Puberty :-
is the sequence of events in the transformation of a child into young adult with the development of secondary sexual characteristics and reproductive capability.-Occur between 8-14 yrs in girls.
-Occur between 9-14 in boys.
During this process there are:
Physical.
Endocrine .
Psychological changes .
Increased sex steroid hormone.
Onset depend on:-
Genetic factors
Geographic location
Nutritional status
Psychological factors
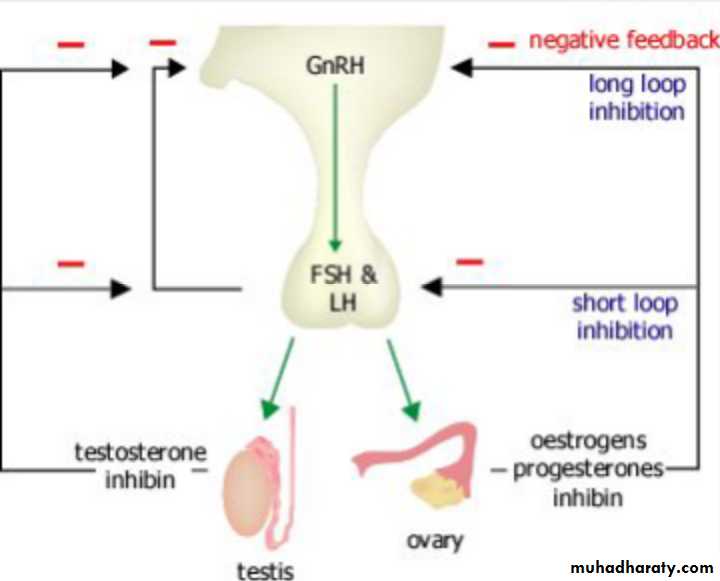
During childhood, the hypothalamic–Pituitary –ovarian axis is suppressed and levels of GnRH,FSH and LH are very low.
However, from the age of eight to nine years, GnRH is secreted in pulsations of increasing amplitude and frequency. These are initially sleep-related, but as puberty progresses, these extend throughout the day.
This stimulates secretion of FSH and LH by the pituitary glands which in turn triggers follicular growth and steroidogenesis in the ovary.
The oestrogen produced by the ovary then initiates the
physical changes of puberty.
Physiology of puberty
*Activation of hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal axis*Induces & enhances progressive ovarian & testicular sex hormone secretion.
*Responsible for biological, morphological &psychological changes.
Puberty; Girls
It involve five stages in girls ;1-growth spurt
2-breast development ( thelarche).
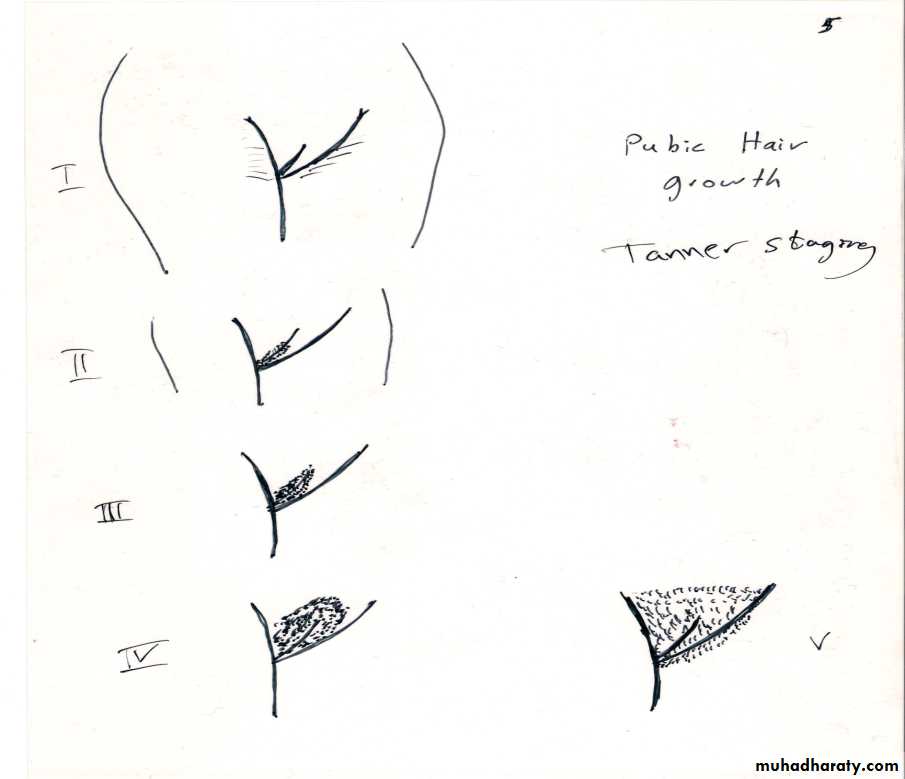
3-pubic hair growth (pubarche)
4-axillary hair growth
5-menstruation (menarche)
Growth spurt is characterized by an acceleration in the growth rate around age 9-10y leading to a mean peake growth velocity around age 12 of about 9 cm/ y. By the age of15 most girls have achieved their final height because of the production of estrogen from the ovary at this time eventually closes the epiphyses.
