CONGENITAL
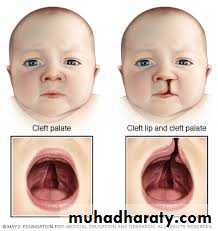
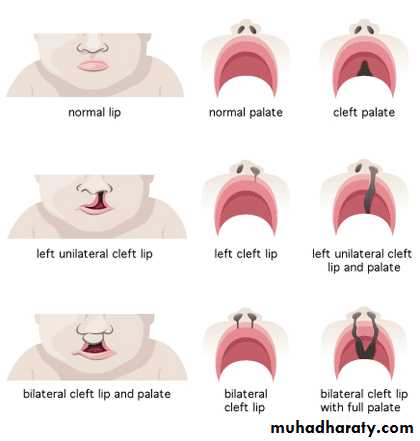
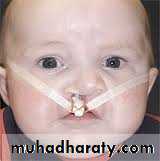
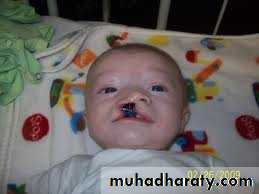
Cleft lip and palateNormally, the tissues that make up the lip and palate fuse together in the 2nd and 3rd months of pregnancy.
But in babies with cleft lip and cleft palate, the fusion never takes place or occurs only part way, leaving an opening (cleft).
. Risk factors :
The incidence of cleft lip and palate is one in 600 (1:600) live births,1-famelial , family history of cleft lip and palate in which the first-degree relative
2-racial : - caucasian and Iceland have high incidence than nigros
3- X ray during pregnancy
4-rubella during pregnancy
5- vitamin deficiency
6- Environmental factors implicated in clefting include maternal epilepsy and drugs (e.g. steroids, diazepam, phenytoin
.
distribution of cleft types is:
• cleft lip alone — 15 %; this deformity affects the left side in 60 % of cases
• cleft lip and palate ------45 % ;which is predominates in males
• isolated cleft palate — 40 % more common in femalesEffect upon function
1- sucking and eating more in cleft palat2- speech unable to make constant sound
(k, g, p, b, ,d, t)
3- teeth
4- nose due to contamination with oral organisim
5- hearing problem due to repeated inf acut or chronic Otitis M
Antenatal diagnosis
An antenatal diagnosis of cleft lip, whether unilateral or bilateral, is possible by ultrasound scan after 18 weeks of gestation.
management
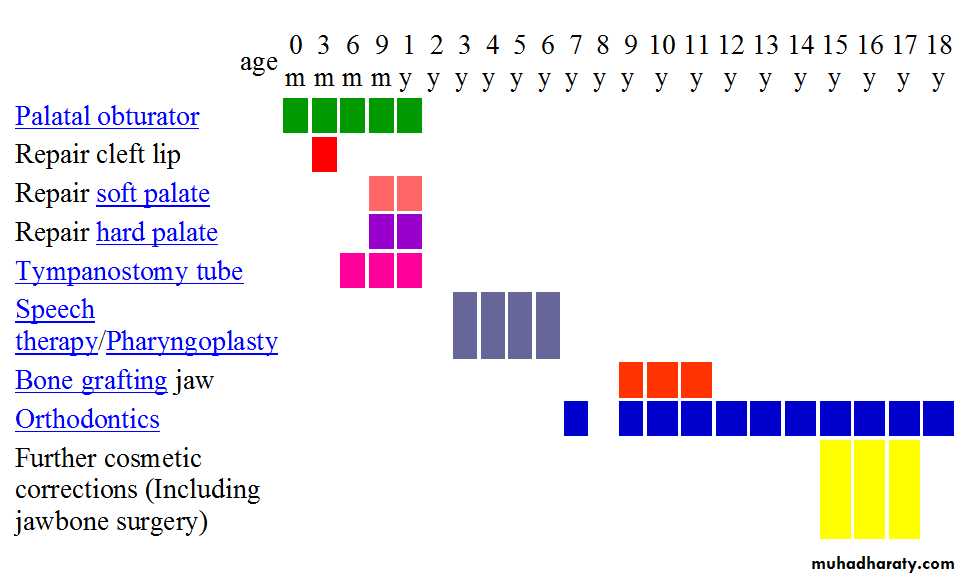
A craniofacial team is routinely used to treat this condition to provide patients with comprehensive multi-disciplinary care from birth through adolescence.
1-Primary management pre-surgical advice
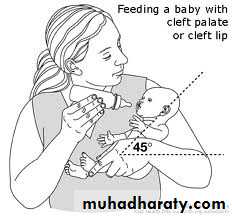
FeedingSimple measures, such as
-- enlarging the hole in the teat, position of feeding
-- For cleft plates palatal obturator (a prosthetic device made to fit the roof of the mouth covering the gap).
Airway
Intermittent airway obstruction is more frequent during sleep and feeding can be life threatening. and managed by:-
--nursing the baby prone.
