
GIT 5
Third year class
By Dr.Riyadh A. Ali
Department of pathology
TUCOM

Titles
• CA Colon

CA COLON
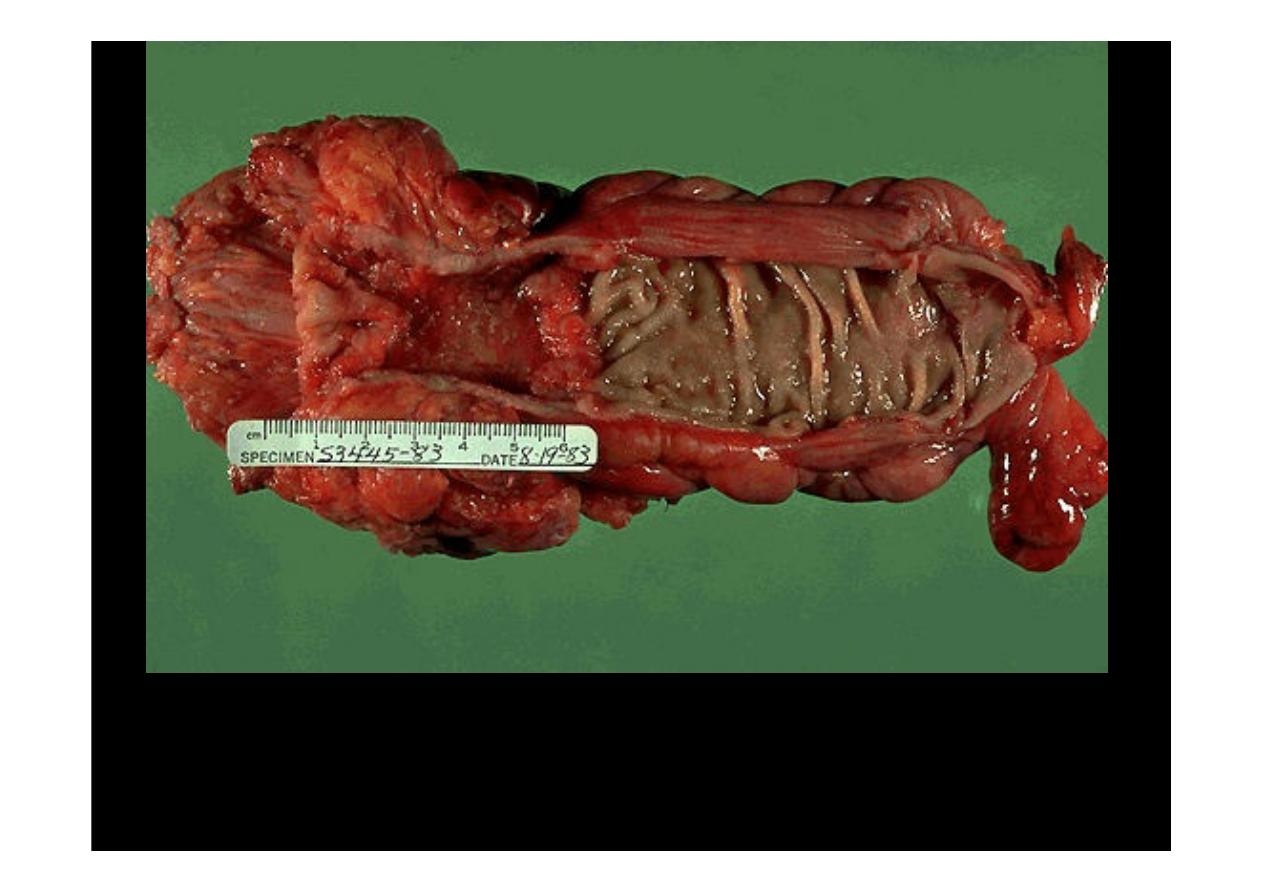
An
adenocarcinoma of the colon
appears above the label at the left. There is a heaped up
margin of tumor at each side with a central area of ulceration. This produces the bleeding that
allows detection through a stool guaiac test. Normal mucosa appears at the right. The tumor
encircles the colon and infiltrates into the wall.
