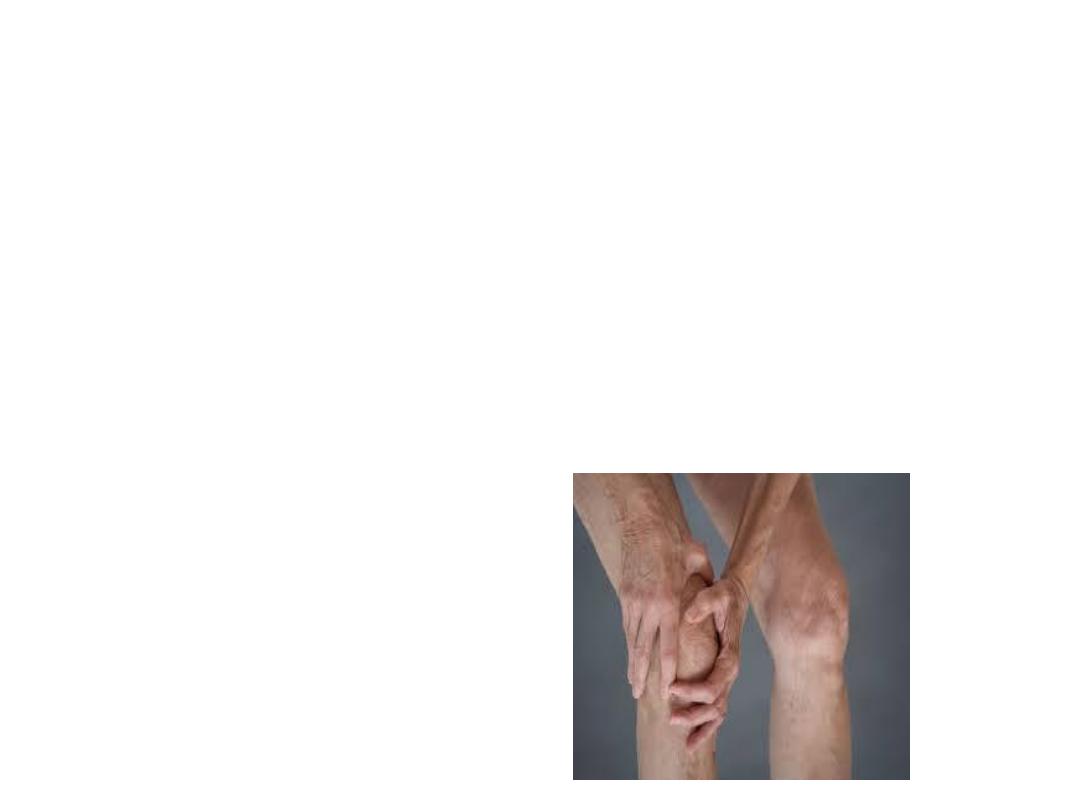
Osteoarthritis
Definition: common form of arthritis and pain,
disability, age-related , focal loss of articular
cartilage cartilage, subchondral sclerosis,
osteophyte formation, joint enlargement.

Epidemiology:
• The prevalence rises progressively with age.
• Knee 45% and hip 25% of people at some point
during life
• Can be asymptomatic ,Pain symptoms more in
female but in hip equal.
• Ethenic: hip OA is lower in Africa, China, Japan
and the Indian than eurepean.

Aetiology:
complex disorder. Enviromental,
mechanical, genetic
Local factors:
Increase in wt., injury, occupation,
developmental abnormalities, joint laxity, RA,
gout.
Systemic factors:
Sex horm. Genetic, racial, low
vit. D and C, hemochromatosis, hyperlaxity.

