• DENTAL MANAGEMENT
• OF THE MEDICALLY COMPROMISED• PATIENTS
• Who are Medically Compromised Patients?
• Dental management:
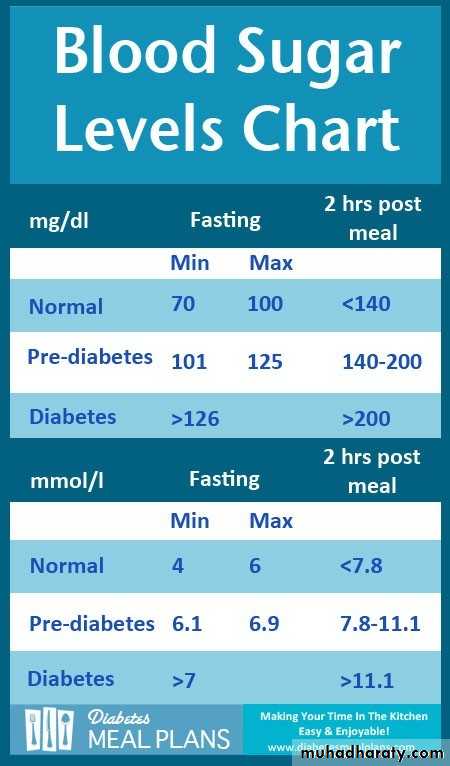
• 1.Defer surgery until the diabetes is well controlled; consult the patient’s physician.• Schedule an early morning appointment; avoid lengthy appointments.
• Use an anxiety-reduction protocol, but avoid deep sedation techniques in outpatients.
• Dental management:
• Monitor pulse, respiration, and blood pressure before, during, and after surgery.• Maintain verbal contact with the patient during surgery.
• Have the patient eat a normal breakfast before surgery and take the usual dose of insulin/hypoglycemic agent• REGIMEN FOR HYPOGLYCAEMIA
• HYPERTENSIVE DISEASES
• ANGINA PECTORIS
• DENTAL MANAGENT OF ANGINA:
• Medical consultation• Reduction of stress & anxiety CLONEZAPAM 1 MG (0+0+1) 10 Days
• Local anesthesia
• General anesthesia
• Treatment procedures MINIMAL INVASIVE
• Drugs used in treatment SUBLINGUAL TRINITRATES
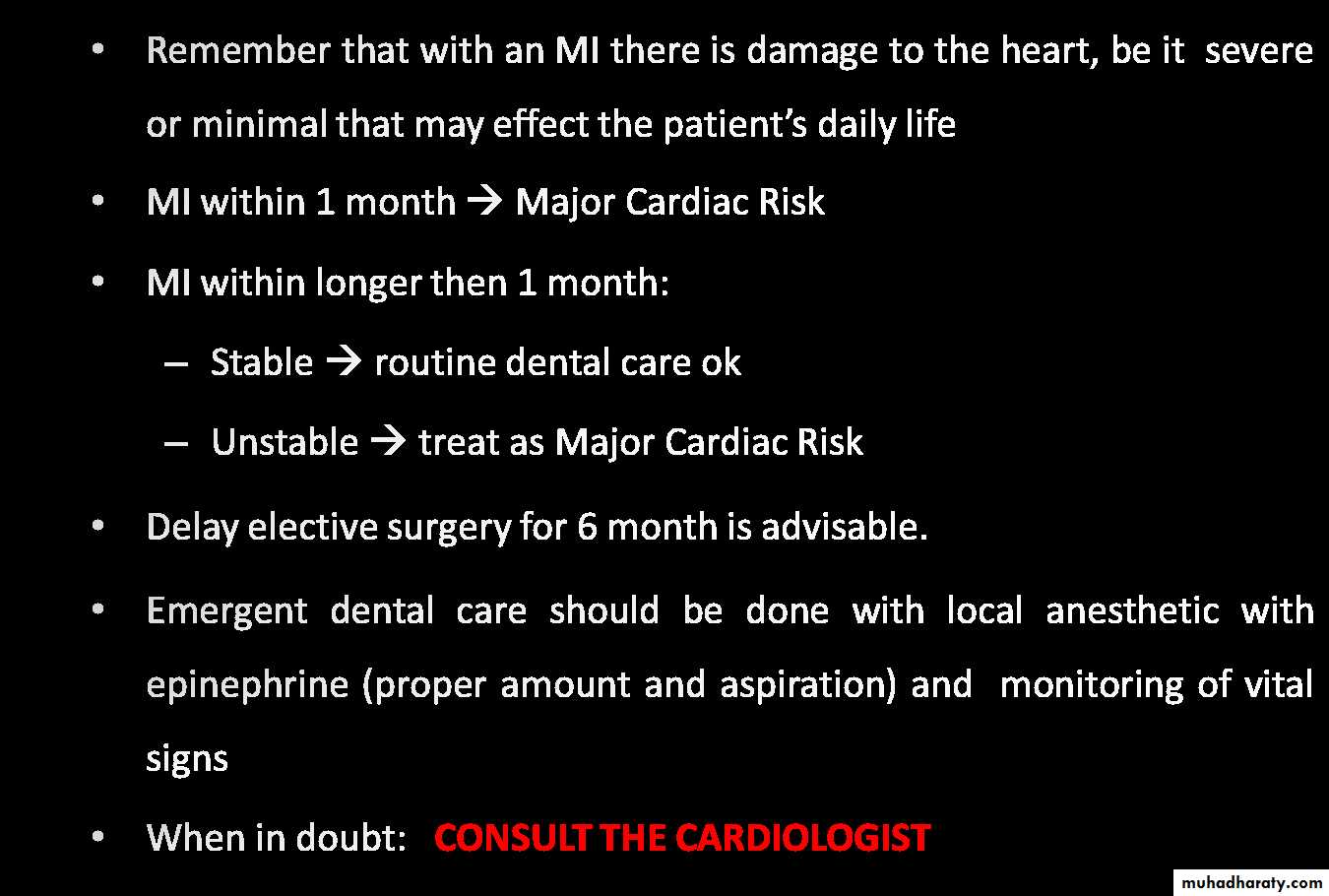
• MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
• CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE
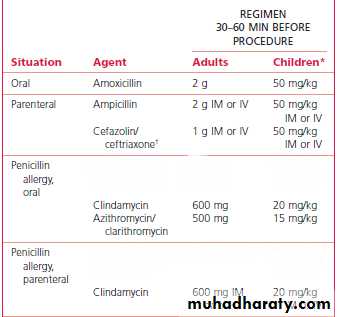
• PROPHYLACTIC ANTIBIOTIC REGIMEN FOR CARDIAC PT.