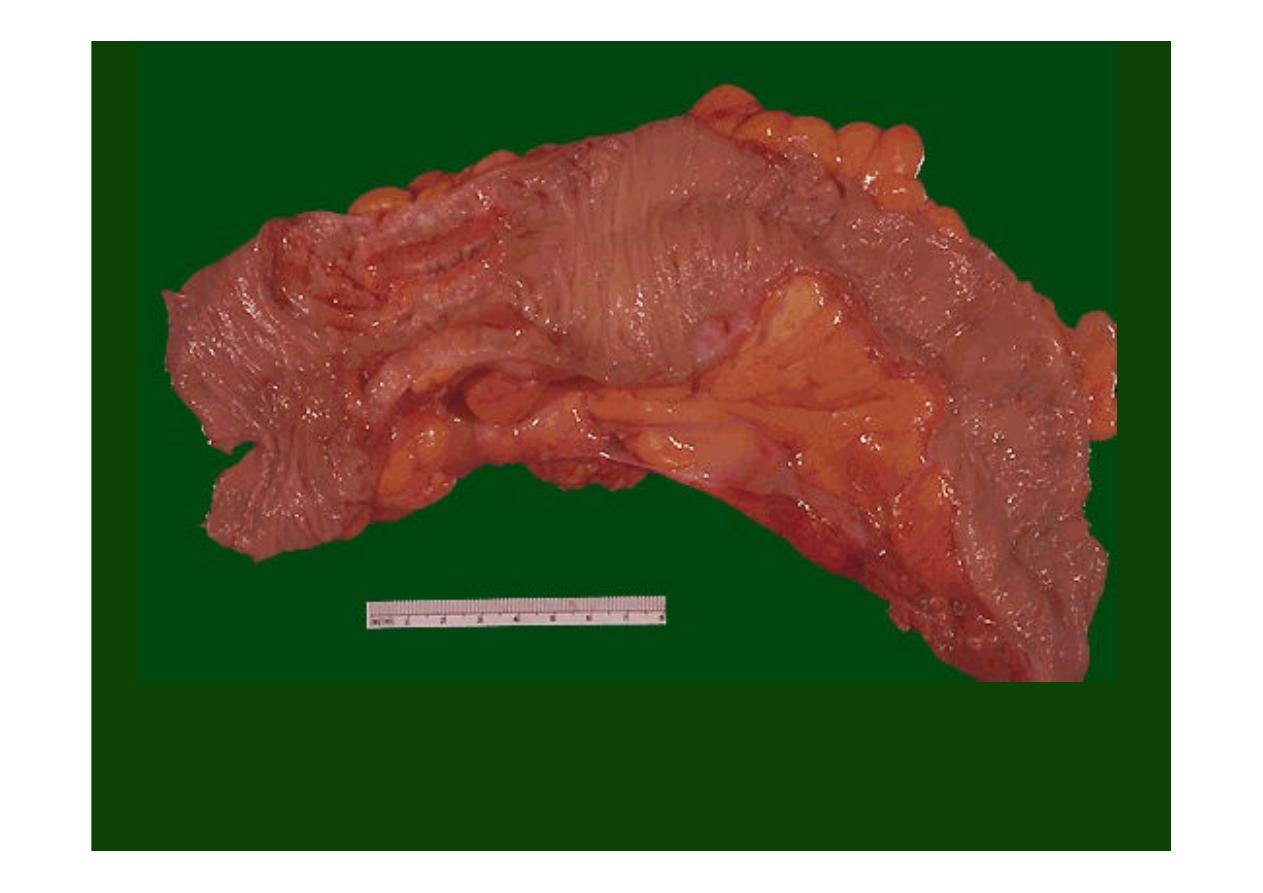
The encircling mass of firm
adenocarcinoma in this colon
at the left is
typical for adenocarcinomas arising in the descending colon.
