
Definition:
inflammatory arthritis, persisting more
than 6 weeks, occurring before the age of 16 years, for
which no apparent cause can be found and other causes
of arthritis should be excluded. Can subdivided into:
.
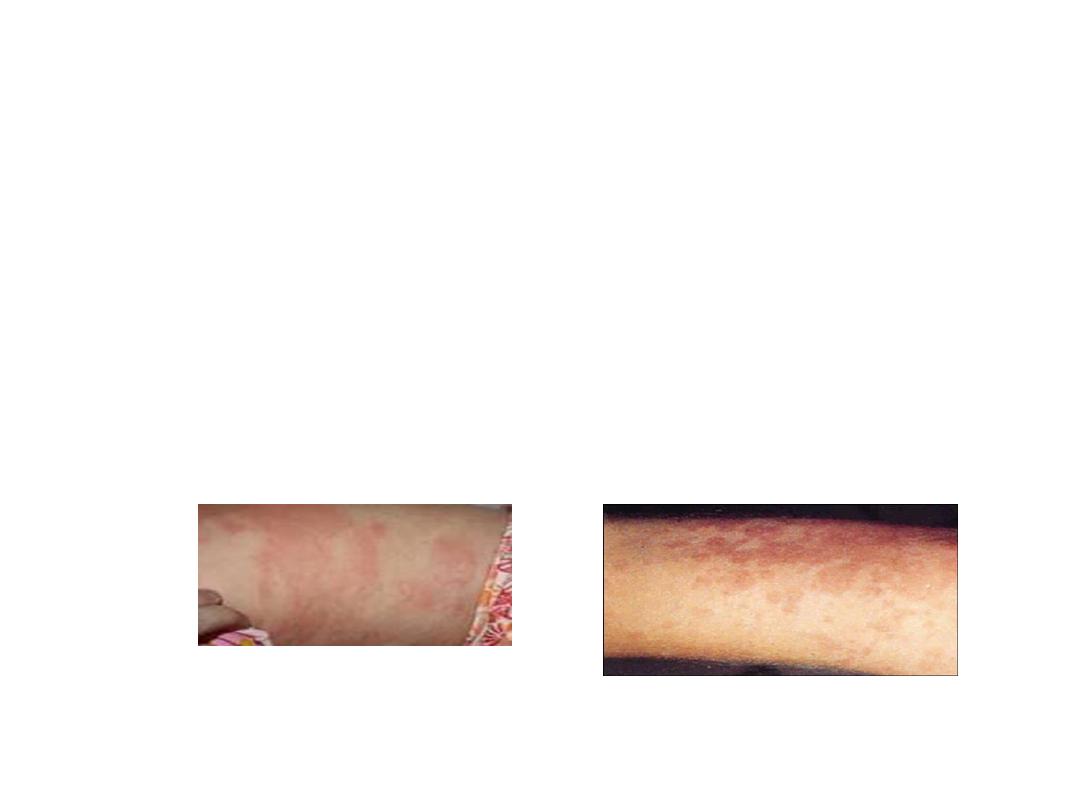
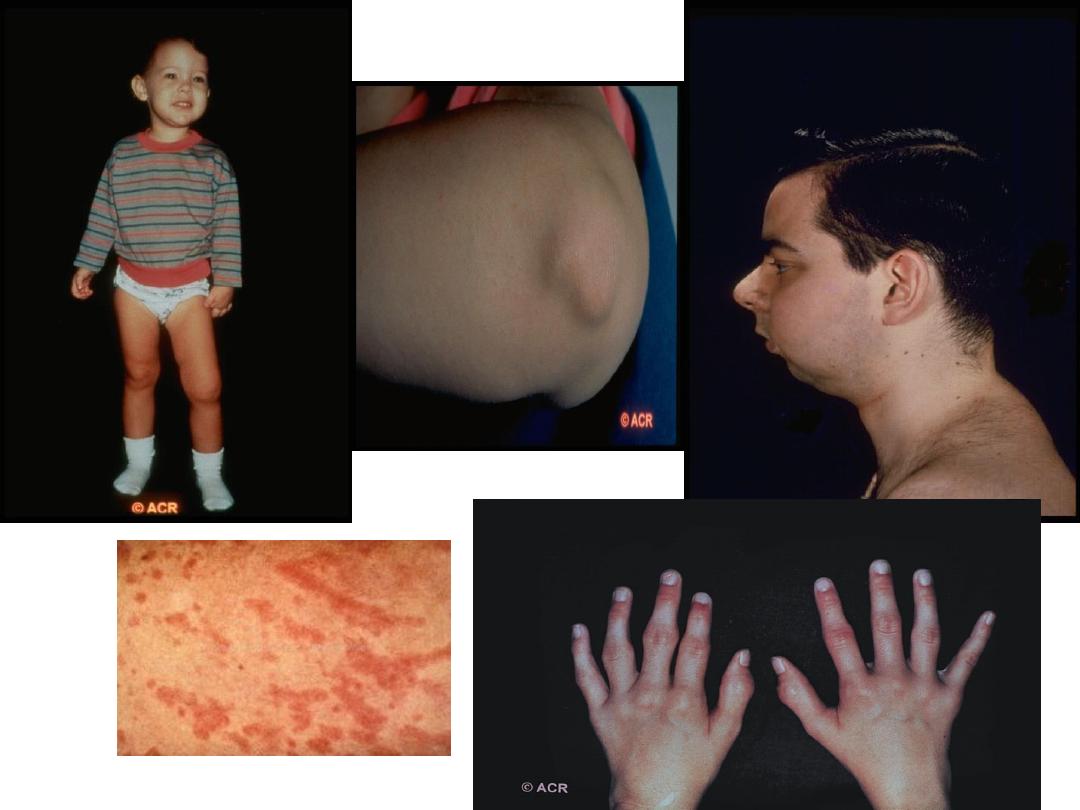
1-systemic type (Still’s disease) : fever, rash,
arthritis, lymphadenopathy,
hepatosplenomegaly and serositis , anaemia
,raised ESR and CRP , negative autoantibodies
,associated with haemophagocytic syndrome.

