Fifth Stage
Internal Medicine
Dr.Fadhil – Lecture 6
1
Crystal Associated Diseases
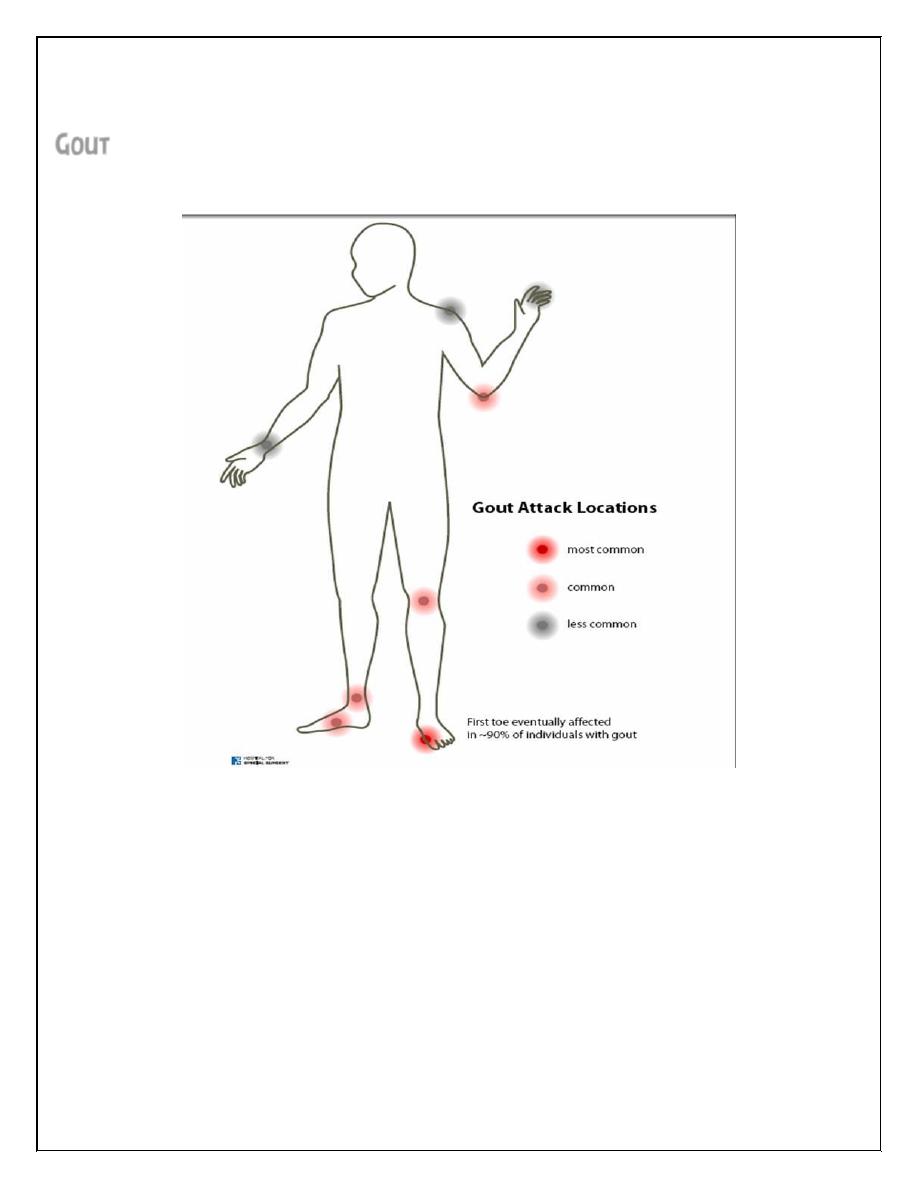
Gout
Gout has been recognized from as early as the 4th century BC.
