
الصمالخ
Ear wax (Cerumen)
:
It is a mixture of secretions of the ceruminous (wax) gland and sebaceous
glands.Which situated in the cartilaginous portion of external auditory canal
with desquamated skin cells of external canal
The quantity of wax produced varies from individual to another .
*majority of wax dried and separated as small flakes ,and expelled out side the
ear canal by epithelial migration and movement of the jaw . The ear have self-
cleaning of the wax.
-
:
Functions of the ear wax
1. Lubrication of the skin of the external canal.
2. Contains fungicidal and bactericidal enzymes.(acidic pH)
3. prevent dust and sand to enter the ear as they stick to it and carried out
wards.
:
Causes of wax accumulation
1. Attempt of the patient to clean his ear with cotton buds (Q tips) leads to
pushing the wax deeper into the canal. Using hearing aids ,ear plug.
2.Increased wax production.
3.Retension by narrow external canal,stiff hair.
;
Clinical feature of wax accumulation
1.Hearing loss (CHL) when completely occlusion of the canal.
2.Pain or discomfort because pressure on nerve ending,
3.Tinnitus,disturbance of balance because of pressure of the wax on the TM.
4.Reflex cough –stimulation of auricular br.of vagus.
to brown color ,gray or black when mixed with
wax is yellow
.
Otoscopic exam
desquamated epith. and dried.
:
Methods of wax removal
. when it was hard give wax softner, like
for soft wax
)
1.Ear syringing (irrigation
sod.succinate(dewax ear drop),5% sod.bicarbonate in glycerin.
se of ring prob,cerumin hook.crocodil forceps
U
:
(instrumentation)
Probing
2.
,for hard dry wax under direct vision.
t is safest when perforation of TM .
I
.
suction
-
3.Micro
.
Technique of ear syringing (wash)
1. Use syringe of ear wash by warm water at body temperature (37º C).
2. Pull the auricle upwards and backwards to straighten the meatus.

3. Direct the nozzle of the syringe of ear wash upward and backward in the
external auditory canal and be gentle and careful during wash.
:
Ear syringing
r
Contraindications.fo
1. Otitis externa . 2.Otitis media. 3.perforated tympanic membrane.
4.Previous ear surgery. 5.young children less than 2 years.
Complications of ear syringing:
:
1.Trauma
*Rupture tympanic membrane.
*Laceration of external auditory canal.
*Osscular damage.
*Damage to inner ear = perilymp fistula (rare).
2.Infection :
*Otitis externa, (diffuse OE, Otomycosis.).
*Otitis media.
: due to caloric effect (hot or cold water).
3.Vertigo and nystigmus
.
due to stimulation of vagus nerve
Reflex cough or syncope
4.
Otalgia :Ear ache(Pain in the ear )
Of two types:
. Pain that originates within the ear.
1.Primary otalgia(otalgia proper)
Pain that originates outside the ear.
.
2. Secondary (Referred) otalgia
:
Causes of primary otalgia
External ear pathology :
I:
1.Otitis externa : (the common cause) * Localized (furunclosis).*Diffuse
Otitis externa.,herpes zoster.
or wax. including live insects
-
Impacted foreign body
3.perichondritis
4.Herps zoster oticus.
5.Neoplasm
Middle ear pathology:
II:
the common cause)
te
2.Acu
3.Barotrauma
4.complications of suppurative otits media (extradural abscess.)
5.Neoplasm.
•
of
structures
: Due to pathology of the surrounding
Referred otalgia
,
auricle
there are normal
Clinically
dermatoms).
same innervations.(same
external auditory canal , tympanic membrane, and mastoid process.
