
• BY : AYADO

DIGNOSIS
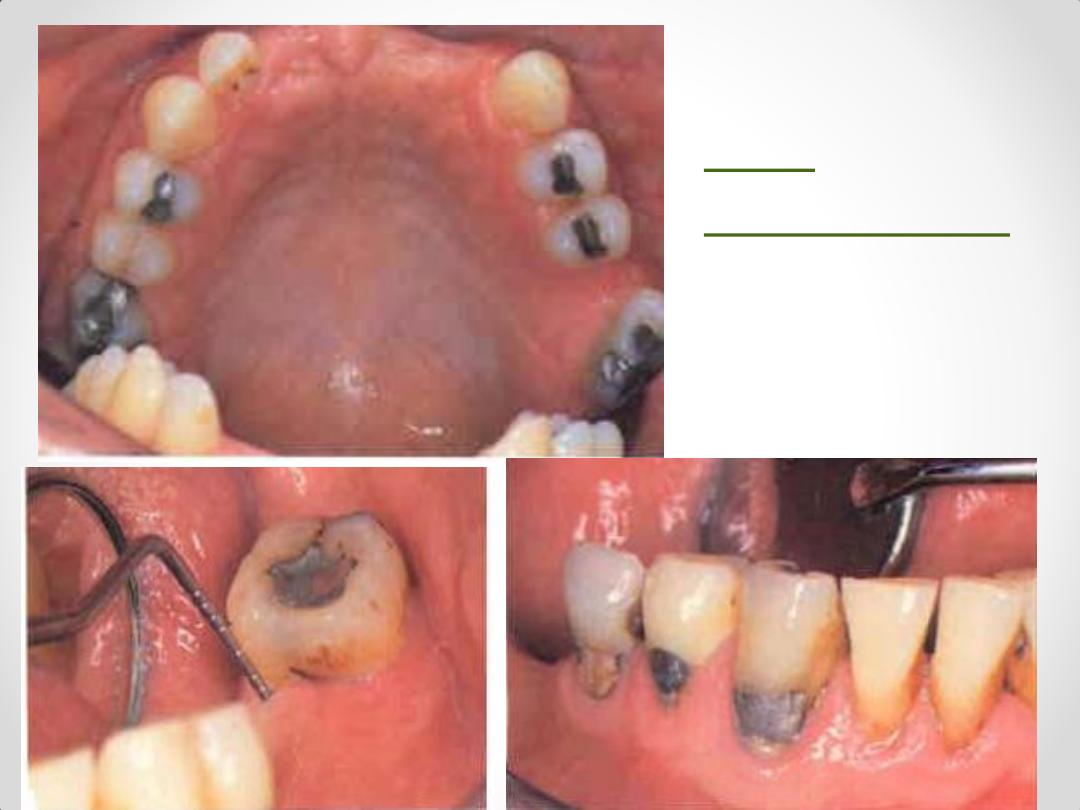
Oral
examination
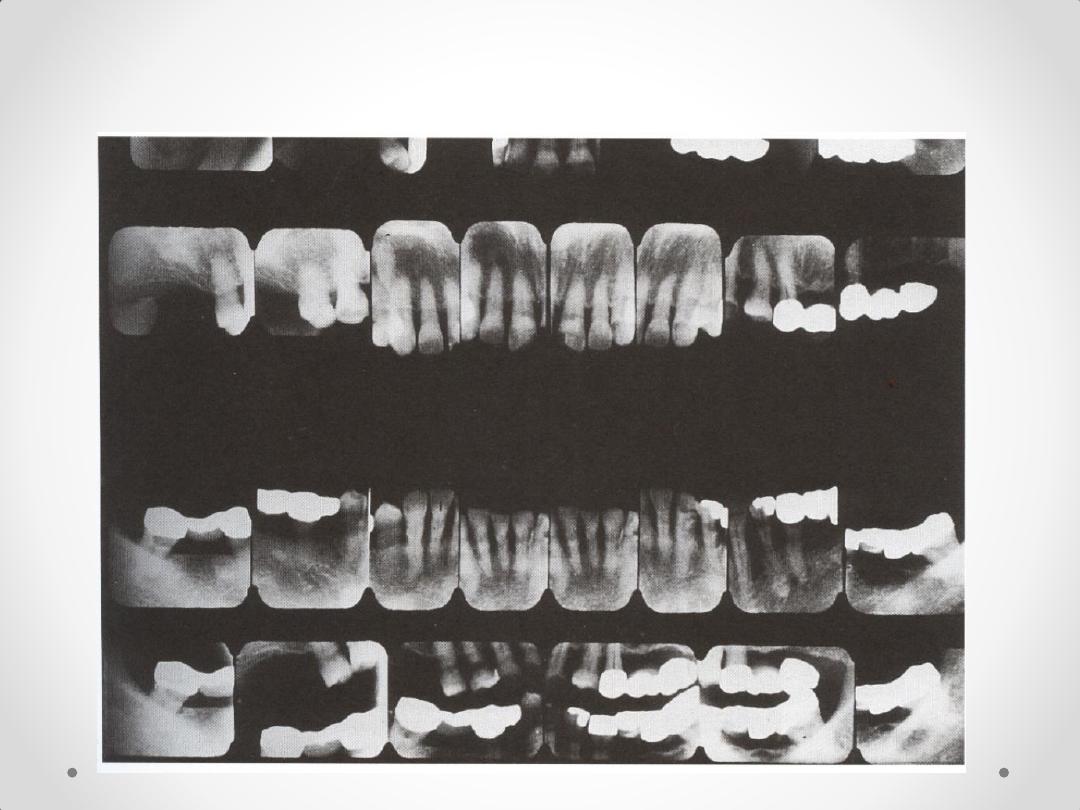
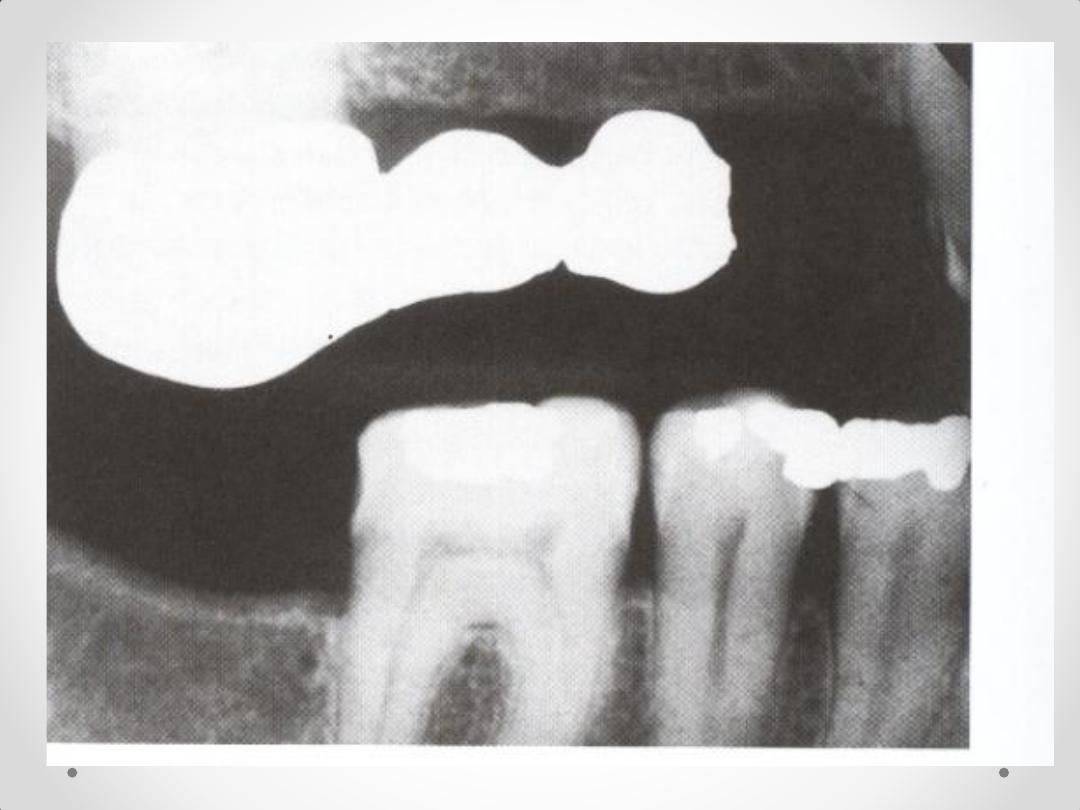
4.Complete Intraoral Radiographic survey
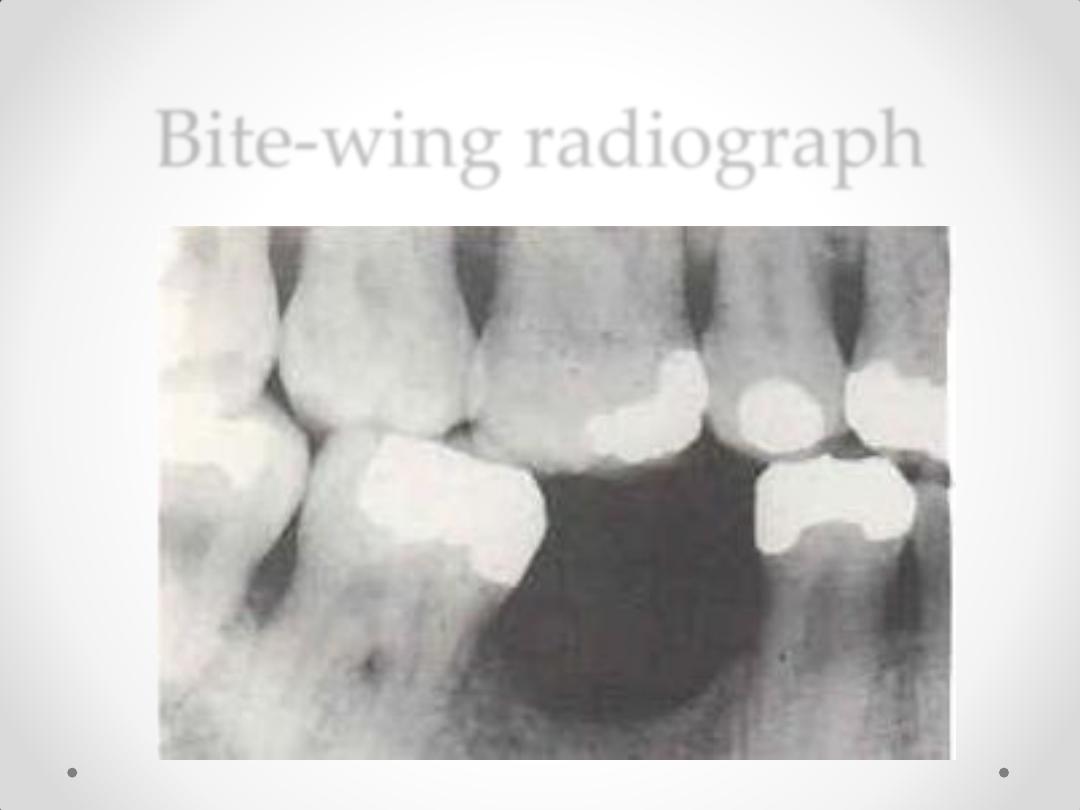
Bite-wing radiograph
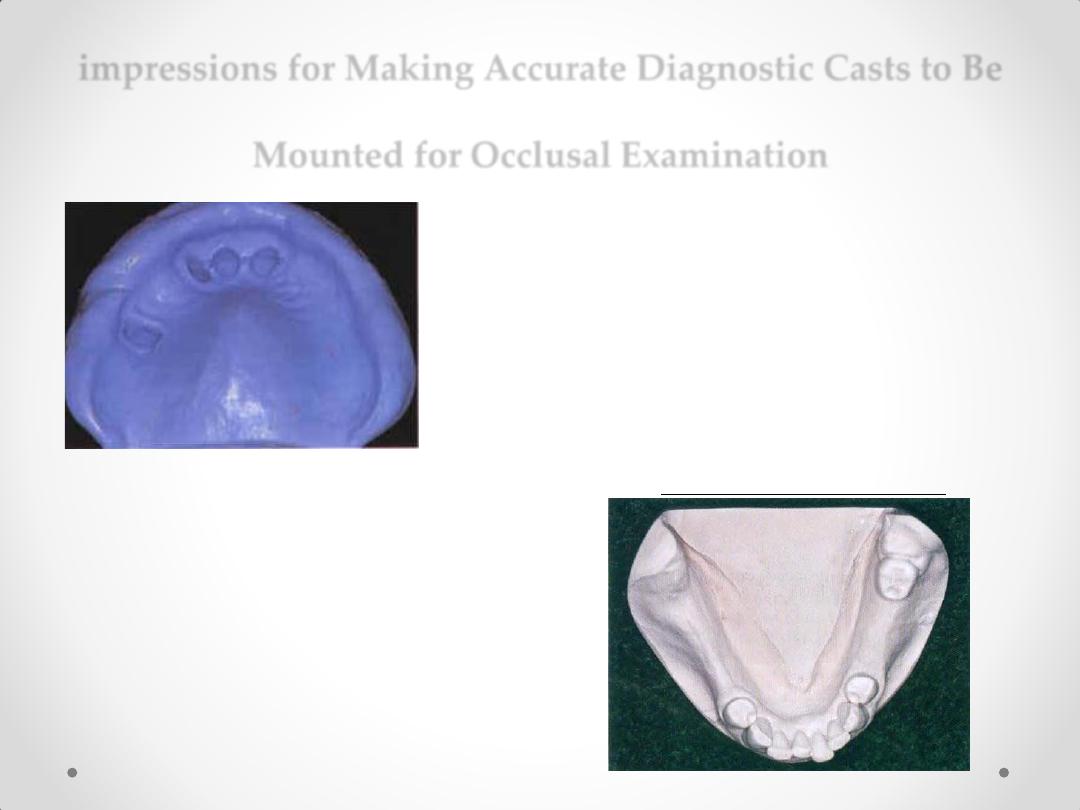
impressions for Making Accurate Diagnostic Casts to Be
Mounted for Occlusal Examination
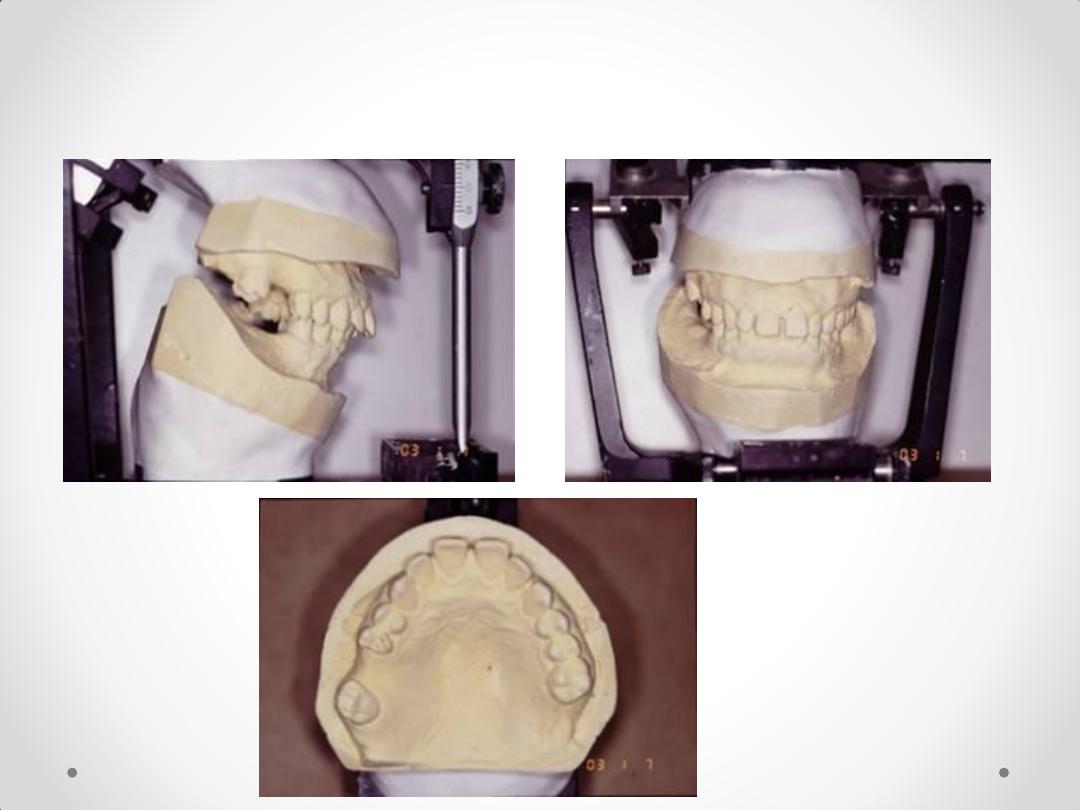
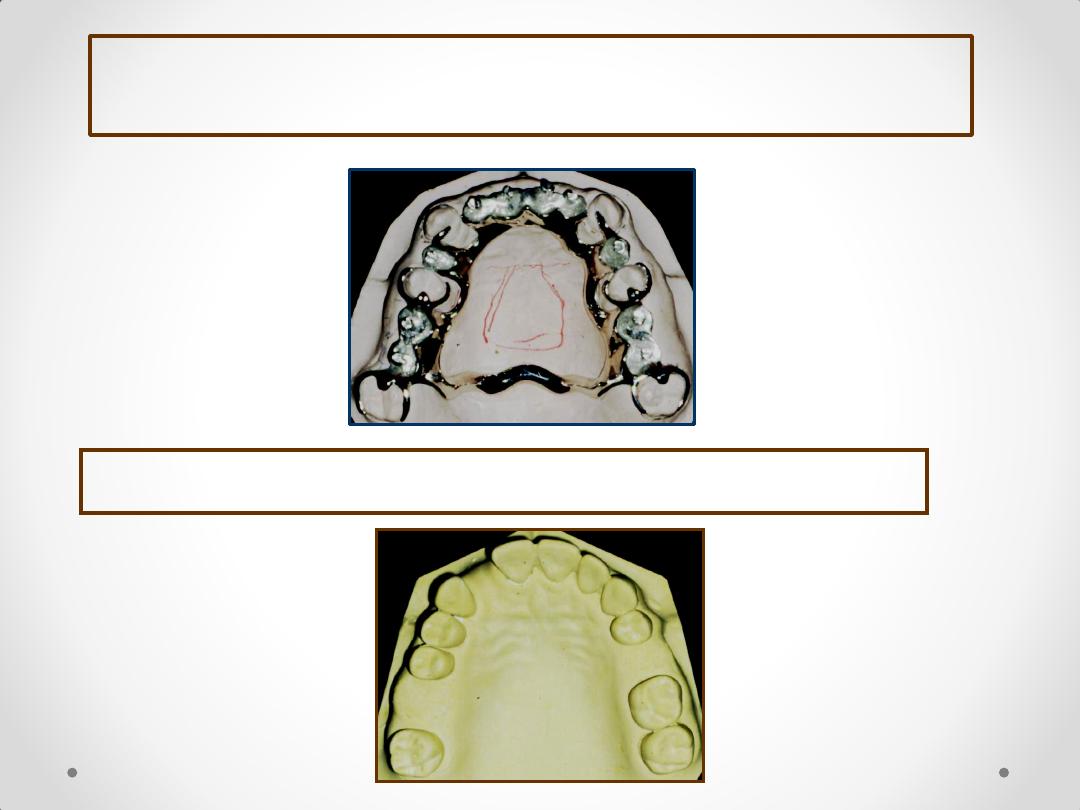
DIAGNOSTIC CASTS

DESIGNING RPD
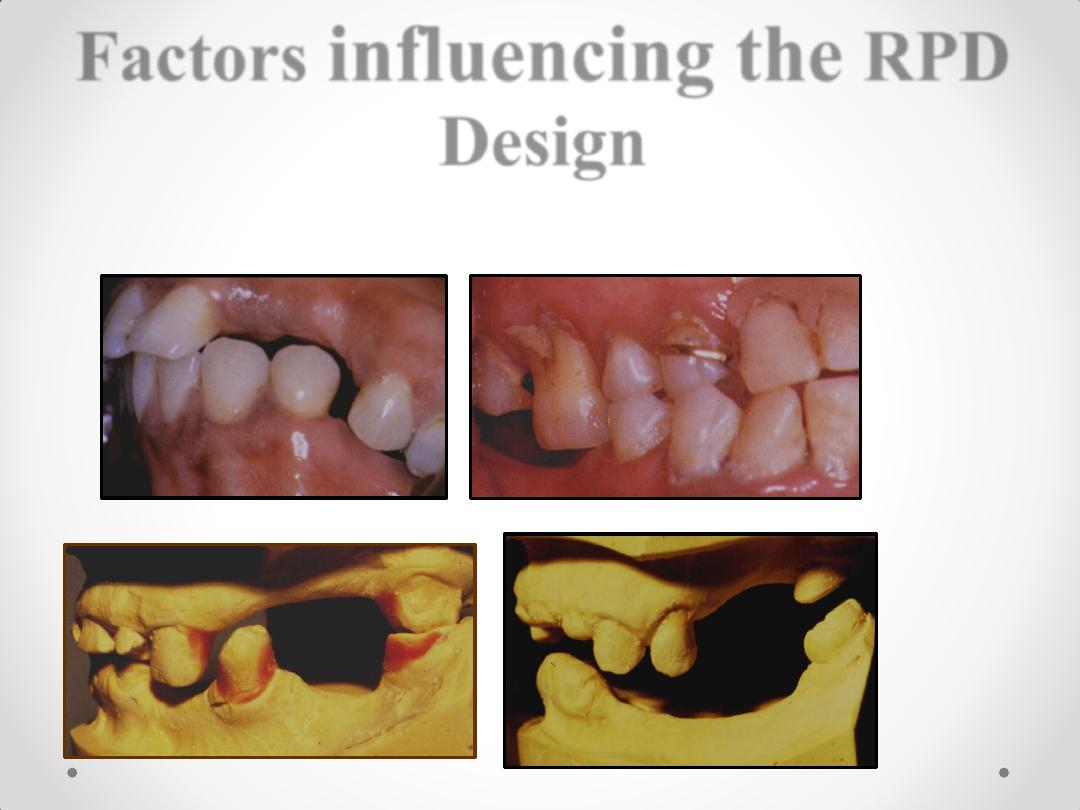
Factors
influencing the
RPD
Design
• 1. One arch is to be restored or both
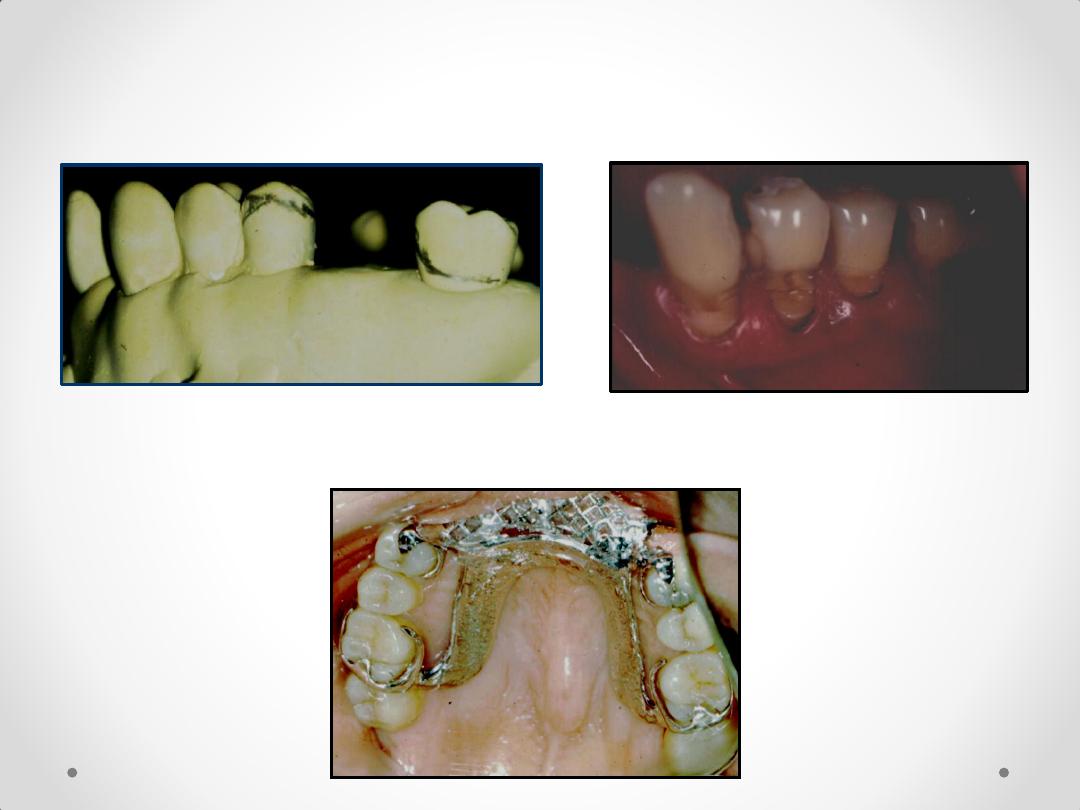
• 4. Need for abutment modification – clasp design.
5. Type of major connector indicated – e.g., a torus.
6. Materials to be used for framework, bases, & teeth
7. Patient’s past experience, i.e., patient’s inability to accept
lingual bar or palatal bar major connector.
8. Replacing a single tooth or anterior teeth – RPD or FPD.
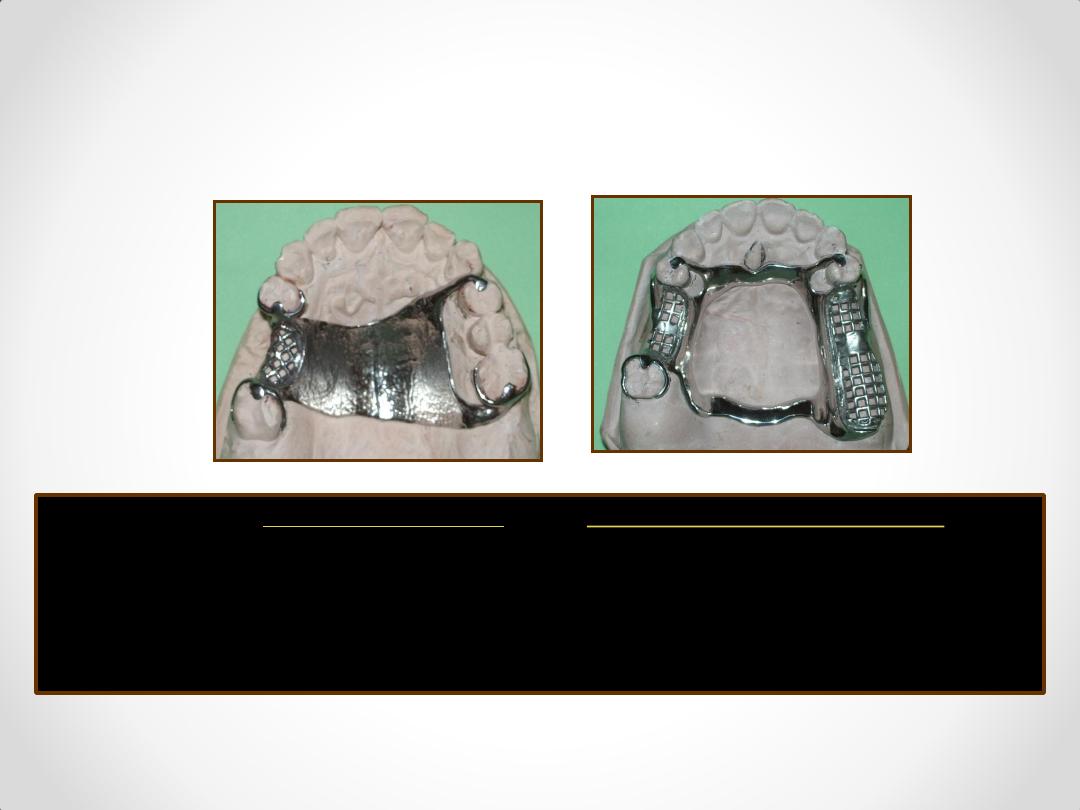
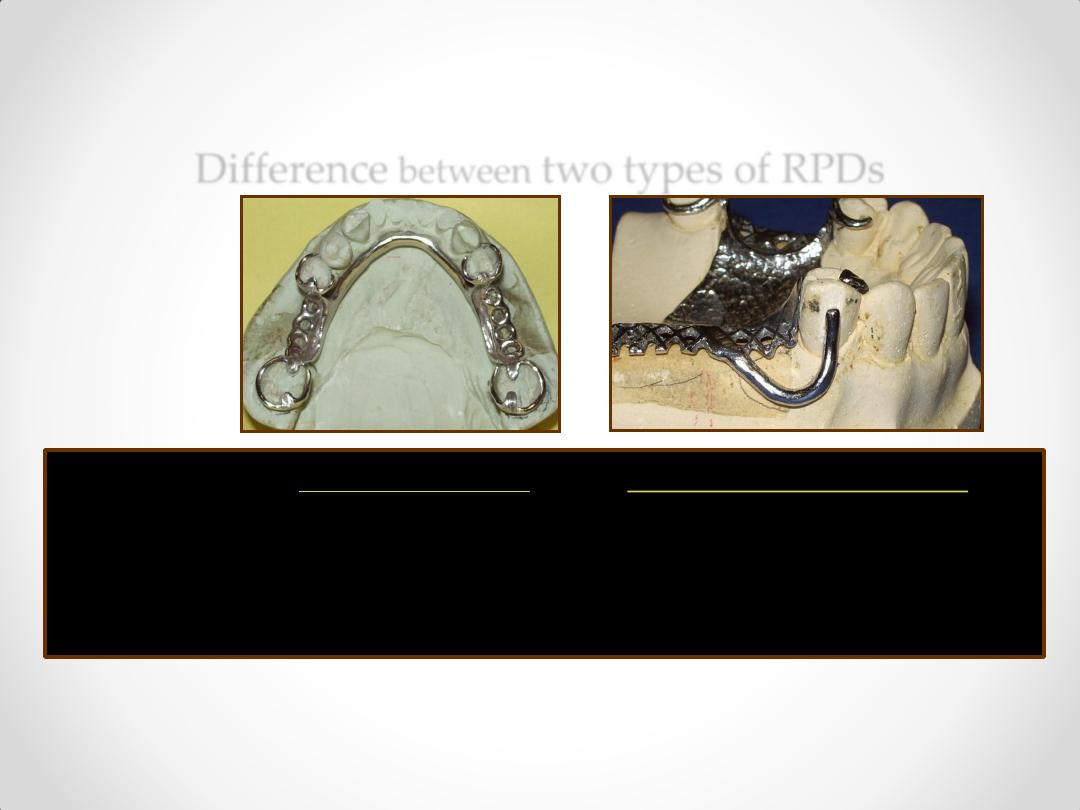
Difference
between
two types of RPDs
Tooth Supported
Tooth & tissue Supported
class III & IV
class I & II
1. Support
Abutment teeth
Combination of
abutment teeth
and soft tissues.

