Introduction to Thoracic Surgery
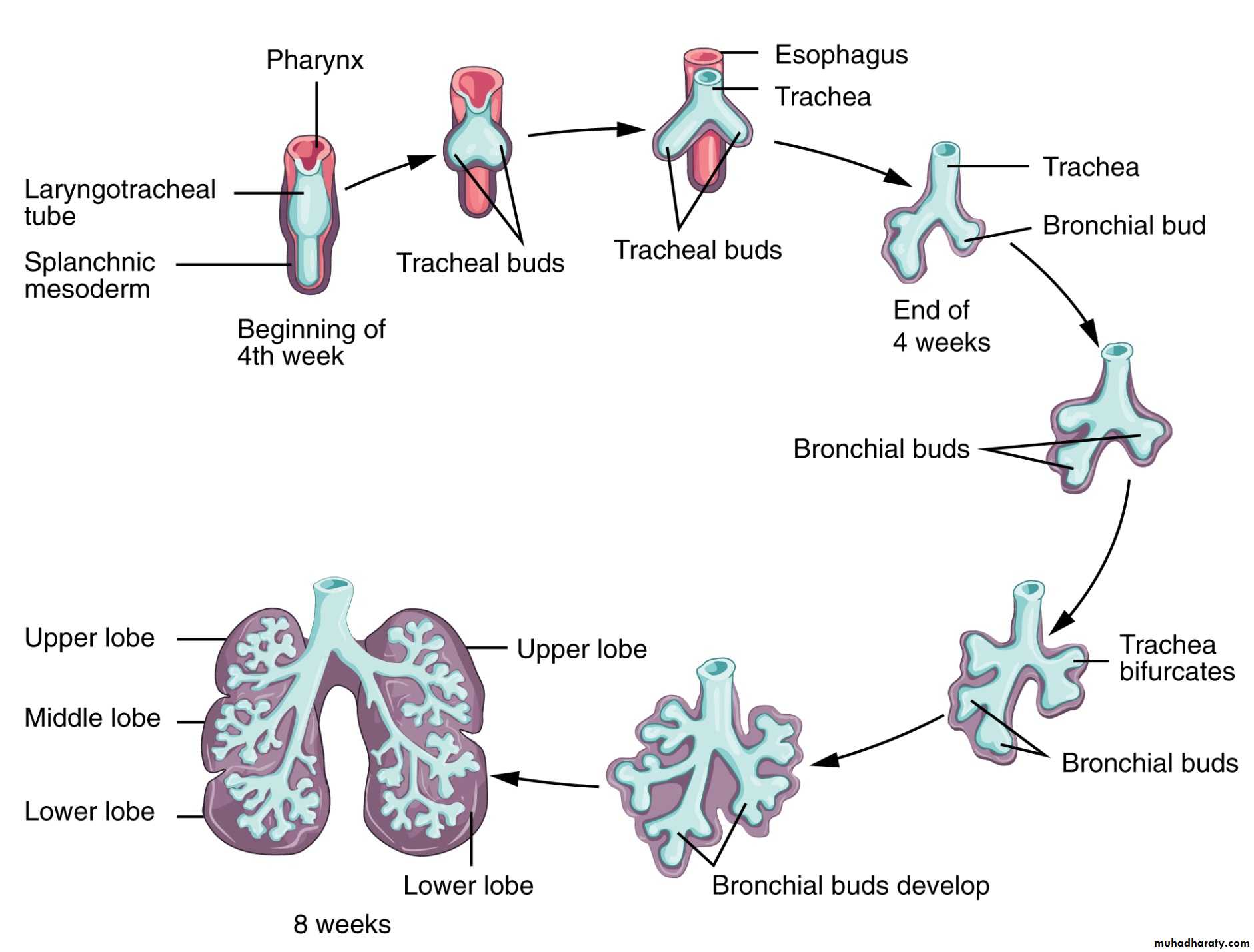
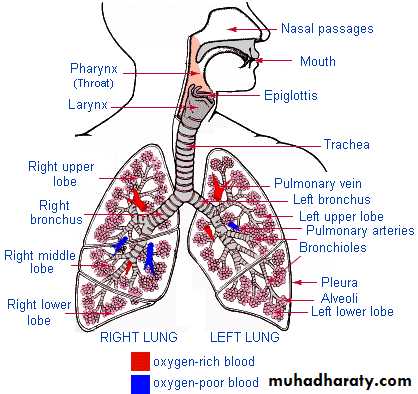
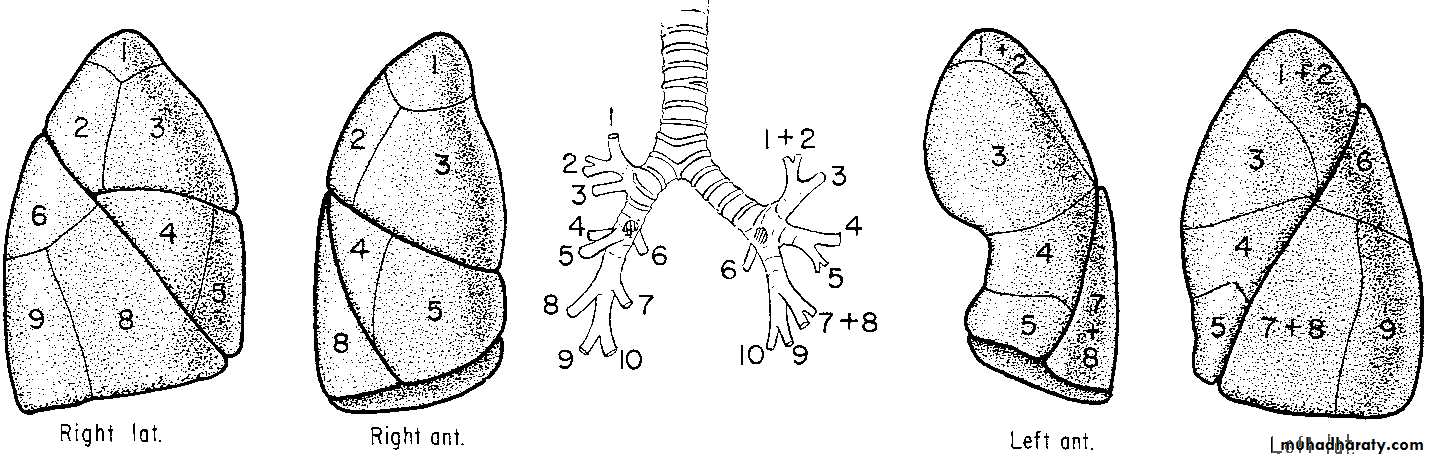
Embryology:Anatomy:
Mechanism of breathing:
What happens during quite breathing??
What happens during coughing?• Spirometry
• ABG• ppo FEV1
• MVV
• DLCO
• VO2 max
• V/P scan
Obstructive vs. Restrictive lung disease
Fitness for surgery
FEV1 >1.5 L. lobectomyFEV1 >2.0 L. pneumonectomy
Further investigations if level below
