
Tumors of the larynx
I:Benign tumors of the larynx:
1. Papilloma
. It is of two types
1
.
Recurrent (Juvenile)respiratory papillomatosis
(RRP).
The commonest benign laryngeal tumor (80% )caused by infection with
Human PapillomaVirus (HPV) subtype 6 and 11,transmitted from the mother to
the child in the birth canal, or in utero.(50%-70%) of patients have mother with
genital warts. Commonly seen at the junction of respiratory epithelium with
sequamous epithelium, generally at the glottis, although it may occur throughout
the air way.
Clinical features:.
The age of presentation is 2-6 years, There are *hoarseness,*aphonia,*stridor
and* dyspnea due to airway obstruction.
It is *usually multiple, warty appearance, mainly involved the true and false
vocal cords, but may extend to subglotic,trachea ,bronchi, and epiglottis.
*Has propensity to recur after local removal, (HPV has been found
consistentlyin the epithelium of papilloma lesions and adjacent normal
appearingtissue; this explains the ability of the virus to cause recurrent disease,
despiteapparent surgical eradication of lesions),
*may regress after puberty,and
*not undergoes malignant changes unless irradiated.
Investigations
1-X-ray lateral-AP view of the neck-look for the patency of the airway.
2-Chest x-ray.
3-rigid and flexible laryngoscopy.
4-biopsy.
5-Bronchoscopy to rule out spread.
Diagnosis
.laryngoscope and biopsy and histopathological study.
Treatment;
1.Avoid tracheotomy. to prevent seeding of the virus to trachea,
2.Surgicalexcision. Best by Co2 Laser vaporization,Cryotherapy to reduce
seeding of the virus. Or by microforceps.the growths recur regularly, requiring
repeat operations
3.Ajuvant medical treatment;aimed the virus and growth of tumors.like Alfa
interferon(subcutaneously),Cidofovir (intralesionally).Indole-3-carbinol.
4.Otherincludes ;preventing and therapeutic vaccines,
2.Adult type laryngeal papillomatosis
.
Common in young adults (18-39 years old)presented with hoarseness
*It is usually single.
*Less propensity for recurs after local excision.
* when recurs may gets malignant changes.
*no spontaneous regression.
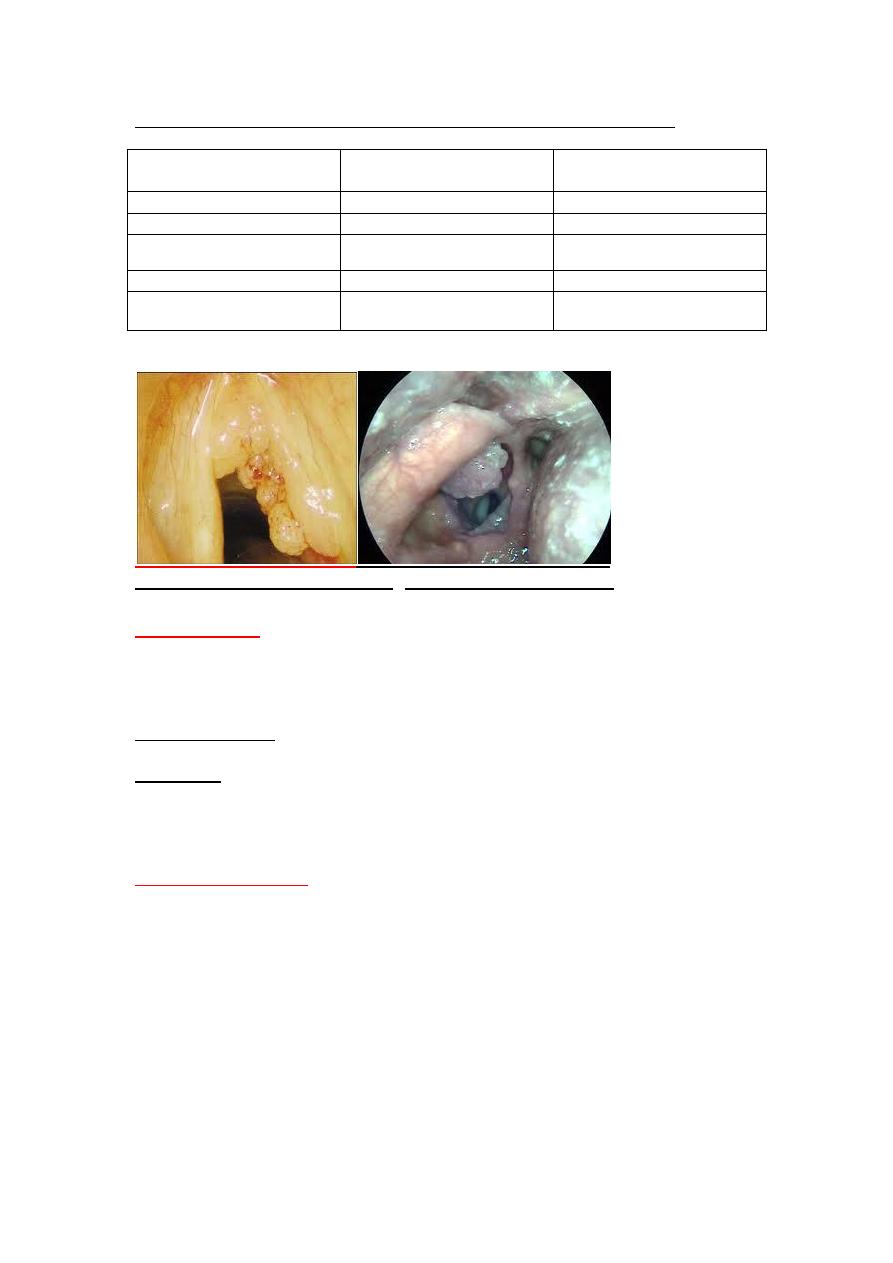
Differences between Juvenile and adult type laryngeal papillomatosis.
