: chronic organic disorder, characterized by
Dementia
-Impairment of mental capacity
-Impairment of memory specially recent memory in the beginning
-Personality deterioration like self-neglect
- Impairment of judgment
- Impairment of interpersonal relationship
- Impairment of abstracted thinking
-
:
Additional criteria
-Emotional liability
-Catastrophic reaction
-Perseveration thought dis.
-Incontinence of urinary and faecal incontinence
-Time disorientation
-Focal Neurological symptom depend
Comparison Of Delirium and Dementia :
Dementia
Delirium
Feature
usu insidious
usu Acute
Onset
Protected, although
some type reversible
usu recover W 1wk
Course
usu normal
usu normal, except late
stage
usu recent
impaired in late stage
impaired in late stage
Hallucination
multifocal myoclonus
clouded
grossly dist.
memory dis.
immediate
grossly disturb
sundown may dist.
asterixis
Clinical feature
a-conscious
b-orientation
c-memory
d-comprehension
e-sleep wake
f-perception
g-other

Dx of Dementia
-decline in memory and thinking
-impaired daily life activities
-disturb in registration, storage, retrieval of new information
-clear consciousness
(D.Dx)
Keep in mind
-
:
Alzheimer's Disease
-commonest type
-seen in 70% of demented patients
-more in women than men
-presence of genetic cause
*earlier subdivided into
Dx of Alzh dx by exclusion
:-
-Lab investigation :-
Autopsy revealed
Microscopical finding
Normal aging process (benign forgetfulness)
Delirium
Pseudo-dementia
Pre-senile
Senile form
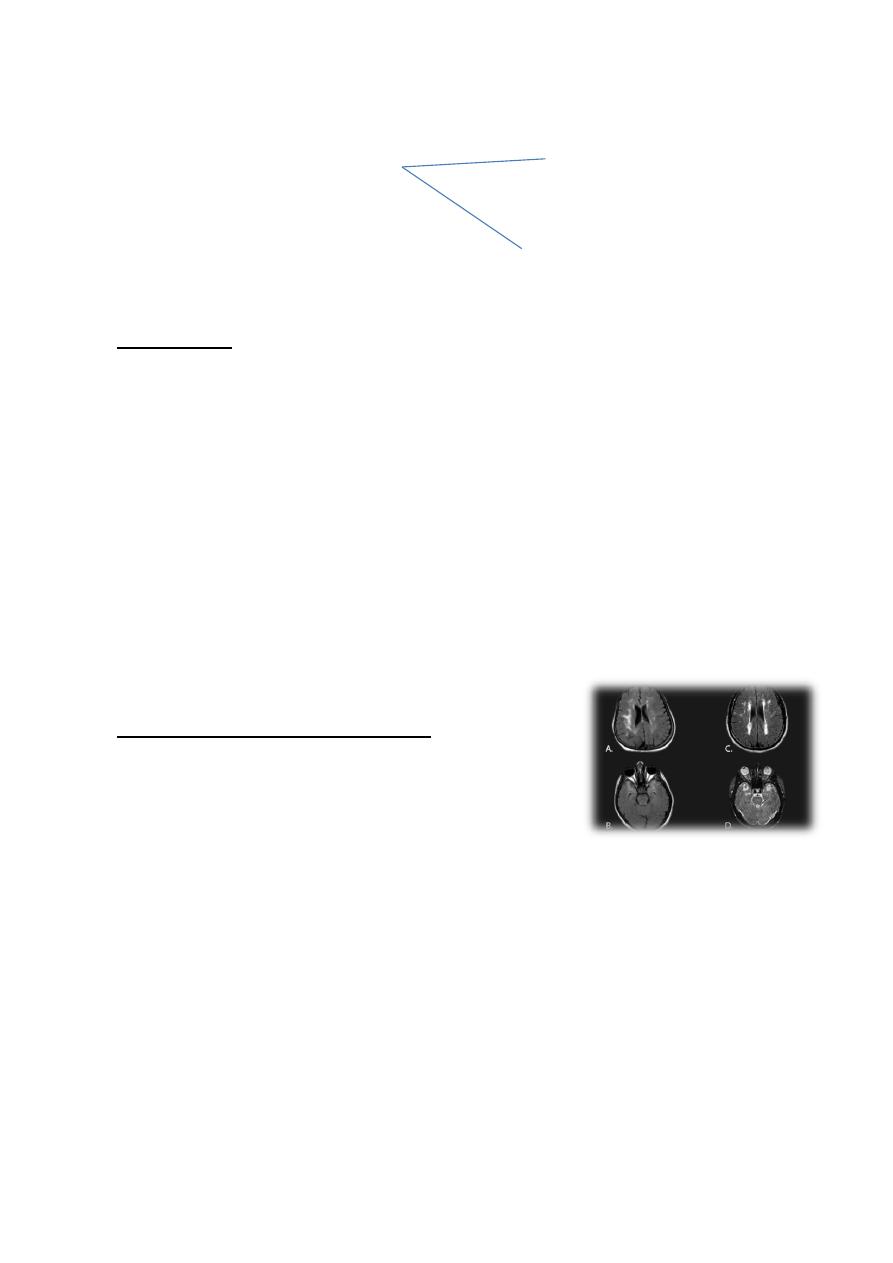
Enlarged vent
Widening of cerebral sulci
Shrinkage of ceretoral corte
Senile plague
Neuro vascular degenerate as a hole
Neuro fibrillary tangle
Neuro chemical changes in Alzh.
Treatment
-No, evidence of improvement
-Choline esterase inhibitor like
1-Rivastigmine (1.5 mg×2 )
2-Donpezile (5-10)mg
3-Galantamine (4mg-12 mg) twice/weekly
5-Memantine (5-20) (11-methyl) NMDA receptor antagonist
6-Vitc, E piracetam
Alpha GPC
infracted dementia MID
-
Muti
-Second common cause of dementia
-10-15% of causes of dementia
-multiple cerebral infraction in cerebral cortex which some time treatable.
Disturb of brain function
Decrease of acetyl choline esterase ( ACT)
Decrease of Acetyl choline transferase