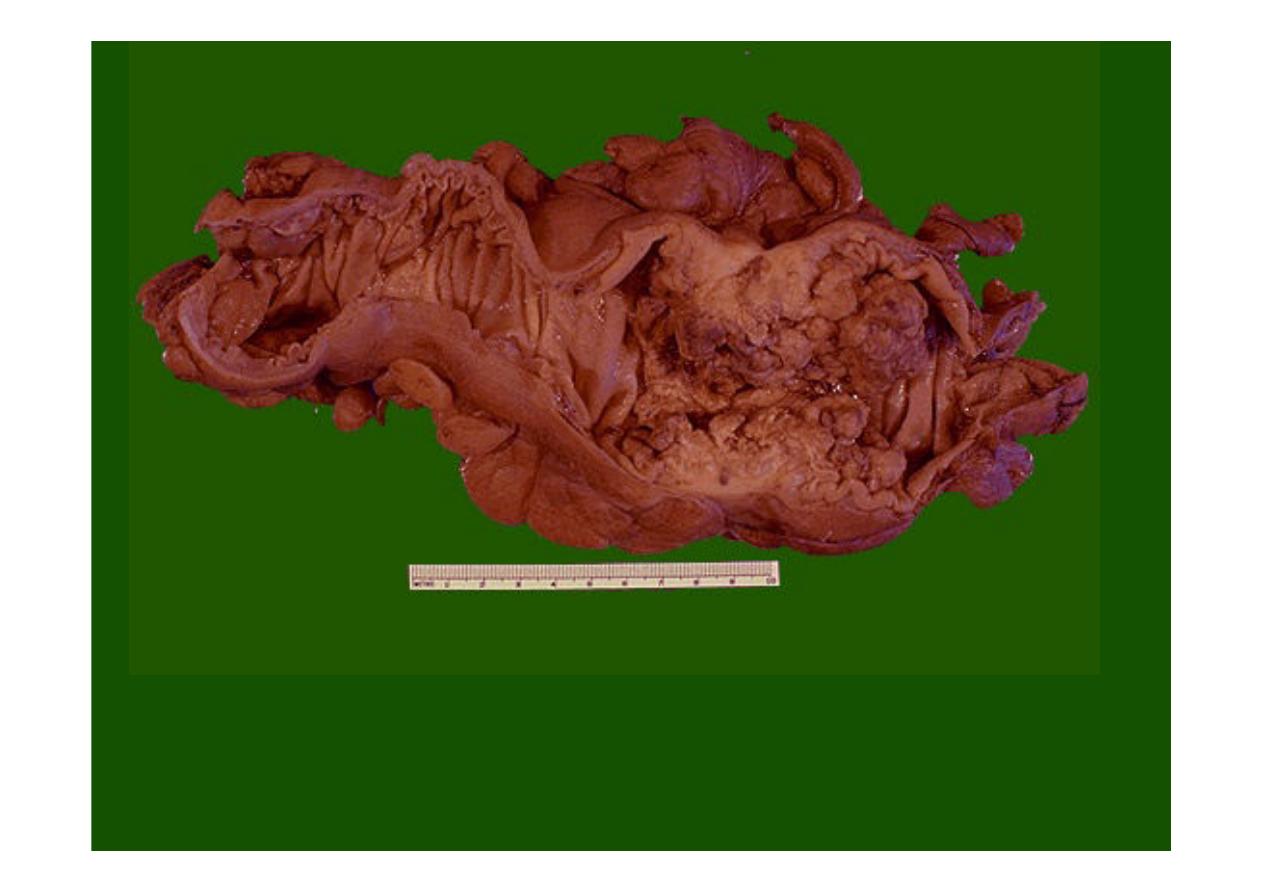
Here is another example of an
adenocarcinoma of colon
. This cancer is more exophytic
in its growth pattern.
