
Lung Diseases 1
Third Year Class
By Dr.Riyadh A. Ali
Department of Pathology
TUCOM

ARTICLES
NORMAL LUNG
EMPHYSEMA
CHRONIC BRONCHITIS
BRONCHIECTASIS

NORMAL LUNG
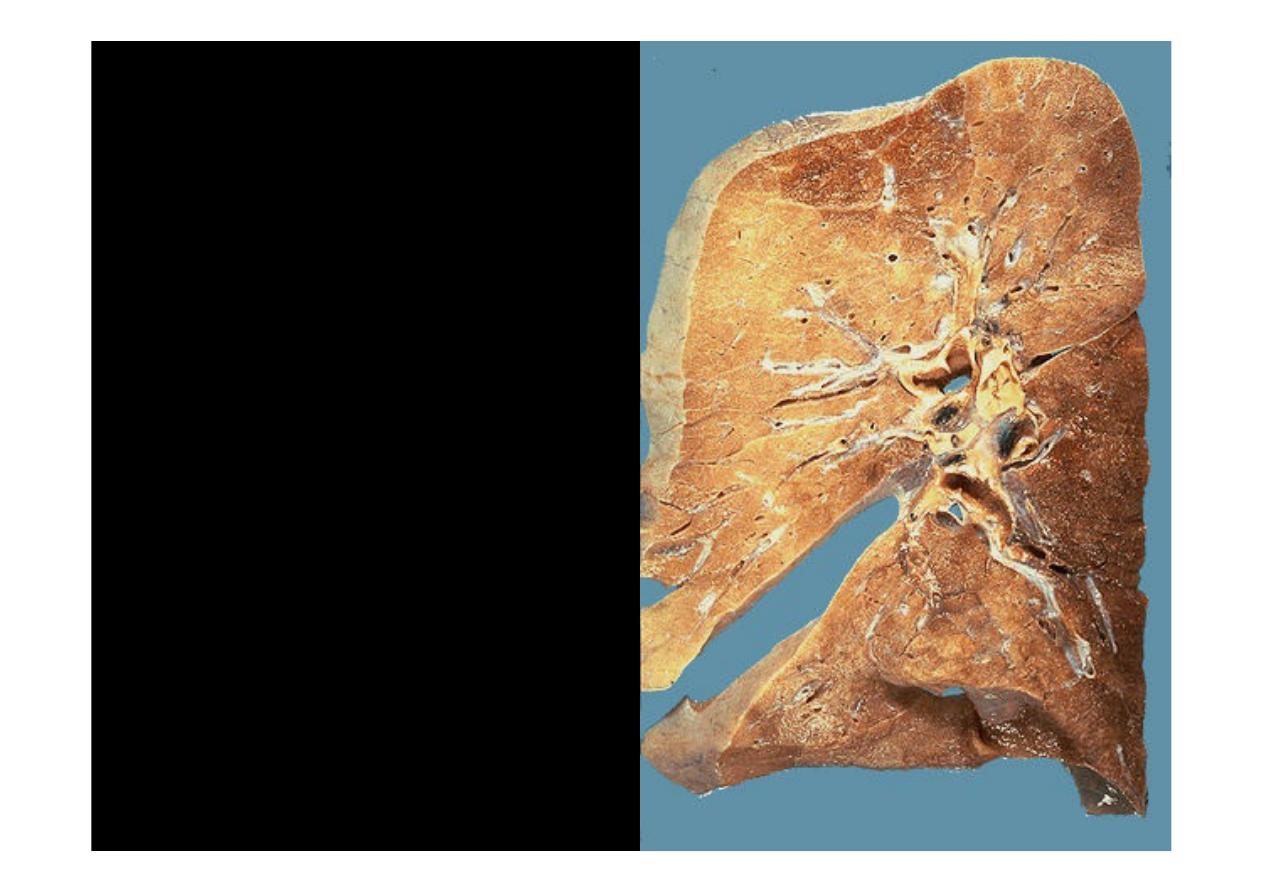
This is a cross-section of
normal lung
(with only
minimal posterior congestion at
the lower right). The hilar
lymph nodes are small and
have enough anthracotic
pigment (from dusts in the air
breathed in, scavenged by
pulmonary macrophages,
transferred to lymphatics, and
collected in lymph nodes) to
make them appear greyish-
black.