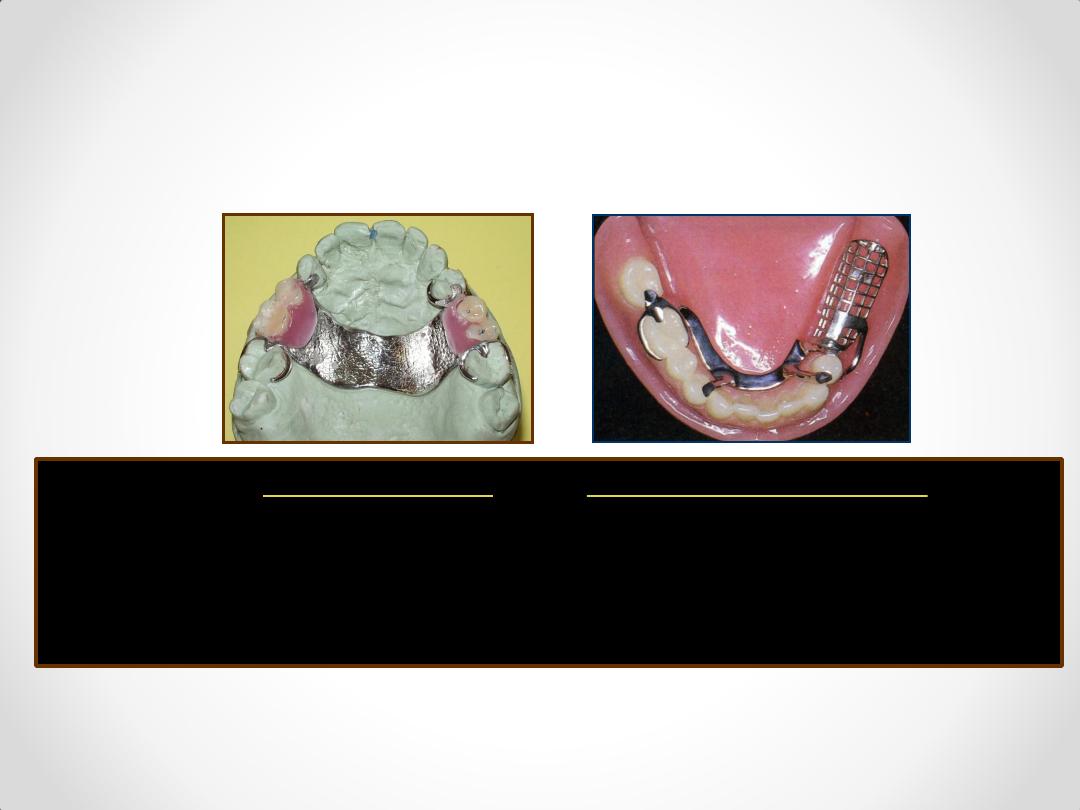
Difference
between
two types of RPDs
Tooth Supported
Tooth & tissue Supported
class III & IV
class I & II
2. Impression Anatomic form Anatomic and functional forms
(altered cast technique).
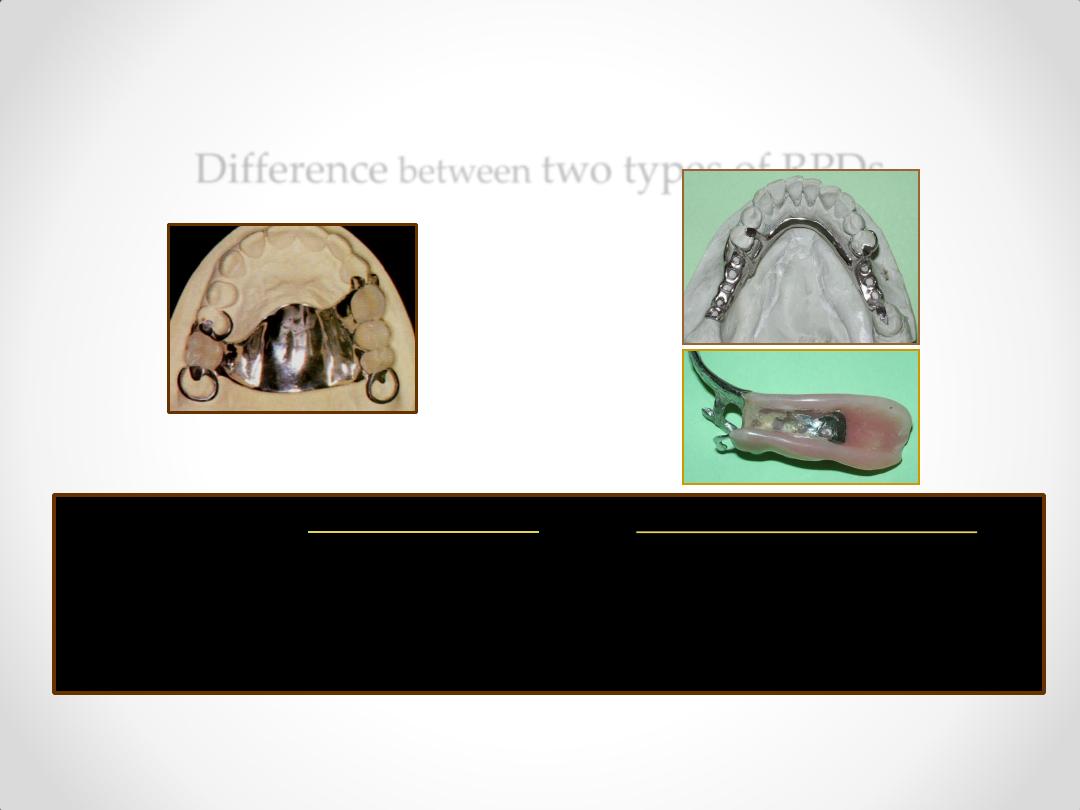
Difference
between
two types of RPDs
Tooth Supported
Tooth & tissue Supported
class III & IV
class I & II
3. Indirect No denture rotation Needed to resist any denture base
Retention hence, not needed lifting away from the tissues
.
Difference
between
two
types of RPDs
Tooth Supported Tooth & tissue Supported
class III & IV
class I & II
4. Base type
Metal base – no future Acrylic base – future reline is
reline is required.
anticipated due to bone
loss.
Difference
between
two
types of RPDs
Tooth Supported Tooth & tissue Supported
class III & IV
class I & II
5. Clasp design Circlet/Embrasure/Ring Stress release design – RPI /
‘No stress release’
RPC, - wrought wire clasp.
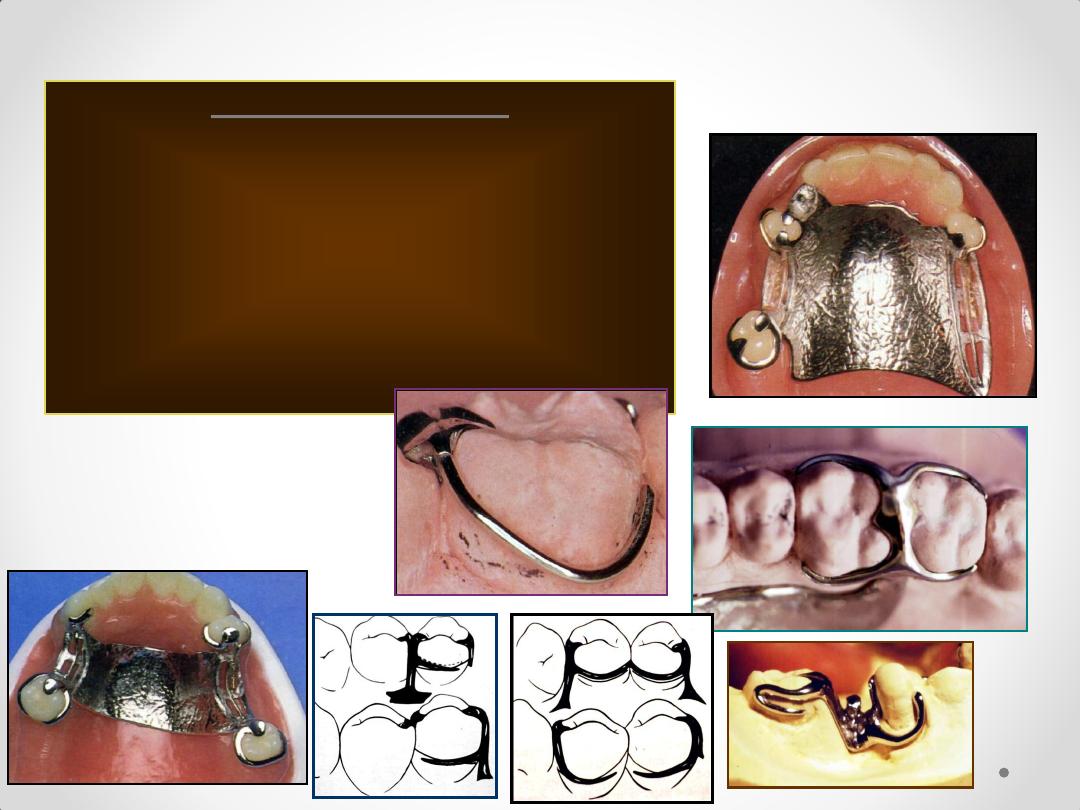
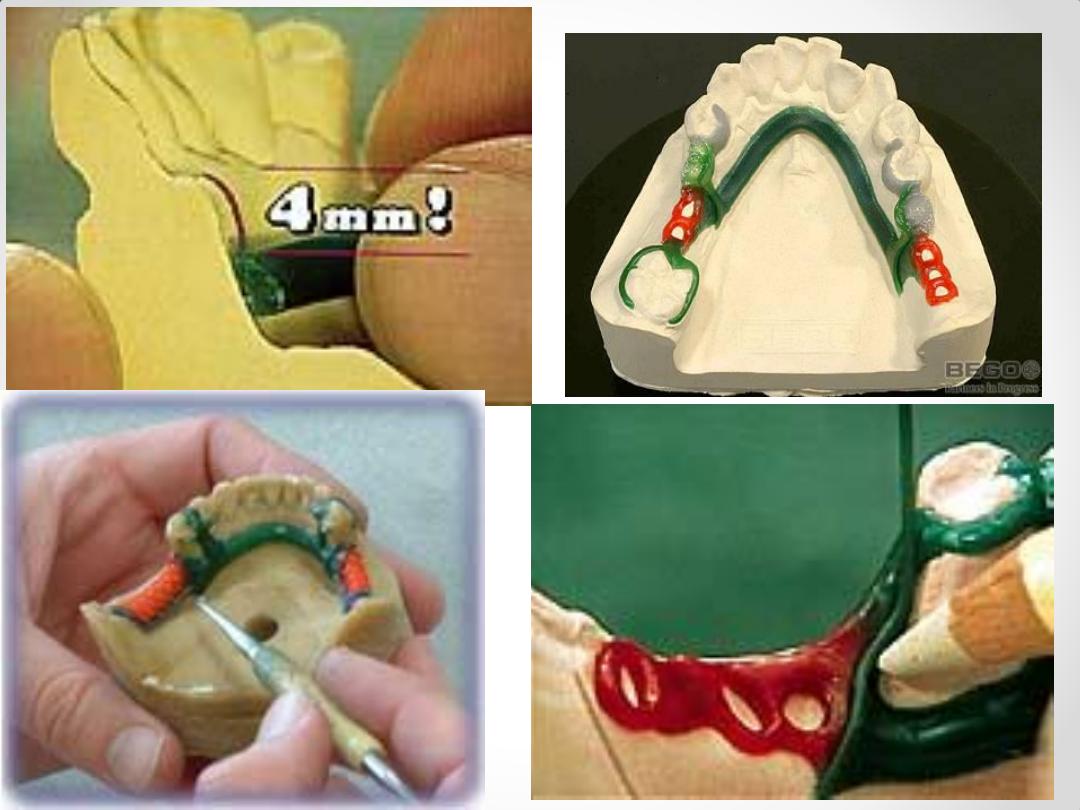
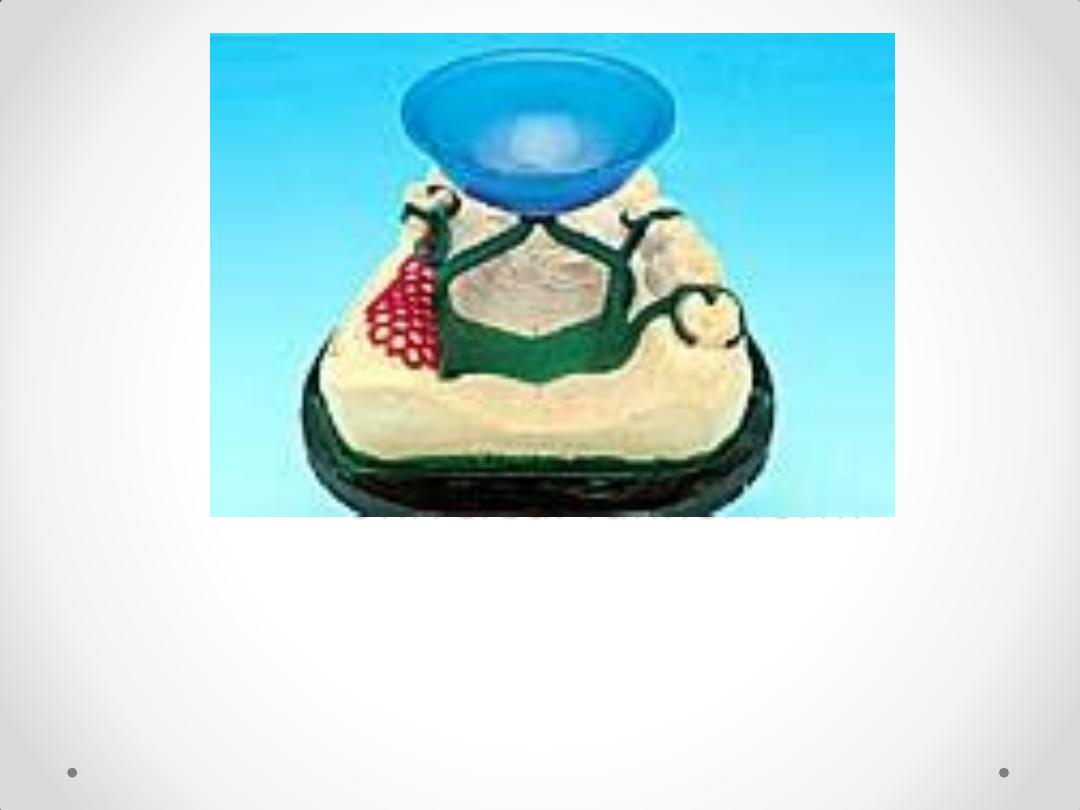
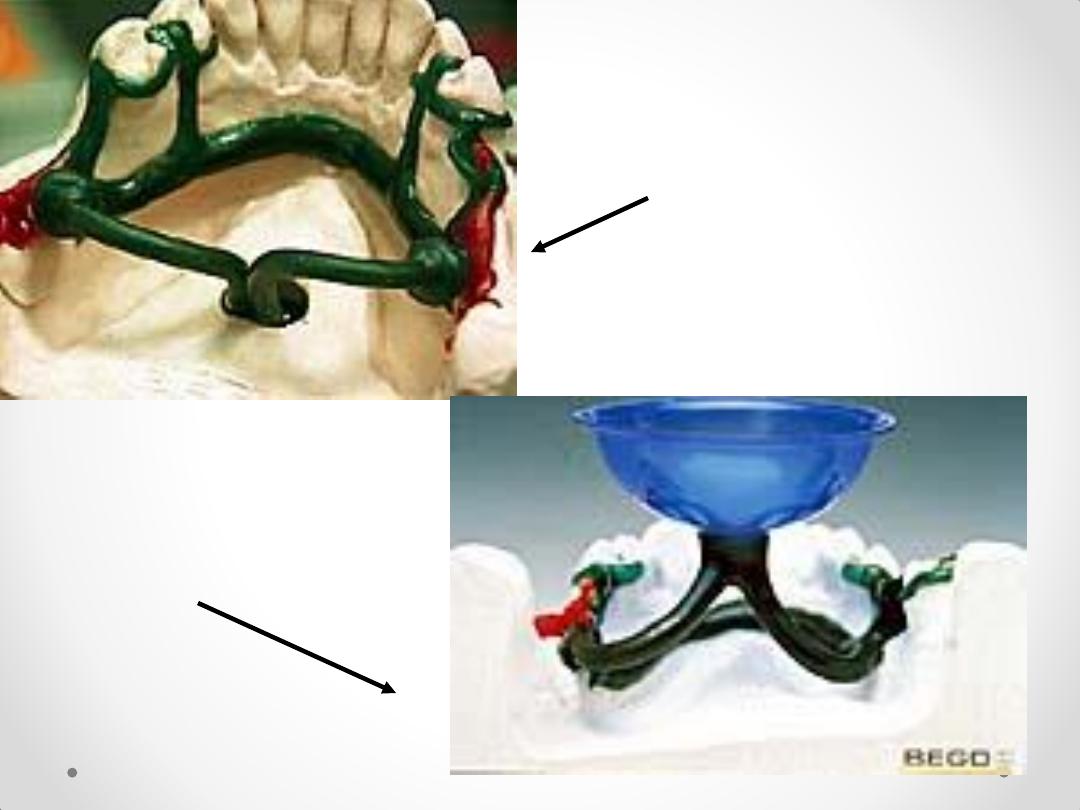
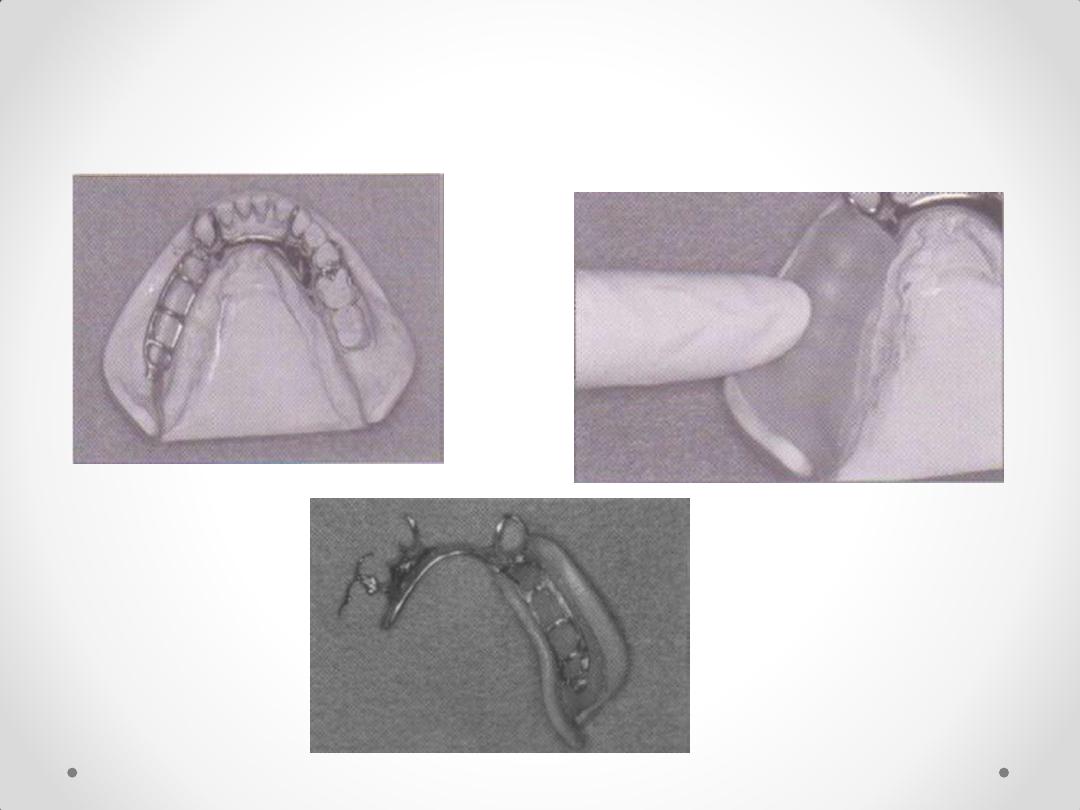
Components of an RPD Framework
Circumferential Clasps
Circlet / conventional / C clasp
Embrasure clasp
Reverse action / Hairpin clasp
Ring clasp
Multiple clasp
Half & half clasp
Combination clasp
Components of an RPD Framework
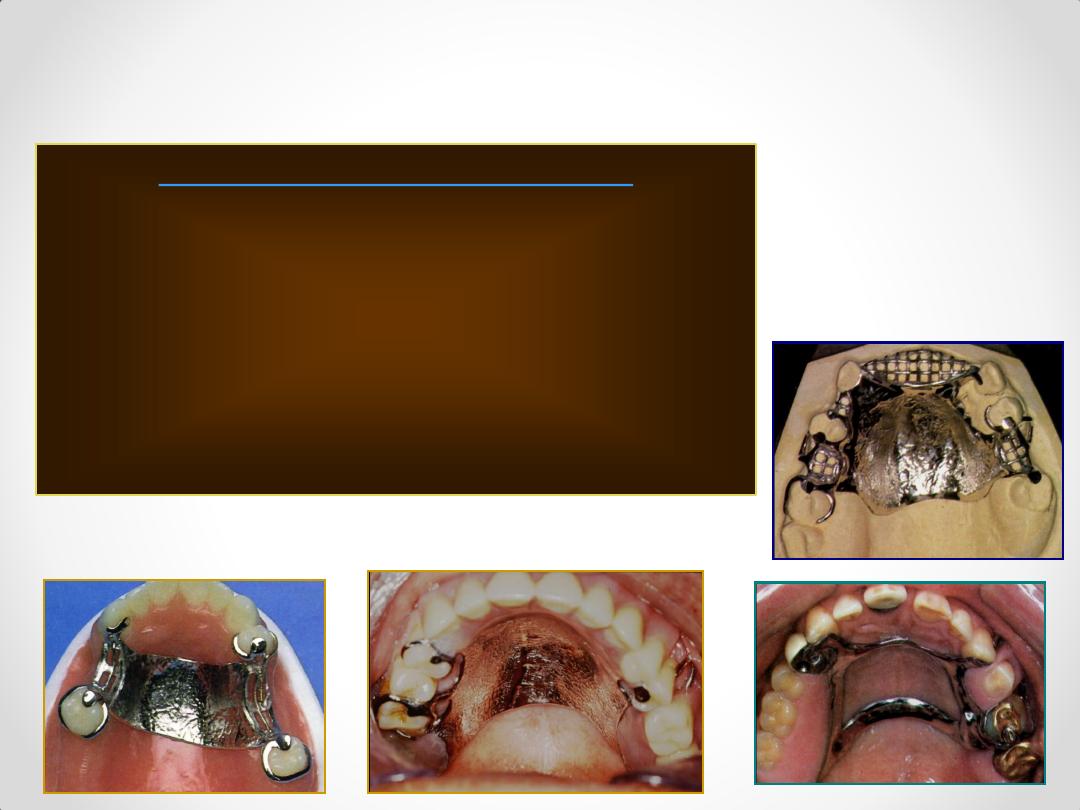
Infra Bulge or Bar type Clasps
1. T – bar
2. Y – bar
3. L – bar
4. I – bar
system
Components of an RPD Framework
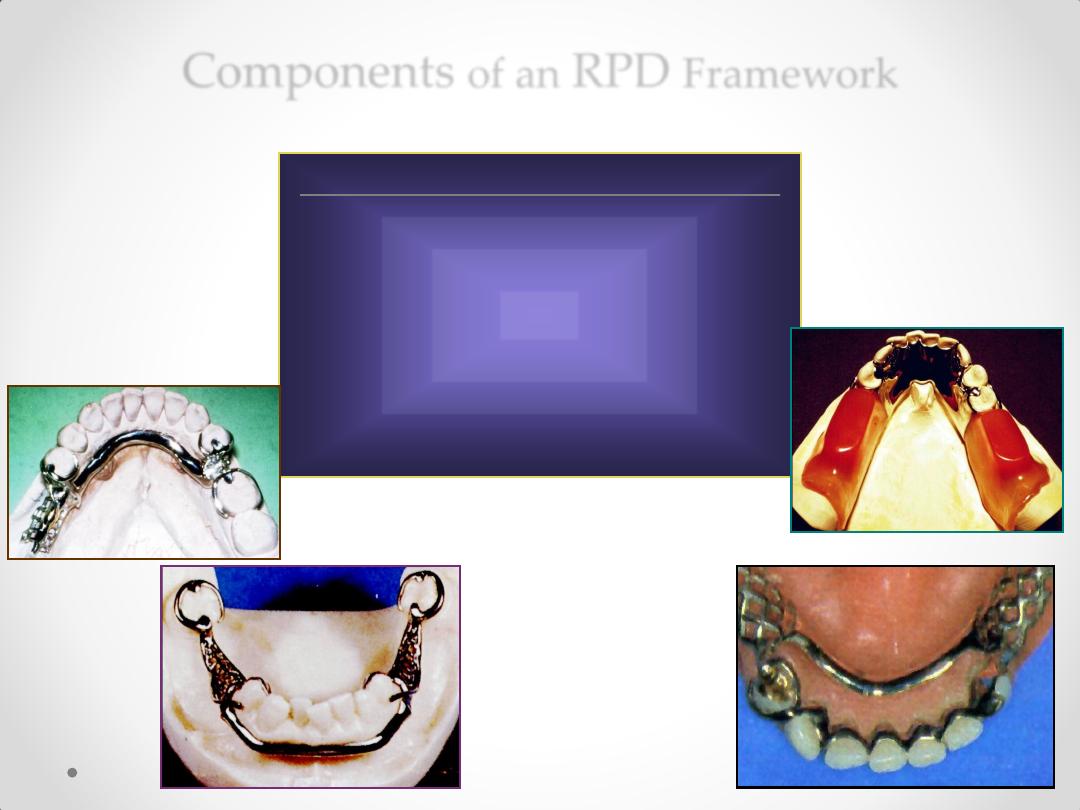
Maxillary Major Connectors
1. Single Palatal Bar
2. Single Palatal Strap
3. U – shaped Palatal Connector
4. Anterior & Posterior Palatal Straps /
Bars
5. Palatal Plate
Components
of an
RPD
Framework
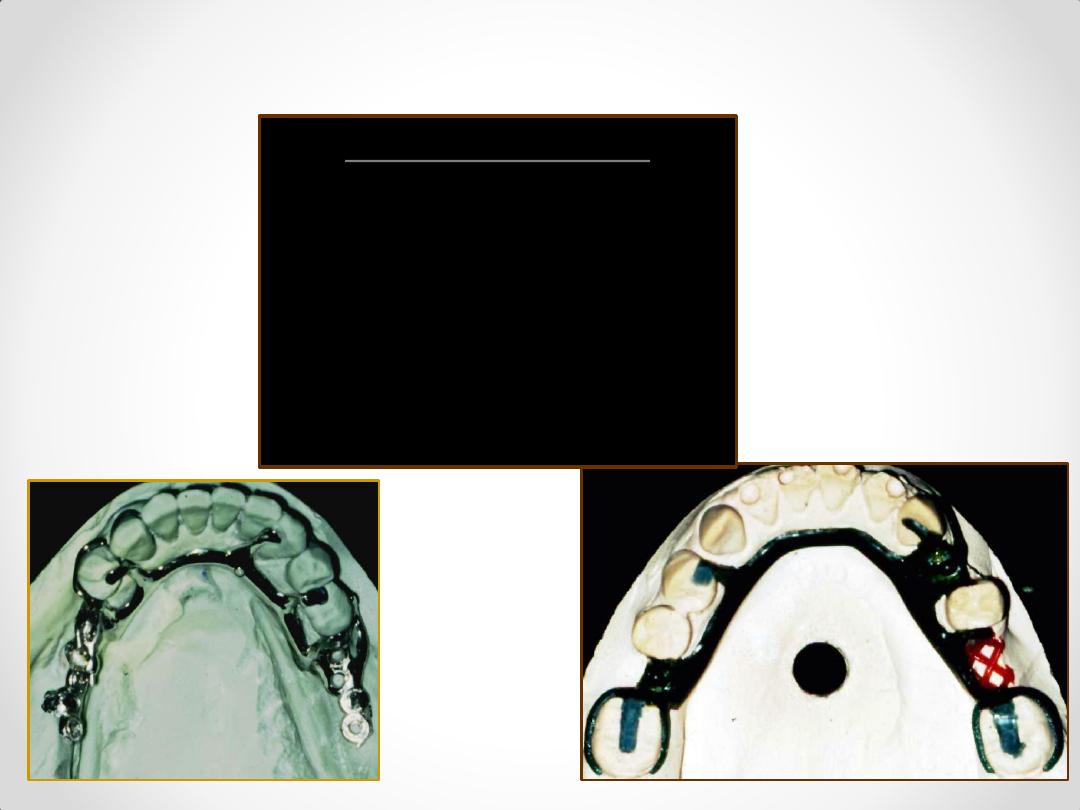
Mandibular Major Connectors
1. Lingual Bar
2. Lingual Plate
2b.Interrupted Lingual Plate
3. Double Lingual Bar
4. Labial Bar
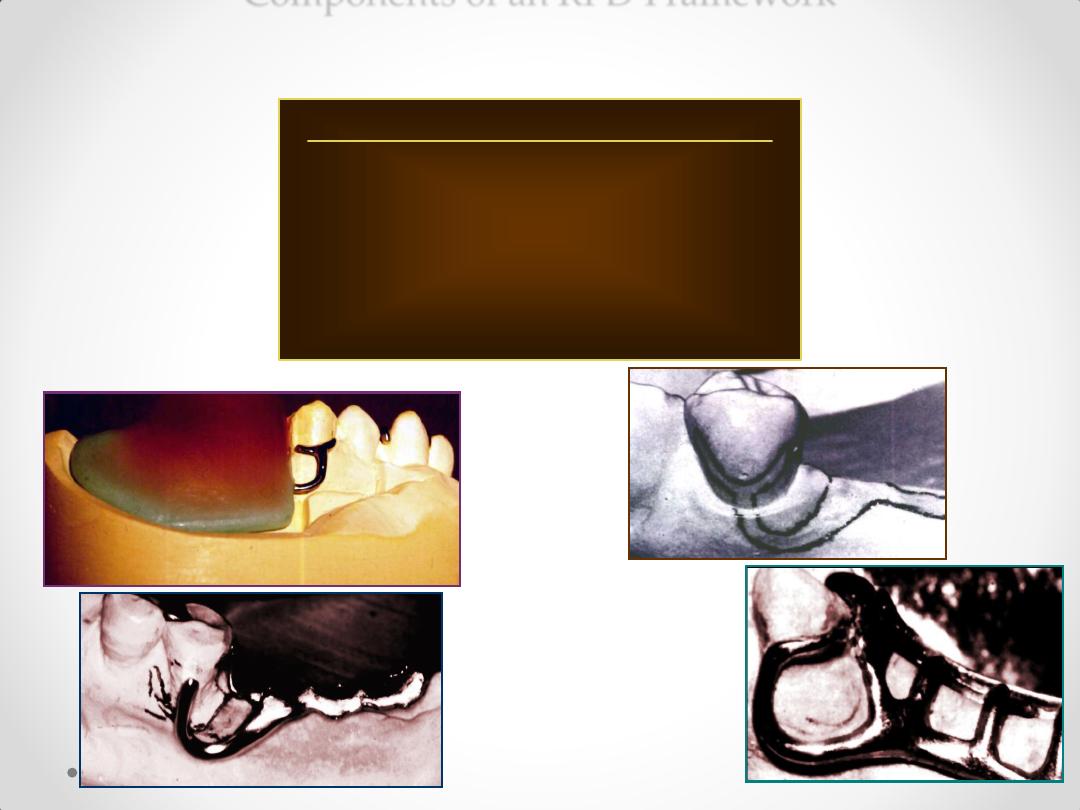
Components of an RPD Framework
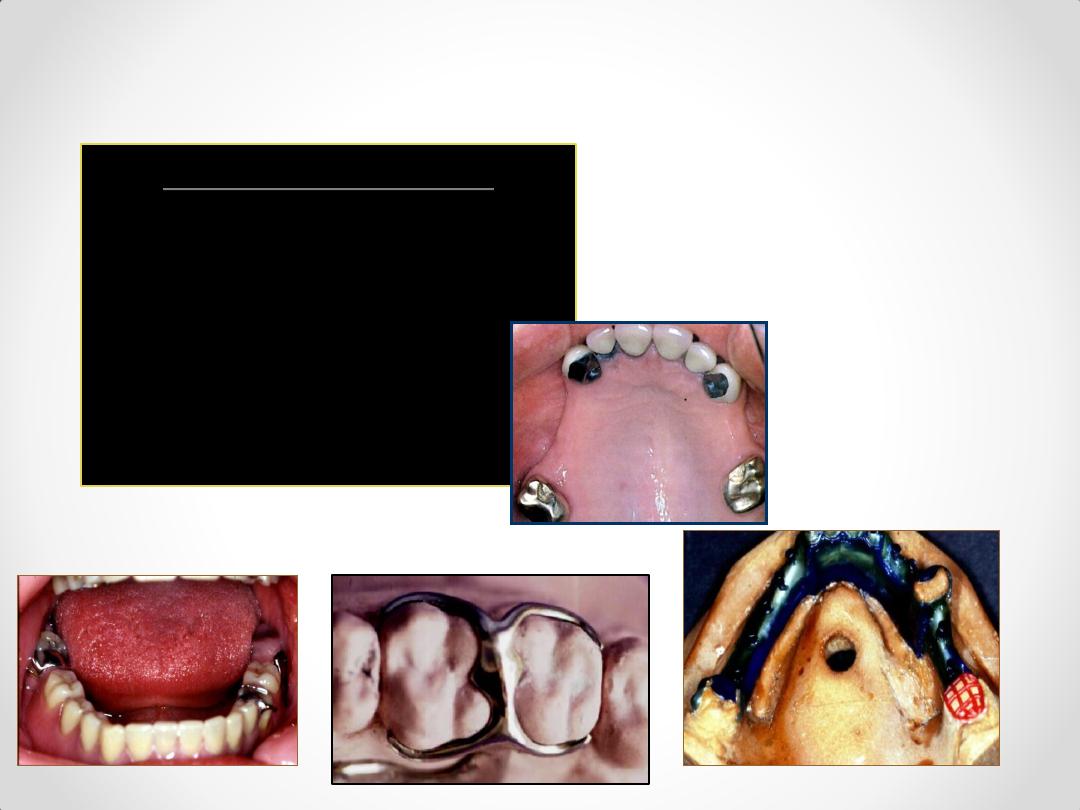
Anterior rest seats
1. Cingulum / inverted V rest.
2. Ledge rest.
3. Ball rest.
4. Incisal rest.
Components of an RPD Framework
Posterior Rest Seats
1. Occlusal rest.
2. Long occlusal rest.
3. Embrasure rest.
4. Onlay/overlay rest.