Pathology:
• Increase in breakdown, degredation of aggrecans
and collagen II---- Mettalo-proteinase.
• Proinflammatory cytokine, prostogly., reactive O2
species.
• Mechanical stress.
• Gradual loss of cartilage., fissuring, deep vertical
cleft.( initially at maximum load) CPPD, HA crystal.
• Subchondral bone, osteophyte, contracted
capsule, M. atrophy.
• Mild syn. Inflammation.
Clinical features:
Symptoms:
• Pain.
• Intermittent, use related.
• Gelling.(short, brief inactivity stiffness
• Correlation ,The correlation between the presence of
structural change, pain and disability varies markedly
according to site. Hip more than knee
• Coexistence with other conditions, so it is important to
remember that pain in a patient with OA may be due to
another cause.
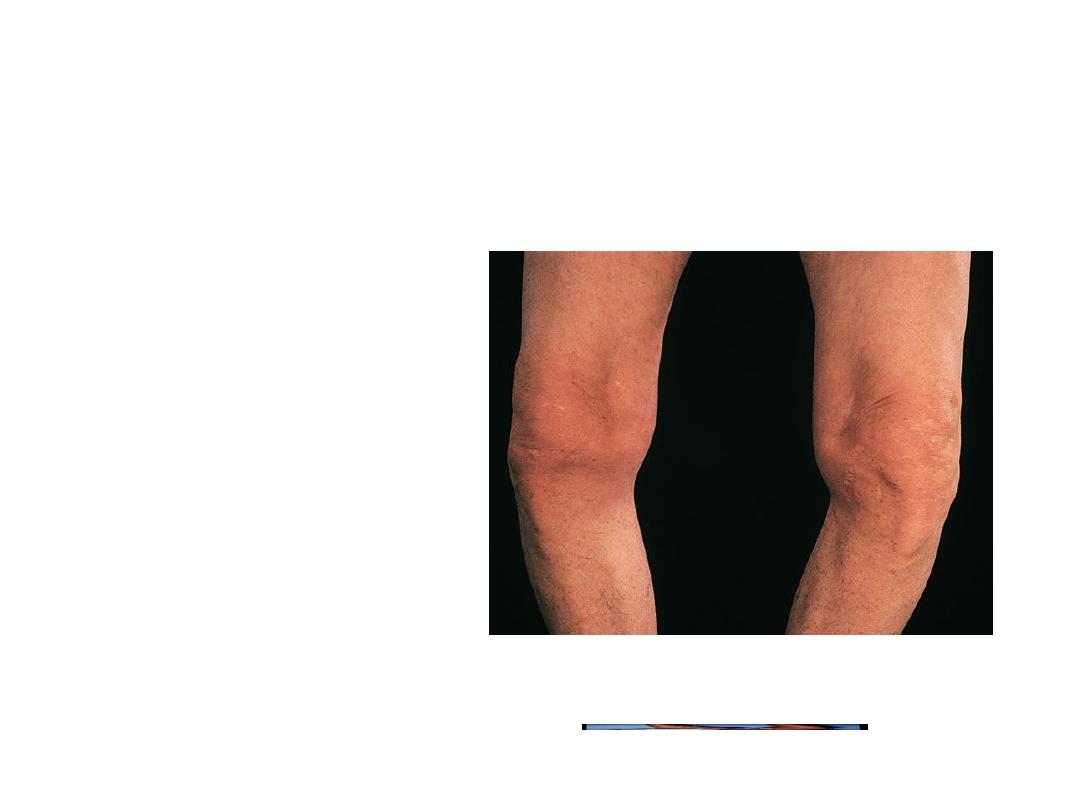
Signs:
• Restricted mov.
• M. spasm.
• Crepitus.
• Bony swelling.
• Deformity.
• M. weakness.
• Synovitis.
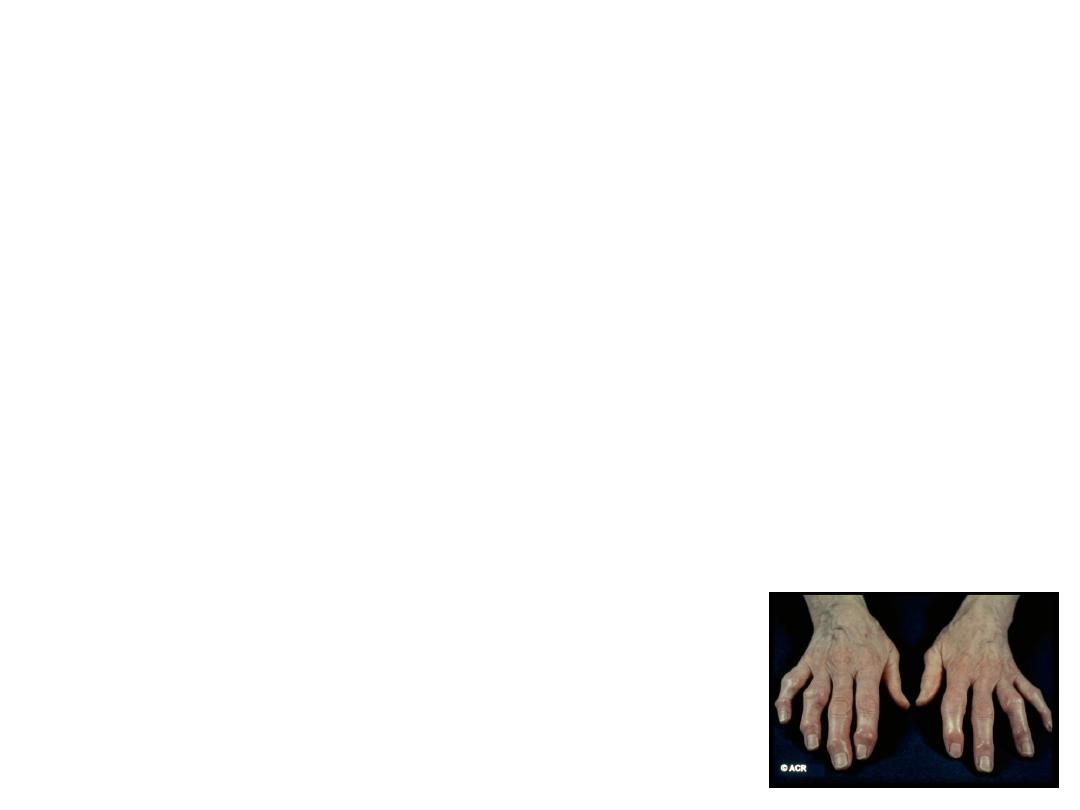