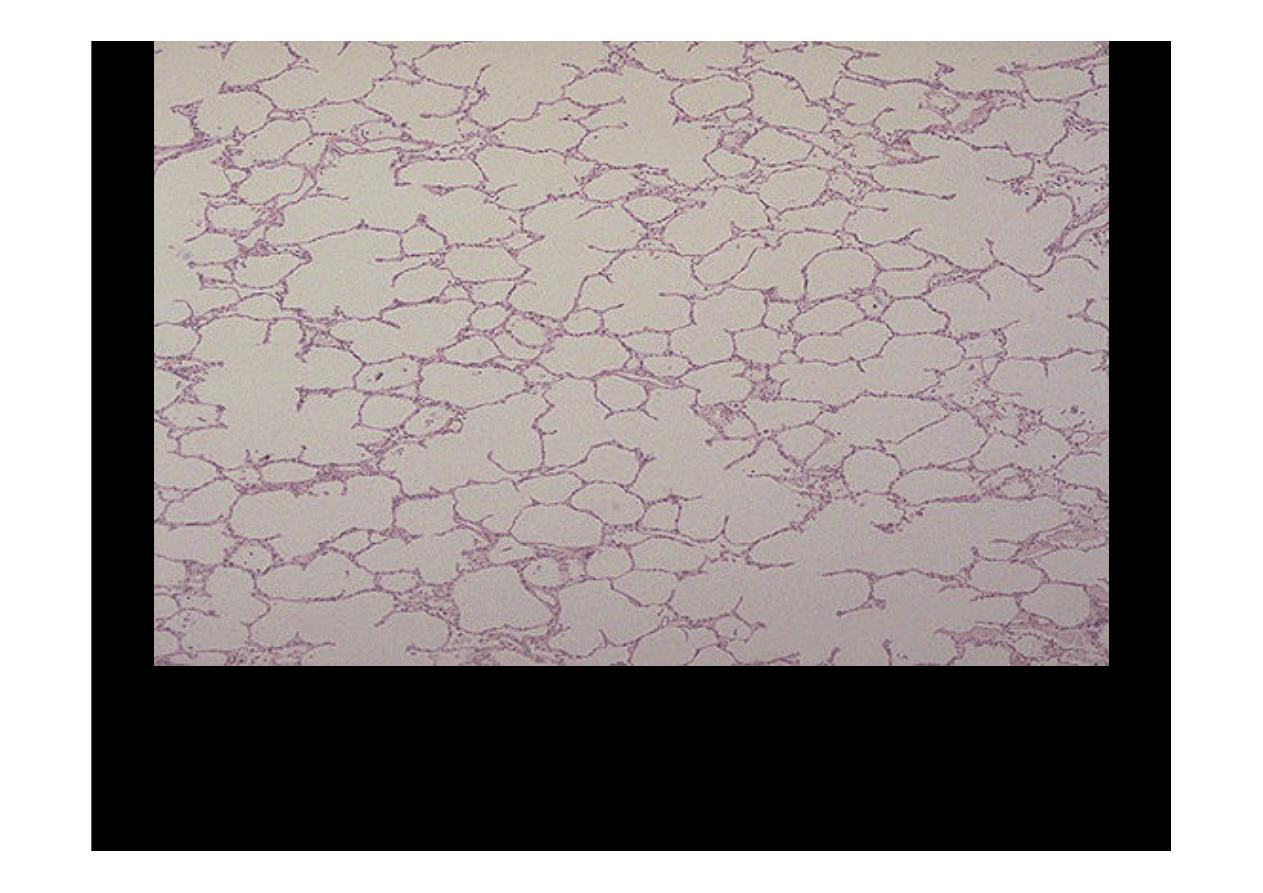
This is
normal lung microscopically
. The alveolar walls are thin
and delicate. The alveoli are well-aerated and contain only an
occasional pulmonary macrophage (type II pneumonocyte.(

EMPHYSEMA
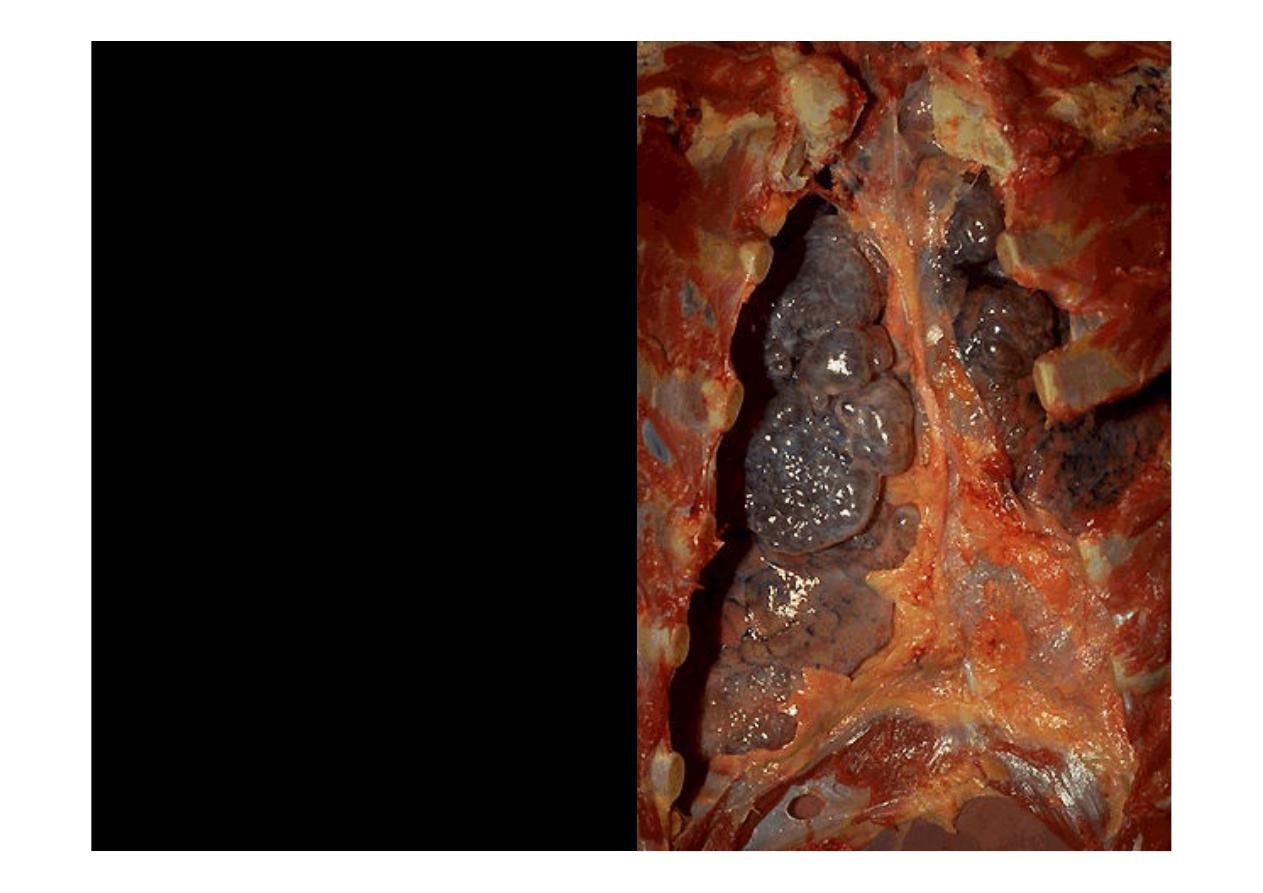
Numerous large bullae
apparent on the surface of the
lungs in a patient dying with
emphysema