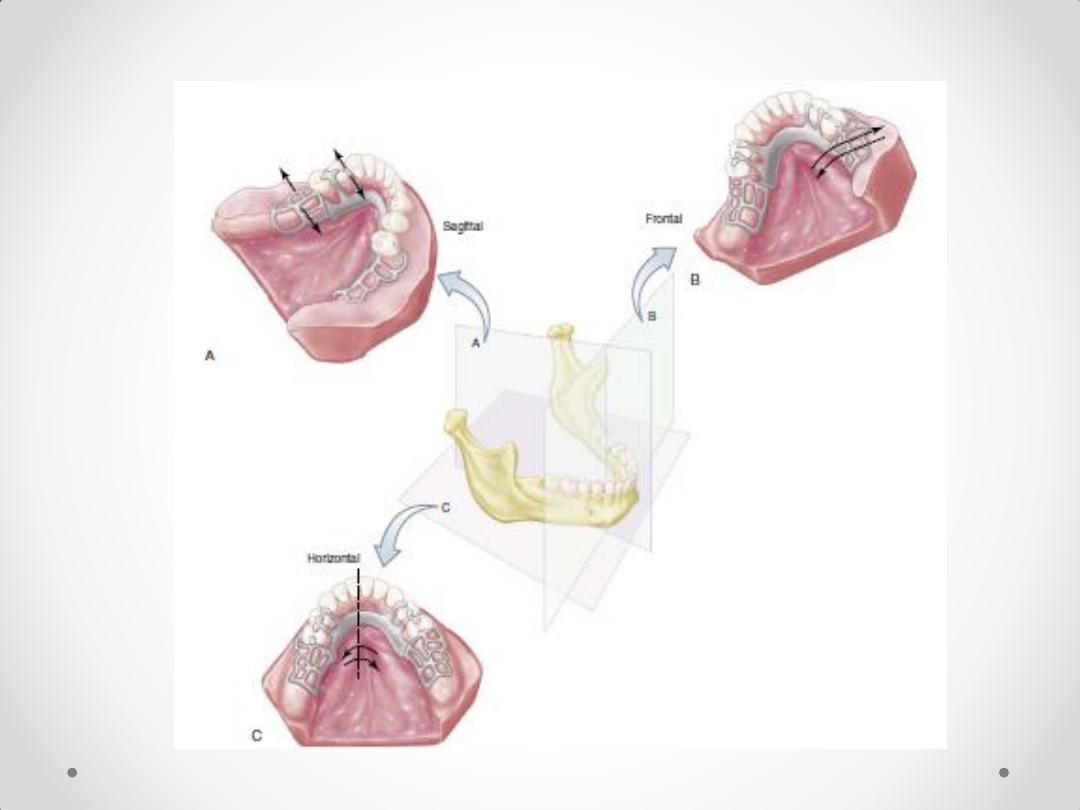
Biomechanics of
removable
partial denture
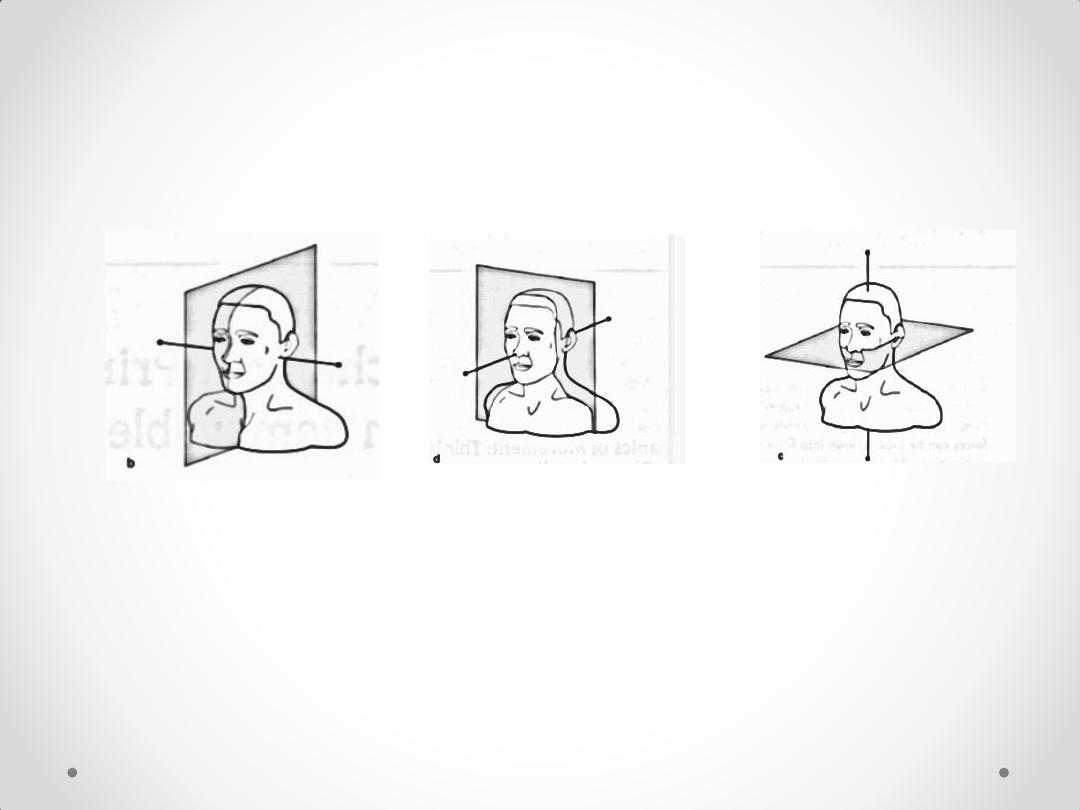
Sagittal plane
and transverse
axis
Horizontal
plane and
sagittal axis
Frontal plane and
vertical axis
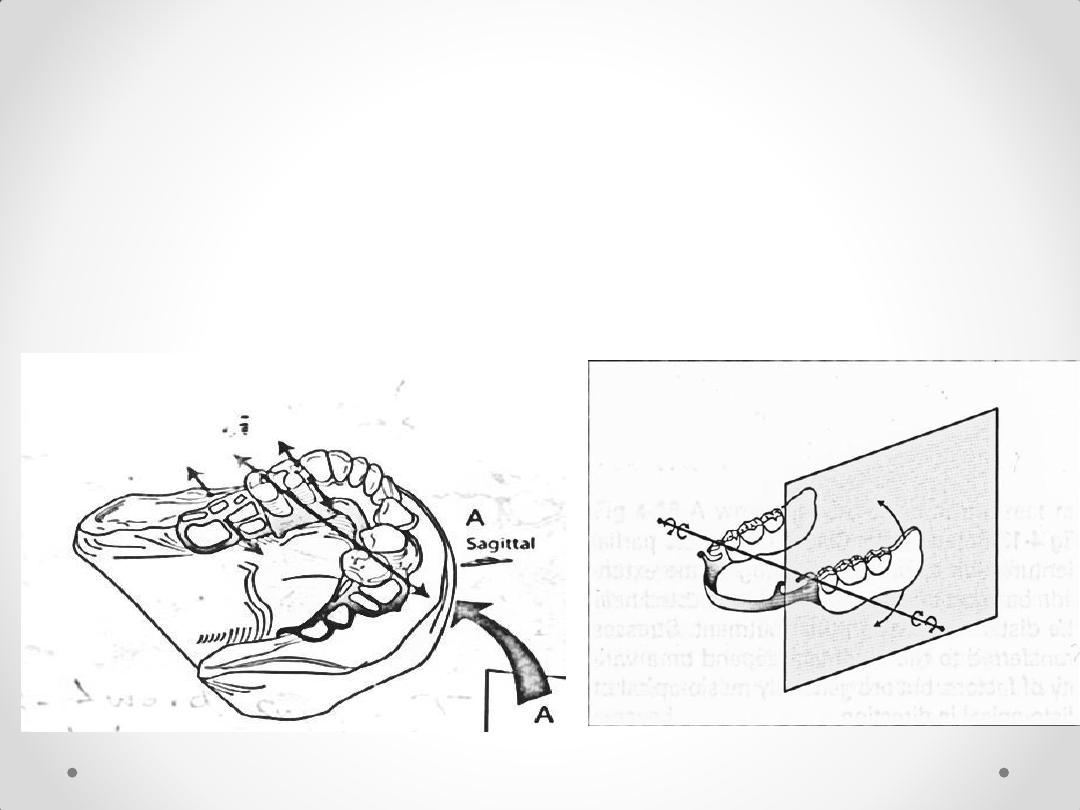
• 1.Rotation of the extension denture base around
transverse fulcrum axis
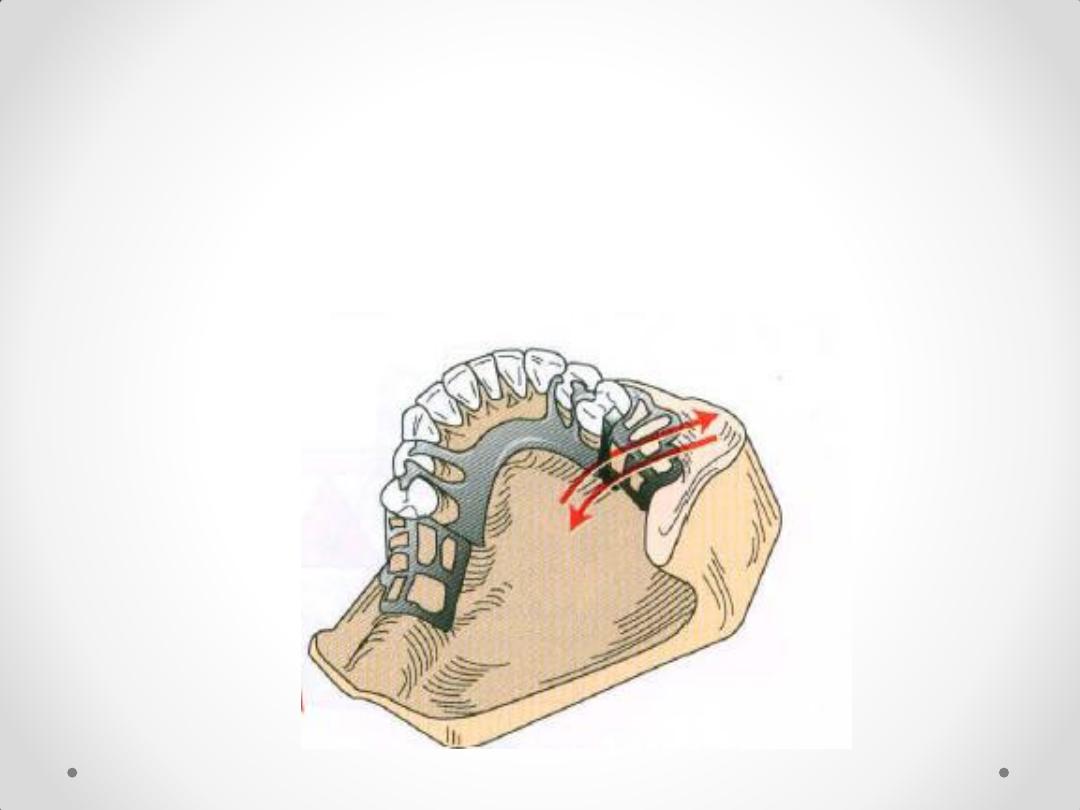
2-Rotation of all bases around
a longitudinal axis parallel to
the crest of the residual ridge
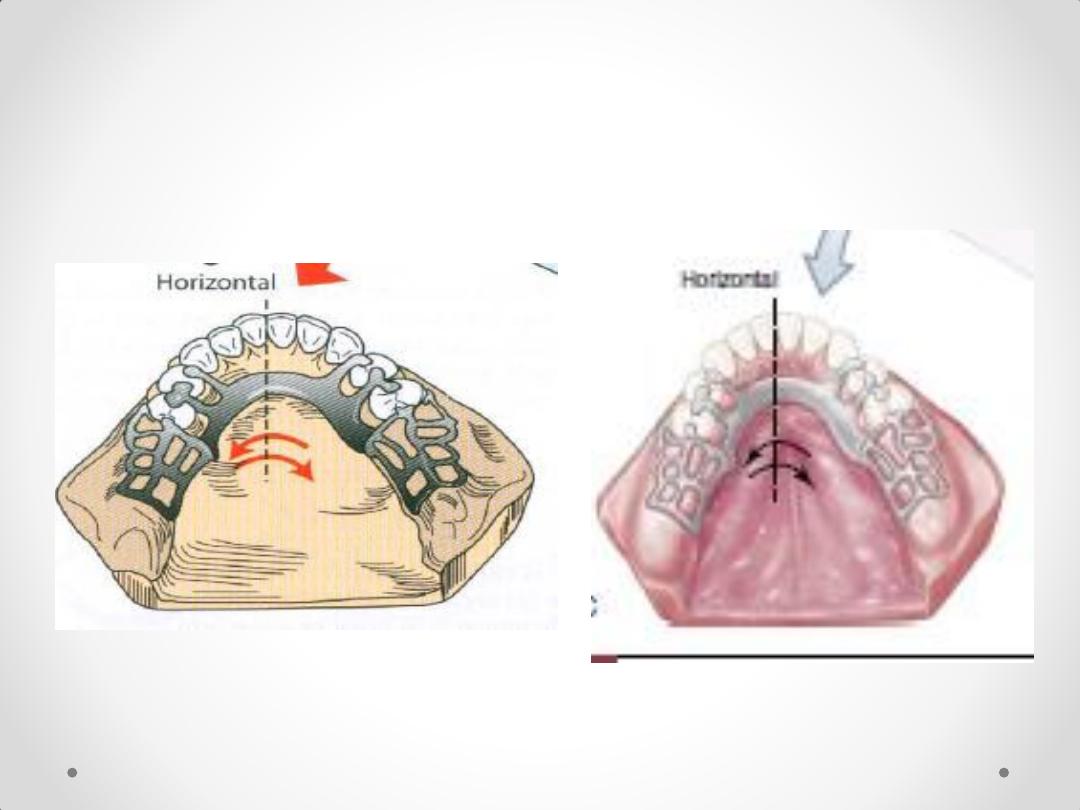
3.Horizontal movement (Lateral
and antero-posterior)
Rotation around vertical fulcrum
line
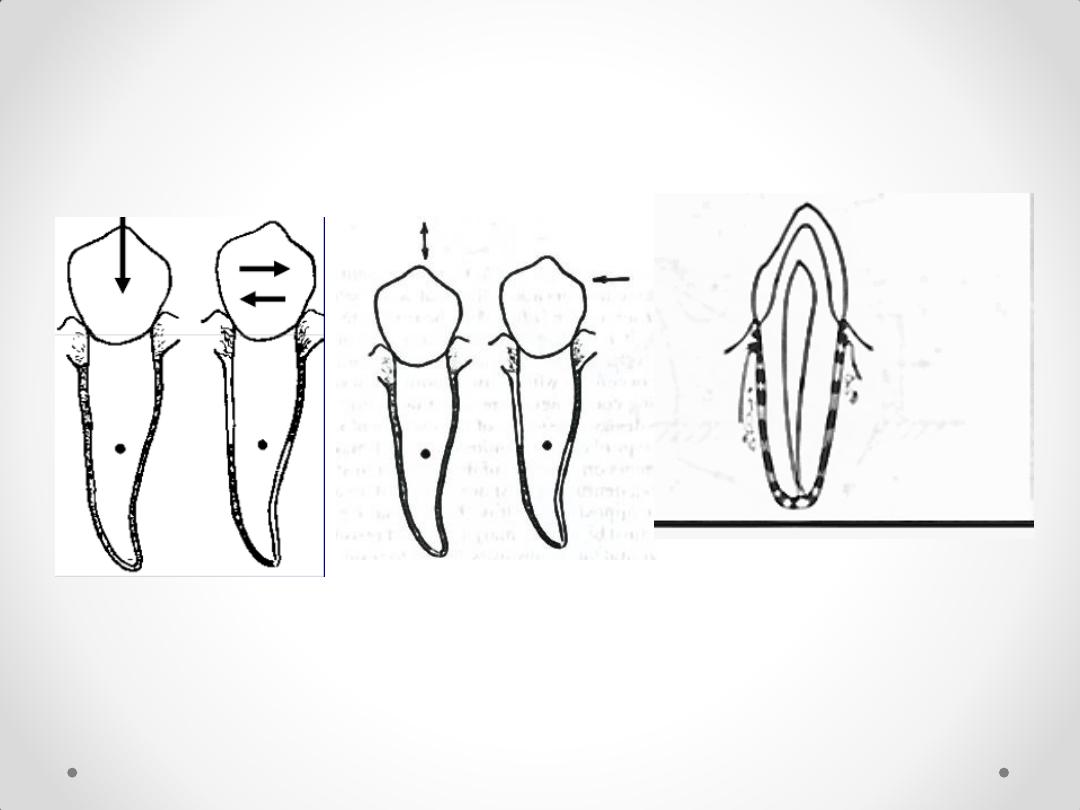
Fibers of periodontal ligament are arranged such that
their resistance to vertical forces is much greater than
that to horizontal forces
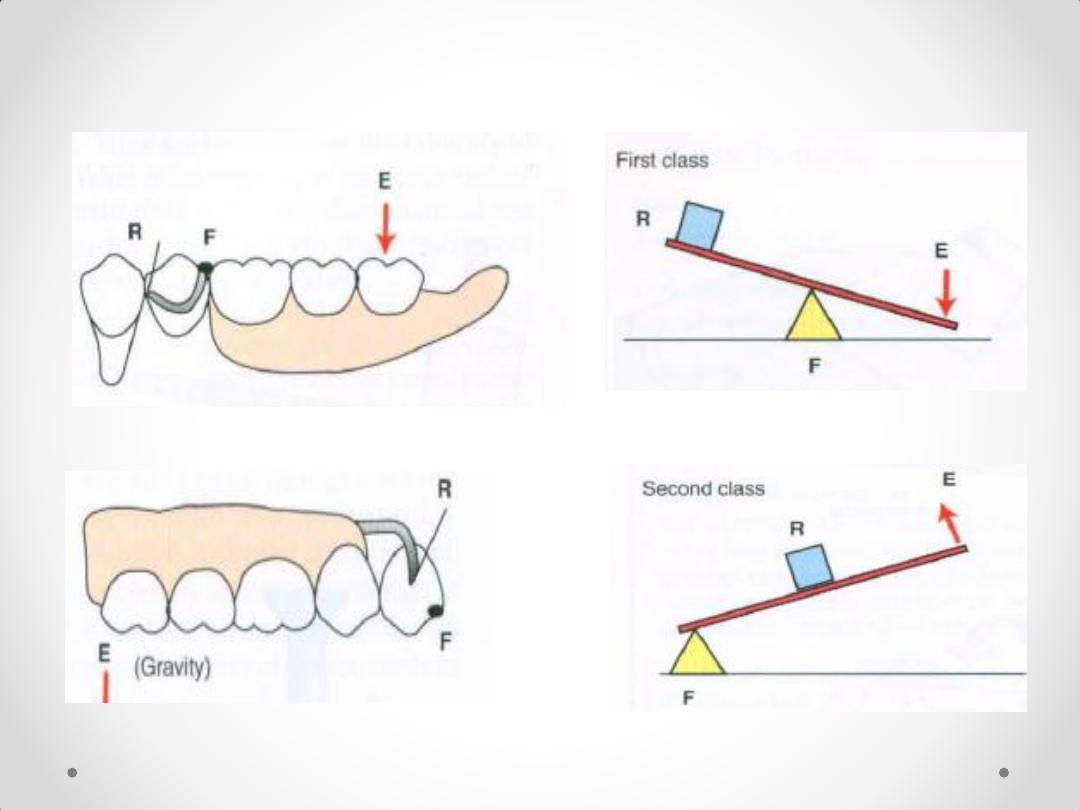
Lever 1
Lever 2
The three classes of
levers
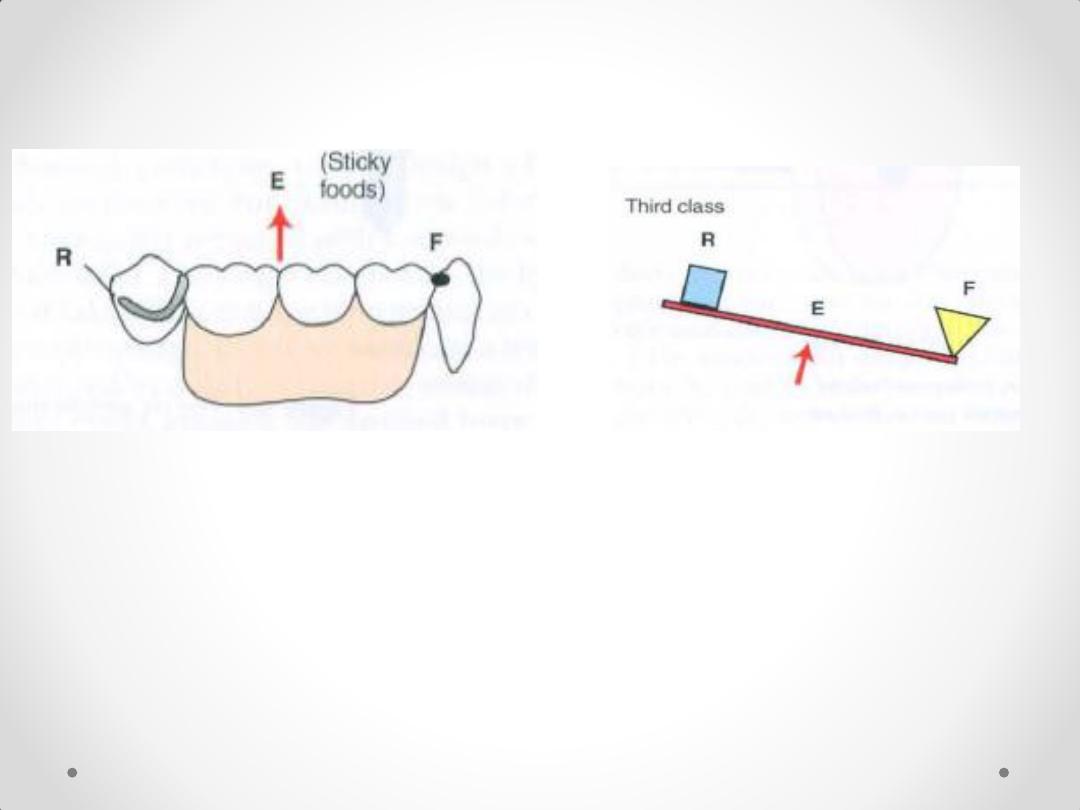
Lever 3
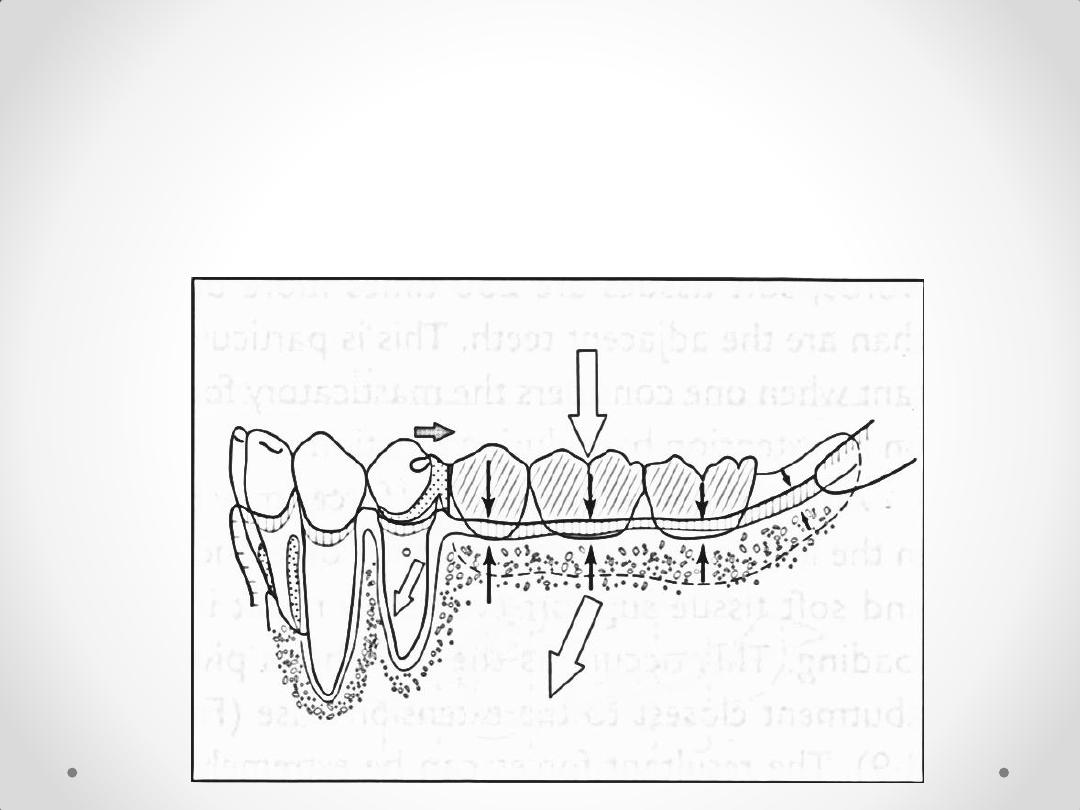
Class I or II removable partial
dentures
distal tipping.
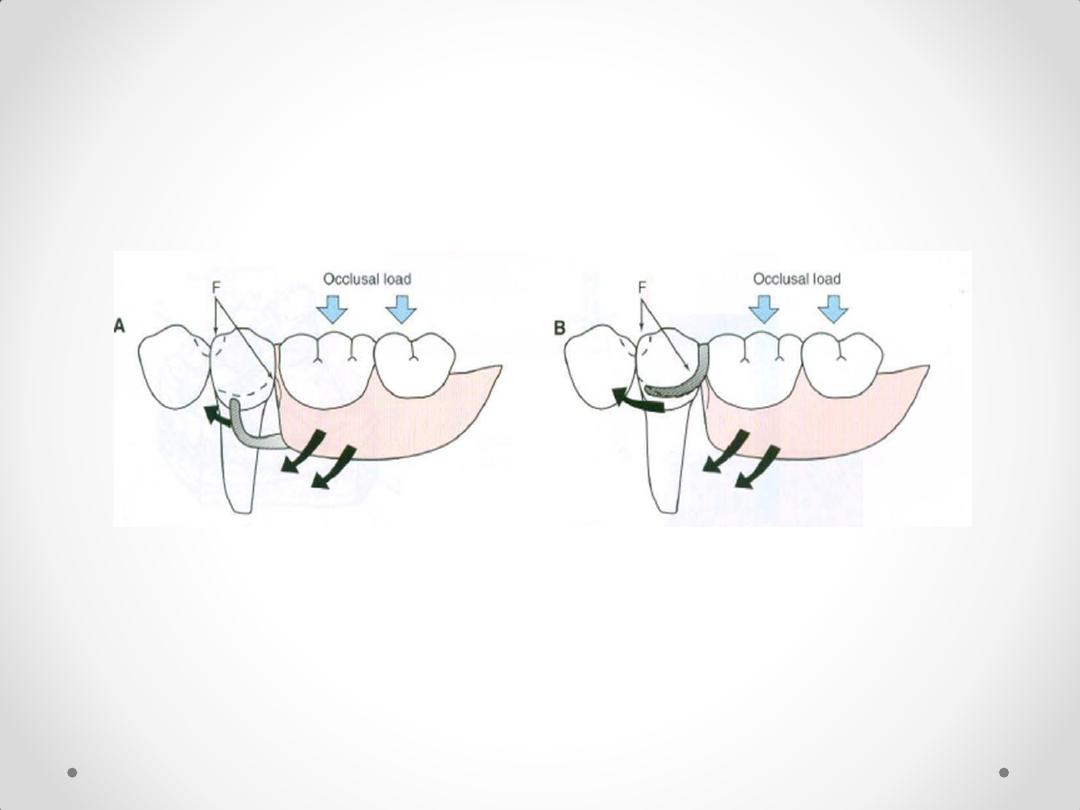
Mesial rest concept for distal extension RPD
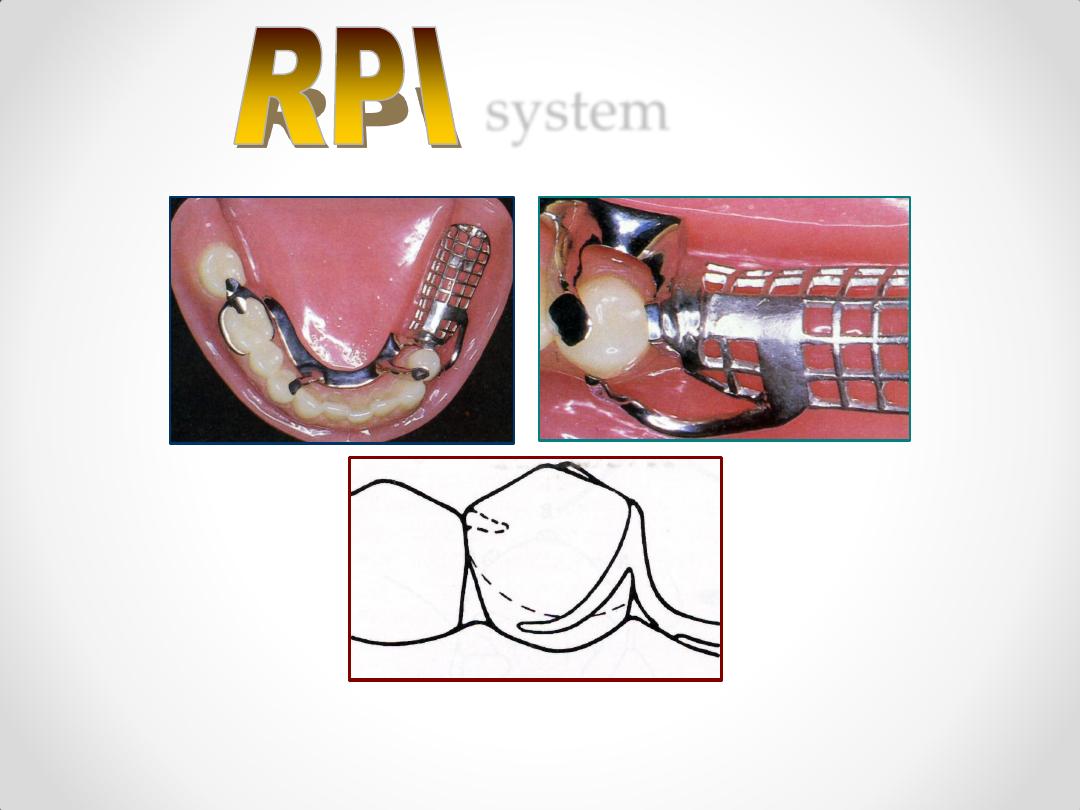
RPI SYSTEM
RPA SYSTEM
Note: tissue support of extension base is key
factor in reducing lever action of clasp
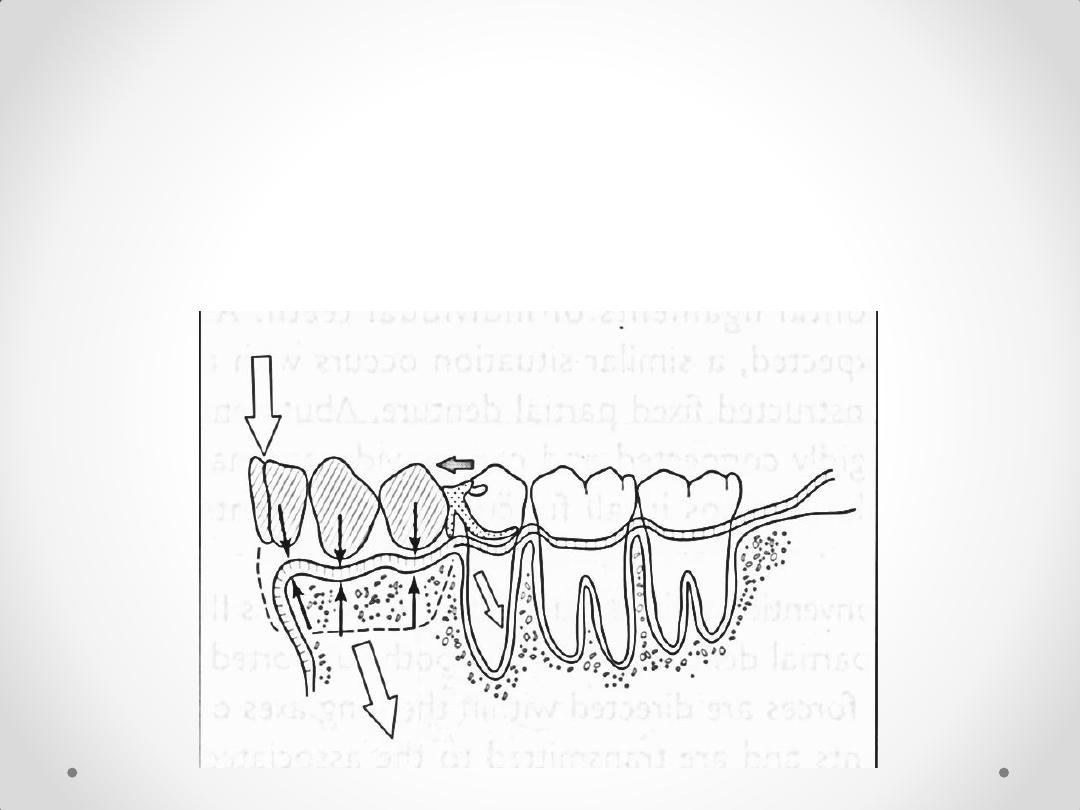
Class IV Removable Partial
Denture
mesial tipping
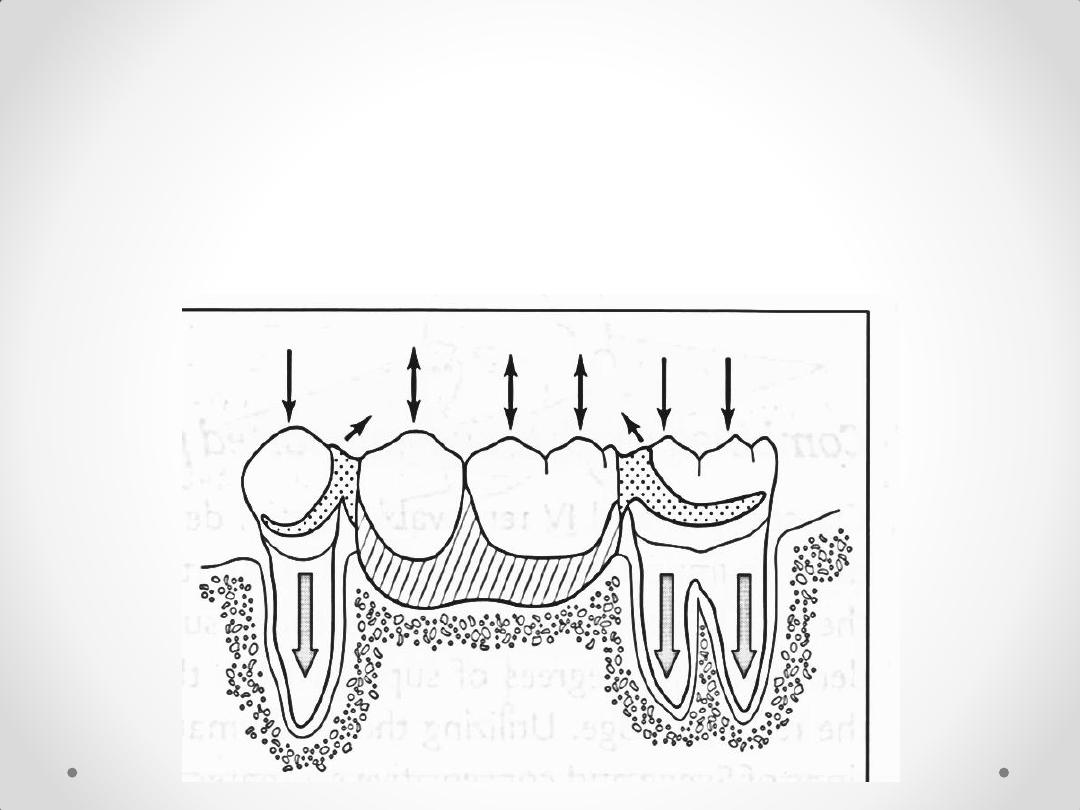
Entirely tooth-supported
prostheses
limited movement

