Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 3
P a g e
1
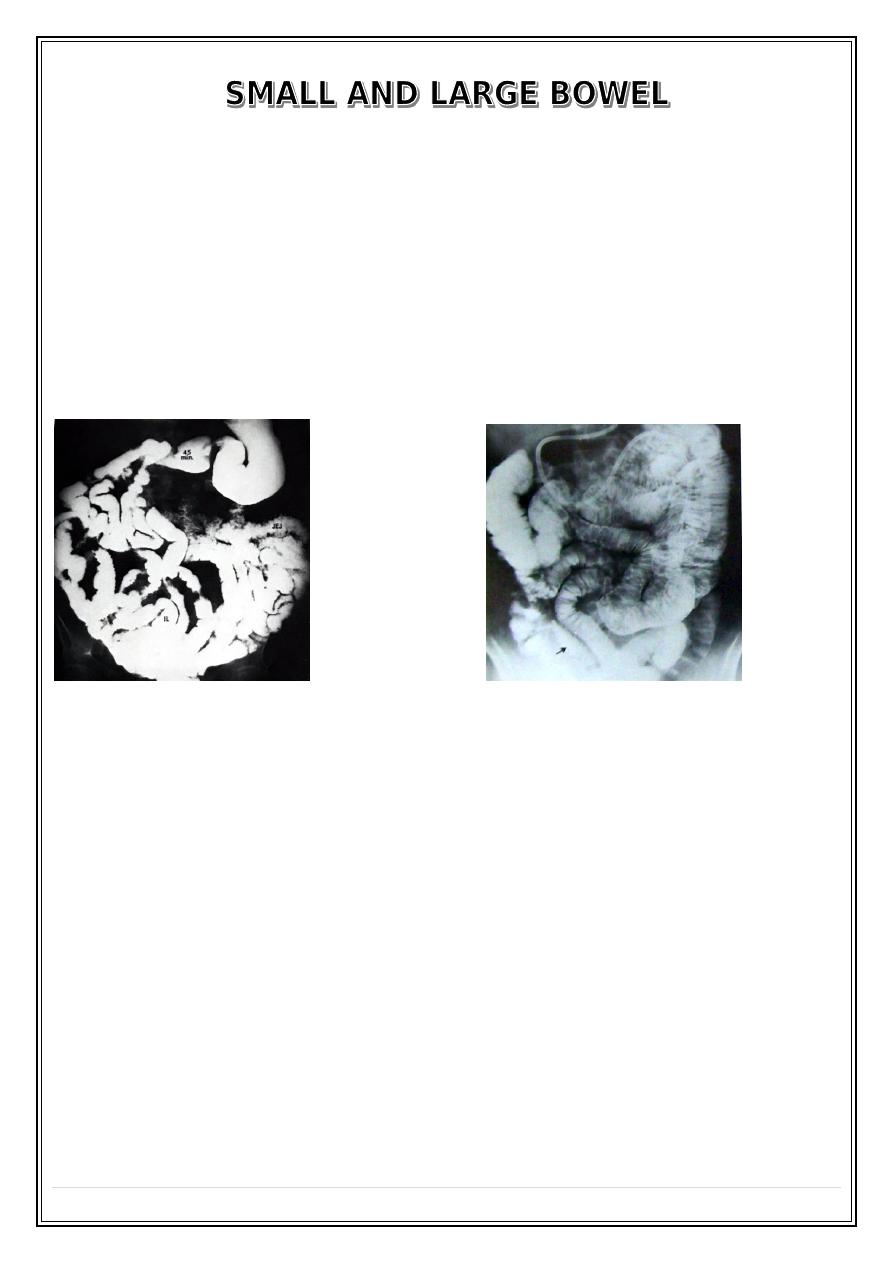
IMAGING TECHNIQUE of SMALL BOWEL
1 – Small bowel follow through .
2 – Small bowel enema ( enteroclysis ) .
3 – C.T .
4 – Ultrasound .
5 – M.R.I .
6 – Nuclear medicine ( MIBG ) .
Normal Ba follow through
Small bowel enema ( enteroclysis )
Indications for Ba follow through
1 – Inflammatory bowel disease .
2 – Suspected stricture .
3 – Malabsorption .
4 – Enterocautanous fistula .
5 – Post operative assessment of small bowel length in short bowel syndrome .
6 – Malrotation .
Imaging signs of small bowel disease
1 – Dilatation of the transverse diameter of the small bowel more than ( 3 cm ) , seen in
small bowel
obstruction , paralytic ilius & malabsorption .
2 – Thickening of the mucosal folds seen in
malabsorption , edema , haemorrhage , inflammation & infiltration .