Clinical features
Juvenile type laryngeal
papillomatosis
Adult type laryngeal
papillomatosis.
Age of presentation
(children)2-6 years
Young adult (18-39 years)
Number
Multiple
Single
Recurrence
High Propensity for
recurrence
Less propensity for
recurrence
Spontaneous regression
Yes
No
Malignant changes
No
When recurs may get
malignant changes
Multiple laryngeal papillomatosis
Single adult papilloma
2.Haemangioma
. Juvenile and adult forms, It is typically located in the subglottic
region, but the supraglottic space, vocal cords or upper part of the trachea may
involved, generally associated with cutaneous haemangioma( 63%),a
characteristic history of rapid growth during the first 6 months of life, and then
after 12 months a slow regression takes place.
Typical symptoms: *stridor, *dyspnoea, *cough, and *hoarseness are present in
the clinical picture of other congenital obstructions of the airway passage.
Treatment ,
*When large tumor require a tracheotomy until their natural resolution.
*Laser surgery.
*Steroid theapy (Dexamethazone)
3.Other benign tumor,
rare includes.Chondroma (mostly cricoids
cartilage),fibroma,schwanoma,neurofibroma,.

Subglottic haemangioma presenting cutaneously in “beard”
distribution over the face, and over the neck and chest.
II:Malignant tumors of the larynx.
Includes
I:Squamous cell carcinoma.
2.Lymphoma .second common malignancy of the larynx
3.Uncommon malignancy.Verrucous carcinoma,adenoca.,sarcoma,minor
salivary gland tumors.
4.metastatic tumors.From renal, prostate,breast,lung ,stomach.(rare).
Squamous cell carcinoma.
Commonest malignant laryngeal tumor ( 94% ).67% glottis,31%
supraglottic,2%subglottic.
Risk factors;
1.Age; Cancer of the larynx occurs most often in people over the age of 55.
2.Sex; Men are four times more than women.
3.Smoking and alcohol abuse, they increase the risk 50%.
4.Irradiation for neck ex. for thyroid .
5.Occupational like asbestoses.
N
N
i
i
c
c
k
k
e
e
l
l, , wood products and painters.
6. Human papilloma virus infections :Solitaryrespiratory papilloma ( infection
with high risk subtype HPV infection (e.g.16:RR3).
7.Others like genetic ,family tendency, Gastroesophageal reflux..
Clinical features:
Common in male 90%,peack age incidence 55-65 year .(usually elderly male with
low socioeconomic status)
1.Progressive unremitting dysphonia(Hoarseness).
2.Stridor and dyspnea due to vocal cordparalysis, or extensive endolaryngeal
lesion in supraglottic ,Glottic,and subglottic.
3.Pain(referred otalgia).indicate deep invasion, involvement of the pharynx.
4.dysphagia.when the tumor involve the hypopharynx.
5.Neck mass.Metastatic node, or local spread.
6.Haemoptysis.is late symptoms in ulcerative or invasive lesion specially
supraglottic lesion.
7.Cough an irritation. By the tumor itself, or associate with pneumonia, chronic
bronchitis, or lung metastasis.
8.Anemia,cachexia,an fetor due to tumor necrosis.
*Glottic cancer tends to present early with voice changes,(Every patients with
hoarseness for three weeks or more require to be seen by specialist)
*Supraglottic tumors delay in presentation are common due to vagueness of
symptoms such as globus, and otalgia therefore may advanced and have nodal
disease at time of presentation
Diagnosis :
1.Indirect laryngoscope (Mirror.or Flexible laryngoscopy.)