It is a true crystal deposition disease, defined as the pathological reaction of
the joint or periarticular tissues to the presence of MonoSodium Urate
Monohydrate(MSUM) crystals. It usually favoring lower rather than upper limbs
especially first metatarsophalangeal & small joints of feet & hands.
Women rarely develop gout before the menopause, because estrogens are
thought to be uricosuric.
Peak incidence in men is in the fifth decade.
Primary gout is associated with: obesity, hyperlipidemia, alcoholism, diabetes
mellitus, hypertension and atherosclerosis.
2
It rarely occurs before young adulthood ( when it suggests a specific enzyme
defect).
Secondary gout due to renal impairment or drug therapy affects people over
the age of 65 mainly & seen in women in whom there is an increased diuretic
use. Serum uric acids are higher in men than women& positively correlate with
obesity , age& ethnicity(being higher in Newzealands).
Hyperuricemia is defined as serum uric acid >7.1 mg/dl .
95% of hyperuricemic subjects never develop gout.
Causes of primary gout:
1- 90% of cases are due to defective renal excretion of uric acid( under
execretors).
2- 9% have intrinsic increased production of uric acid (overproducers).
3- 1% have specific inherited enzyme defect of purine synthesis & this is when
the age is below 25 years.& in patients with urate stones.
CLINICAL FEATURES
Clinically, gout may present as asymptomatic hyperuricemia, acute arthritis,
chronic arthritis, or chronic tophaceous
gout.
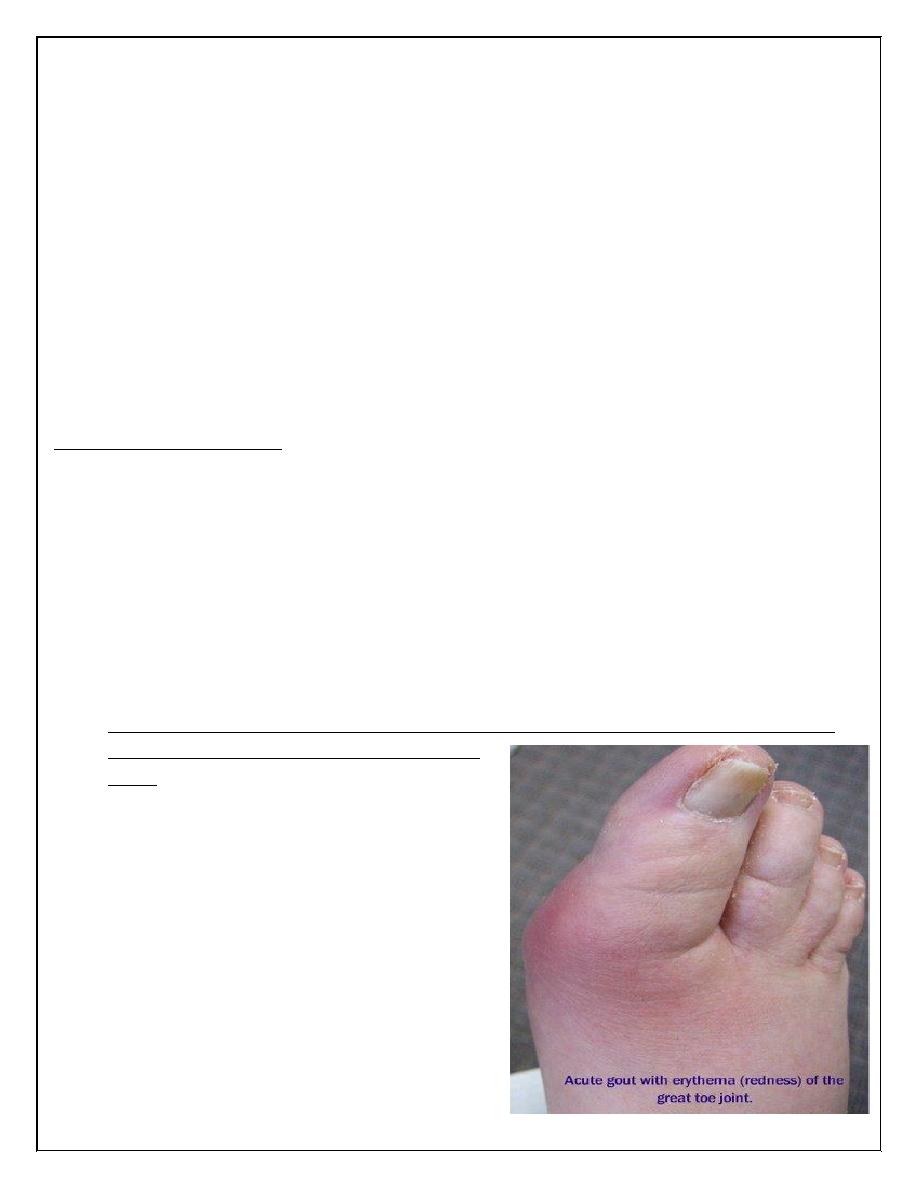
Attacks of pain are rapid in onset,
waking the patient in early morning.