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 3
P a g e
2
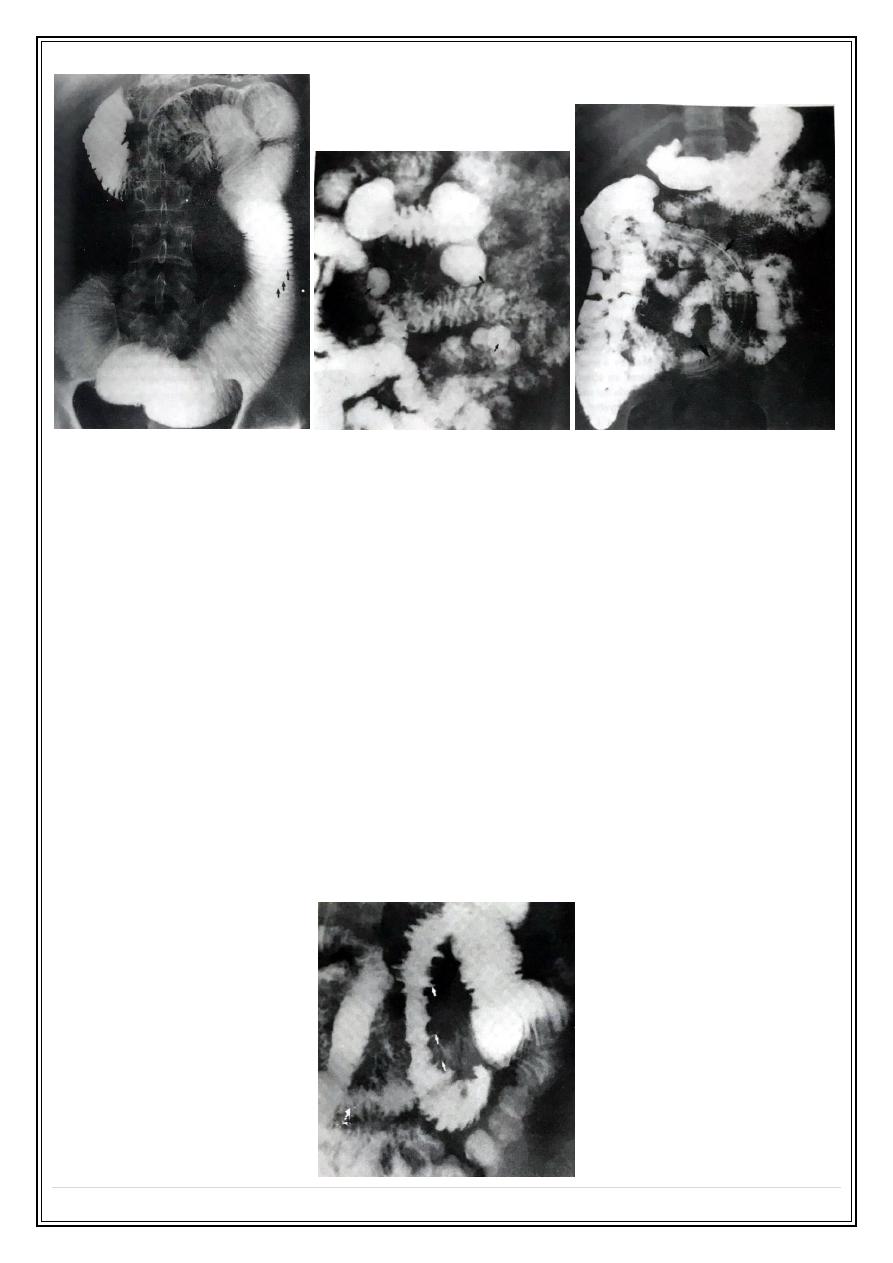
Small bowel obstruction
Small bowel diverriculum
Ascaris Small bowel
3 – Narrowing ( stricture ) the common cause are Crohn's disease , T.B & lymphoma in
which there is stricture & mucosal thickening with proximal
dilatation of the small bowel .
4 – Ulceration appears as spikes projecting outward in cases of Crohn's disease , T.B &
lymphoma .
Crohn's disease
Chronic non-specific granulomatous inflammation which can effects any part of the G.I.T
mainly the terminal ileum leaving normal part in between lesions known as skip lesions .
Imaging signs
1 – Stricture which could be small or large with normal bowel in between .
2 – Involvements of terminal ileum & caecum in continuity cause their contraction .
Small bowel deep ulcerations Crohoins disease
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 3
P a g e
3
3 – Dilatation of the bowel proximal to the stricture .
