orthopedic of the upper limb
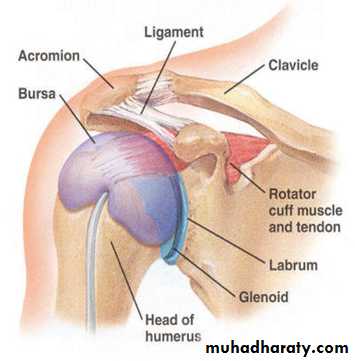
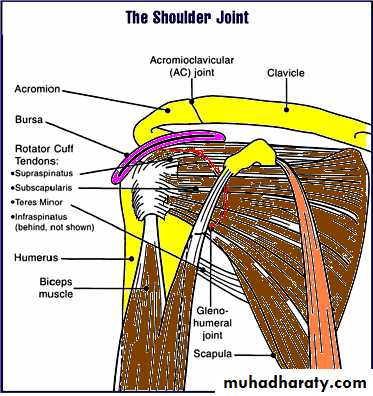
Shoulder jointShoulder joint consist of 5 joints : sterno- clavicular , acromio- clavicular, thoraco- scapular, subacromial , and gleno- humeral (proper shoulder).
The Dynamic “cuff” of shoulder muscles consist of: subscapularis muscle anteriorly, supraspinatus muscle superiorly, infraspinatus muscle postero-superiorly, Teres minor posteriorly, and Long head of biceps intra-articular .
Shoulder deformities :
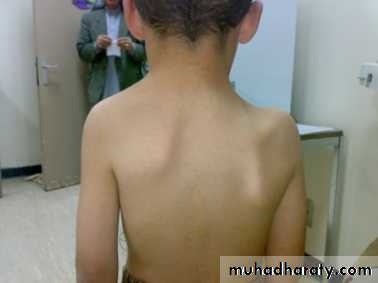
Congenital elevation of the scapula (sprengel’s shoulder): is a result from failure of descend of scapula, painless, associated with other anomalies of spine. Sever type need surgical treatment.Klippel-Feil syndrome : is bilateral failure of scapular descend.
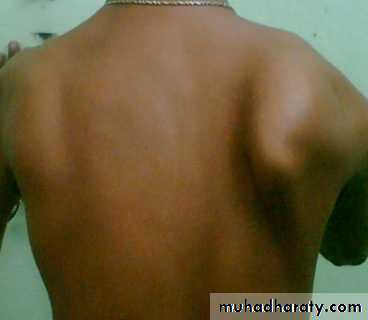
Winged scapula : is a result from injury or disease of serratus anterior or its nerve supply long thoracic nerve.
congenital elevation of left scapula.
Winged scapulaPainful shoulder
The differential diagnosis of painful shoulder is variable, the common of them are:• 1- Rotator cuff disorders like tendinitis , tendon rupture , and frozen
• shoulder.
• 2- Instability of shoulder like dislocation and subluxation.
• 3- Joints disorders like glenohumeral arthritis, and acromioclavicular
• arthritis.
• 4- Bone lesions like infection and tumors.
• 5- Nerve injuries like suprascapular nerve entrapment, brachial plexus
• lesions.
• 6- Referred pain like cervical spondylosis , mediastinal pathology, and
• cardiac ischaemia always should be excluded.
