
Liver disease 1
Third year class
By Dr.Riyadh A. Ali
Department of pathology
TUCOM

Articles
• Normal liver
• Fatty cahnges
• Cirrhosis

Normal Liver
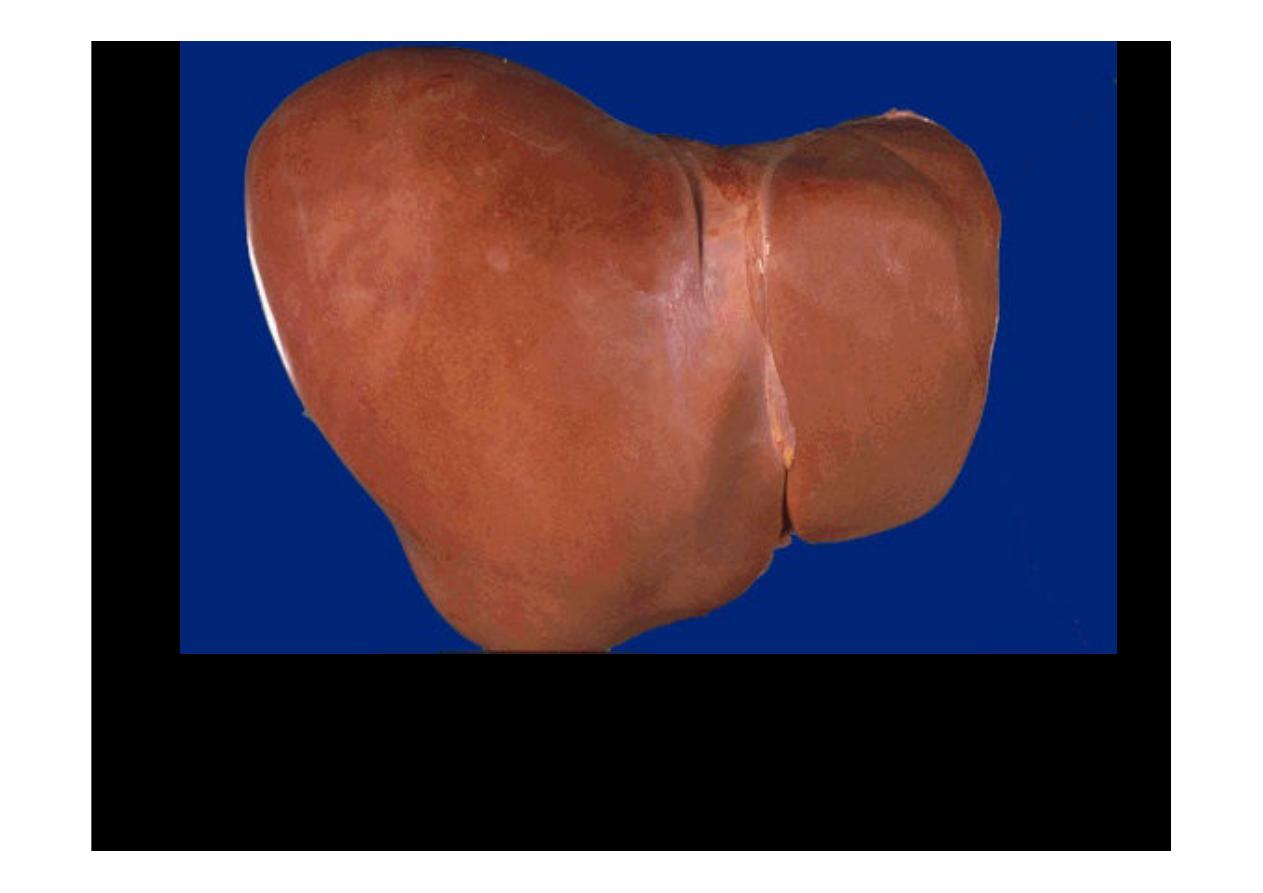
This is the external surface of a normal liver. The color is
brown and the surface is smooth. A normal liver is about
1200 to 1600 grams.
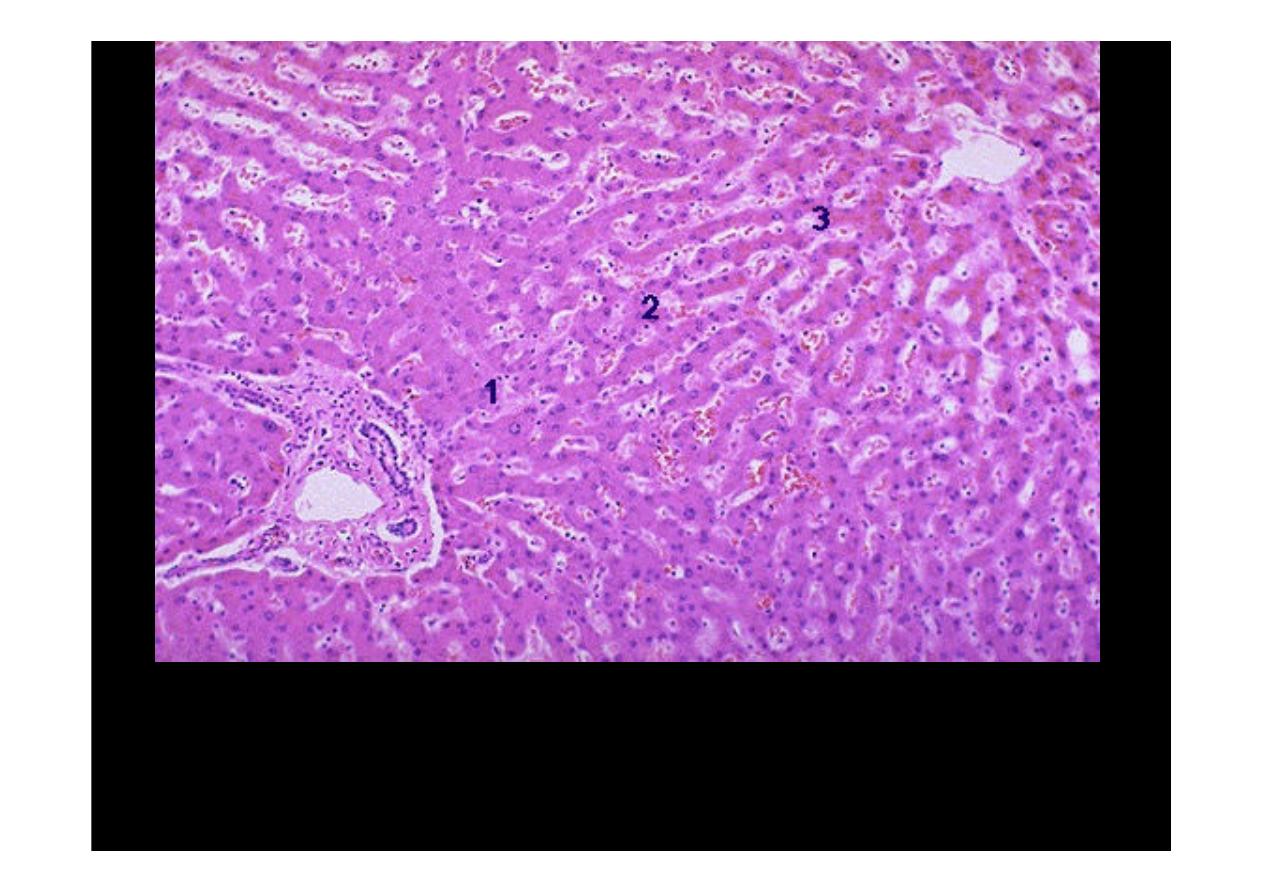
Normal Liver
is divided histologically into lobules. The center of the lobule is the
central vein. At the periphery of the lobule are portal triads. Functionally, the liver can
be divided into three zones, based upon oxygen supply. Zone 1 encircles the portal
tracts where the oxygenated blood from hepatic arteries enters. Zone 3 is located
around central veins, where oxygenation is poor. Zone 2 is located in between.