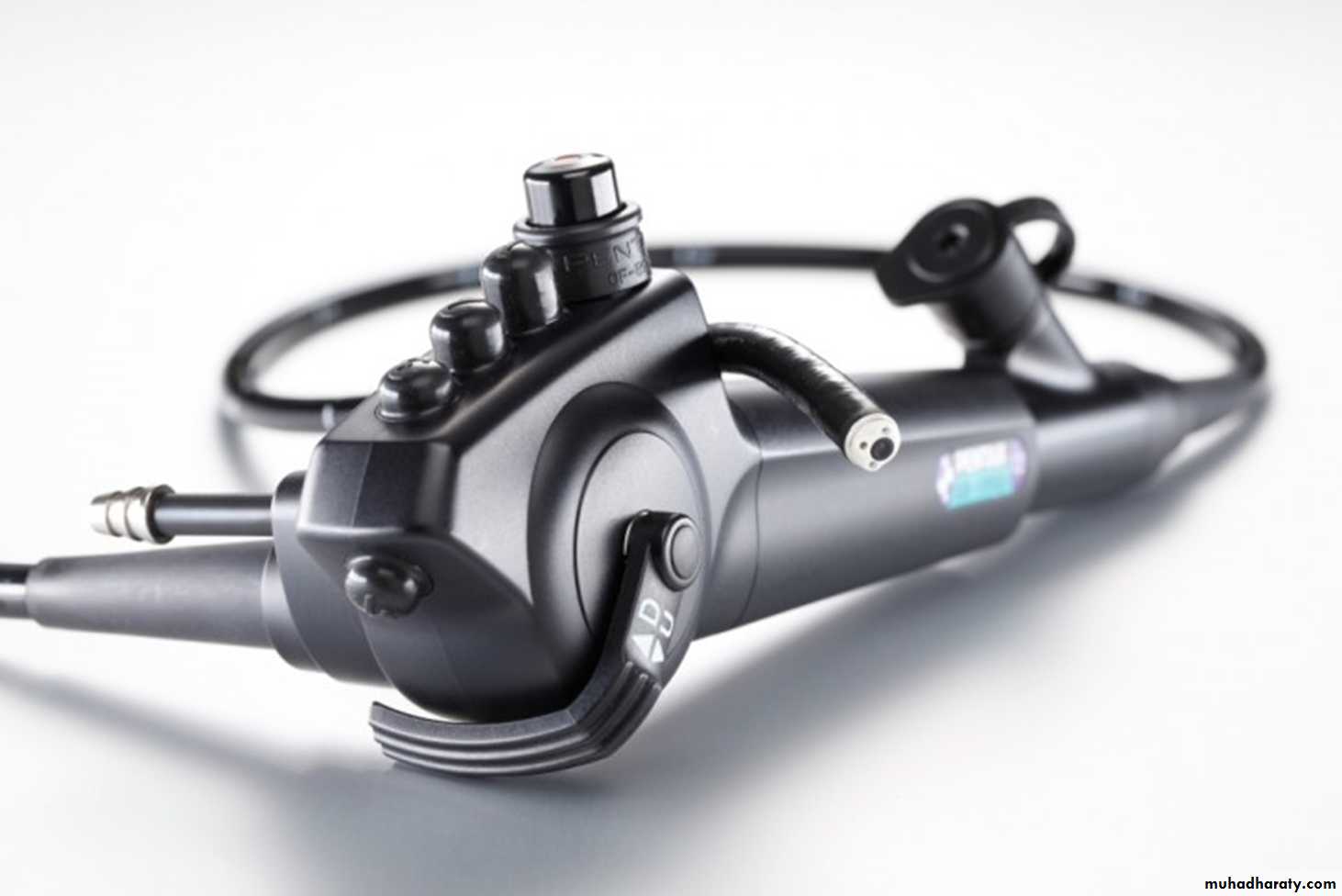
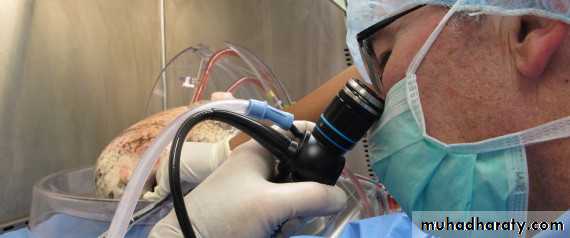
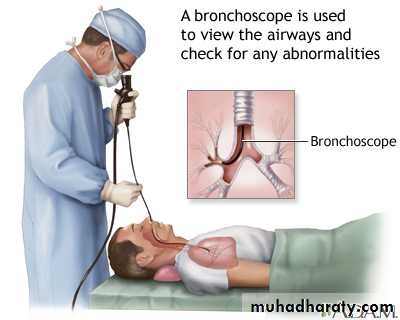
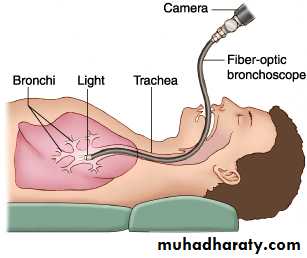
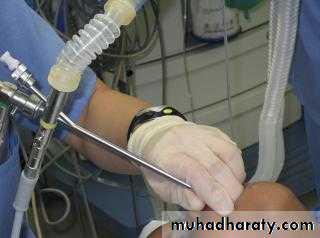
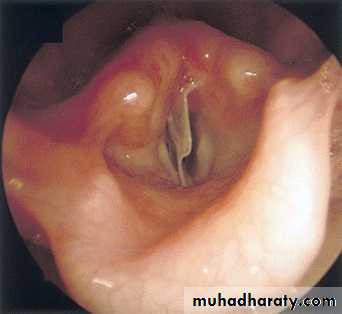
Bronchoscope
Indications:
• Diagnostic Bronchoscopy:• Massive, recurrent or persistent hemoptysis (suspicion of malignancy)
• Chronic cough not responding to medical treatment
• Patient with a persistent localized wheeze on chest auscultation.
• Pulmonary mass on chest X-ray
• Recurrent or unresolved pneumonia
• Investigate and follow up:
• malignancy or
• pulmonary fibrosis or
• assessment of degree of inhalational injury or
• airway trauma.
Indications (cont.)
• Preoperative assessment :• Before lung resection
• Before esophageal resection
• Persistent hemoptysis
• Therapeutic Bronchoscopy:
• Foreign body inhalation
• Difficult intubation
• Atelectasis
• Stricture dilatation
• Lung abscess drainage
• Laser therapy
• Cryotherapy
• Brachytherapy.