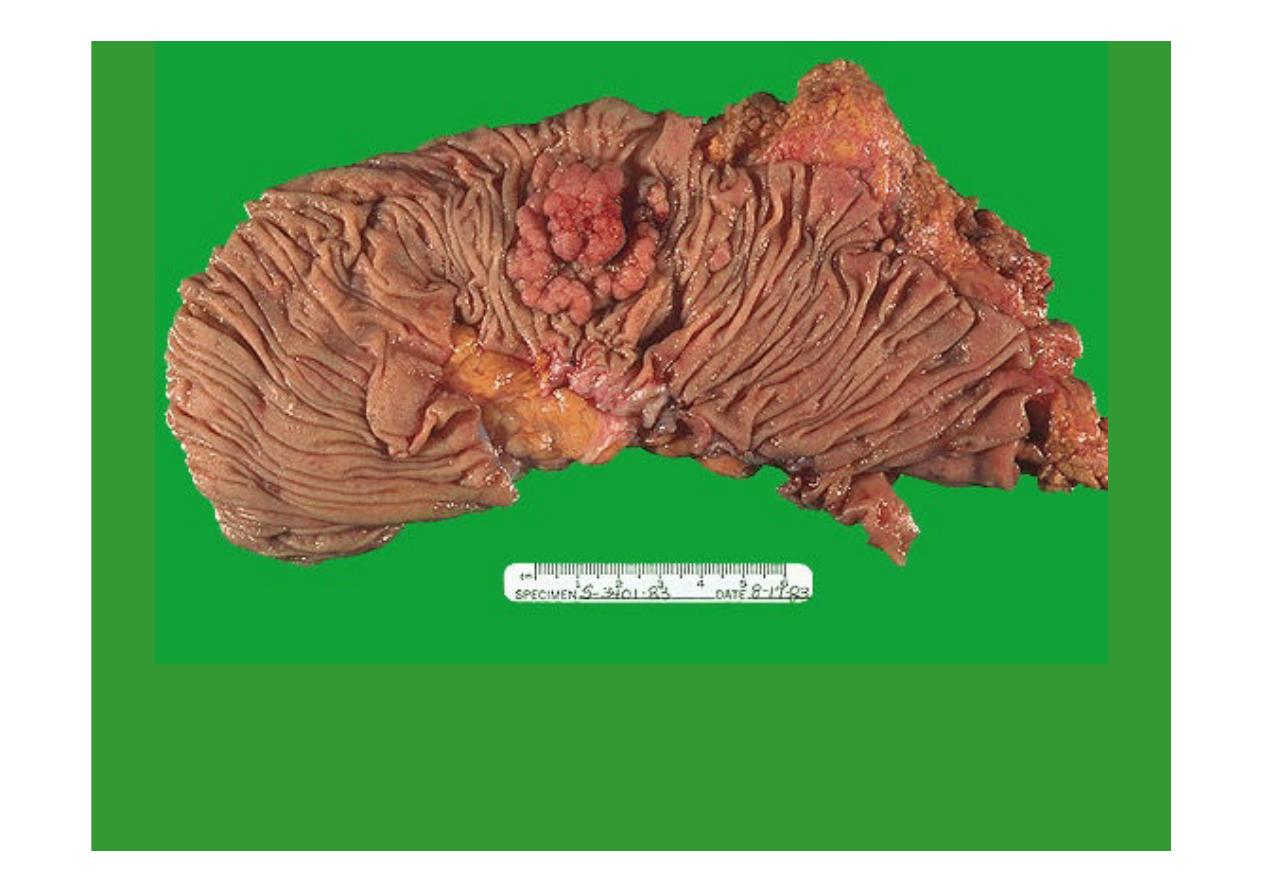
This is an
adenocarcinoma arising in a villous adenoma
. The surface of the neoplasm is
polypoid and reddish pink. Hemorrhage from the surface of the tumor creates a guaiac
positive stool. This neoplasm was located in the sigmoid colon.