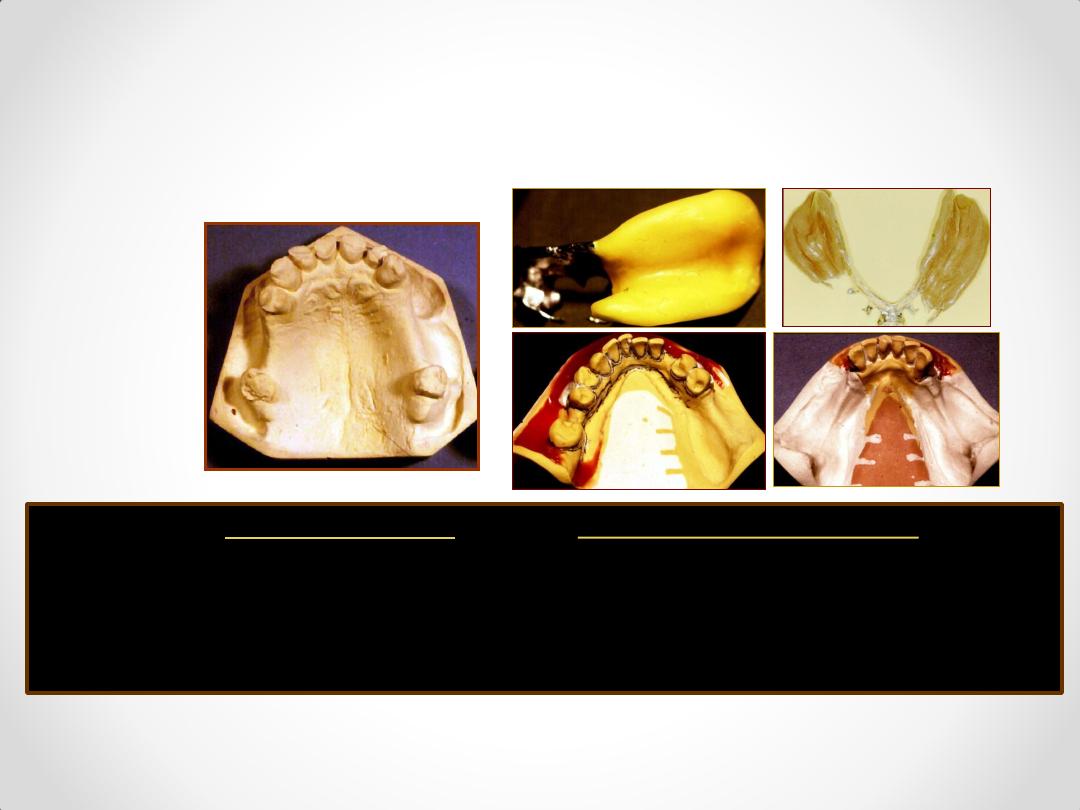
Laboratory Procedures
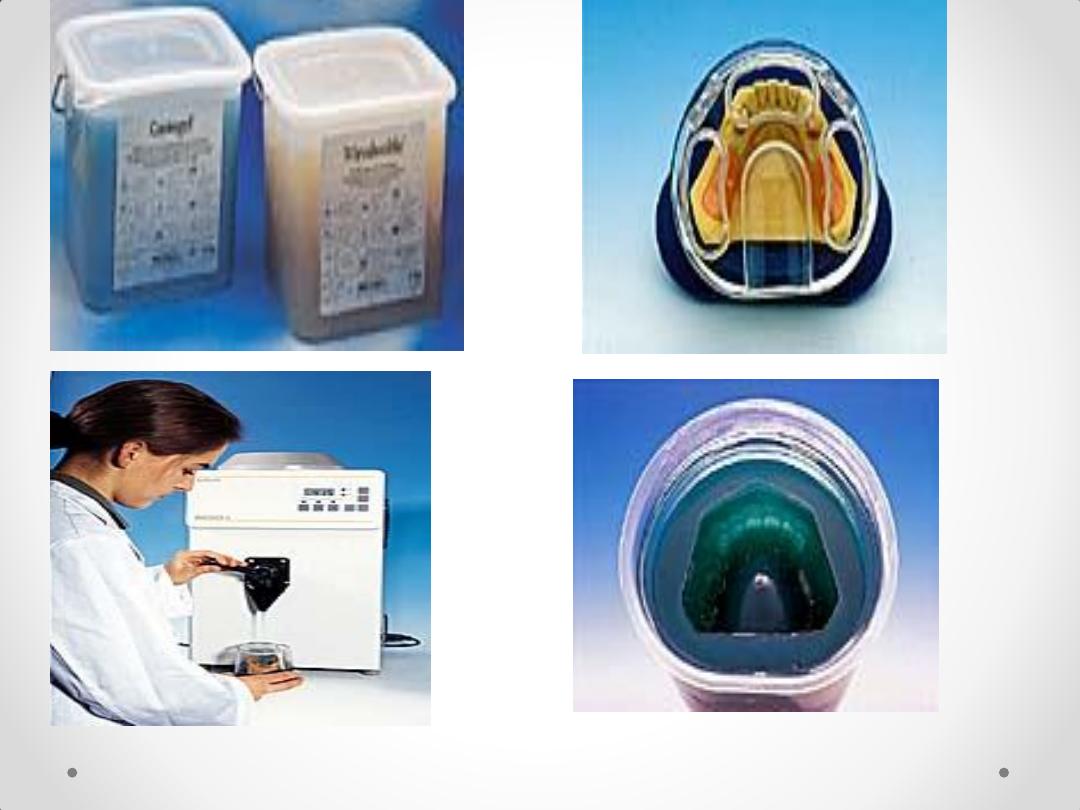
Duplication using agar
agar

The property of this
material is the resistance
to very high temperatures

refractory cast


Preformed plastic patterns

Universal funnel form
Wax pattern sprued and ready to
invest

Types of sprue
1.multiple sprue
2. single sprue
Casting from the
top
Casting from the
bottom
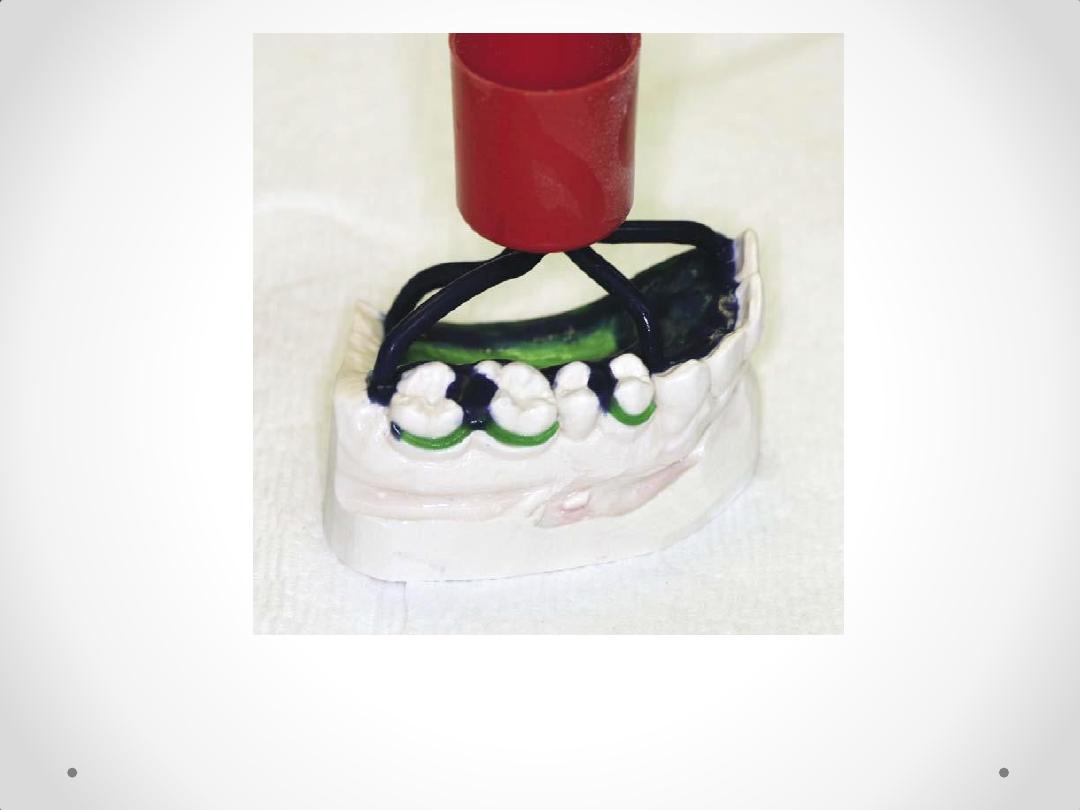
Wax pattern sprued and ready to
invest

Investing The sprued pattern
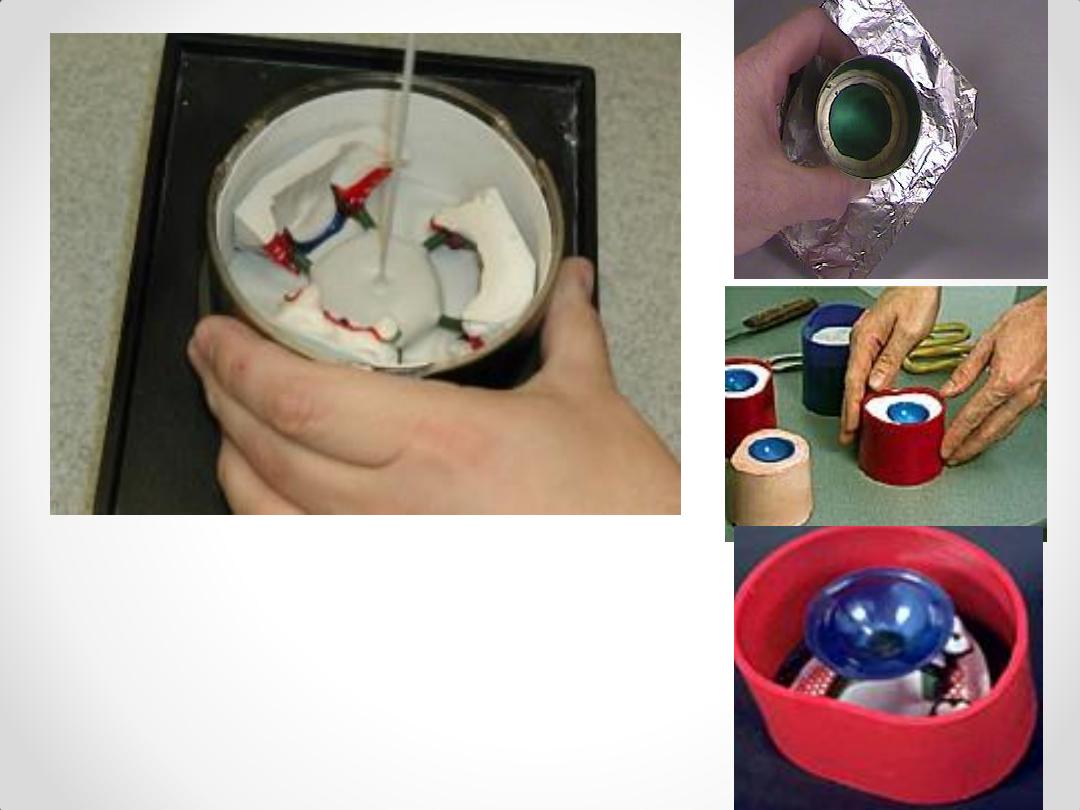

Investing The sprued
pattern
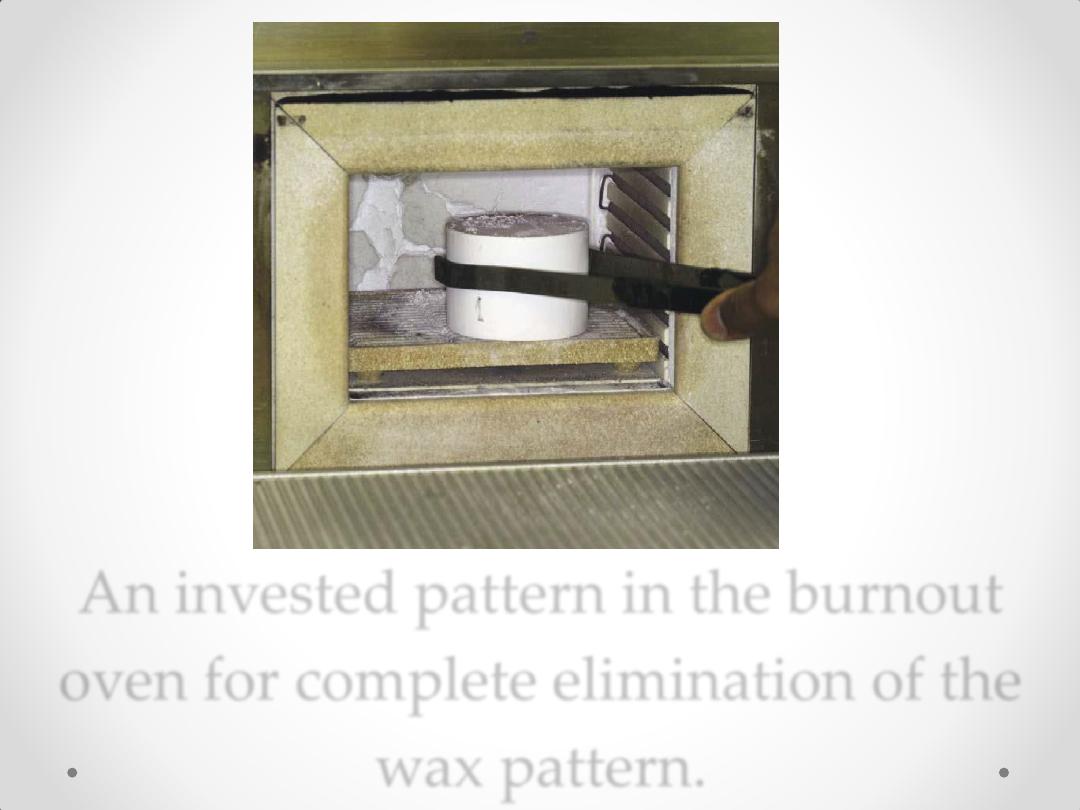
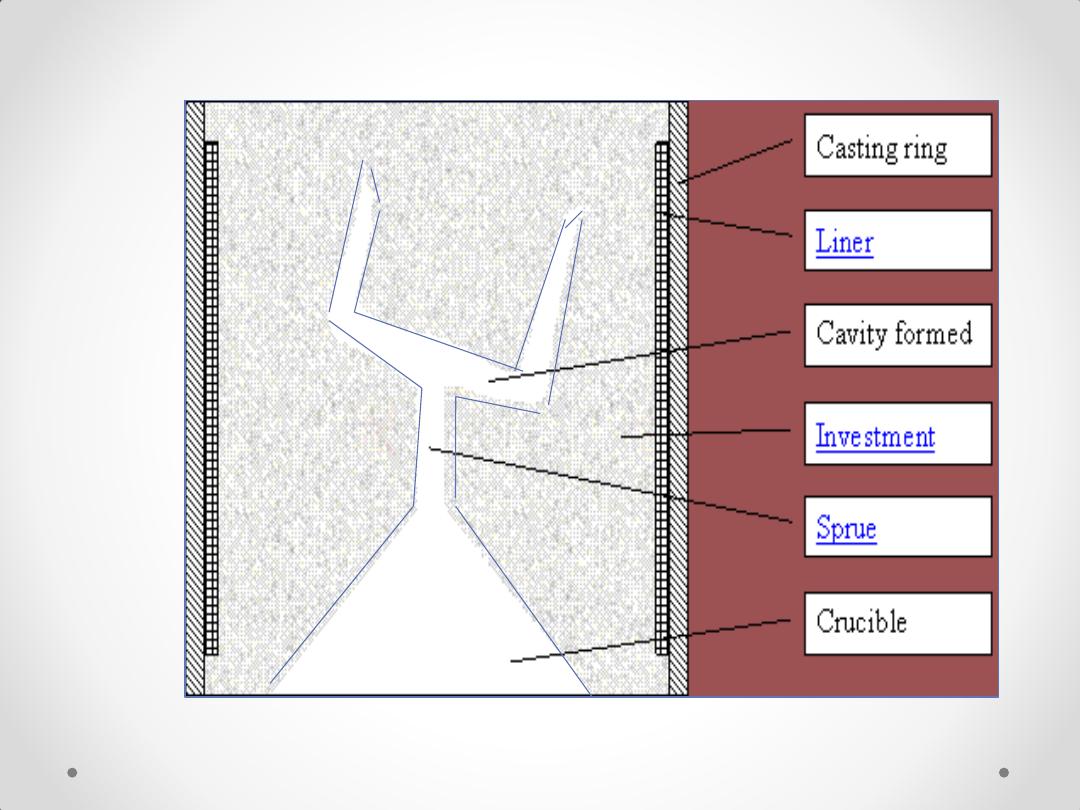

An invested pattern in the burnout
oven for complete elimination of the
wax pattern.
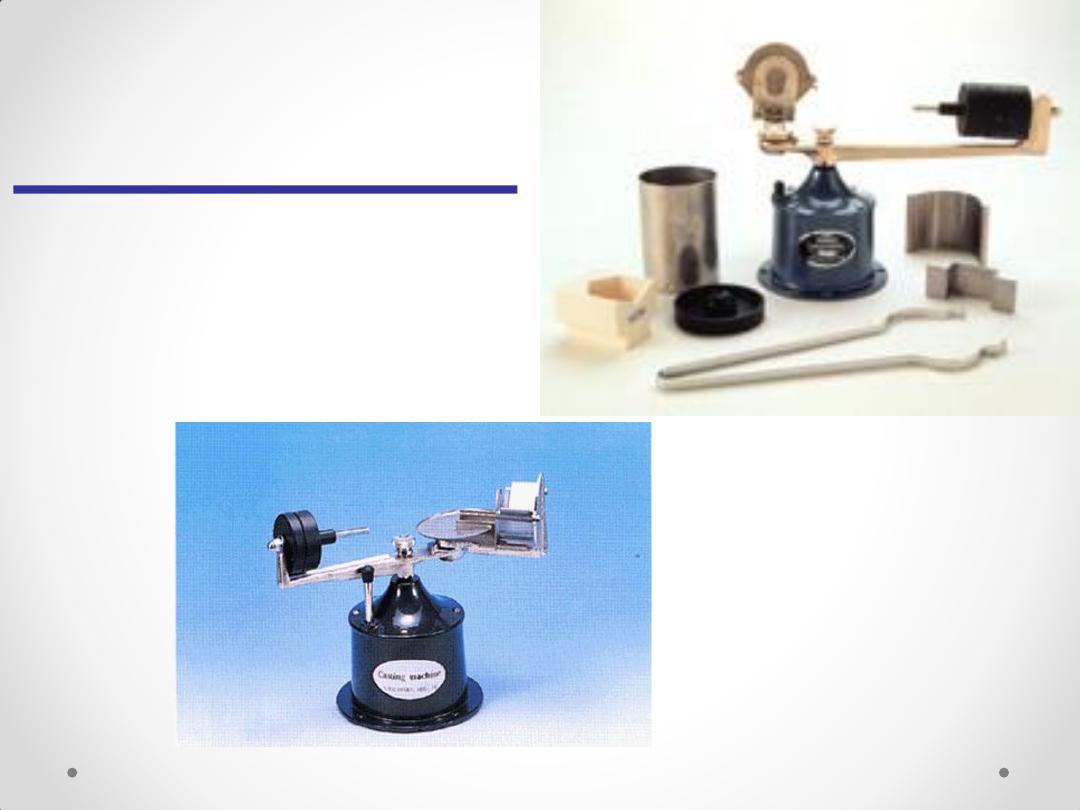

