
• Objectives:
• Definition.
• Etiology & Risk factors.
• Classification.
• Complications.
• Diagnosis.
• Treatment options

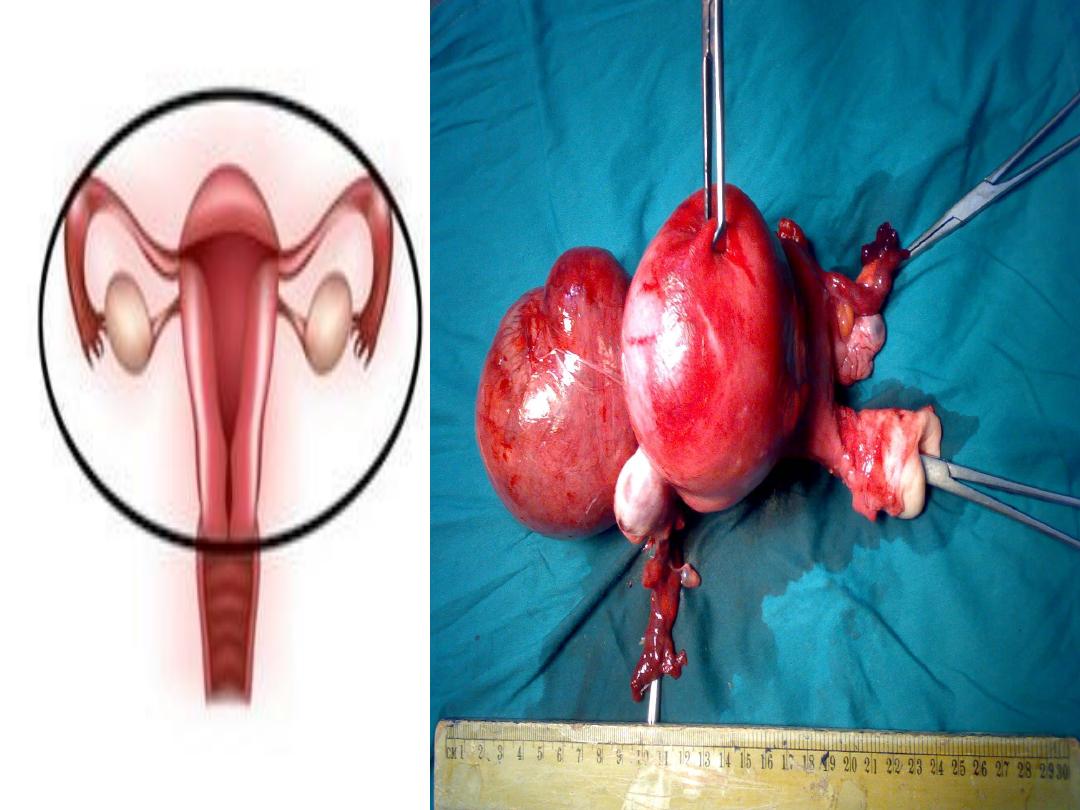
UTERINE FIBROIDS:
• They are the most prevalent benign tumour
of uterine corpus.
• clinically apparent in 20 -30% of women &
70% of uterus removed during hysterectomy.
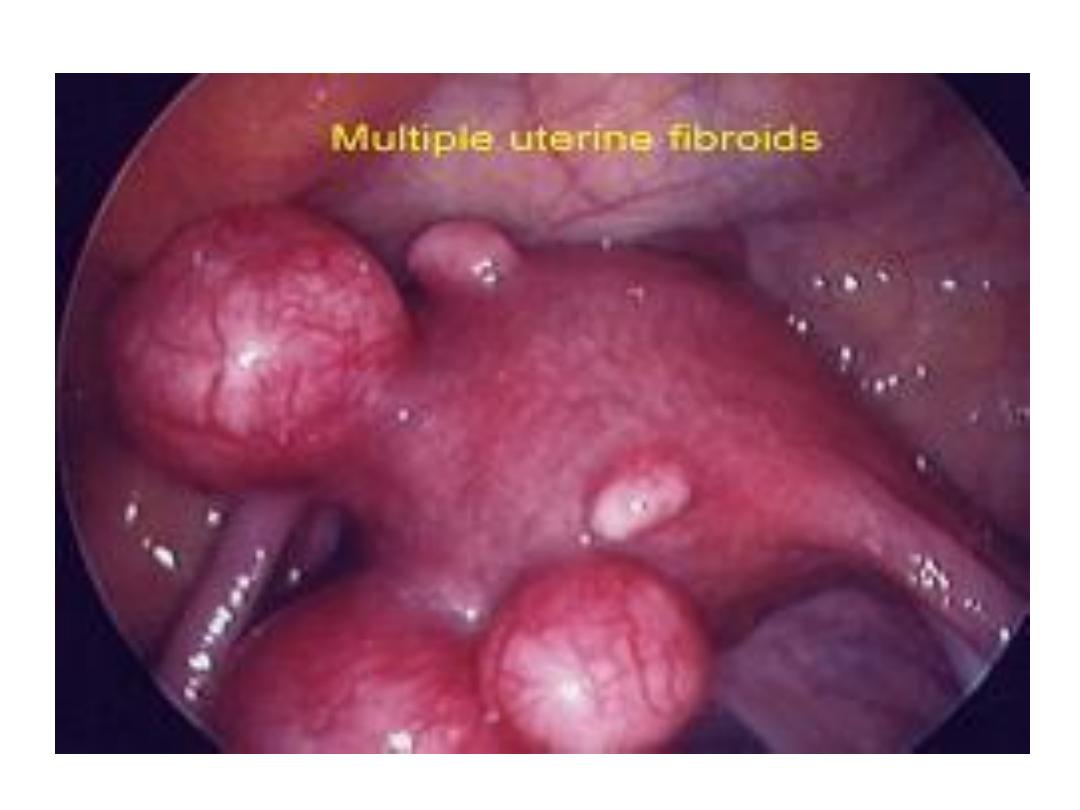