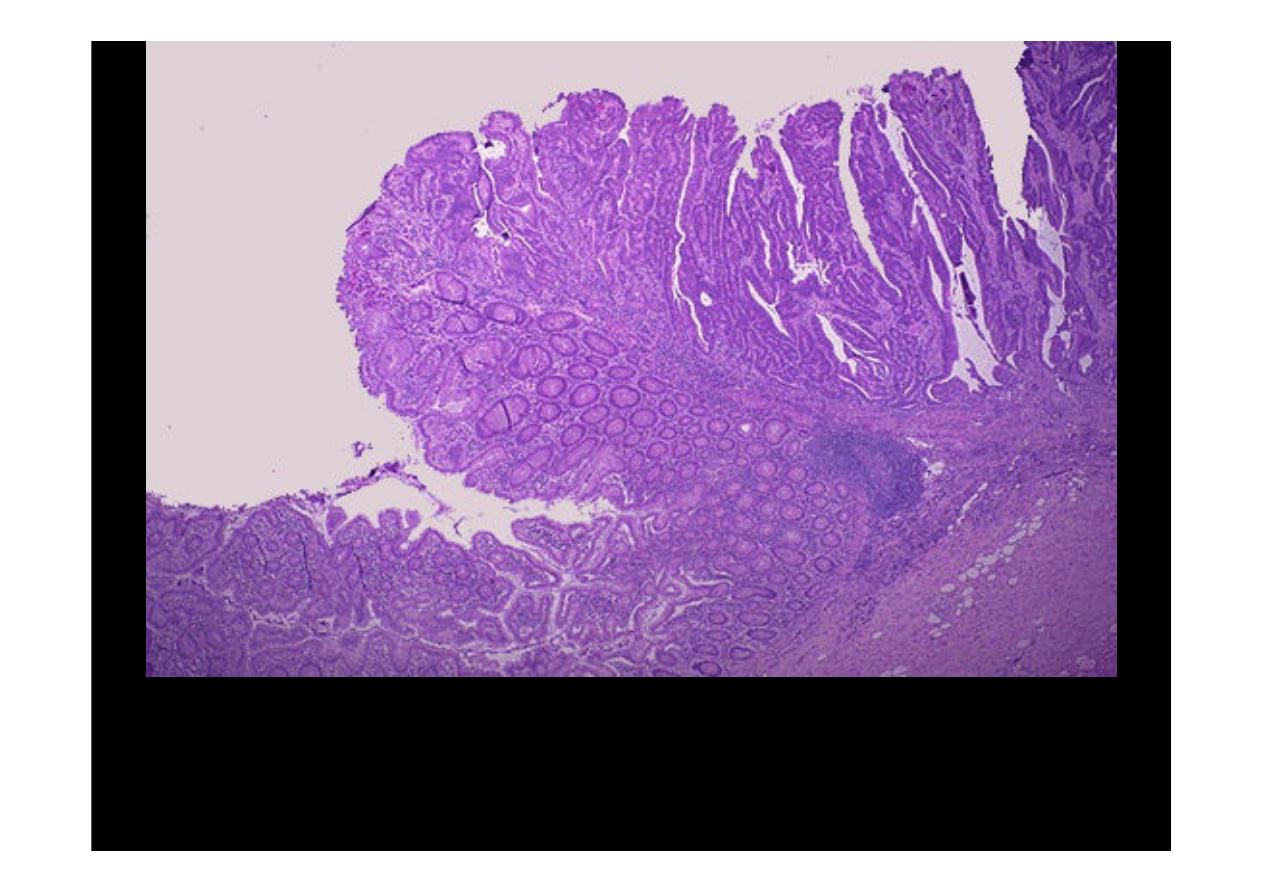
The edge of the
carcinoma arising in the villous adenoma
is seen here. The neoplastic
glands are long and frond-like, similar to those seen in a villous adenoma. The growth is
primarily exophytic (outward into the lumen) and invasion is not seen at this point.