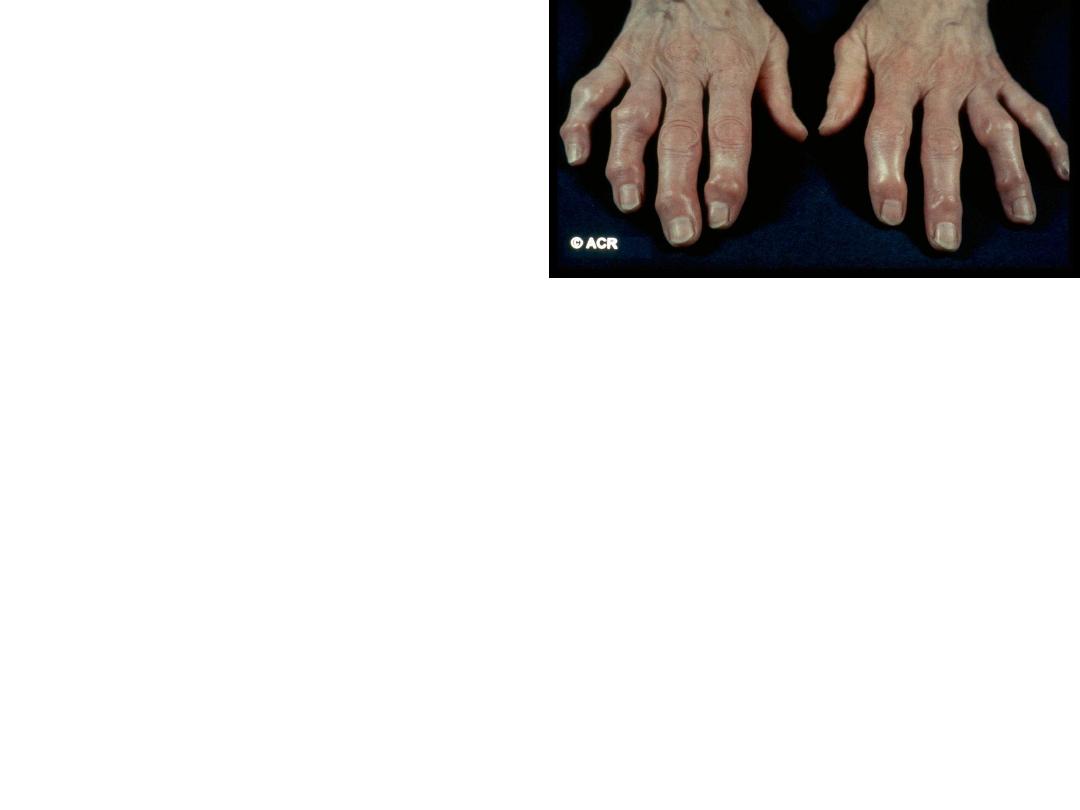
Nodal generalized OA
• Polyarticular finger interphalangeal joint OA
• • Heberden’s (± Bouchard’s) nodes
• • Marked female preponderance
• • Peak onset in middle age
• • Good functional outcome for hands
• • Predisposition to OA at other joints, especially
knees
• • Strong genetic predisposition

