Screening
Dr. SIJAL FADHIL
F.I.C.M.S
M.Sc.
M.B.Ch.B.

Definition
– Is the search for unrecognized disease by means of rapidly
applied tests or examinations in apparently healthy
individuals.
– The intention of screening is to identify disease in a
community early ,thus enabling earlier intervention and
management in hope to reduce mortality and suffering
from a disease.

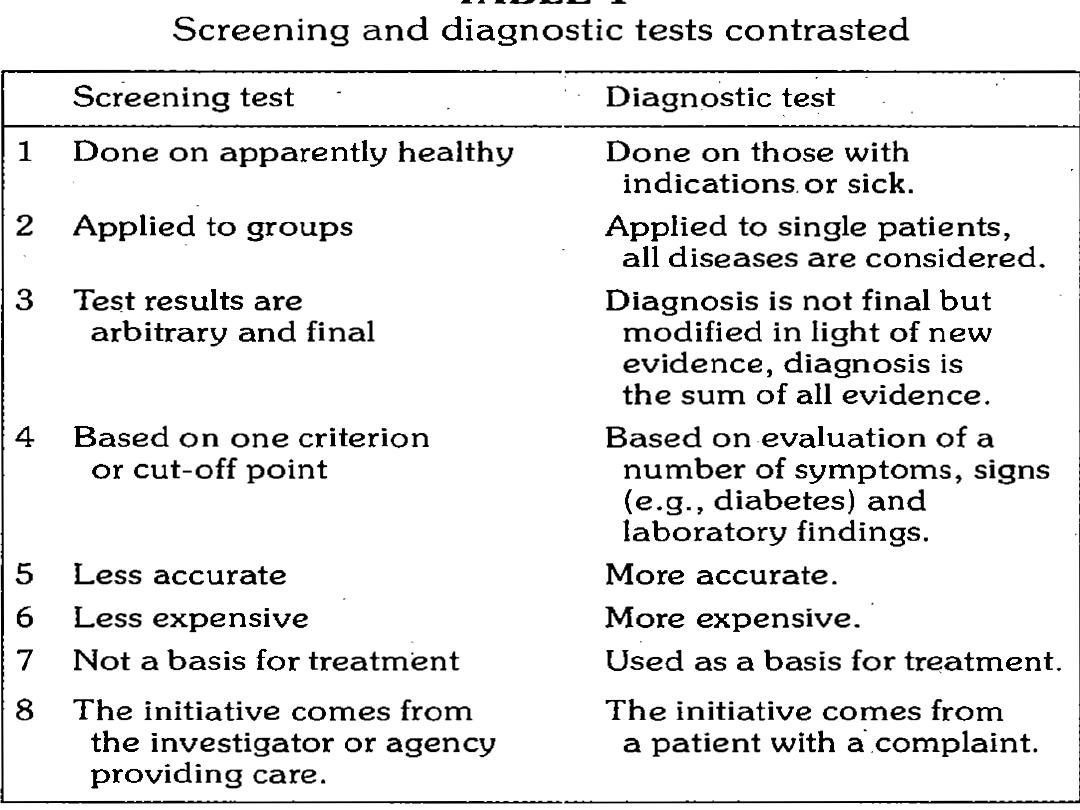
Screening test
– in general: Is a test for a particular disease given to asymptomatic people.
– What are the differences between screening test and diagnostic
test??
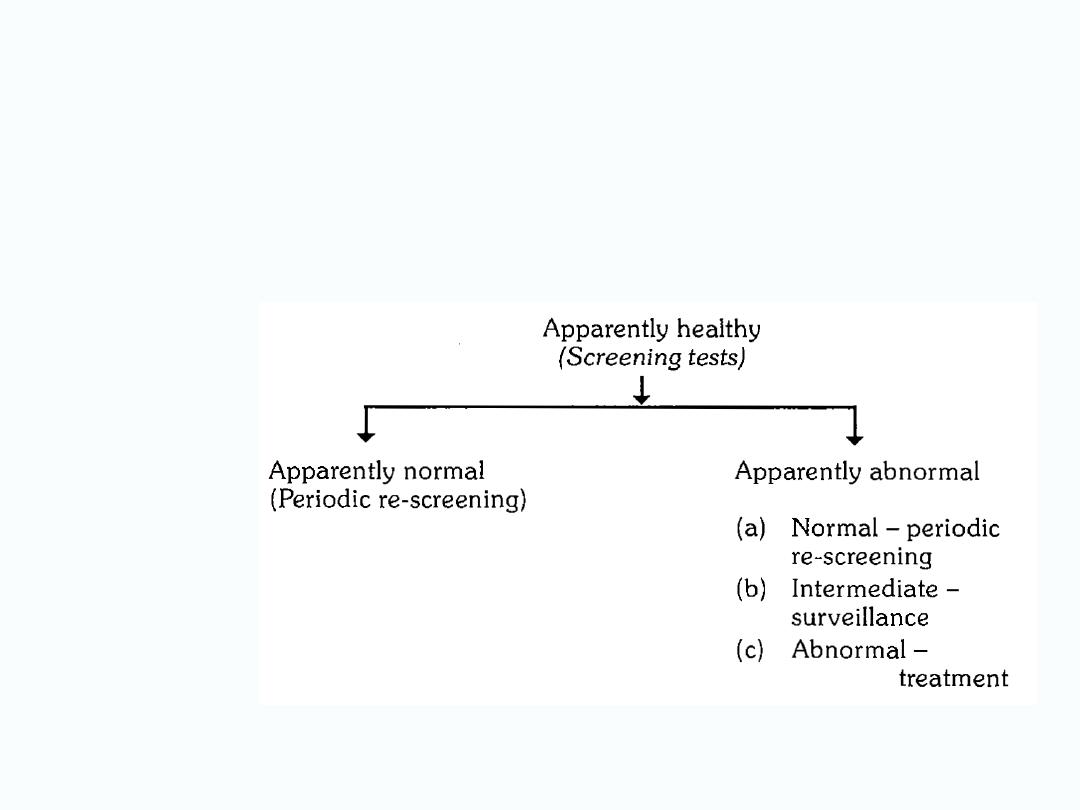
Possible outcome of
screening