4 – Deep ulcerations .
5 – Thickening & effacement of mucosal folds .
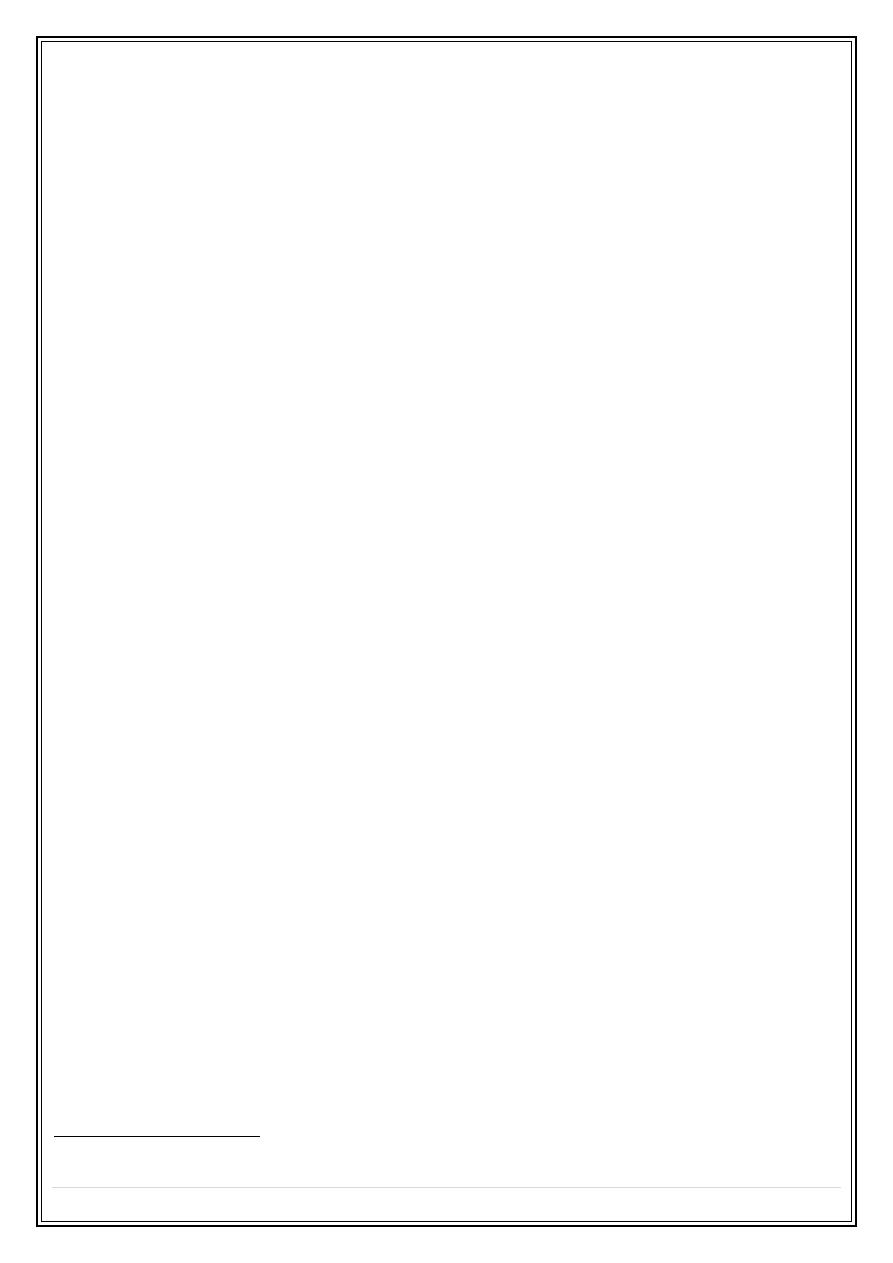
6 – Fistulae between small bowel & colon , urinary bladder & vagina .