.Bullae are large
dilated airspaces that bulge
out from beneath the
pleura.Emphysema is
characterized by a loss of lung
parenchyma by destruction of
alveoli so that there is
permanent dilation of
airspaces
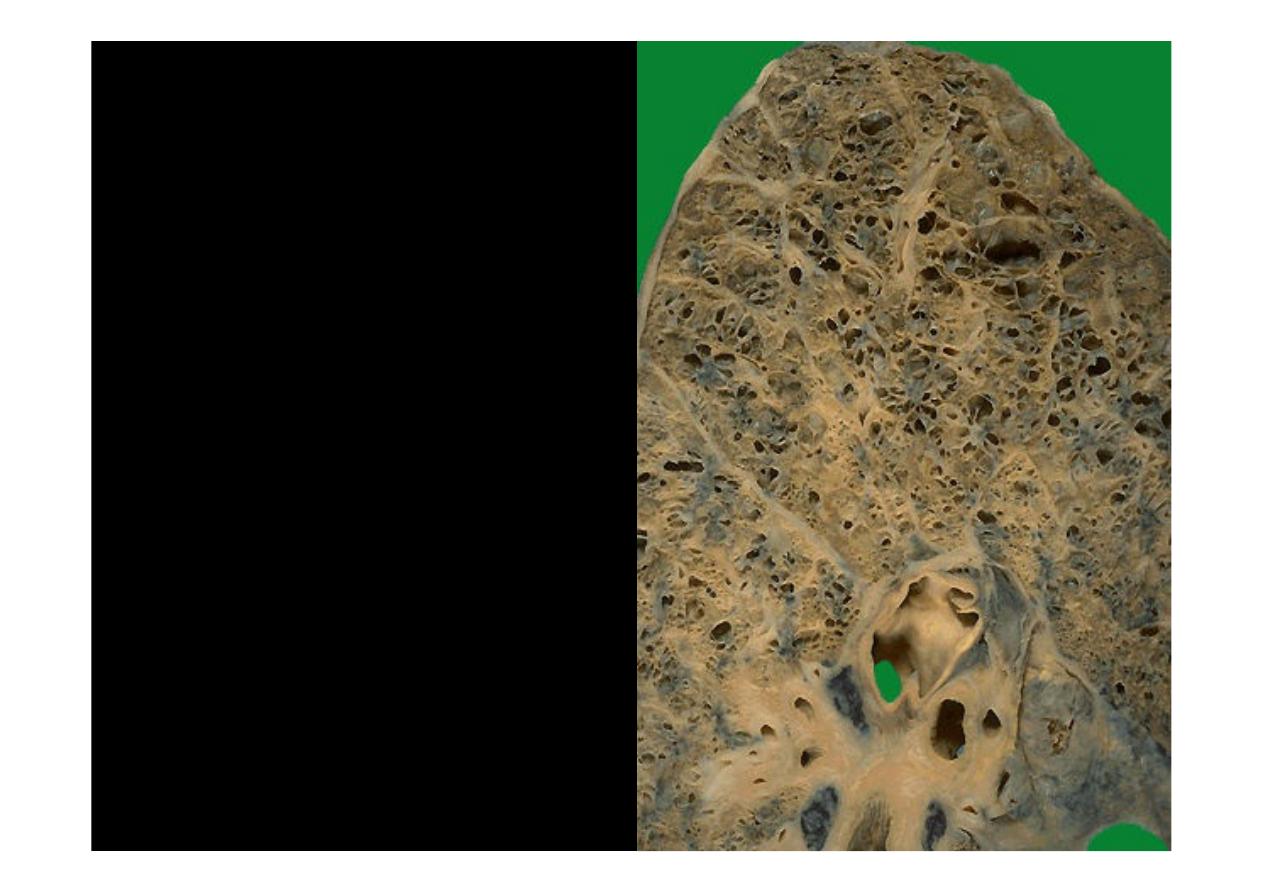

On cut section of the lung,
the dilated airspaces with
emphysema
are seen.
Although there tends to
be some scarring can bee
seen over.