Fatty change
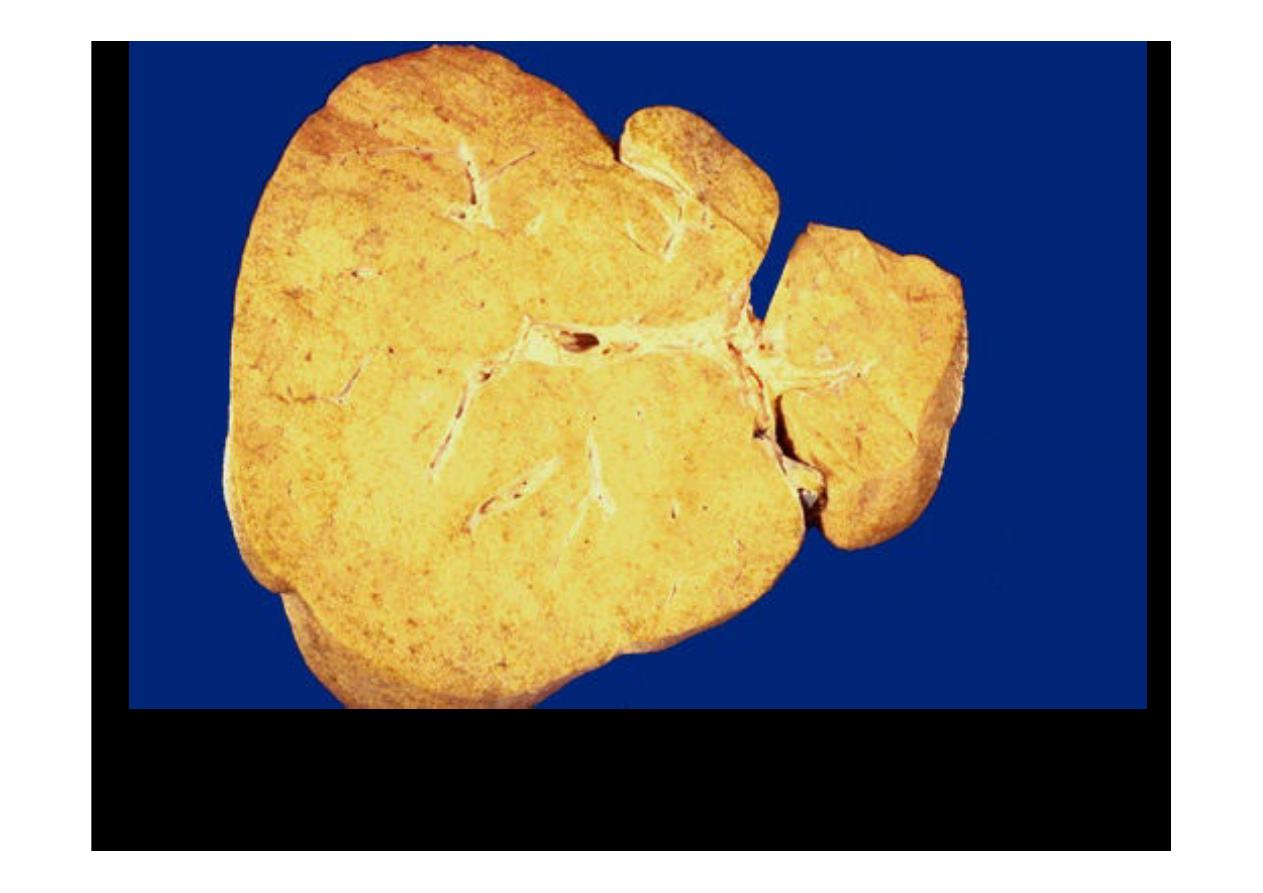
This is a larger liver with more pronounced
fatty change
.
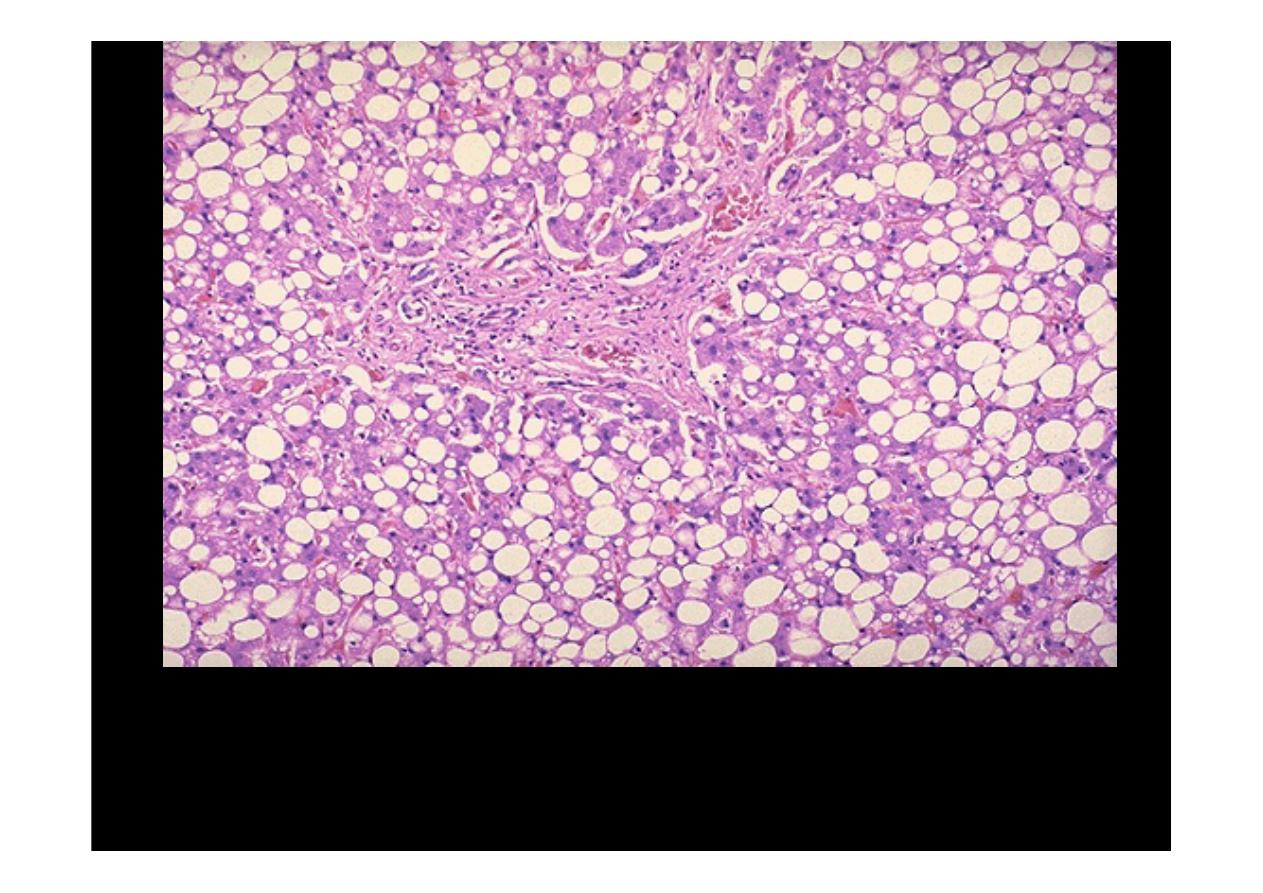
This is the histologic appearance of
hepatic fatty change
. The lipid
accumulates in the hepatocytes as vacuoles. These vacuoles have a clear
ppearance with H&E staining
.