Fibroids develop from smooth muscular
tissue of the uterus.
• A single cell divides repeatedly, creating a
firm, rubbery mass distinct from nearby
tissue.
• It may grow slowly or rapidly, or remain
the same size.
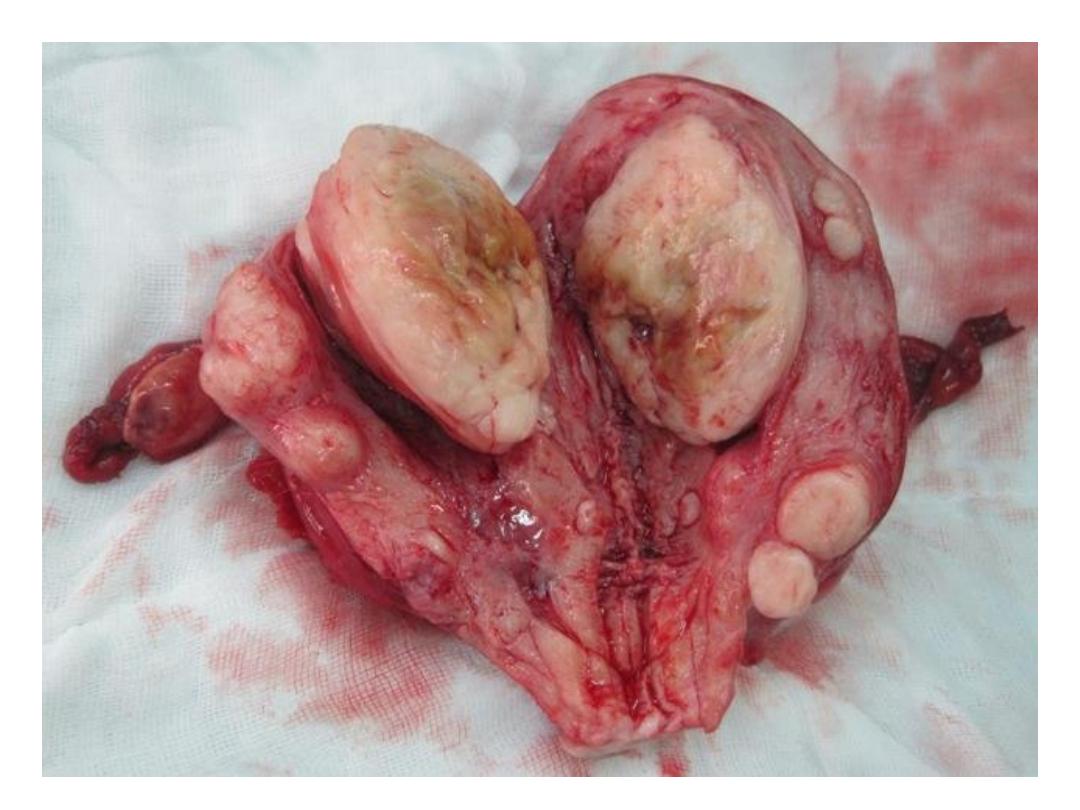

Aetiology &Risk factors:
Patho -physiology is poorly understood.
• Cytogenetic abnormalities in 40% translocation
or deletion of chromosome 7, 12 &14.
• Ovarian hormones :F. shrinks after
menopause.E2 ,Progesterone role less clear.
• Afro Caribbean more prone to have UF.
• Null parity , obesity , PCO,D.M ,H.T.