thelarche, its the first phenotypic sign of puberty, characterized by appearance of breast bud, usually occurring at the beginning of puberty around age 10 in girls noticed as a firm, tender lump directly under the center of the nipple, may occur on one side first or both sides simultaneously, the full development take around 5 yrs.
pubarche, the onset of growth of pubic hair, stimulated by androgens released by the ovary & adrenal gland. Its usually occurs around age of 11 & it is often accompanied by growth of axillary hair.
Menarche ( first menstrual cycle ) the average age is between 12 &13 y or 2.5 yrs after the development of breast buds. The adolescent MC is usually irregular for the 1st 1-2 yrs after menarche, reflecting anovulatory cycles.
Ovarian development
*rising levels of plasma gonadotrophins........stimulate ovary to produce increasing amounts of estradiol.....secondary sex characteristics;breast growth & development ,reproductive organ growth & development ,fat redistribution &bone maturation.
*increase ovarian volume to reach 4cm³ post pubertal preparing to ovulation.
Uterine development
*pr-epubertal uterus is tear-drop shaped , following production of estrogens, uterus become pear shaped.*uterine body increases in length & thickness.
*vaginal mucosal surface become thicker & more pink in color in response to increasing level of E.
Body shape, fat distribution & bone age
In response to rising levels of estrogen, the lower half of pelvis &thus hips widen. The bony pelvis acquires female characteristics.
Bone age correlates well with the onset of secondary sexual charact. & menarche, its determined by X-ray of the left wrist comparing them with an index population.
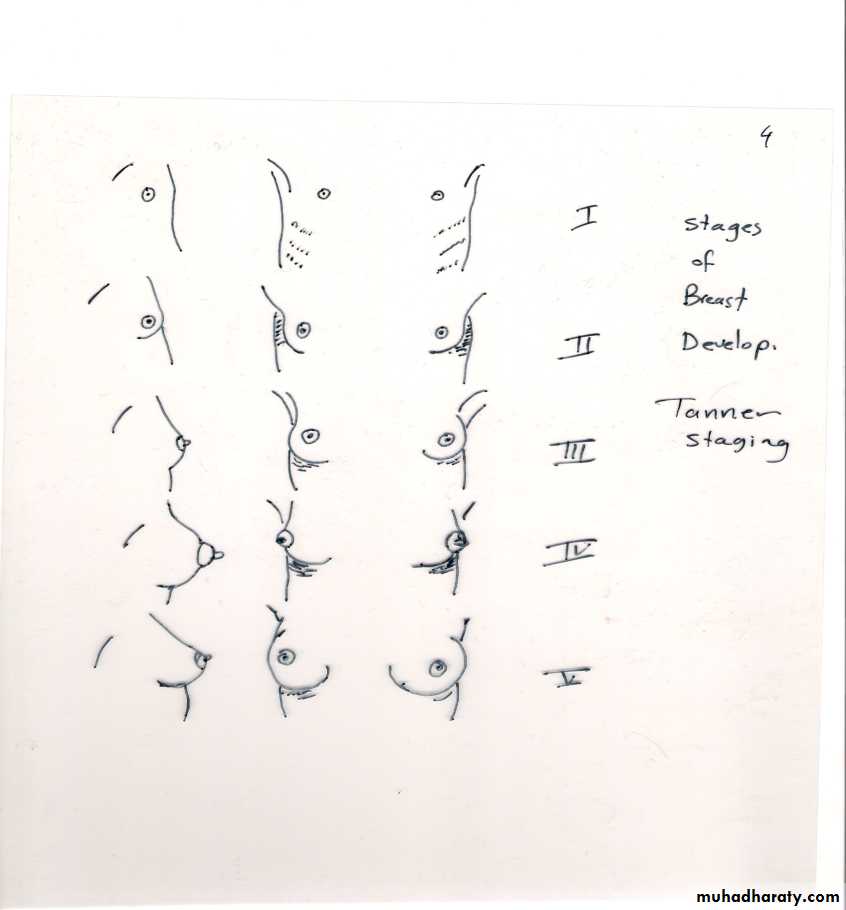
Pubertal stages (Tanner)
P1...prepubertal ( typically age 10 &younger )
P2... early development of subareolar breast bud+/- small amount of pubic & axillary hair.