--nasopharyngeal intubation ’ to maintain the airway in more severe cases
Feeding care
Strapping To reduce the distance of defect with growing
Latham appliance
One of the new innovations of cleft lip and cleft palate repair is surgically inserted by use of pins during the child's 4th or 5th month. After it is in place, the doctor, or parents, turn a screw daily to bring the cleft together to assist with future lip and/or palate repair.2-The Surgical management
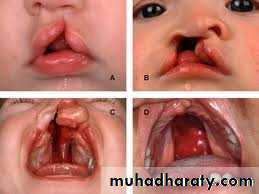
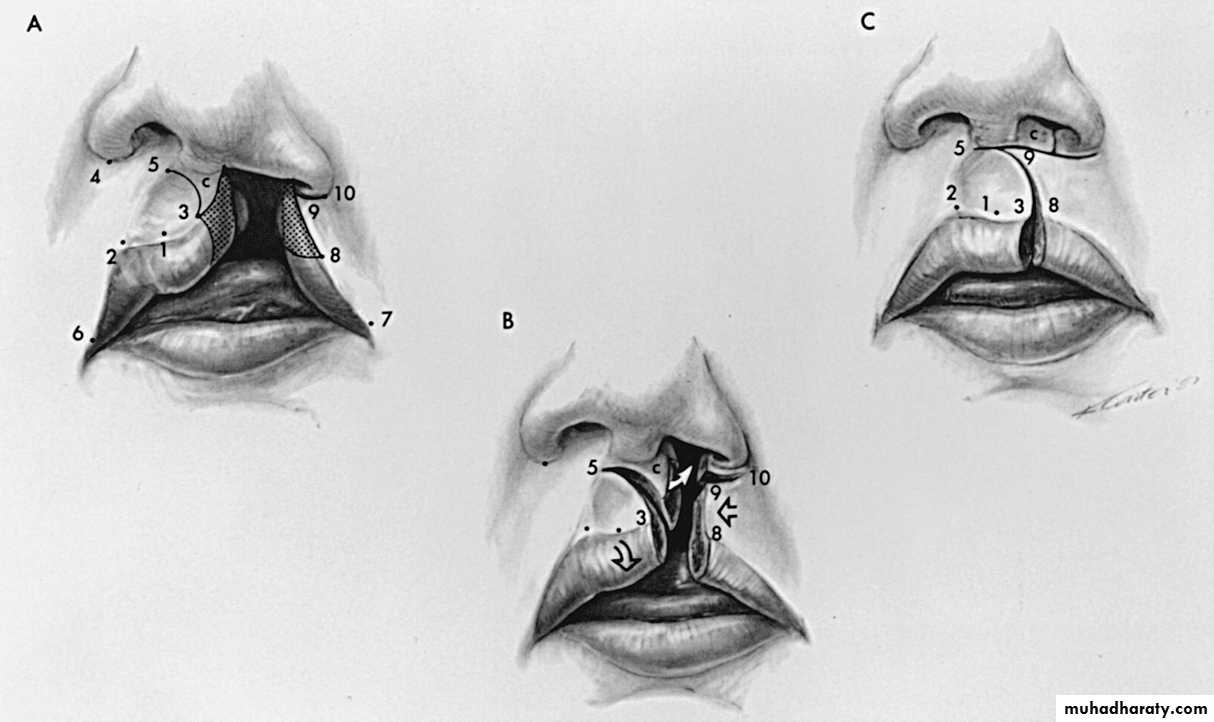
--Millard operation for Cleft lip repairperformed between 3 and 6 months of age, (skin flaps done then reconstruction of orbicularis oris )
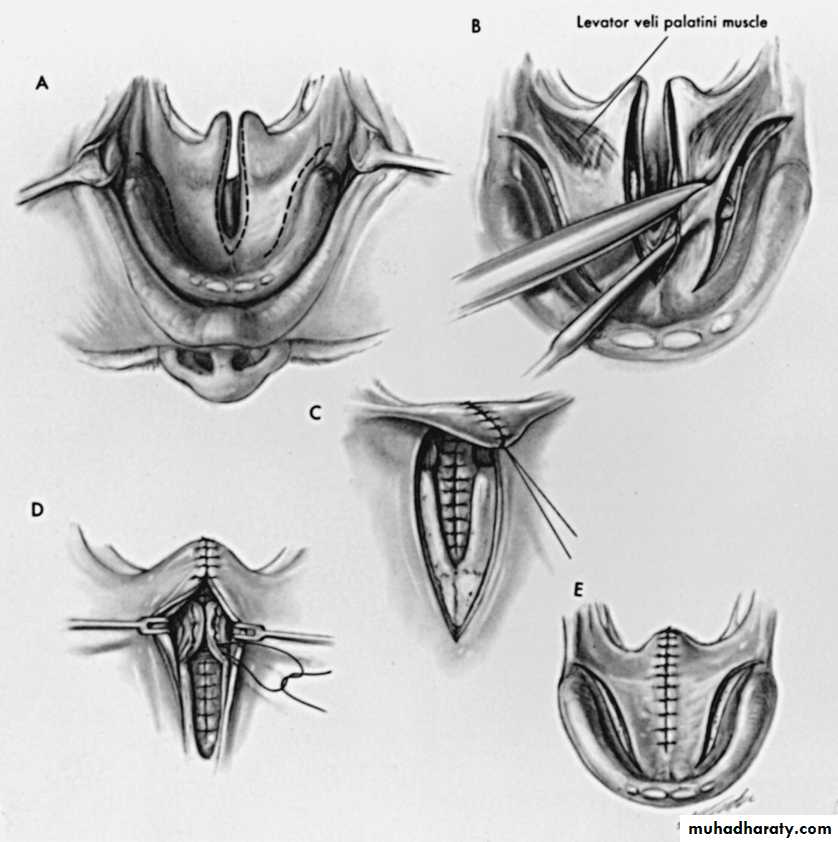
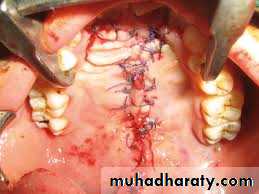
-- palatoplasty .V-Y plasty and 4 flaps for cleft palate repair
performed between 6 and 18 months, Cleft palate closure can be achieved by one- or two-stage
Millard operation
6m girl 1m after op 8y old
3-Secondary management
Hearingshould undergo regular audiological assessment before 12 months of age , if sensori neural hearing loss is managed with a hearing aid,
Speech
Initial speech assessment should be performed early (18 months)
secondary palatal surgery:
— speech-training devices.
— other operations
-- intravelar veloplasty (muscular reconstruction of soft palate);
-- pharyngoplasty;
Dental
delayed tooth development and delayed eruption of teeth; morphological abnormalities