• FIGO Classification:
• 0 pedunculated intracavitary.
• 1 submucosal <50% intramual;
• 2 Submuscoasl >50% intramual;
• 3 100% intramual in contact with
endometrium.
• 4 Intramual
• 5 Subserosal,>50% intamual
• 6 Subserosal <50% intamual
• 7 Subserosal pedunculated
• 8 Other (e.g cervical,parasitic)
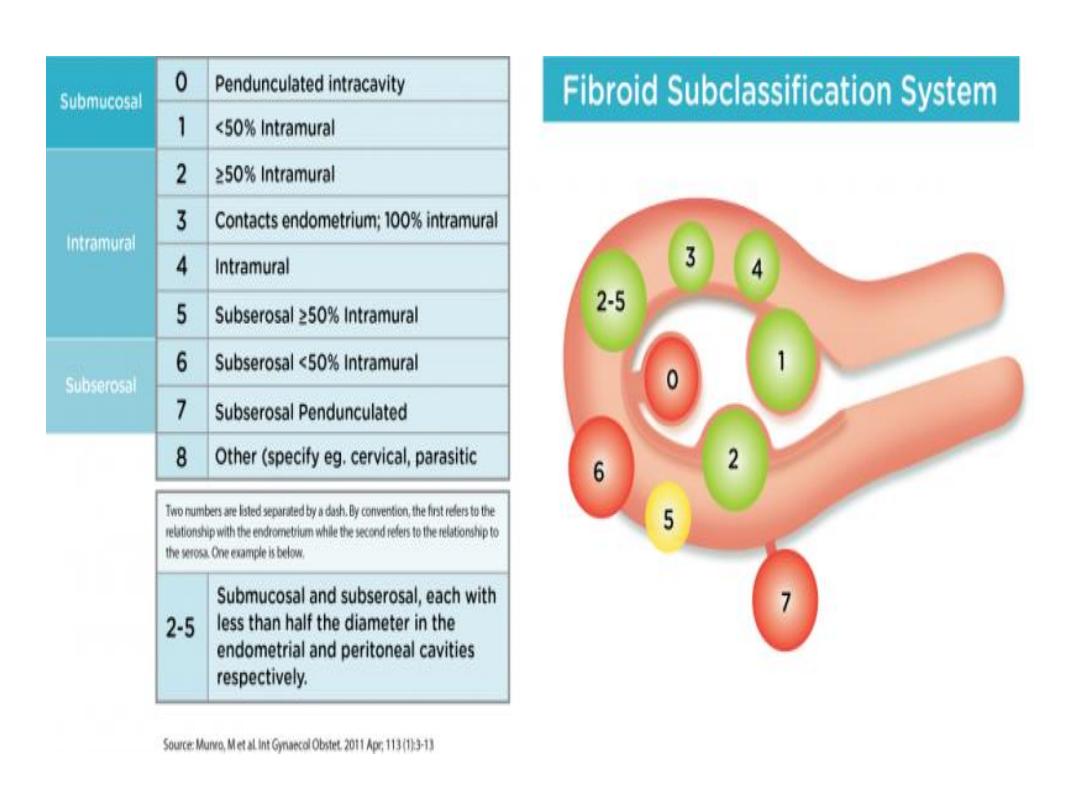

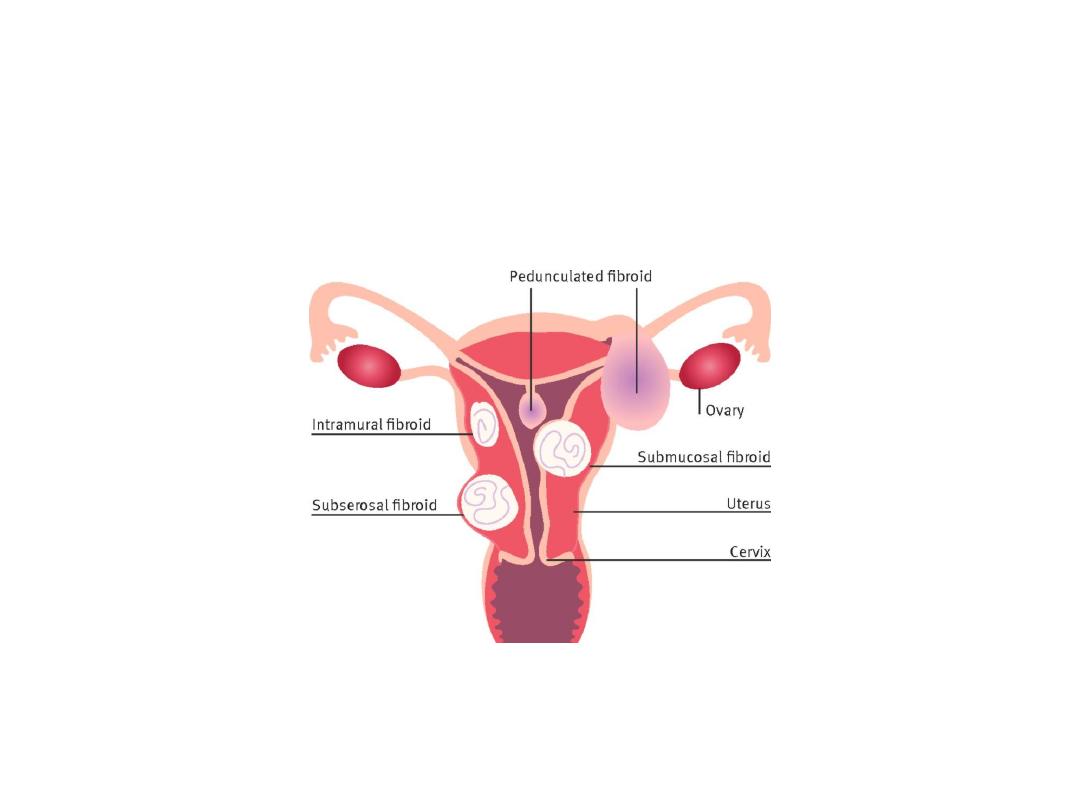
Classification:
according to it’s location:
• Sub-mucosal fibroids: grow into the inner cavity
cause HMB & problems in pregnancy.
• Sub-serosal fibroids: project to outside can press
on urinary bladder, causing urinary symptoms or
can press either on the rectum, causing a
pressure sensation, or on spinal nerves, causing
backache.