-
:
Characteristic of MID
*
1-Abrupt onset
2-Acute exacerbation ( due to repeated infrection)
3-Step-wise deterioration
4-Fluration course
5-Hypertension CV disease
6-History of TIA
7-Focal neurological signs
-
:
Hypothyroid Dementia
-Most common treatable cause and reversible
-Although it represent 1%, but thyroid screening is essential in each dementia
-Complete recovering occur, if treatment start within onset of dementia
-
:
AIDS Dementia Complex
-About 50-70% of patient suffering AIDS
-Exhibit a triad of
-AIDS virus (lenti-virus) retero virus
-Highly neurotropic virus, it cross blood brain barrier in the course of disease
Dx
1-Established by ELISA
2-westren blot test (establish AB of HIV-Specific protein
3-C.T scan show brain atrophy
Cognitive
Behavioral disturbance of subcortical dementia
Motor
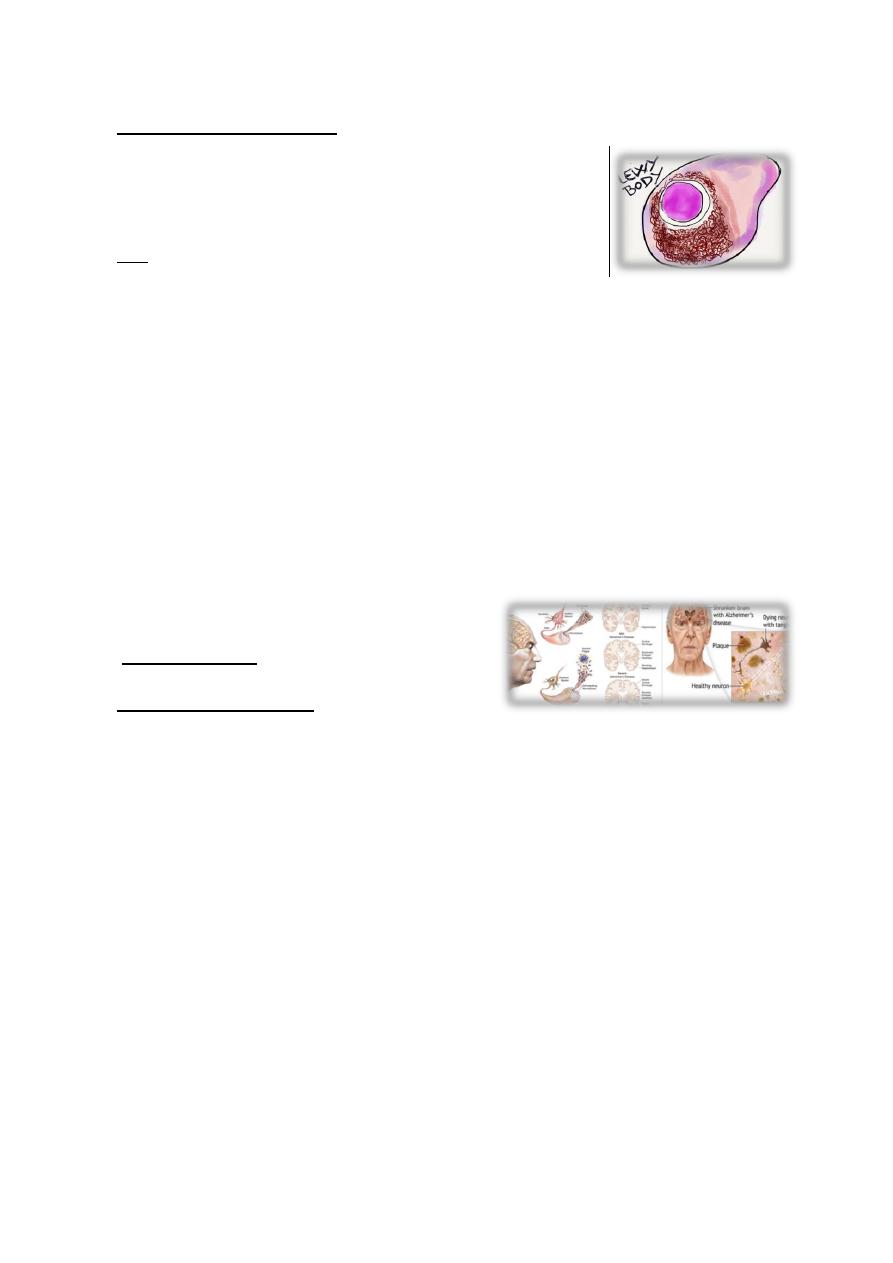
Lewy Body Dementia
-2nd most common cause of degenerative dementia
-account for 4% of all dementia
C.F
1-fluctuting of cognitive impairment in a week or a month (involving
memory, language, visuo-special, praxis, reasoning)
2-visual hallucination
3-extra-pyramidal symptom or parkinsonism like rigidity and tremmer
4-Neurolopic sensitivity syndrome sensitivity to traditional anti-psychotic
5-urine incontinence
6- Lewi-body intra cytoplasmic inclusion body PET (post Emission
Tomography)+SPECT shows reduce dopamine ganglia
-
:
Management
-
:
Basic investigation
-Before diagnosis of Alzheimer, we should exclude other cause
-Complete blood picture, urine analysis, B. sugar. serum electrelyf, renal
function, TFT.
-Sexological test for syphilis
-Arterial por, pcor, CXR, ECG, skull X-Ray
-C.T scan, MRI
-Drug screening