Single distal joint is often affected(first
metatarsal joint- podagra) , but
eventually other joints are affected. The
pain is associated with extreme
tenderness that the patient is unable to
wear a sock. The swelling is marked with
overlying shiny red skin. Complete
resolution of swelling & pain occur in 5-
14 days.
3
When the attacks subside; pruritus & desquamation of overlying skin is
common.
Some patients have only mild attacks lasting few days(petit attacks). Other
have one attack fallowed by other one(cluster attacks). Some patients have
only one attack & other have repeated episodes with further deposition of
MSUM.
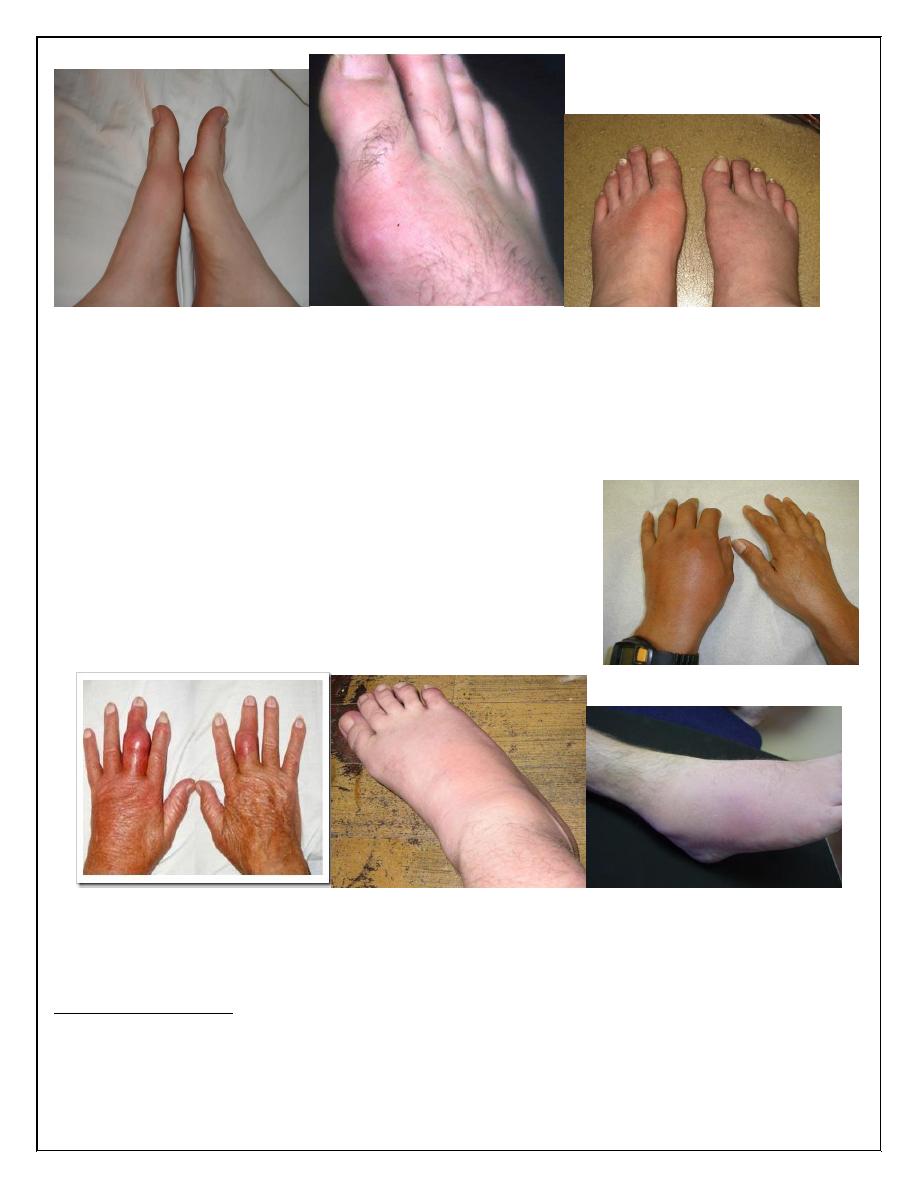
Eventually chronic pain & joint damage occur.
White colored tophaceous nodules are formed at
the extensor surface of fingers, hand, feet,
elbow& sometimes helix of the ear. These nodules
may ulcerate & rupture& associated with local
inflammation.
Renal stones occur in 10% of urate type in gout patients. Progressive renal
disease is an important complication of untreated chronic tophaceous gout
with subsequent glomerulosclerosis& pyelonephritis.
INVESTIGATIONS
Definitive diagnosis requires identification of MSUM crystals in synovial fluid
from joint , bursa or tophus. Synovial fluid reveals increased viscosity &
turbidity ( > 90% neutrophils).

4
Hyperuricemia is usually evident , but normal serum uric acid does not exclude
gout (uric acid falls as part of acute phase response in acute gout ). 24 hour
urine collection for uric acid on low purine diet reveals overproducers.
X ray findings can be delayed until late in the disease, where there is joint