• Intramural fibroids. grow within the muscular
tissue, can distort the shape of the uterus and
cause prolonged, heavy periods, pain and
pressure.
• Cervical Fibroid:
• Broad ligament Fibroid:

Complications of Uterine Fibroids:
Red degeneration:
seen in pregnant in the second trimester, the
excess oestrogen causes the fibroid to grow too
rapidly so the vessels around the fibroid start to
congest and swell, turning the centre of the
fibroid soft and red.

• Presentation: pelvic pain, can cause fever,
gastric pain and contractions in pregnant
women. It’s treatment conservative.
• Hyaline Degeneration:
• Calcification:
• Sarcomata's Changes: 0.64 in 100000
• Torsion: the presentation of acute abdomen.

• DIAGNOSIS:
• History:
• Presentation:
• Asymptomatic: accidentally discovered.
• Menstrual abnormalities: heavy menstrual
bleeding ,inter-menstrual bleeding.

•
Abdominal swelling noticed by the women.
•
Pressure effect.
• Sub-fertility:
Distorting the uterine cavity to cause
mechanical obstruction of the tubes.

Pain:
- Congestive dysmenorrhoea.
- Dull backache.
- Pain of torsion in pedunculated Fibroid.
- Pain associated with red degeneration.

Complications of pregnancy:
- Recurrent miscarriage.
- Preterm labour .
- Mal-presentation &mal-position.
- Increase operative delivery.
- Postpartum haemorrhage.
- Torsion of pednculated fibroid,
- Sub-involution.

• Examination:
• General exam.: anaemia.
• Abd. Exam.: abdominal mass
• Pelvic exam.
- polyp protruding through the cervix,
- Enlarged uterus, symmetrical or asymmetrical
- Mass in the adnexia matted with the uterus or
full the Pouch of Douglas.