Treatment
-Treating underlying cause specially reversible type like treatment of :
1-Hypertension
2-Thyroxin replacement
3-Shunting of hydrocephalic dementia
-Use of Levo-dopa in parkinsonism
-Removal of toxic agent-toxic dementia
-
:
treatment
Symptomatic
-Red stress, daily activity
-Treat any medical condition
-Care of food and personal hygienm
-Family care
-Anti-anxiety – small dose (short-acting)
-Depression should be treated by SSRT
-Such as atalopram, sertraline
-Psychotic symptom low dose of anti psycho small dose and
Risperidon anti-psychotic should avoided in lewi-body
-Short term hospitalization :-
Drug therapy
*
Choline esterase inhibitor such as
-donepezil, rivastagmin, Galantamin
-in Alzheimer Memantine (anti-NMDA)

Organic Amnestic Syndrome
C.F
1-Impairment of memory clue to underlying organic cause
2-No, sever disturbance of conscious unlike deferline
3-No, gbbal disturbance of intellectual function
4-Memory impairment
-sever impairment and recent memory or short term memory
-inability to learn new information
-remote memory well remembered
-disorientation and time and place
-confabulation (fu gap and memory)
Dx :- disturb of
-recent memory
-anterescale-reterogy rade amnesia
-bilateral involvement cause global amnesia
-
:
Transient Global Amnesia
-abrupt onset
-sever distress
-cause by transient ischemia
-disturbance of posterior cerebral circulation

Etiology
1-Thiamin deficiency
-Chr. alcoholic
-Wernk's-korsakoff
-Limbic syst. dist :-
●Head trauma
●Bilateral lobectomy
●Hypoxia
●Post. ceretoral artery stroke
●Herps simpler involvement
●Space Occupying Lesion
Management
●Treat the underlying cause
●Use of high thiamin dose in korsakoff
●Supportive care