• 2-
Oligo arthritis: is more common (60% ). most in
females and tends to affect large joints in an
asymmetrical pattern, an association with uveitis .many
patients are ANA-positive. Some can extend to poly
articular type
.

• 3-
Poly-articular type :
RF negative .either extended
from oligo articular type some are ANA positive
• Or presented with polyarticular similar to adult RF
negative RA
.

• 4-
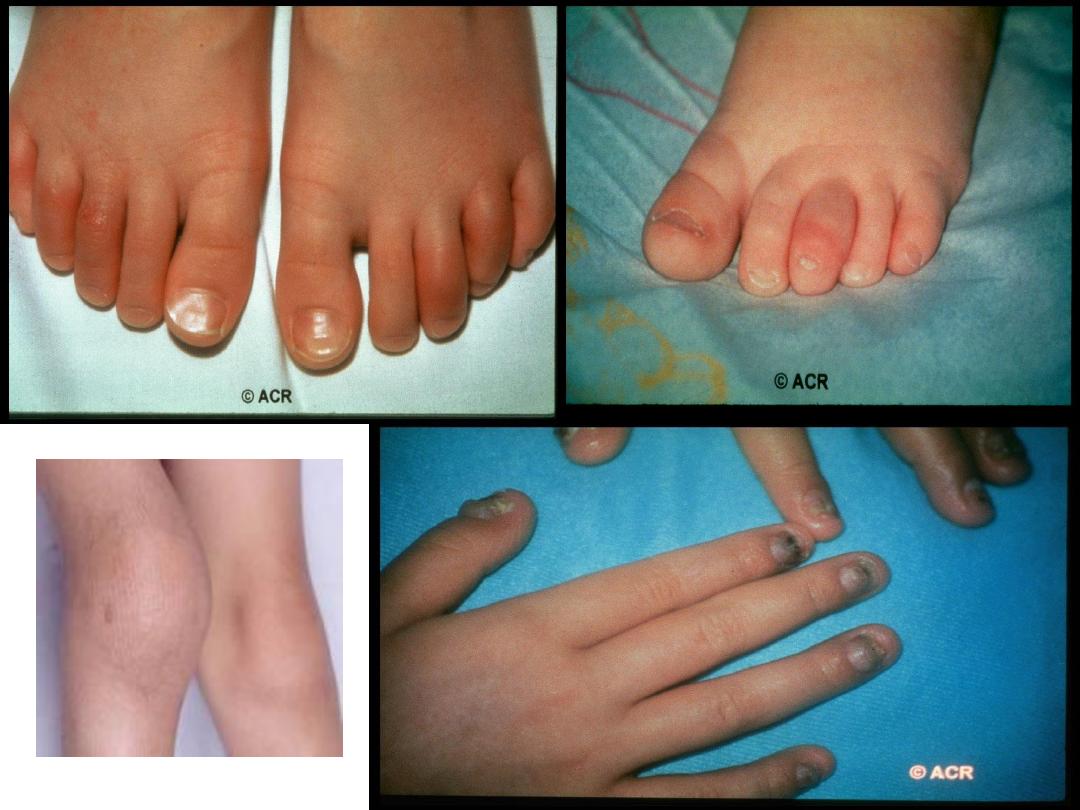
poly articular similar to adult type RF +ve ,
ACPA positive, usually female, and similar to adult
RA and may persist to adulthood, patient may
have nodule , joint erosion , deformity
,

• 5-Enthesis-related artheitis 5% Sacroiliitis, enthesopathy
HLA-B27-positive (juvenile form of ankylosing
spondylitis)
Many cases of enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA) are likely to
be self-limiting forms of spondyloarthritis
But other May progress over time to more obvious form of
spondarthropathy
.