P3... increase in size of palpable breast tissue & areola, increased dark curled pubic/axillary hair.
P4... breast tissue & areola protrude above breast level. Adult pubic hair but no spread to medial thighs.
P5... mature adult breast. Pubic hair extends to upper thigh.
Puberty: boys
*testicular enlargement (12-13yrs) is first sign. Prepubertal testis-2ml diameter, puberty begins when volume reaches 4ml.*penile growth & scrotal changes , pubic hair occur approx 1-2 yrs after testicular enlargement.
*late signs, growth spurt, acne ,voice deepening, facial hair, pubertal growth spurt occur later than in female.
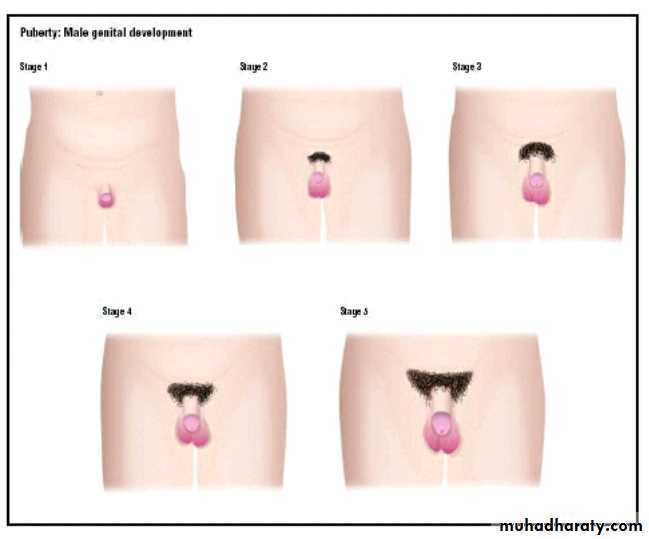
*Pubertal stages (Tanner)
P 1...prepubertal (testicular volume < 2 ml, small penis) typically age 9 & younger.
P 2...enlargement of scrotum & penis, few long dark pubic hair.
P 3...lengthening of penis. Further growth of testes & scrotum. Pubic hair darker, coarser & more curled.
P 4...penis increases in length & thickness. Increased pigmentation of scrotum. Adult pubic hair but no spread to medial thighs.
P 5...genitalia adult in size & shape. Pubic hair spread to medial aspect of thighs.
Precocious puberty
Refers to the development of secondary sexual characteristics <8yrs in girls &<9yrs in boys. Incidence 1/ 10000Male / female ratio 1/5,75% of all cases are constitutional idiopathic
Typically taller than their peers as children but short as adult due to premature closure of epiphyses.
In girl, pregnancy can reported as early as 5.5 yrs !
In boy, testicular biopsies has shown stimulation of all elements of testis & spermatogenesis as early as 5-6 yrs.
Causes may be;
1-Gonadotrophin dependant(True precocious puberty)
-idiopathic (constitutional)
-congenital (hydrocephalus).
-acquired (irradiation/ surgery, sever head trauma)
-tumours (gliomas).
-hypothyroidism (TSH act on FSH receptors).
2-Gonadotrophin independent(Pseudo-precocious puberty)
-virilisation of female (CAH).
-feminisation of boy (estrogen producing leydig tumour).
-adrenal tumour.
-ovarian tumour.
-exogenous androgens, estrogen.
Mc Cune Albright Syndrome (patchy cutaneous pigmentation &fibrous dysplasia of skeletal system
-HCG-secreting tumour (teratoma).