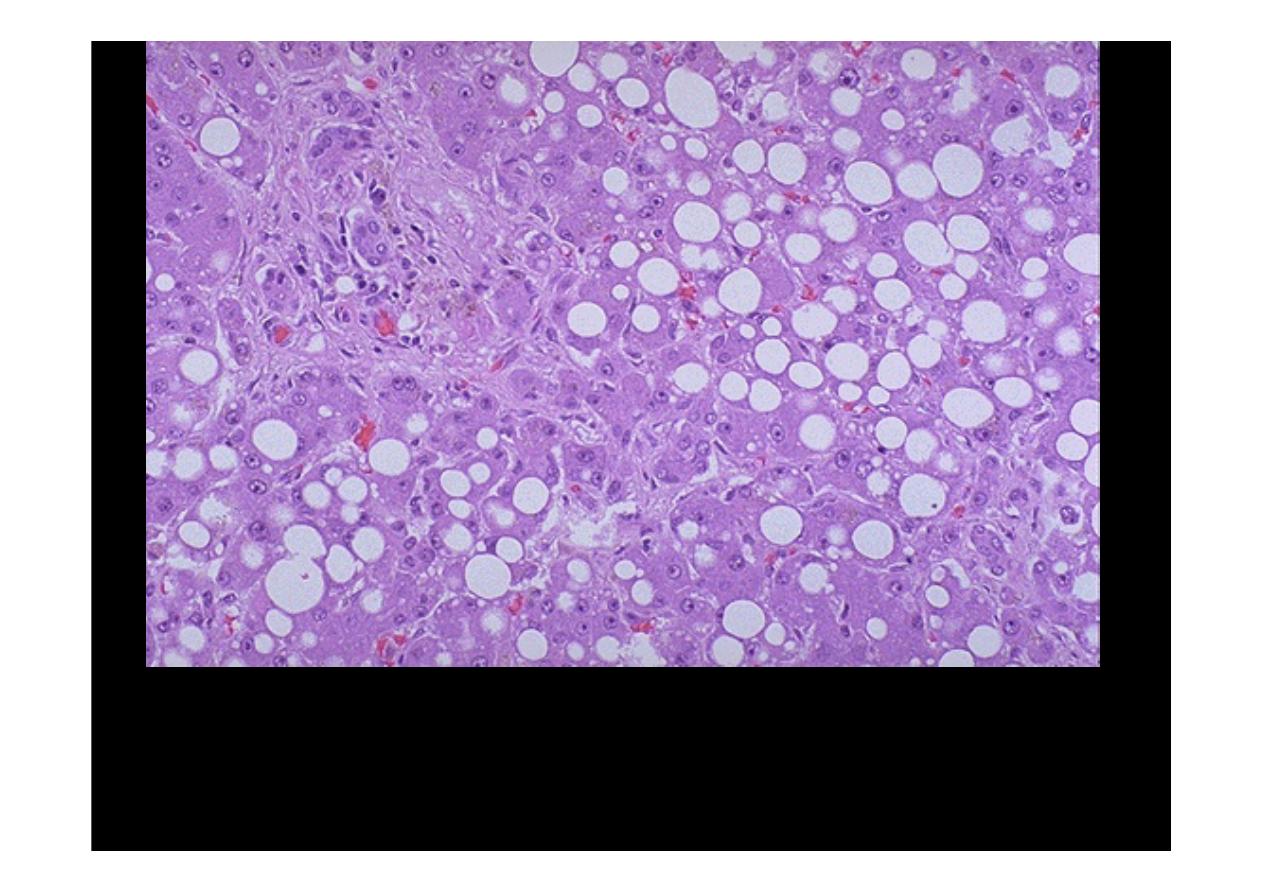
Here are seen the lipid vacuoles within hepatocytes. The lipid
accumulates when lipoprotein transport is disrupted and/or when fatty
acids accumulate. Alcohol, the most common cause.
Fatty change
.

Liver cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis
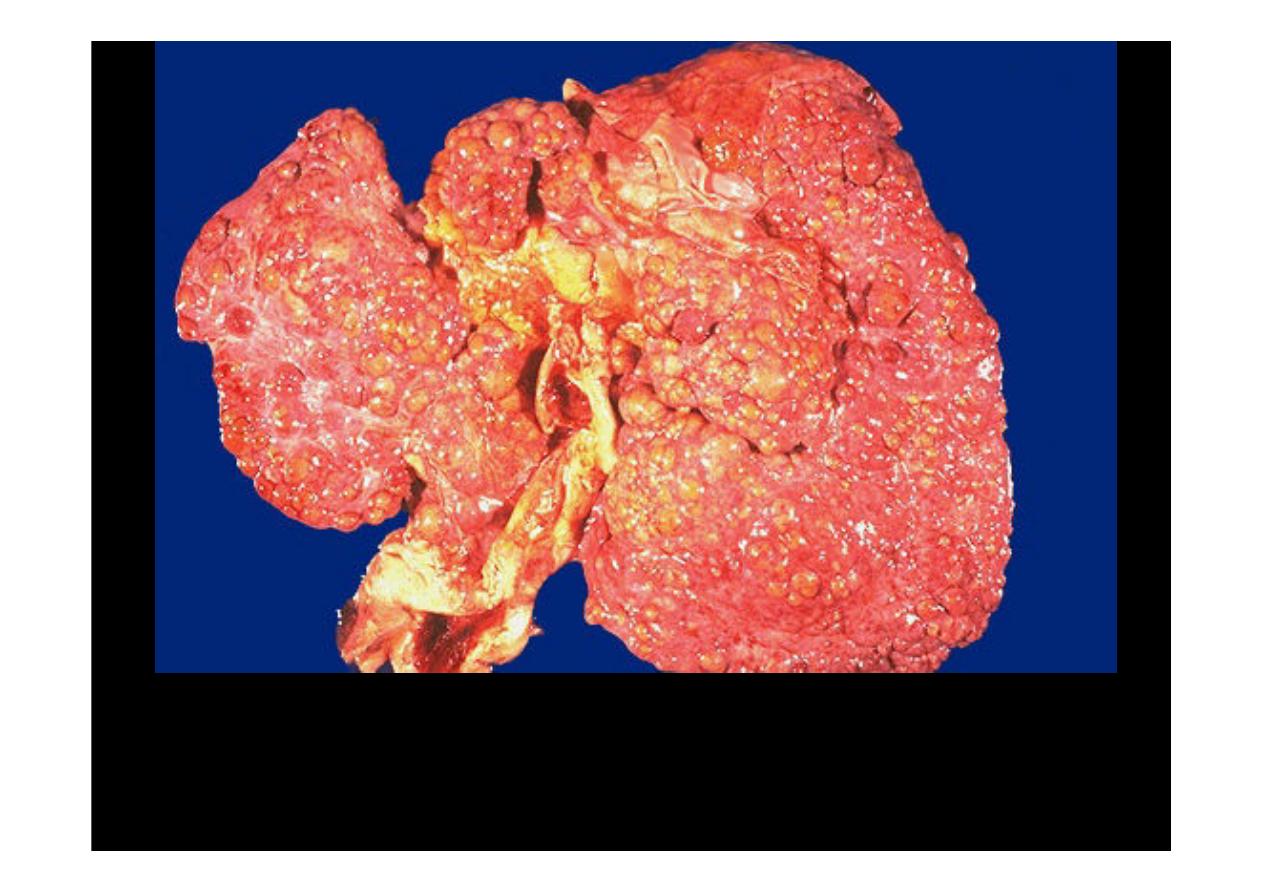
Ongoing liver damage with liver cell necrosis followed by fibrosis and hepatocyte
regeneration results in
cirrhosis
. This produces a nodular, firm liver. The nodules
seen here are larger than 3 mm and, hence, this is an example of "macronodular"
cirrhosis
Here is another example of
macronodular cirrhosis.
