
Lung Diseases 3
Third Year Class
By Dr.Riyadh A. Ali
Department of Pathology
TUCOM
Articles
Articles
• CA lung
• Squamous cell carcinoma
• Adenocarcinoma
• Oat cell (small cell) carcinoma

Squamous Cell
Carcinoma
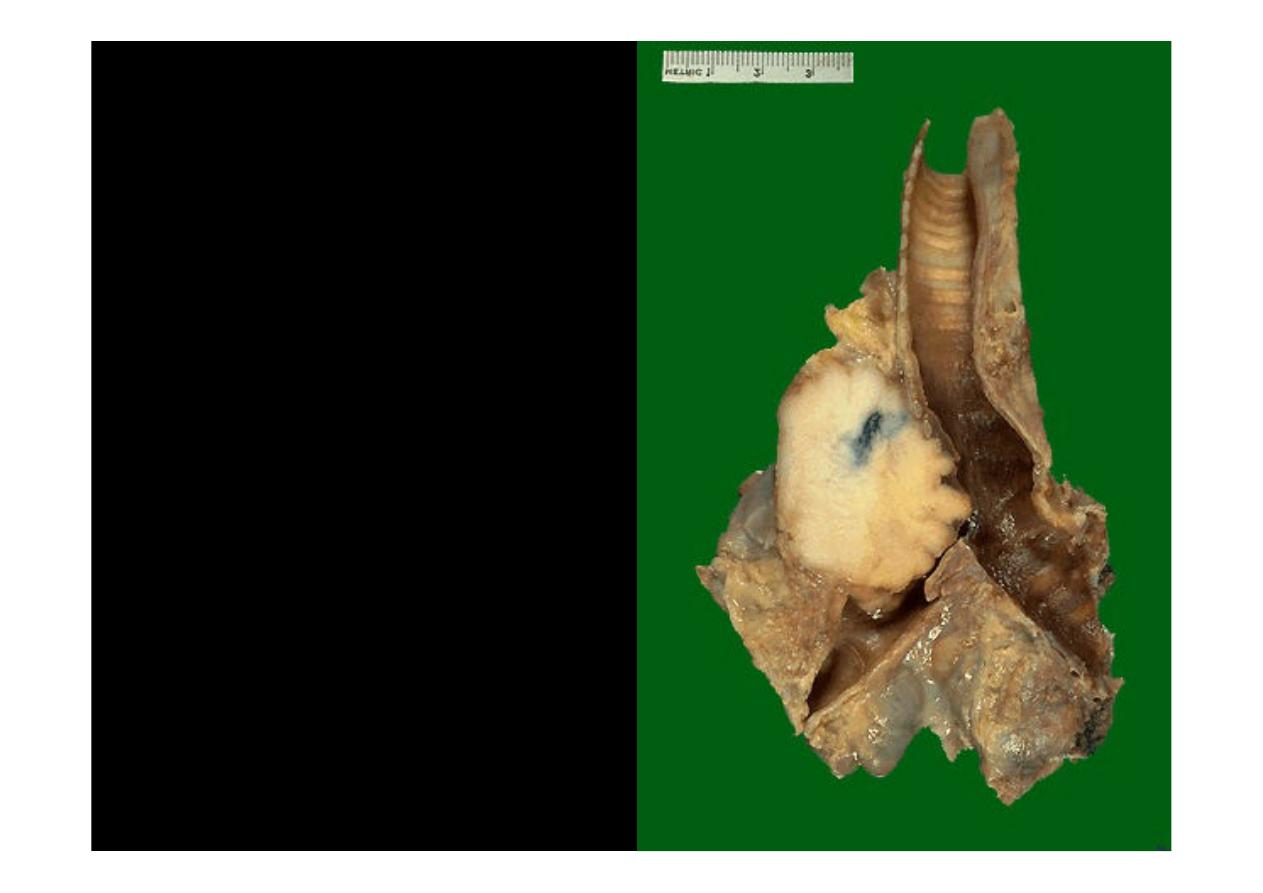
This is a
squamous
cell carcinoma
of the
lung
that
is
arising
centrally in the lung (as
most
squamous
cell
carcinomas do). It is
obstructing
the
right
main
bronchus.