Uses of screening
–
1-Case detection:
–
2-Control of disease:
–
3-Research purposes:
–
4-Educational opportunities
:

Types of screening
or population screening: involves the
A: Mass
screening of a whole population with no reference to
high-risk group:
A-Single disease screening: cervical screening.
B-Multiphasic screening: biochemical profiles on
hospital patients.
(targeted) screening: involves identifying
Selective
-
B
members of the population at risk, i.e. test for disease
in high risk group:
A-Single disease screening: CXR for
pneumoconiosis.
B-Multiphasic screening: antenatal examinations.

Opportunistic
screening:
involves
taking
the
opportunity to administer a screening test when the
contact with the individual or group is not primarily for
screening
purposes,
e.g.
during
a
medical
consultation when the individual was attending for an
unrelated health problem.

Examples on screening programs:
#Childhood anemia screening programs are
considered cost effective for targeted
populations
#Cervical cancer screening programs are
considered cost effective for targeted
populations

Criteria for screening
The criteria for screening are based on two
considerations:
1-Disease to be screened:
2-Screeing test to be applied:

1- Disease to be screened
It should fulfill the following criteria:
1-The condition sought should be an important
health problem(prevalence should be high).
2-There should be a recognizable latent or early
asymptomatic stage.
3-The natural history of the condition including
development from latent to declared disease should
be adequately understood
.

4-There is a test that can detect the disease prior to
the onset of signs and symptoms.
5-Facilities should be available for confirmation of
the diagnosis.
6-There is an effective treatment.
7-there should be an agreed-on policy concerning
whom to treat as patients(e.g border line diabetes)

8-There is a good evidence that early
detection and treatment reduces morbidity
and mortality.
9-The expected benefits of early detection
exceed the risks and costs.

2-screening test to be applied
1-Acceptability:The test should be acceptable
to the people at whom it aimed
2-repeatability(reliability):
It means the test must give consistent results
when it repeated more than once on the same
individual under same conditions

It means the results of the test are precise(exact),so
repeatability is some time called precision,
reliability or reproducibility
It depends on:
1- observer variation :
A-intra-observer variation(within observer): same
observer taking 2 or more readings give varied
results.