Most common
cause
of
macronodular cirrhosis
are hepatitis B and C
Here is another example of
macronodular cirrhosis
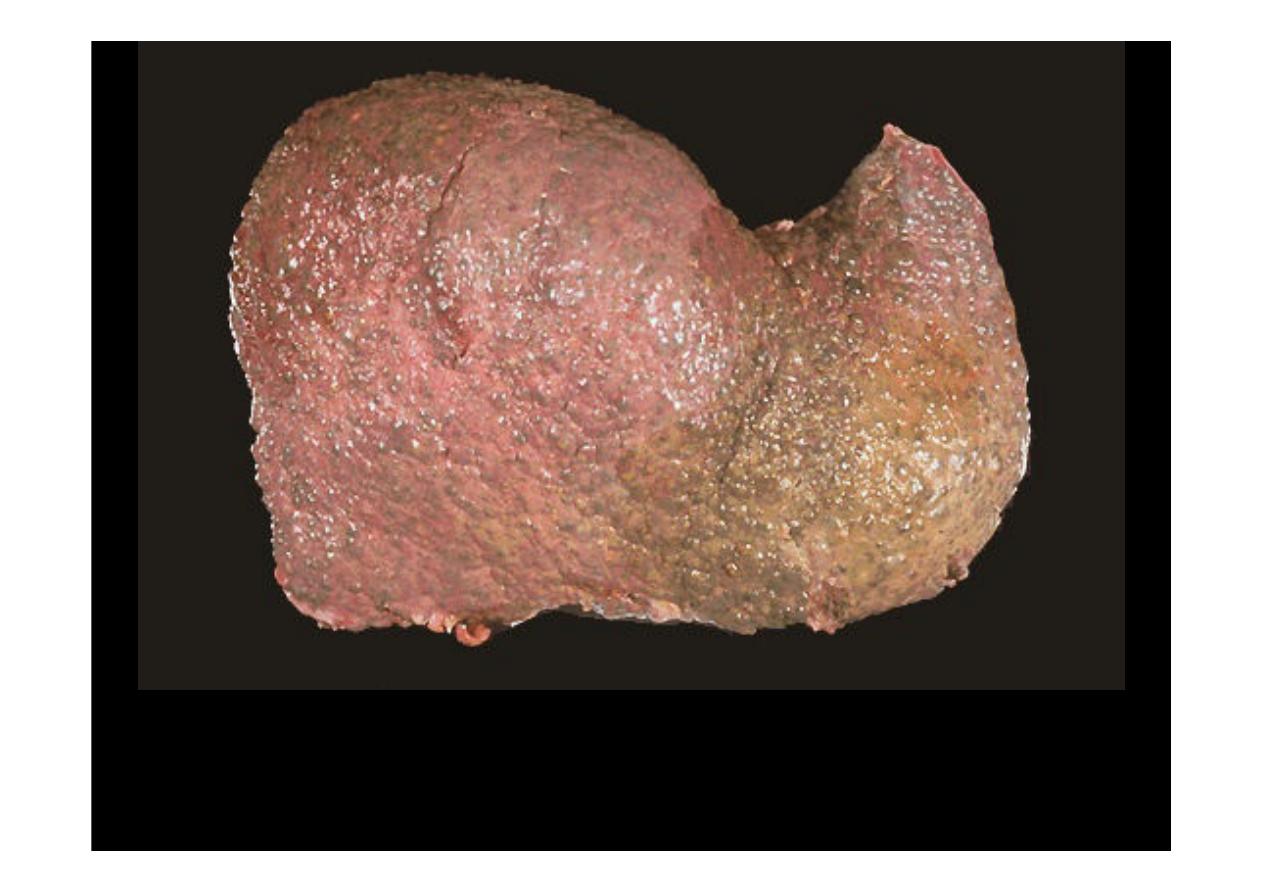

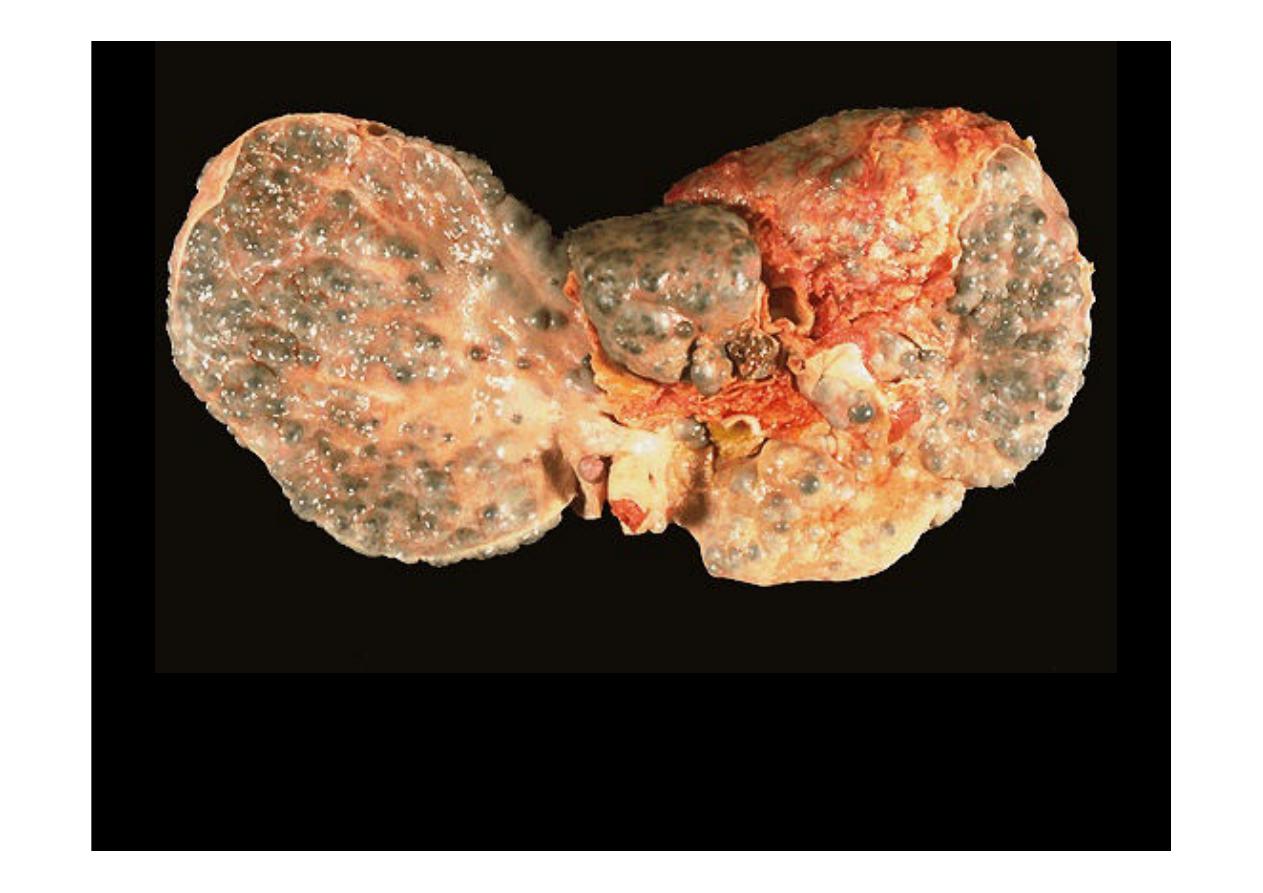
This is an example of a micronodular