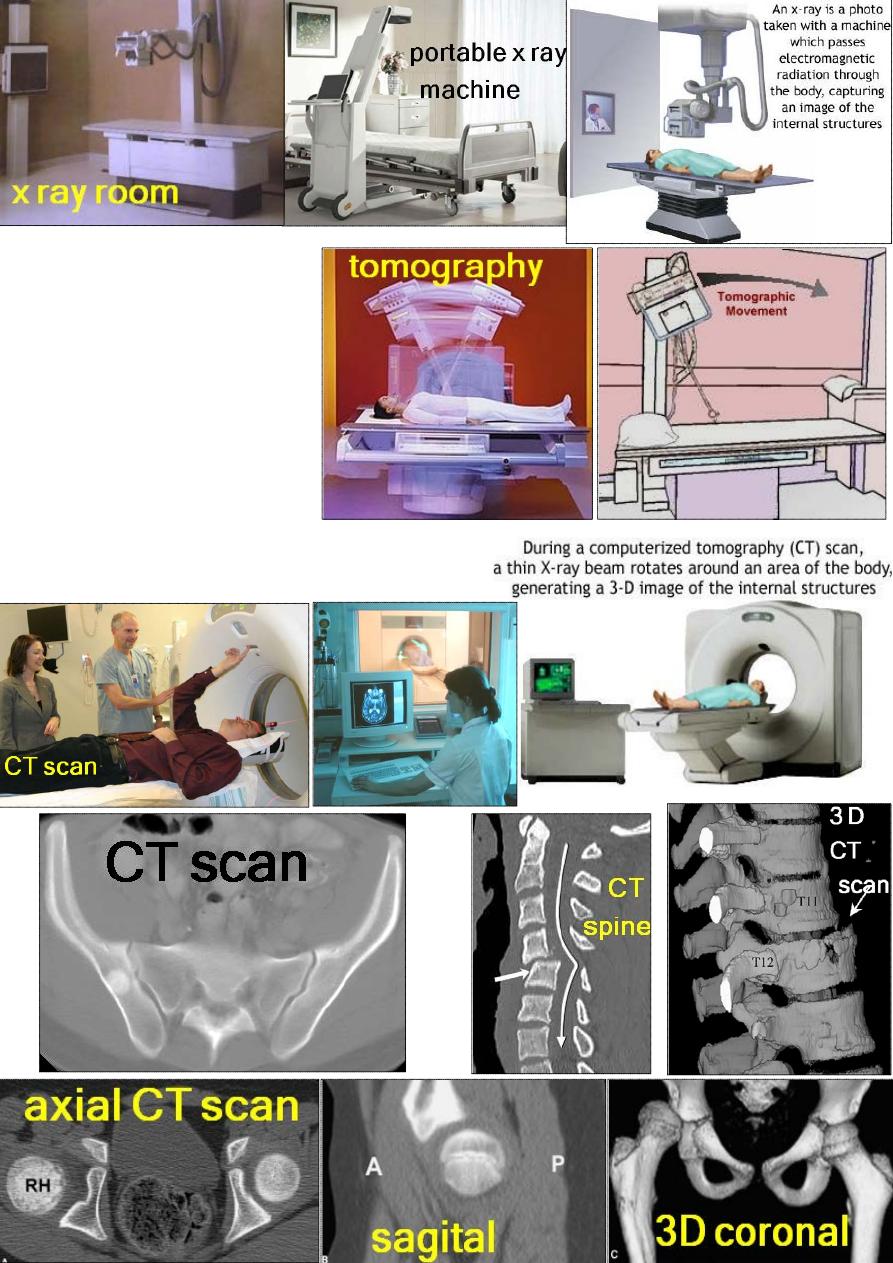
Ш –Tomography:
IV- CT scanning.