All children with cleft lip and palate should undergo regular dental examination.
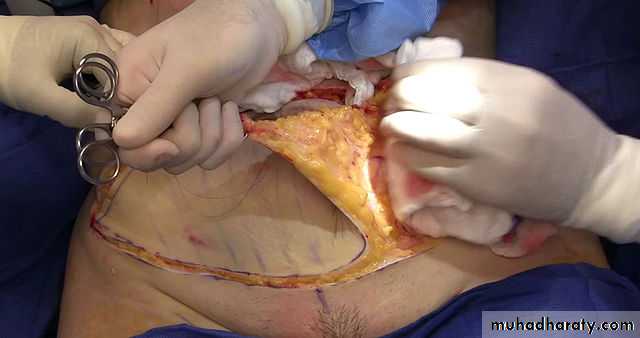
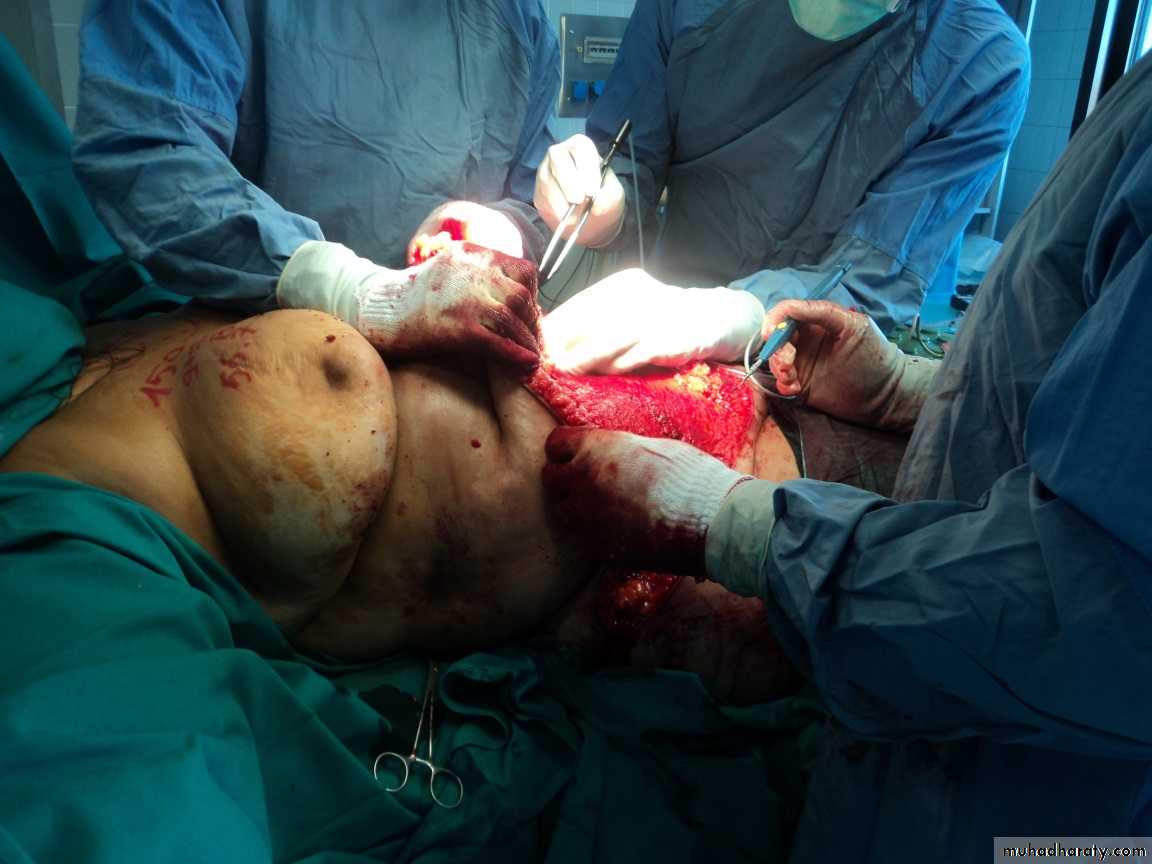
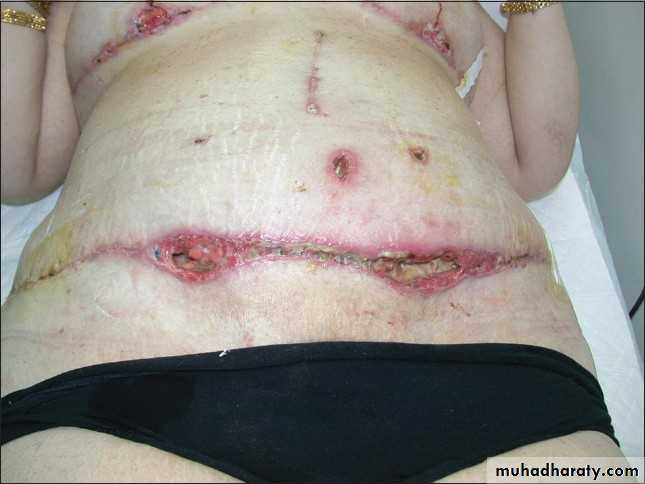
Abdominal wall reconstruction (abdomenoplasty)
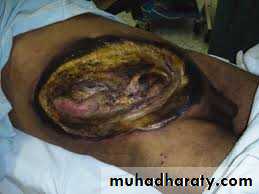
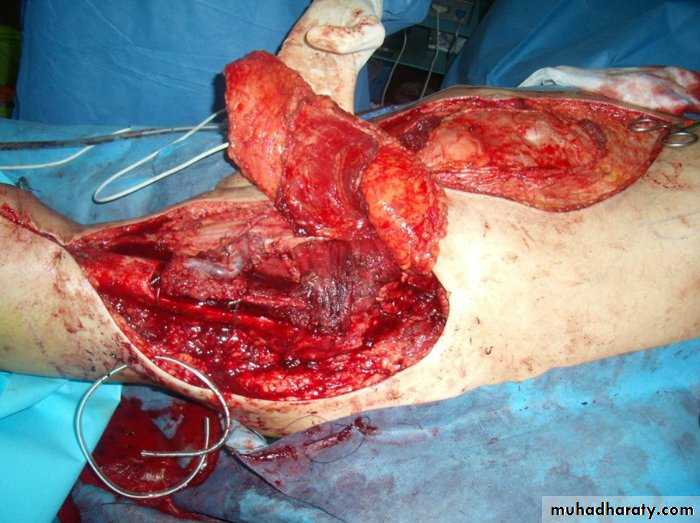
1- Large defect of abdominal wall reconsitruction after:-- Trauma
- infection( progressive bacterial synergestic gangrene
-after surgery for cancer, resection of fistulas,
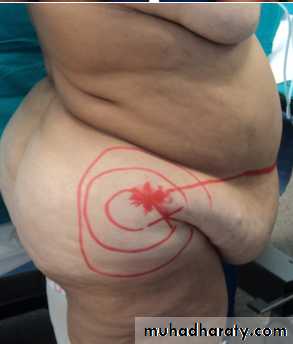
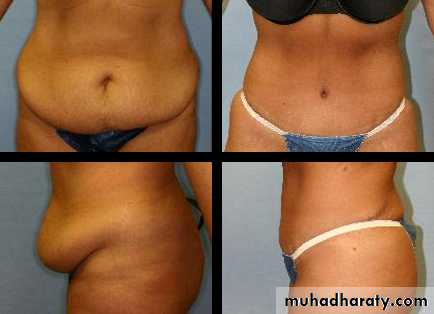
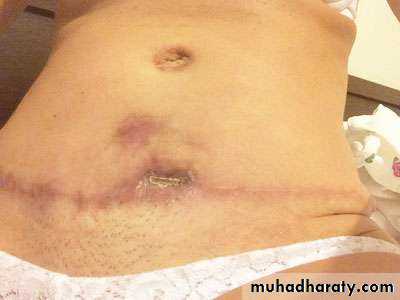
2-Abdomenoplasty for pendulous abdomen
Usually after multipregnancy , sever loss of Wt
(mini tummy tucks vs. full tummy tucks)
Bacterial synergestic gangrene
1-abdominal wall reconstruction
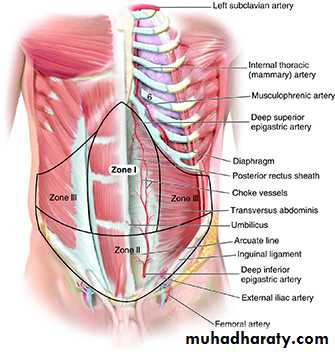
Blood supplyterritory
Zone
Deep epigastric arcade
Midcentral abdominal wall above the umbilicus.
I
Epigastric arcade, superficial inferior epigastric, superficial external pudendal and superficial circumflex
Lower abdominal wall below umbilicus.
II
Intercostal, subcostal, and lumbar arteries
Lateral abdominal wall..
III
should be asses the defect result from trauma or tumor removal, evaluate size of missing tissues and donor vessels as well as planning for flap transfer depend on the zone defected :-
methods of reconstruction.