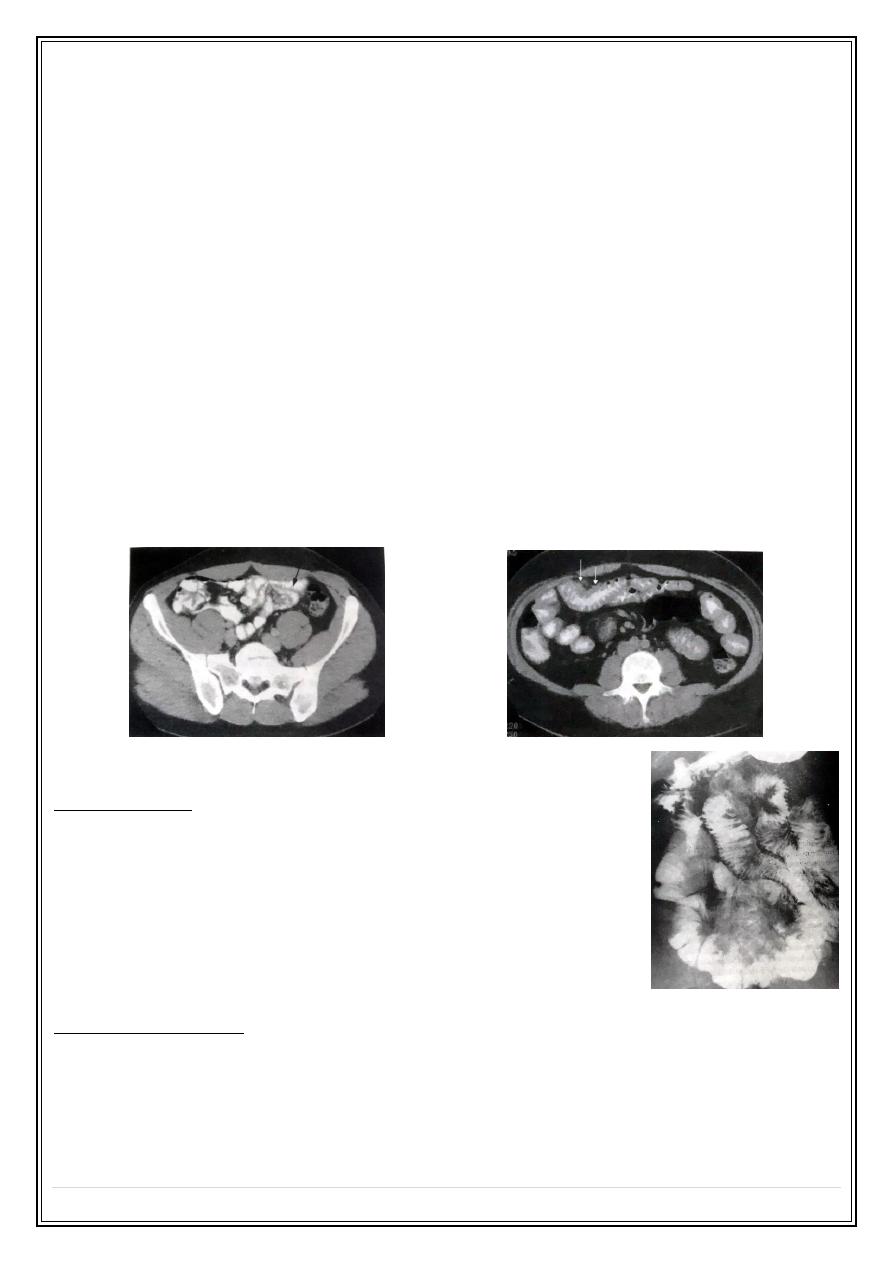
Ultrasound & C.T
Ultrasound & C.T shows bowel wall thickening & abscess collection in the lower
abdomen .
D.D
T.B & lymphoma which give same appearance as of Crohn's disease .
Features which help to differentiate lymphoma includes tumor nodule in the bowel ,
displacement of the bowel by enlarged L.N , hepatosplenomegaly , para-aortic L.N
enlargement .
