
C
OUNSELING
IN
F
AMILY
M
EDICINE
1
Dr. Zaid M. Yassen
Family Medicine

C
OUNSELING
Counseling:
various technique & methods by which
people can be helped to understand themselves & to be
more effective.
●
Sometimes reassurance, advice & explanation are
insufficient and the doctor may be required to assure a
more formal counseling role to help patient work through
or come to term with their problems.
Counseling is therefore more than Just given advice but
●
falls short of psychotherapy.
2

C
OUNSELING
(
CONT
.)
The task in counseling is first to clarify
the problem and then to aid the patient
in finding his own solution.
Counseling should be incorporating into
every day practice.
3

C
OUNSELING
(
CONT
.)
The
Fundamental aim of counseling
is to:
ASSIST
a patient to
IDENTIFY and
IMPLEMENT
his own unique solution to a
particular problem.
This is done by helping the patient not only
to develop insight into their particular
situation but also to identify the range of
possible courses of action open to them
from which they can make action.
4

C
OUNSELING
(
CONT
.)
Effective counseling provides comfort to the
patient and can result in demonstrable
improvement in physical and mental well being
and health.
The doctor becomes good counselor when:
1)
He listens
2)
Is aware of the patient feelings
3)
Is able to help him explore his difficulties and
work with them using
his own resources.
5
C
OUNSELING
(
CONT
.)
Any one can offer tea and sympathy.
Professionals know that only helping the
patient to help himself is likely to be
effective.
A growing literature demonstrates the
effectiveness of physician counseling of
patient about lifestyle-related illness.
6

C
OUNSELING
(
CONT
.)
Communication skills & Evidence Based Medicine
are important in counseling.
Clinicians must also understand the nature of
effective health communications and practice
counseling skills to ultimately facilitate lifestyle
changes for patients.
To be successful in helping patient change their
health behaviors you should know the
epidemiology of medical problems and be aware
of the scientific evidence that support the
intervention chosen.
Education and counseling help patients make
behavioral changes.
7

H
EALTH
BEHAVIORS
WERE
DIVIDED
INTO
THREE
CATEGORIES
1) Add behavior:
Add fiber to diet, folic acid, exercise and increase
physical activity. Disease prevention such as dental
flossing and routine dental care.
Periodic Health Examination (PHE) e.g. breast self-
exam., colon cancer screening, regular use of condoms,
use of seat belts.
2) Eliminate nonaddicting behavior:
Reduce dietary fats and excessive calories in diet,
eliminate unsafe sexual activity.
3) Eliminate addicting behavior:
Eliminate smoking, excessive alcohol use and other
addicting substances
8

S
TEPS
TO
MAXIMIZE
PATIENT
EDUCATION
FOR
B
EHAVIORAL
CHANGE
1)Understand the power of physicians expertise as a
motivator toward behavior change.
2) Be patient-centered and patient responsive
(understand patient perceptions of their
illness/behavior and their readiness to change).
3) Choose one or at most two behavioral goals for
changing at any one time.
4) Be specific in giving advice.
5) Obtain a firm commitment from patient to change.
9