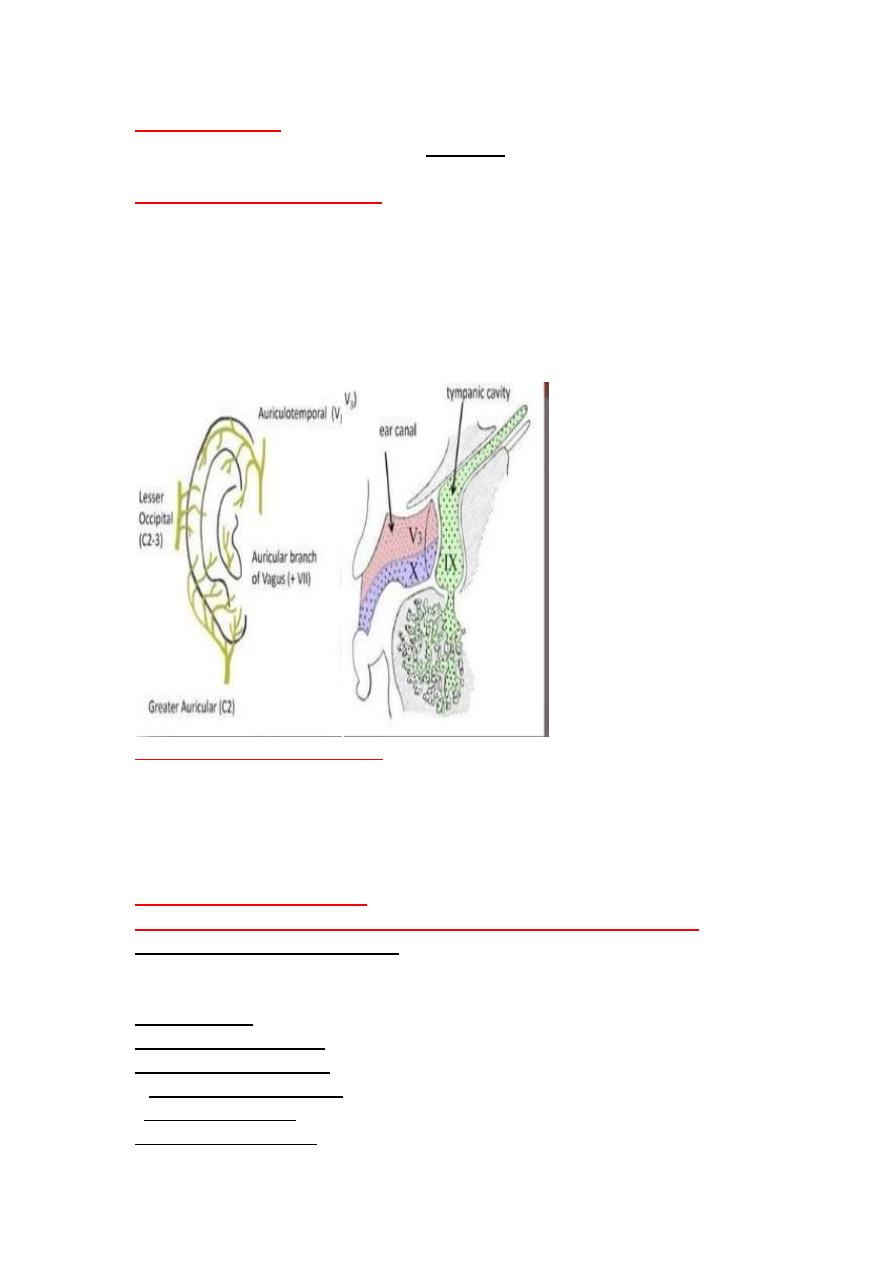
*Sensory innervation of the ear:
By six nerves :four cranial nerves and two cervical nerves.
1.
Trigeminal n. (V)
: Auriculotemporal nerve of mandibular division (V3)
2.
Facial n. (VII).
Auricular br.
3.
Glossopharyngeal n.(IX);
Jacobson (tympani:c ) n . and tympanic plexus.
4
. Vagus n.(X);
Arnold (auricular) br.
5.Greater auricular n.(C2,C3)
6.Lesser occipital nerve (C3)
Mechanism of Referred Otalgia
*The most accepted theory is
the convergence-projection theor
y, which states
that multiple nerves converge (join)onto a single shared neural pathway, with
the central nervous system (CNS) unable to differentiate the origin of
stimulation. The CNS unable to correctly pinpoint the location of pathology.(
sensory “error”.).
•
:
Causes of referred otalgia
I.Via auriculotemporal nerve of mandibular division of trigemenal n(V3).
joint
mandibular
-
: a. Temporo
1.Temporomandibular joint lesion
dysfunction(TMJD). b.osteoarthritis and c.trauma (Displacement of the
meniscus)
Malocclusion.
teeth.
caries ,abscess,impacted wisdom
Dental
.
2.Dental causes
ulceration ,malignancy.
;
3.Anterior 2/3 of tongue
,ca.)sialabdenitis,sialectasis,and tumours.