Flexible Bronchoscope
Advantages:• Better patient tolerance
• The need for only topical anesthesia
• Ambulatory setting (so can be done in outpatient clinic, ward, ICU,…etc.)
• Wider field of view
• Flexibility allowing it to pass further than the rigid scope
• Useful in patients with cervical spine problems.
• Allows assessing movement of vocal cords.
Disadvantages:
• Small instrument channel size (smaller biopsies, less suction power)• Difficulties in sterilization and maintenance
• Impinges on the airway (interferes with the patients breathing)
• Needs patient cooperation (difficult in children)
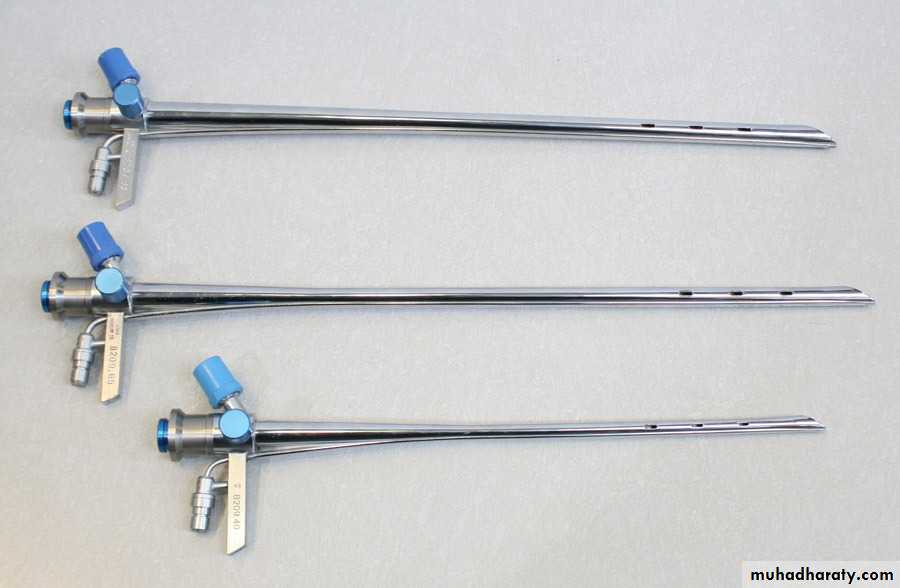
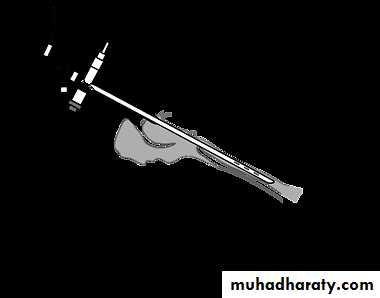
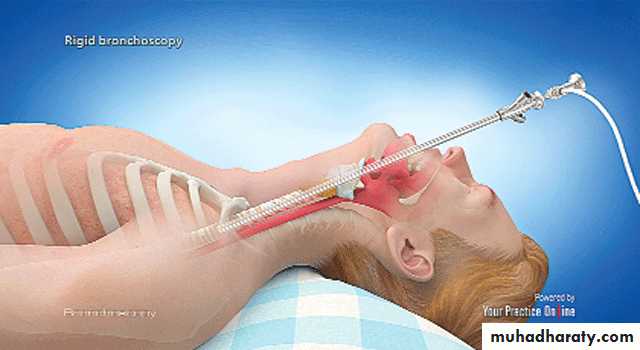
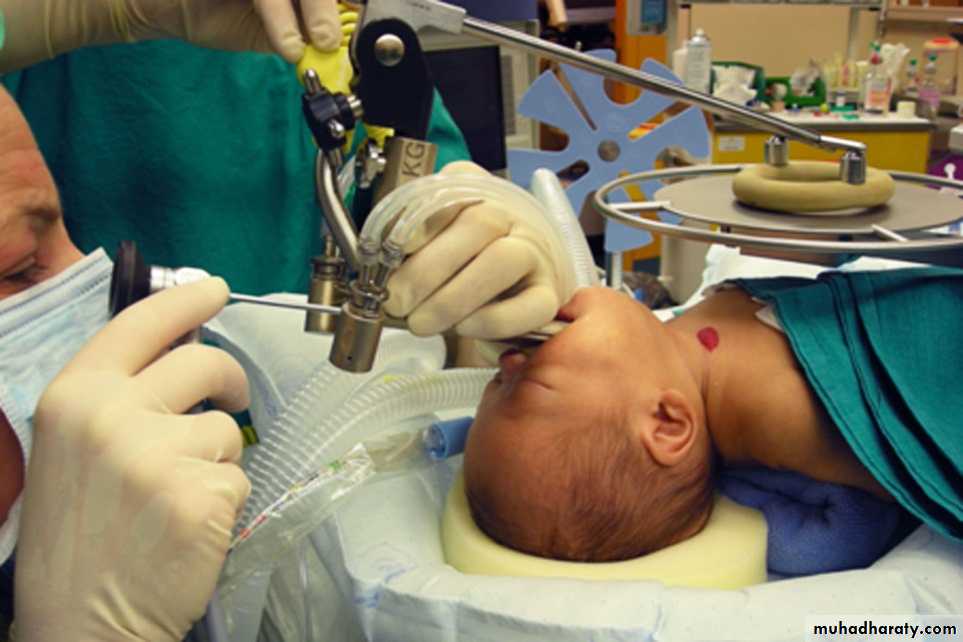
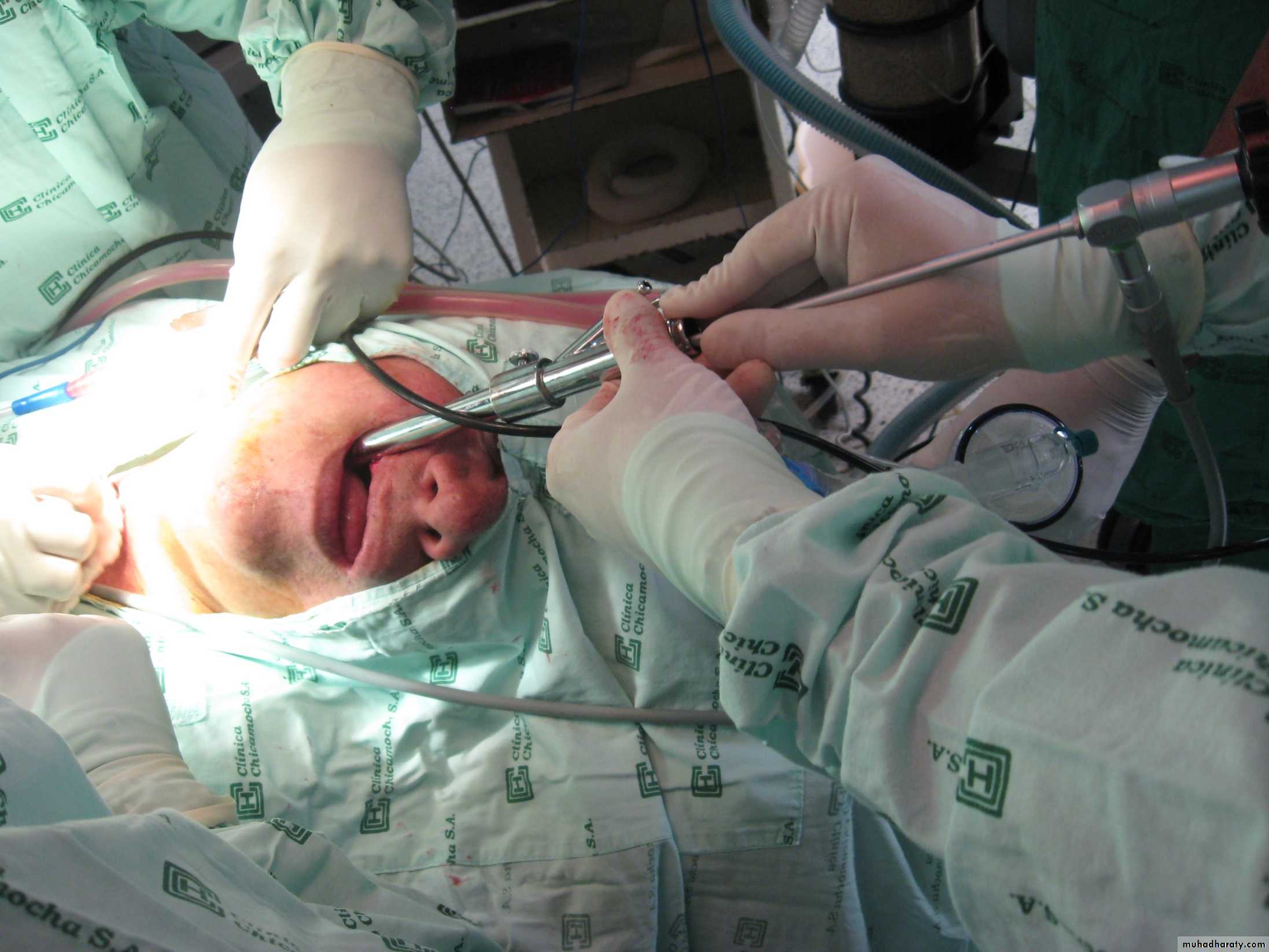
Rigid Bronchoscope
Advantages:
• Durability (less incidence of damage and breakdown)• Large instrument channels
• Control of airway as the patient is mechanically ventilated.