cirrhosis. The regenerative nodules are
quite small, averaging less than 3 mm in size. The most common cause for this
is chronic alcoholism.
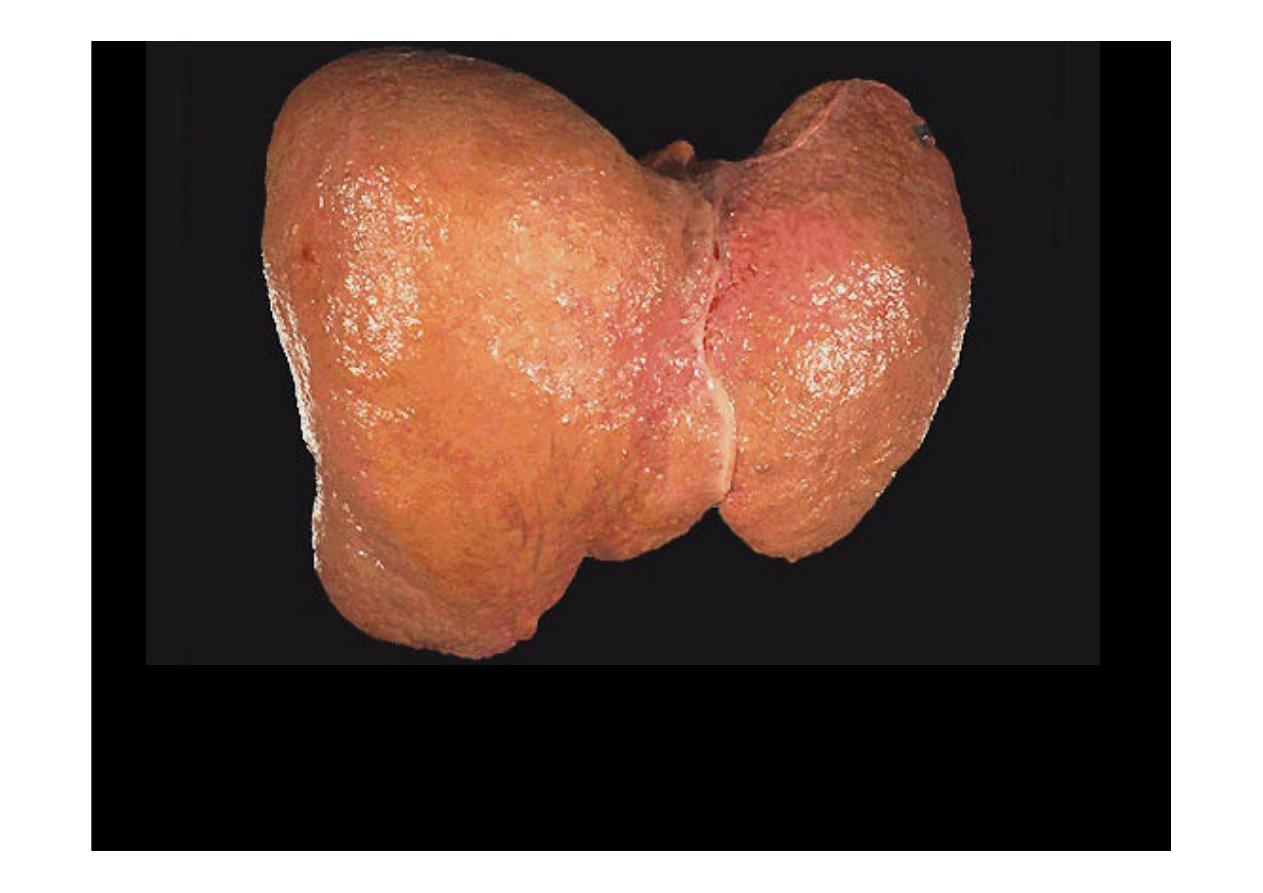
Here is another example of
micronodular cirrhosis.