2.Direct laryngoscopy. To assess.
a.Site an limit of the tumor.
b.see the hidden areas (Ventral surface of
epiglottis,anteriorcommisure,theventricle,subglottic region.)
c.Probing the vocal cord for fixation or paralysis.
d.Take biopsy for histopathological study.
3.CT scan(ComputerizaedTomography).
4.Magnatic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
( 3&4) with enhancement use for further evaluation of the tumor.
*MRI better for soft tissue detail evaluating the supraglottis, subglottic ,and soft
tissue involvement (preepigloticspace,paraglottic space,cartilages,thyroid
gland,muscles,)
*Lymph node involvement(Number,site,and relation to the major vessels.)
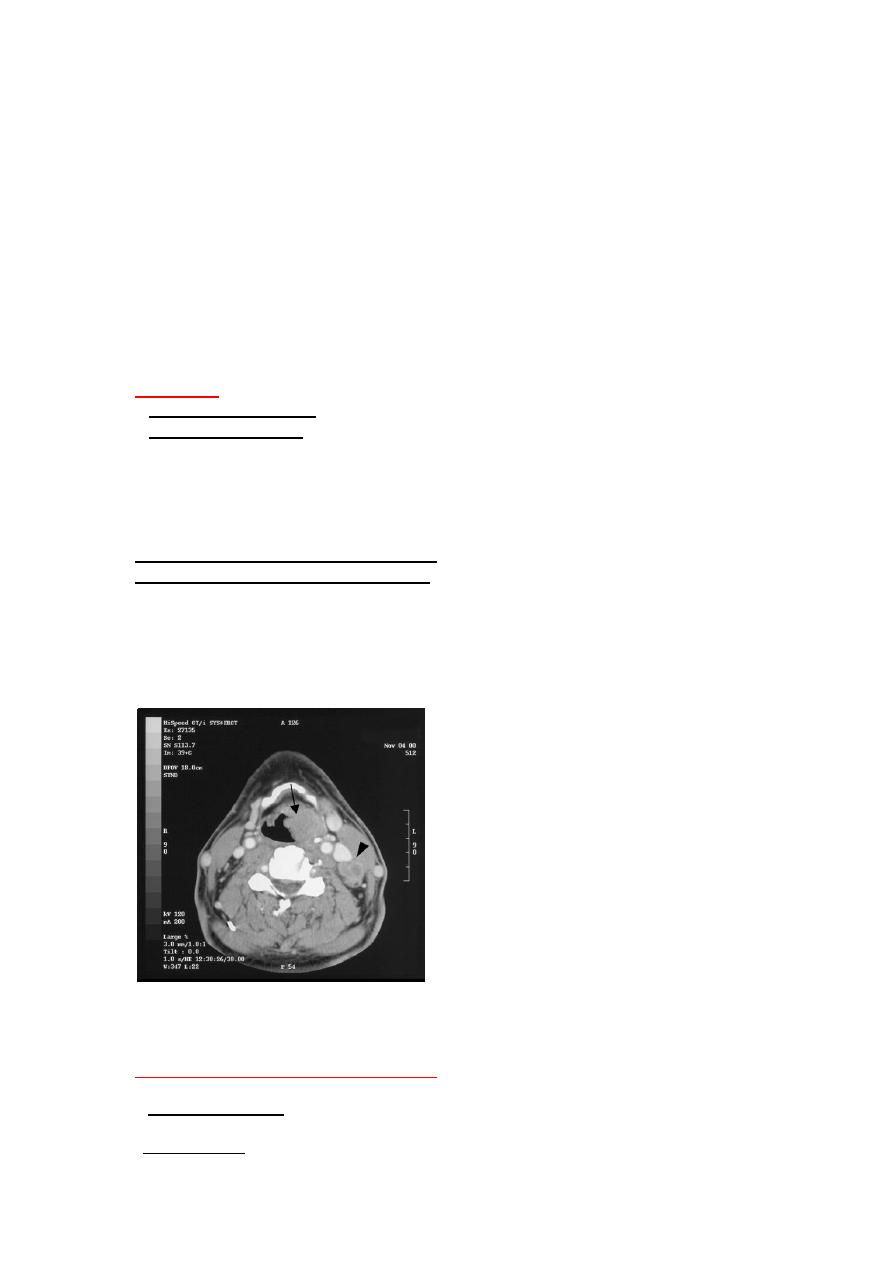
Contrast CT scan showing bulky left supraglottic tumor (arrow) with ipsilateral lymph node
metastasis (arrowhead)
The (T) Classification laryngeal carcinoma
The larynx divided anatomically in to three parts.