CT normal small bowel folds
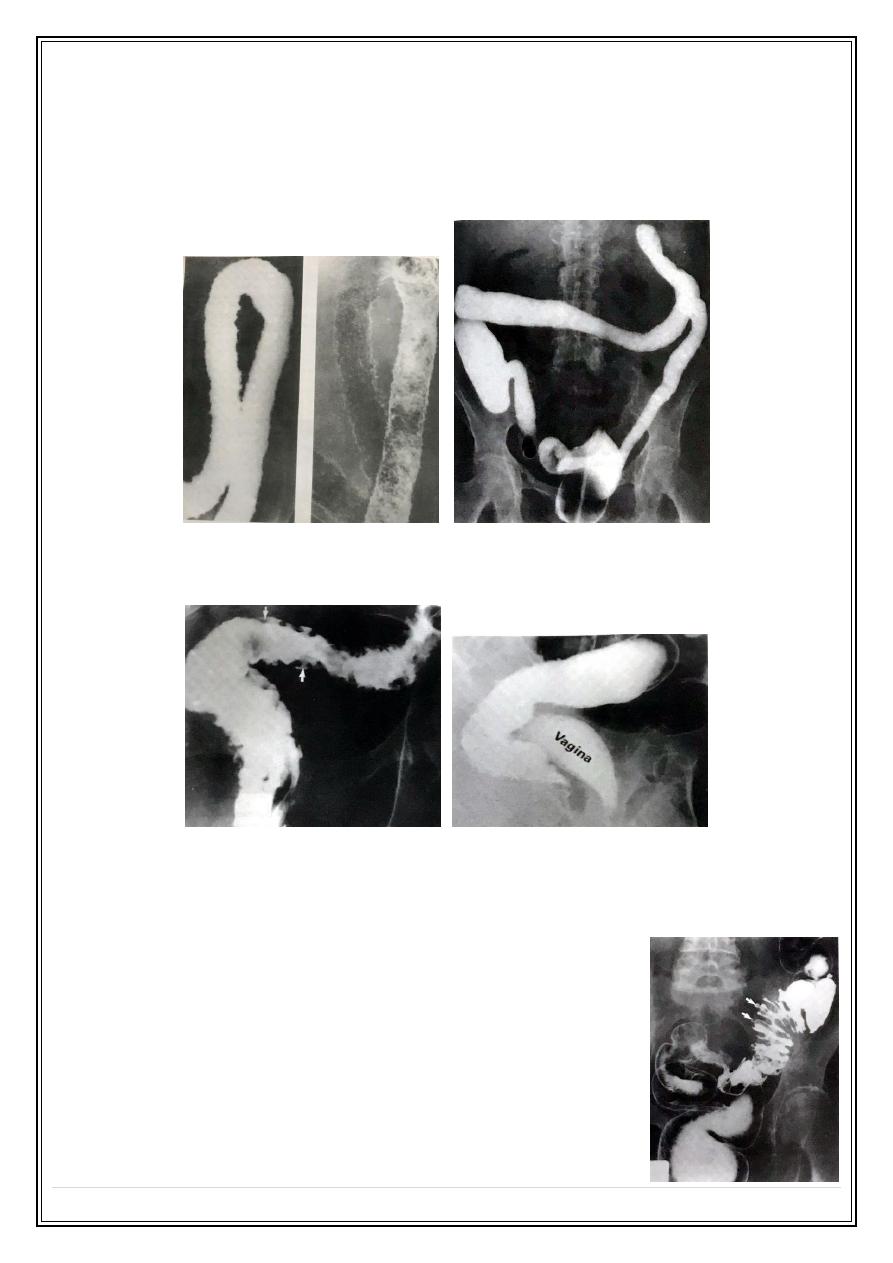
Small bowel thickening in lymphoma CT
Malabsorption
Imaging signs
1 – Small bowel dilatation mainly in the jejunum .
2 – Mucosal wall thickening .
3 – Dilution of Ba by excessive bowel fluid ( flocculation ) .
4 – Anatomical abnormalities like surgical resection & fistulae .
Large bowel
Imaging modalities
1 – Double contrast Ba enema .
2 – C.T pneumocolon .
3 – M.R.I .
4 – Nuclear medicine study .
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 3
P a g e
4
Double contrast Ba enema
1 -Bowel preparation by purgatives or washout enema .
2 - Ba injection through the rectum followed by air to
push Ba around the colon & to distended the colon with
air for mucosal coating with Ba .
3 -Films taken in various positions & views which can
shows tumors , mucosal diseases , diverticuli & presacral
space .