• IF PATIENT IS ALLERGIC:
• Adult --------- Clindamycin 600 mg OR• Azithromycin 500 mg OR Cephazolin 1 gm
• (1 hour before Orally)
• ( ½ ,,, ,,,, injection)
• Child --------- Clindamycin 20 mg per Kg.
• Azithromycin 15 mg per Kg.• 2. Under G.A
• a)Adults----- 1gm Amoxicillin I.V at induction.• OR 3gm Amoxicillin orally 4 hours before induction followed by 3gm Amoxicillin immediately after recovery.
• OR 300mg Clindamycin I.M ½ hour before induction.
• OR 300mg Clindamycin I/V at induction
• b) Children ------ (5–10 years)1/2 adult
• (< 5 years) 1/4 adult• Use an anxiety-reduction protocol.
• Have nitroglycerin available; use it prophylactically if the physician advises.• Administer supplemental oxygen (optional).
• Provide profound local anesthesia.• POST Myocardial Infarction
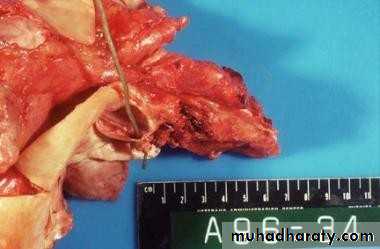
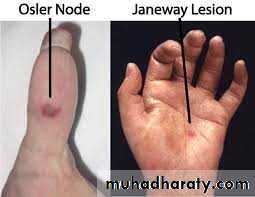
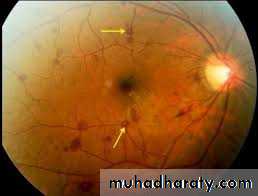
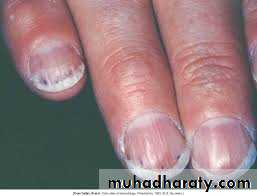
• Infective Endocarditis
• Diagnosis – Duke’s Criteria
• Complications
• Prolonged Bleeding – Failure of Haemostasis• Severe Internal Bleeding – Risk of Shock
• High risk of Postoperative Infections.
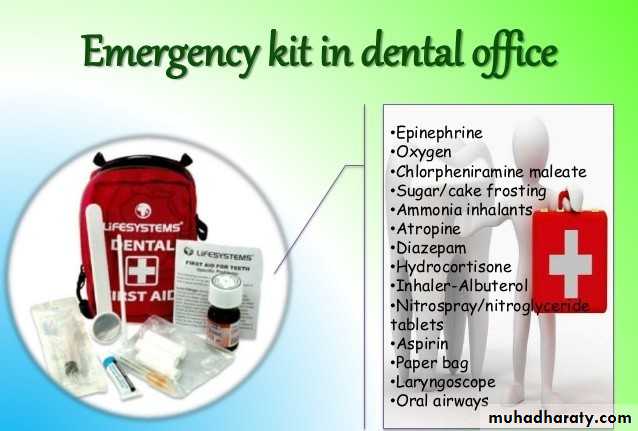
• Emergency in MC Patients
• RESPIRATORY DISORDERS
• BRONCHIAL ASTHMA
• Dental management
• 1. Medical consultation.• Emotional stress factors can precipitate
• an attack, nitrous oxide sedation is suggested
• Morphine is contraindicated
• Bronchodilator inhaler should be available
• asthma is well
• no signs of a• Dental management
• 1. Defer dental treatment until the controlled and the patient has respiratory tract infection.
• 2. Use an anxiety-reduction protocol, including nitrous oxide, but avoid the use of respiratory depressants.
• is or has provide
• been chronically prophylaxis for
• taking adrenal
• 3. If the patient corticosteroids, insufficiency.
• Keep a bronchodilator-containing inhaler easily accessible.
• Avoid the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in susceptible patients.
• LIVER DISORDERS
• Dental management