1.Supraglottic region. Includes *a. Epiglottis.*b.False vocal cord.*c.The ventricle.d.The
arytenoids. e.Aryepiglotticfold.
2.Glottic region. Involves True vocal cord(anterior an posterior commissure.)
3.Subglotticregion.Extened from below the vocal cord to the inferior border of the
cricoid cartilage.
Generally the (T) classification ,can be applied to any region.
Tis=Cacinima in situ.
T
1
a= Ca.limit to on site.
T
1
b=Ca in two sites, but within one region.
T
2
=Ca. affected two regions,e.g. supraglottic and glottis,or glottis an subglottic region.
But mobile vocal cords.
T
3
=Tumor within the larynx but fixed vocal cord.
T
4
=Tumor out side the larynx.
Treatment ofCa. larynx:
1.Ca. in situ :
Endoscopic resection
; by microlaryngeal instruments or by
Carbon dioxid (CO2) laser.
2;T1,andT2 :*
Radiotherapy.
*. Partial laryngectomy
.It is Voice preservation surgery. An operations in which
part of the larynx is removed, includes.
A. Vertical partial laryngectomy(PL).(Hemilaryngectomy
).like cordectomy,
Frontal partial laryngectomy(PL).Lateral partial laryngectomy, Extended
frotolateral PL.
B.Horizontal partial laryngectomy.
Remove the portion of the larynx above the