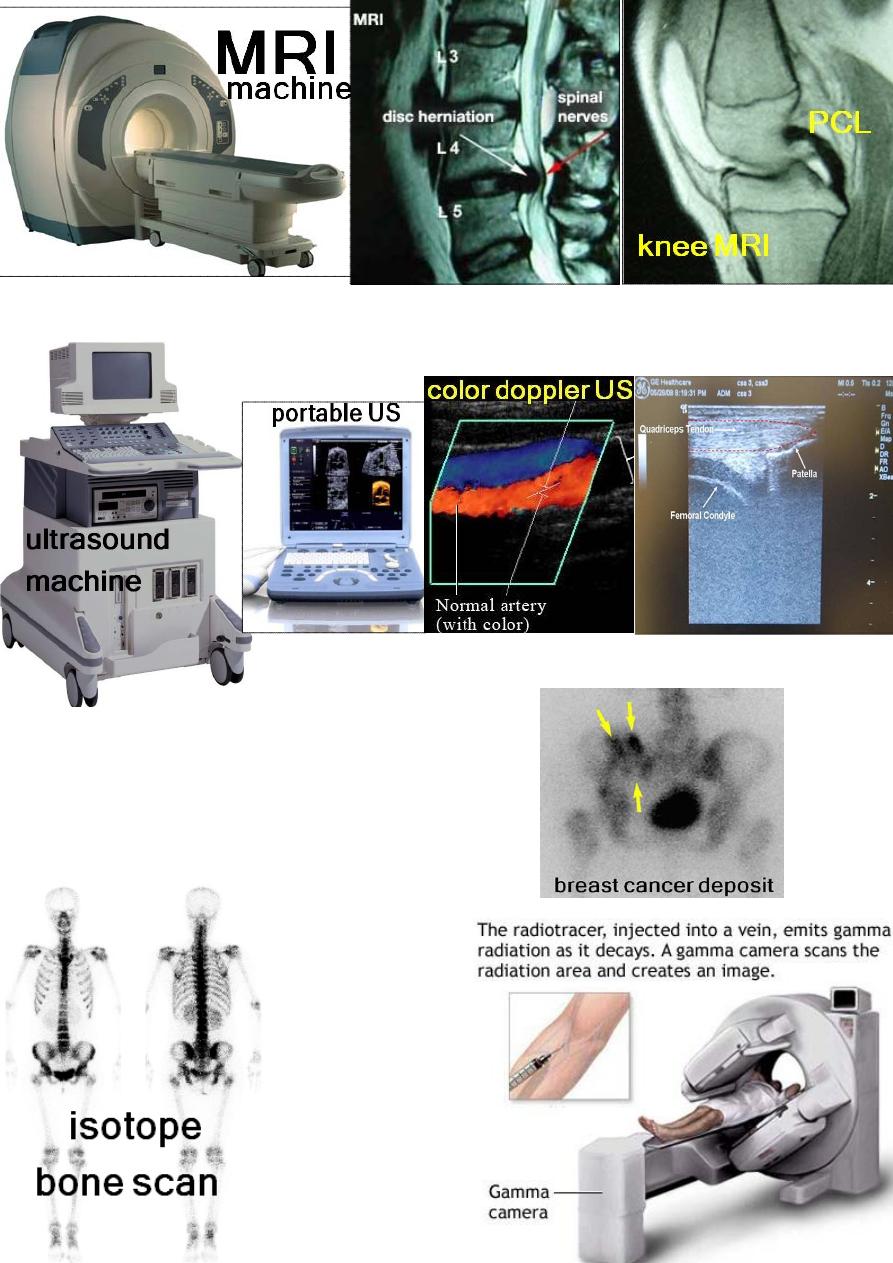
V- MRI.
VI- Ultrasound.
VП-Radionuclide imaging:
Using: Technetium 99,
Gallium 67,
or Indium 111.
Blood tests:
Hb, WBC, ESR,
C-reactive protein,
Rheumatoid factor,
Tissue typing (HLA
antigens) and
biochemical tests.
