Surgical extraction
Assistant lecturerWaseem Khalid Mahmood
BDS , MSc ,
2020-2019
Methods of tooth extraction
1- forceps extraction (intra alveolar extraction) (closed extraction)consist of removing of the tooth or root using forceps ,elevator or both.2- surgical extraction (Transalveolar extraction) ( open extraction) achieved by removal of some of the bone investing the root which will be delivered by the use of an elevator and\or forceps.
Transalveolar extraction (surgical extraction )
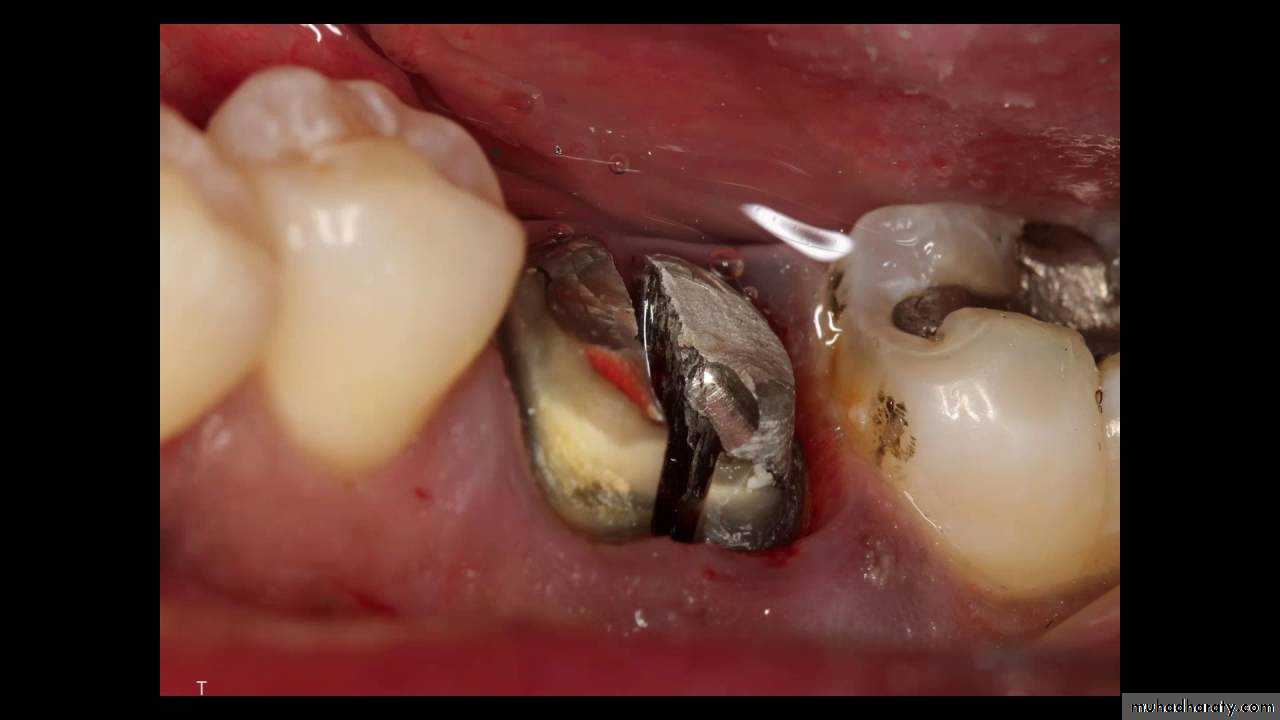
Surgical tooth extraction : is a procedure that's used to remove a tooth that includes additional surgical steps that aren't performed with routine extractions.It involve the dissection of the tooth or root from it's boney attachment
Indications for trans alveolar extraction
1: Failed attempted forceps extraction
2: Retained roots which can not be grasped with forceps or delivered with an elevators
3: History of complicated extraction
4: Heavily restored tooth specially when root canal filled
5: Hypercementosed or ankylosed tooth
6: geminated or dilacerated tooth
7: impacted teeth.8: teeth near vital structures.
9: when bone preservation is required (like in implant)
10: tooth that would be used as an auto transplant (like in canine ).