The
neoplasm is very firm
and has a pale white to
tan cut surface.
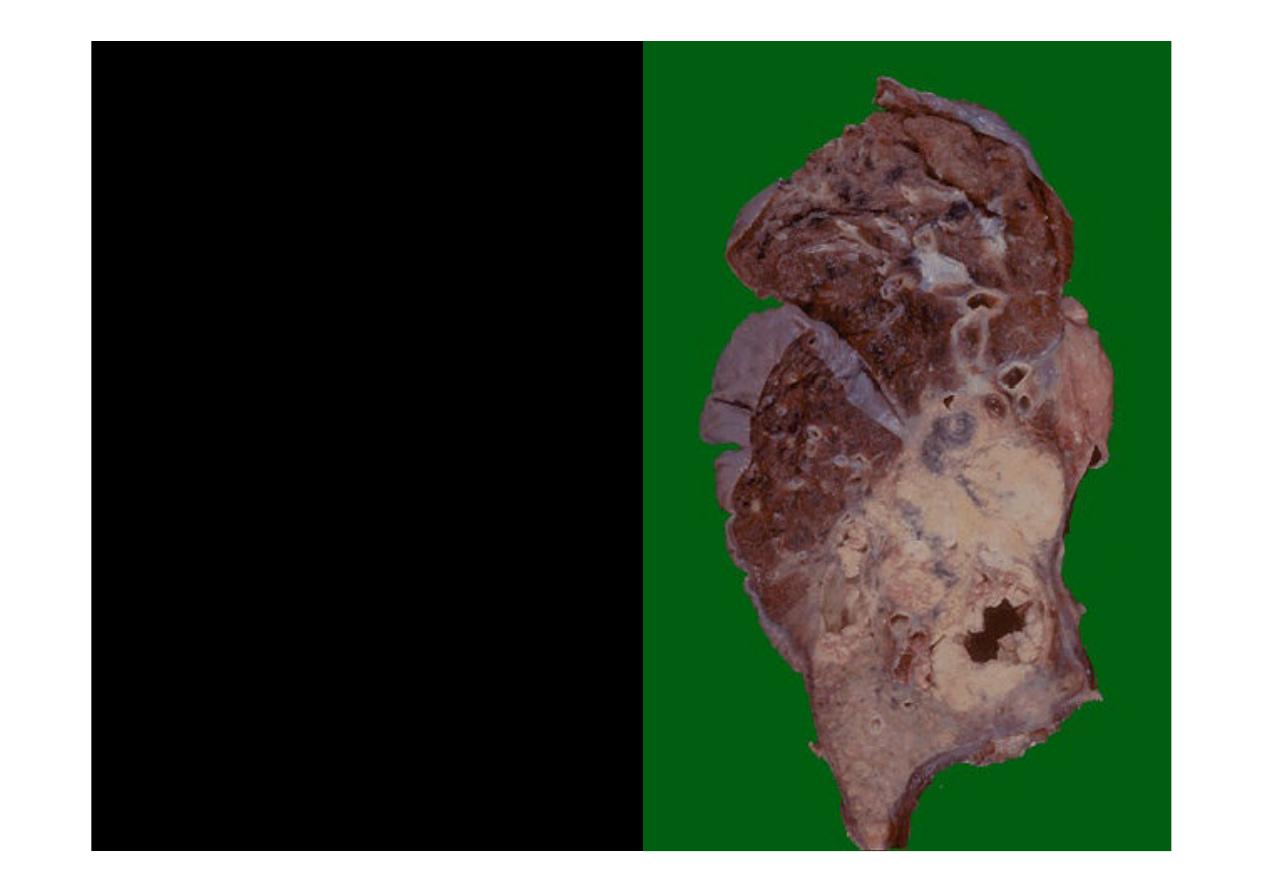
This is a larger
squamous
cell carcinoma
in which a
portion of the tumor
demonstrates central
cavitation, probably
because the tumor
outgrew its blood supply
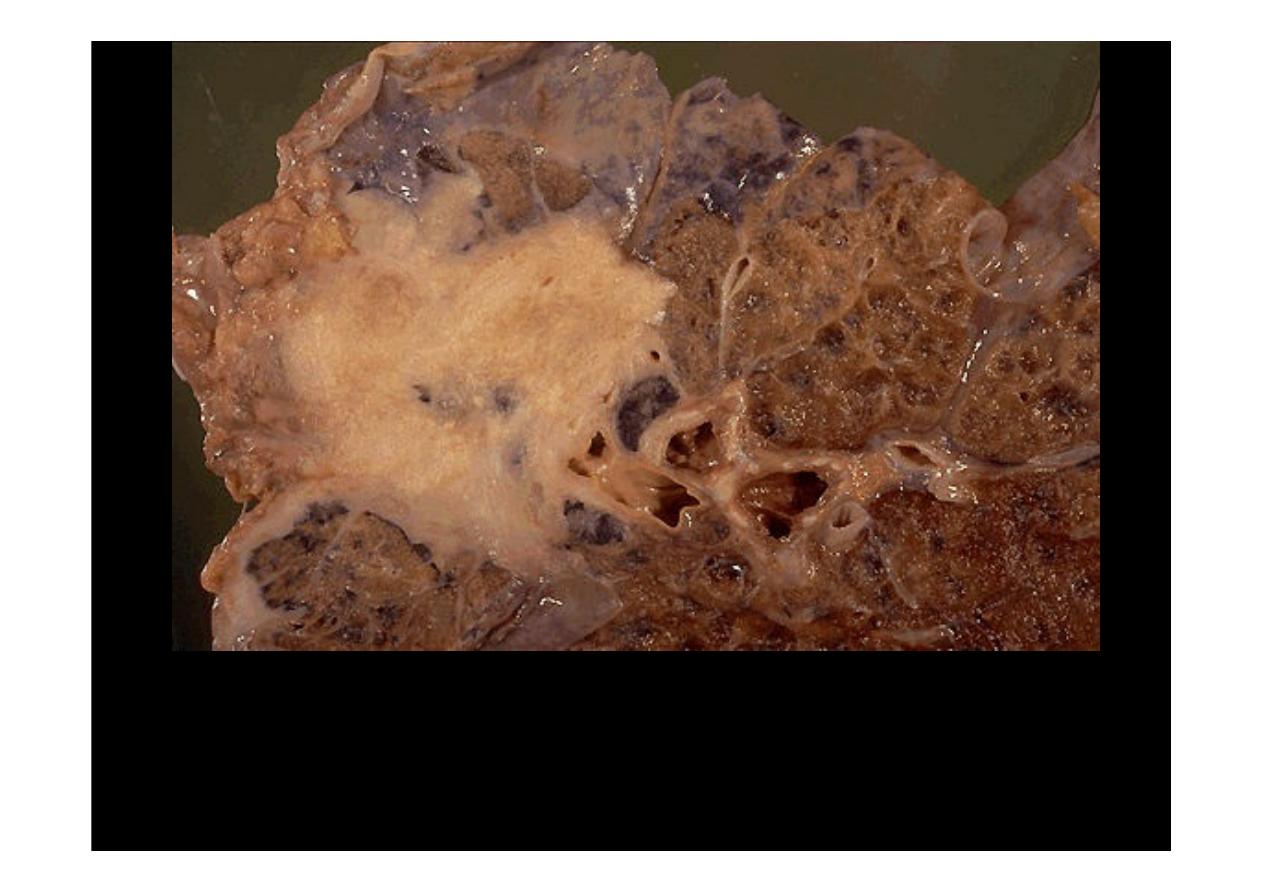
This is a
squamous cell carcinoma
of the lung. It is a bulky mass
that extends into surrounding lung parenchyma.