Centrifuge
for casting
Casting
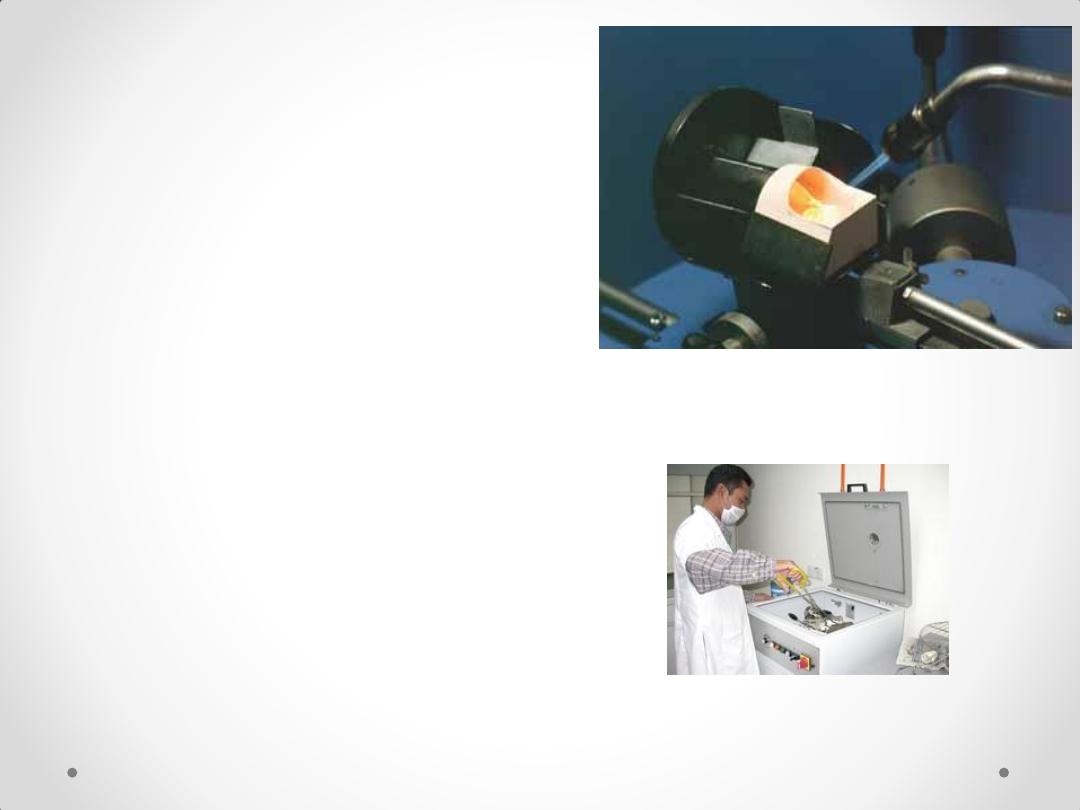

The metal is melted by
1.Gas-oxygen torch
2.Electrical machine
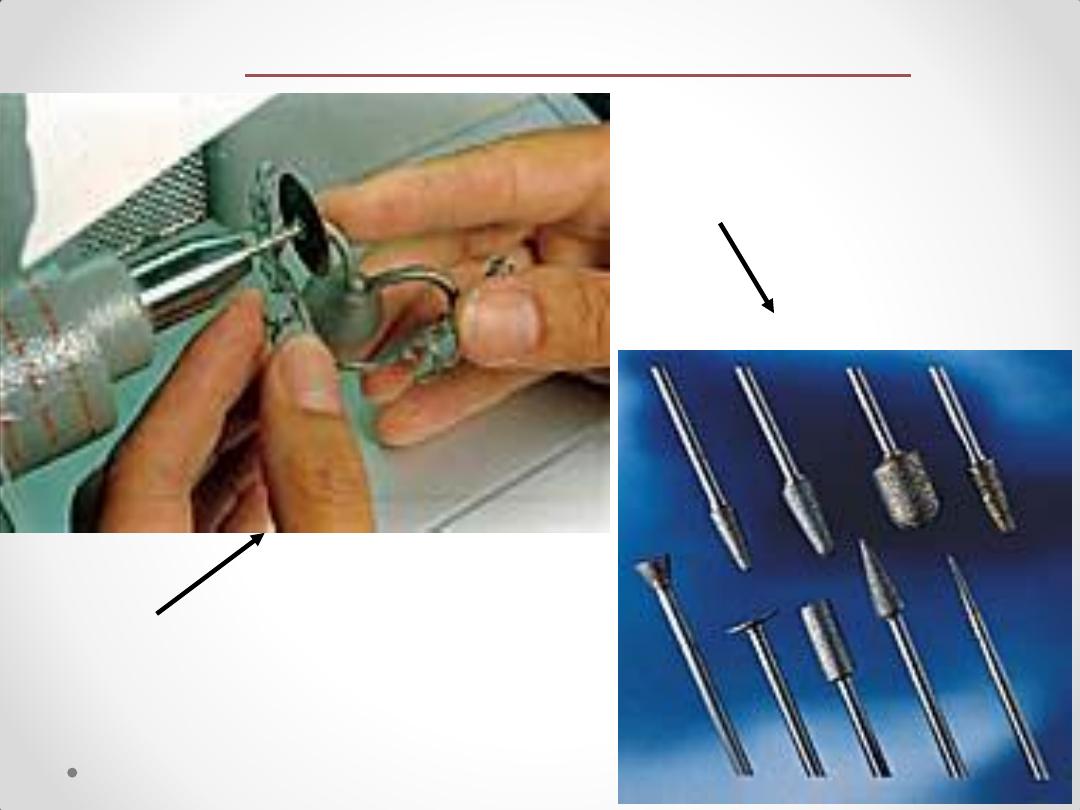
Nonstop high-speed
grinder
Diamond grinding
stones - sintered
Finishing & Polishing
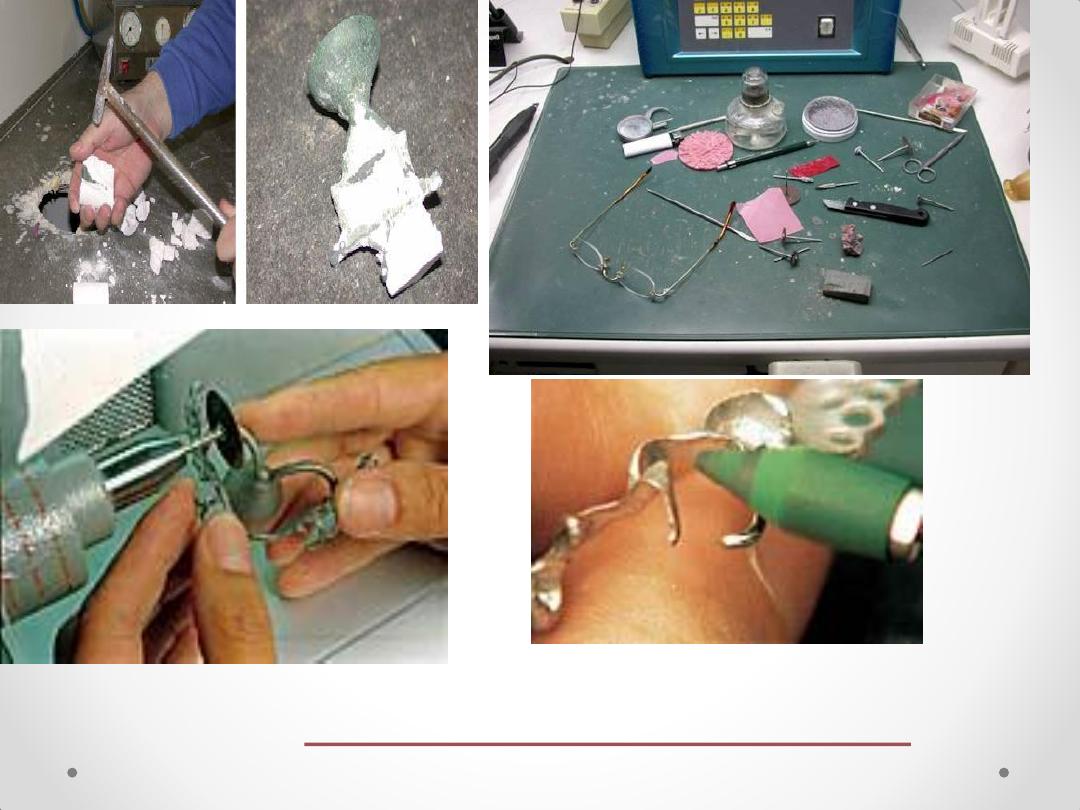
Finishing & Polishing
equipments
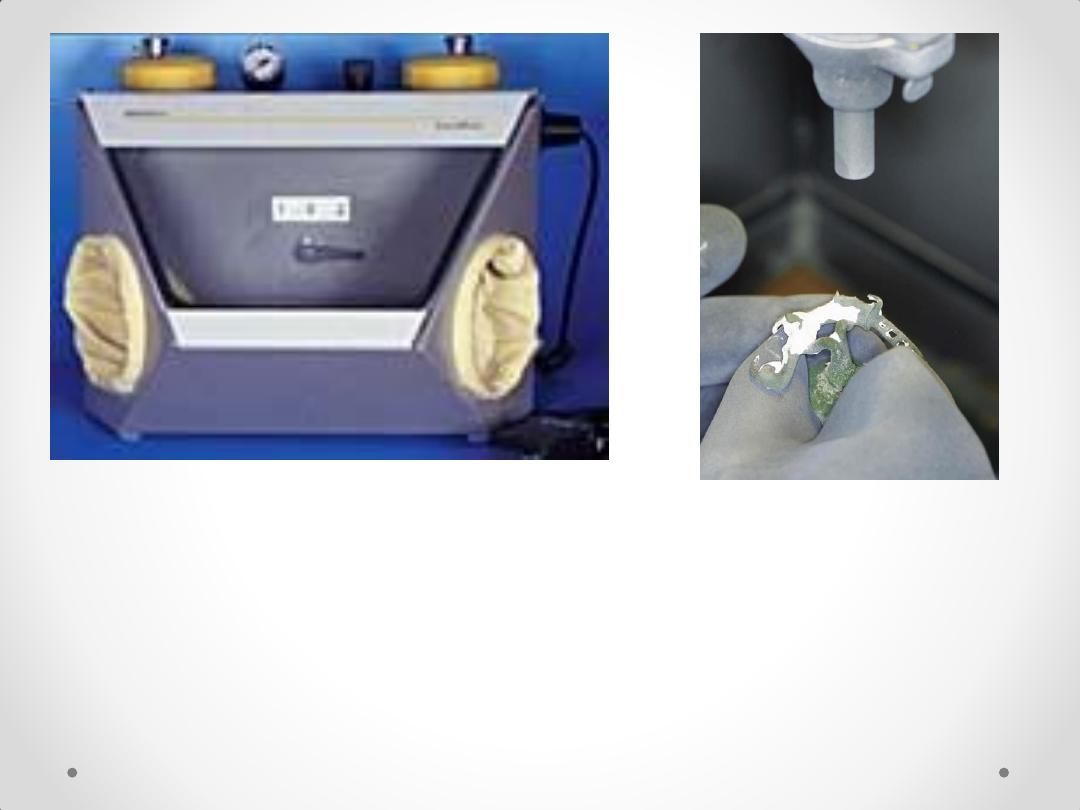

Air-blasting unit
The framework is divested
with aluminum
oxide

The final framework

METHODS FOR
ESTABLISHING
OCCLUSAL
RELATIONSHIPS
م اسماء عبد السالم عبد القادر
Centric Relation

Methods for taking maxillo mandibular
relation ships for partially edentulous patient
1- Direct Apposition of Casts.
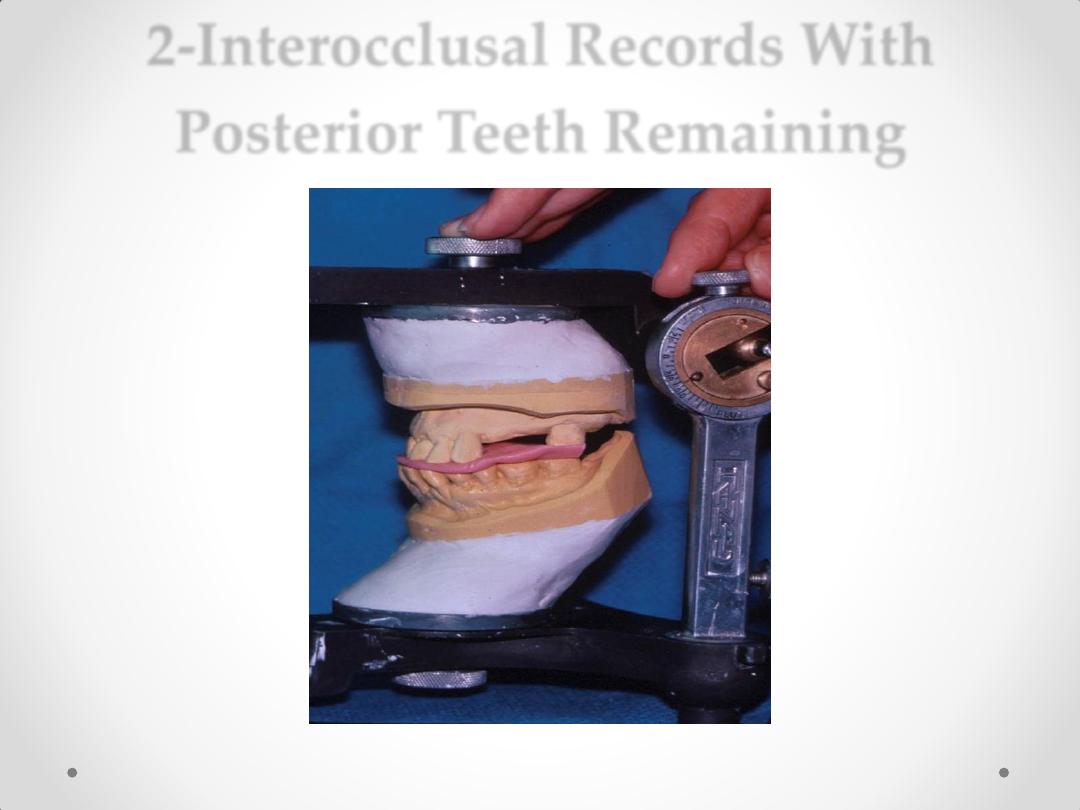
2-Interocclusal Records With Posterior Teeth
Remaining.
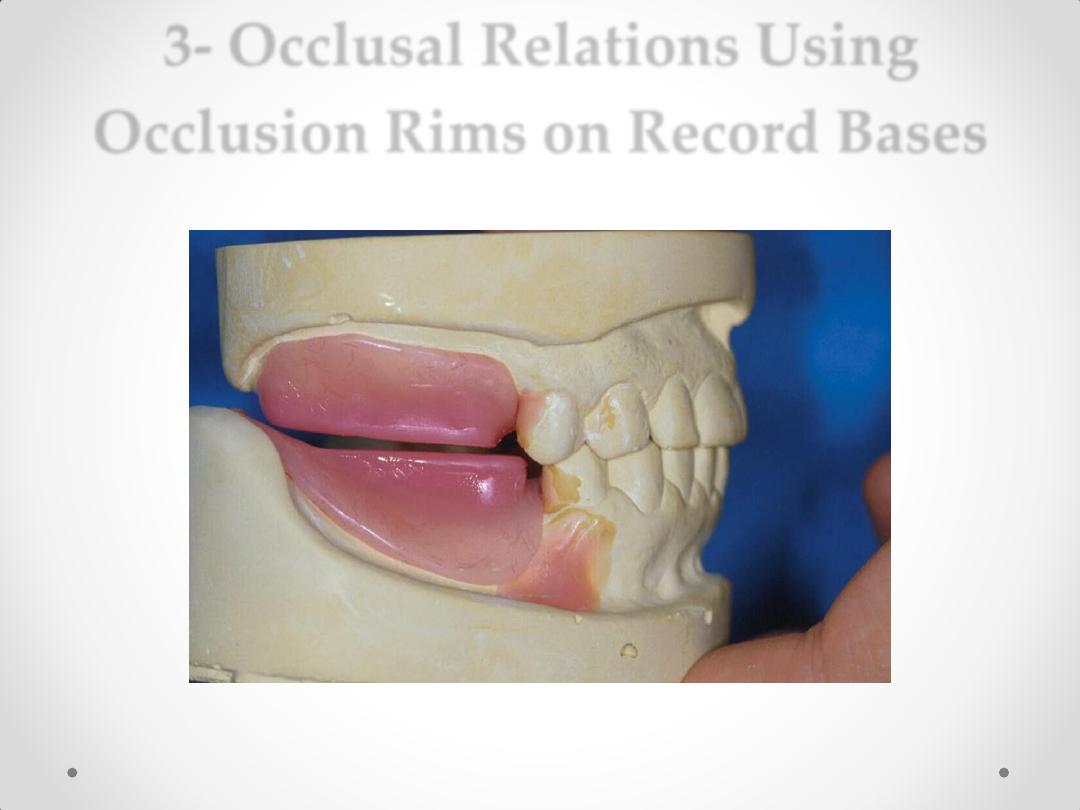
3- Occlusal Relations Using Occlusion Rims on
Record Bases .
4- Jaw Relation Records Made Entirely on
Occlusion Rims.
5-Establishing Occlusion by the Recording of
Occlusal Pathways.
2-Interocclusal Records With
Posterior Teeth Remaining
3- Occlusal Relations Using
Occlusion Rims on Record Bases
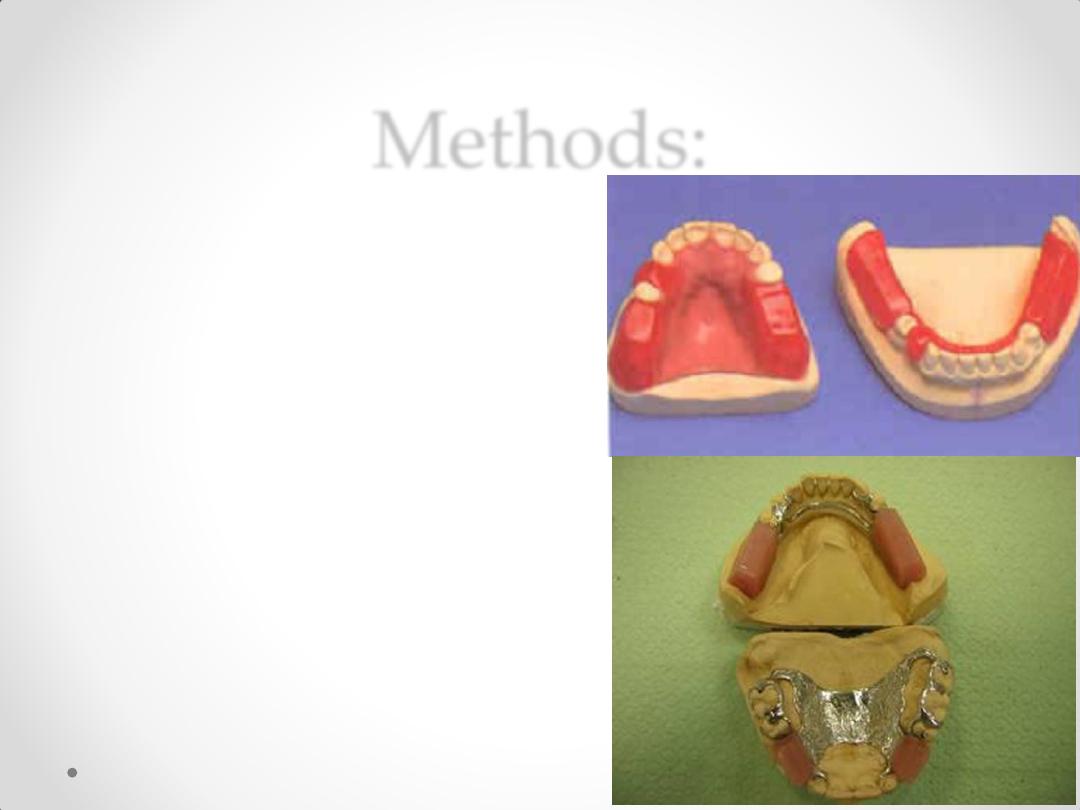
Methods:
• Construction
of record base
(cold cure
acrylic) with
occlusion
rims.
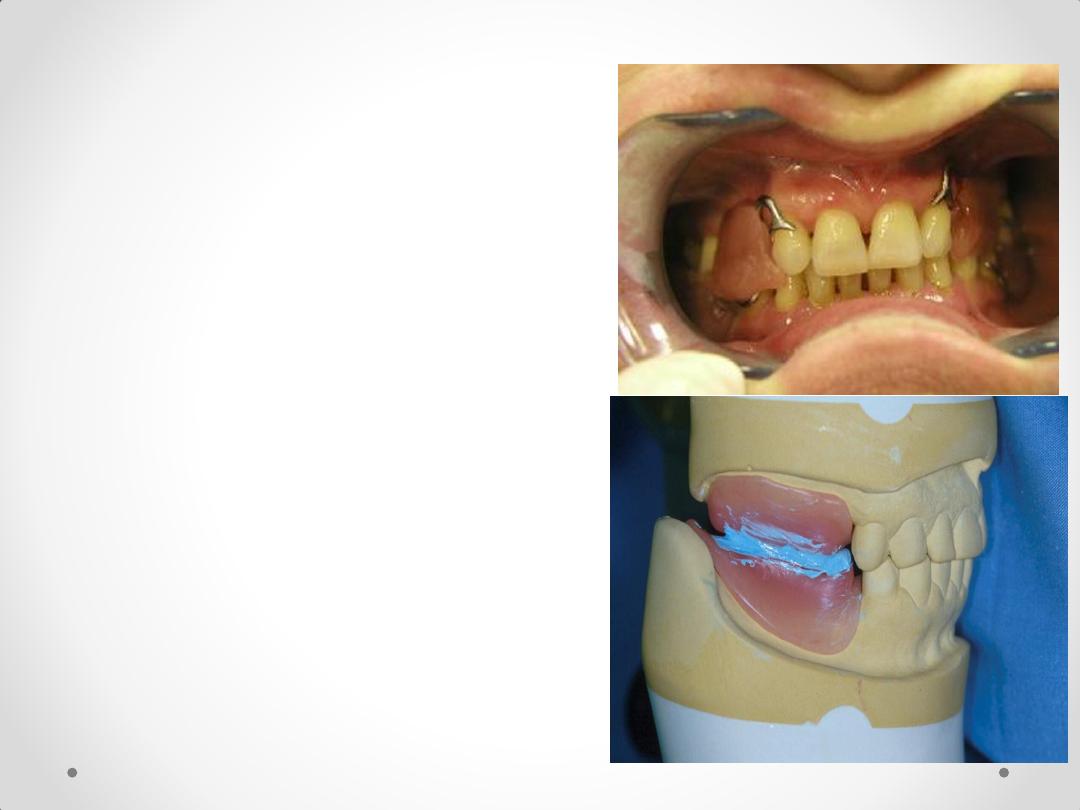
• Checked in patient
mouth
• Recording the vertical
dimension.
• Adjust the occlusion
rim according to
vertical dimension.
• Bite registration
material
(ZOE paste, Wax,
Compound, Silicone)

4- Jaw Relation Records Made
Entirely on Occlusion Rims
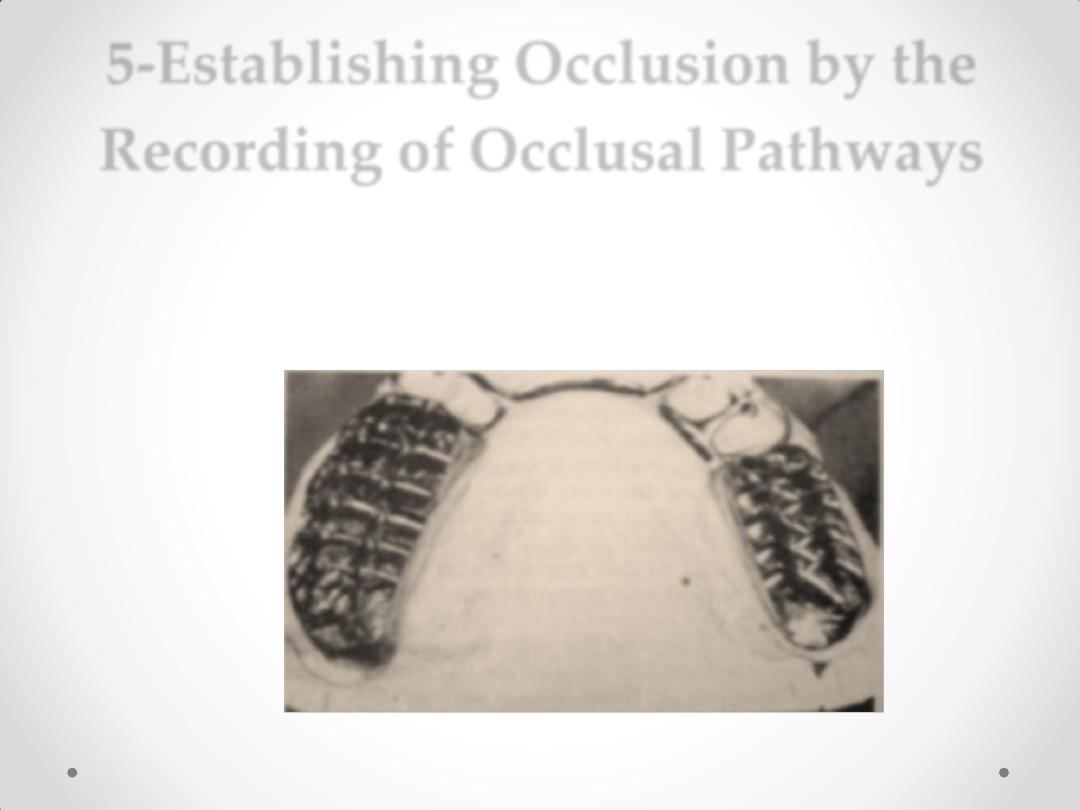
5-Establishing Occlusion by the
Recording of Occlusal Pathways
بسم هللا الرحمن
الرحيم
Impression Materials and Impression
Procedures
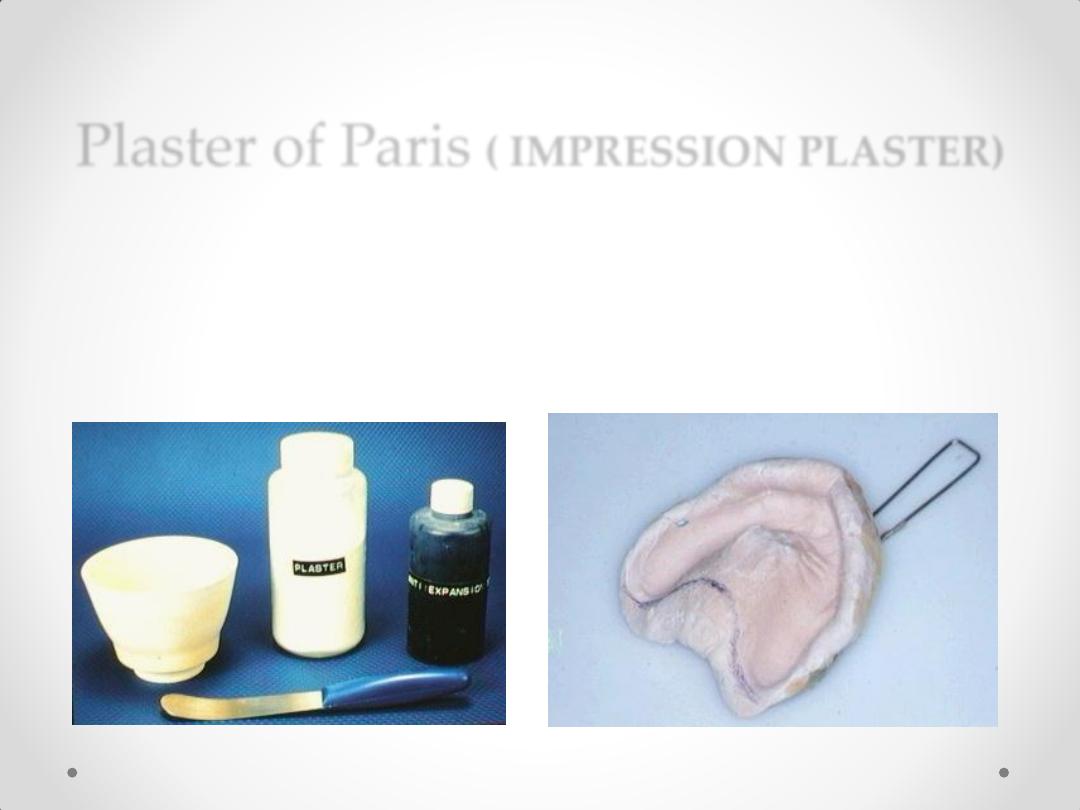
Plaster of Paris
( IMPRESSION PLASTER)
Impression plaster, used for taking final impression for
completely edentulous patient.
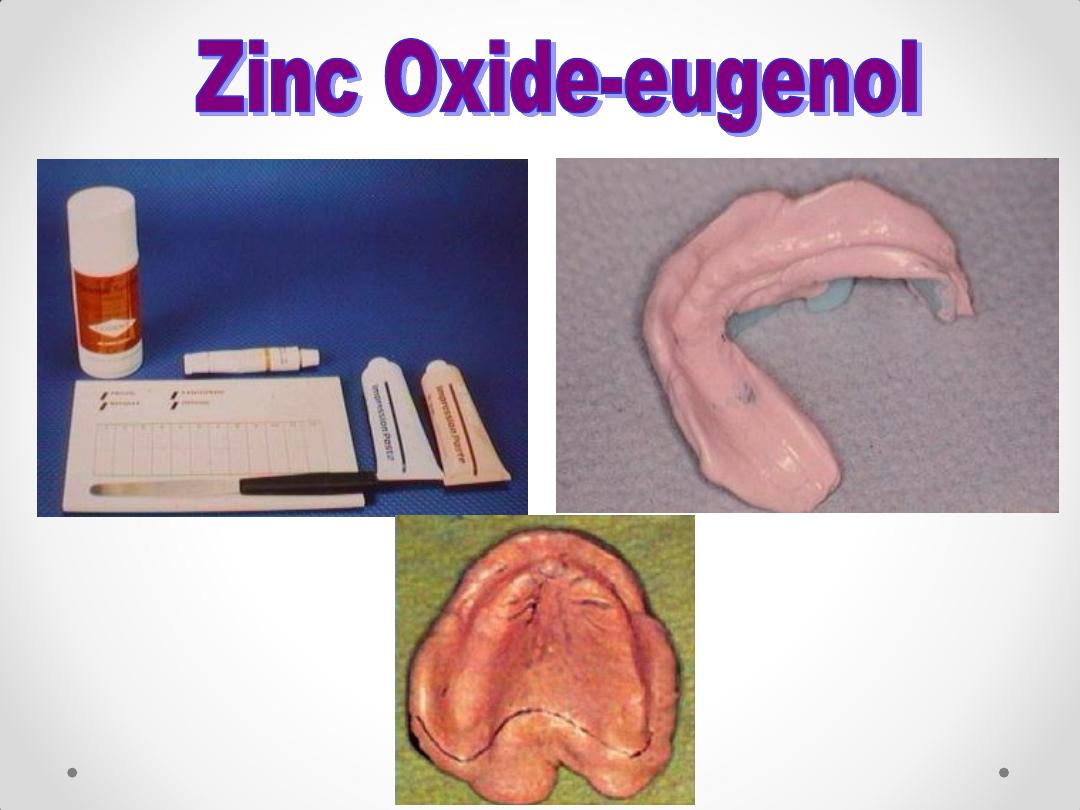
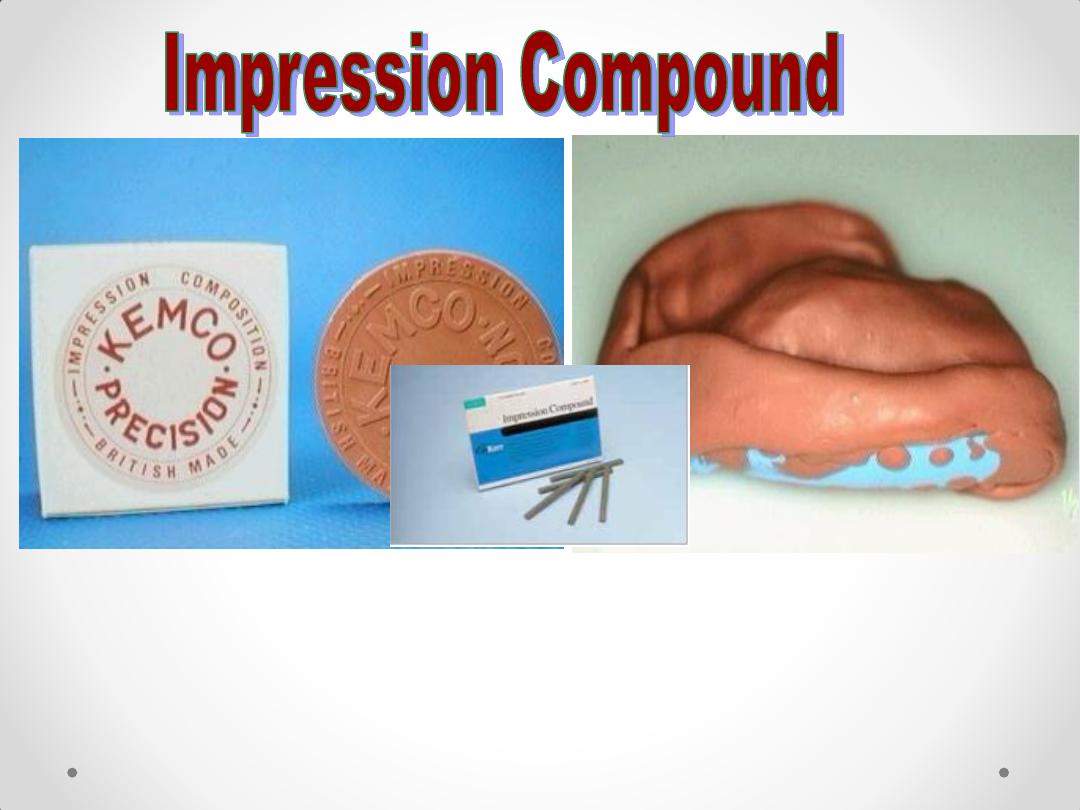
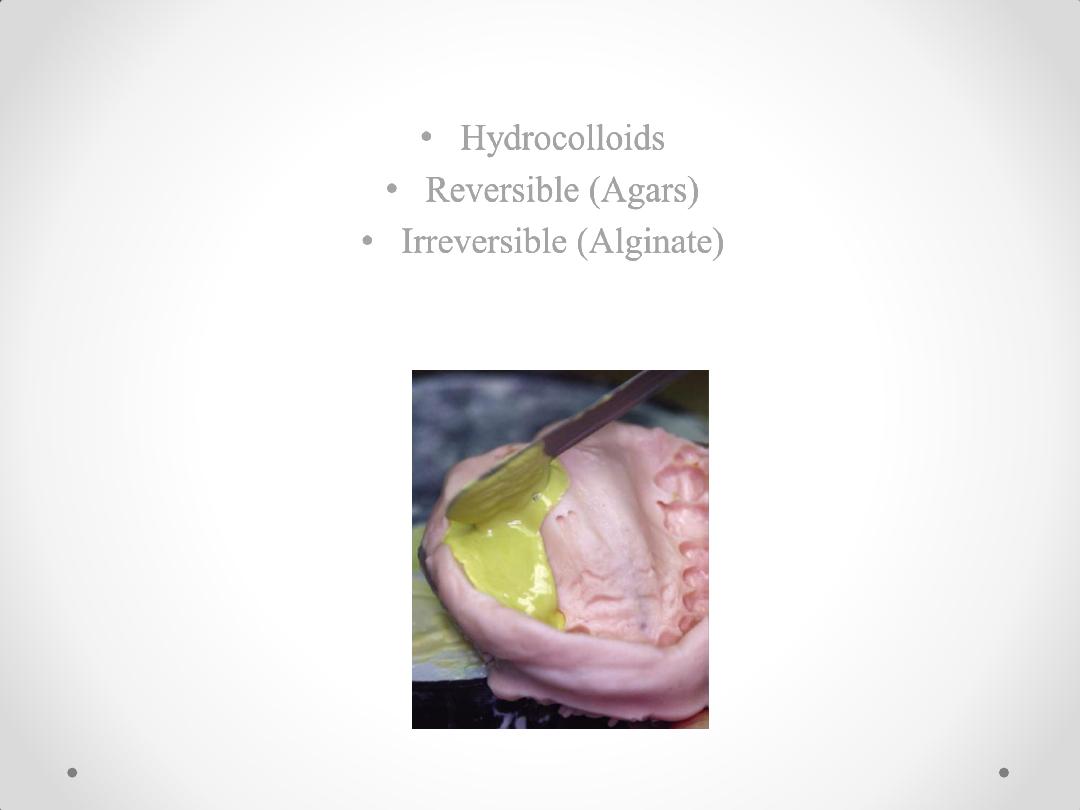
• Hydrocolloids
• Reversible (Agars)
• Irreversible (Alginate)

