Predisposing factors for periodental diseaeses
Food ImpactionIt is the forceful wedging of food into the periodontium by occlusal forces.
The factors leading to food impaction:-
-Uneven occlusal wear.
-Opening of the contact point as a result of loss of proximal support or from extrusion.
-Congenital morphologic abnormalities.
-Improperly constructed restorations.
Food Impaction
Food debris liquefied by bacterial enzyme & cleaned from oral cavity within 5 min.after eatingFactors accelerate clearance;
1- chewing
2- low viscosity of saliva
3- mechanical action of tongue,lip and cheek.
4- alignment of teeth
4- types of food (sugary diet sustain for 1h.)
Food Impaction
Forceful wedging of food into periodontium by occlusal force can leads to gingival inflammation & delay of periodental treatment.
Normally:-
There are firm proximal contact relationship,proximity of contact point to occlusal plane and good contour of occlusal surface (marginal ridges & developmental groove) so avoid food impaction.
Wearing of tooth & flattened surfaces may replace normal convexities in old age persons;so the wedging effect of opposing cusp into interproximal space would be exaggerated.
Food Impaction
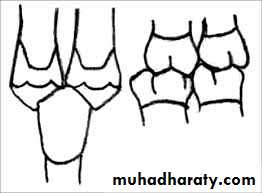
Plunger cusp; cusp that tend to forcibly wedge food interproximally ,occur due to wear or shift in tooth positionFood impaction
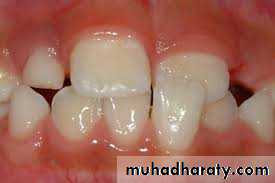
Excessive anterior overbite;Food impaction at labial gingiva of lower anterior teeth & palatal gingiva of upper teeth.
Factors lead to food impaction
Lateral food impaction:-
pressure from lips & cheek into large gingival embrassure (due to tissue destruction with gingival rescission ).
Sequalae of food impaction
1- Feeling of pressure & insisting on removing impacted materials.2- Vague pain radiate deep in jaw.
3- Gingival inflammation with bleeding and foul taste.
4- Gingival recession.
5- Periodontal abscess.
6- Inflammation of periodontal ligaments with elevation of tooth (premature contact & sensitivity to percussion).
7- Destruction of alveolar bone.
8- Root caries.
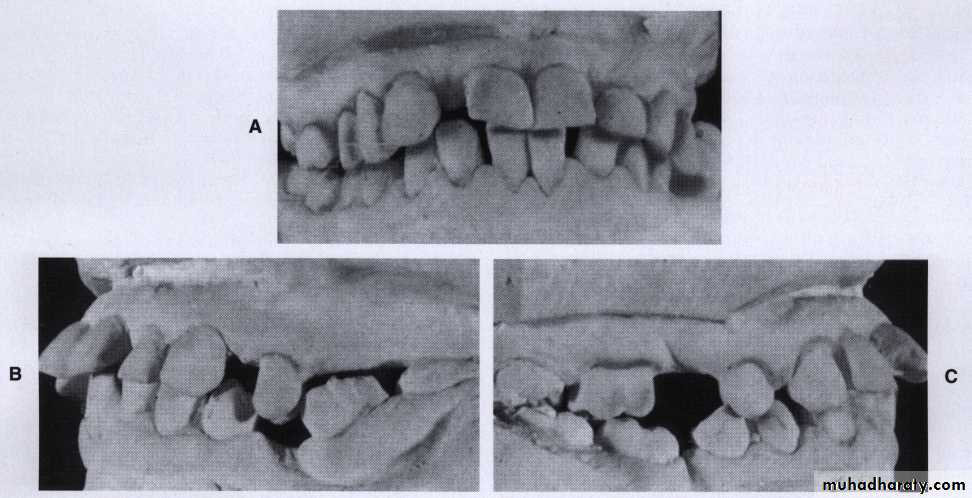
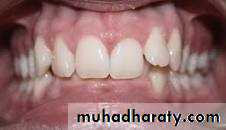
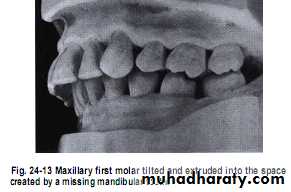
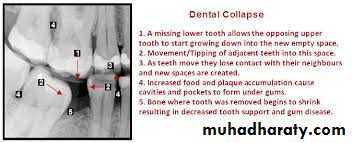
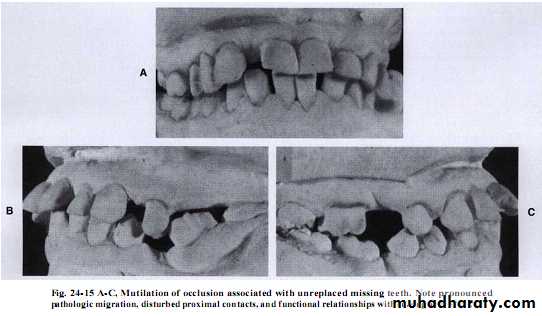
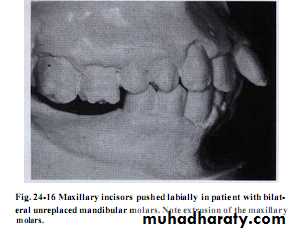
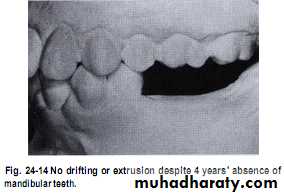
Unreplaced missing teeth
If the lower 6 has been missed & not replacedThere will be mesial drifting & tilting of lower 7& 8 with the extrusion of upper 6.