Centrilobular
emphysema
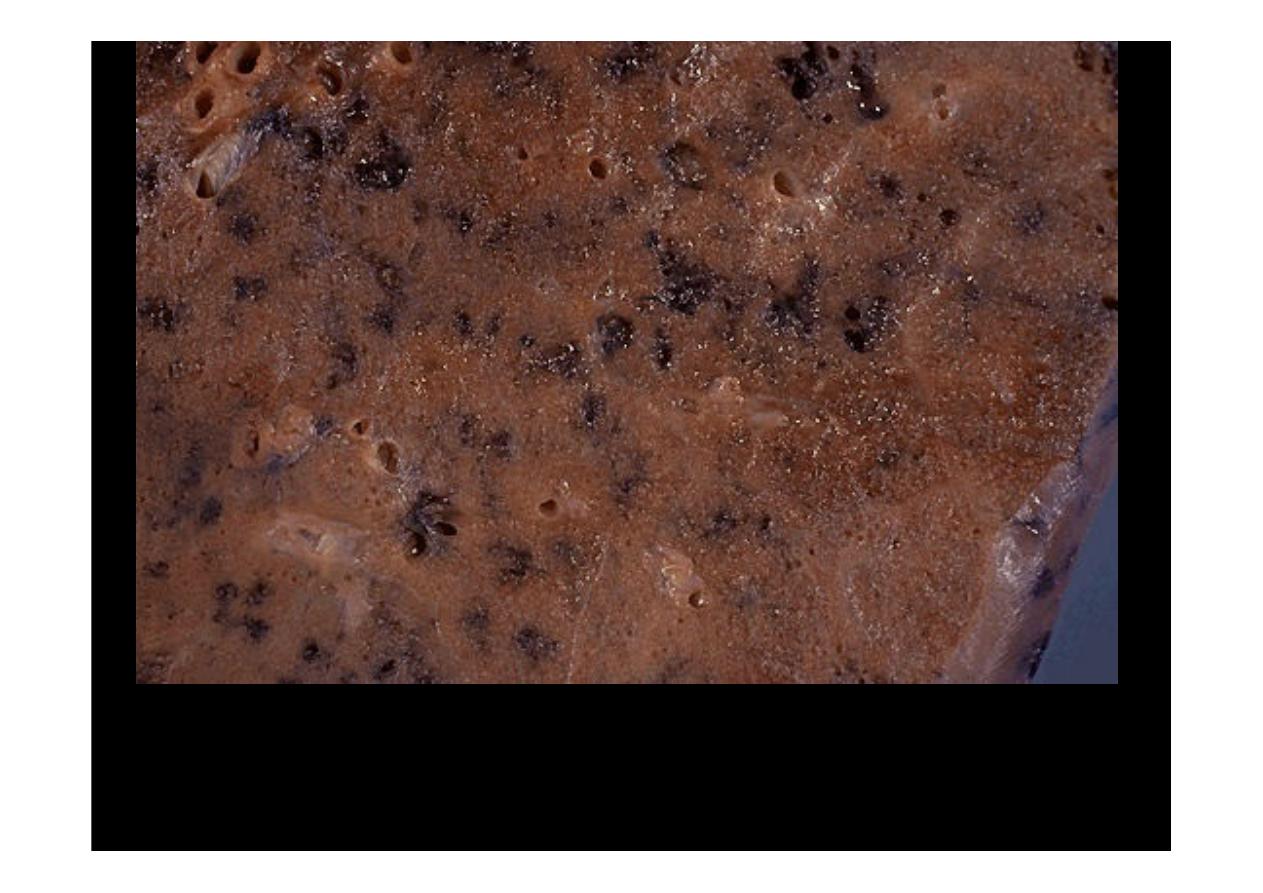

This is a more subtle appearance for
centrilobular emphysema
in which
there are "dirty holes" that appear focally where the central portions of lung
acini have lost lung parenchyma while collecting anthracotic pigment at the
same time. This pattern is typical for smokers.
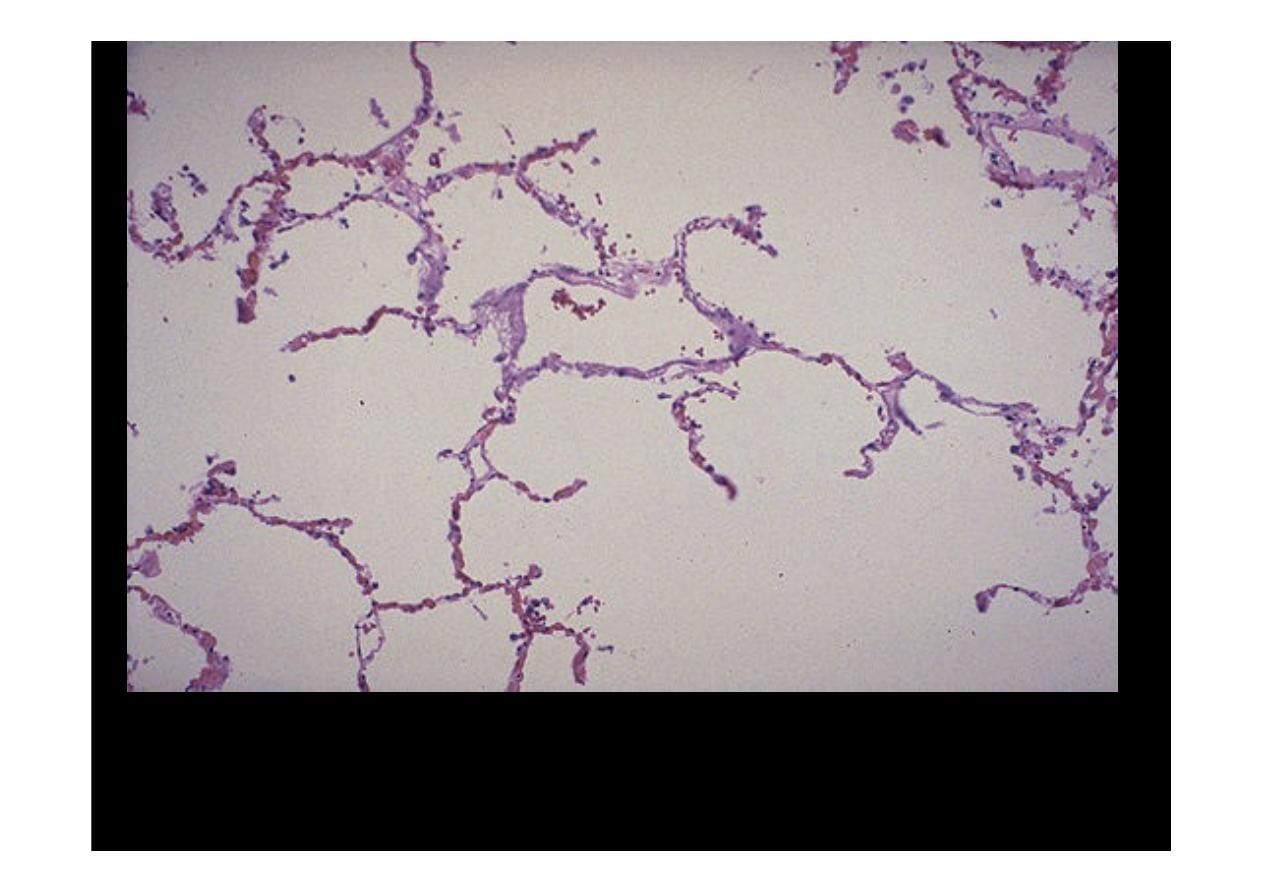
Microscopically at high magnification, the loss of alveolar walls with
emphysema
is demonstrated. Remaining airspaces are dilated.