• EARLY ONSEOSTEOARTHRITIS
• symptoms and signs of OA may present before the age of
45
• Single joint , trauma, localized cause
• Several joints: unsual sites for OA:
• Juvenile idiopathic arthritis • Metabolic or endocrine
disease
• Haemochromatosis, Ochronosis
• Acromegaly • Spondylo-epiphyseal dysplasia
• • Late avascular necrosis, Neuropathic joint
• Kashin–Beck. is a rare form of OA that occurs in children,
typically between the ages of 7 and 13, in some regions of
china (celenium defecincy, mycotoxin contamination?)

Erosive OA
Usually hand, prolong symptoms , more
inflammations, more .disabilty and worse outcome
than nodal hand OA function
mainly PIP subchondral bone destruction , even
bony ankylosis, not asscociated with OA else
where .

•
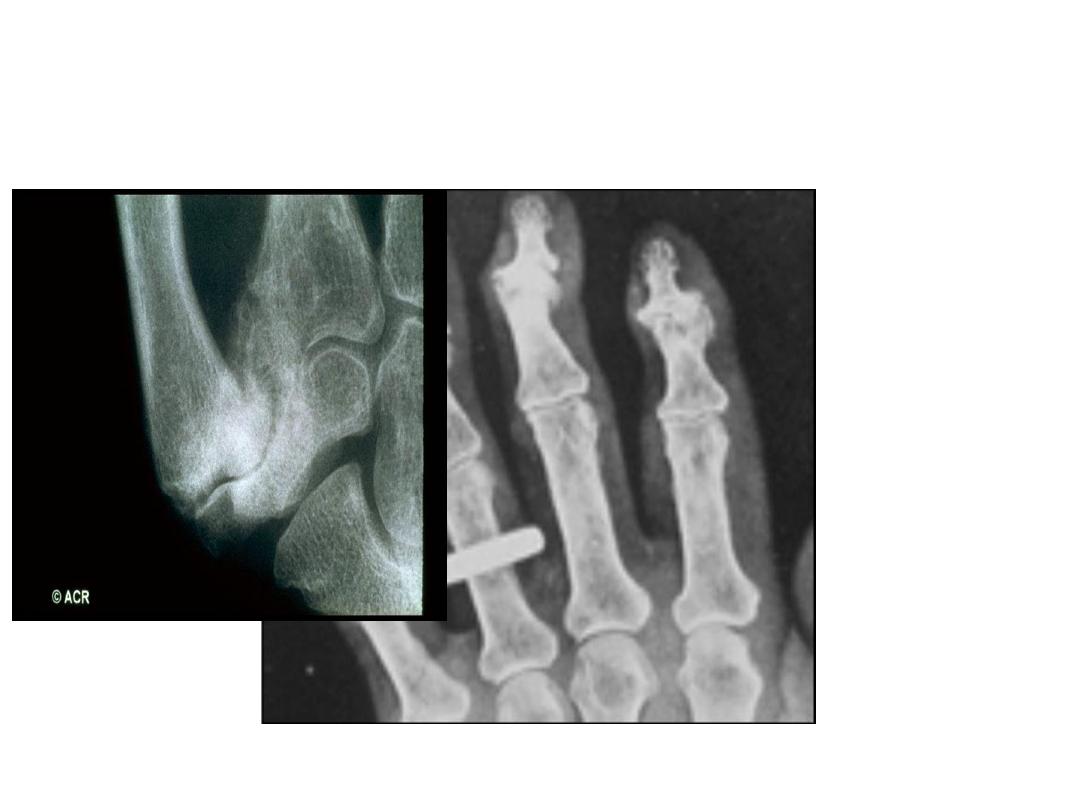
Investigations
•
-
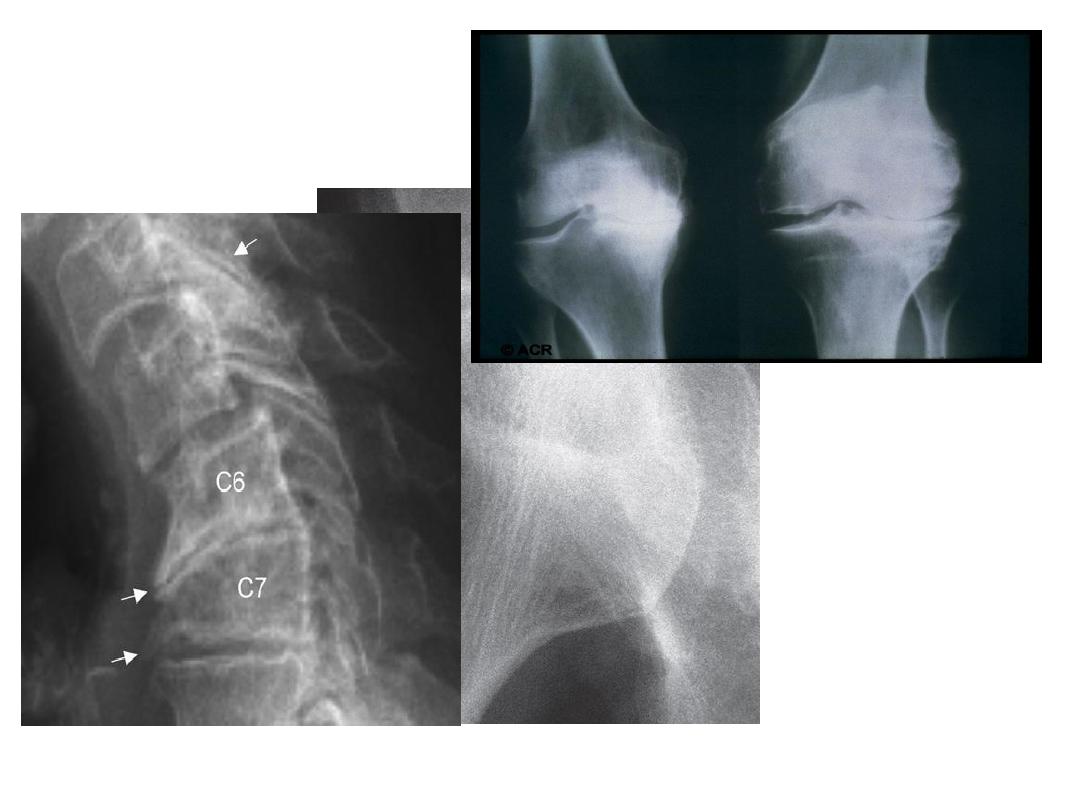
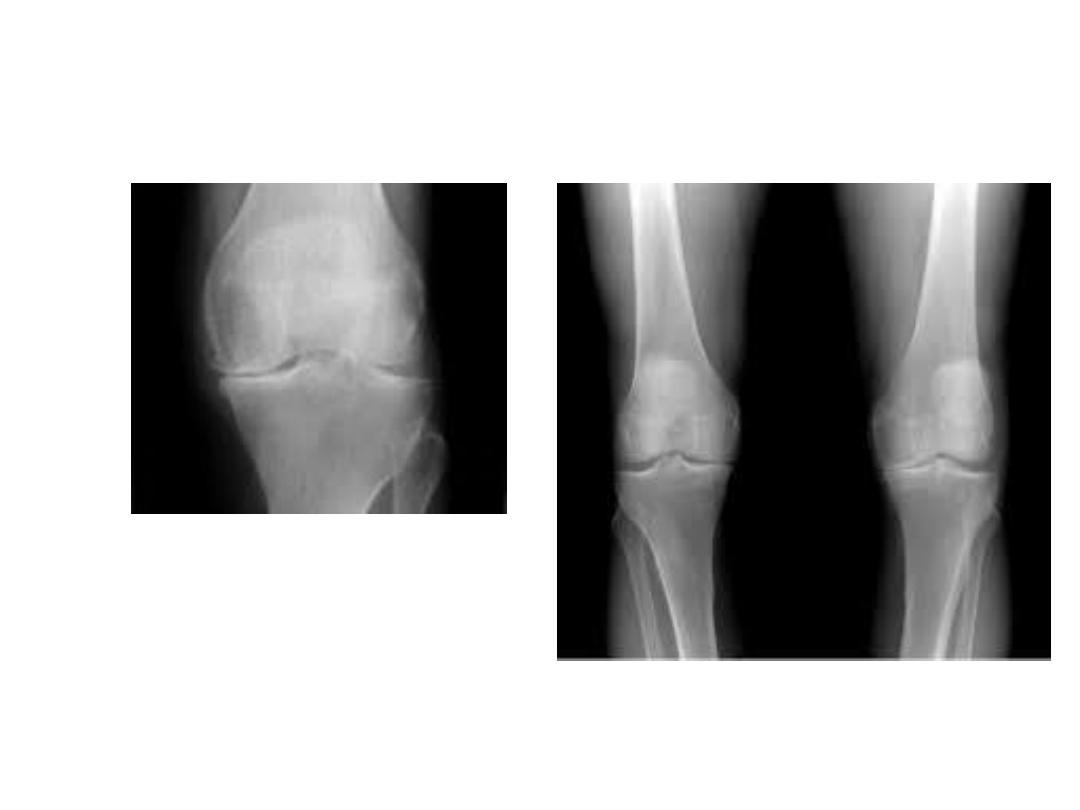
A plain X-ray of the affected joint show one or more of
typical features of OA.
•
joint space narrowing , subchondral sclerosis , marginal
osteophytes and bone cysts .
•
X-ray of spine OA typically shows evidence of disc space
narrowing and osteophytes.
•
If nerve root compression or spinal stenosis is suspected,
MRI should be performed
•
.
Radiological
• Synovial fluid
• aspirated from an affected joint is viscous
with a low cell count