Distal cusps of lower 7are elevated & act as plunger cusp between extruded upper 6 & 7.
Unreplaced missing teeth
Distal drifting of lower 5 will open contact between premolars that led to food impaction & pocket formation.Extraction of impacted third molar
This could induce vertical defects distal to 7Its unrelated to flaps design .
It occurs in individuals older than 25y
The factors that enhance such defect includes ;
-presence of plaque
- bleeding on probing
-root resorbtion in contact area.
-Inclination of 8
-close proximity of 8 to 7
SO early exo.of 8 is essential from periodental point of view ?
As the roots of impacted 8 are not well formed ,so there will be atraumatic extraction.Malocclusion
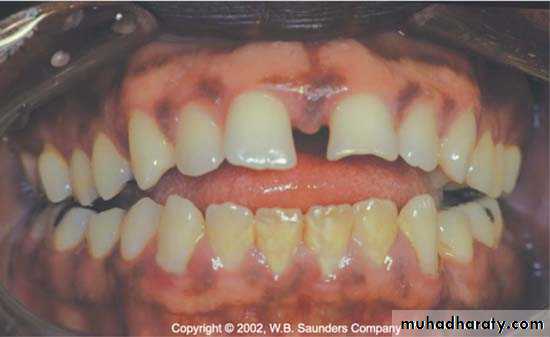
Irregular teeth alignment make plaque control difficult.Gum recession (especially in anterior teeth).
Prominent root in the arch or associated with high frenal attachment.
Trauma from occlusion
Sever overbite
It can leads to food impaction,
pocket formation & plaque accumulation.
Malocclusion
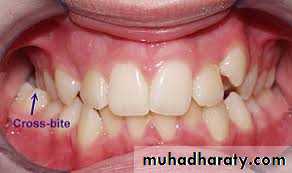
CrossbitePlaque accumulation & trauma from occlusion.
Malocclusion
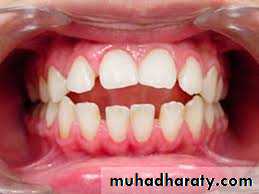
Openbiteheavy plaque accumulation with sever gingivitis due to loss of mechanical cleansing by cheek, lips & tongue.
Malocclusion
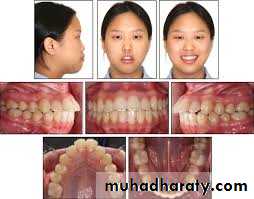
Bimaxillary protrusion
May induce gum recession
Habits
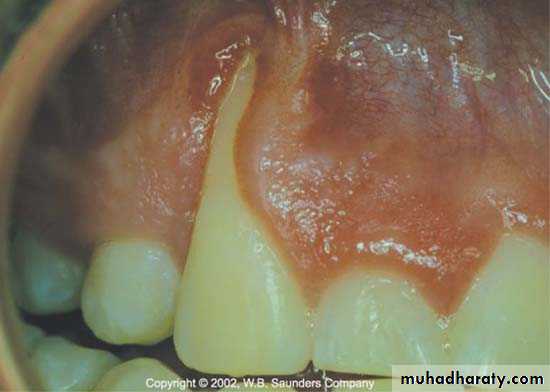
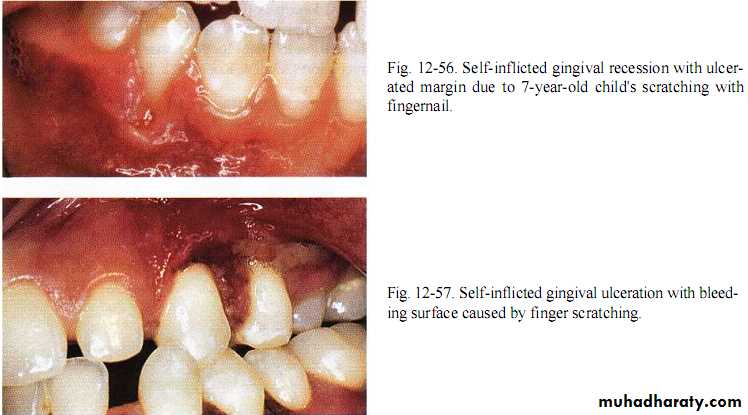
Lip,cheek,toothpick,fingernail or pin bitting may induce trauma from occlusion.Application of fingernail pressure against gingiva or incorrect tooth brushing.