Disadvantages:
• Needs general anesthesia• Limited distal visualization
• Higher cost (to the patient)
• Higher risk of trauma
Procedure:
Countraindications:
• Thoracic aortic aneurysm• Cervical spine disorders
Complications:
• Laryngospasm and / or bronchospasm• Hypoxemia
• Tracheal or bronchial obstruction
• Tracheal or bronchial perforation
• Bleeding
• Arrhythmias and cardiac arrest
• Pneumonia
• Air embolism
• Pneumothorax
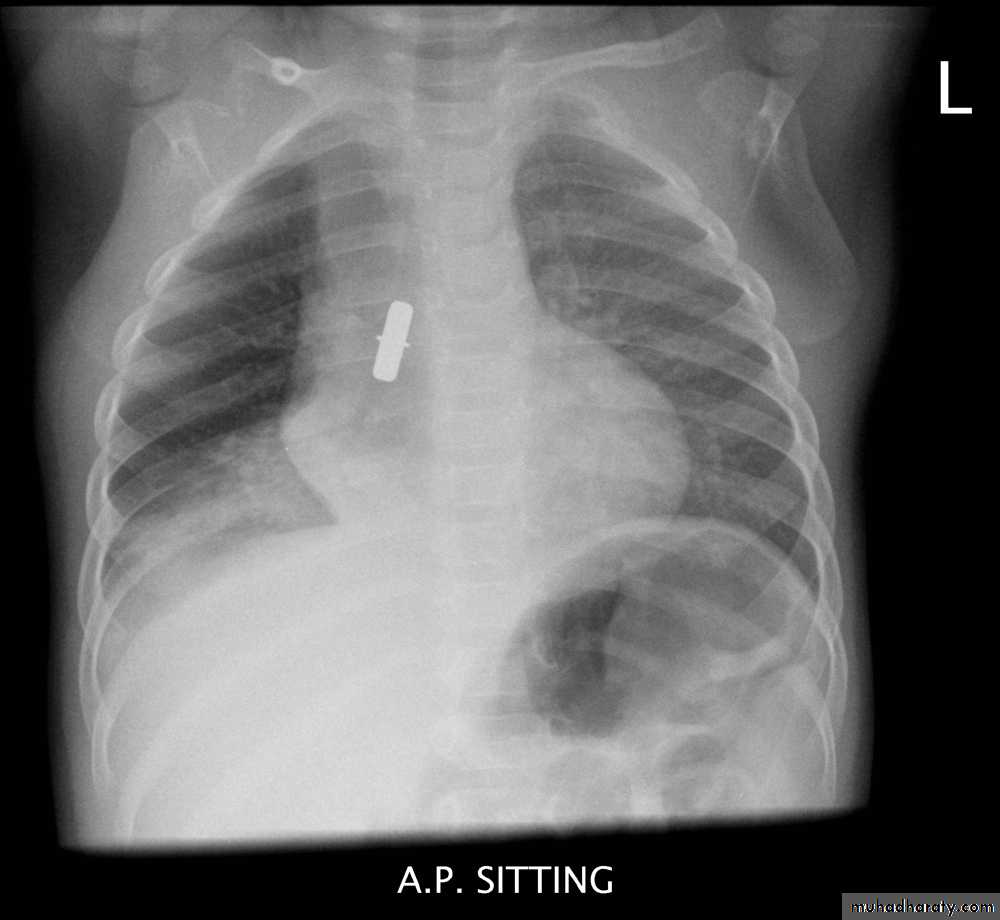