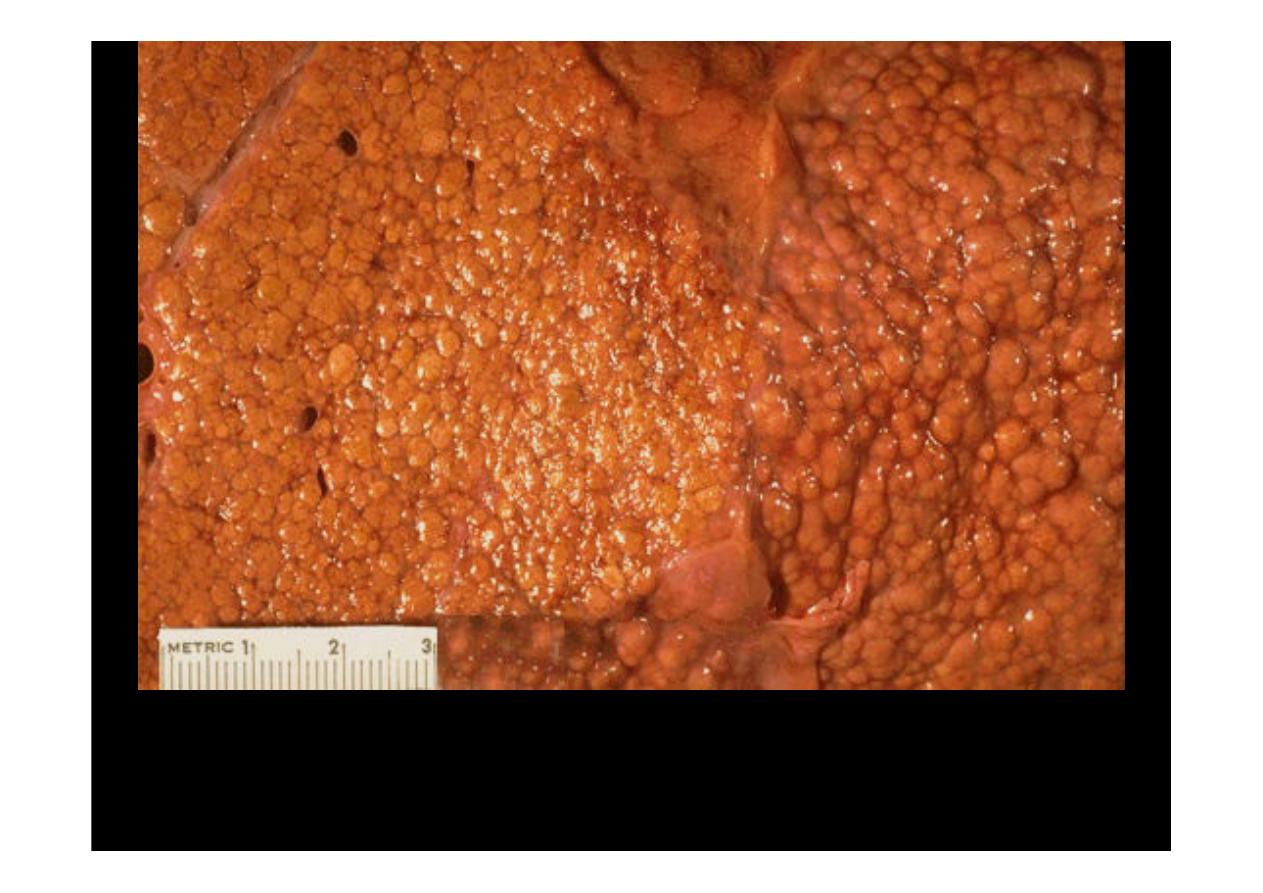
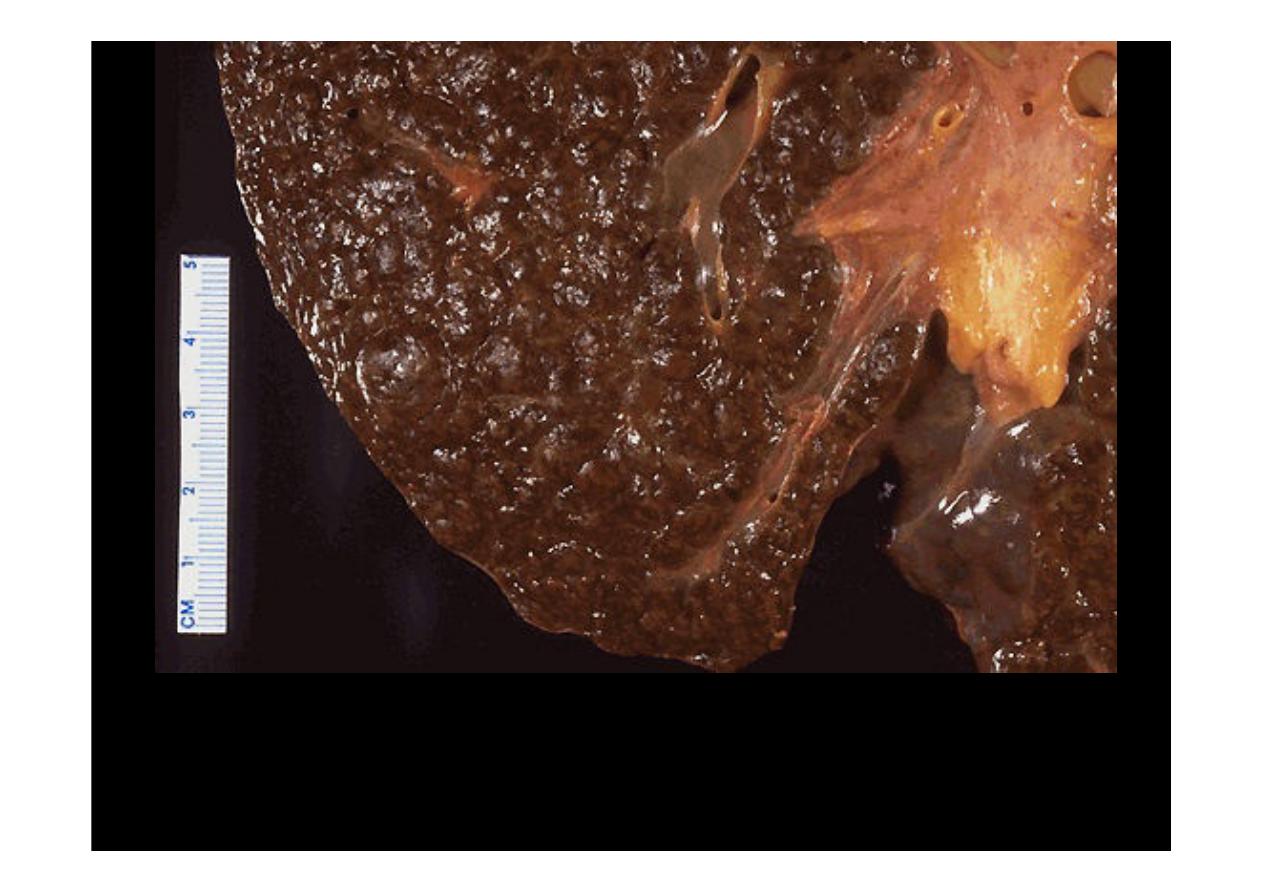
A close-up view of a
micronodular cirrhosis
in a liver demonstrates the small,
yellow nodules.