Surgical steps of trans alveolar extraction
1: Mucoperiosteal flap design and incision.2: Bone removal
3: Tooth division(sectioning or separation)
4: Tooth removal
5: Socket toilet
6: Suturing
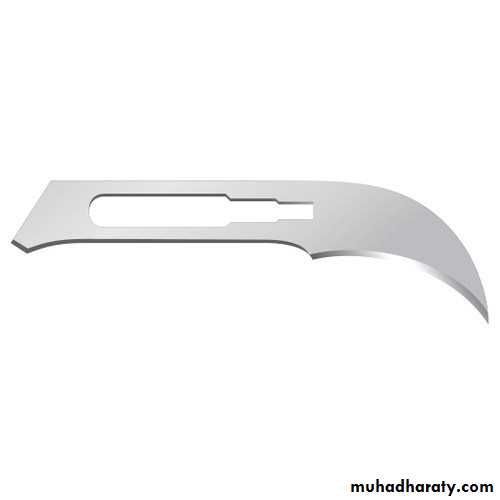
The No.15 blade has a small curved cutting edge and is the most popular blade shape ideal for making short and precise incisions. It is utilized in a variety of surgical procedures including most of minor oral surgical procedures .
Blade no. 15
The No.11 is an elongated triangular blade sharpened along the hypotenuse edge with a strong pointed tip making it ideal for stab incisions needed when lancing an abscess or inserting a chest drain. It is held like a pencil and often upside down by the surgeon to prevent it inadvertently being inserted too deep.
Blade no. 11
Blade no. 10
The No.10 blade with its curved cutting edge is one of the more traditional blade shapes and is used generally for making varying sizes of incision in skin and muscle.The number 12 blade is a small, pointed crescent-shaped blade sharpened along the inside edge of the curve. It sometimes used as a suture cutter. The number 15 blade has a small, curved cutting edge ideal for making short, precise incisions.
Blade no. 12
Scalpel handles sizes
mounting of blade in scalpel
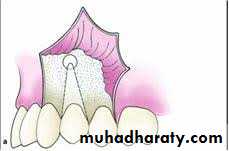
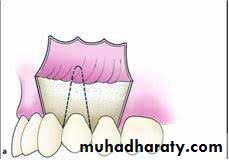
Principles of mucoperiosteal flap design :
These are raised to render the operative site clearly visible:1 : the base of the flap should be wider than it's apex
2: at suturing the wound margin should be supported by intact bone.
3: full thickness (mucoperiosteum)
4: The inter dental papilla should be kept not traumatized , so that , it is either included or excluded at flap incision or design.
5: Anatomical structure should be avoided . Like the canine eminence and the mental foramen.
6- In surgery at lower premolar region , the incision should be either mesial to the first premolar or distal to the second premolar, why ?
7-Scalpel should be held in a pen grasp to provide a good control and enhance tactile sensation .
8-incsion should be applied at right angle to the underlying tissue
9-scalpel should be applied and moved at a single ,firm and constant manner
10- the flap should be handled gently and delicately ( without tension)
Types of flaps used in Transalveolar extraction.
Different type of flaps can be used in dento- alveolar surgery like :1- two sided flap .
2- three sided flap.
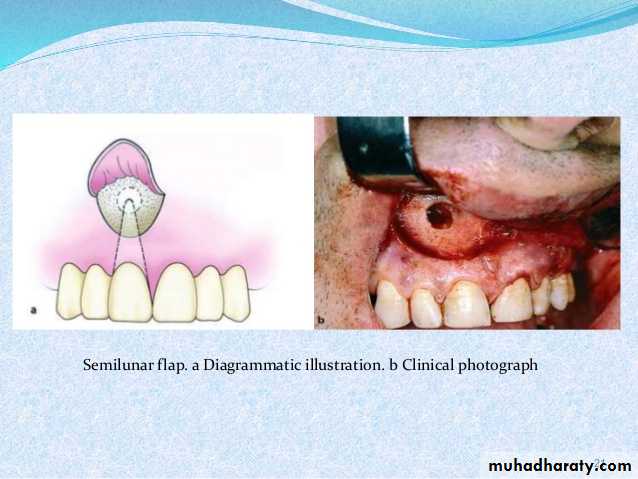
3- semilunar flap .