• unxplained early-onset OA requires
additional investigation, guided by the
suspected underlying condition.

• Management.
• Education : about
• -The nature of the disease .Although
established structural changes are
permanent but, pain and function can often
be improved.
• -Relevant risk factors such as obesity,
heredity trauma.
• -Prognosis , wich is generally good for nodal
hand OA and better for knee than hip OA .

• Non pharmological treatment:
• -Weight loss is one of most effective treatment for
lower limbs joints.
• -. Strengthening and aerobic Quadriceps
strengthening exercises are particularly beneficial
in knee OA.
• -Shock-absorbing footwear
• - Pacing of activities
• -Use of a walking stick for painful knee or hip OA
• - Built-up shoes to equalise leg lengths .

• -
Acupuncture and transcutaneous electrical nerve
stimulation (TENS) have been shown to be effective in
knee OA.
• Local, heat or cold, can sometimes give temporary relief.

• . Pharmacological therapy :
If symptoms do not respond
to non-pharmacological measures,
• Paracetamol should be first tried.
• -Addition of a topical NSAID, and then capsaicin, for knee and
hand OA can also be helpful.
• -Oral NSAIDs , when symptoms persist and can be successfully
combined with paracetamol or compound analgesics if the pain is
severe . You should considered the hazardous side effects and its
contraindications.
• -Strong opiates may occasionally be required temporarily .
• -Antineuropathic drugs, such as amitriptyline, gabapentin and
pregabalin, are sometimes used in patients with symptoms that
are difficult to control but the evidence base for their use is poor.