Zone I the upper abdomen rectus abdominis muscle flap,
external oblique muscle flap,
latissimus dorsi muscle flap,
Zone II mid-abdomen,
rectus abdominis muscle flap,
rectus femoris muscle flap ,
tensor fascia lata flap,
Zone III suprapubic and groin areas.
tensor fascia lata flap
groin flap,
gracilis muscle flap
rectus abdominis muscle flap
Bacterial synergestic gangrene
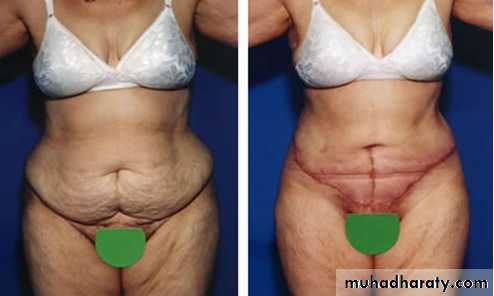
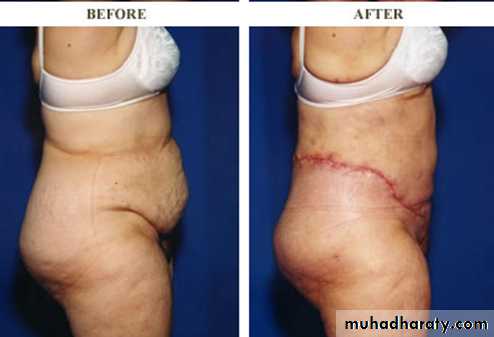
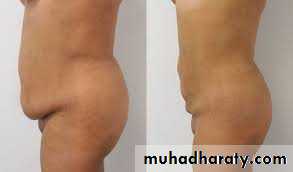
2-Abdomenoplasty for pendulous abdomen (mini tummy tucks vs. full tummy tucks)
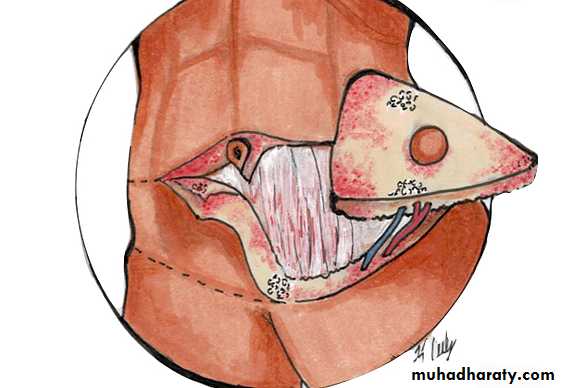
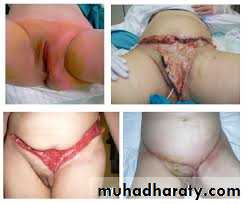
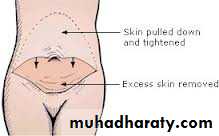
pendulous abdomen usually result after pregnancy , obesitythe transverse incision should be low down ,can change position of umbilicus by do island flap , excise the excess of skin and fat
full tummy tucks
mini tummy tucks
A good candidate for Abdominoplasty Surgery (Tummy Tucks):
1-Is close to their ideal body weight (within 30%)
2-Wants to remove specific areas of loose skin or fat that is diet- and exercise-resistant
3-Weight has been stable for 6 months or more
4-Has good skin tone and elasticity
5-Has realistic expectations , emotionally stable Understands the risks of surgery
Procedure:-
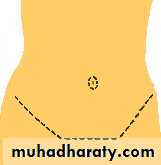
-- incision around umbilicus :-full tummy tuck involves an incision around the umbilicus and across the lower abdomen,
mini tummy tuck leaves the umbilicus intact and requires a smaller incision.
--Liposuction is sometimes
employed and the fat is
removed from below the
umbilicus
-- tightening muscles
from the umbilicus to the
pubis.
complications:
1-Bleeding ,Hematoma (risk is 3-4%)2-Infection (risk is less than 1 %)3-Keloid (heavy scar)4-Puckered skin and Skin irregularities 5-Seroma6-Skin necrosis or skin death (more likely with smokers)7-Slow healing8- wound dehecenceCosmetic surgery
Operative procedure in which the principal purpose is to improve the appearance,, especially on the face. Also called aesthetic surgery
Cosmetic operations include those on the nose (rhinoplasty), the ears (otoplasty), the chin (mentoplasty) and the breasts (augmentation or reduction mammoplasty)
Who is a Good Candidate?
People who have health problems such as DM, HT, lung disease, heart disease, high cholesterol, arthritis, emphysema, are malnourished, severely depressed, obese and/or smokers are not generally good candidates for cosmetic surgery.So the good candidates
1-ideal weight (within 30%),2- non-smokers, if smoker should stop for at least 2 weeks prior to surgery and remain smoke-free until at least 2 weeks after surgery,
3- emotionally stable, with low stress, exercise and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
4-. A good candidate person who accepts the disadvantages of plastic surgery (cost, inconvenience, discomfort, and medical risk).
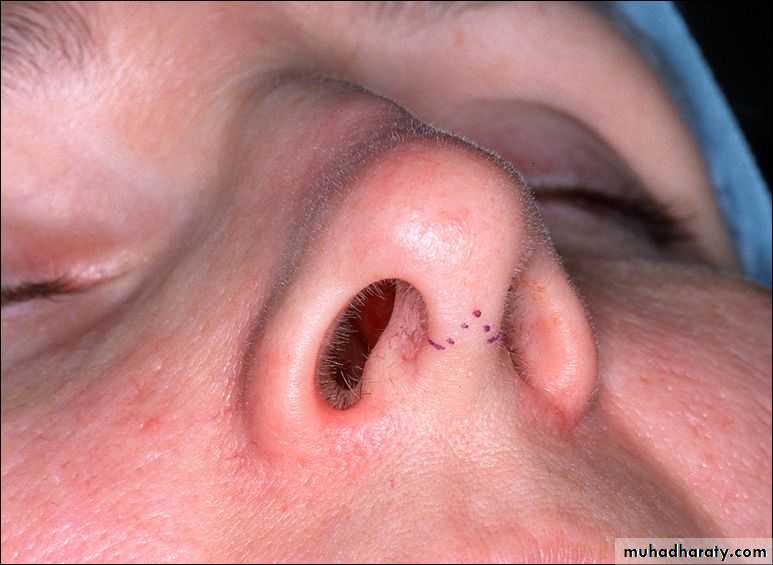
Nose Rhinoplasty
Rhinoplasty is change irregularity of nasal contour
-- performed after the nasal skeleton has matured in adolescence.
Types of Rhinoplasty
open rhinoplasty or closed rhinoplasty
In open rhinoplasty,
the surgeon makes a small, irregular
incision to the columella( fleshy
external end of the nasal septum,).
