Fifth Stage
E.N.T
Dr. Mushtaq – Lecture 11
1
Neck spaces
Anatomy
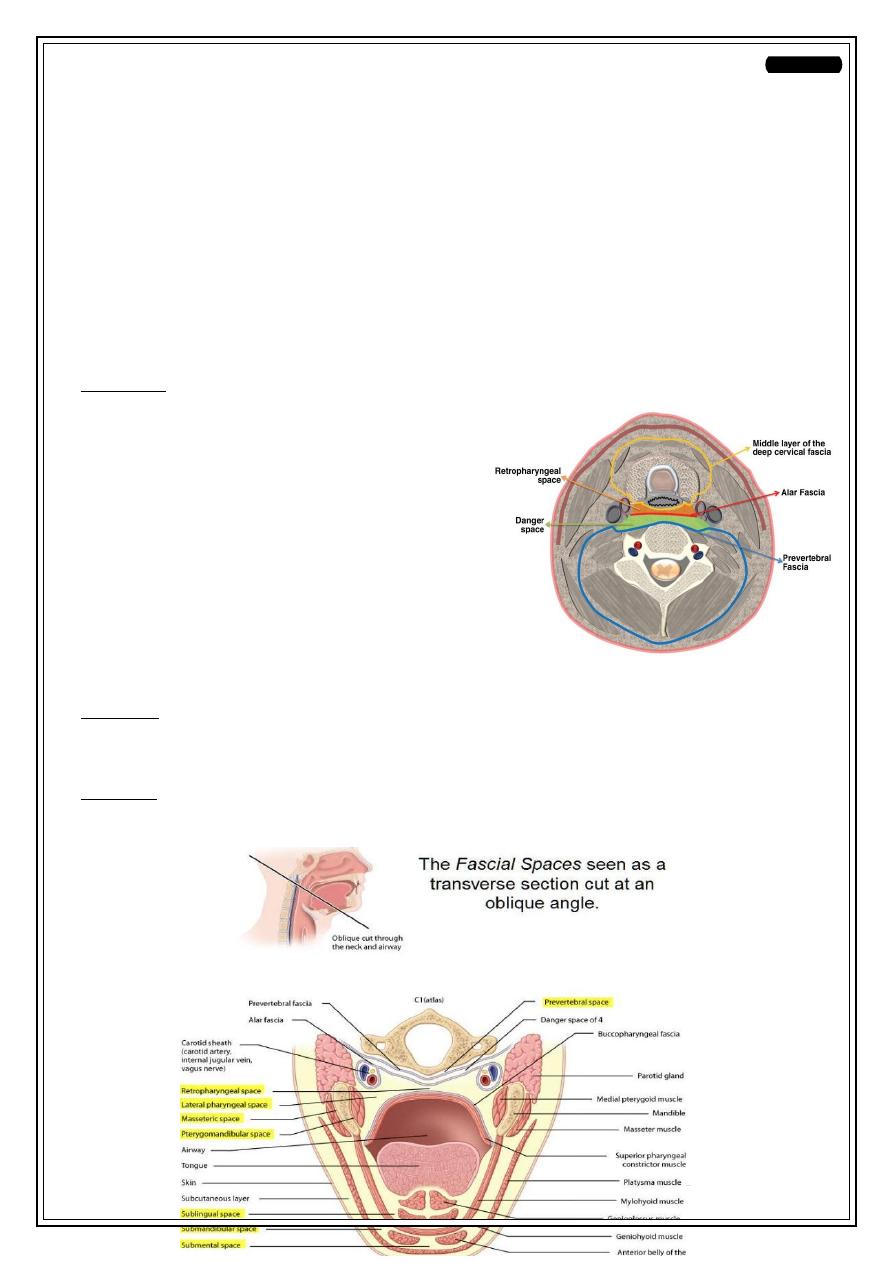
Parapharyngeal space :
•
Potential space
•
Extends from the base of skull to superior mediastinum
•
Bounded medially by buccopharyngeal fascia & laterally by ascending ramus of
the mandible ,parotid gland & sternocledomastoid muscle .
Contents:
•
Carotid arteries & jugular v
•
Deep cx. Ln.s
•
Last four cranial n.s
•
Cx. Sympathetic trunk.
Retropharyngeal space
•
Potential space lies behind the pharynx
•
Extends from skull base to T1-T2
Bounded ant. By post. Pharyngeal wall and it`s covering fascia
post. By alar layer of the deep fascia
Content:
•
Retropharyngeal Ln.