S
TEPS
TO
MAXIMIZE
PATIENT
EDUCATION
FOR
B
EHAVIORAL
CHANGE
(
CONT
.)
6)
Use positive reinforcement and short-term
rewards.
7)
Use multiple educational modalities when possible.
8)
Use social support when possible.
9)
Assure appropriate follow up.
10)
Be realistic.
10
B
RIEF
C
OUNSELING
I
NTERVENTIONS
(BCI)
BCI of one to three visits can substantially help
patients change problem behaviors particularly
in the areas of
smoking cessation, hazardous
alcohol use and exercise.
11
T
HE
ELEMENTS
OF
AN
EFFECTIVE
BRIEF
INTERVENTION
THAT
HELP
TRIGGER
PATIENT
MOTIVATION
TO
CHANGE
ARE
: (FRAMES)
1) Giving feed back based upon a thorough assessment.
2) Helping the patient take responsibility of changing.
3) Giving clear advice on what behavior must change.
4) Offering a menu of options for making the changes.
5) Expressing Empathy for the ambivalence and
difficulty in making changes.
6) Evoking self-efficacy to foster commitment and
confidence.
►
Only 20% of patient are ready to take action to change
during an office encounter, the other 80% are in
different stages and need something other than
clinician advice.
12
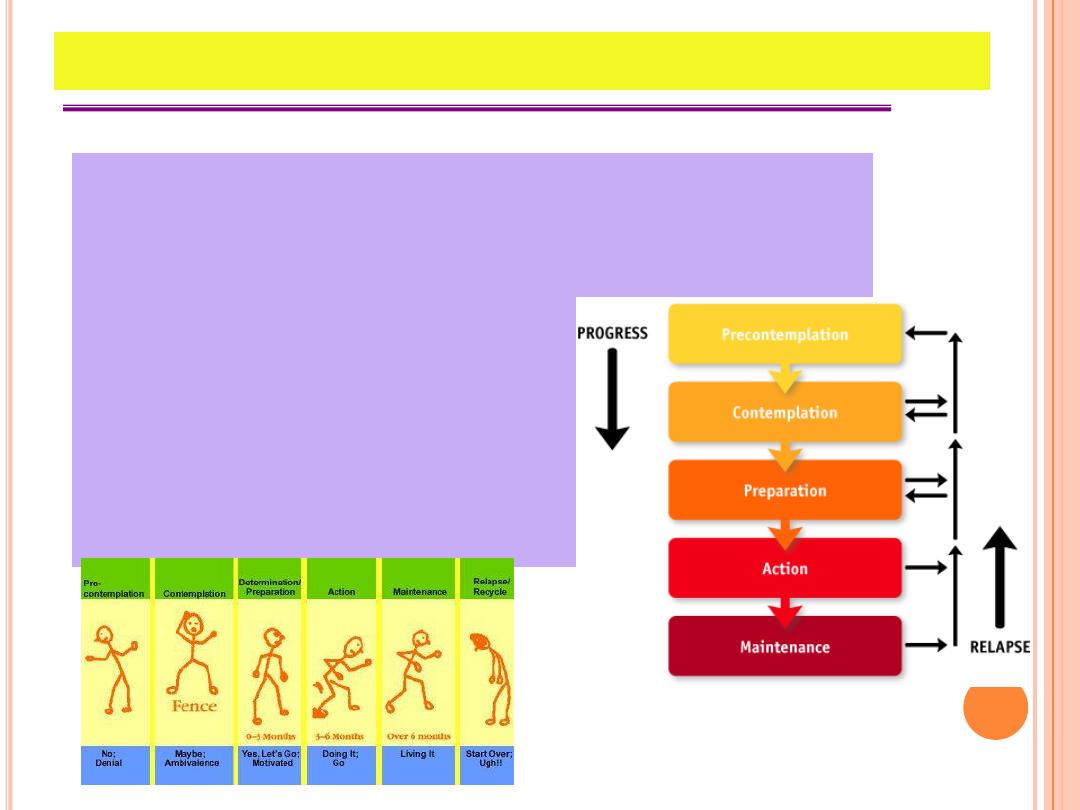
S
TAGES
OF
C
HANGE
1)
Precontemplation.
2)
Contemplation
3)
Determination
4)
Action
5)
Maintenance
6)
Relapse
7)
Termination
13

S
TAGES
OF
C
HANGE
(
CONT
.)
1) Precontemplation:
●
Person is not yet considering the possibility for changes.
Precontemplators do not make appointments, they are
detected through routine screening.
●
They respond with surprise when approached about the
need for changes.
The tasks of precontemplation are learning about the
problem, developing self-awareness and considering
the possibility of changes.
14

S
TAGES
OF
C
HANGE
(
CONT
.)
2) Contemplation:
●
Once aware of the problem the person enters
contemplation and experiences about the possibility of
change.
●
The contemplator oscillates between reasons for change
and reasons to remain the same.
The counseling task in contemplation is to tip the
balance in favor of changes.
15

S
TAGES
OF
C
HANGE
(
CONT
.)
3) Determination:
Patients in determination are a pt to say I must do
something about this, I think this is trouble, what will I do?
Changes continues if the patient takes action otherwise
determination closes and the patient steps back into
contemplation.
The counselor’s task is not to motivate but to help find
an appropriate strategy for action.
16

S
TAGES
OF
C
HANGE
(
CONT
.)
4) Action:
Action requires little from the clinician since the patient
does the work to change.
The counseling task during action is to support the
patient as he or she experiences the changes.
5) Maintenance:
The patient enters maintenance stage when measures to
sustain the new behavior become routine.
17

S
TAGES
OF
C
HANGE
(
CONT
.)
6) Relapse:
During relapse the patient experiences a loss of control
and a lapse into the old behavior. relapses are normal
when changing most health habits esp. addicting ones.
Understanding that relapse is expected frees both the
physician and patient from guilt or blame and transforms
the relapse into a learning opportunity.
The counselor should help the patient avoid
demoralization, continue the reevaluation of
contemplation and develop the commitment and
confidence.
18

S
TAGES
OF
C
HANGE
(
CONT
.)
7) Termination:
Termination is outside the circle of change. This final
stage occurs when individuals have made a permanent
change. They no longer struggle to maintain the behavior
nor are they tempted to relapse.
Termination may not be possible for many longtime
behaviors.
19

B
ARRIERS
TO
OFFERING
PREVENTIVE
SERVICES
1) By definition preventive services are offered to
patients who are currently well and therefore may
have less motivation to change behavior.
2) Physicians have no control over the intervention, only
the patient can make the change.
3) Patient may experience psychological or physiological
withdrawal symptoms when they give up some
behavior.
4) Adding new behavior such as exercise may cause
some initial pain and even injury.
20

P
HYSICIAN
F
RUSTRATION
Physician may become frustrated with counseling
for a number of reasons
1) Lack of time.
2) Lack of physician education.
3) Patients often fail to follow advice.
21

E
XAMPLES
OF
C
OUNSELING
Counseling to prevent Tobacco use
Counseling to promote physical activity
Counseling to promote a healthy Diet
Counseling to prevent Motor-Vehicle injuries
Counseling to prevent low back pain
Counseling to prevent cancers
Counseling to prevent STD, AIDS
Counseling to promote breast feeding
Counseling for sleep disturbance
22