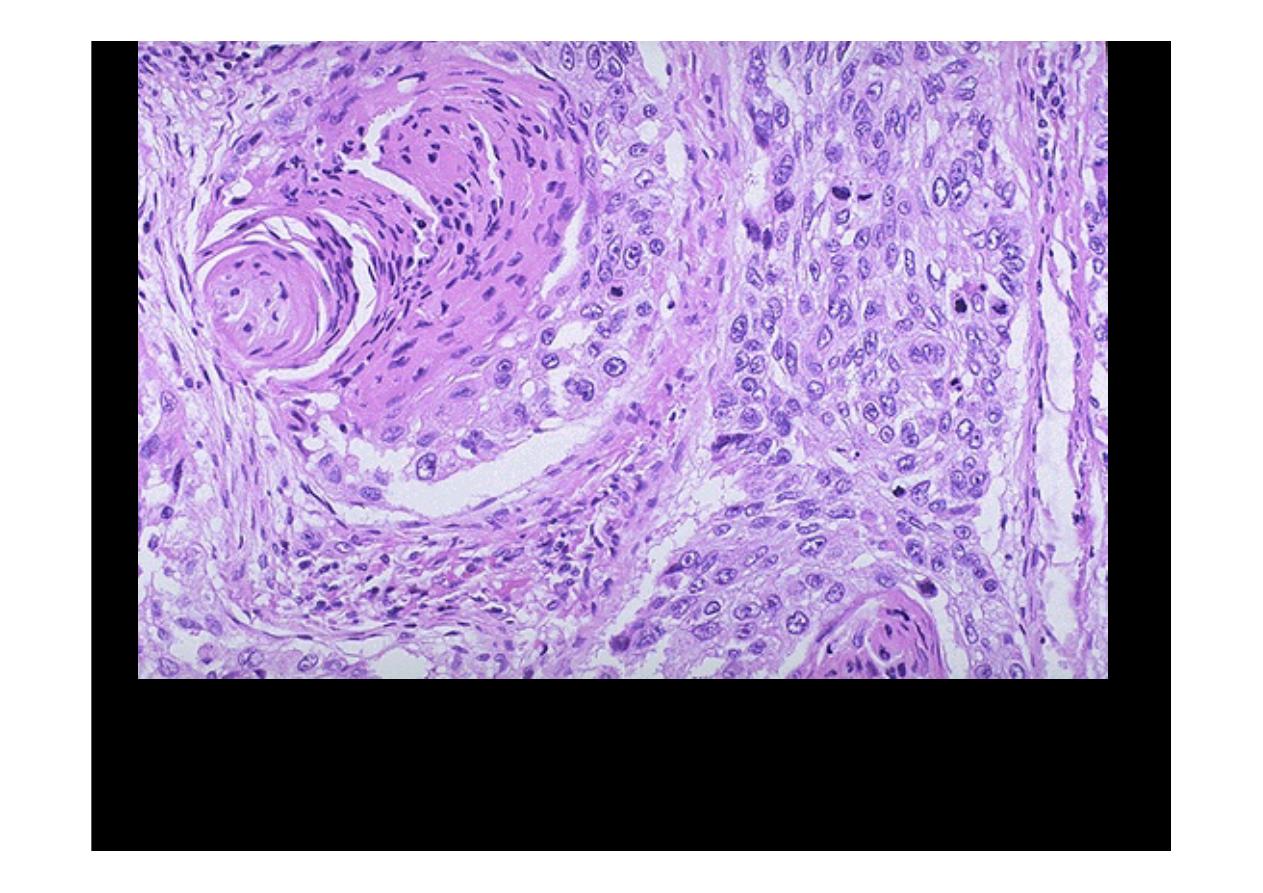
In this
squamous cell carcinoma
at the upper left is a squamous
eddy with a keratin pearl. At the right, the tumor is less differentiated
and several dark mitotic figures are seen.
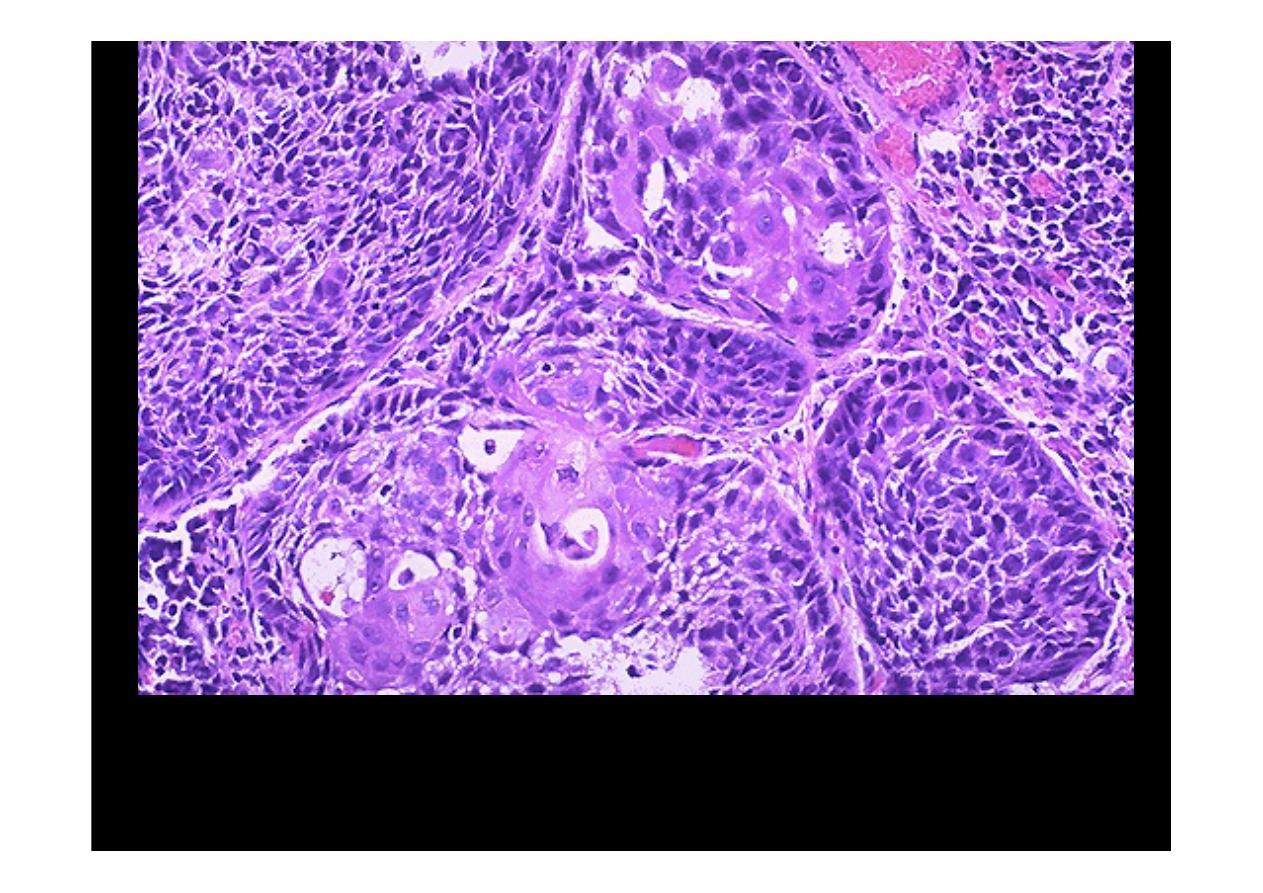
This is the microscopic appearance of
squamous cell carcinoma
with
nests of polygonal cells with pink cytoplasm and distinct cell borders. The
nuclei are hyperchromatic and angular.
