
Obstetrics
د. بان عامر موسى
Lec. 5
المرحلة الرابعة
Induction of labour (IOL)
Induction of labour (IOL):- is defined as the artificial
initiation of labor , it is considered when the risk–benefit
analysis indicates that delivering the baby is a safer option for
the baby, the mother, or both, rather than continuing the
pregnancy, and when there are no clear indications for
caesarean section and no contraindications for vaginal
delivery.
Indications :-
Post-term gestation,
prelabour rupture of membranes (at term and preterm)
fetal growth restriction
medical disorders (such as hypertensive disorders of
pregnancy),
suspected fetal macrosomia,
intrauterine fetal death,
multiple gestations,
chorioamnionitis
maternal request
IOL is not used when there are contraindications for vaginal
delivery such as transverse lie , placenta previa , previous
classical C\S or previous myomectomy through endometrial
cavity .
Relative contraindication : women with previous C\S has
increased risk of uterine rupture.
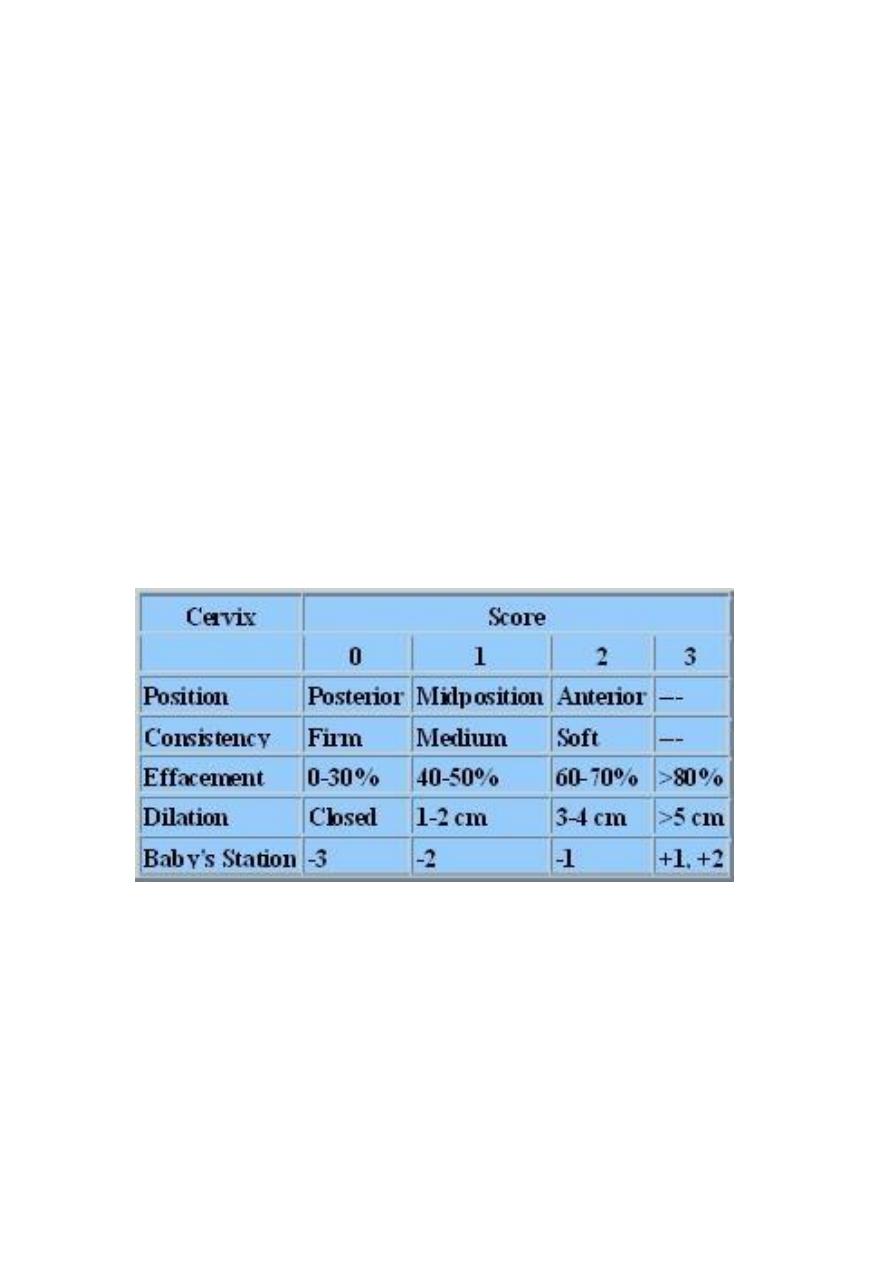
Success of IOL
IOL is most successful when the cervix is ripe at the time of
induction .Clinically , the most commonly used assessment of
cervical ripping is the calendar modification of the Bishop score
.this score composed of five components of the cervix , all
assessed on vaginal examination ( cervical length ,dilatation
,consistency, position and its station relative to the ischial spine .
Labor induced with unripe cervix will require more uterine
contractions to effect cervical dilatation , potentially causing a
longer labor , more pain and stress for both mother and baby ,
high risk of uterine rupture , increased risk of C\S delivery .
When the score > 8 the likelihood of successful indication was
good and the C/S rate was uncommon .
NOTE :-
Add 1 point for Preeclampsia and Each previous vaginal
delivery
Subtract 1 point for Postdate , Nillipara and PROM

Pharmacological and mechanical method of IOL
-
Mechanical methods :
Extra amniotic saline solution infusion , Laminaria and extra
amniotic folly's catheter but all of these increase the risk of
maternal infection .
Membrane sweeping is recommended on routine antenatal
visits as it reduces the risk of pregnancy prolongation beyond 41
weeks .
Forewater amniotomy ( ARM =Artificial Rupture Membrane )
-
Medical methods :
PGE2 (dinoprostone), PGE1(misoprostol)
Oxytocin infusion
Complications of IOL
The most common complication of induction of labor is the risk
that procedure is not successful and the labor does not ensure
which occur in around 15% of primi with unfavourate cervix
,but less commonly in multi or those with high bishop score
from the start .
C\S is widely considered a complication of IOL .
Hyper stimulation which define as contraction frequency of
more than 5 in 10 min. or contraction exceeding 2 min. in
duration .
Tachy systole occur when uterine hyperstimulation is
accompanied by an abnormal FHR pattern , which require
immediate delivery by C/S , in the presence of less severe FHR
alteration , tocolysis eg. Terbutalin may be sufficient to treat
hyperstimulation in the majority of women .

Assessment of fetal maturation
1-LMP if regular cycle.
2-serum or urine PT
3-early U/S (1
st
trimester )
Monitoring
CTG should perform to confirm that FHR is normal prior to
PG insertion and then should be repeated when contraction
begin 2-6 hr. after PG administration.