Agar-Agar
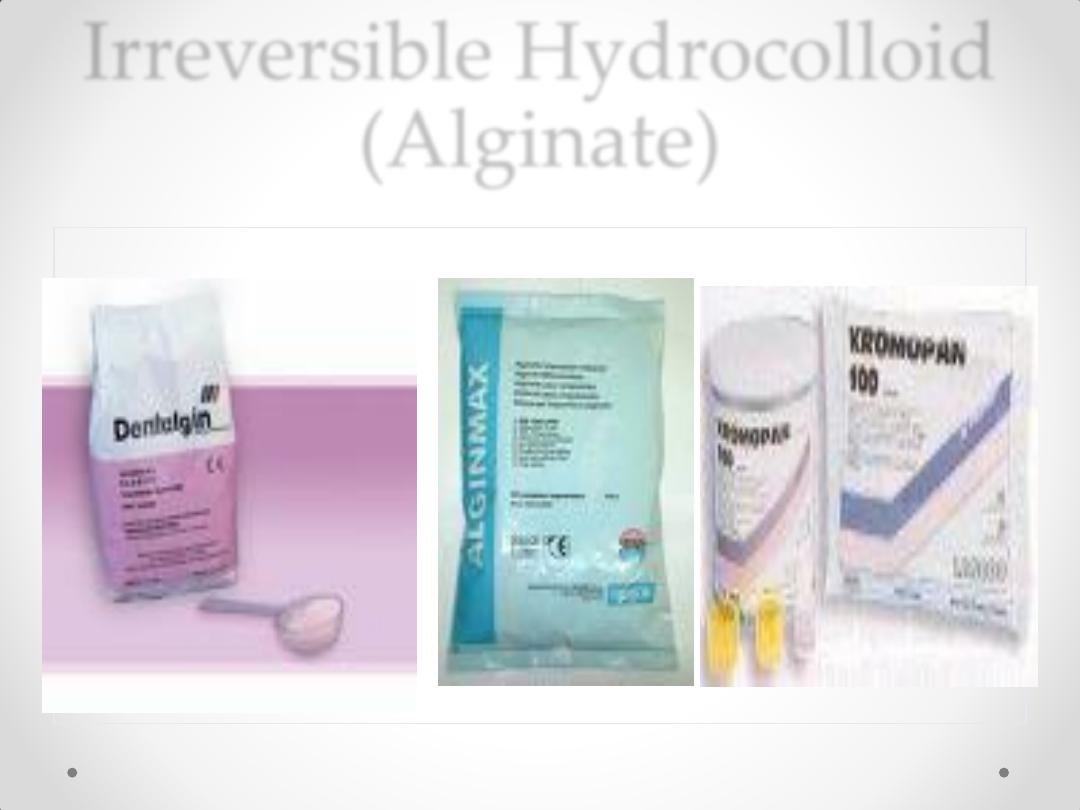
Irreversible Hydrocolloid
(Alginate)
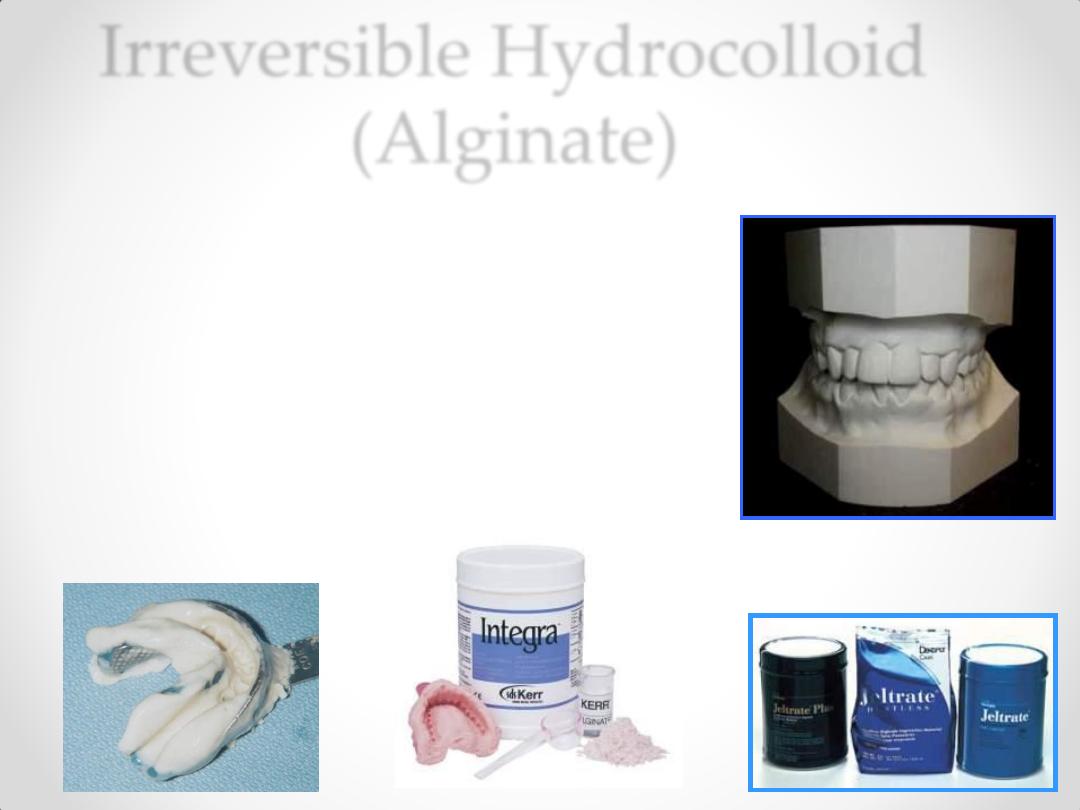
Irreversible Hydrocolloid
(Alginate)
Elastomers
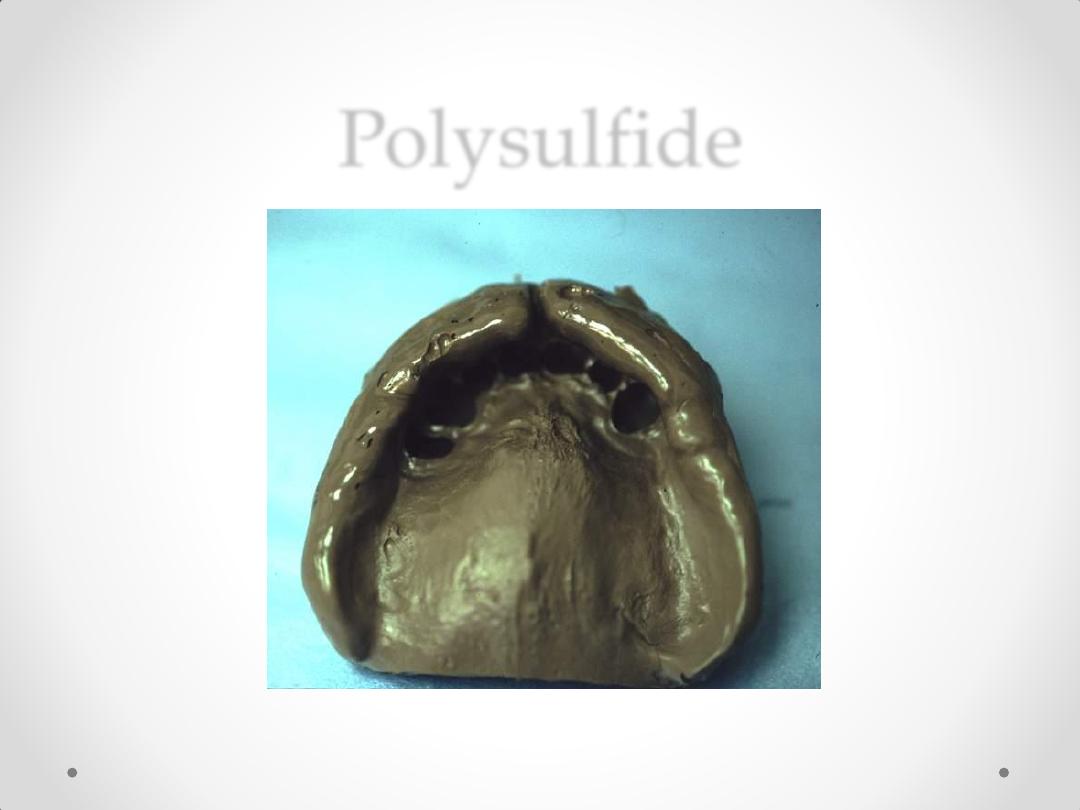
Polysulfide
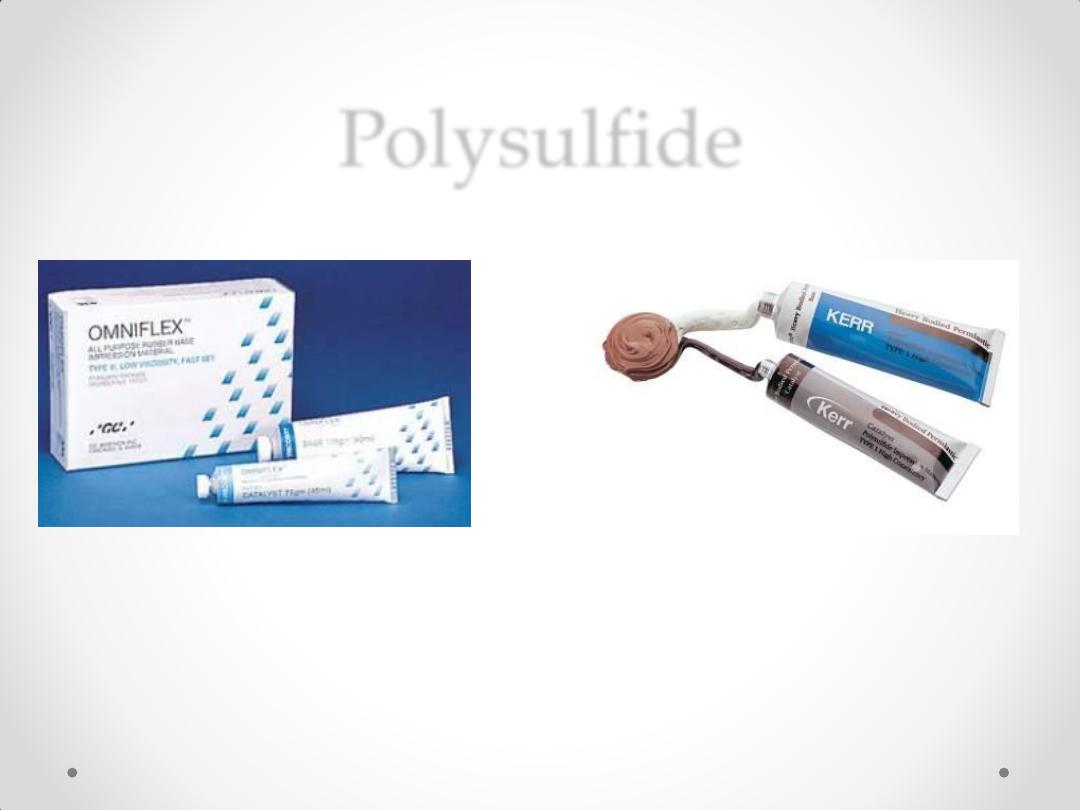

Polysulfide
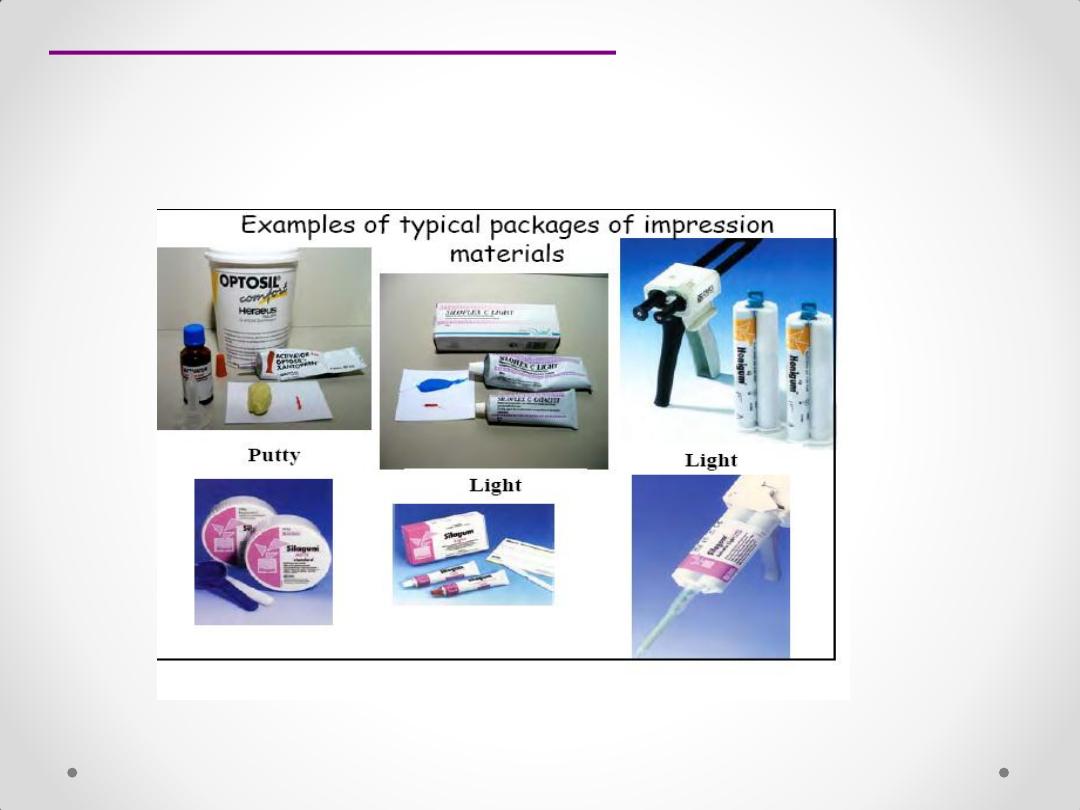
Silicone impression material

Addition Silicones
Condensation Silicone
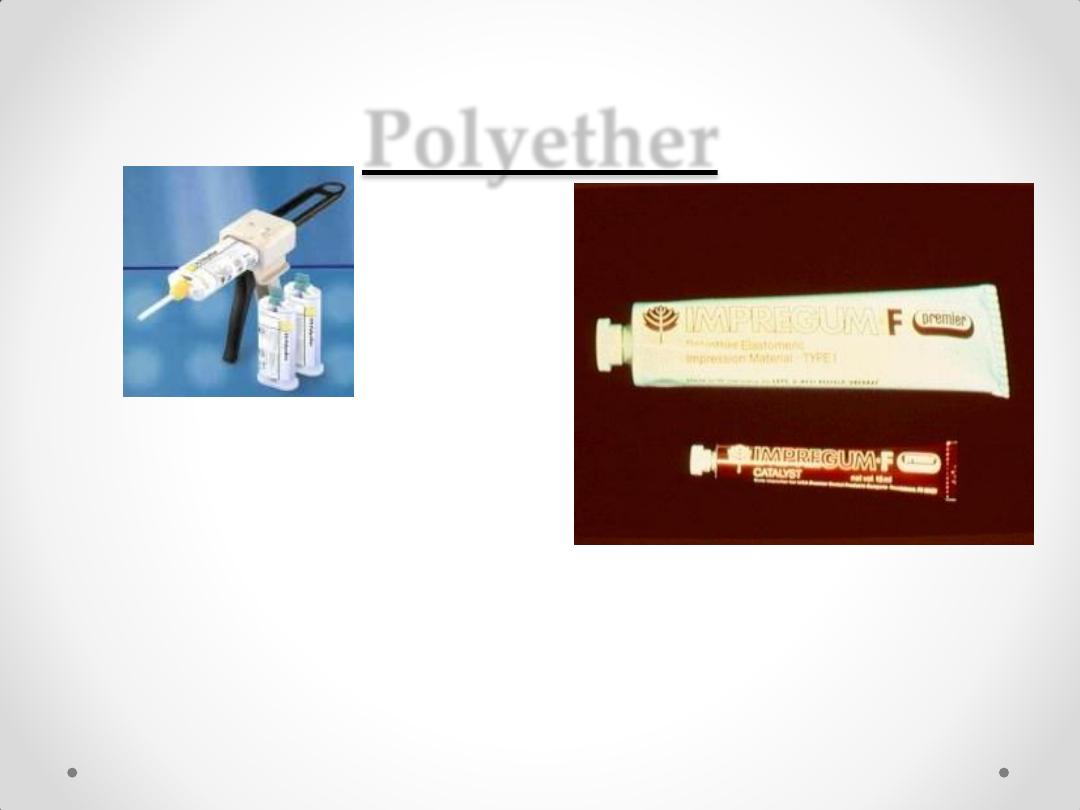