In closed rhinoplasty, surgeon
performs incision endonasally(exclusively within the nose), and
does not cut the columella
Types of rhinoplasty – primary and secondary
primary rhinoplasty reconstructive, functional, or aesthetic corrective procedure.The midline dorsal prominence osteotome for the bone and a scalpel for the cartilage. The medial borders of the upper lateral cartilages may require resection as they also produce some dorsal prominence.
septal deviation, which may interfere with nasal breathing and alter the timbre of the voice.
the mucoperichondrium is elevated from both sides of the septum through an incision in the membranous septum
secondary rhinoplasty revision of a failed rhinoplasty, 5–20 % of rhinoplasty operations
The corrections usually "open approach", is more technically complicated, usually because the nasal support structures either were deformed or destroyed in the primary rhinoplasty
Rhinoplasty midline dorsal prominence
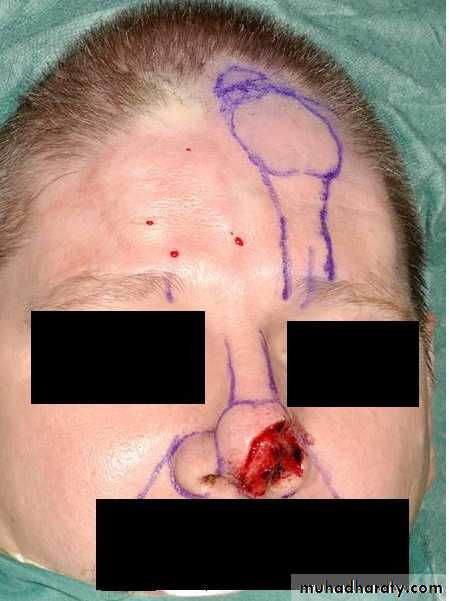
Reconstruction rhinoplasty
Reconstruction rhinoplasty is indicated for the correction of defects and deformities caused bySkin cancer. The most common cause for a nasal reconstruction melanoma and BCC
Traumatic nasal defect.
Less common blunt (impact),
penetrating and blast trauma.
Congenital deformities. Cleft lip and palat .
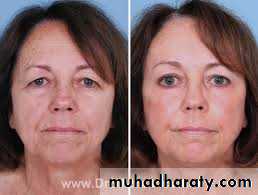
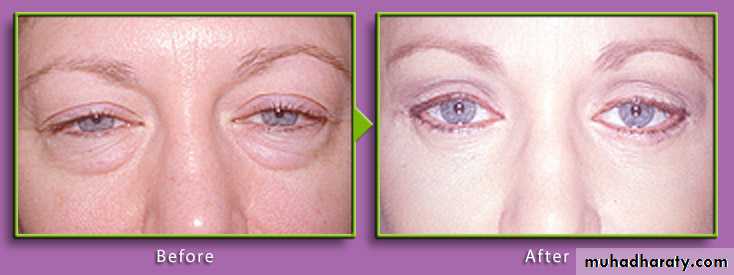
:Eye lid Blepharoplasty and brow lift
wrinkles. Around eye may be due to:-- Excess skin in the upper and lower eyelids
- herniated periorbital fat
- can be a familial characteristic that worsens with age.
can be corrected by a blepharoplasty or a blepharoplasty combined with a brow lift.
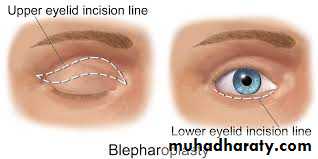
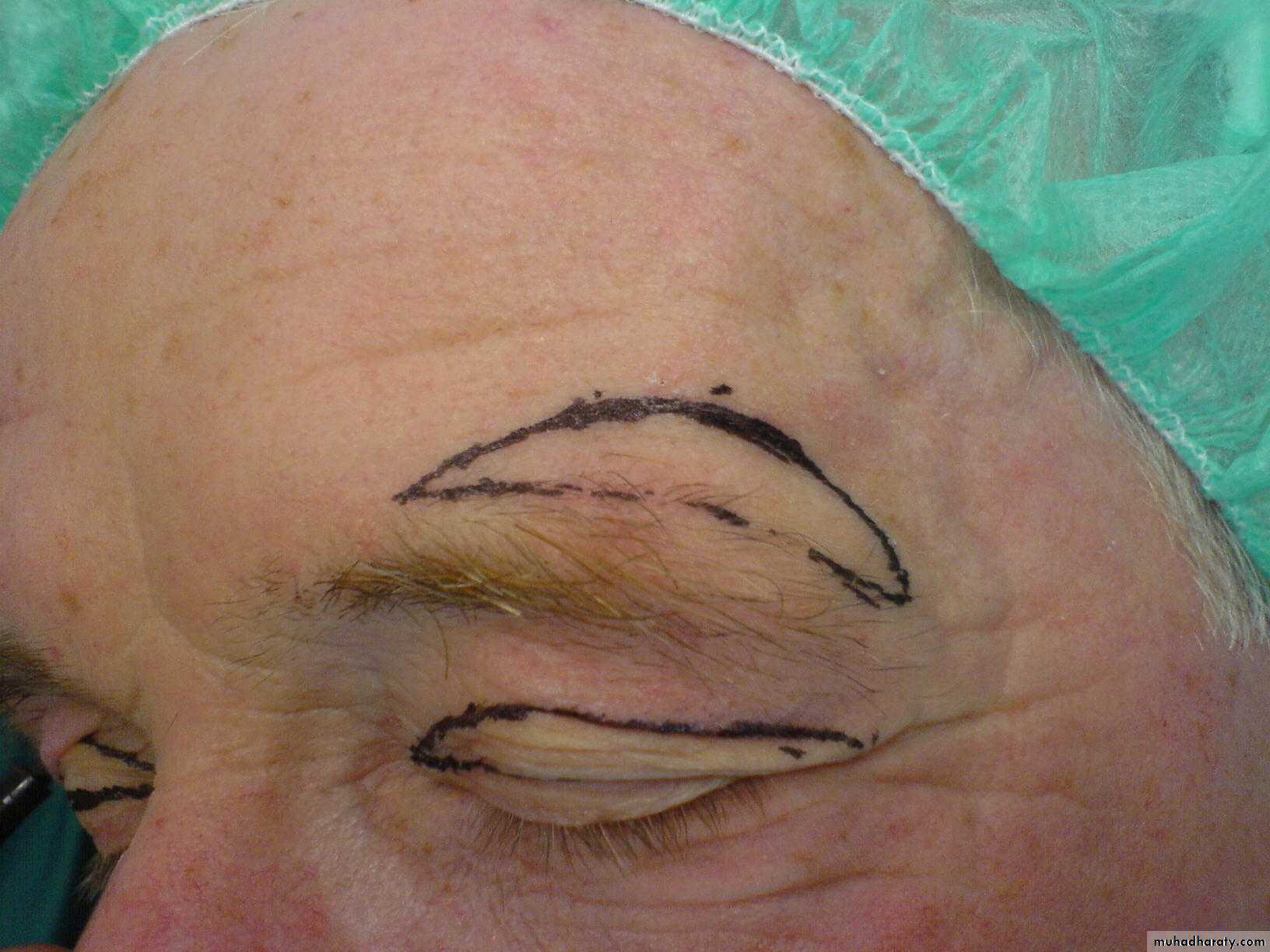
subciliary incision carried out laterally into one of the laterally radiating wrinkles.