space narrowing, gouty erosions(bony tophi), sclerosis& OA changes.
MANAGEMENT OF GOUT: a fast acting NSAIDs (naproxen, diclofenac sodium,
indomethacin ) can give rapid relief of the pain & given as maintenance dose.
Oral colchicine can be very effective but associated with severe vomiting &
diarrhea(1 mg loading dose then 0.5 mg 6 hourly) until symptoms abate. Joint
aspiration with or without corticosteroid intraarticular injection can sometimes
improve the symptoms.
Hypouricemic drugs are indicated for recurrent attacks of acute gout, tophi,
evidence of bone or joint damage , renal disease& gout with high serum uric
acid. Allopurinol in a dose of 100-300 mg daily is the usual drug . It inhibits
xanthine oxidase & reduces the conversion of hypoxanthine& xanthine to uric
acid.
Uricosuric drugs such as probenecid or sulfinpyrazone can achieve equivalent
reduction in serum uric acid to Allopurinol.
Pseudogout
Pseudogout It is an acute synovitis caused by deposition of Calcium Pyro
Phosphate Dihydrate(CPPD) in hyaline & fibro cartilage of joints resulting in
chondrocalcinosis. It is the most common cause of acute monoarthritis in
elderly
Shedding of crystals into a joint precipitates acute synovitis which resembles
gout, except that it is more common in elderly females& usually affects knee
joint or wrist. In young people it may be associated with hemochromatosis,
hyperparathyroidism, or Wilson's disease.
Clinically, it is similar to OA & management is similar to gout but aspiration of
synovial fluid& intra-articular corticosteroid injections are mandatory treatment
options.