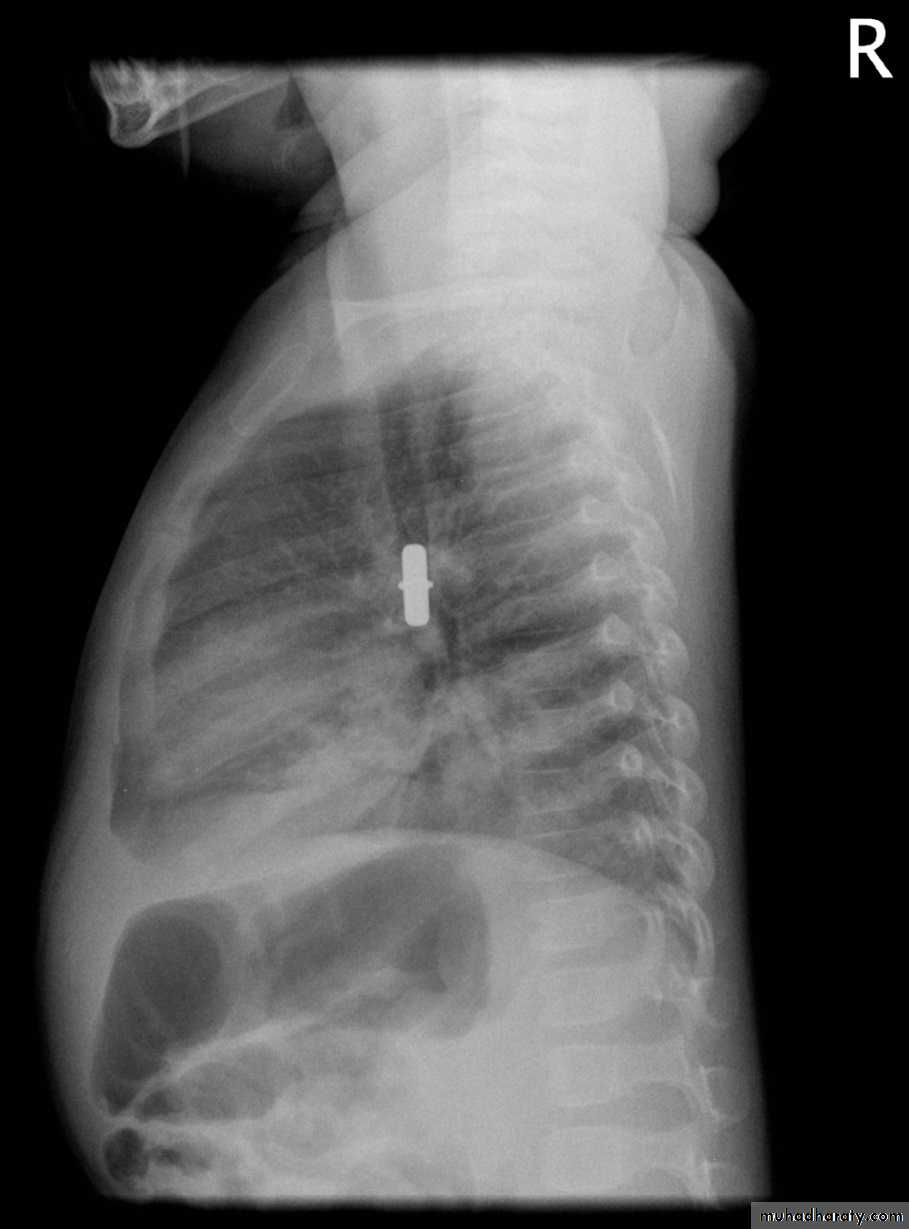
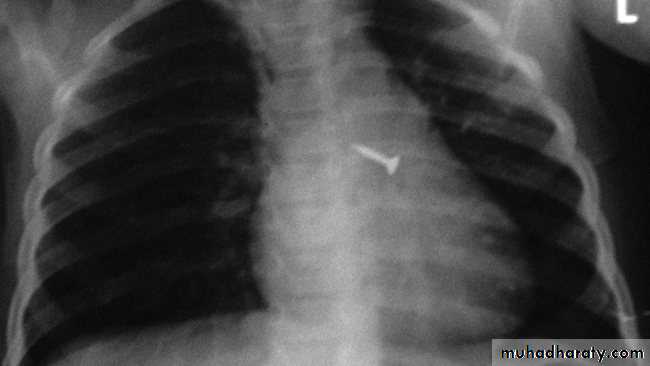
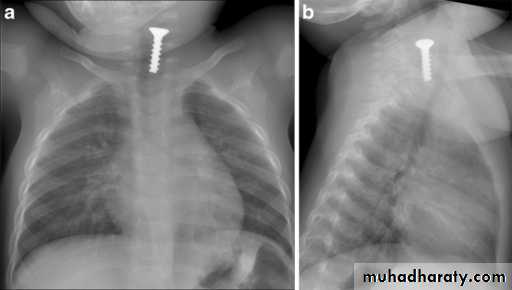
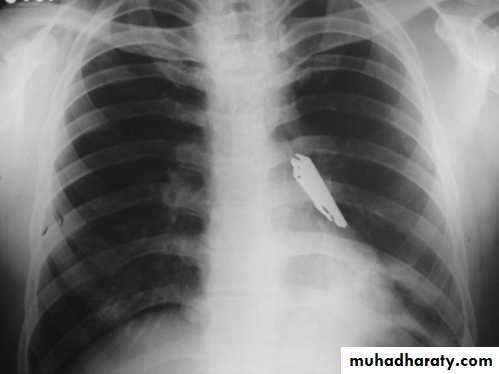
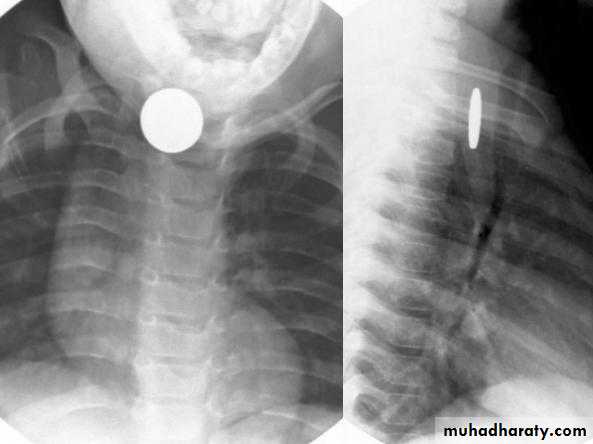
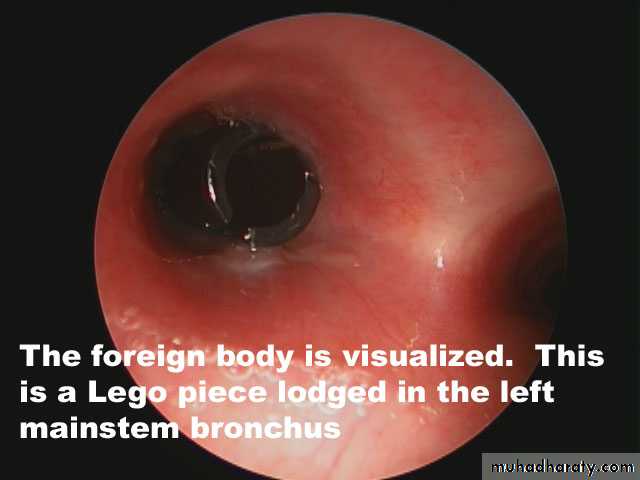
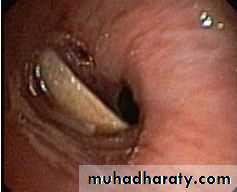
Foreign Body Inhalation
A common problem
Most common site for foreign body inhalation is?Clinical presentation:
• Asymptomatic only discovered by a witness• Stridor with dyspnea if stuck in the trachea or larynx