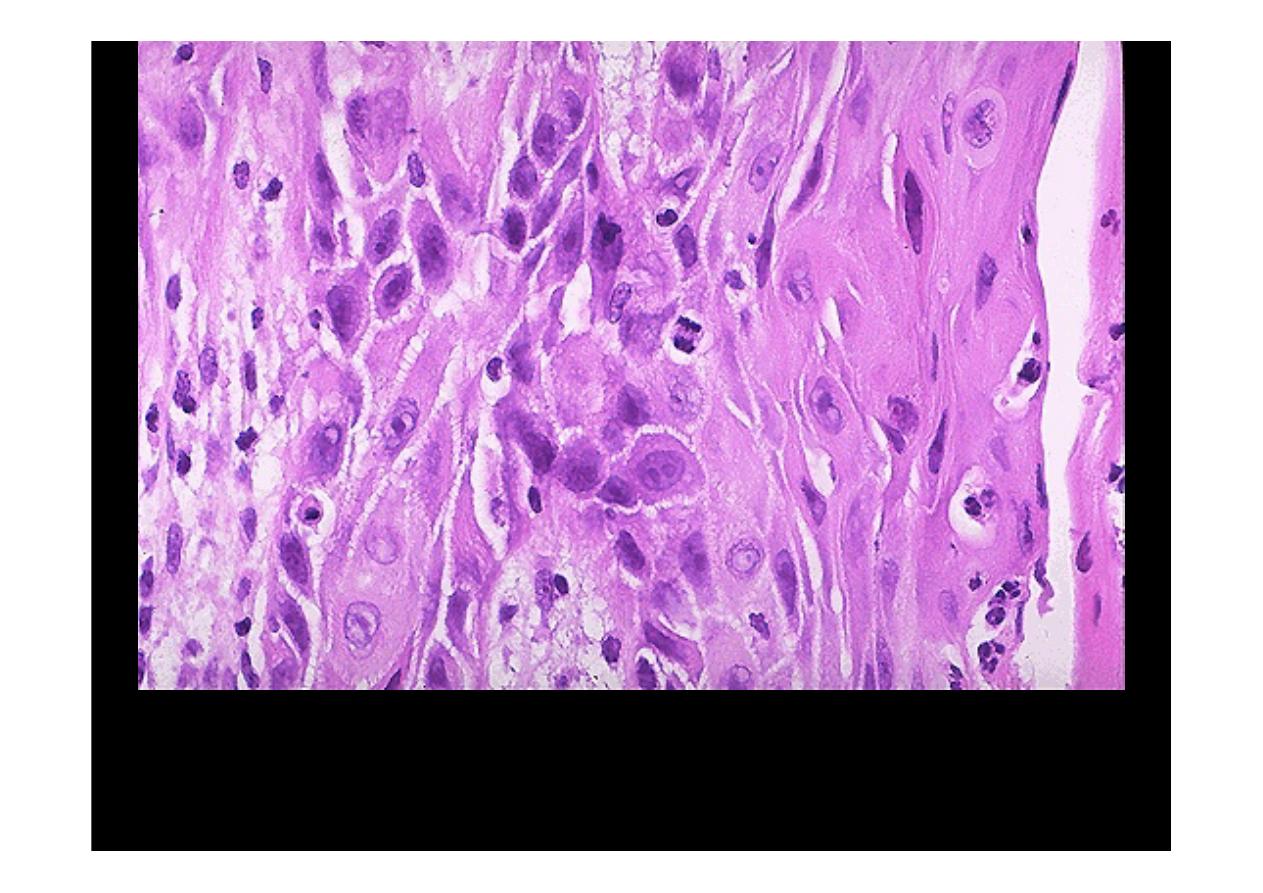
The pink cytoplasm with distinct cell borders and intercellular bridges
characteristic for a
squamous cell carcinoma
are seen here at high
magnification. Obvious mitosis seen and hyperchromatism with
pleomorhism

Adenocarcinoma
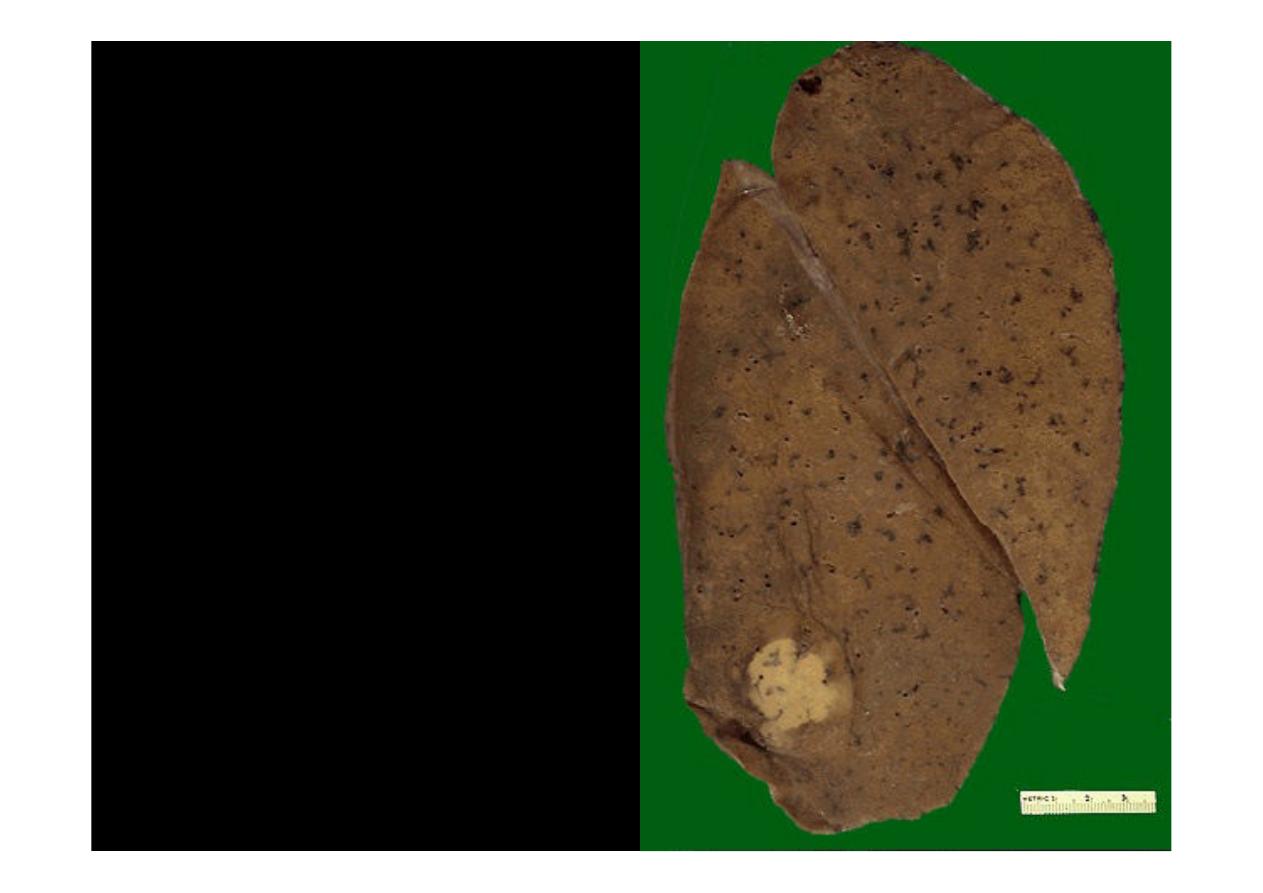

This is a peripheral
adenocarcinoma
of the
lung. Adenocarcinomas
and large cell anaplastic
carcinomas tend to occur
more peripherally in lung.