• Investigations:
• CBC.
• TV or TA U/S.
• Endometrial biopsy in cases of bleeding.
• Hysteroscopy or Laparoscopy.
• MRI:
• CT.
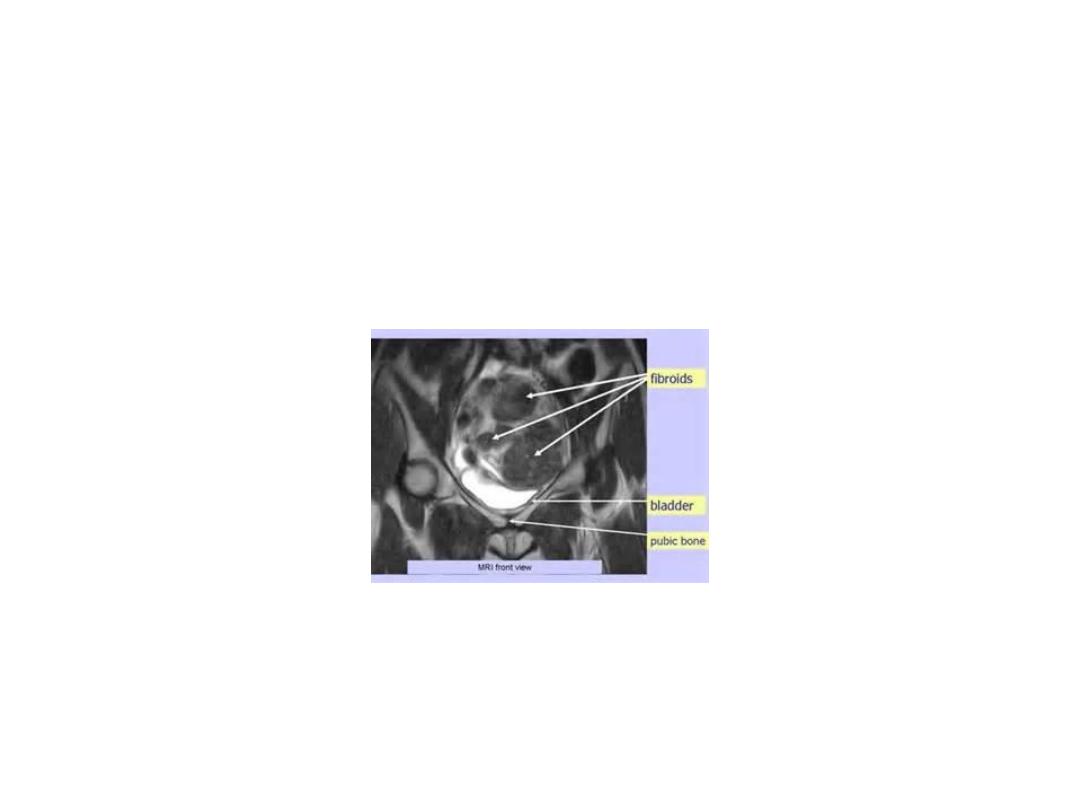
MRI Multiple Uterine Fibroid
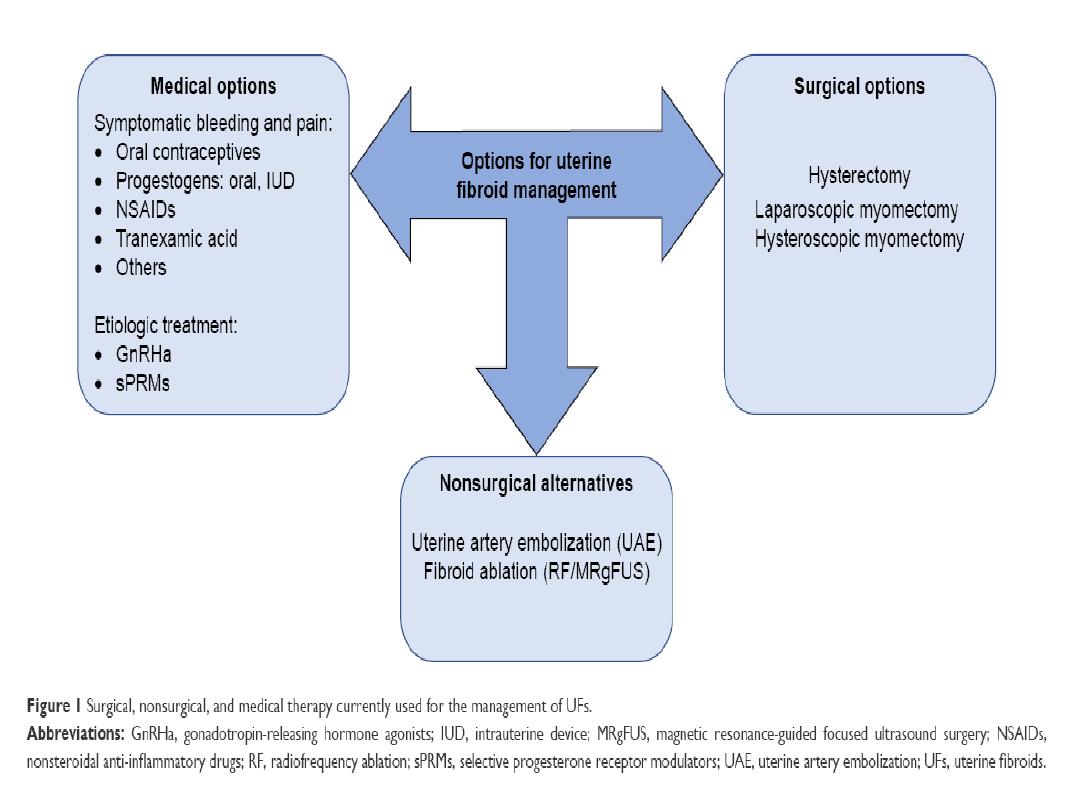

• TREATMENT:
• No treatment:
• Asymptomatic ,small ,follow up.
• Medical treatment:
• Indications:
- For correction of anaemia prior surgery.
- Shrink size ,less blood loss during surgery.

1 - GnRH analogue:
2- Danazol, Gestrinone .
3- SERM , Tibolone.
4-Antiprogesterone.
PRM (Asoprisnil).
5- Ulipristal.

Treatment for symptoms of fibroids may include:
• combined pills:
for control heavy periods.
• Intrauterine system (Marina):
That release hormone to reduce heavy
bleeding and pain

• Iron supplements:
to treat anaemia .
• NSAID : ibuprofen or naproxen mefenamic
acid for pain.
• Hormone therapy help shrink fibroids only
for a short time.

SURGICAL TREATMENT:
• Myomectomy:
is the surgical removal of fibroids .
The approaches:
• Abdominal myomectomy:
removes fibroids through an incision in
the abdomen.

• Laparoscopic or Robotic Laparoscopic
myomectomy :
uses several small incisions in the abdomen to
remove fibroids.
• Hysteroscopic Myomectomy:
by resectoscope .