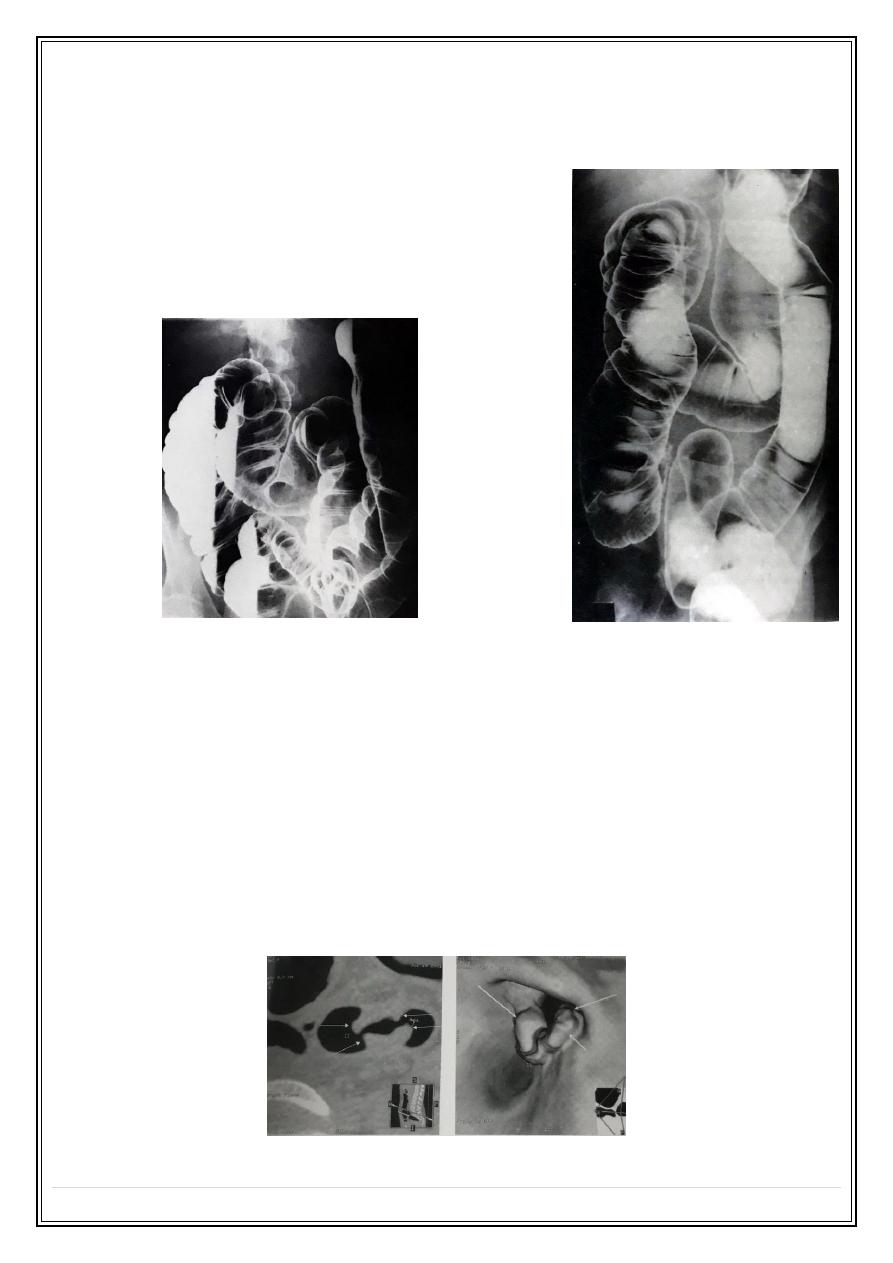
C.T pneumocolon
Mainly used for colonic tumors diagnosis .
Patient preparation by purgative to clean the colon .
Smooth muscle injection .
Rectal injection of air or Co2 .
Intravenous contrast injection for tumor enhancement .
Scan done in supine & prone position .
CT pneumocolon Ca colon
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 3
P a g e
5
M.R.I
Mainly used for the evaluation of the rectum & anal canal .
Look for liver metastases .
Imaging signs of large bowel diseases
1 – Stricture :
A – Carcinoma .
B - Diverticuli disease .
C - Crohn's disease .
D - Ischaemic colitis .
E - Extrinsic compression .
2 – Dilatation :
A – Obstruction in which Ba enema & colonoscopy shows one end of the stricture
while C.T shows the cause of obstruction .
B – Paralytic ileus there is small & large bowel dilatation as seen on plain film .
C – Volvulus .
D – Ulcerative colitis with toxic dilatation of the colon .
E – Hirschsprungs disease & megacolon .
3 – Filling defects :
A – Intraluminal ( faecal material ) .
B - Attached to the wall ( polyps & tumors ) .
C - Intramural ( haemorrhage , edema , pneumatosis coli ) seen as smooth filling
defects arise within the wall .
4 – Diverticuli .
5 - Ulcerations seen as small projections from the lumen into the bowel wall cause
shaggy appearance main causes ulcerative colitis , Crohn's disease , rare cause amaebic
& bacillary dysentery .