B-Inter-observer variation (between -observer):
variation between different observers on same
subject/material
2-Biological (subject) variation:
it occurs due to:
A-changes in parameters observed.
B-variation in perceptions and answers of patients.
C-Regression to the mean.

3-Error relating to technical methods:
A-defective instrument
B- erroneous calibration
C-Faulty reagents
D-inappropriate/unreliable test

3-validity(accuracy):it refers to what extent
the test accurately measures which is
suppose to measures, that means a valid test
distinguish the people who have the disease
From those who do not.
It has 2 components:
Sensitivity and specificity
4-Others(simplicity,safety,rapidity,low
cost,and ease of administration)
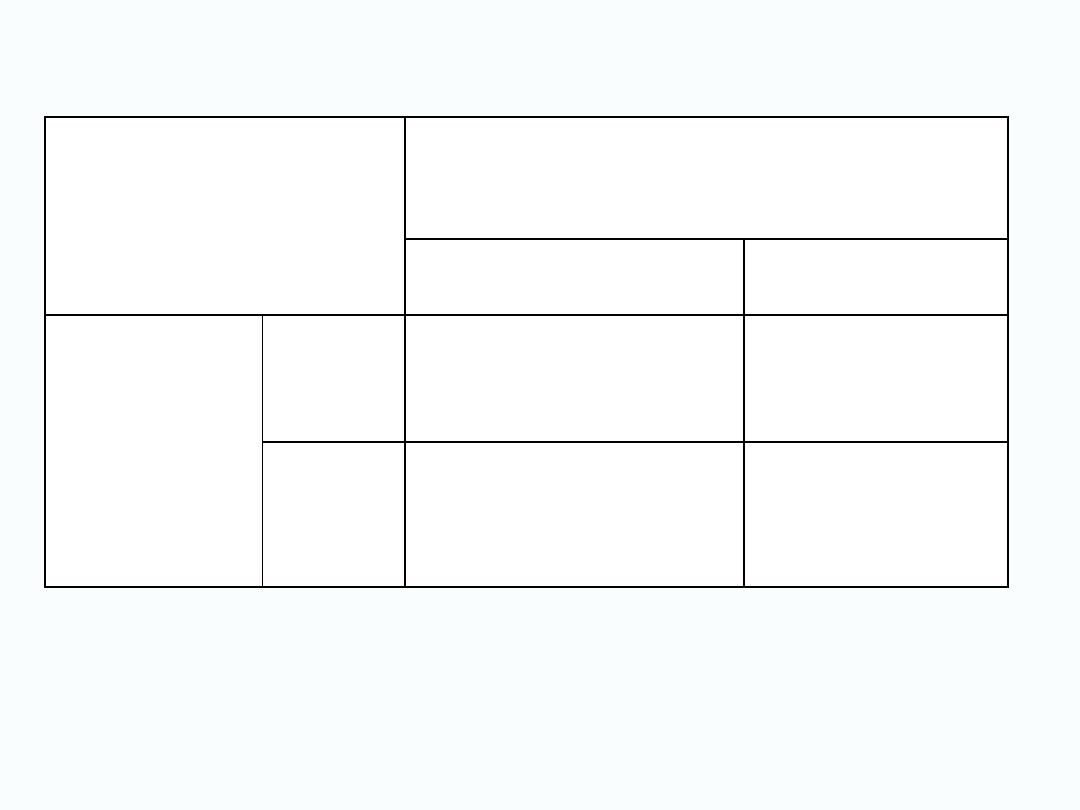
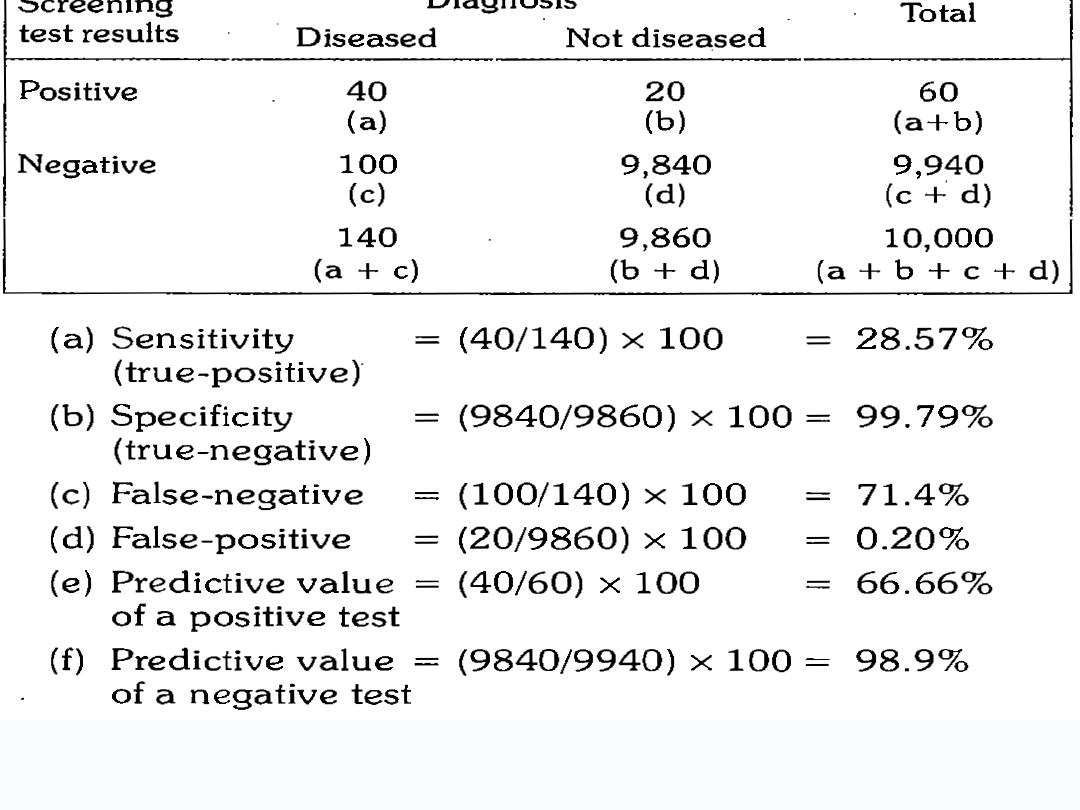
Diagnosis
Disease
Not diseased
Screening
test
positive
TP (true positive)
FP (false positive)
negative
FN (false negative)
TN (true negative)