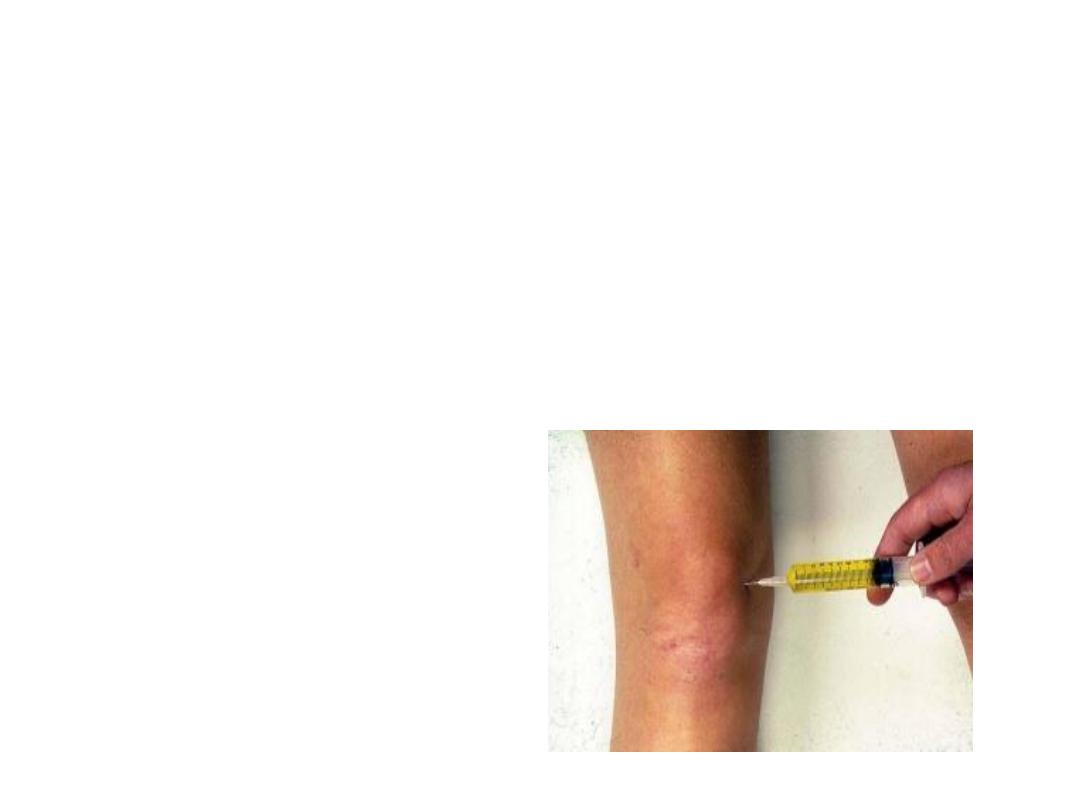
• Intra-articular glucocorticoid injections
• especially in knee OA and first CMC joint.
• . Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid are
effective in knee OA but the treatment is
expensive and the effect short-lived

• Neutraceuticals Chondroitin sulphate and
glucosamine sulphate for the treatment of
knee OA.
• Evidence from RCT that these agents can
improve knee pain to a small extent (3–5%)
compared with placebo.