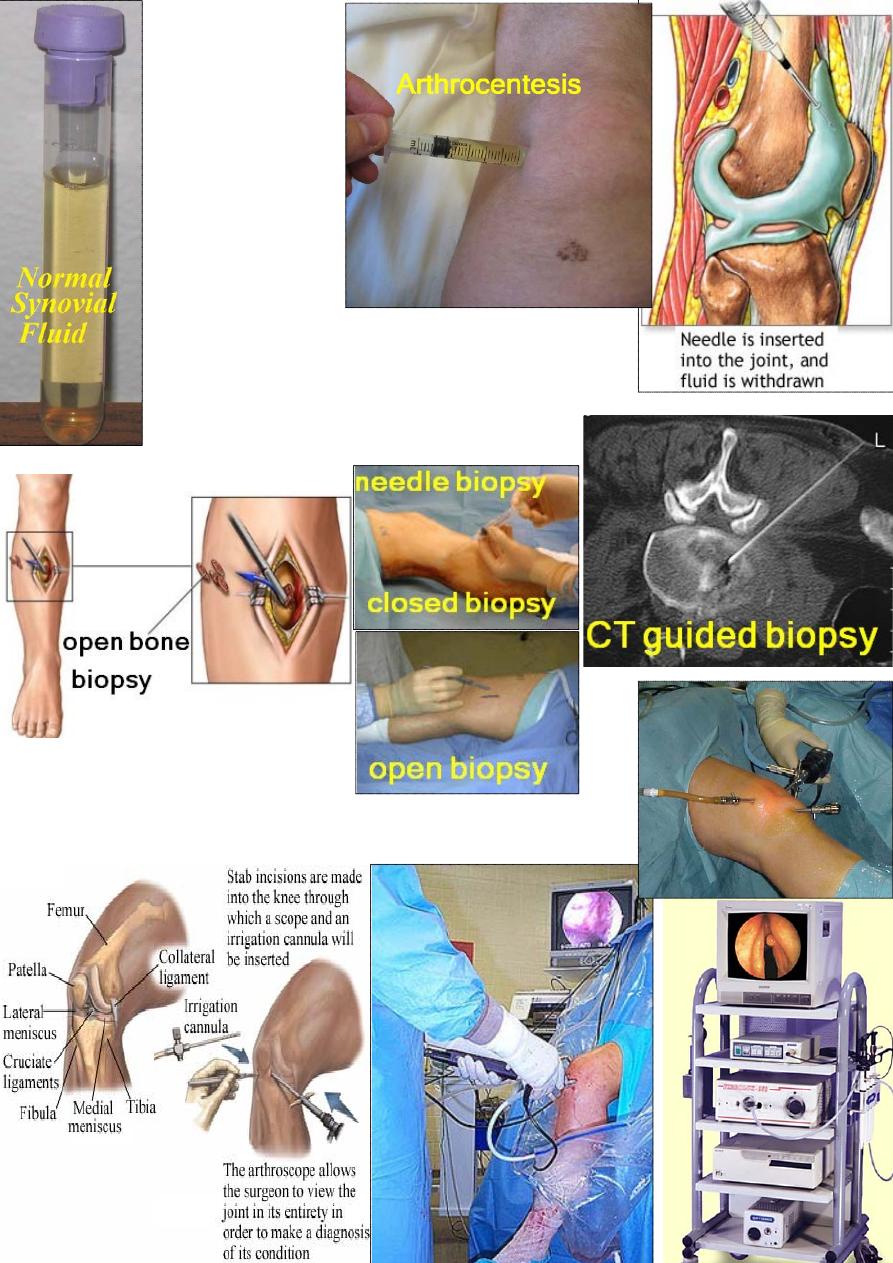
Synovial fluid analysis:
organism,
WBC count, culture and sensitivity.
Bone biopsy:
either open or "closed".
Arthroscopy:
Introduce a tube and light to see interior of the joint
(diagnostic), or to do certain procedures (operative).