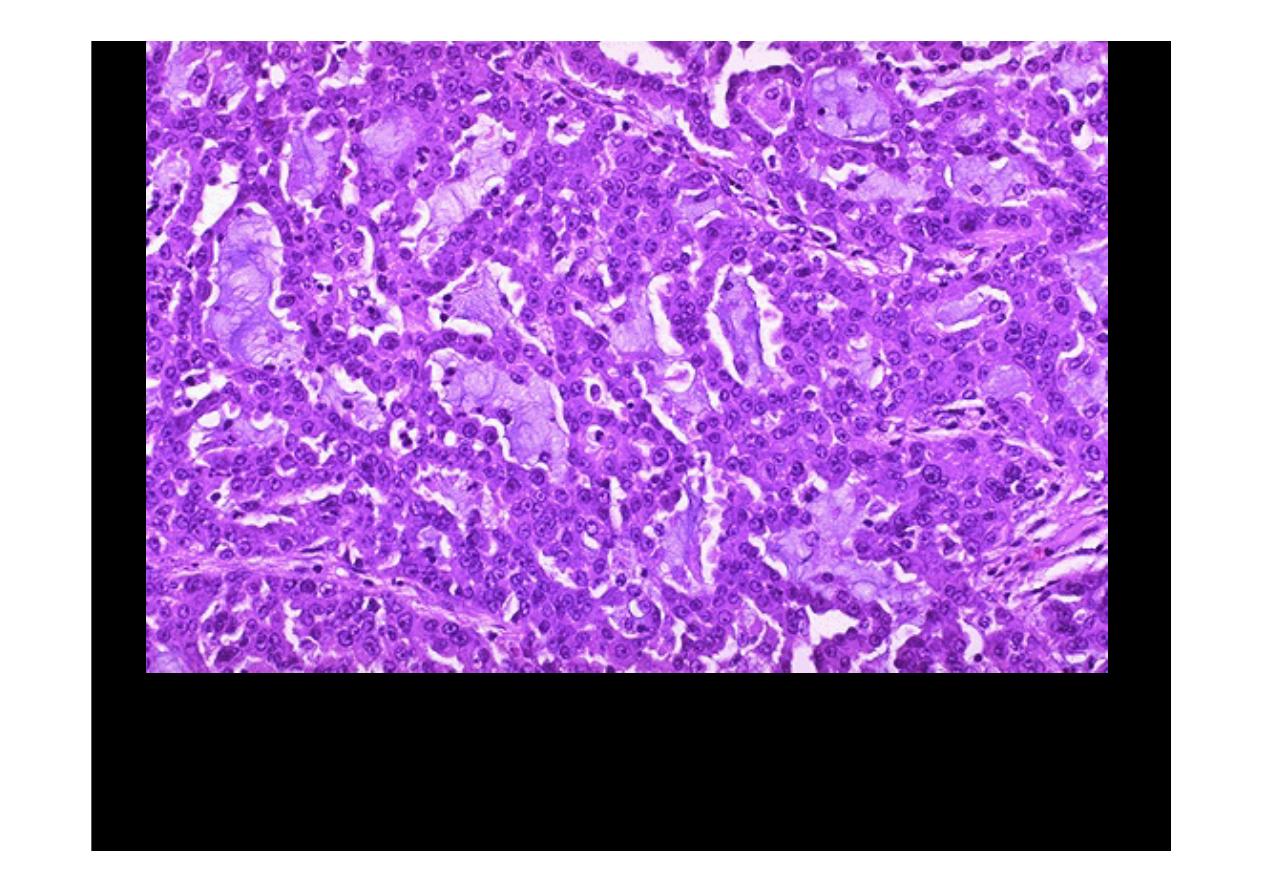
Microscopically, a
moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of colon
is
seen here. There is still a glandular configuration, but the glands are irregular
and very crowded. Many of them have lumens containing bluish mucin.