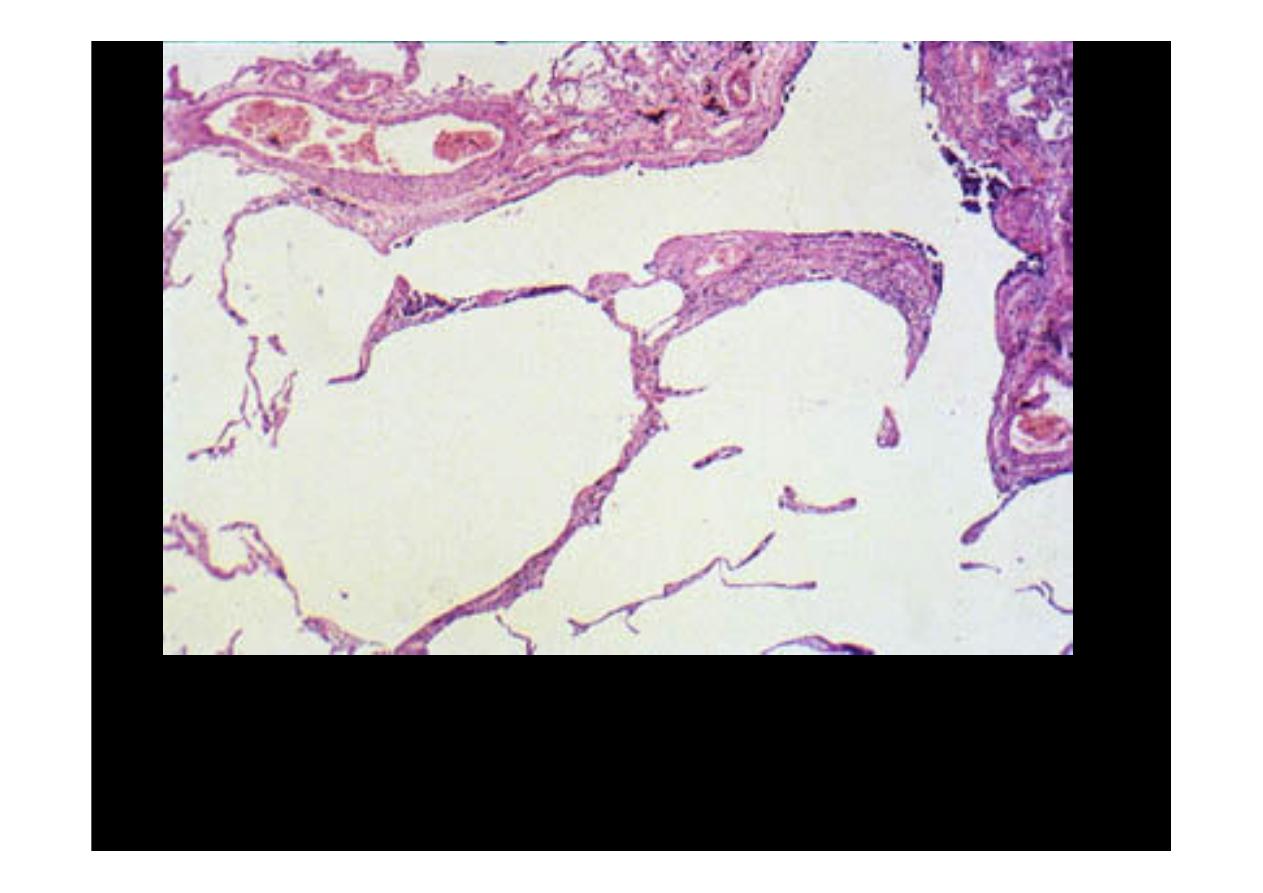
A higher magnification shows very clearly the permanent enlargement of
the airspace, accompanied by destruction of the septa.
emphysema
.