Habits
Tongue thrustingThe tongue in such case is thrust forward against lower anterior teeth during swallowing instead of placement of dorsum of tongue against palate with tip behind upper teeth .
It is happened due to; macroglossia,nasopharyngeal & allergic diseases or habit.
Excessive lateral pressure that are traumatic to periodental that lead to tilting & spreading of anterior teeth with open bite.
Plaque & food debris accumulation.
Habits
Tobacco smokingInduce more attachment & bone loss due to
1-Poor oral hygiene (seen in most of smokers).
• 2-Vasoconstrictive effect of nicotine reduce the blood supply to the periodontium so decrease the amount of oxygen & nutrients that are necessary for tissue with the reduction of waste product removal.
• 3- Smokers are usually infected with a large number of Actinobacillus actinomycetocomitans ,Prevotella gingivalis & Bacteriod forsythus .
4- Depressed no.of T helper cell, thereby reducing serum levels of IgG to pathogens.
Habits
5- Nerve dysfunction ( impaired phagocytic & chemotactic) due to low level of IgG.6- Response to periodental treatment is less than in non-smokers.
7- High rate of calculus formation.
8- Cigarettes smoked/day * no.of y.=pack years correlate with the periodontal disease.
Habits
Oral changes in smokers:-• Brownish tar-like deposits & discoloration of teeth (nicotine & cotinine)
• Diffuse grayish discoloration & leukoplakia of gingiva.
• High relationship between smoking & necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis .
• Delayed post surgical healing due to blood flow that impair revascularization in soft & hard tissue.
Habits
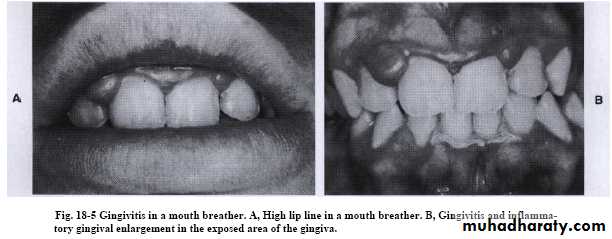
Mouth breathingGingivitis;erythema,edema,enlargement & surface shining in exposed area(occur in the maxillary anterior region).
Its caused by irritation from surface dehydration and the plaque become thicker & more sticky.
Many studies were showed controversial results
1- no effect except in patients with calculus.
2- more severe gingivitis was seen in mouth breathers than non breathers with similar plaque.
3- others showed no relationship except slight increase in its severity.
4- while others concluded that crowding associated with gingivitis only in mouth breathers.
Effect of Radiation Therapy on Periodentium
Obliterative endarteritissoft tissue ischemia & fibrosis, bone become hypovascular & hypoxic.
Dermatitis & Mucositis
of irradiated area with fibrosis & trismus of muscles.
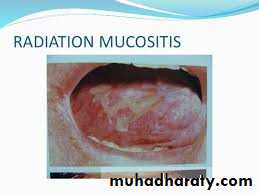
Mucositis
It develops 5-7 days following radiation
(treated by chlorohexidane & instruct the patient to quit smoking ,alcohol & spicy food consumption ).
Effect of Radiation Therapy on Periodentium
XerostomiaPatient needs to improve oral hygiene with fluoride application.
Its associated with teeth & attachment loss.
The radiated patient require prophylactic antibiotics before non-surgical periodental therapy ( There is increase risk of infection so consultation with oncologist).
Osteoradionecrosis risk
It should be assessed before surgery
prophylactic antibiotics ,culture & sensitivity, restrict use of local anesthesia with vasoconstrictors.
Heavy metal intoxication
Ingestion of metals like mercury, lead & bismuthas medication or through industrial contact lead to oral manifestation due to either intoxication or absorption without evidence of toxicity.
Bismuth and lead
Blue black line in marginal gingiva with pre existing inflammation due to precipitation of particles of bismuth sulfide and lead .
Ulcerative gingival stomatitis with pigmentation, metallic taste , salivation ,burning sensation ,sore & inflamed tongue.
Skin lesion and GIT disturbances.
Heavy metal intoxication
Mercury intoxication
Headache ,insomnia ,nerval symptoms,salivation , metallic taste, linear and pigmented gingiva .
It act as an irritant:
_accentuate pre existing inflammation.
_ulceration of gingiva & mucosa .
_destruction of bone.
Heavy metal intoxication
Phosphorus, arsenic & chromium;Inflammation & ulceration of gingiva that is associated with necrosis of bone, loosening & exfoliation of teeth.