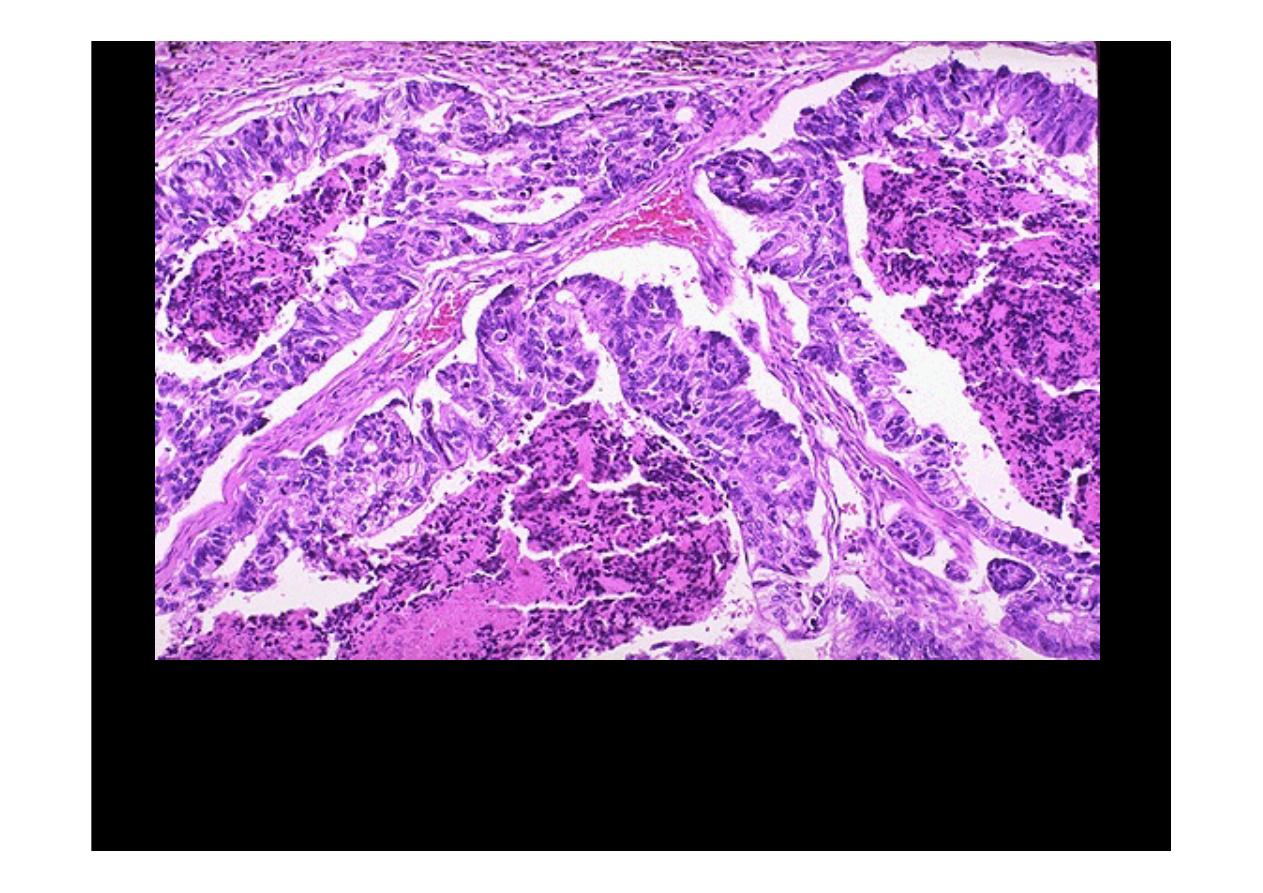
Here is an
adenocarcinoma
in which the glands are much larger and filled
with necrotic debris.