The solitary white tan color
mass appearance of this
neoplasm suggests that
the tumor is primary rather
than metastatic

Adenocarcinoma
of lung known.
Seen
here
is
the
multifocal
variant that appears grossly (and
on
chest
radiograph)
as
a
pneumonic consolidation. Most of
the upper lobe toward the right
has
a
pale
tan
to
grey
appearance
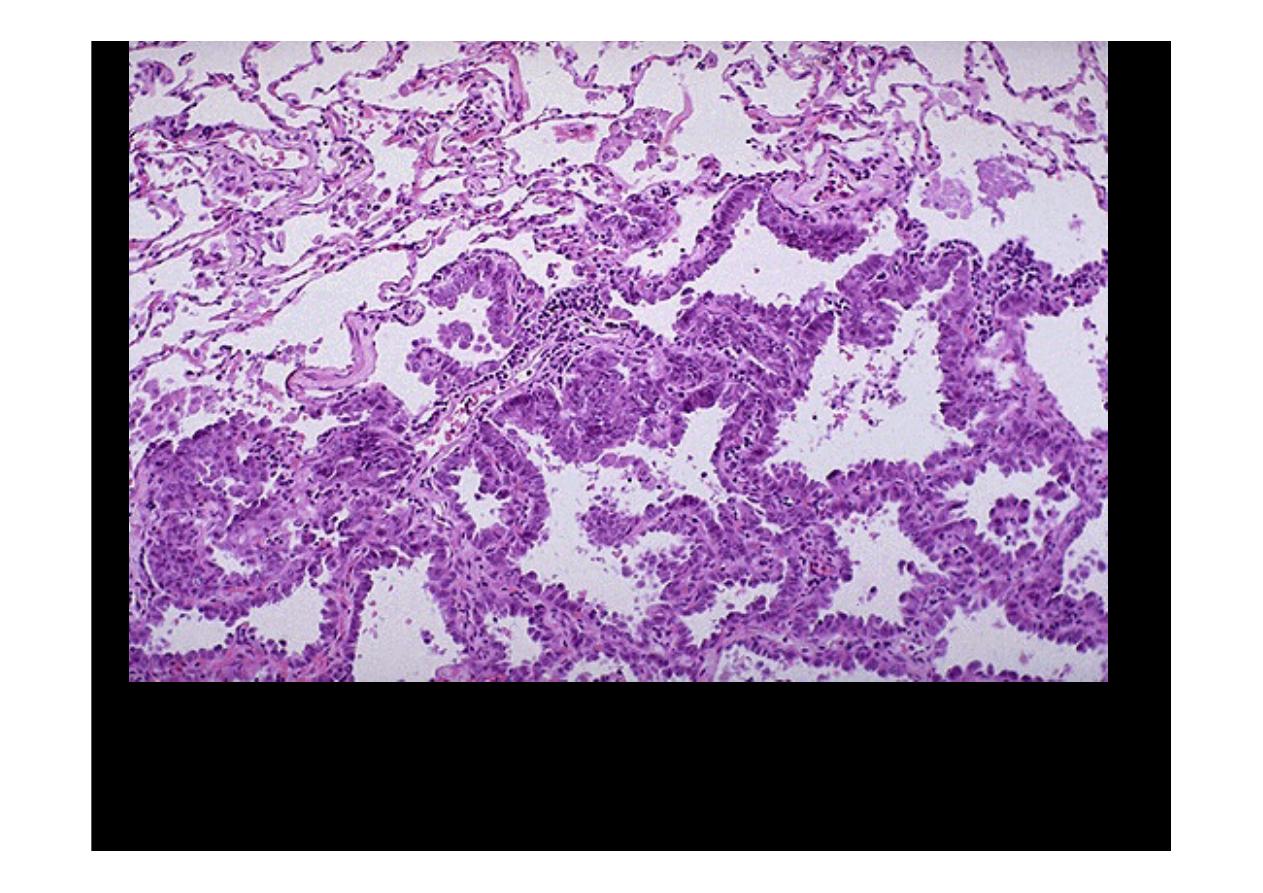
Microscopically, the
adenocarcinoma
is composed of columnar cells that
proliferate along the framework of alveolar septae. The cells are well-
differentiated.
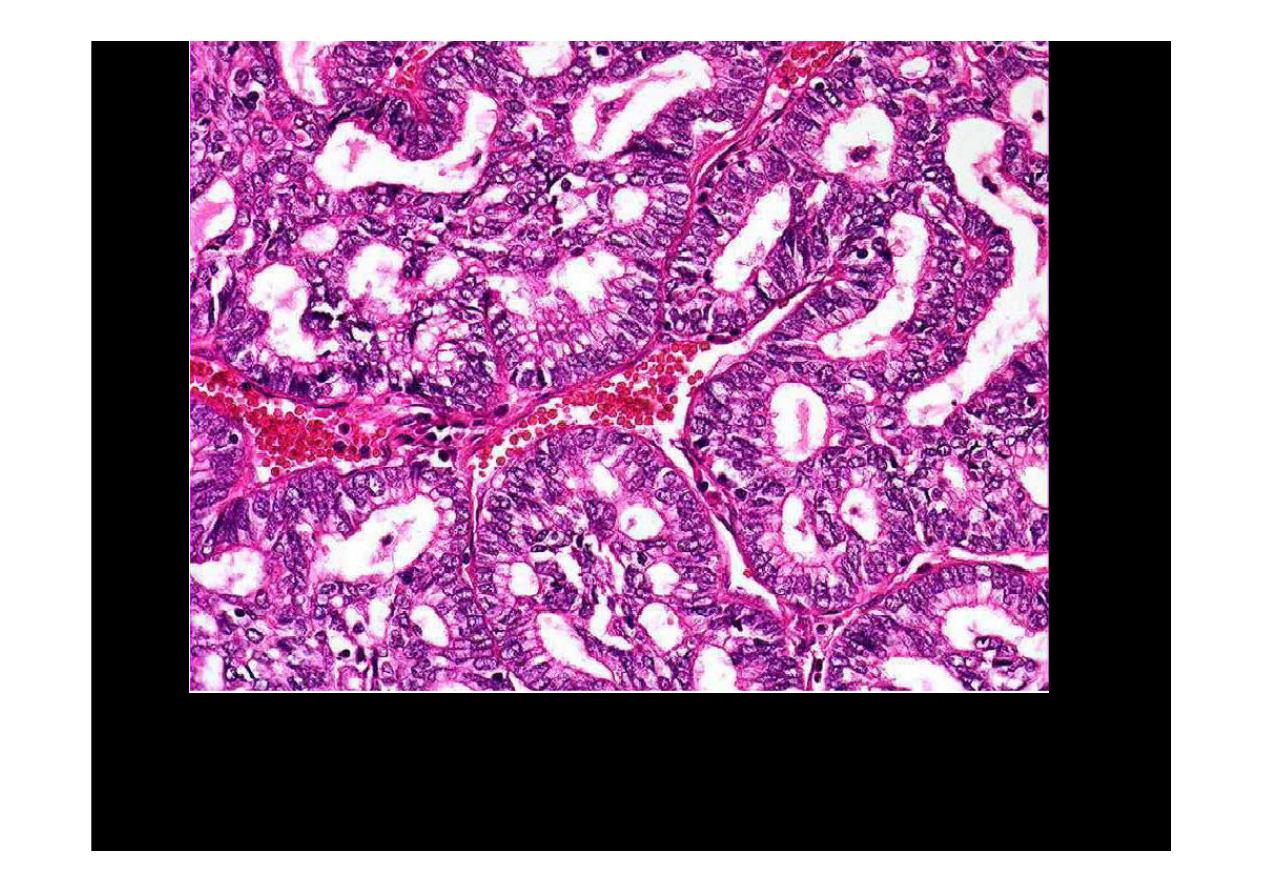
Microscopically showed glandular architecture . Epithelial cells are cuboidal,
columnar in type with goblet type, hyperchromatism and mitosis, moderately
differentiated
adenocarcinoma of lung
Microscopically showed glandular architecture . Epithelial cells are
cuboidal, columnar in type, moderately differentiated
adenocarcinoma of
lung.