5
Systemic sclerosis
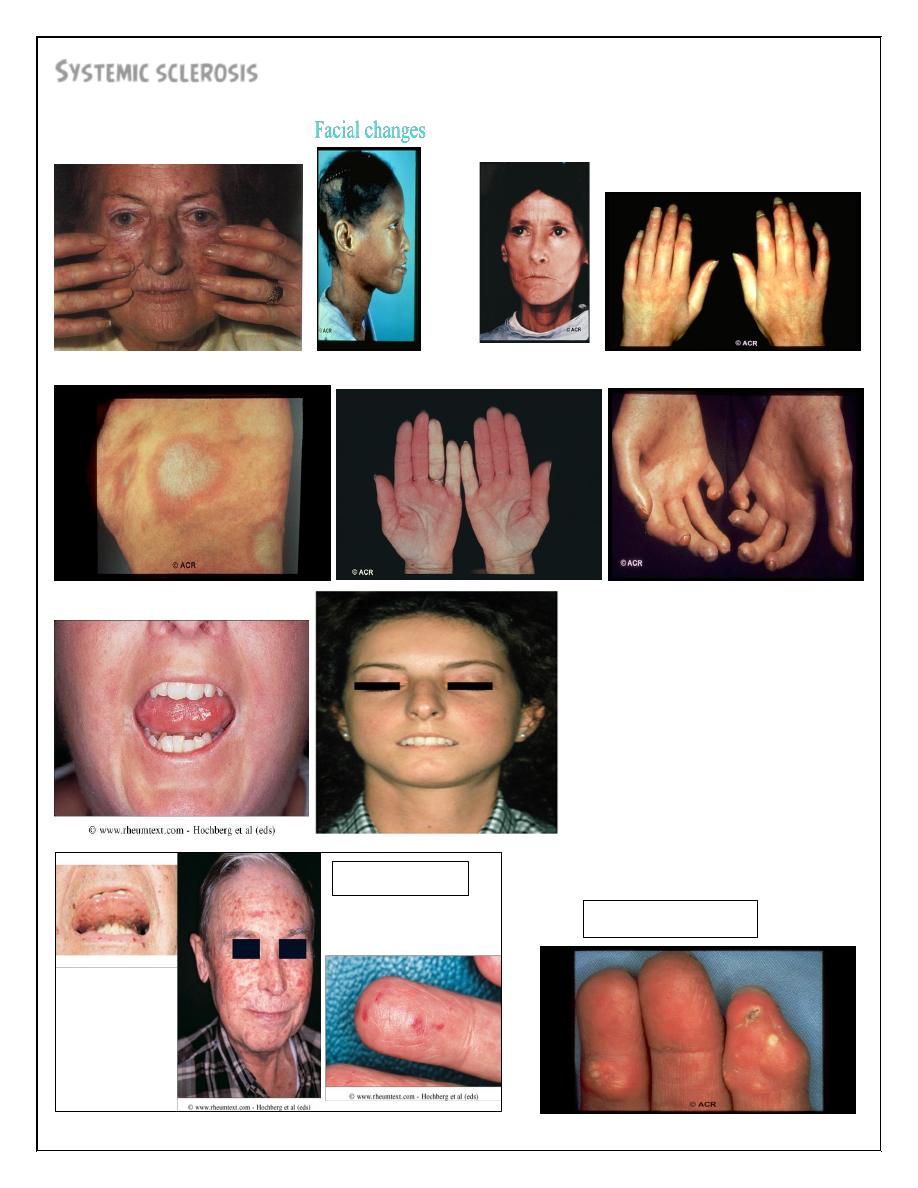
Morphea:
Calcinosis:
Telangectasia
6
Previously called SCLERODERMA, is a generalized disorder of connective tissue
affecting the skin, internal organs & vasculature. This distinguishes it from
localized scleroderma syndromes , such as morphea, that do not involve
internal organs& are rarely associated with vasospasm( Raynaud's disease).