Polyether
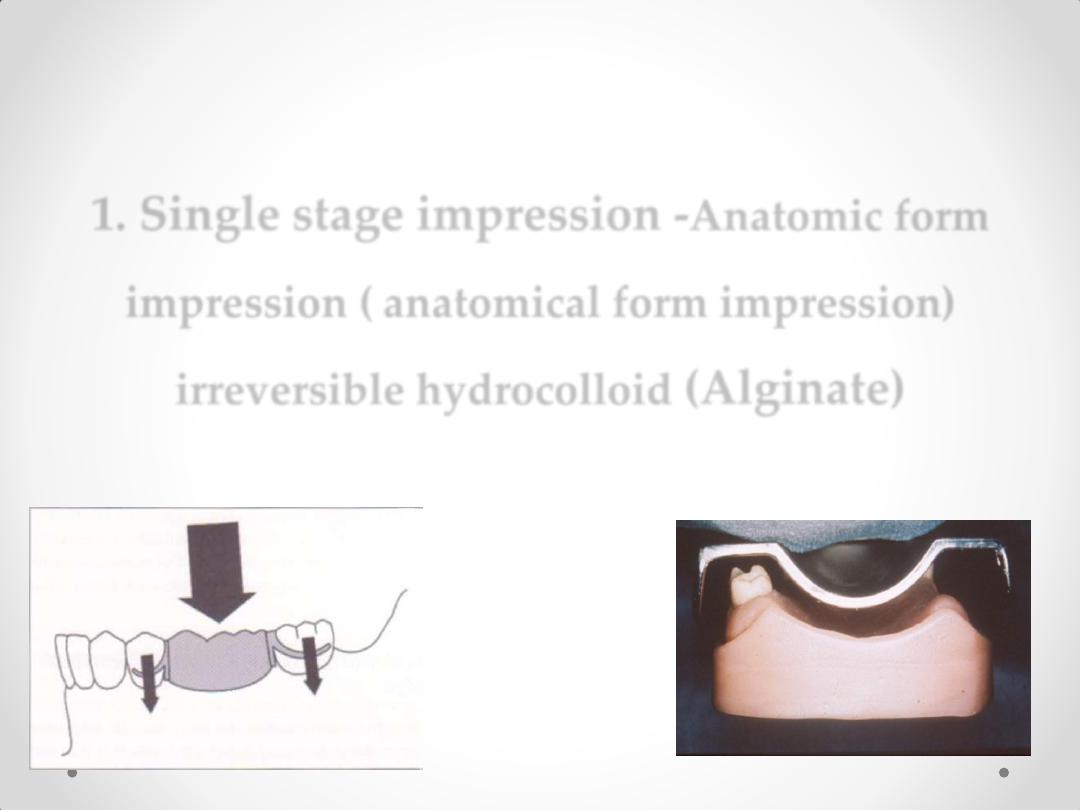
1. Single stage impression -
Anatomic form
impression (
anatomical form impression
)
irreversible hydrocolloid
(Alginate)
Impression techniques
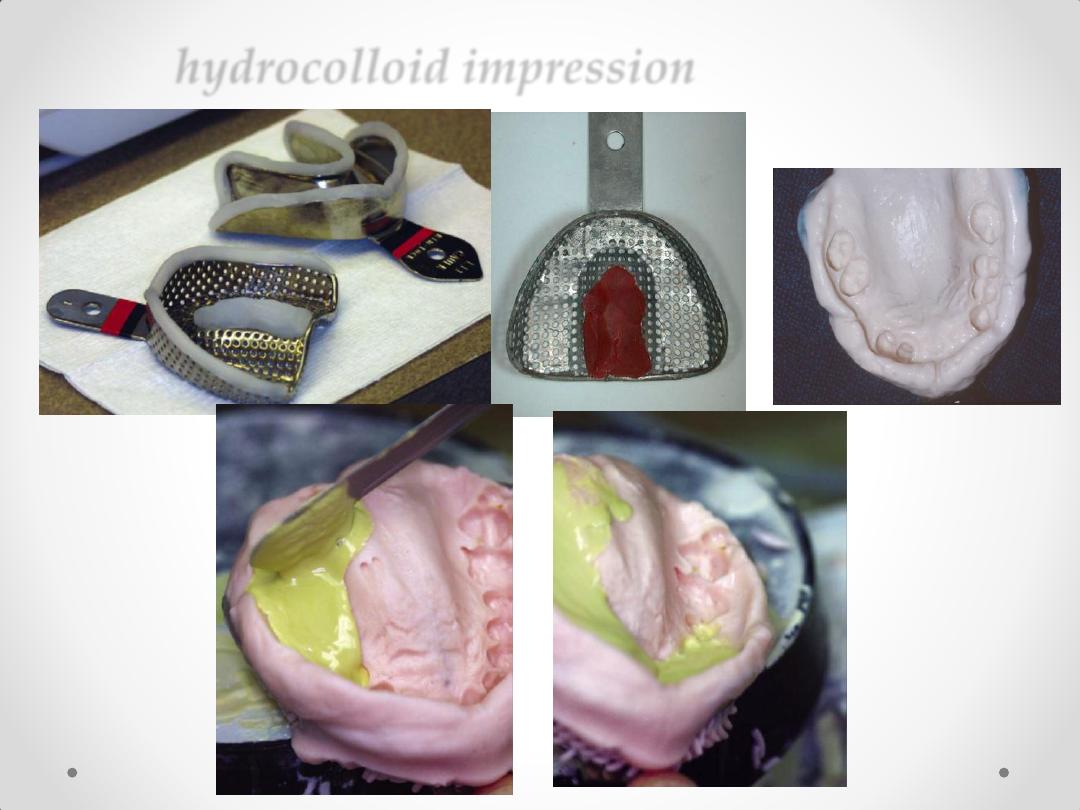
hydrocolloid impression
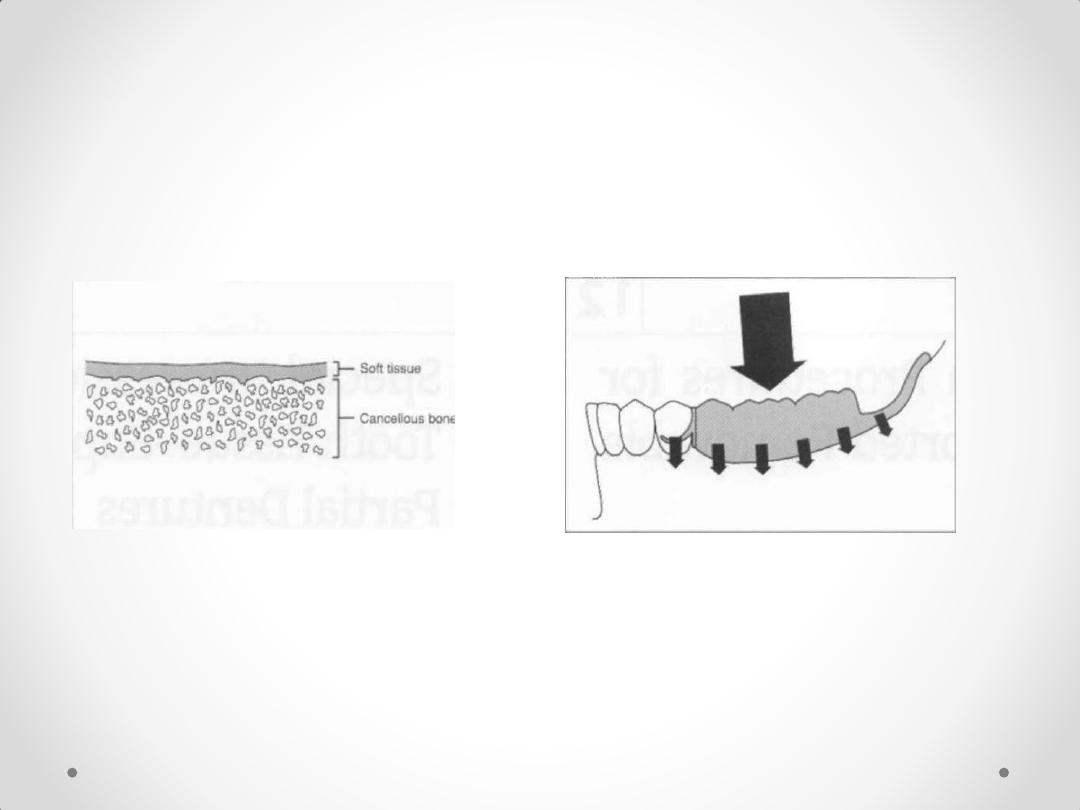
2. DUAL STAGE SELECTIVE PRESSURE
IMPRESSION
(ALTERED CAST IMPRESSION) (
anatomical and
functional form impression
) .
ALTERED CAST IMPRESSION
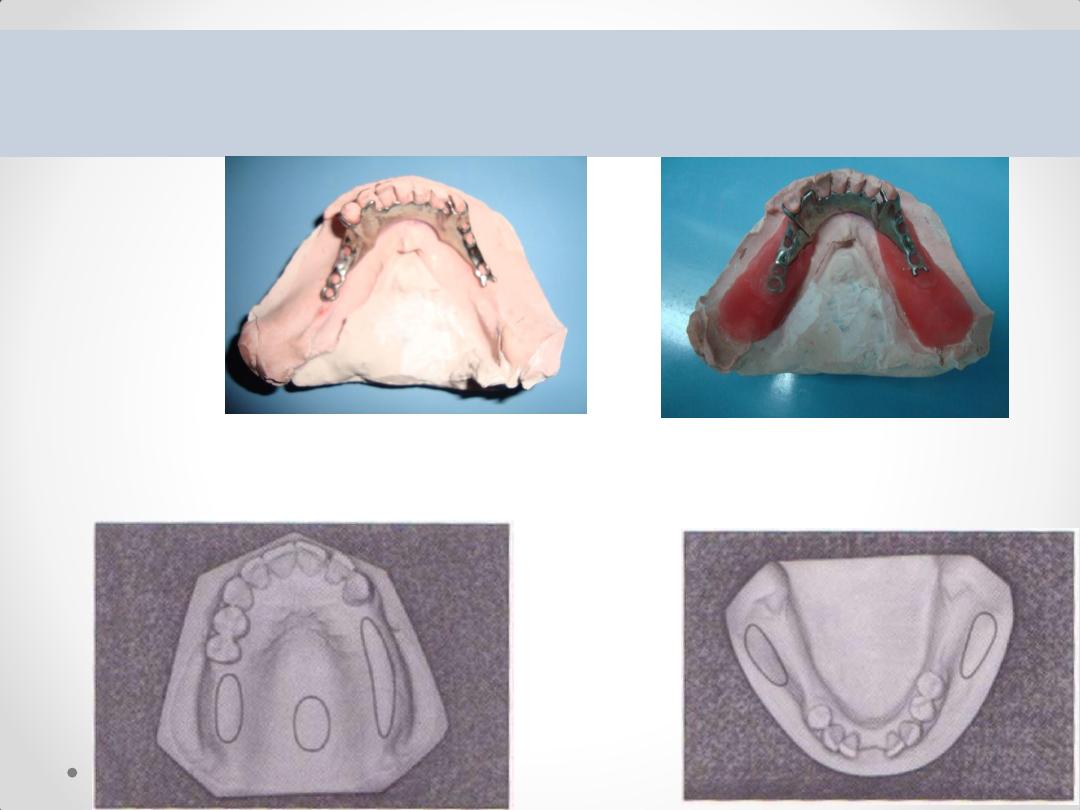
The steps in this procedure are as follows:
1.
The metal framework is constructed on a cast produced by anatomic
impression procedure using alginate impression material.
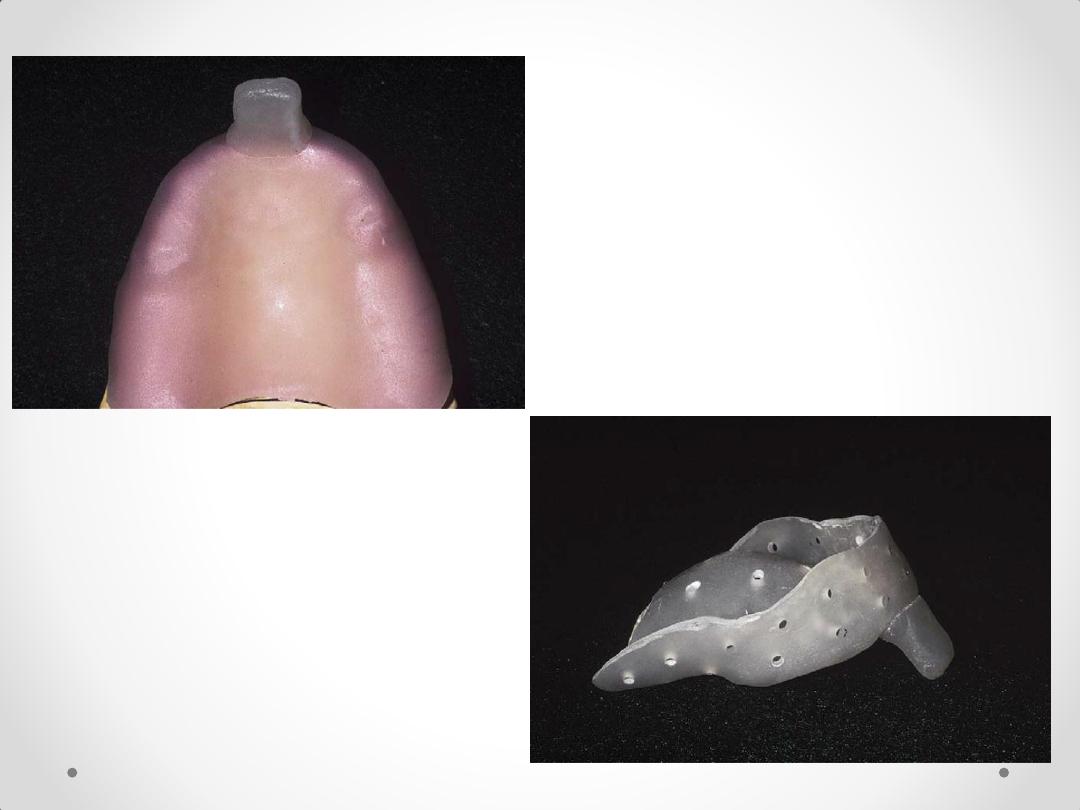
2. Fabricate custom trays on the framework over the muco-osseous denture
supporting areas. Be certain that the primary supporting areas are covered (e.g.
buccal shelf)
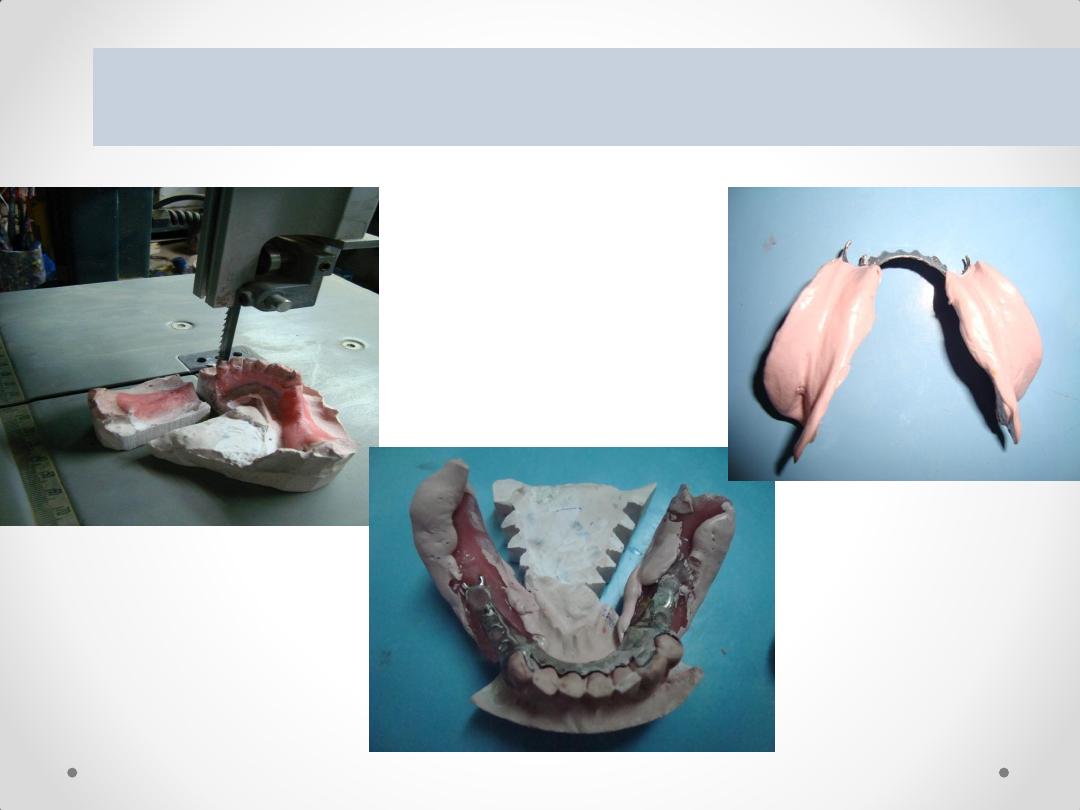
3. Cut the cast in correspondence with the internal finish
line of the framework or slightly closer to the abutment
teeth
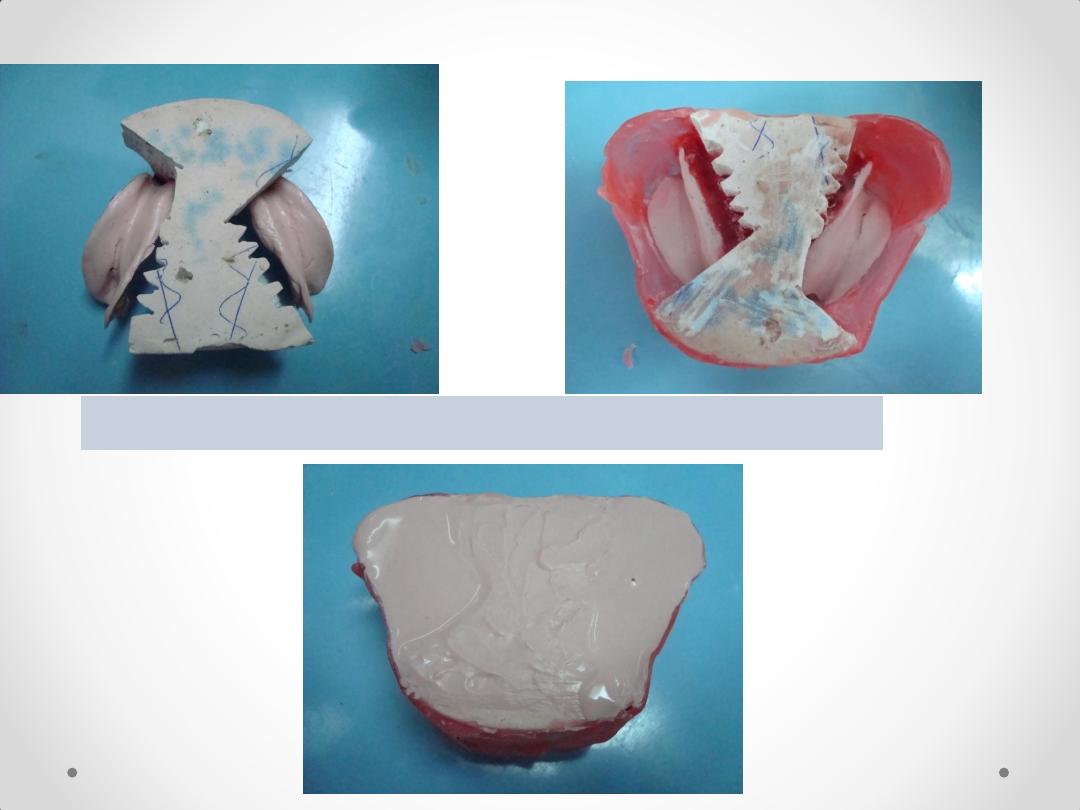
5. Box the impression, and pour the altered cast.
4. Seat the framework with the impression onto the sectioned
cast
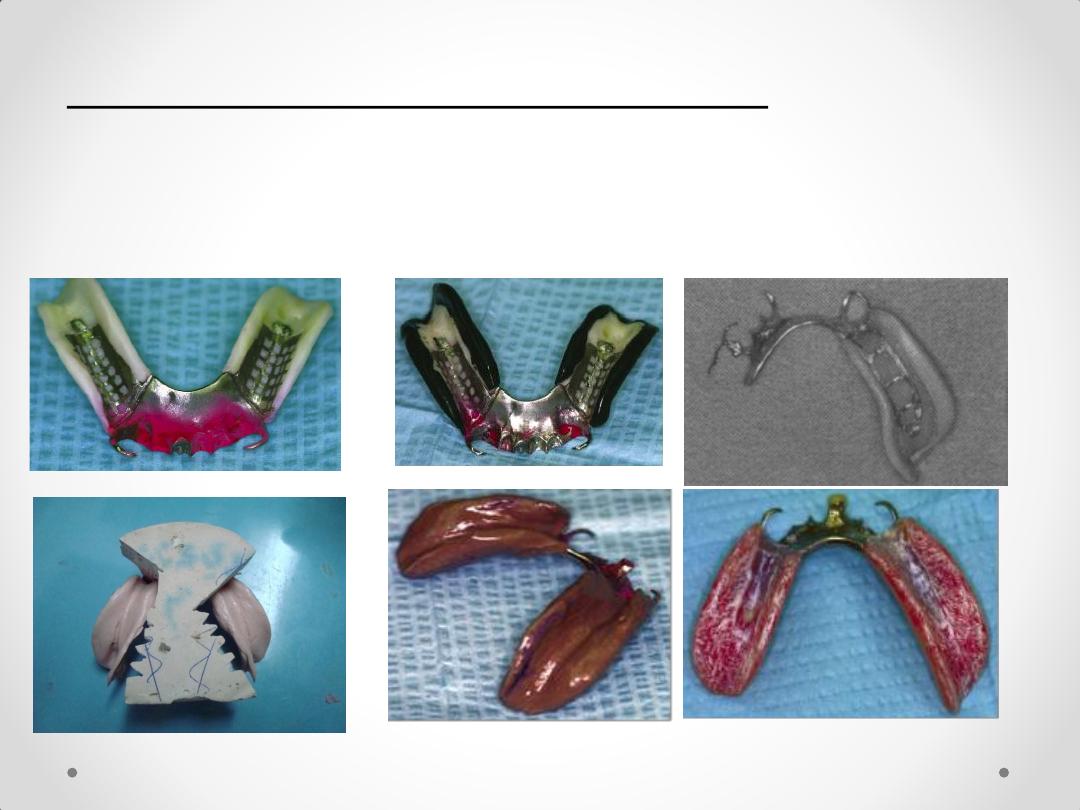
ALTERED CAST IMPRESSION
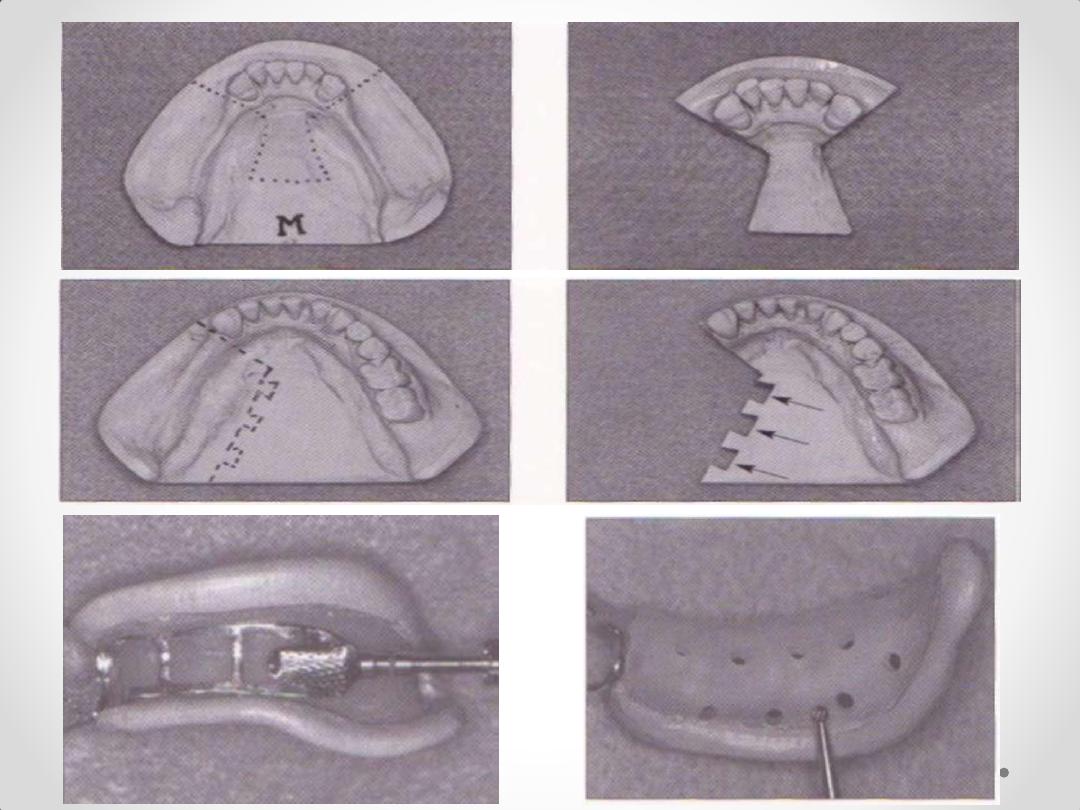
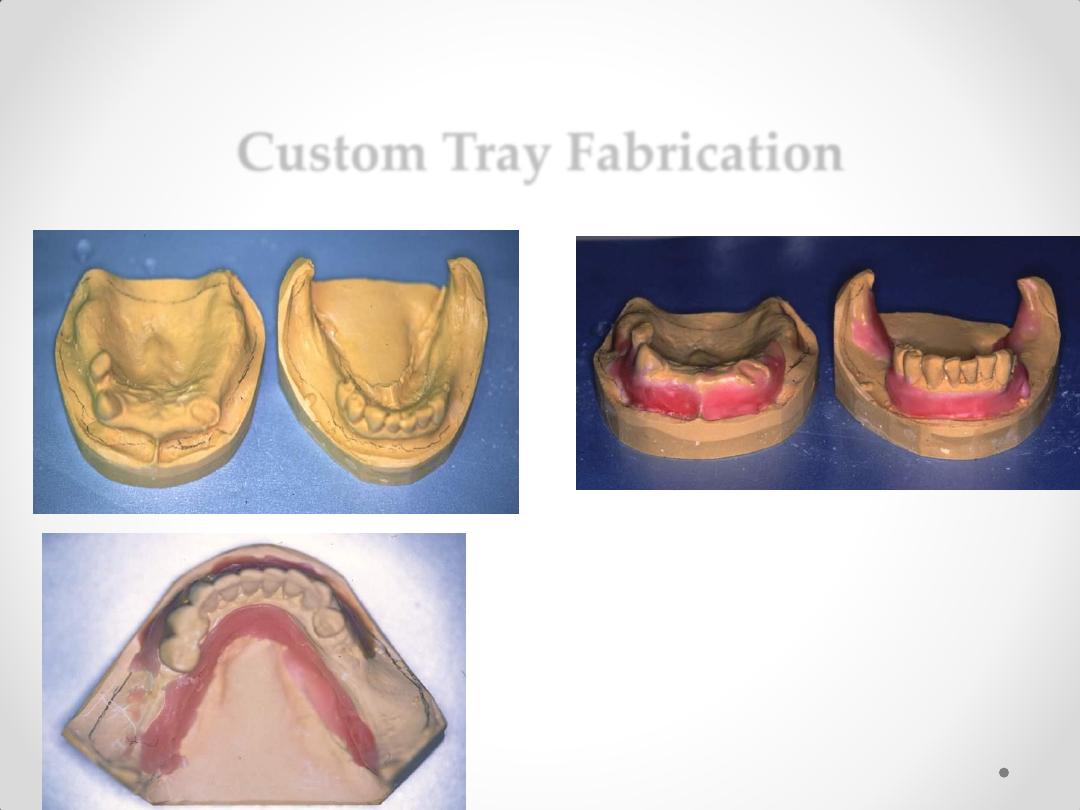
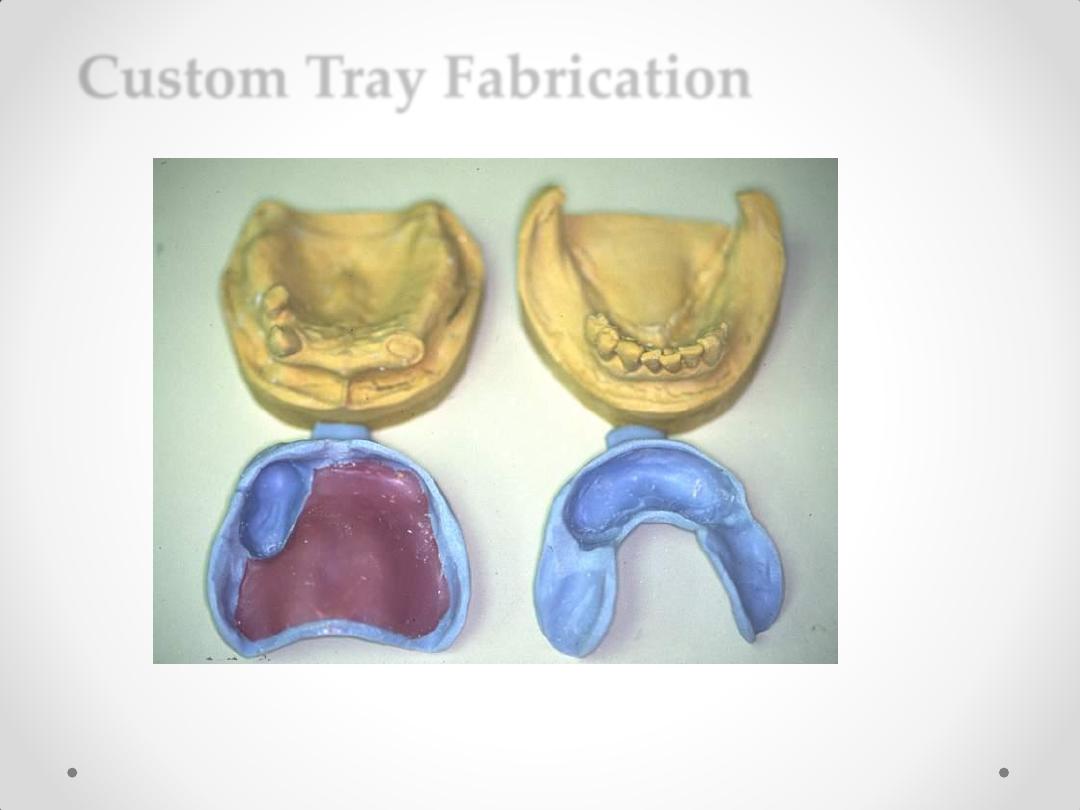
Custom Tray Fabrication
Block-out Soft, Hard
Tissue Undercut Areas
.
3. Technique for making individual (special) acrylic resin
impression tray. (
functional form impression)
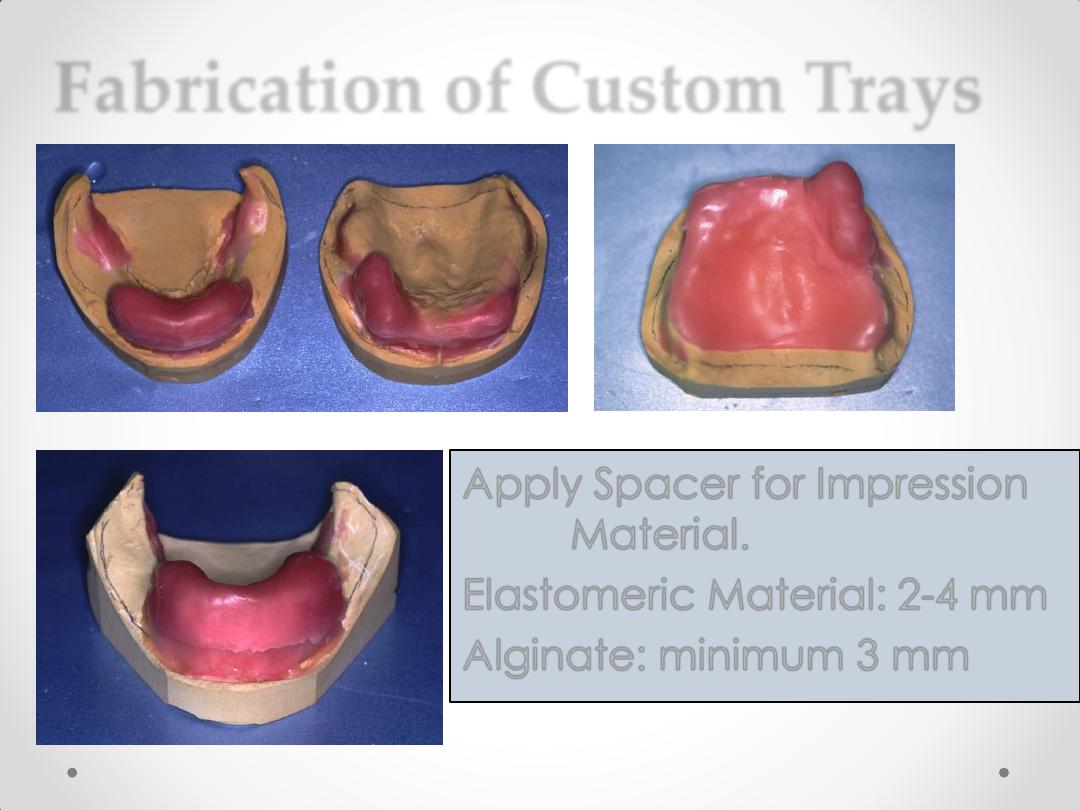
Fabrication of Custom Trays
Apply Spacer for Impression
Material.
Elastomeric Material: 2-4 mm
Alginate: minimum 3 mm
Custom Tray Fabrication
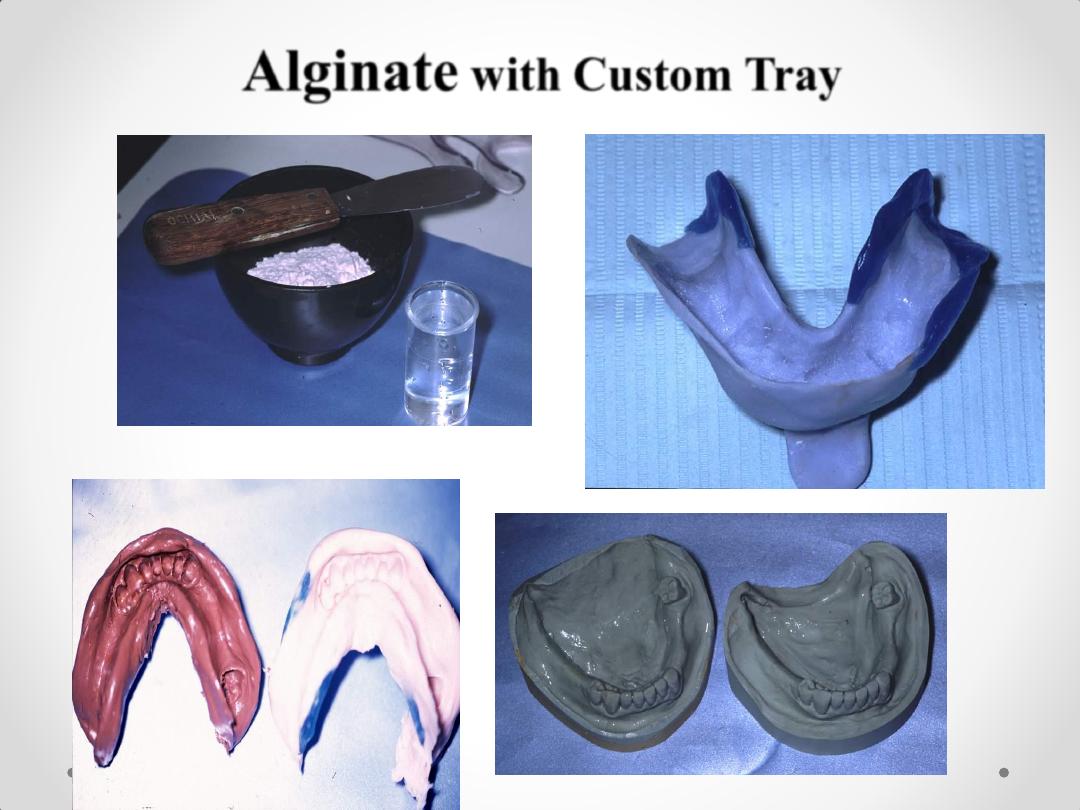
Alginate
with Custom Tray
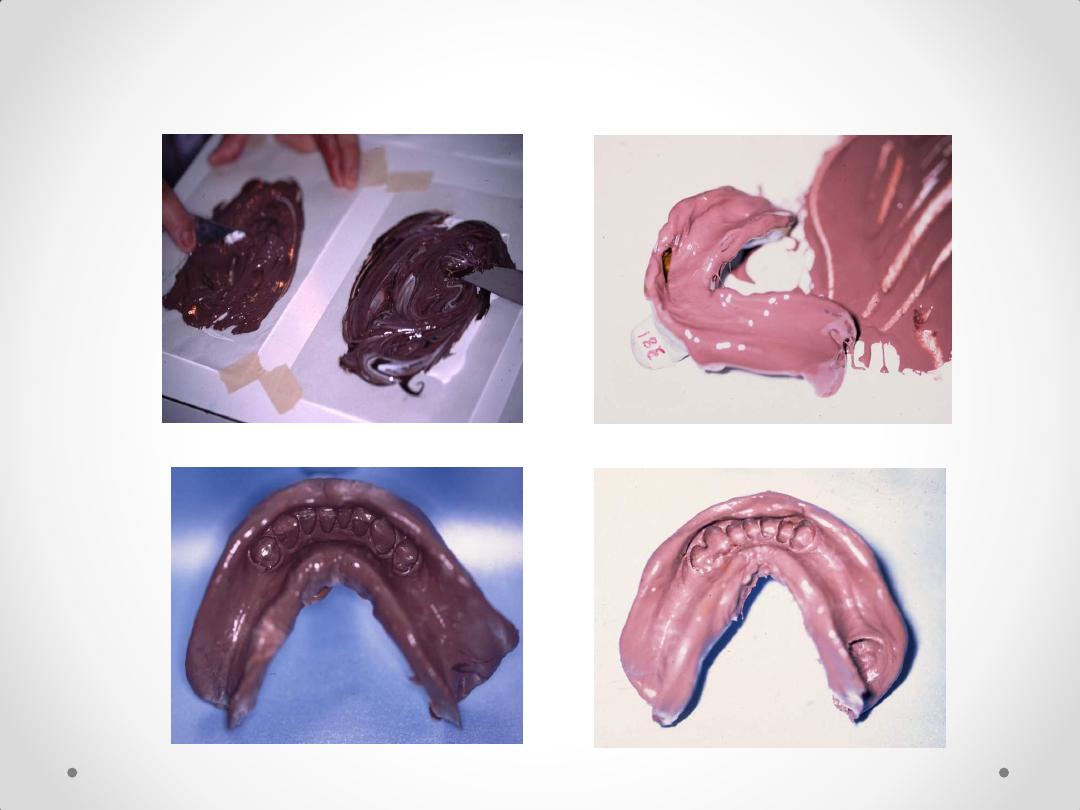
Silicone and Rubber Base Impressions