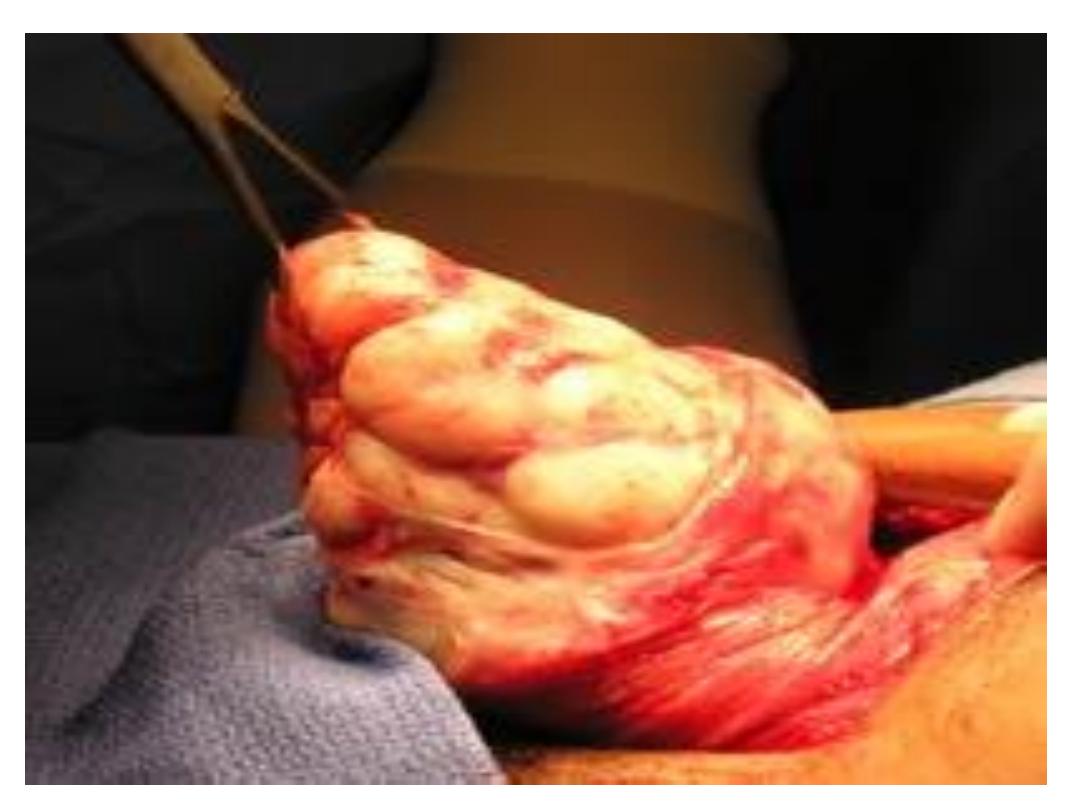
• Vaginal Myomectomy:
removal of the fibroid through the vagina.
Advantage:
• Preserve fertility.
Disadvantage:
• recurrence.

• Hysterectomy:
removal of the uterus &Fibroids.
• Abdominal hysterectomy:
• Vaginal hysterectomy:
• Laparoscopic hysterectomy:

• Robotic Hysterectomy: Similar to a
laparoscopic hysterectomy except that the
instruments are connected to robotic arms,
allowing the surgeon to have enhanced
dexterity and visualization.
• Advantages: less blood loss ,cure ,no
recurrence.

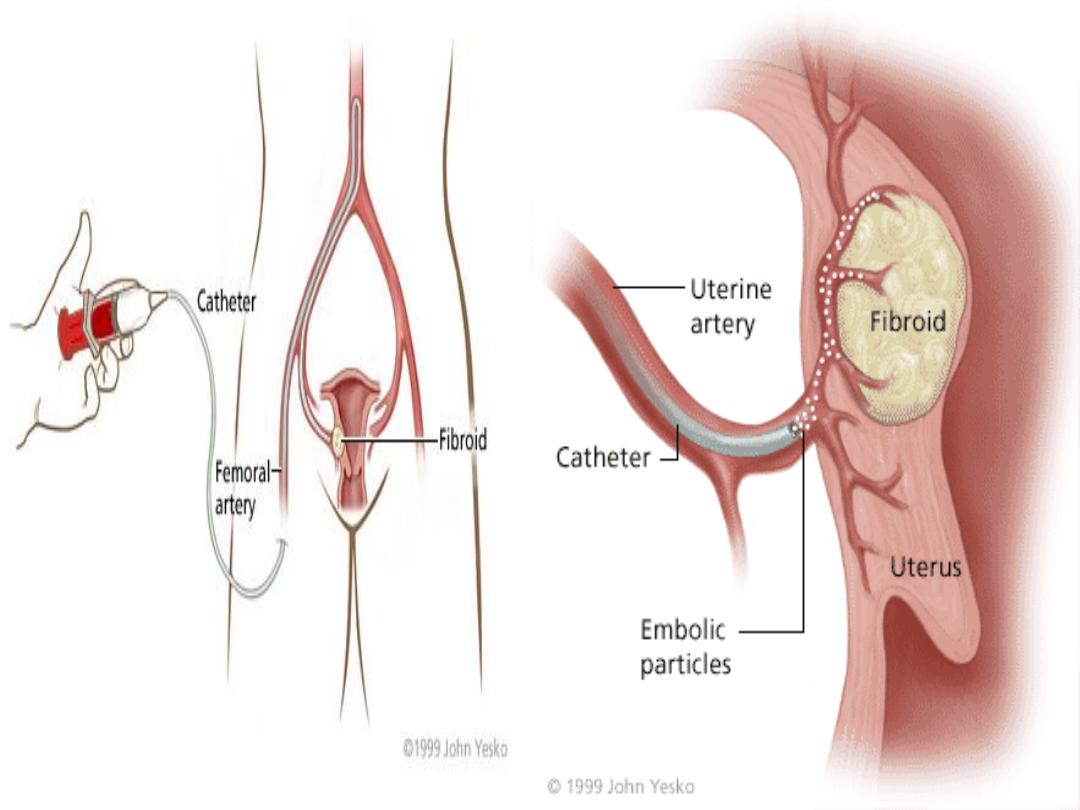
Non-surgical Treatment:
• Uterine Artery Embolisation:
• Advantages: decrease menstrual loss by 85%.
• Decrease myoma size by 30- 46%.
• Short hospital stay.
• Disadvantages: pain, nausea ,fever , vaginal
discharge , ovarian dysfunction and elevated
FSH.