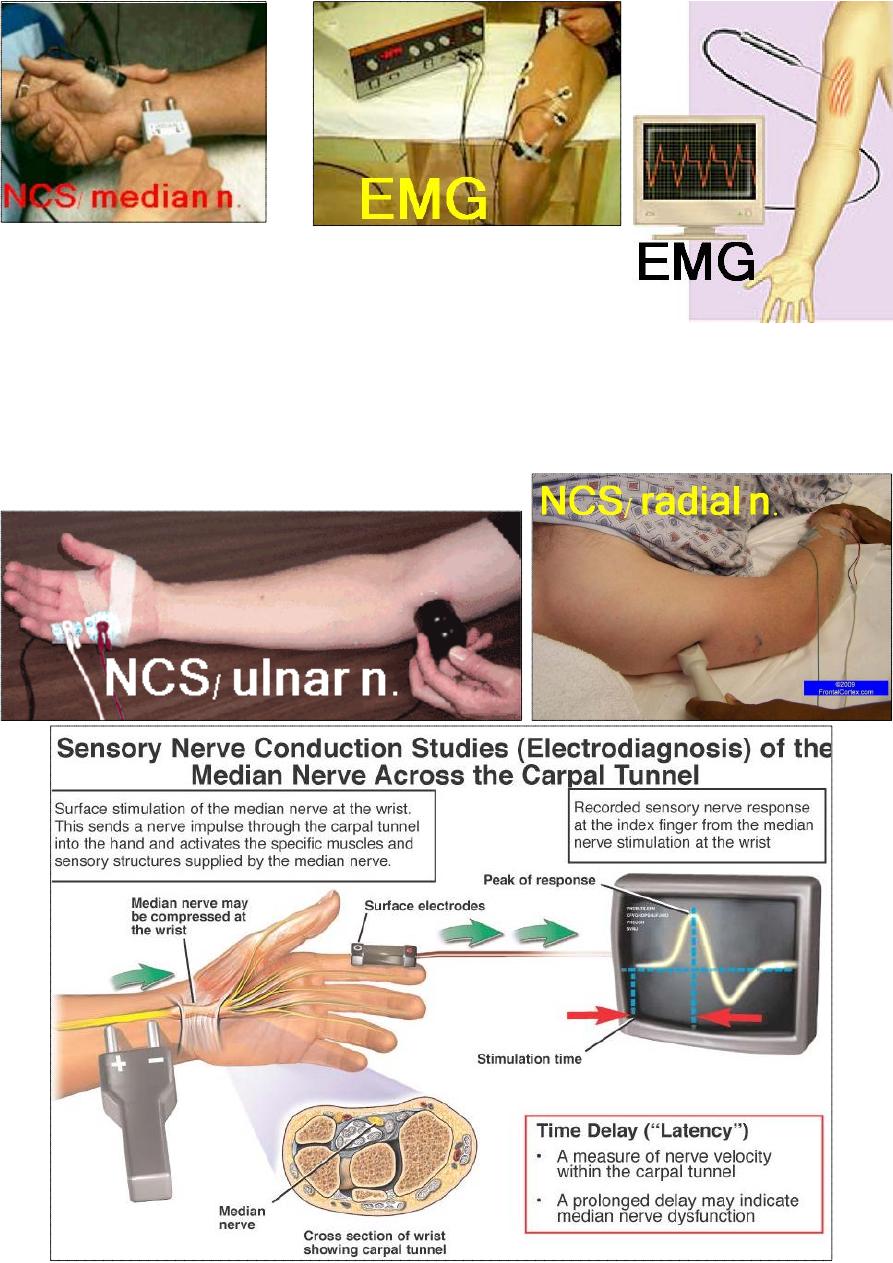
Electro diagnosis:
This test the nerve and muscle function:
Nerve conduction study: measure the conduction velocity
e.g. a compressed nerve cause a delay in conduction.
Electromyography (EMG): test the activity of a muscle at rest
and during contraction; e. g. a denervated muscle has
spontaneous abnormal activity at rest.
It can also differentiate between neuropathic
and myopathic disorders; though, nerve
and muscle biopsy may be necessary.