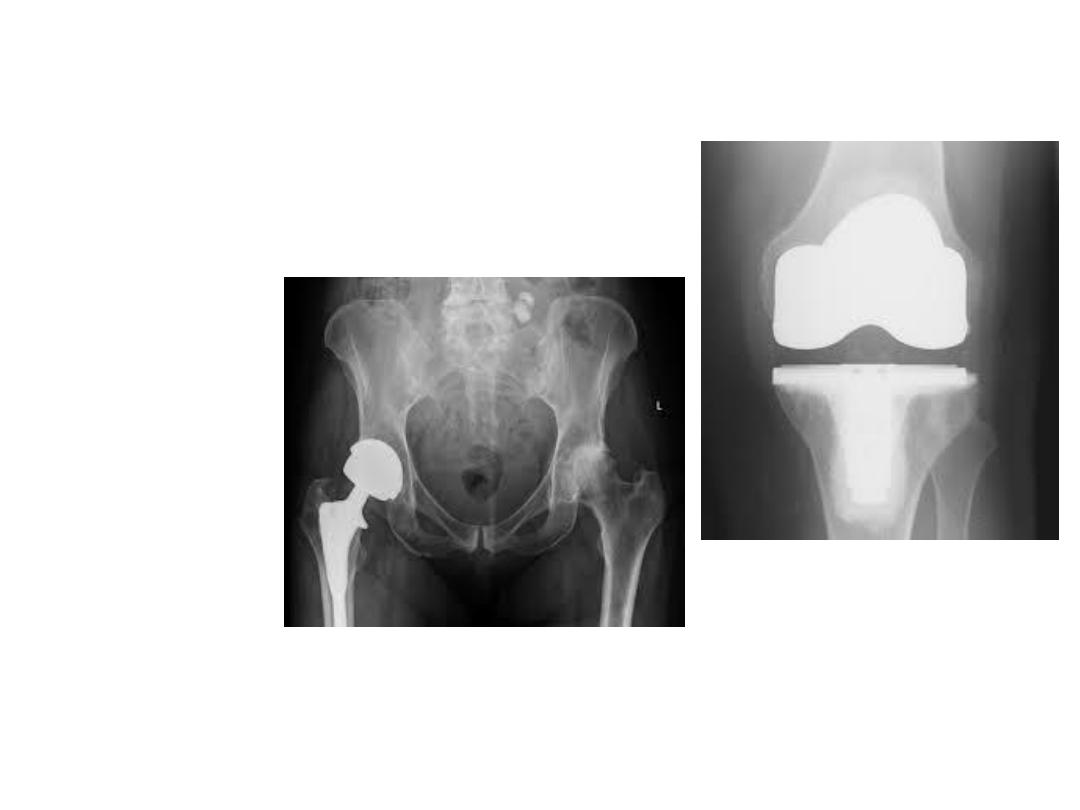
• . Surgery :
• For patients with severe functional impairment despite
of optimal conservative treatment
• -Total joint replacement surgery is by far the most
common surgical procedure for patients with severe
knee or hip OA.
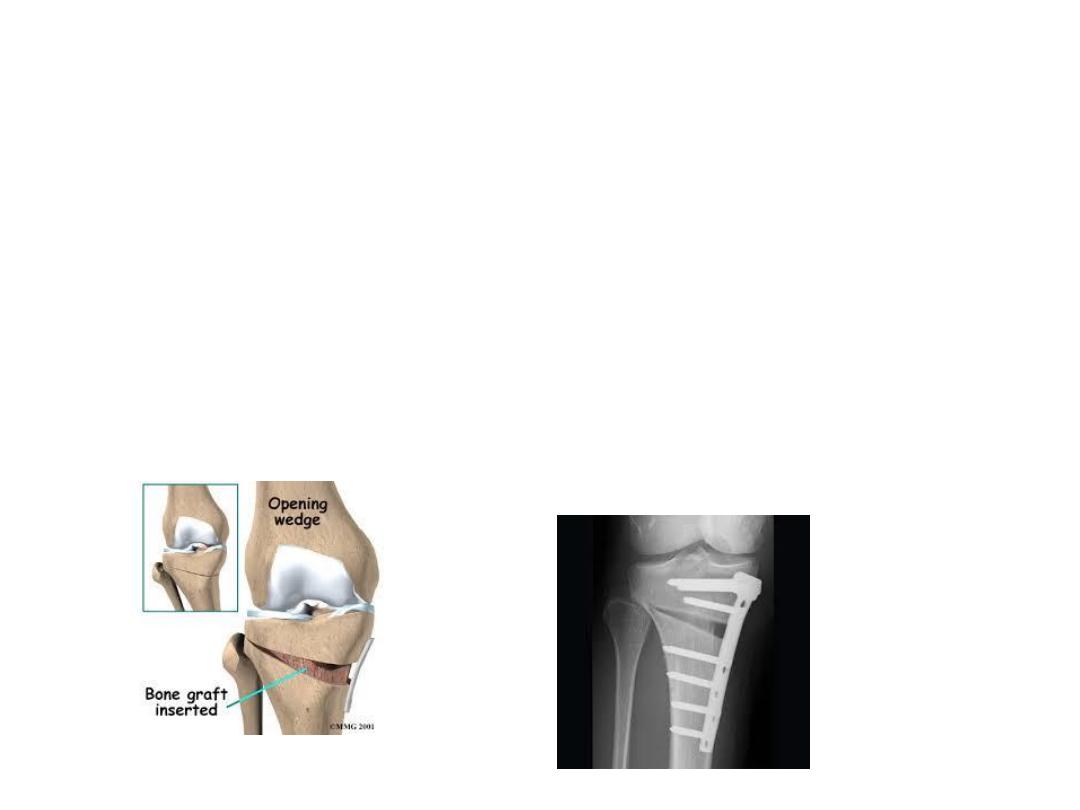
• -
Osteotomy
‘
• is occasionally carried out to for malaligned joints
• - Cartilage repair is sometimes performed to treat focal
cartilage defects resulting from joint injury