• 6-
Psoriatic arthritis: simlar to adult type , neg
antibodies

Complications:
1- Uveitis:may be clinically sielent and may persist to
adulthood, so routine eye examination is essential
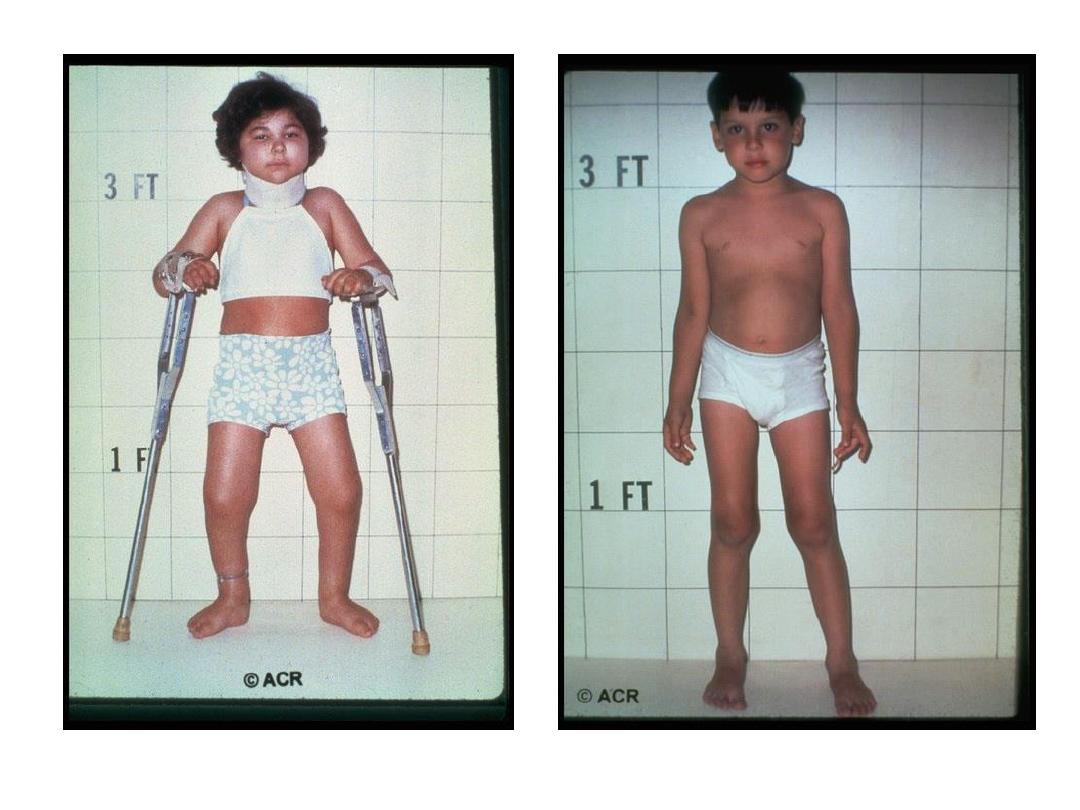
2- Growth disturbance: due to
a- generally the growth is suppressed, due to active disease.
b- by long term glucocorticosteroid therapy.
c- local effects of synovitis may diminish or accelerate
epiphysial growth.
d- early fusion of epiphyses [short limbs, micrognathia].
3- Loss of schooling and family disruption, social and psych.
conseq. for child and family.
4-reduce peak bone mass especially in systemic, poly articular
form

Management: In young children, effective disease
control can repair joint damage before puberty
*pediatric rheumatologist and Team approach:
* Family education * Active physiotherapy
Drug therapy: similar to adult inflammatory disease.
MTX (subcutaneous )
Alternative treatment includes leflunomide,
sulfasalazine and hydroxychloroquine.
Azathioprine and ciclosporine can be used in JIA with
uveitis

Mycophenolate and tacrolimus may have a
role in uveitis alone.
biologic therapy including anti-TNF should be
considered in refractory cases, or
methotrexate or other non-biolog.
Immunosuppressive drugs intolerance.
.
Tocilizumab is also effective in sJIA

• Prognosis is good in uncomplicated oligo-articular
type and some of them may got resolution at
puberty. while systemic type and poly articular
form carry poorer prognosis and about half of the
cases may run to adulthood.

Adult-onset still disease
A rare syst inflammatory dis.
Intermittent fever, rash, arthralgia, hepato splenomegaly,
lymphadenopaty may present
Acute phase reactant elevated, marked elevated serum ferretine
RF and ANA are negative
Most respond to CS but DMARD is needed as steroid sparing
agent
Biological DMARD as anti –TNF, anakinra, tocillizumab can
be helpful in resistant case but non of them has been
investigated in non randomized trials