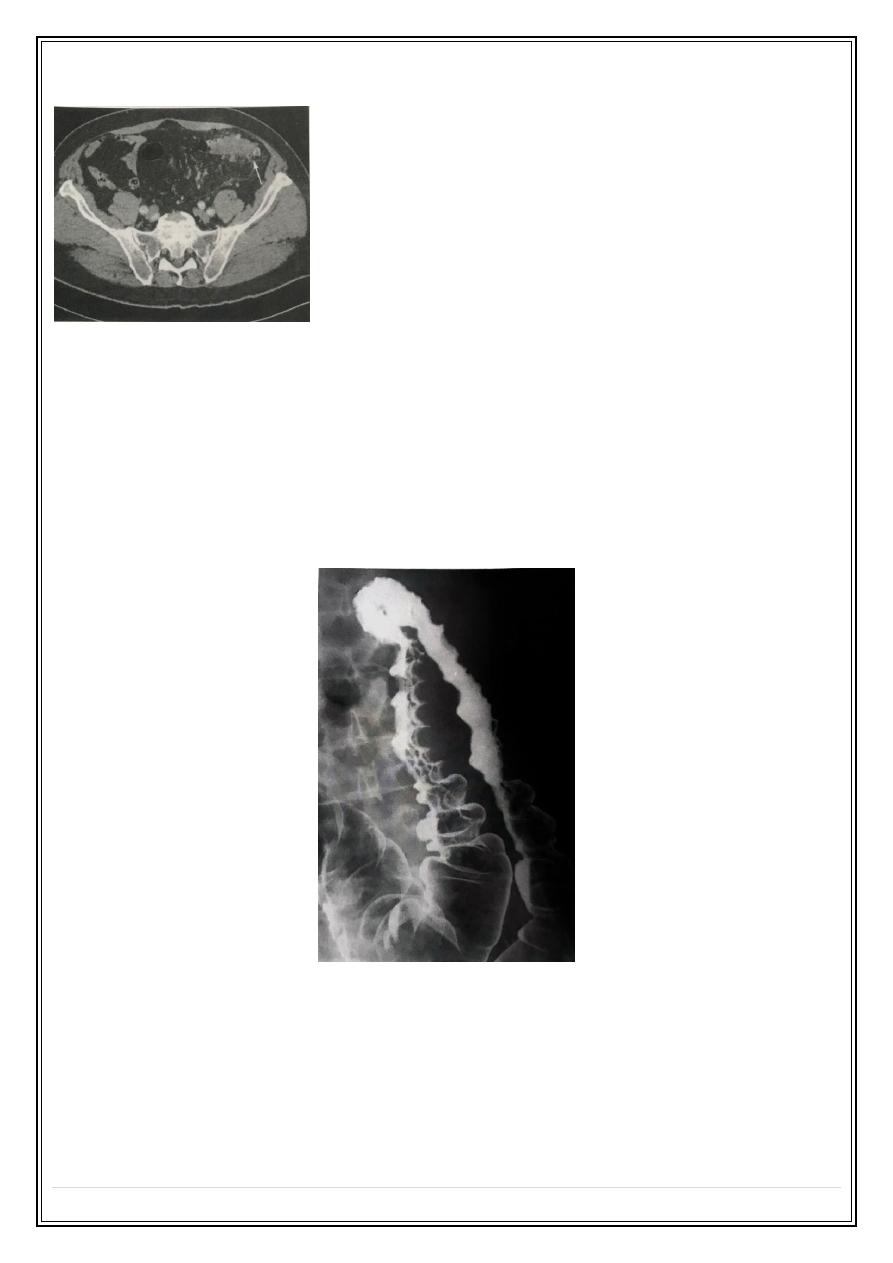
Inflammatory bowel disease
Ulcerative colitis
Unknown etiology characterized by inflammation & ulceration of the colon , the rectum
usually involved , in extensive disease the colon involved in continuity .
Main radiological signs:
•
Shallow ulcerations .
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 3
P a g e
6
•
Loss of normal colonic haustra .
•
Widening of presacral space .
•
Pseudopolyposis .
•
Dilatation of terminal ileum in cases of pan colitis .
Acute ulcerative colitis
long standing ulcerative colitis
Crohn's disease
Rectovaginal fistula
Diverticular disease
Out-pouching of the colonic mucosa through muscularis layer where blood vessels
penetrate the muscle , commonly seen in the sigmoid .
Complications:
1 – Infection .
2 – Perforation .
3 – Pericolic abscess ..
4 – Fistula .
5 – Stricture with or without local abscess .
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 3
P a g e
7
Diverticular disease CT:
Ischaemic colitis
Initially there is edema & haemorrhage seen as smooth indentation give thumb prints
appearance , later cause smooth tapered ends stricture the usual site is between
splenic flexture & sigmoid colon .