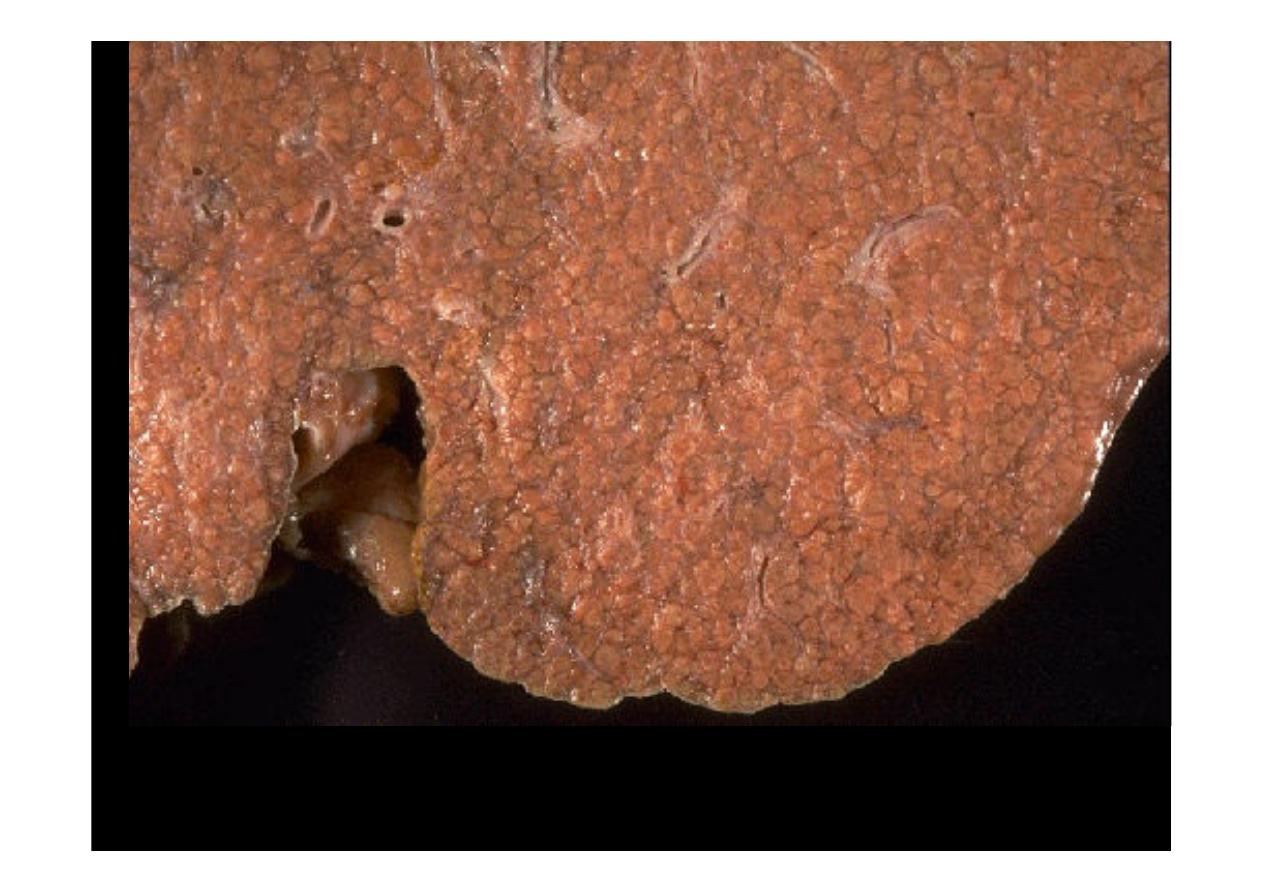

A close-up view of a
micronodular cirrhosis
in a liver demonstrates
the small nodules.
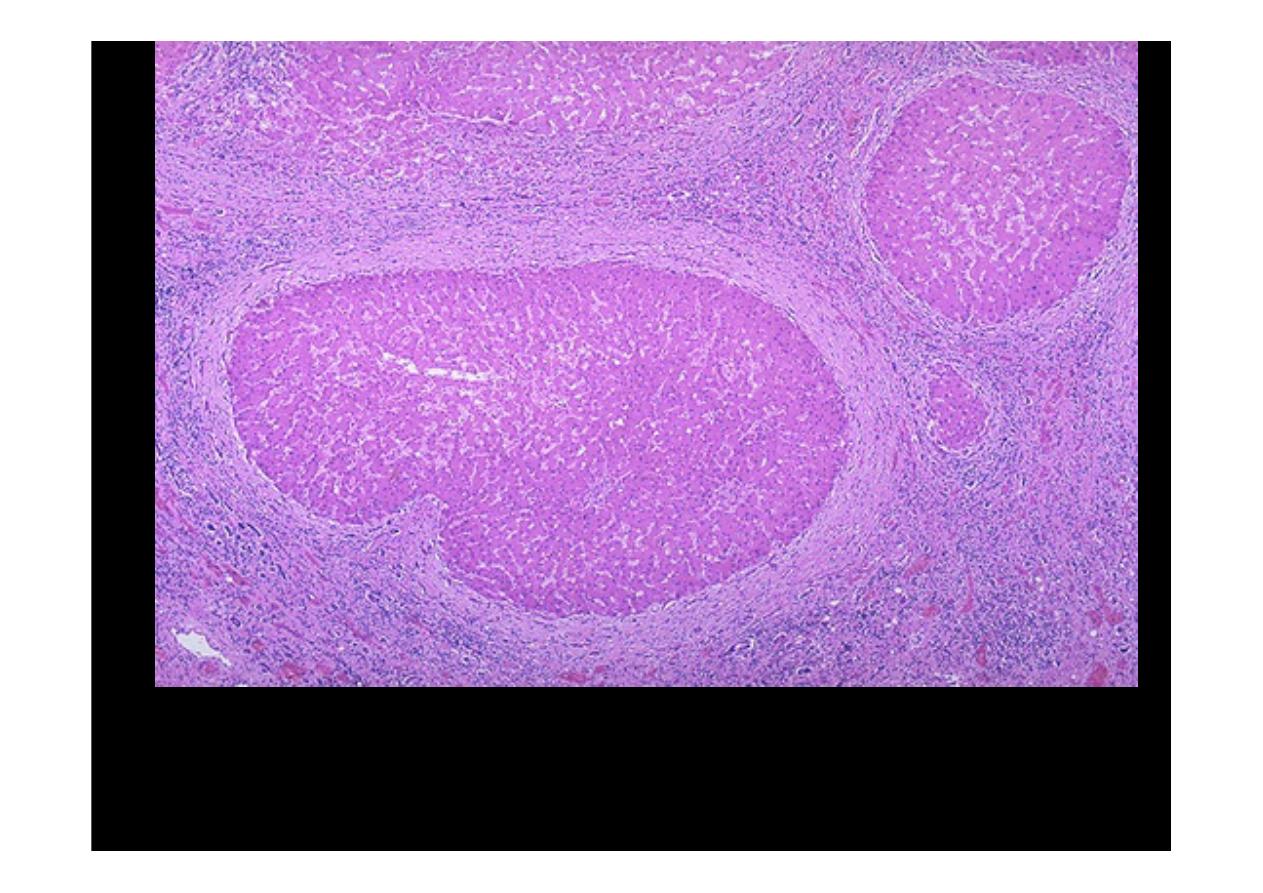
Microscopically with
cirrhosis
, the regenerative nodules of hepatocytes are
surrounded by fibrous connective tissue that bridges between portal tracts.
Within this collagenous tissue are scattered lymphocytes as well as a
proliferation of bile ducts.