Measures of validity of screening test
Sensitivity: The ability of the test to identify
correctly all those who have the disease,
that is (true positive).
SN = [TP / (TP +FN)] x100% = TP%…….the
denominator represents diseased people.
SN(TP%) = a/a+c x100%

Specificity: The ability of the test to identify
correctly those who do not have the disease
(true negative)
SP = [TN / (TN +FP)] x100 %= TN%… the
denominator represents non-diseased
people.
SP(TN%) =d/b+d x100%

Predictive value
In addition to SN and SP ,the performance of
predictive value
screening test is measured by the
diagnostic power of the test .
which reflect the
The predictive value measures whether or not an
individual actually has the disease given the results
of the screening test

(Predictive value of the positive test):
PVP
It is the percentage of truly diseased
people among those who show positive
test results
PVP = [TP / (TP + FP)] x100 %
PVP= a/a+b x100%

(Predictive value of the negative test):
PVN
It is percentage of healthy people among
those who show negative test results.
PVN = [TN / (TN + FN)] x100%
PVN= d/c+d x100%

1-
TP
is directly related to
SN
FN
is inversely related to
SN
TN
is directly related to
SP
FP
is inversely related to
SP
2-PVP depends on:
SN , SP , prevalence of disease

FP %= [FP / (FP + TN)]x100%
FP%=b/b+d x100%
FP%= 1-SP
FN % = [FN / (TP + FN)] x100 %
FN%=c/a+c x100%
FN%=1– SN
Criterion Standard Test
Screening
test
Disease (+)
Disease (-)
Test (+)
True positive rate (TP%) or (SN)
False positive rate (FP%) or (1-SP)
Test (-)
False negative rate (FN%) or (1-SN)
True negative rate (TN%) or (SP)