The incision can also be created through the conjunctival fornix. Through the subciliary incision the skin and orbicularis oculi muscle are elevated as a single flap.
Blepharoplasty
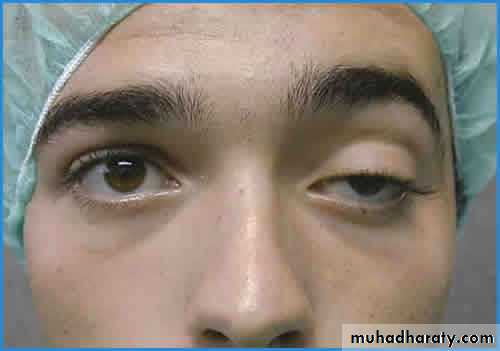
treatment of ptosis
The therapy of choice is not an upper lid blepharoplasty, but rather a direct brow-lift.Ear otoplasty
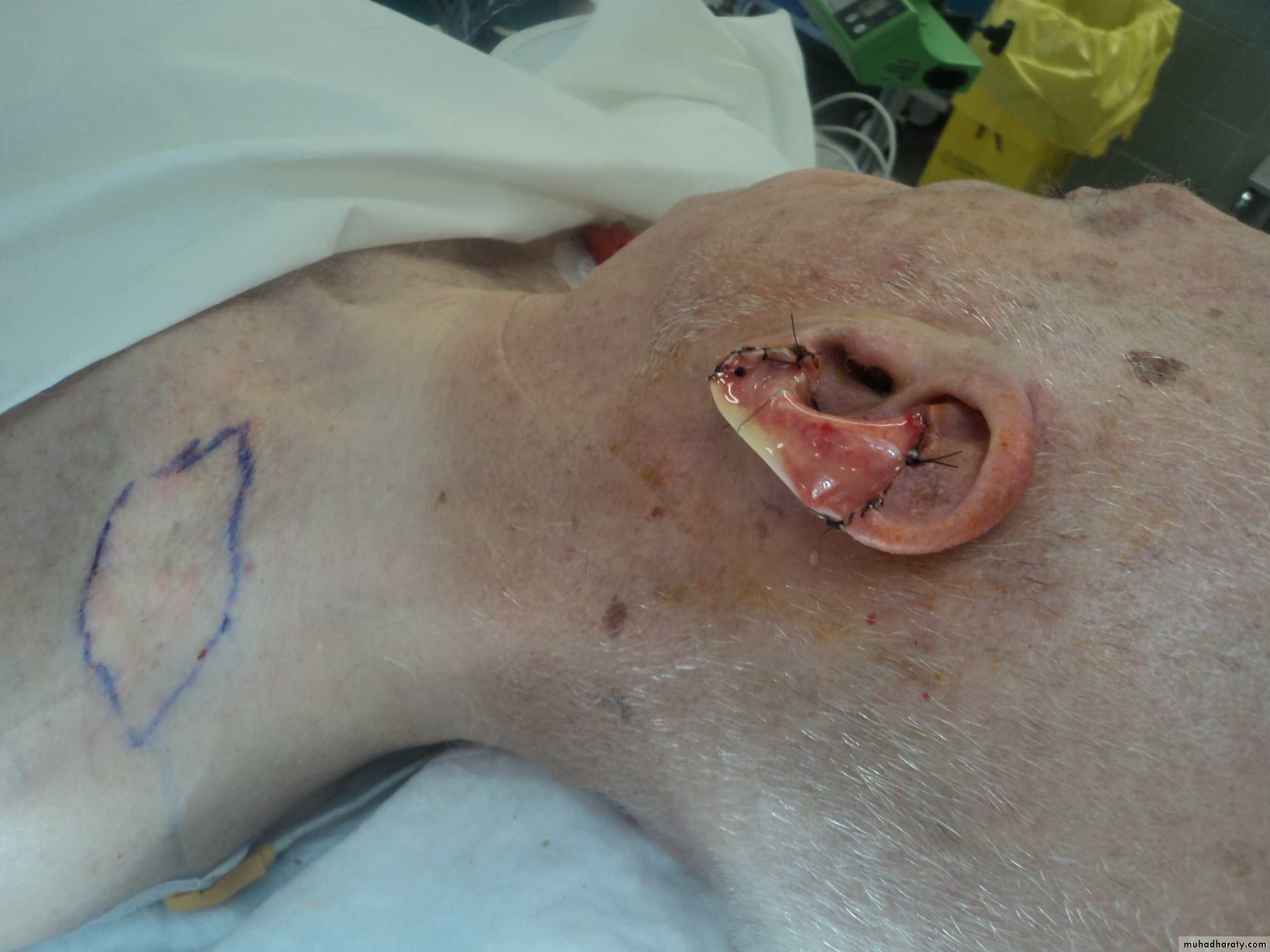
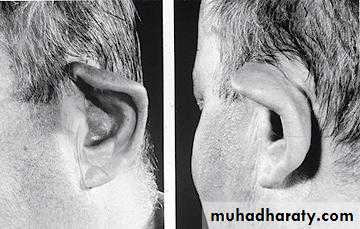
Reconstruction of all or part of the ear for either a congenital or a post-traumatic defectrequires a cartilage framework and a thin-flap skin cover.