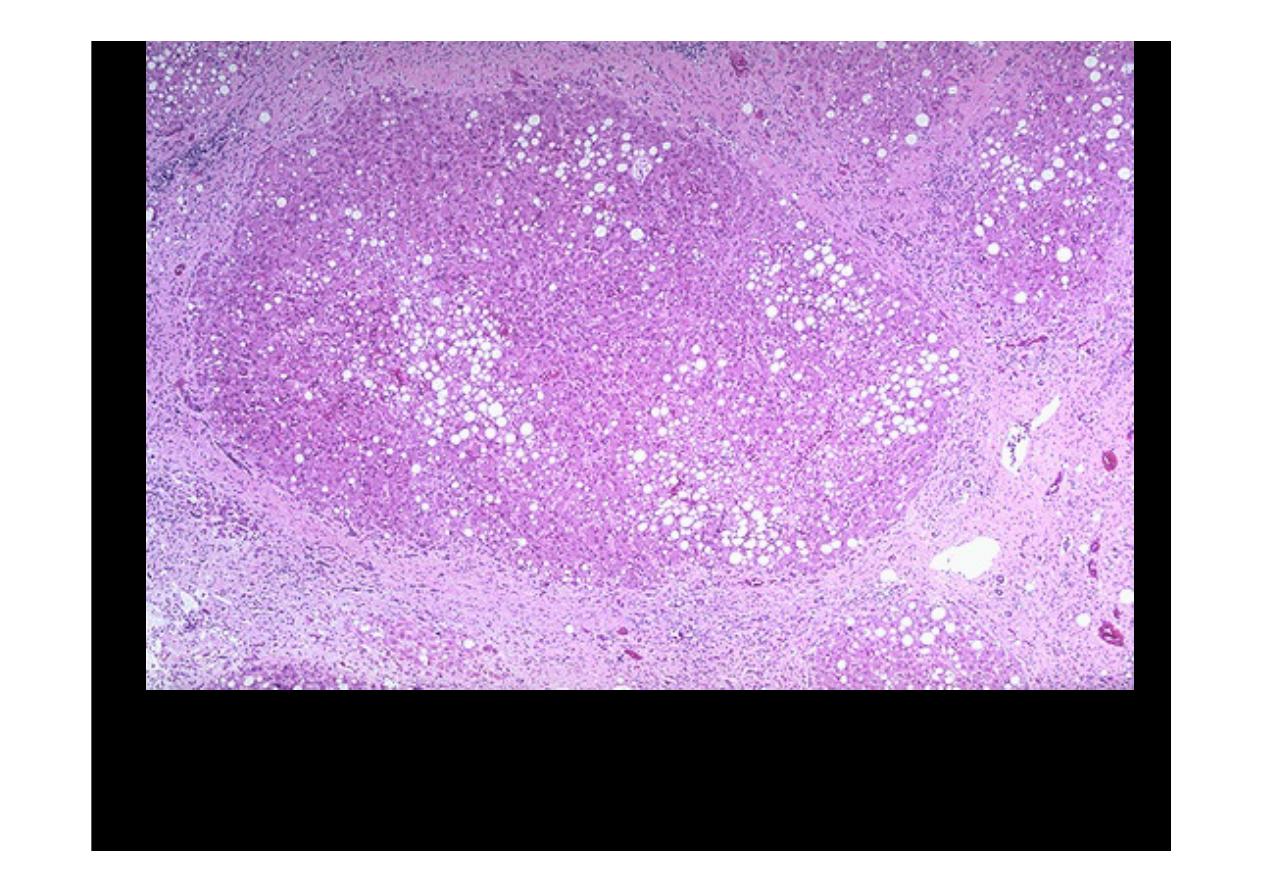
Cirrhosis
is seen along with moderate fatty change. Note the regenerative
nodule surrounded by fibrous connective tissue extending between portal
regions.
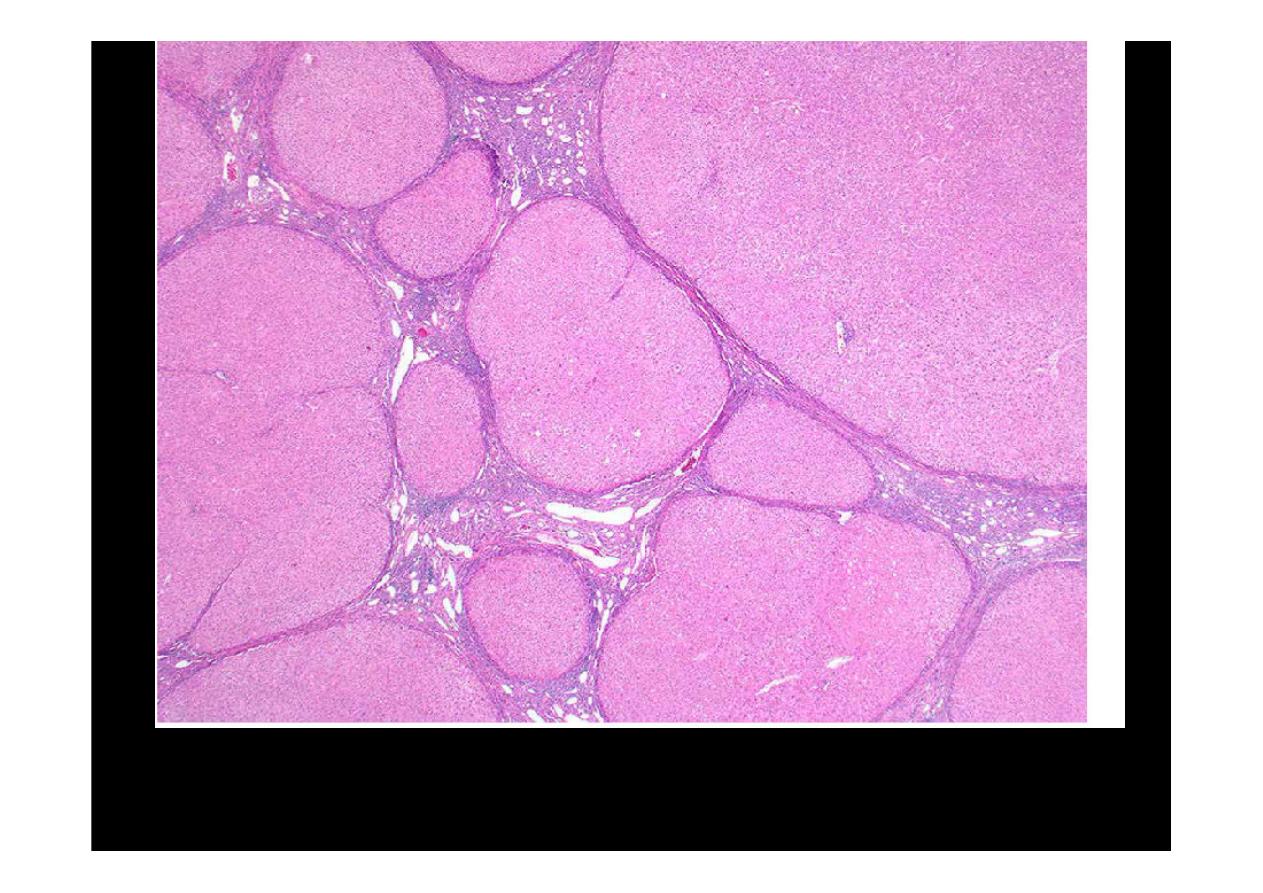
Cirrhosis
, the regenerative nodules of hepatocytes are surrounded by fibrous
connective tissue that bridges between portal tracts. Within this collagenous
tissue are scattered lymphocytes as well as a proliferation of bile ducts.