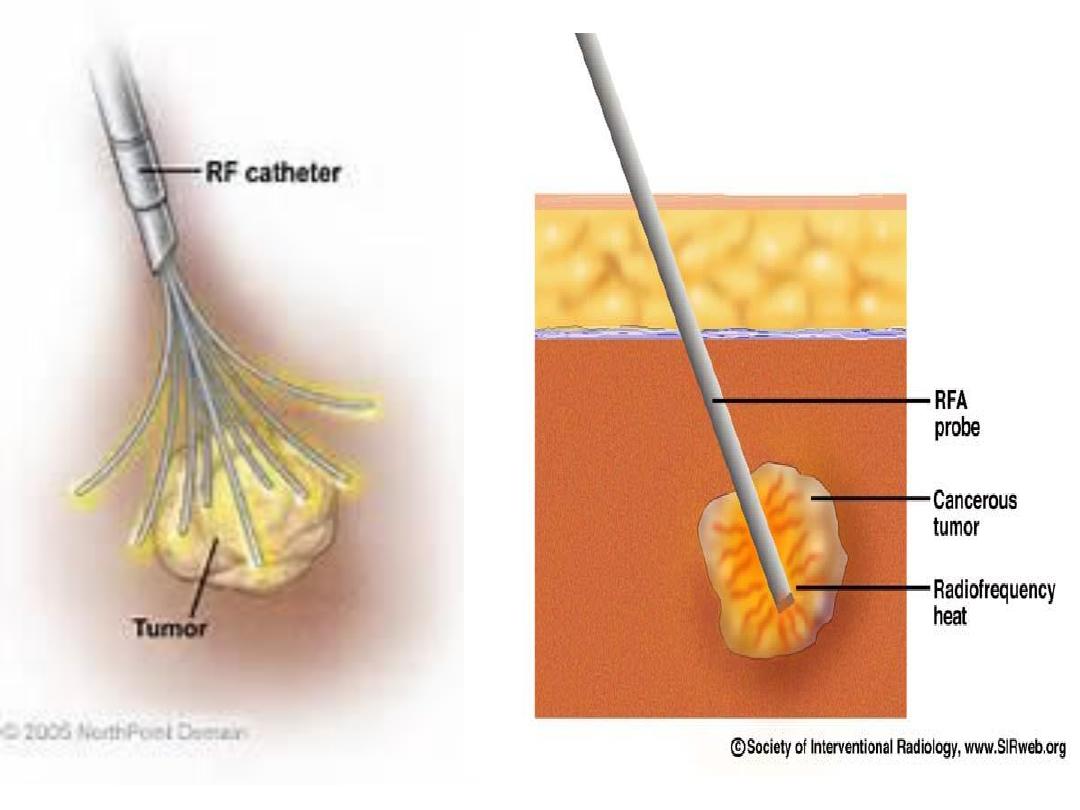
Radio frequency ablation :
It’s minimally-invasive therapy for fibroids
under U/S guidance probe introduced each
fibroid is destroyed by applying energy through
a small needle array.
The surrounding normal tissue is not affected.
The destroyed tissue may then be completely
reabsorbed.