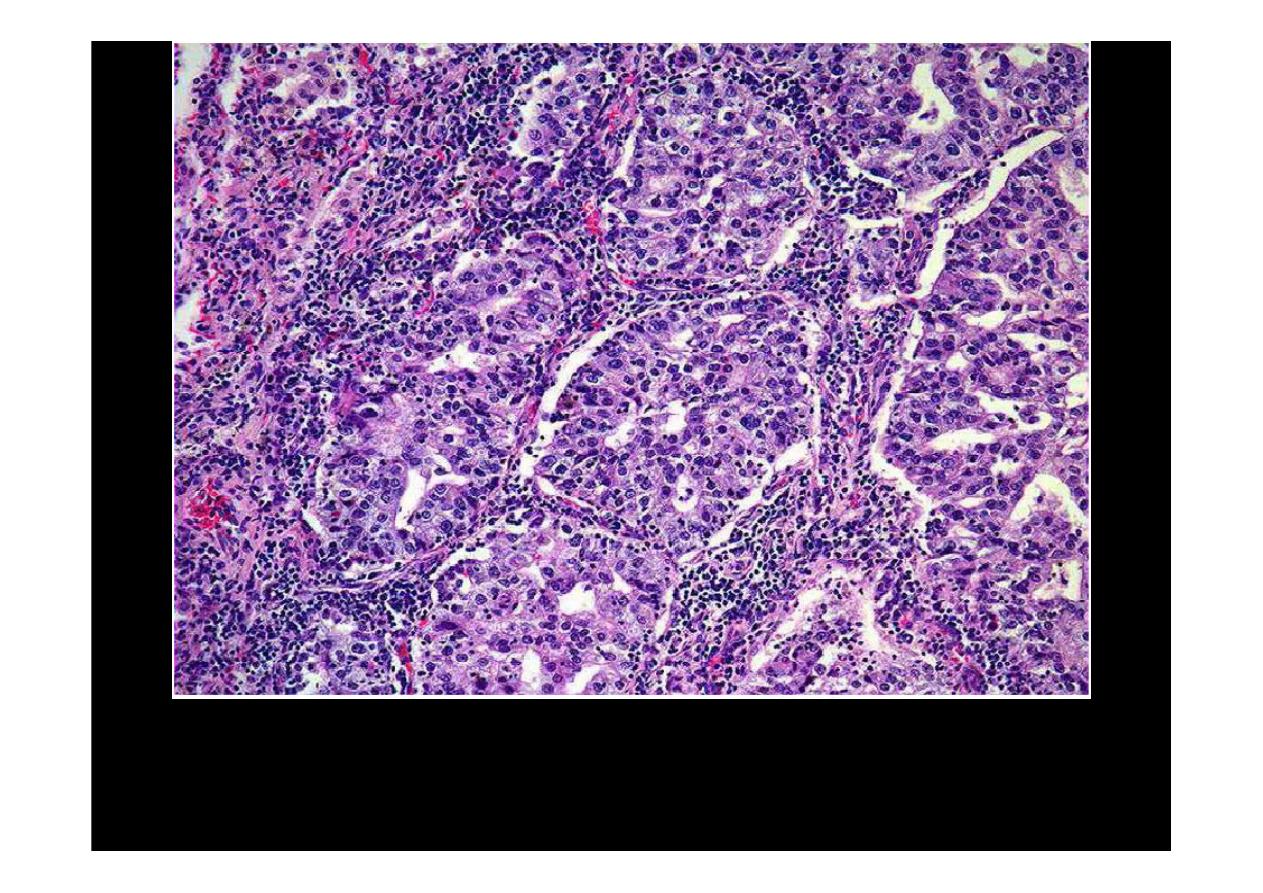
Oat cell (small cell)
carcinoma
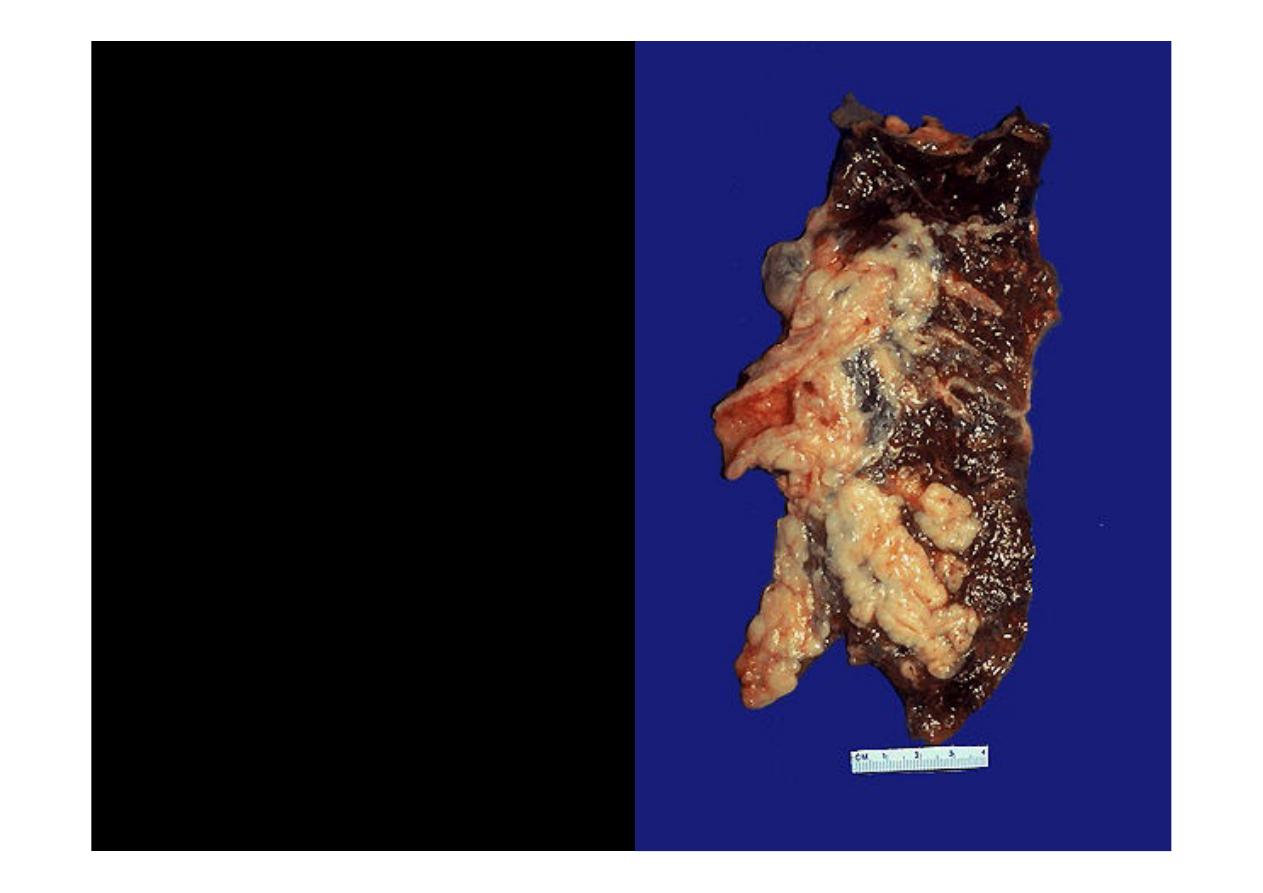