The best source of cartilage graft is the confluence of the lower costal cartilages
Cauliflower ear
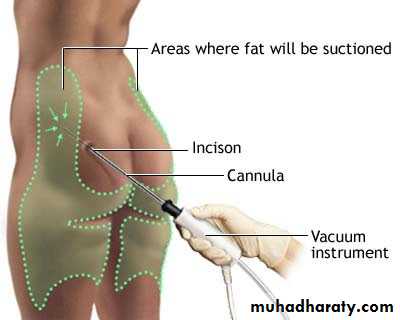
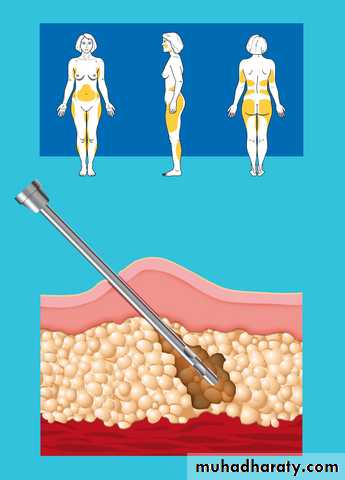
Liposuction (lipoplasty)
--is removes very stubborn fat from body--Can reinjected to another areas of body
--can be performed on many parts of the body including the stomach, hips, waist, thighs, arms
--Can used in conjunction with other operations such as a tummy tuck, a face lift and breast reduction procedures
-- immediate weight loss, and a slimmer, more contoured shape
procedures and techniques used in liposuction
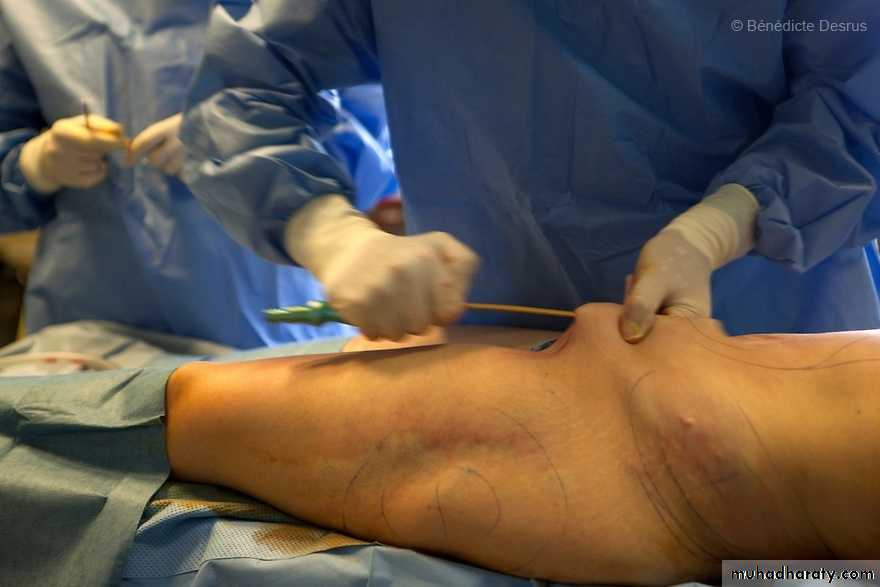
makes a very small incision in the skin, and inserts a tiny tube (cannula) through the skin into the fat layer. The tube is attached to a vacuum that sucks out the fat.It may be using general anesthesia or local anesthesia,
Liquification methodes
- water assisted liposuction (WAL)
- ultrasound assisted liposuction (UAL)
- Laser-assisted liposuction(LAL)
loosening or partially liquefying the fat to make it easier to extract. through a small cannula.
If reinjected fat , so inserted in many test tubes , transfuge then injected in other areas
side effects of liposuction
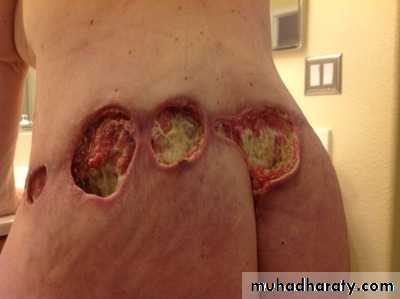
1-Temporary swelling, bruising, soreness, and numbness.2-Irritation and minor scarring around the incision sites.
3-Baggy or rippling skin. The skin will usually tighten and retract after a few months. But in some people the skin may remain somewhat loose.
4-Permanent color changes in the skin.
5-Damage to the nerves and skin.
Serous complications
1-Excessive blood and fluid loss, leading to shock. (rare)
2-Fat clots or blood clots, (pulmonary embolism).
3-(pulmonary edema). This is most likely to occur when a large volume of fluid is injected into the body.
4-Infection. In some cases, antibiotics may be given before or after liposuction
Baggy or rippling skin
infection
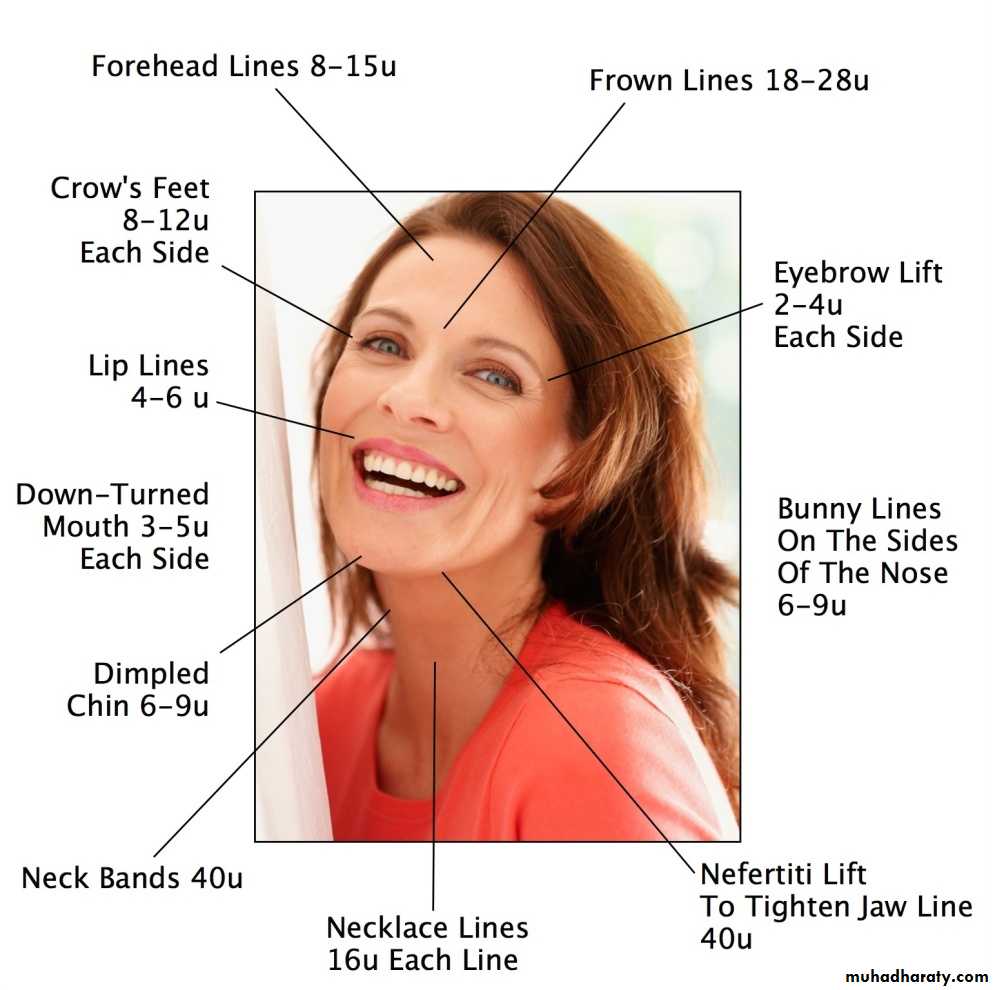
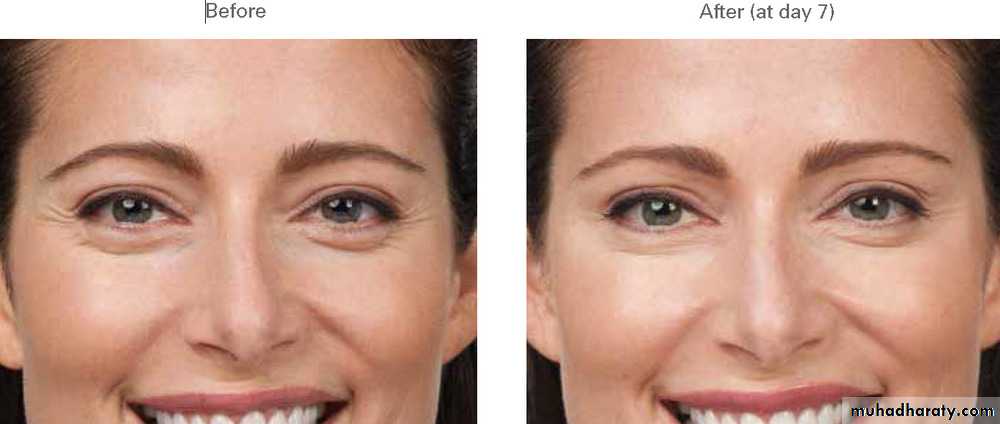
Botox
Botox injections are a diluted form of botulism which paralyzes or weakens the muscles that form wrinkles. Botox is the most popular non-surgical cosmetic procedure performedhistory of Botox®Botulinum toxins were first researched in the late 1960s to treat neurological disorders.