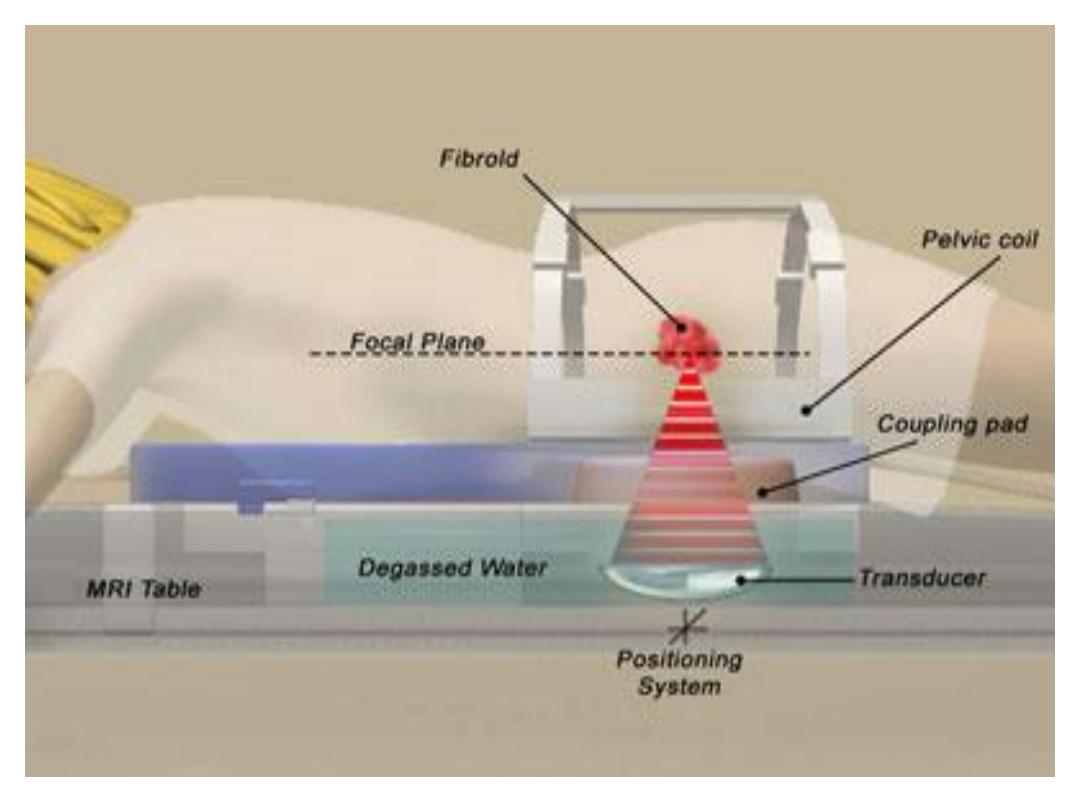
• Focused Ultrasound Therapy:
• MR-guided, focused ultrasound obliterates tumours by
focusing high-intensity ultrasound beams on the
growths, raising the temperature enough to destroy
them.
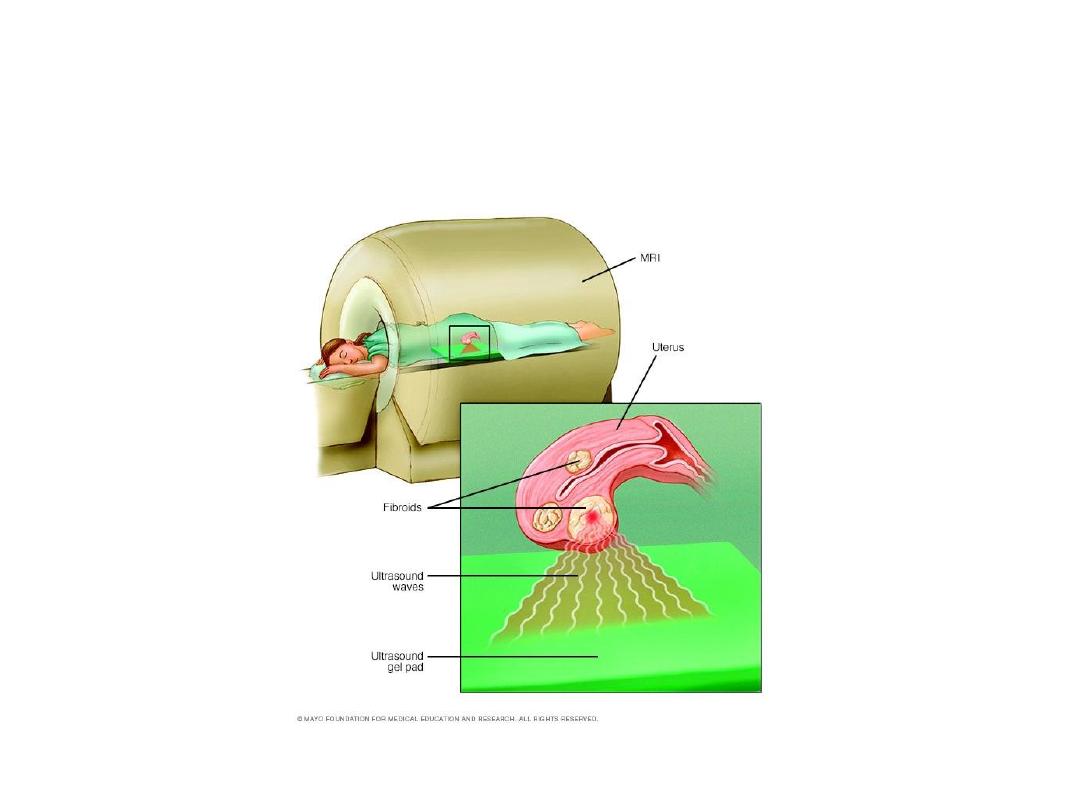
Focused u/s Therapy

• By the MR scanner the Interventional
Radiologist localise the fibroid, a small spot is
treated at a time and it is repeated, about 50
times per session, until the fibroid is destroyed.
• It’s uses for symptomatic women, complete
family who have few fibroids.
• Large and multiple small fibroids are difficult to
treat.
• it’s is new the long-term effects are not yet
clear.