CHRONIC BRONCHITIS
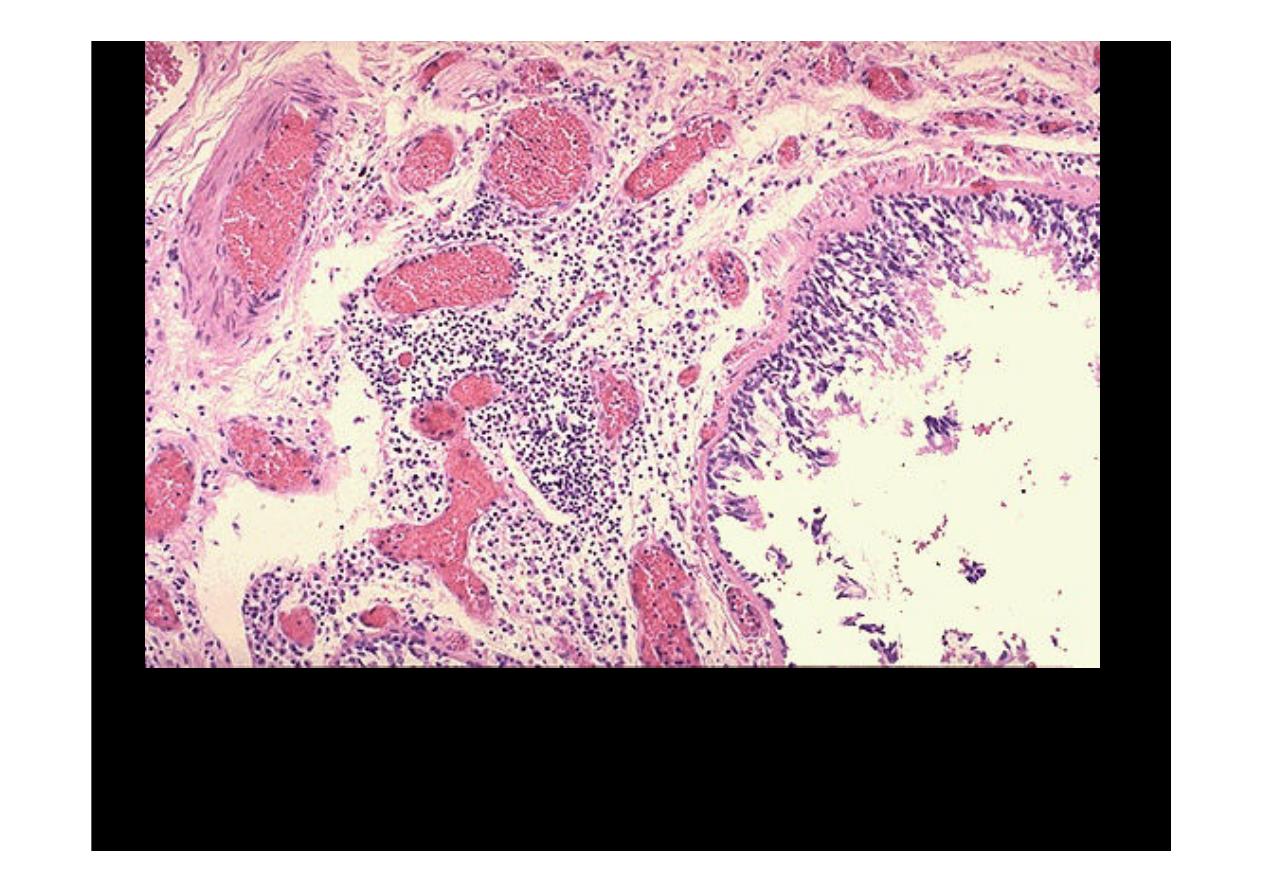
This photomicrograph demonstrates a bronchus with increased numbers
of chronic inflammatory cells in the submucosa.
CHRONIC
BRONCHITIS
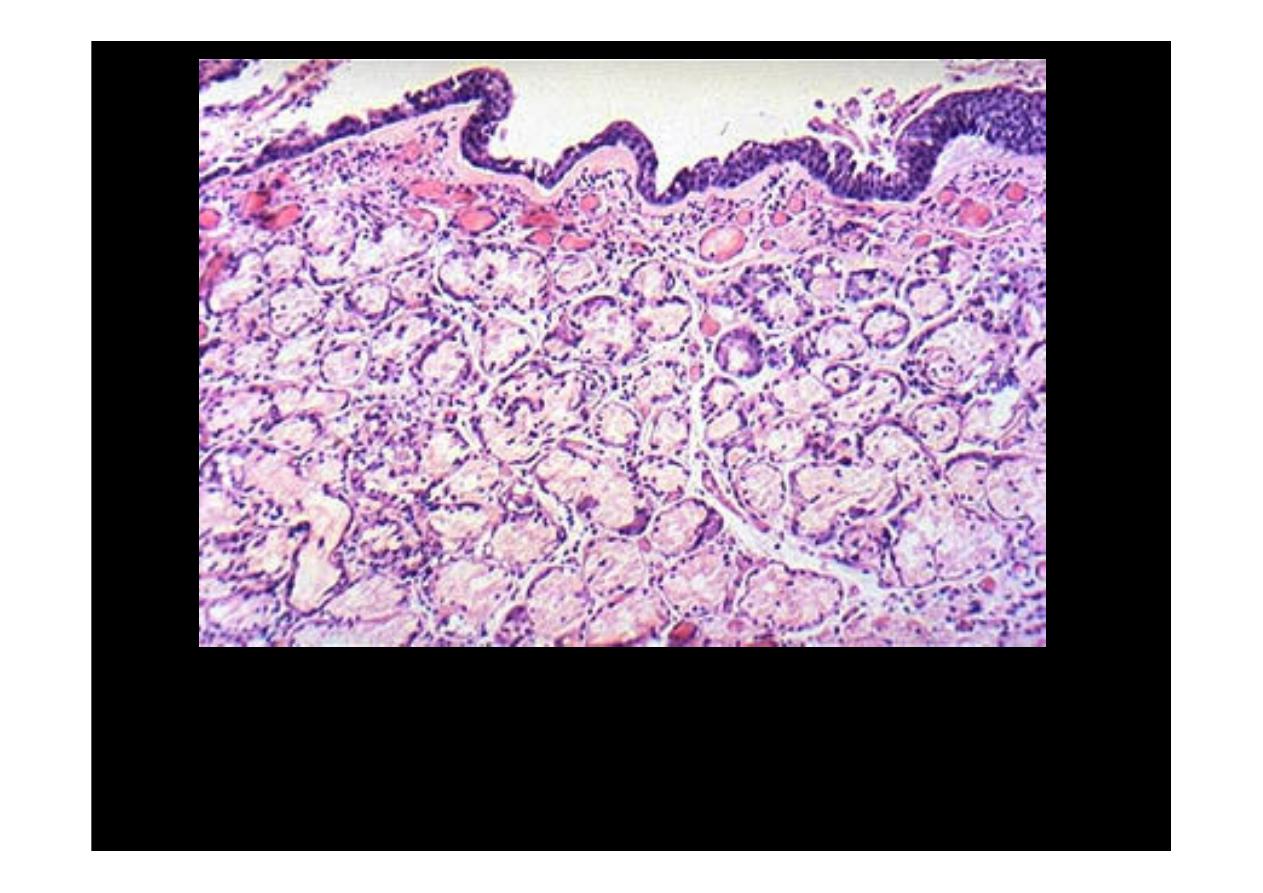
The bronchial wall has mucous gland hyperplasia, characteristic of
patients who have
chronic bronchitis.