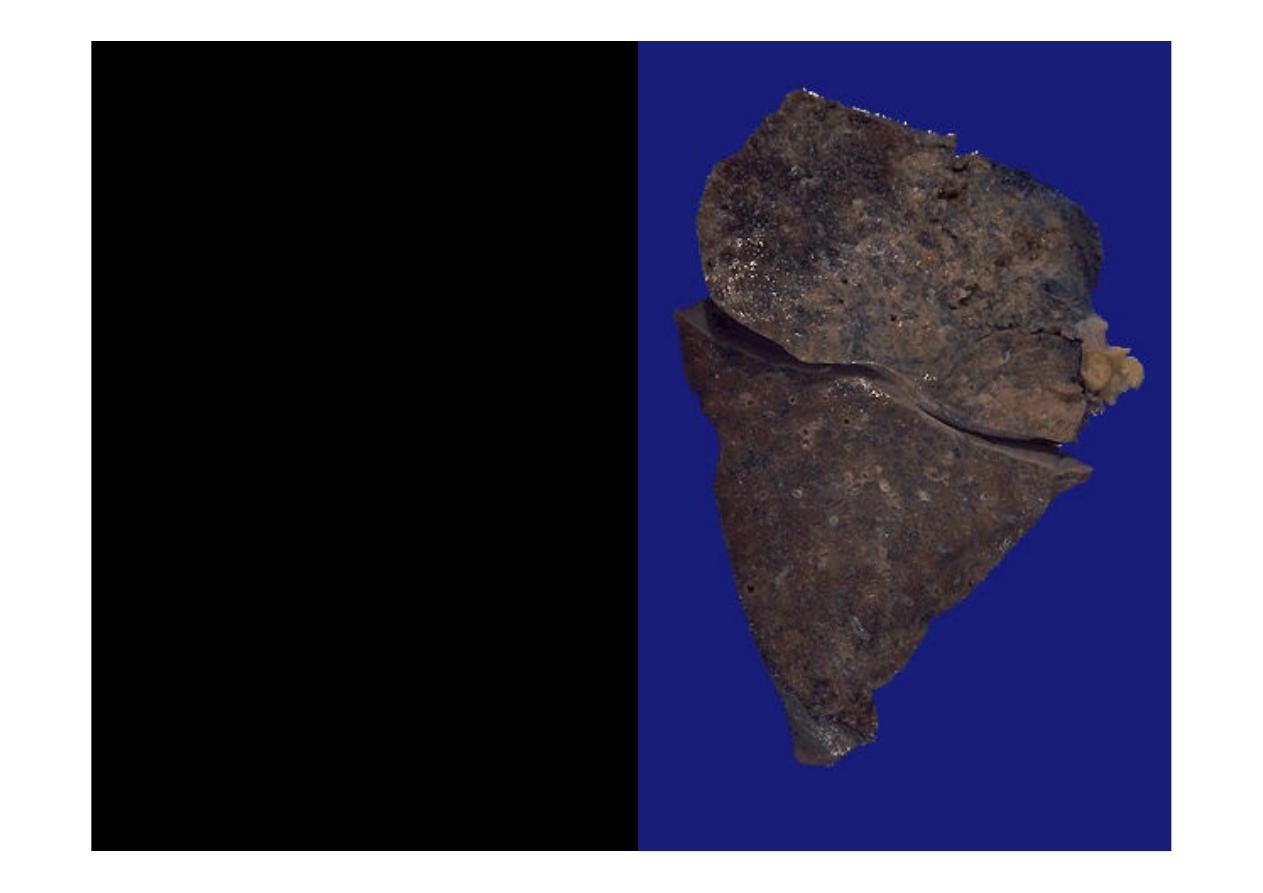
Arising centrally in this lung
and spreading extensively is
a
small cell anaplastic (oat
cell)
carcinoma.