In 1989, use of Botox for eye muscle disorders.
In December 2000, Botox treat cervical dystonia (a disorder that causes severe neck and shoulder contractions)
In April 2002, Botox for treatment of frown lines.
In July 2004, it was approved for treatment of hyperhidrosis (severe underarm sweating).
In May 2010, used for upper limb spasticity (a condition that causes stiffness in the finger, wrist, and elbow muscles).
In October 2010, used for treatment of chronic migraine headaches in adults.
What kind of wrinkles do Botox injections treat?
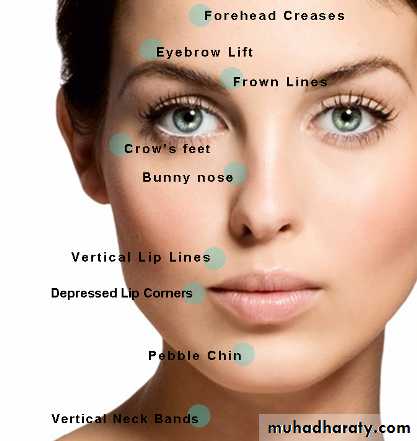
Botox can safely and successfully treat wrinkles that are caused by muscle contraction. These include frown lines, forehead creases, crows feet, and neck bandsResults are normally seen within a few days. The results should last 3-4 months
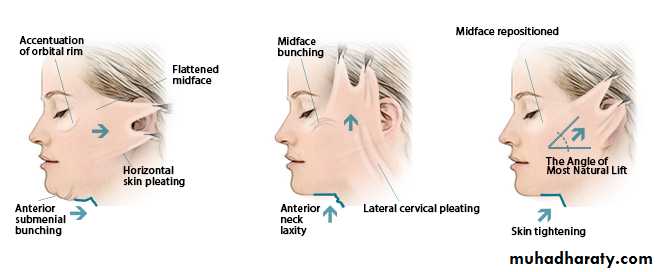
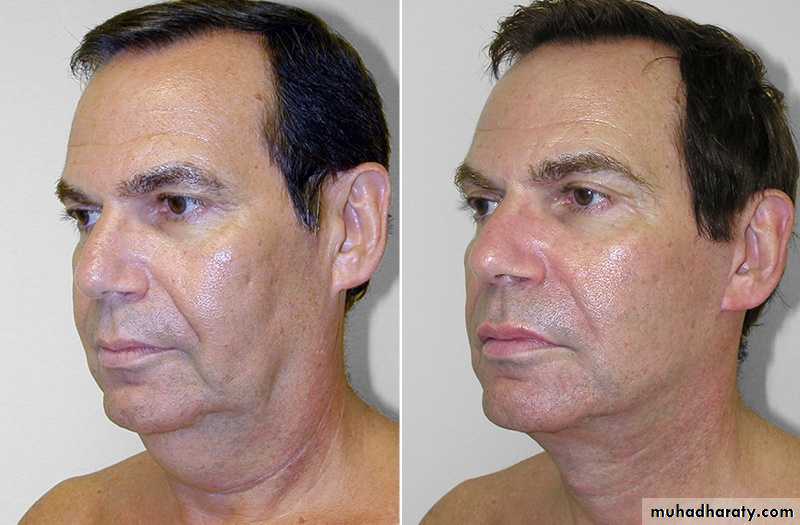
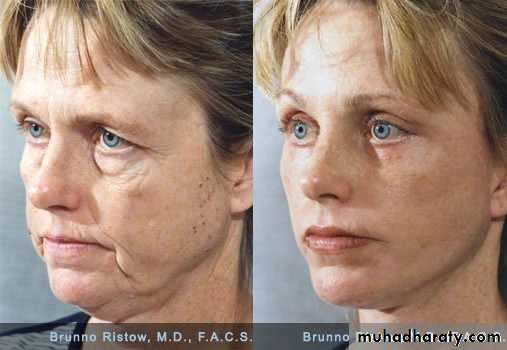
Face lift
Excess facial skin and fat, particularly in the lower face, can be removed or reducedTwo symmetric incisions are made from the hair line of scalp to the preauricular skin to the postauricular sulcus and into the posterior scalp to allow the elevation of bilateral cheek flaps, which are then advanced posteriorly to resects an ellipse of facial and scalp skin and tighten the facial tissues along a vector parallel to the jawline.
submental fat
A submental incision may be made specifically to excise submental fat and to excise or suture the medial borders of the platysma muscle.
The supraplatysmal fat within the neck may be removed by direct excision or by suction lipectomy.
Excess facial skin and fat
The supraplatysmal fat
Multiple surgeries
quiz
One of following about complication of scar is true :-A) -Hypertrophy of scar usually extend beyond wound margin
B) - Hypertrophy of scar continue enlarge after 6 mounths so regard type of fibroma
C) -contrecture of scar in joint may cause stiffness and deformoty of joint
D) - Marjolin ulcer is chronic unhealed scar should be treated with good local antiseptic and systemic broad spectrum antibiotic
E) -hyperpigmentation occur on full thickness burn while depegmentation in partial thickness
All are risk factors of cleft lip except :-
A) family history of cleft lip and palate in which the first-degree relativeB) X ray during pregnancy
C) rubella during pregnancy
D) caucasian have high incidence than nigroos
E)typhoid fever during pregnancy because may pass through placenta