BRONCHIECTASIS
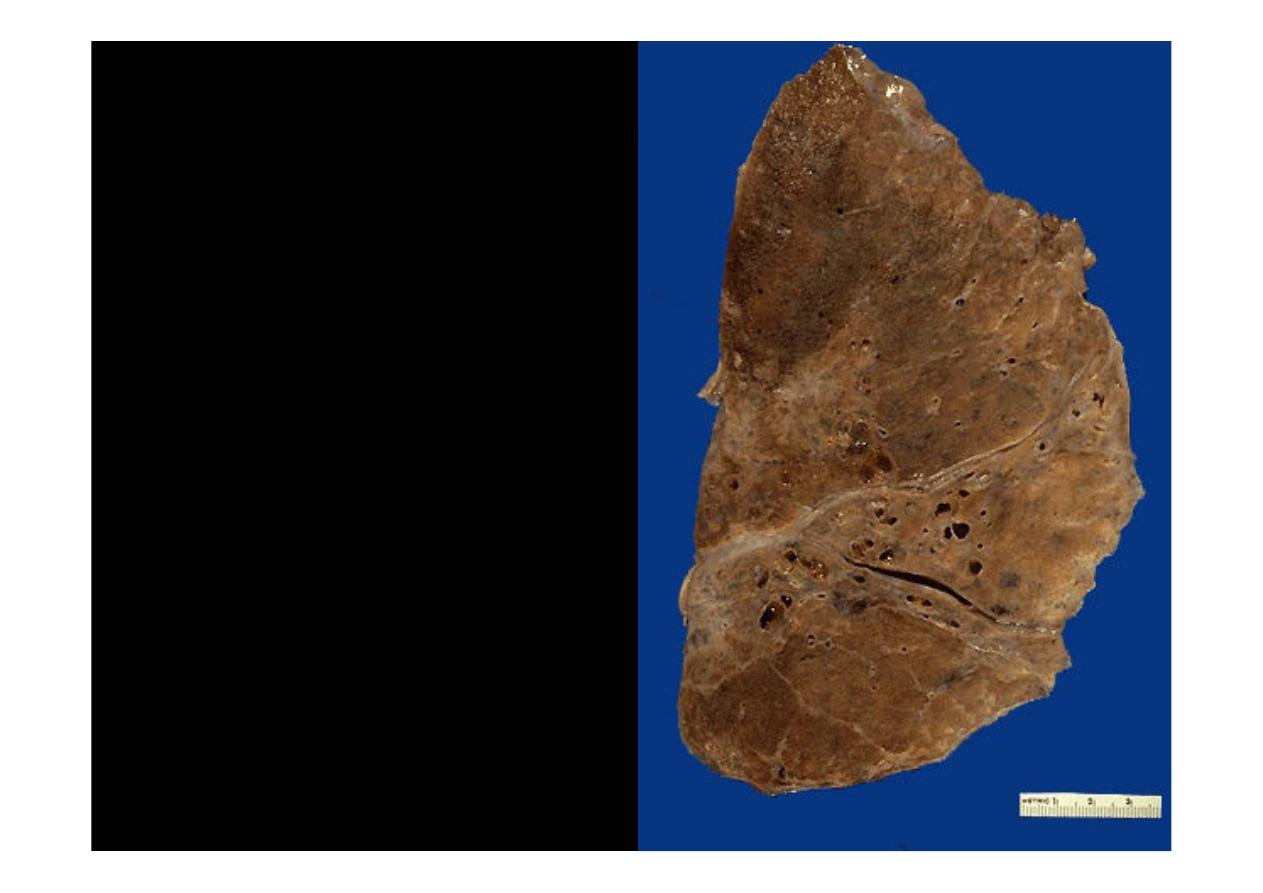
There is permanent
dilation in bronchi,
the dilated bronchi
are present, in the
mid lower portion of
the lung.
Bronchiectasis
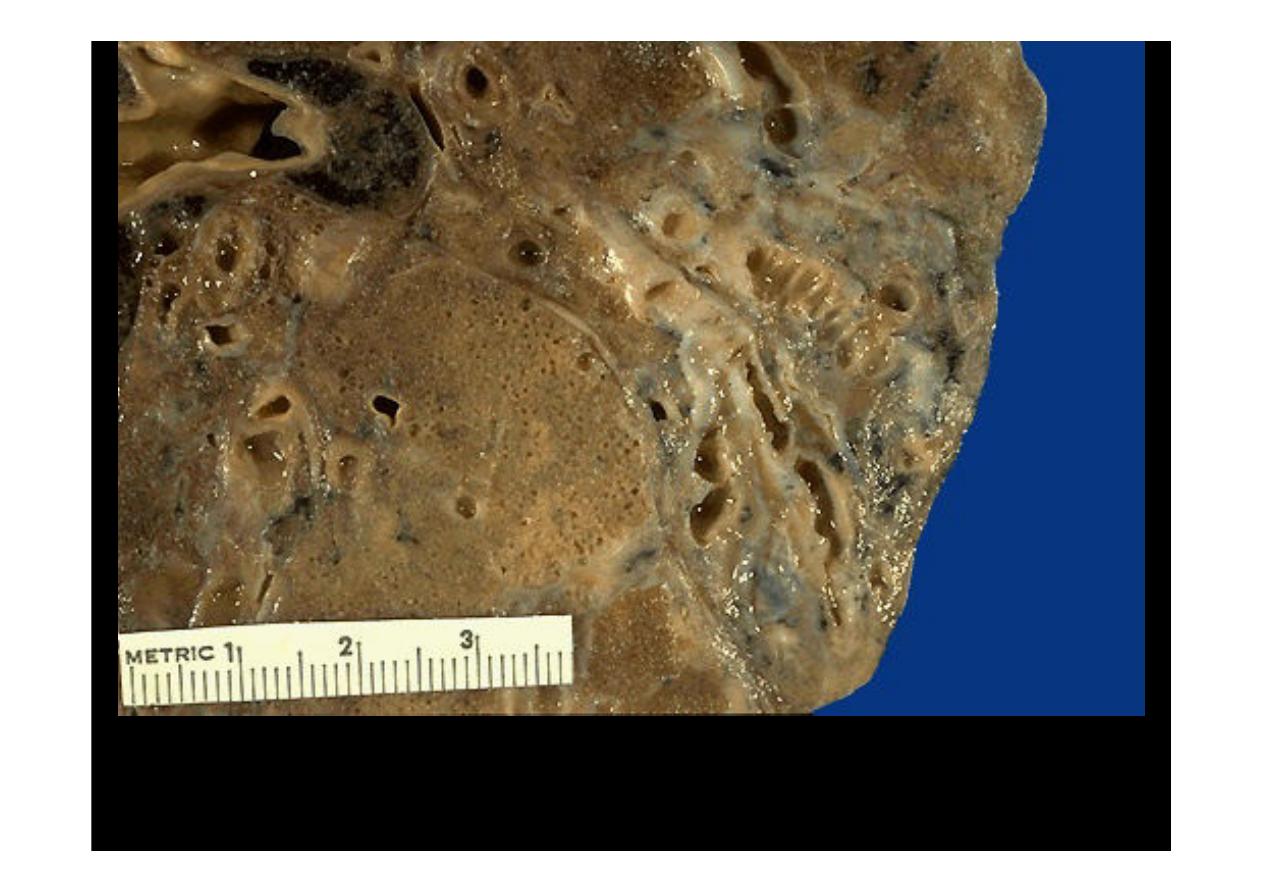