The peak age of onset is the 4
th
& 5
th
decades of life with prevalence of 10-20/
million population & 4:1 female :male ratio. It is rare in children.
Skin involvement distal to elbow& knee( apart from face) is classified as limited
cutaneous systemic sclerosis(LCSS) or CREST( Calcinosis, Raynaud's,
Esophageal involvement, Sclerodactyly, Telangiectasia). Involvement proximal
to knee & elbow& on the trunk is classified as diffuse cutaneous systemic
sclerosis(DCSS).
ETIOLOGY & PATHOGENESIS :the etiology is unknown with no genetic ,
geographical or racial associations. Environmental factors are important in isolated
cases, such as exposure to silica dust, vinyl chloride& hypoxyresins. Bleomycin can
cause a similar picture.
Early in the disease, there is infiltration of T-lymphocytes& fibroblast activation
with increased type 1-collagen production resulting in symmetrical thickening ,
tightening & indurations of skin. In addition, there is an arteriolar narrowing &
vessel wall inflammation with release of vasoconstrictors& platelet activation
resulting in further ischemia.
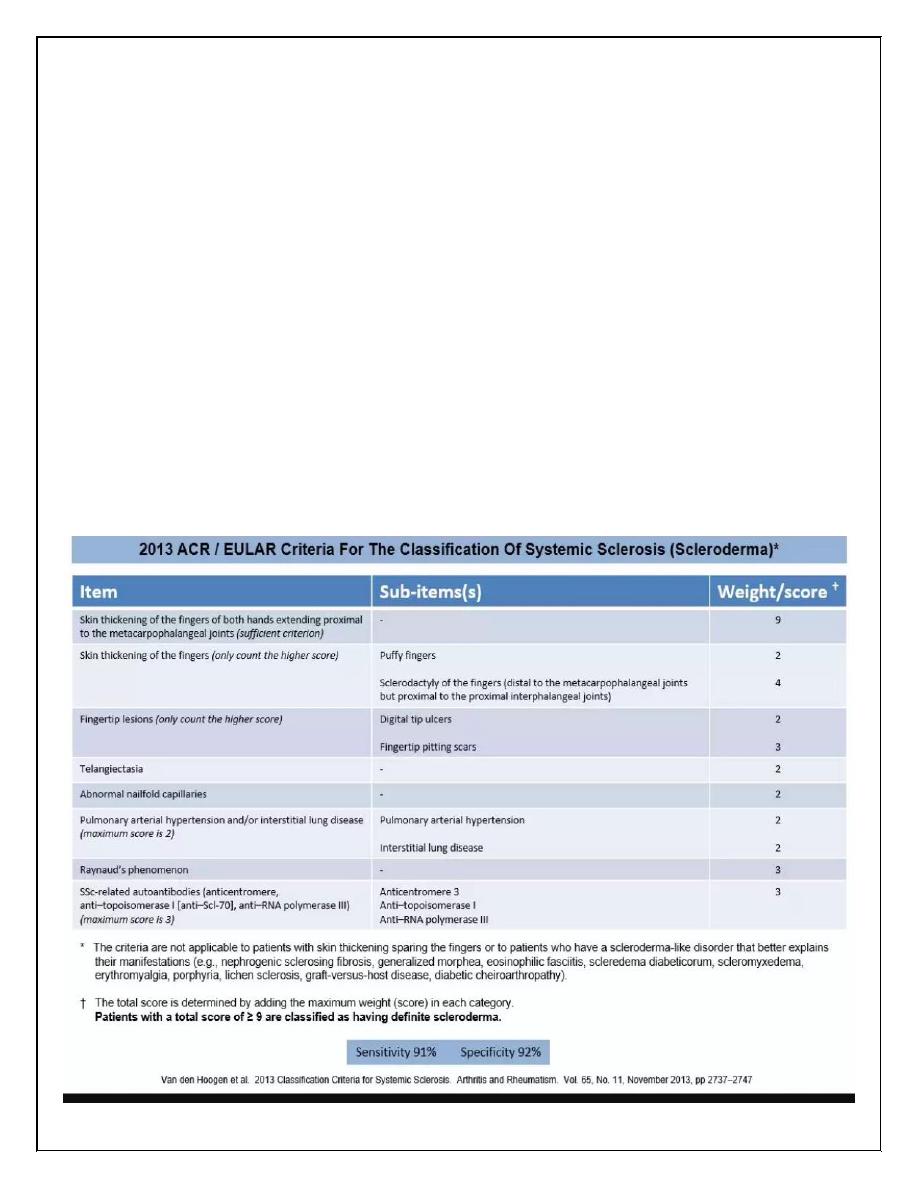
DIAGNOSIS: systemic sclerosis is a clinical diagnosis, based on the presence of
sclerodactyly(finger pulp atrophy), beaking of nails(pseudoclubbing),atrophic nails,&
telangiectasia(nail- fold capillaries . Most patients have positive ANA. 30% of diffuse
type have antibodies to topo-isomerase(scl-70)& 10% of LCSS have antibodies to
centromere.