• wheezing with a persistent cough when in the bronchus
• repeated or persistent pneumonia with suppuration (late presentation).
Complications:
Early: change in the foreign bodies position and moving proximally leading to asphyxia & cardiopulmonary arrestLate:
• Recurrent chest infection
• Tracheo-Esophageal fistula
• Bronchiectasis.
• Emphysema
• Lung abscess
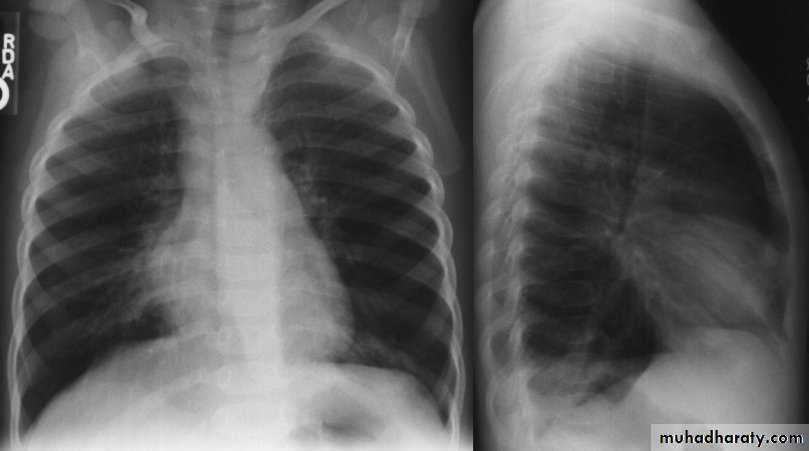
Investigations:
Chest X-ray:
DDx: FB in the esophagus