A view demonstrates the focal area of dilated bronchi with
bronchiectasis
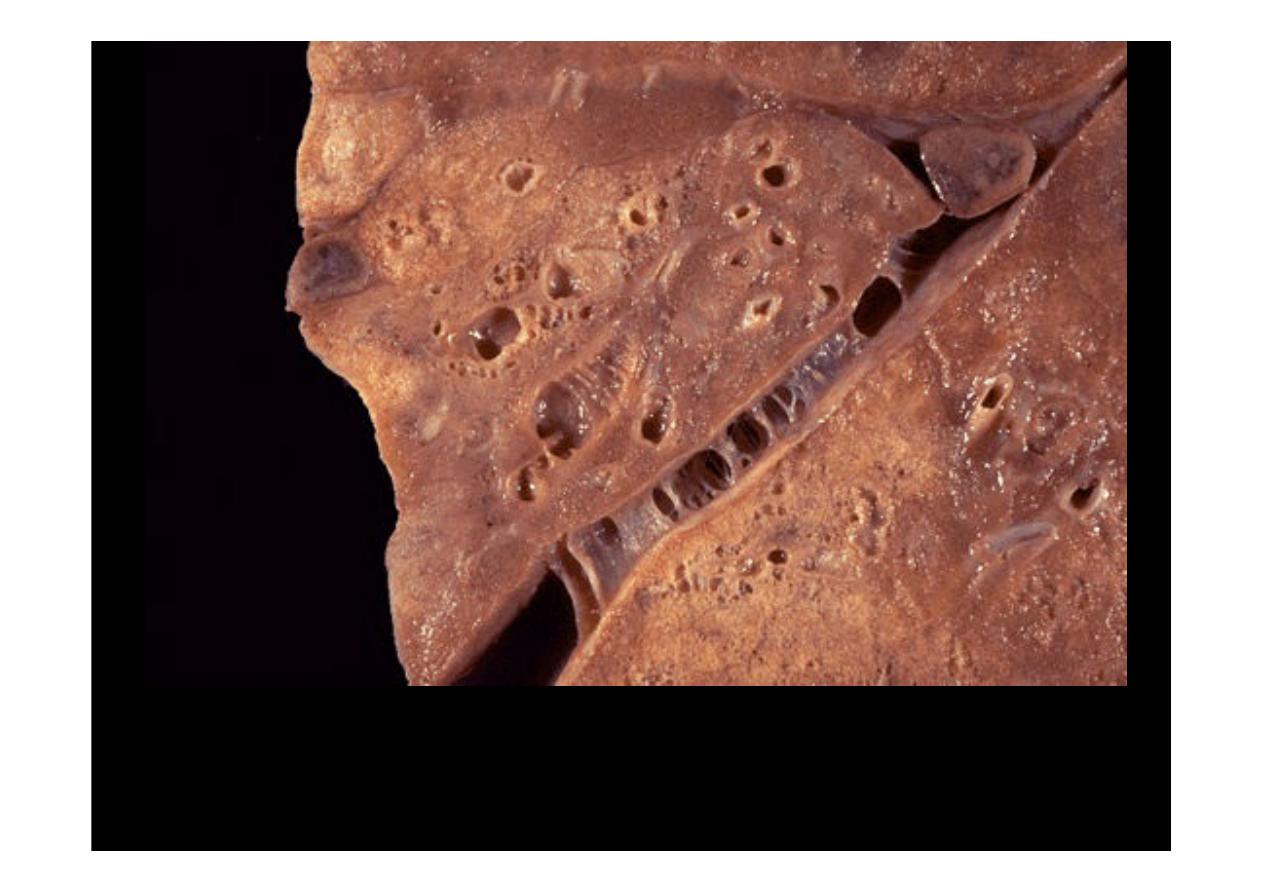
Bronchiectasis
is seen here. The repeated episodes of inflammation can
result in scarring, which has resulted in fibrous adhesions between the lobes