CA colon.
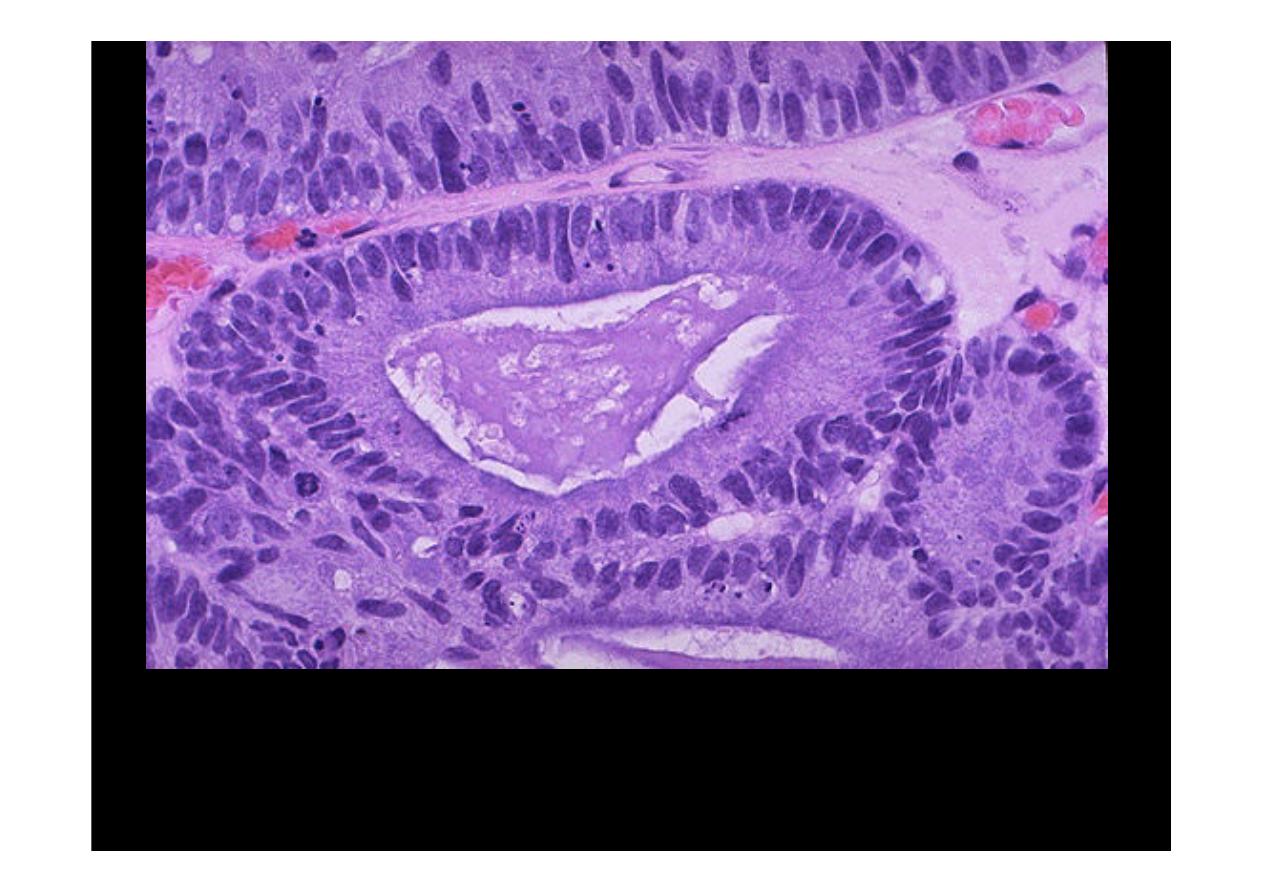
At high magnification, the neoplastic glands of
adenocarcinoma
have crowded
nuclei with hyperchromatism and pleomorphism. No normal goblet cells are
seen.
CA colon