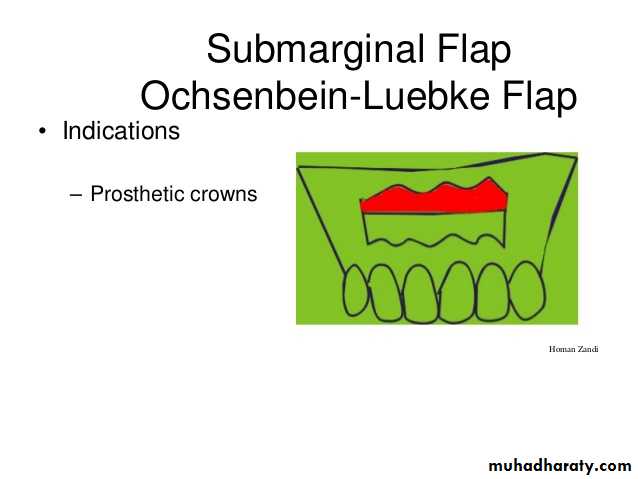
4- sub marginal flap .
3 corners ( 2 sided flap )
4 corners ( 3 sided flap )
Semilunar flap
Submarginal flap (Ochsenbein- Lubke ) flap
Flap reflection
The flap are raised subperiosteally. This is done by blunt dissection with a periosteal elevator , making use of the well defined plane between the soft tissues and hard tissuesBone removal
Bone should only be removed to expose the root or tooth to provide a point of application for an elevator or forceps. After the tooth or root has been extracted all sharp bony edges and boney projection should be removed ( using bone file ).Methods of bone removal
1: surgical bur either guttering or postage stamp method2:chisel and mallet pressure
3: rounger forceps is a valuable instrument for trimming bone edges after extraction of the tooth or root
4-bone file for reaming of the sharp bony margin
A constant stream of irrigation must accompany the drilling to :
1- avoid overheating the bone that leads to trauma and thus impairs healing .2- improving visibility by removing the cut bone and tooth debris and blood clot (flushing effect) .
3-Lubricating effect .
4- sterilizing and disinfectant effect .
Ronger`s forceps
5- peizo electric surgery. Is a new technique of bone removal .
6- laser (homework).Piezoelectric bone surgery known simply as piezosurgery is a new technique of bone removal which require the use of micro vibrations by ultrasonic frequency scalpel . the vibration is amplified and transferred into a drill which when rapidly applied with slight pressure up on the bony tissues , results in cavitations phenomena , with a mechanical cutting effect exclusively on mineralized tissue .
the advantage of using this technology is that piezoelectric surgery dose not cut soft tissues , so damage to the soft tissue is less likely to occur .
Tooth division
If the roots have different path of removal or the root trunk can not be grasped with forceps , the root mass must be divided and the separated roots removed along their individual path of withdrawal.Methods of tooth division
1 : Surgical bur and handpiece .
2: Osteotome or chisel .
Tooth removal using elevator or forceps
Toilet of the socket
1- un wanted boney prominence should be removed2- the socket should be irrigated with normal saline of chlorhexidine
3- the mucoperiosteal flap should then be replaced and a decision is made as to weather suturing is needed
Suturing
The purpose of suturing are :1 – TO hold the wound margins together to promote wound healing by first intention if possible
2- To approximate the wound margin to minimize wound contamination with food debris
3- To arrest hemorrhage
Usually use sterile black silk gauged 000 is the material of choice and either simple interrupted suture or horizontal matrices suture is used .the needle of cutting type is widely used in dentistry
Principles of suturing
1- The needle is grasped with a needle holder at its 2\3 of its curvature .it never held by the eye or the point2- the area to be sutured is dried with either a sucker or cotton guaze so that the cut edge are clearly visible ( never use air to dry, why ? ).
3- suturing from the movable to the fixed wound margin
4- toothed dissecting tweezers are used to grip the flap and fix it .
5- the needle should pass at least 3 mm from the wound margin
6- the knots should be lied at one side of the wound margin.
7- the knots should be not too tight and not too loose .
The removal of suture
The suture should be remain in situ for up to 7 daysThey loosen in the tissues and should be removed by grasping of the knots and cutting the suture where it enter the tissues.
If the suture is cut at a distance from point of entry into the tissues, contaminated suture material may be dragged through the healing wound thus infecting it .
Indications for leaving a root tip:1. Small root fragment (4 mm or less).2. No evidence of periapical pathology or infection associated with the root fragment.3. Inability to visualize the root tip.4. Removal of root tip will cause extensive bone loss .5. Proximity to the inferior alveolar nerve.6. Proximity to the maxillary sinus.7. Uncontrolled hemorrhage .