vocal cords
(supraglotticlaryngectomy),Epigloectomy.*Supraglotticlaryngectomy,Extenesup
raglotticlaryngectomy.
3.T3,T4,Failure of treatment of T1,and T2 :
Total laryngectomy
.
4. Nodal metastasis:
*
Elective neck dissection
is commonly preferred for T 2-4 Supraglottic
cancer even with No.
*
Neck dissection
. It is usually done at the same time as surgery to remove an
already existing tumor. The type of surgery (Radical neck dissection or modified
radical neck dissection.)depends on the stage of cancer.
5.Combine surgery*Surgery +Radiotherapy, or chemotherapy.
*Radiotherapy+Chemotherapy.
Prognosis:
5years survival of ca.larynx
Stage 1 = >95% , Stage II = 85-90 %,
Stage III =70-80% , Stage IV=50-60%
*patient considered cured after being disease free for five years.
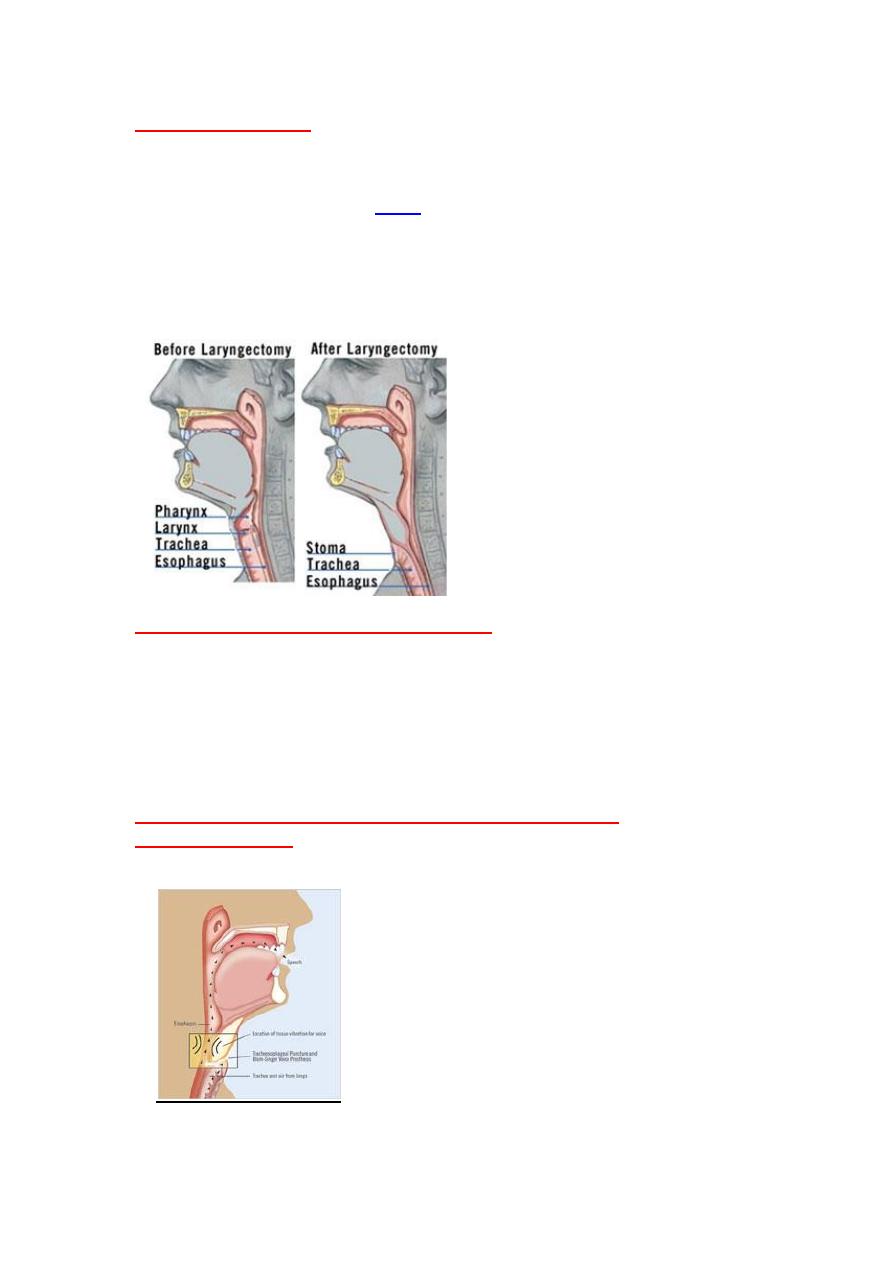
Total laryngectomy
:
*Indicated in stage T3,T4 tumor, and failure of treatment of stage T1,andT2
The mainstay of treatment for advancedlaryngeal carcinoma.
It is a surgical
procedure when the whole larynx (voice box)is removed, and
the trachea
sutured to the skin anteriorly (
) as permanent tracheotomy,the patient