Volvulus
Intussusception
Thump printing of ischaemic colitis
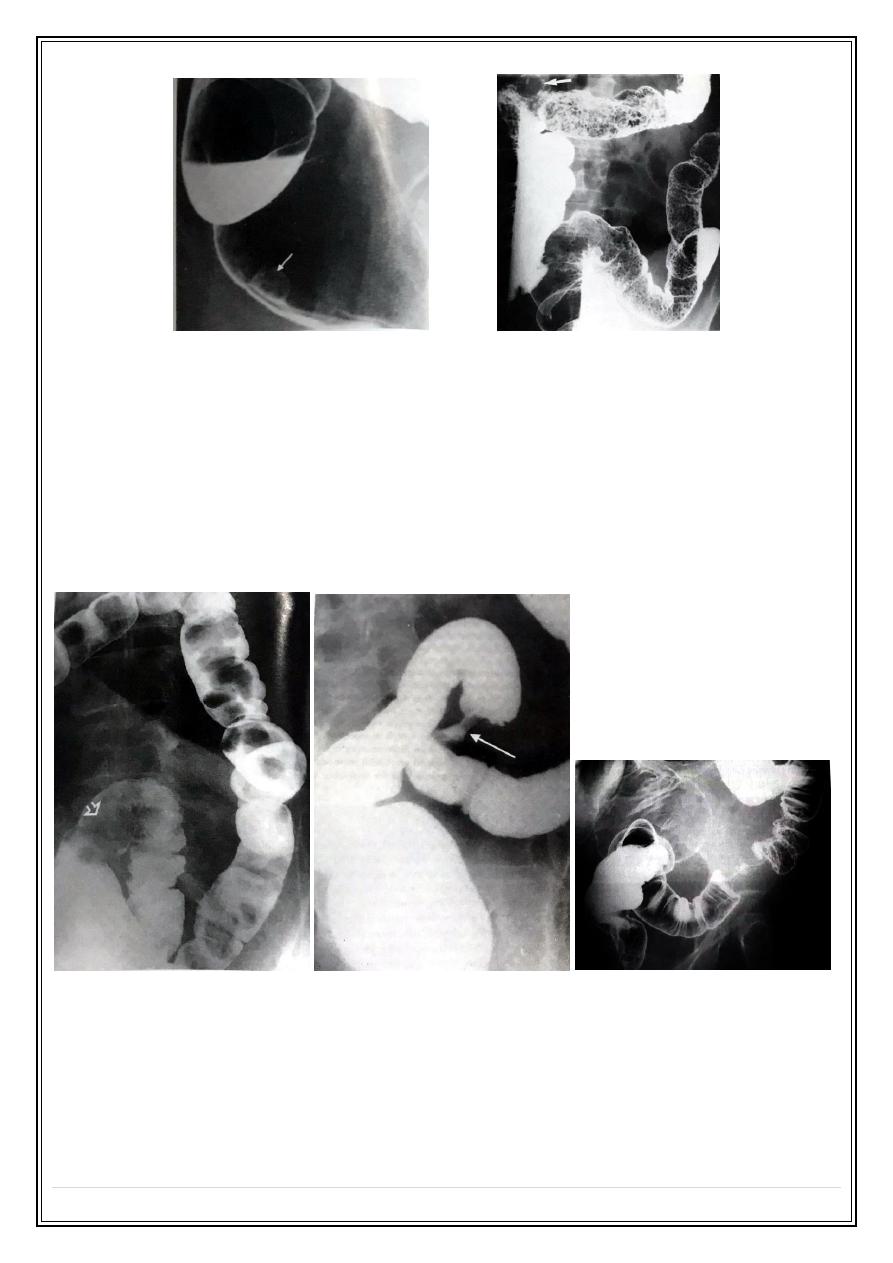
Colorectal tumors
Polyps
Soft tissue mass arising from the colonic wall projecting into the lumen .
Small polyp less than ( 1 cm ) mostly benign .
Polyp larger than ( 2 cm ) with short thick stalk & irregular surface mostly malignant .
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 3
P a g e
8
Sessile polyp
Familial polyposis
Colonic carcinoma
Can be seen any where in the colon & rectum , but are commonest in the rectosigmoid
region & the caecum Signs on Ba enema .
1 – Stricture in the rectosigmoid region .
2 – Filling defects in cases of polypoidal or fungating carcinoma .
3 – Multiple primary tumors seen in 5% .
Ca sigmoid faecal material
Ca sigmoid
Apple-core Ca colon
C.T pneumocolon
Used in the diagnosis of Ca colon which seen as bowel wall thickening & irregular
narrowing of the colon lumen .
Staging of colorectal carcinoma by showing metastases to the liver , lung & para-aortic
L.N .
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 3
P a g e
9
Hirschsprungs disease
Absence of ganglion cells in certain level in the colon usually in the sigmoid or
rectosigmoid region .
Ba enema signs
Narrowing of involved segment with distended colon proximal to the aganglionic
segment .
D.D
Idiopathic megacolon
Thank you,,,