Diagnosis of precocious puberty:
History:-
Similar family history
Sequence of sexual maturation
Speed of sexual maturation
Exposure to drug or hormones
CNS (meningitis, encephalitis, abscess, TB, tumor, neurofibromatosis trauma, seizures, headache, blurring of vision, numbness, muscle weakness,…
Physical examination:
Vital signs
Record of serial height and weight
Detailed record of secondary sex.charec. Tanner staging
Abd. Pelvic exam * (no PV)
Thorough neurological exam.
Skin exam (café au lait macules, neurofibroma, acne.)
Galctorrhea
Investigations:
Skull X ray
Serial bone age estimations X ray hands&elbow
CT, MRI head sella turcica & hypothalamus
U/S , MRI abdomen & pelvis
FSH, LH, hCG
DEHAS, androsteindione, testosterone, E2, Progesterone(P)
Prolactin
Thyroid function tests
GnRH stimulation test
EEG
Visual field .
Treatment
*-Psychological support.
GnRH analogues (triptorrilin , decapeptyl )
It is similar to GnRH but it is of long action attach to pituitary GnRH receptors permanently and cause stimulation of FSH & LH at first week and then cause down regulation of pituitary receptors ie. Decrease the number of functioning receptors → suppression of the pituitary gland → Triptorrilin injection every 28 days , till reach the determined height by 13-14 years then stop GnRH analogues and the hypothalamo - piuitary – ovarian axis resume normal activities
In gonadotrophin independent ,in girl, aromatase inhibitors as letrozole (1.25-2.5 mg/d orally) or antiestrogen as tamoxifen. In boy, combination of antiandrogens ( such as spironolactone 50-100 mg twice daily or flutamide 125-250 mg twice daily)
*-treat systemic disease
*-surgery to remove tumour.
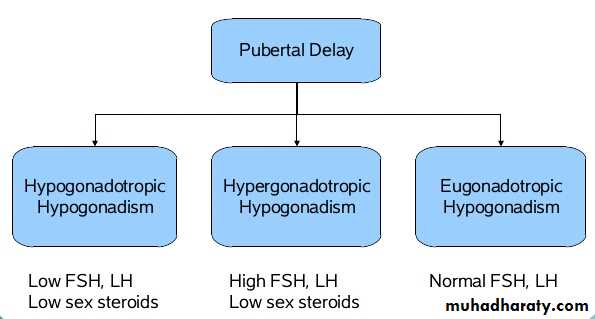
Delayed puberty
Puberty delay if:*no breast development by age 14 in female , no menses by age of 16.*testicular size <2.5 cm or 4 ml or pubic hair is not present by age of 14 in male.
Causes may be;
1-Hypogonadotrophic
-idiopathic (familial/ sporadic)
-chronic illness (renal failure/ Crohns dis).
-malnutrition.
-exercise.
.-tumour of pitutary/ hypothalamus (craniopharyngioma).
-hypothyroidism (interferes with gonadotrophin secretion)
-hyperprolactinemia, PCOS.
-isolated GnRH deficiency........(Kallman's Syndrome)
2-Hypergonadotrophic
-congenital (Turner syndrome/ klinefelters syndrome, complete androgen insensitivity, mixed gonadal dysgenesis)
-acquired......irradiation/ chemotherapy.
.surgery
.testicular torsion, trauma
.infection (mumps orchitis).
.autoimmunity.
3-Eugonadotrophic
-congenital anatomic anomalies:imperforate hymen ,vaginal atresia ,vaginal aplasiaIn these cases,, secondary sexual characteristics are normal.
Treatment
*Psychological support.
*Treat systemic disease
*Promote puberty/ growth if necessary.
in male case.
.... testosterone,it cause virilization, accelerates development of secondary sexual characteristics & stimulate growth spurt).
Its either oral form, testosterone undecanoate 40mg daily or I.M.injection 50-200mg using testosterone esters have been used for a period of 6-12 months or use transdermal patches.
.....hCG 200-500 Units, can use to stimulate development of secondary sexual characteristics, increase testicular size & to stimulate fertility.
In female case
......estrogen replacement, initial replacement at age of 10-12 yrs &should continue over course of normal puberty (approx 3 yrs). Effect of estrogen on growth plate is dose dependent, higher dose stimulate epiphyseal growth plate closure, to start with 2mcg/day ethinylestradiol. Once adose of 10-15 mcg ethinylestradiol have been reached, a break through bleeding becomes apparent & when this occur, progesterone should be added to prevent endometrial hyperplasia.
*in some cases of hypogonadotrophic delayed puberty, pulsatile administration of GnRH has resulted in induction of puberty.