breathe through the stoma. The pharynx closed and sutured to the base of the
tongue .
*In total laryngectomyRemoval of the larynx, thyroid cartilage,criciod cartilage,
epiglottis, hyoid bone, strap muscles, one or both lobs of thyroid gland,2-3
tracheal rings.
Rehabititation after total laryngectomy.
The chief problems where rehabilitation is likely to be required are:
1.Speech.(Voice restoration)
2.Swallowing
3.Tracheostomy problems.
4.Problem with loss of glottis occlusion,e.g.lifting.swiming,bathing and shower
5.problems with airway diverging,e.g.loss of olfaction.because the air not pass
through the nose and mouth .
6. Body image/psychological/social problems.
Methods of voicerestoration after total laryngectomy.
1.Esophagealspeech
.
Thelaryngectomee patient can learn from a speech therapist
. where air is injected, then expelled in a controlled way to form voice.
Esophageal speech.
A. Tongue press to inject air into esophagusB. Air enters esophagusC. Air released from
esophagus to produce voiceD. Voice shaped into speech
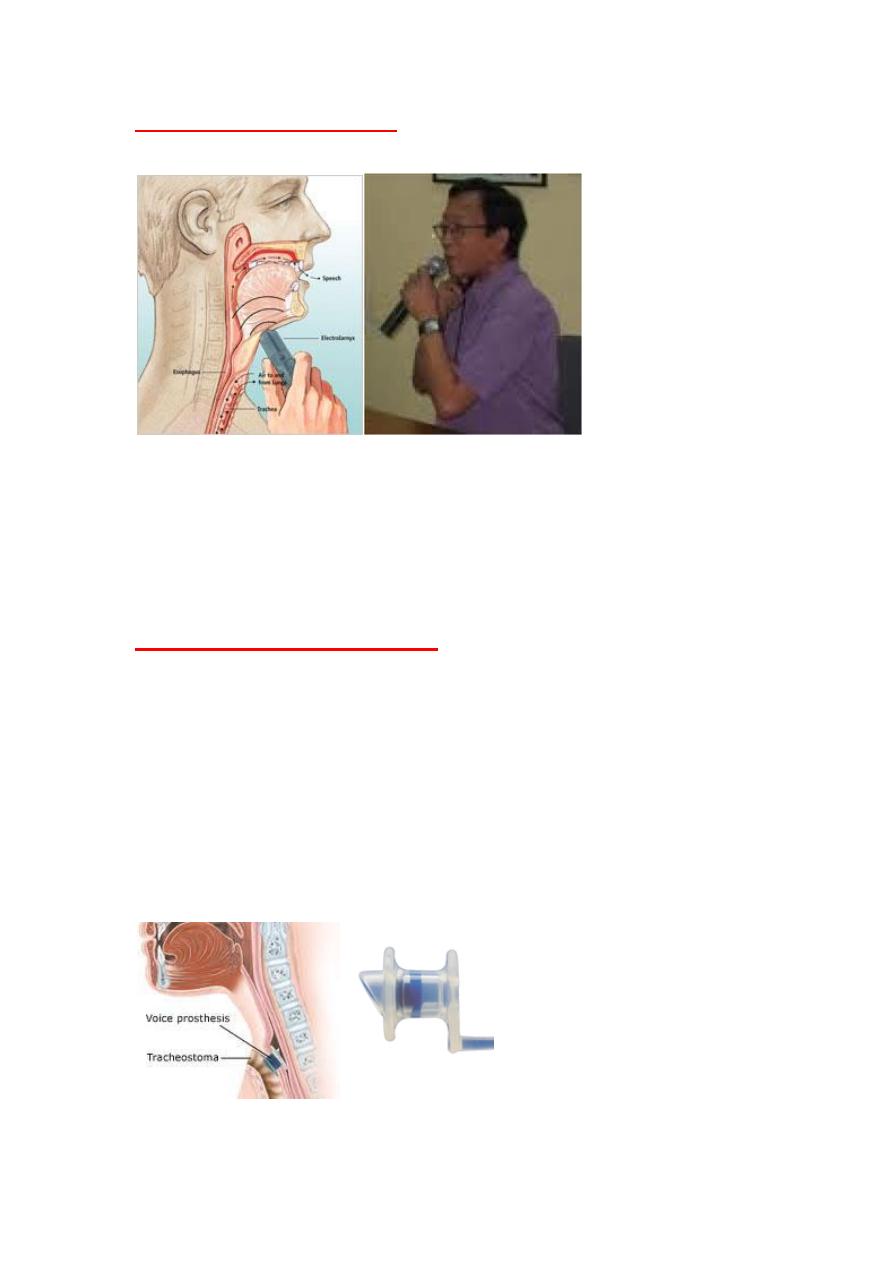
2.Artifical (electronic) larynx
..
It is a device emits a vibrating noise and is