2
Parapharyngeal abscess
Aetiology:
1. Tonsillitis
2. Penetrating foreign body
3. Infected lower wisdom tooth
Clinical features
1. Sore throat
2. Pyrexia and toxaemia
3. Trismus
4. Tender Swelling of the neck
5. Tonsil is pushed medially
Investigations
Complications:
1. Acute oedema of the larynx
2. Thrombophlibitis of the int. jug. V.
3. Spread to mediastinum.
Treatment:
•
Systemic antibiotics
•
Drainage through the neck.
3
Retropharyngeal abscess
•
Pus collected between buccopharyngeal and alar fasciae.
•
Acute
•
chronic
Acute ret. Ph. Abscess
Aetiology:
- tonsillitis, nasopharyngitis , and rarely
acute sup.o.m.
- strept.pneumonia is the commonest m.o.
- mostly are infants & young children
Clinical features:
1. Difficulty in breathing & suckling
2. Pyrexia
3. Toxaemia
4. Stiffness of the neck or torticollis
5. Lat. Swelling of the post. Ph.wall
6. Spontaneous rupture & aspiration
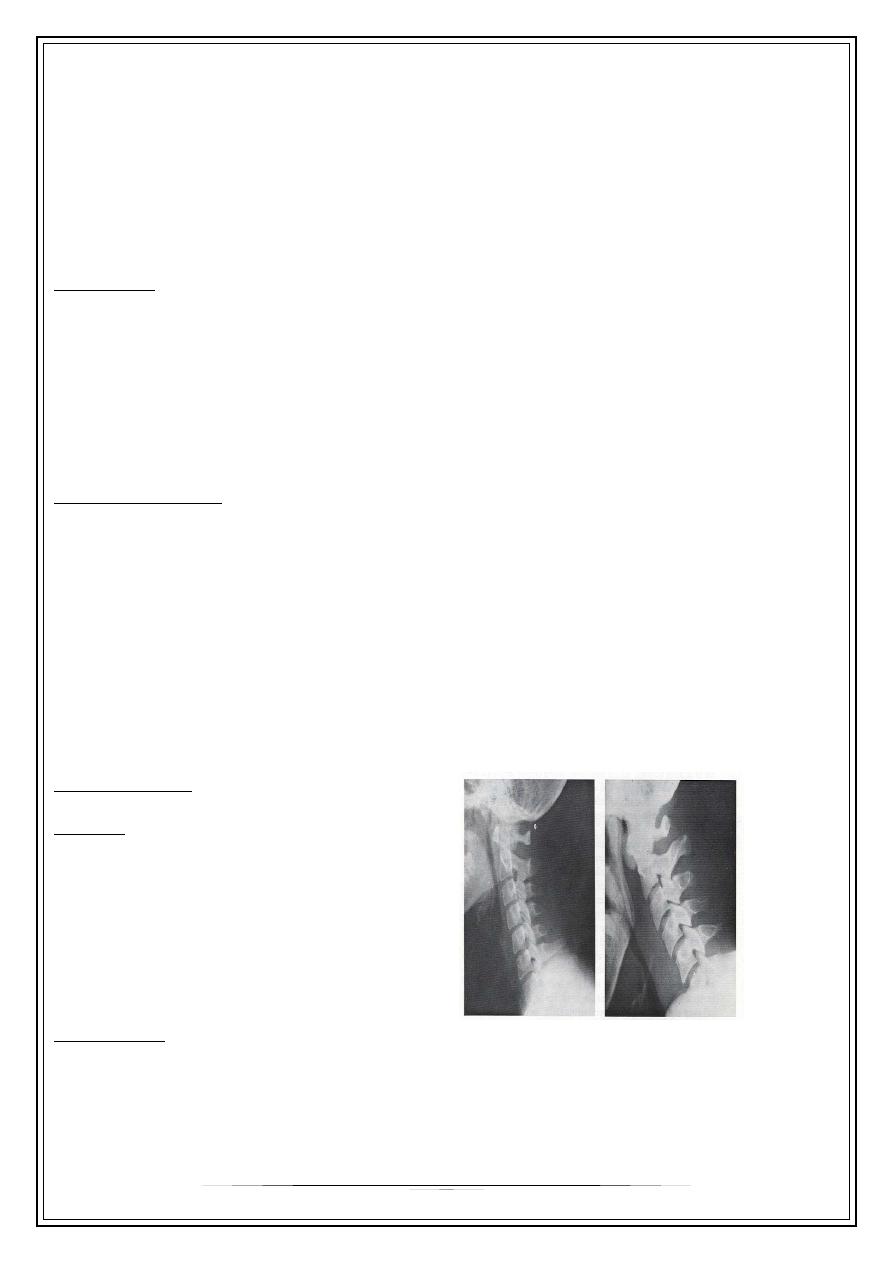
Investigation:
imaging
Lateral neck plain film
-Normal: 7mm at C-2
-14mm at C-6 for kids,
-22mm at C-6 for adults
Treatment:
•
Drainage without intubation with head down position
•
Systemic antibiotics
•
Tracheostomy may become necessary
4
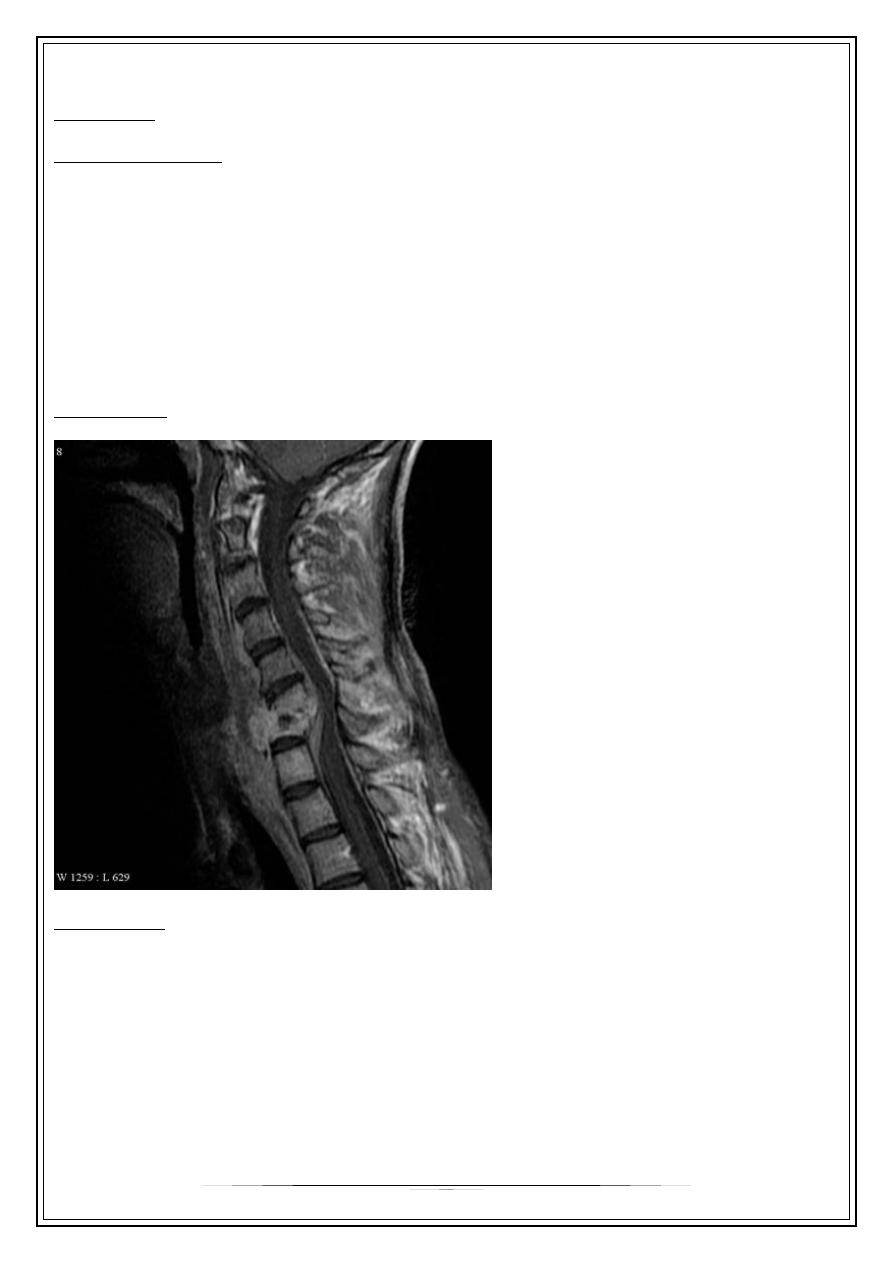
Chronic retropharyngeal abscess
Aetiology: Tuberculosis
Clinical features:
1. old children & adults
2. sore throat
3. slight dysphagia
4. cold abscess in the post. Wall
5. painless enlarged L.n.
X-ray of cx. Spine shows sign of tuberculosis
Treatment:
* incision through the neck
* antituberculus drugs
Thank you,,,