Rotator cuff disorders
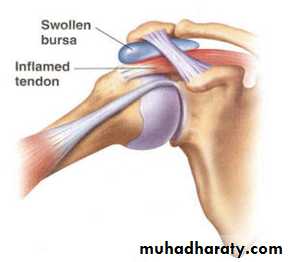
Rotator cuff is conjoint tendon of subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor fused with shoulder capsule. It is main shoulder stabilizer. The arch above cuff is consist of acromion, coracoacromial ligament, and coracoid process. The subacromial bursa separate these two structures. Under the arch and during abduction, the cuff may be irritated or damaged as it glides in confined space.The common primary lesions can give rise to rotator cuff disorders :
Supraspinatus tendinitisCalcified deposit in Supraspinatus tendon
Minor tear of Supraspinatus tendon
Subacromial bursitis
Injury of greater tuberosity
Acute tendinitis ( acute calcification):
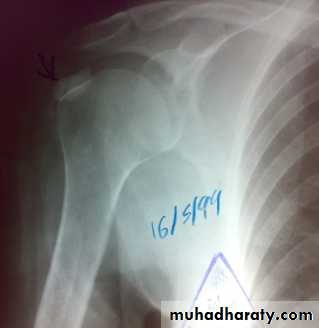
Calcium hydroxyapatite deposits in critical zone of cuff(1 -2 cm.) from insertion.When vascular reaction and swelling occur it become painful. Patient usually adult (age 40-60 years ) develop shoulder pain after overuse, but can be sudden. The pain increased gradually to very sever grade, on lateral aspect of upper arm( over the deltoid muscle), worse at night. The arm held immobile and joint is tender. After few days the pain gradually decreased. The shoulder looks normal. Crepitus or clicking occur during movement. In long standing cases there is wasting of the muscles , and loss of power . Movement specially abduction and external rotation are restricted. X-ray show deposit of calcification above greater tuberosity. MRI may demonstrate detailed lesions.
Calcification in acute tendinitis
Treatment : The treatment started by rest, analgesia and anti-inflammatory drugs, local steroid injection indicated in severe cases . Surgical removal of calcification for persistent condition may needed.
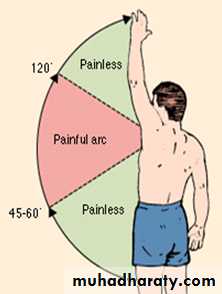
Chronic tendinitis (Painful arc) or( impingement) syndrome :
Overuse and degeneration initiate chronic vascular response. The impingement of rotator cuff against the coracoacromial arch may play part in this process. Painful arc is a clinical syndrome characterized by pain in the shoulder and upper arm during the mid-range of gleno-humeral abduction, with freedom from pain at the extremes of the range.
Patient usually 40-60 years old complain of shoulder pain, increased in night and certain movement. Tenderness felt over shoulder. On abduction pain aggravated as the arm traverse an arc between 60-120 degree. Crepitus may elicited indicate partial tear. X-ray shows calcification with upward sublaxation of humeral head . MRI show cuff changes.
Some patients improve with rest and anti-inflammatory drugs. Steroid injection can used if symptom persist. Surgery used in some cases by decompress the rotator cuff by partial excision of acromion.
Painful arc
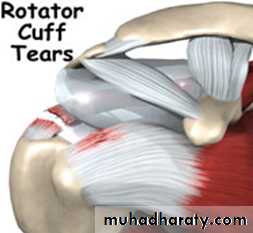
Rotator cuff tear
In minor tears the rotator cuff is still able to function. In a major tear there is no activity of the rotator cuff. Partial tear of cuff are common precipitate by degeneration, cause painful arc syndrome, and few weeks later abduction slowly recovers.Complete tear follow sudden strain or as complication of partial tear. The patient is adult or old age (aged 45-75 ) develop pain in shoulder and inability to lift the arm following strain or fall, while lifting a weight or protecting himself from falling, he 'sprains' his shoulder. Pain is felt immediately, patient unable to lift his arm sideways. The appearance is usually normal.
Rotator cuff tear
To distinguish between partial and complete tear local Xylocaine injected, if active abduction is now possible the tear is partial. In complete tear pain subsided weeks later and active abduction is impossible. Drop arm occur when the arm lowered from sideways position in complete tear.
MRI , US, Arthroscopy confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment in acute phase is conservative. After three weeks, the treatment of complete tear in young and active patients is surgical repair. Patient with partial tear or tear in old and sedentary patients treatment is conservative.