hand-held against the throat. By mouthing words, the laryngectomee converts
the vibrations to speech.
Artifical larynx.
3.Tracheo-esophageal speech.(preferred methods)
.
By creating a small surgical passage (TEP, or Tracheoesophageal Puncture
(fistula)), inside the stoma, from the back wall of the trachea into the esophageal
wall, a small one-inched valved tube (voice prosthesis) can be placed into this
passage to enable tracheoesophagealspeech.
Voice is produced by blocking the stoma, either with a finger or an adjustable
tracheostoma valve, so that exhaled air from the lungs can be directed from the
trachea through the prosthesis into the esophagus (where vibrations are
produced) and vibrations which are modified by the tongue, palate, and lips to
produce speech. Fluent, conversational speech is usually acquired within a few
days.
Use of one way valve like ,Blom-Singer voice prostheses, and Panje Voice Button
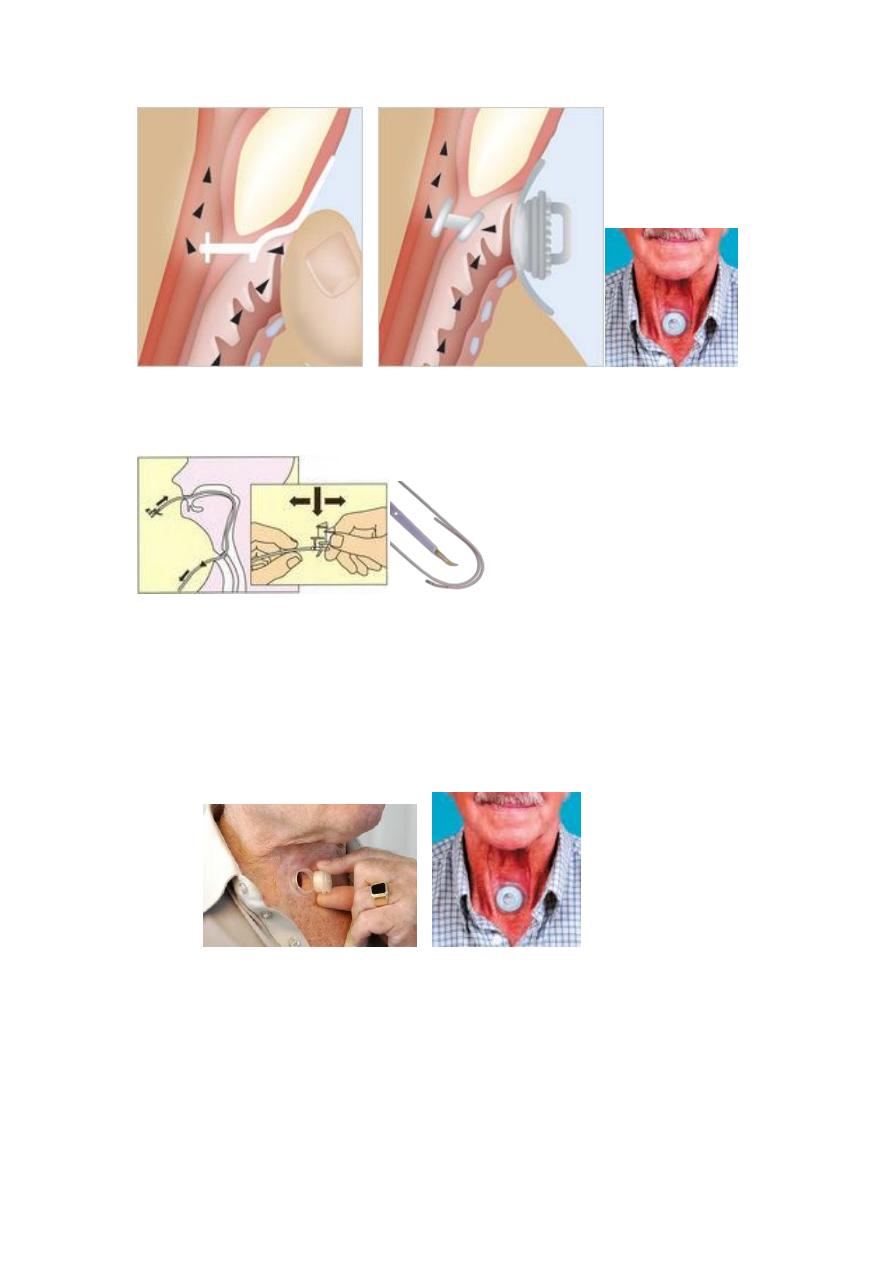
Stoma occlusion with thumb. Adjustable tracheostoma
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Adjustable tracheostome.
*
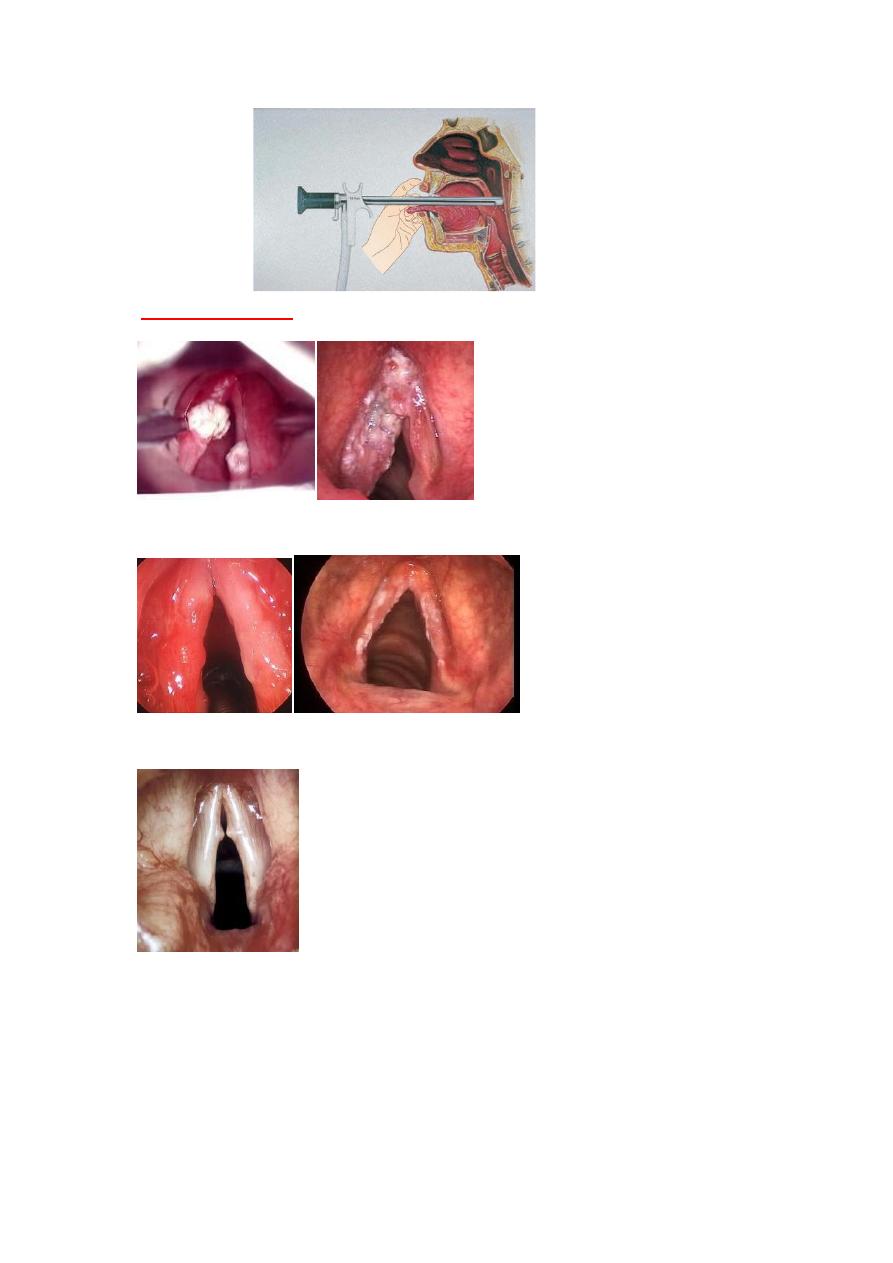
,
Rigid endoscopy
Laryngeal masses
Squamous cell carcinoma .