Parotitis
4. major salivary glands (
(sinusitis.neoplasm).
Nose and paranasal sinus
.
5
.Temporal arteritis.
6
7.Trigeminal neuralgia.

II:Via glossopharyngeal n.
: inflammation,post tonsillectomy,malignancy.
Tonsillar lesions
1.
tongue. (lingual tonsillitis ,ulceration,tumor.
the
.Posterior third of
2
ulceration ,Carcinoma.
;
3.Nasopharyngreal lesion
(
. (eagle syndrome.
.Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
4
agus nerve.
ia v
III;V
,GERD.
body , Carcinoma
Foreign
; inflammation,
1 Pharyngeal lesions
…
tumor ,
,
epiglotitis)
inflamation )
;(
2.Larynx
.thyroiditis,ca.
3.Thyroid gland
.Myocardial ischemia.
4.Heart
oma (nervous
r
Bells palsy , acoustic neu
Facial n.
Via
IV:
intermedius).geneculate neuralgia.
.
V:Via greater auricular and lesser occipital ns (C2,C3)
1.cervical spine lesion (spondylosis and osteoathritis).
2.Fibrosistis of sternomastoid M.
3.whiplash and trauma.
:
of otalgia
Management
*Proper history, and ear examination
*when due to ear causes (primary otalgia) : Treat the underlying cause.
*when normal ear examination.(referred otalgia)
:which are
of referred otalgia
s
1.Think of common cause
a. Dental causes.
b.Temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMJD).
c.Tonsillitis and pharyngitis.
d.Cervical spine arthritis.
they
; Age > 50 year ,smoking ,alcoholic,
2.For patients with risk factors
have risk of head and neck malignancy
.
includes
was indicated ,
If there are no cause is found further examinations
.
ndoscopic examination and biopsy for any mass
E
*
*MRI for head and neck is indicated
and
*The incidence of referred otalgia in Nasopharyngeal ca. is (57%),
hypopharyngnx and larynx(26%),oropharynx (17%),acoustic neuroma(4%).
So associated dysphonia, strider,dysphagia,neck mass suggest laryngeal and
pharyngeal and esophageal ca.
Otitis media with effusion suggest nasopharyngeal ca.
*Patients with Ischemic heart disease = Myocardial infarction.

•
Tinnitus:
Sensation of noise in the ear or head in absence of any relevant
external signal.
•
Is a symptom of an underlying condition not a specific disease .
•
* Persistent Subjective Tinnitus usually leads to anxiety, depression
, insomnia and concentration difficulties, as well as seriously affects
normal daily activities .
*Anxiety as the patient often worry about serious intracranial disease or the
beginning of madness .
:It is of two types
Types and causes of tinnitus
: The sound heard by the patient only .It is the most
A. Subjective tinnitus
common type; includes
causes)
:( most common
1.Tinnitus with hearing loss
causes) .
A:With Conductive hearing loss.
1.Ear wax. 2.Otitis media.3.Otosclerosis.
B:With Sensorineural hearing loss.
1. Presbyacusis ; common cause .2. Noise inducing HL. 3.Ototoxicity
(aspirin,aminoglycosides) 4. Menier's disease, 5.Acoustic neuroma.
: Pulsatile tinnitus.
2.Tinnitus without hearing loss
A. Persistent stapedial artery.
B. Blood changes: Hypotension,hypertension,high cardiac output in
aneamia, fever,thyrotoxicosis, pregnancy, or migraine.
C. Patulous E.T.(with respiration).
•
:
B. Objective tinnitus
The sound heard by the patient and the examiner .It is rare due to:-
1) Palatal myoclonus.
2) Vascular: Pulsatile
* Aneurysms of the internal carotid artery ,* vascular intracranial
tumours,* A-V shunt between the occipital artery and transverse sinus.