The
cut
surface of this tumor has a
soft, lobulated, white to tan
appearance. The tumor seen
here has caused obstruction
of the main bronchus to left
lung so that the distal lung is
collapsed
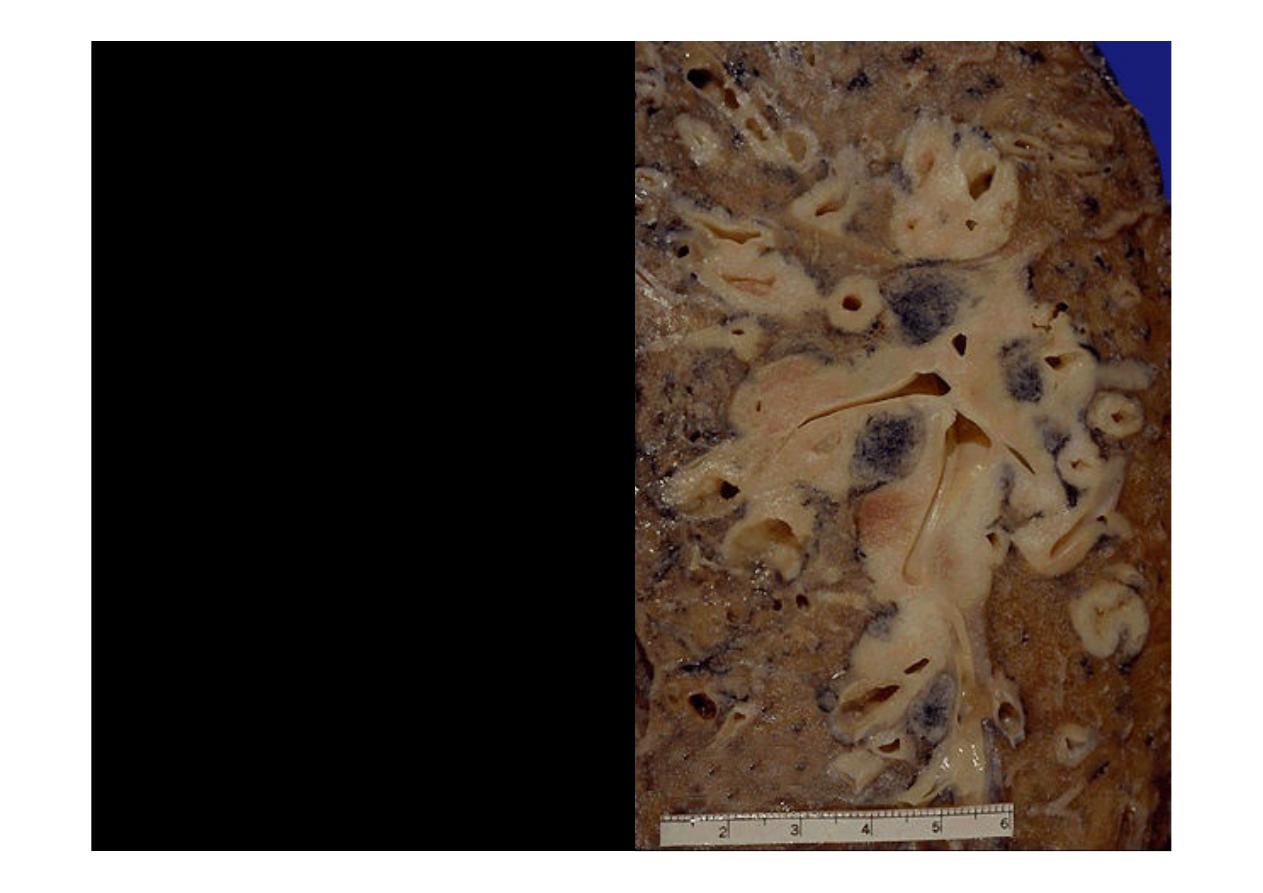
Here is an
oat cell
carcinoma
which
is
spreading
along
the
bronchi. The speckled
black rounded areas
represent hilar lymph
nodes with metastatic
carcinoma
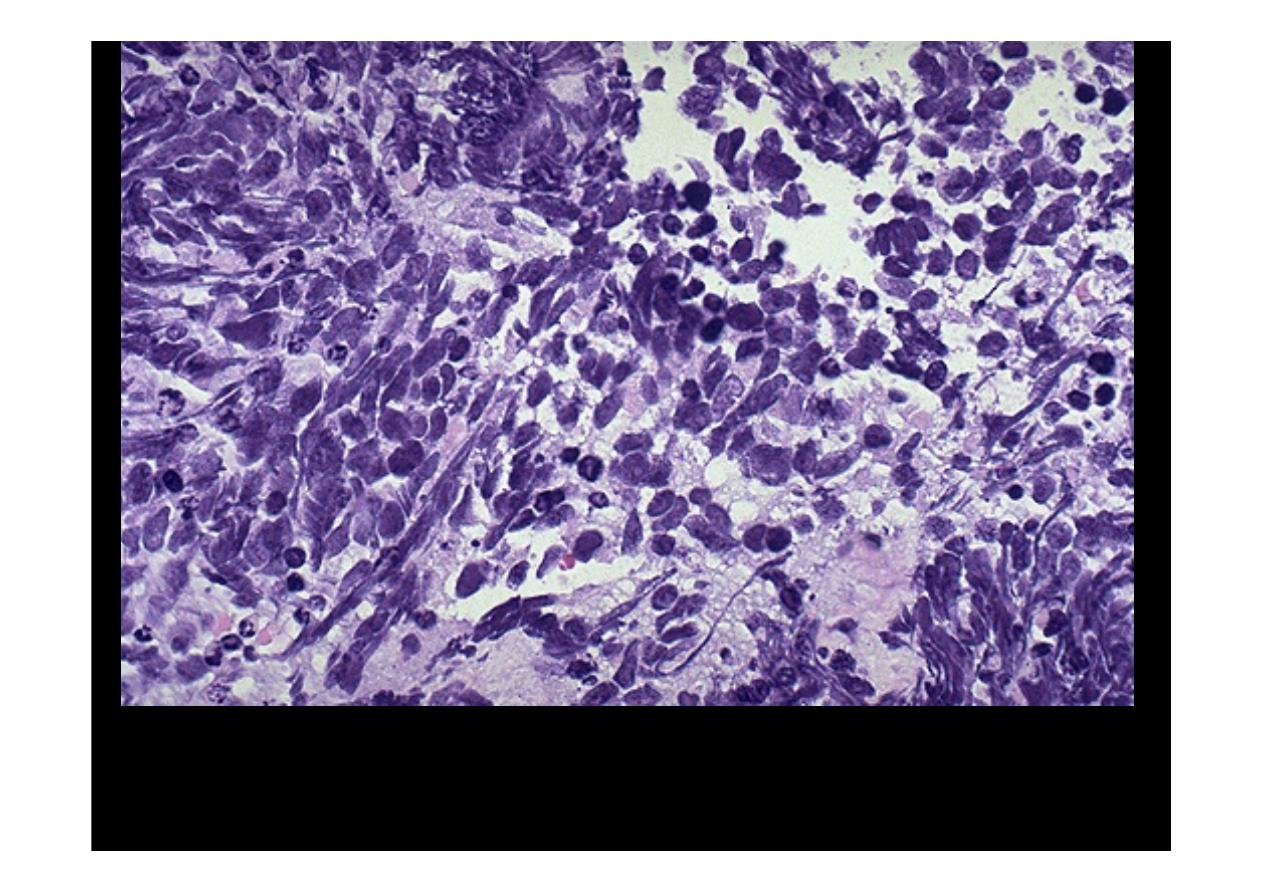
This is the microscopic pattern of a
small cell anaplastic (oat cell) carcinoma
in which small dark blue cells with minimal cytoplasm are packed together in
sheets