Dysplasia of vocal cord,
Leukoplakia
pre-cancerous diseases of the vocal cords.
Singers 's nodules
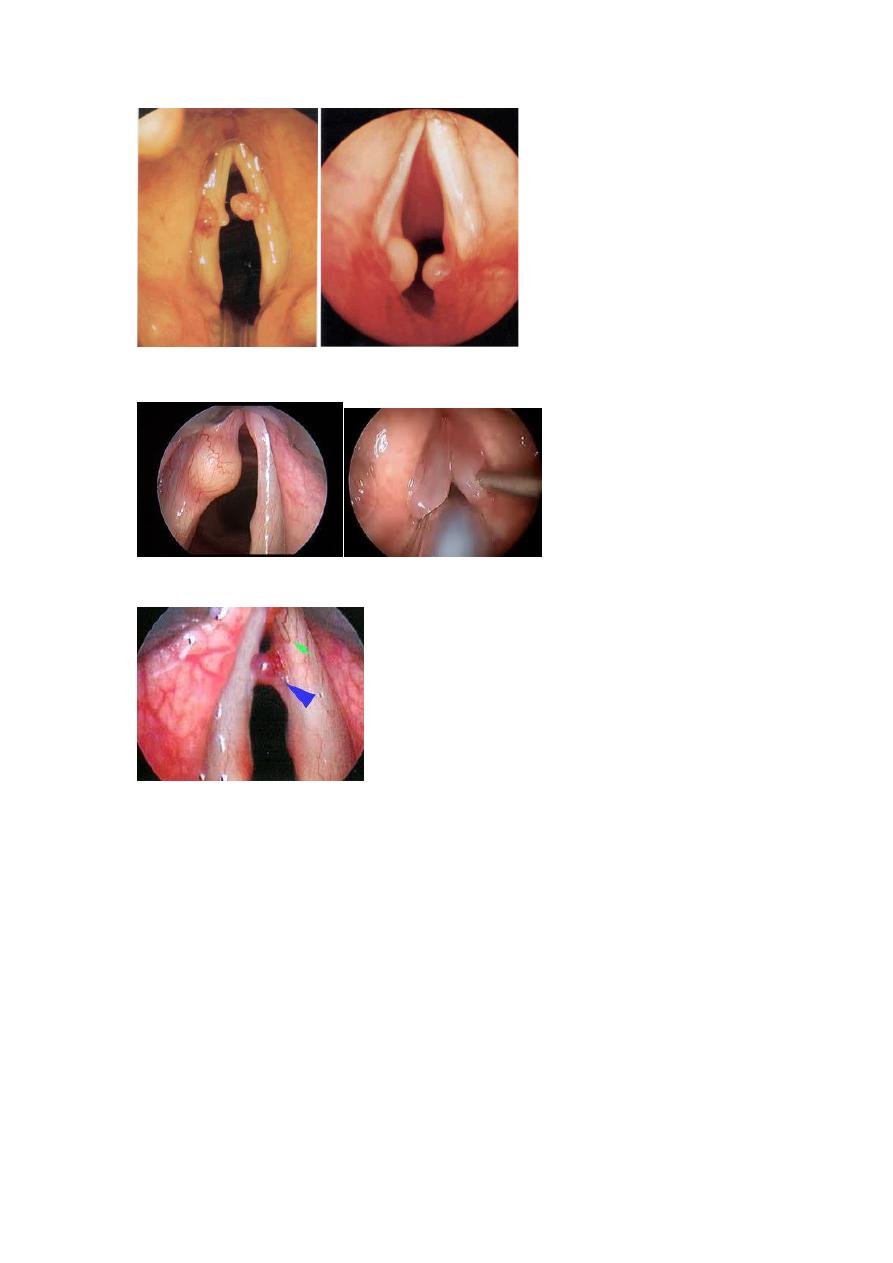
Vocal cord nodules. Intubation granuloma
laryngeal cyst
Renkiesodema
haemorrhagic Vocal cord polyps
==========================================