•
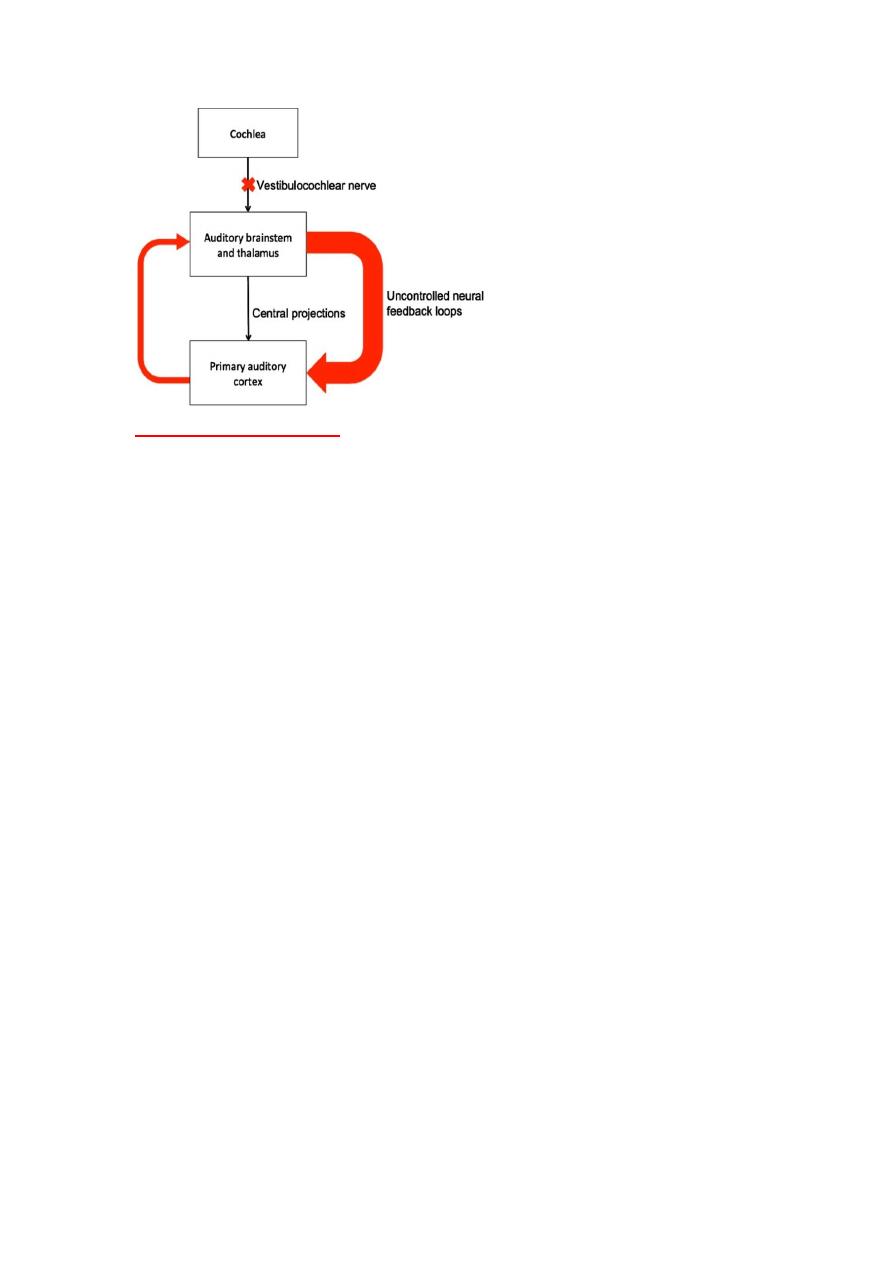
Pathogenesis of subjective tinnitus
•
A loss of cochlear input to neurons in the central auditory system (in hair
cell damage or vestibulocholear n.) can results in abnormal neural
activity in the auditory cortex. leads to creation of uncontrolled neural
feedback loops which leads to the abnormal auditory perception
(tinnitus).
.
Treatment of tinnitus:
1.Treatable causes ; Appropriate medical or surgical treatment .
2. Reassurance and sedation ,when the noises interfere with sleep and to allay
anxiety as the patient often worry about serious intracranial disease..
3. Anti tinnitus drugs like lignocaine,clonazepam,tegretol.
4. Rehabilitative:
- Hearing aids if there is significant hearing loss
- Tinnitus maskers device ,when no hearing loss .
-combined HA and tinnitus masker.
- Biofeedback training to modify patient's reaction to tinnitus.
*Even with recent medical advances, no treatment has been found to be
uniformly effective in the treatment of tinnitus.
* care to
1. Unilateral tinnitus with hearing loss, vertigo should be fully investigated
to exclude serious medical conditions(acoustic neuroma).
2. Pulsatile tinnitus.
===========================================