Raynaud's phenomenon is common& may be the first clinical picture *
*cutaneous features: initially there is non pitting edema of fingers& tendon
sheaths, then the skin becomes shiny, taut& distal skin creases disappear with
involvement of the nose(peaked nose)& lips.
GIT* : smooth muscle atrophy& fibrosis in the lower two third of esophagus
lead to acid reflex & esoghagitis which should be treated with proton pump
inhibitors. Dysphagia & odynophagia may occur.
Involvement of stomach causes early satiety& outlet obstruction . Watermelon
stomach( antral vascular ectasia) may cause occult upper GIT bleeding & this
occurs in 20% of patients.
7
Small intestine involvement leads to malabsorption, bacterial overgrowth ,pain
& constipation. Autonomic neuropathy may cause dilated small & large bowel
& pseudo obstruction.
Cardiopulmonary diseases*: pulmonary involvement is a major cause of
morbidity & mortality. Fibrosing alveolitis occurs mainly in diffuse disease &
associated with positive anti topo-isomerase -1.
Pulmonary hypertension occurs in limited than diffuse type& characterized by
progressive dyspnea, right sided heart failure& angina. Treatment includes
vasodilators, continuous infusion of epoprostenol, oral endothelin-1 antagonist
bosentan& heart-lung transplantation.
Renal features*: one of the main causes of death is hypertensive renal crises
which characterized by malignant hypertension & renal failure. Treatment is
usually with ACE inhibitors even in the presence of renal impairment. It is more
common in topo-isomerase -1 positive diffuse type. Some clinicians use
prophylactic ACE inhibitors to prevent this complication.

8
Causes of anemia in scleroderma:
1-iron deficiency from chronic oesophigitis
2-folate &vitaminB-12 deficiency from malabsorption
3- anemia of chronic disease
4-microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
MANAGEMENT
Avoidance of peripheral cold exposure is important. Infection of ulcerated skin
should be treated with heavy dose of antibiotics& for long time because the
drug poorly penetrate the infected skin. e.g. flucloxacillin 500 mg 6 hourly.
Calcium antagonists( nifedipine, amlodipine)& angiotensin 2 receptor
antagonists(valsartan) may be effective for Raynaud's disease.
For digital ischemia, intermittent infusion of epoprostenol may be helpful.
Corticosteroids & cytotoxic drugs are indicated for patients with myositis or
alveolitis. D-pencillamine is effective for skin lesions. No agent has been shown
to arrest or improve skin lesions.
PROGNOSIS :5 years survival is approximately 70%.
Risk factors at presentation that associated with poor prognosis include old age,
DCSS type, protein urea, high ESR, low gas transfer factor for carbon
monoxide(TLCO) & pulmonary HT.
Thank you,,,