Box and Pour Master Cast
Carefully remove salivary residues and dry the cast.
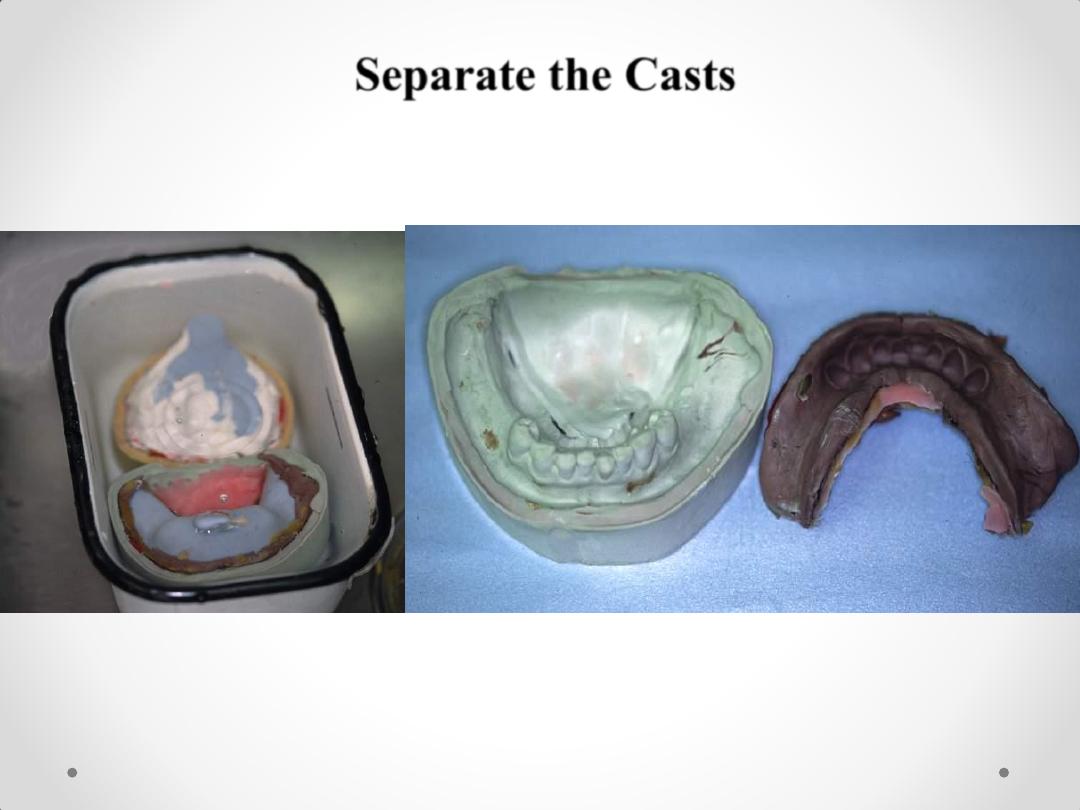
Separate the Casts

Acrylic partial denture
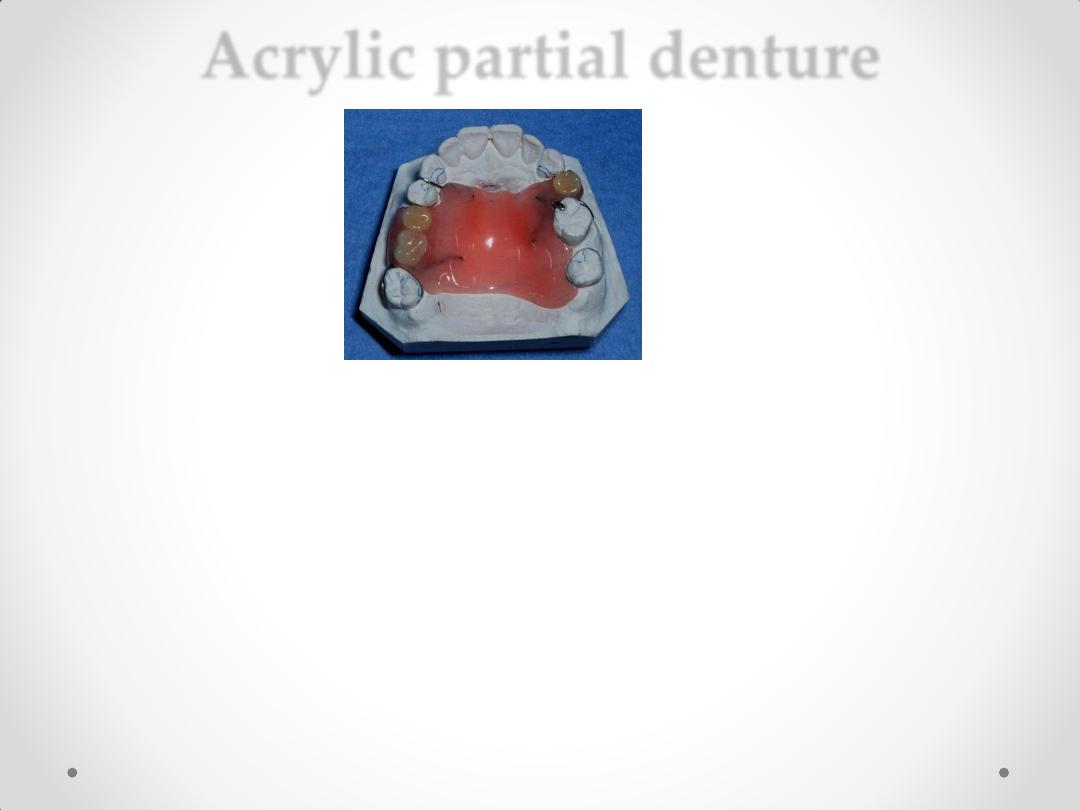
Acrylic partial denture
Types
Temporary RPD 1-
2-Interim Removable Partial Dentures
3-Transitional Denture
4-Treatment Denture
5-Immediate RPD
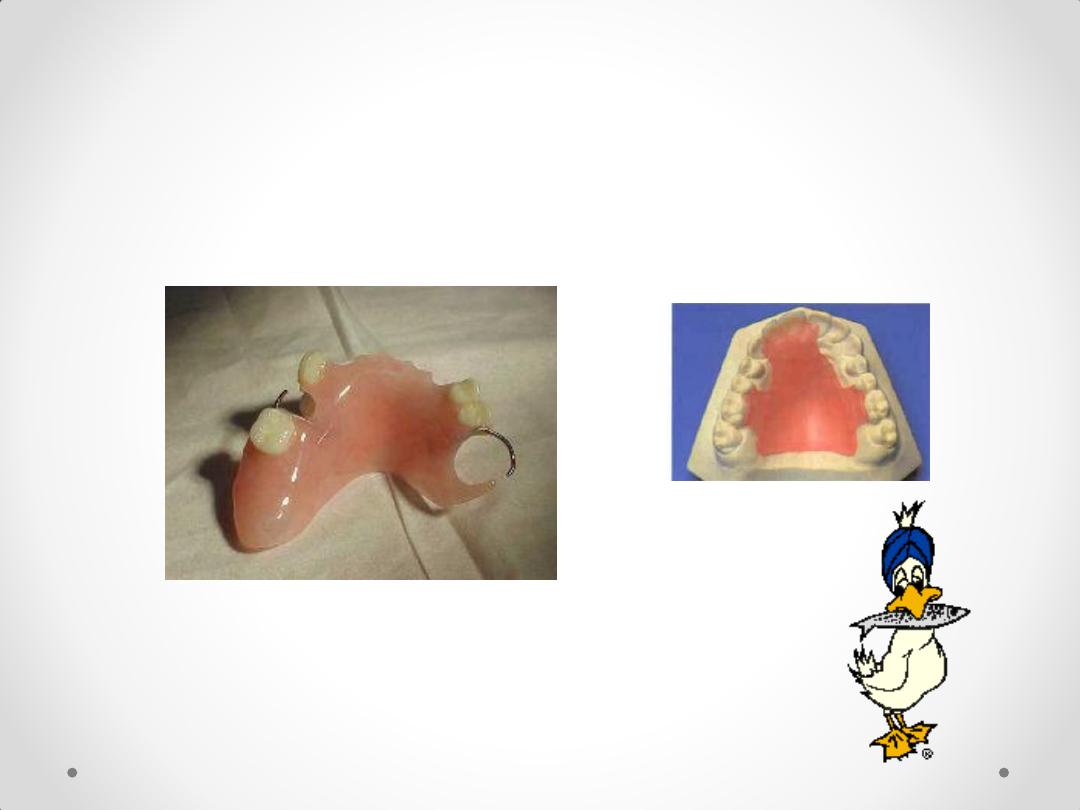
1-Temporary RPD: a removable prosthesis that is
used temporarily for a period of time until a more
definitive prosthesis can be provided
.
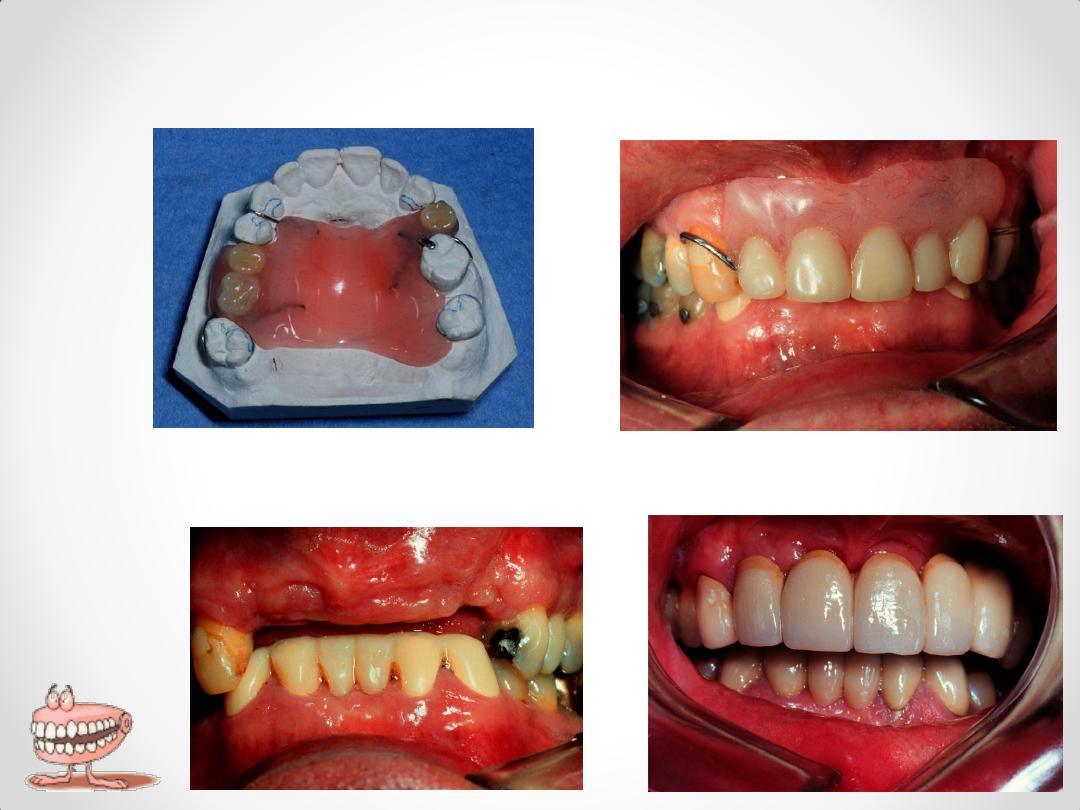
Acrylic major connector,
wrought wire clasps
2-Interim Removable Partial Dentures
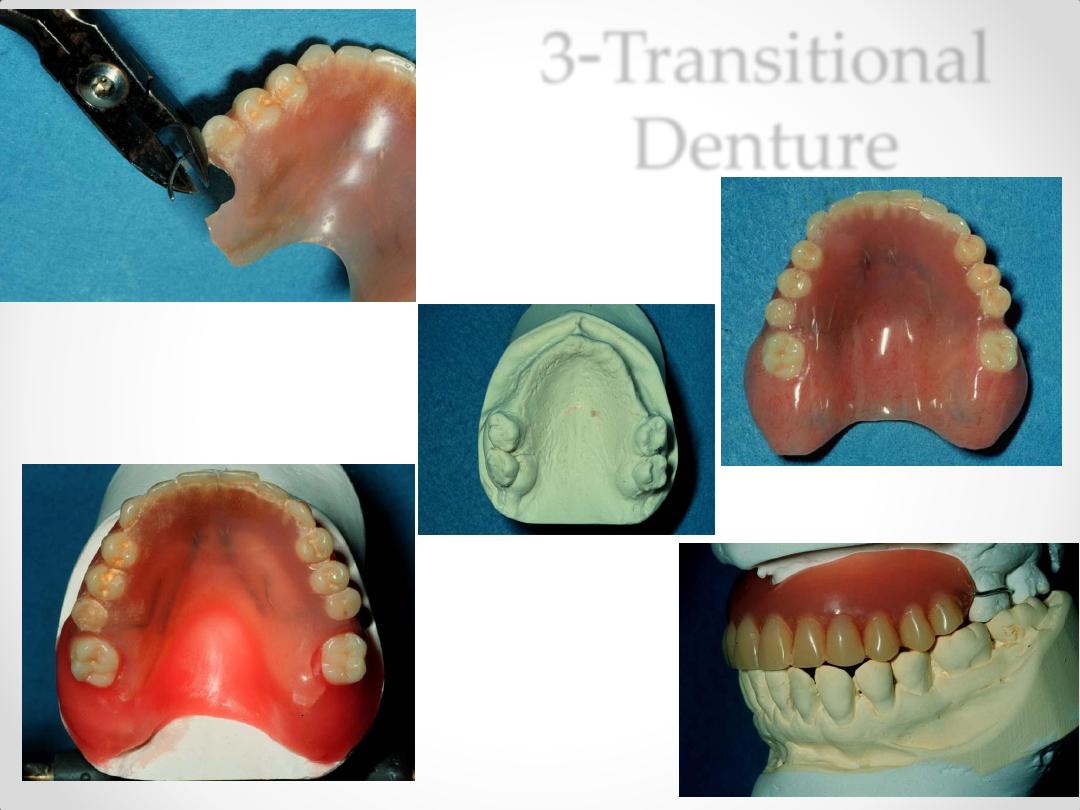
3-Transitional
Denture
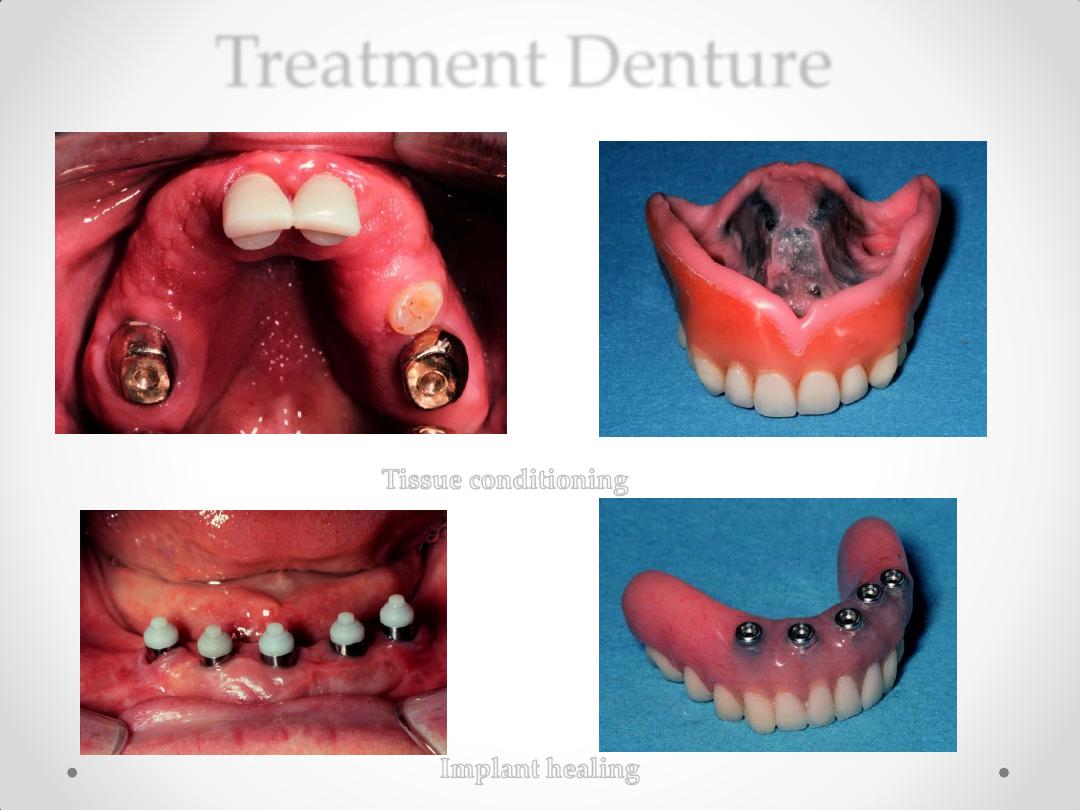
Treatment Denture
Tissue conditioning
Implant
healing
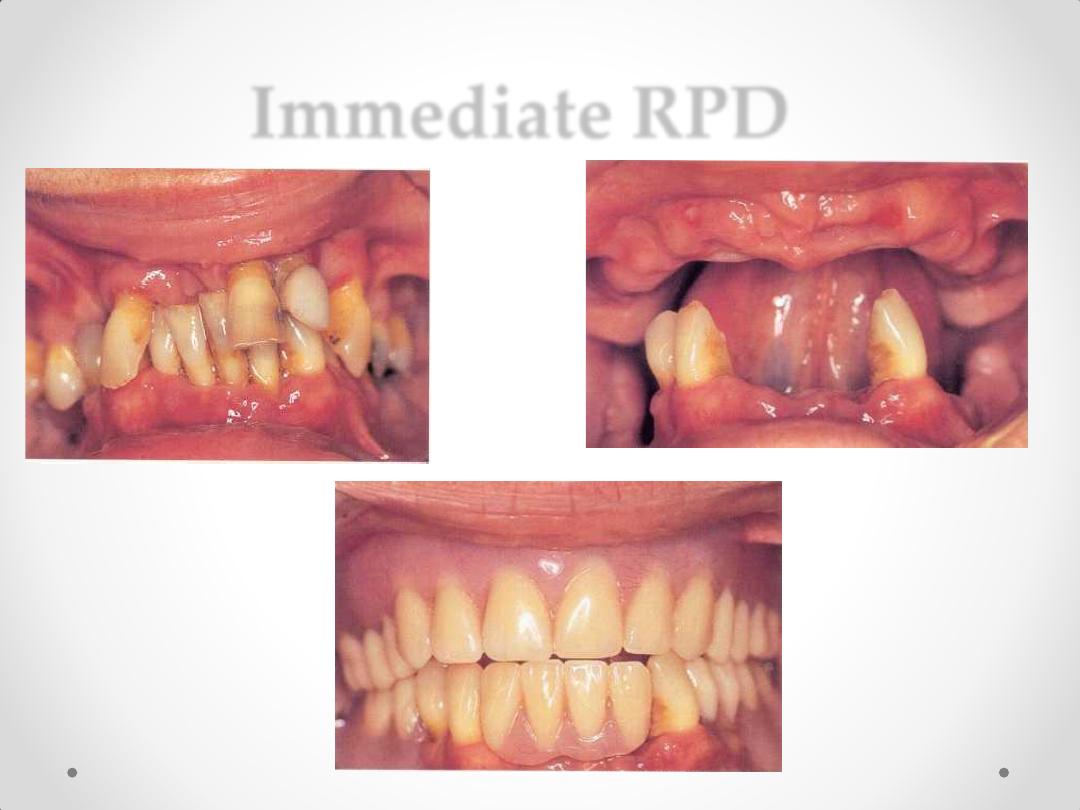
Immediate RPD
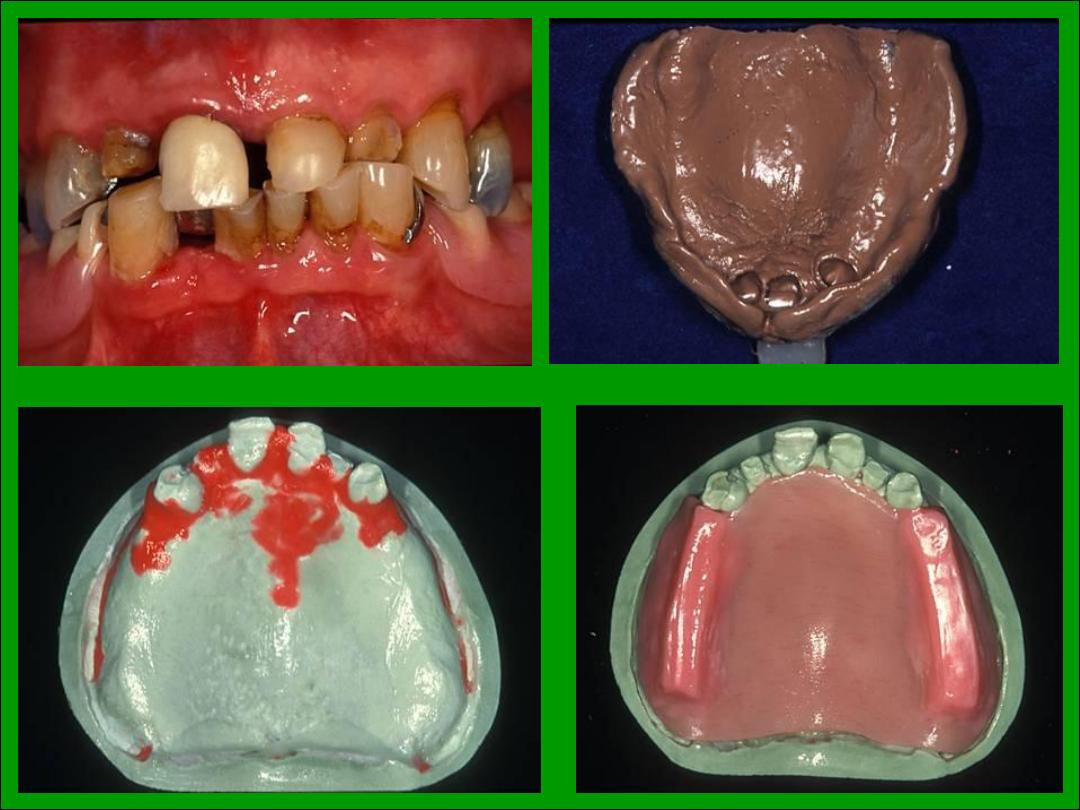
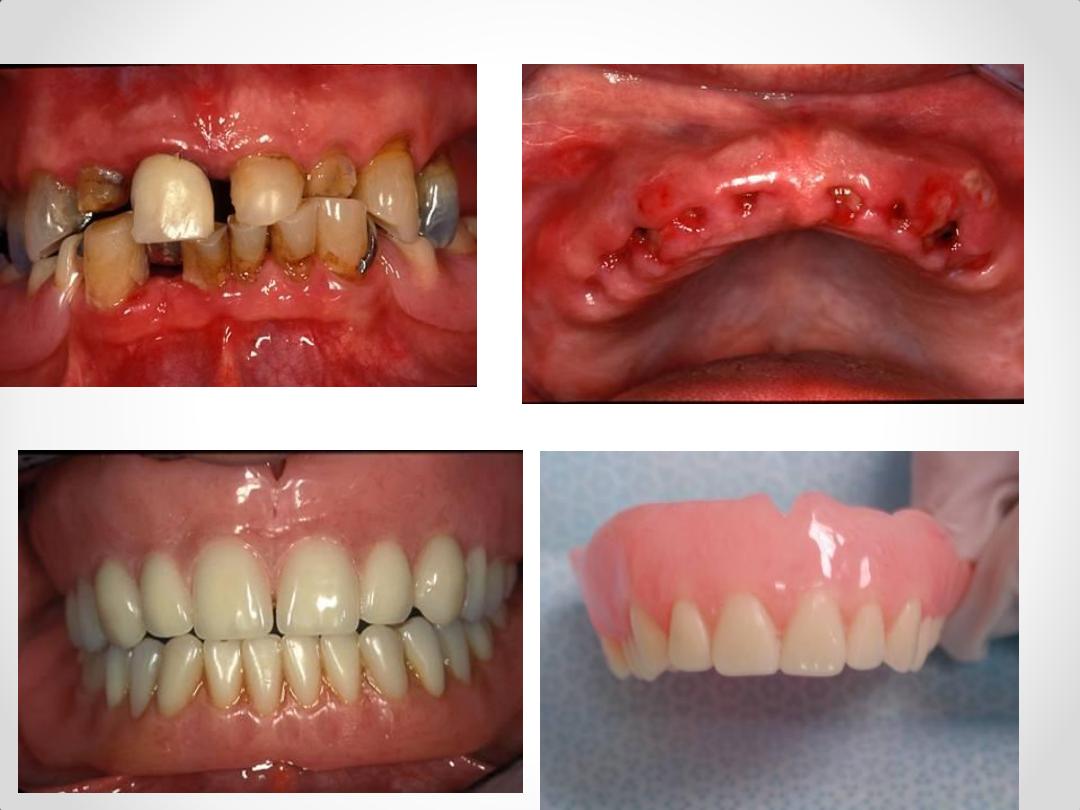
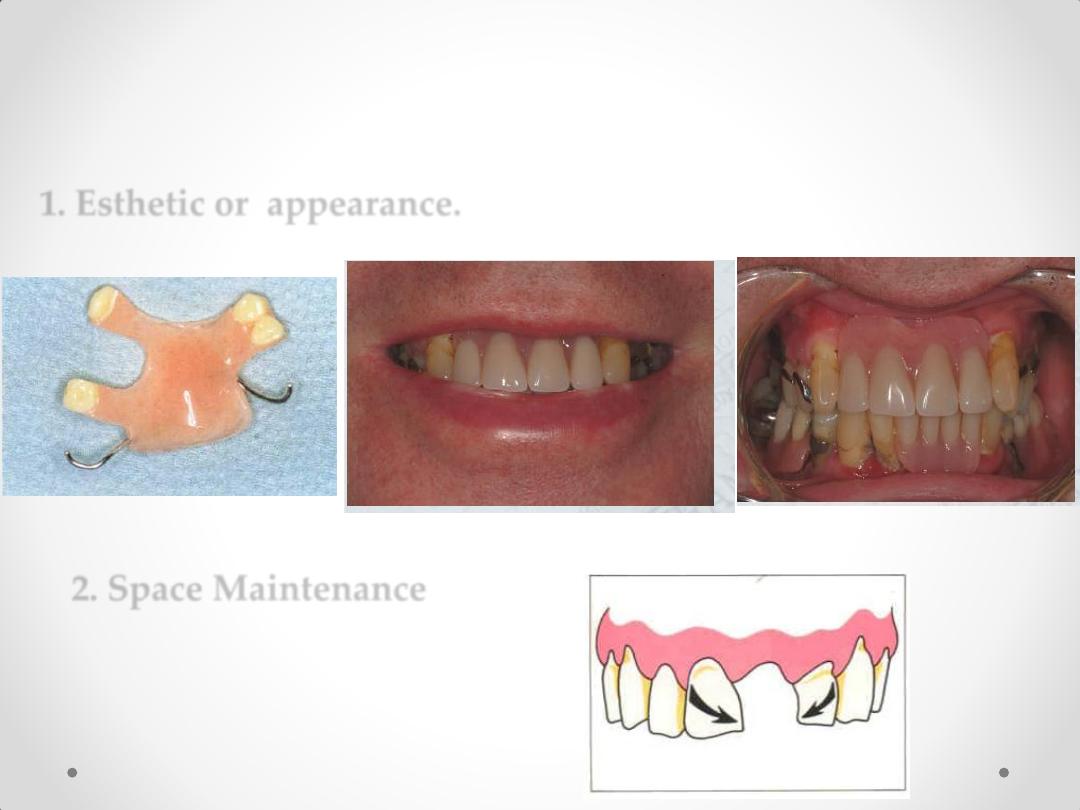
1. Esthetic or appearance.
Indications of Temporary
Removable Partial Dentures
2. Space Maintenance
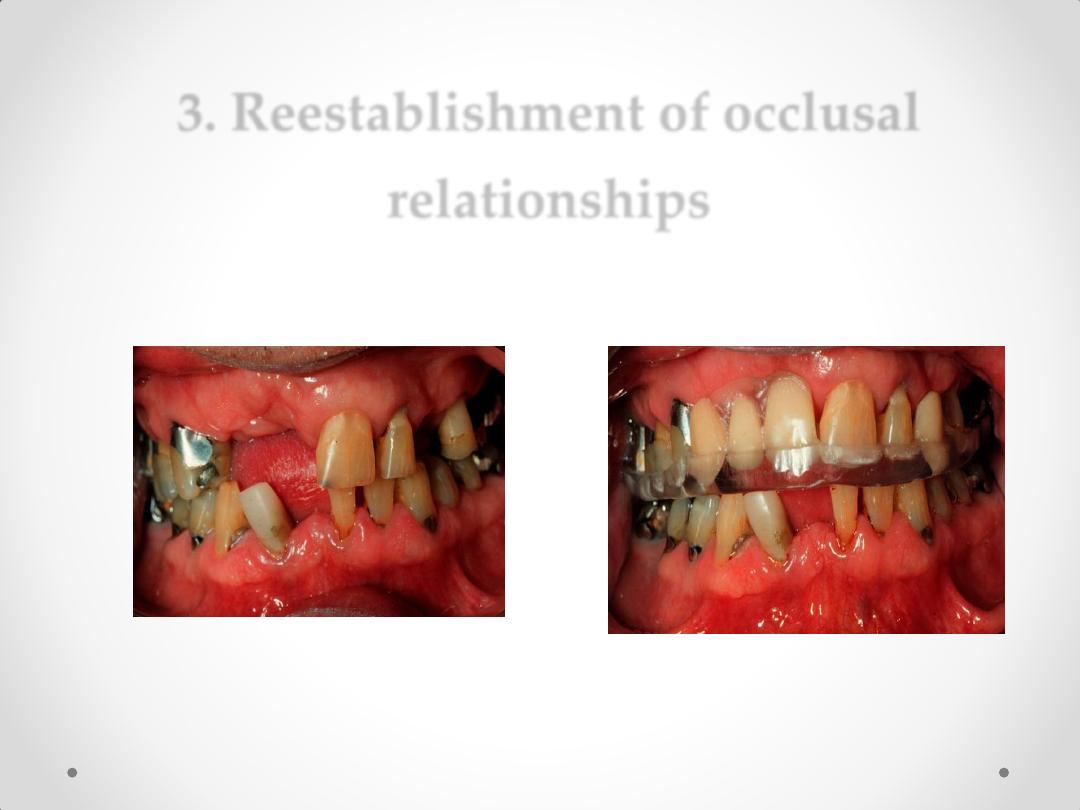
3. Reestablishment of occlusal
relationships
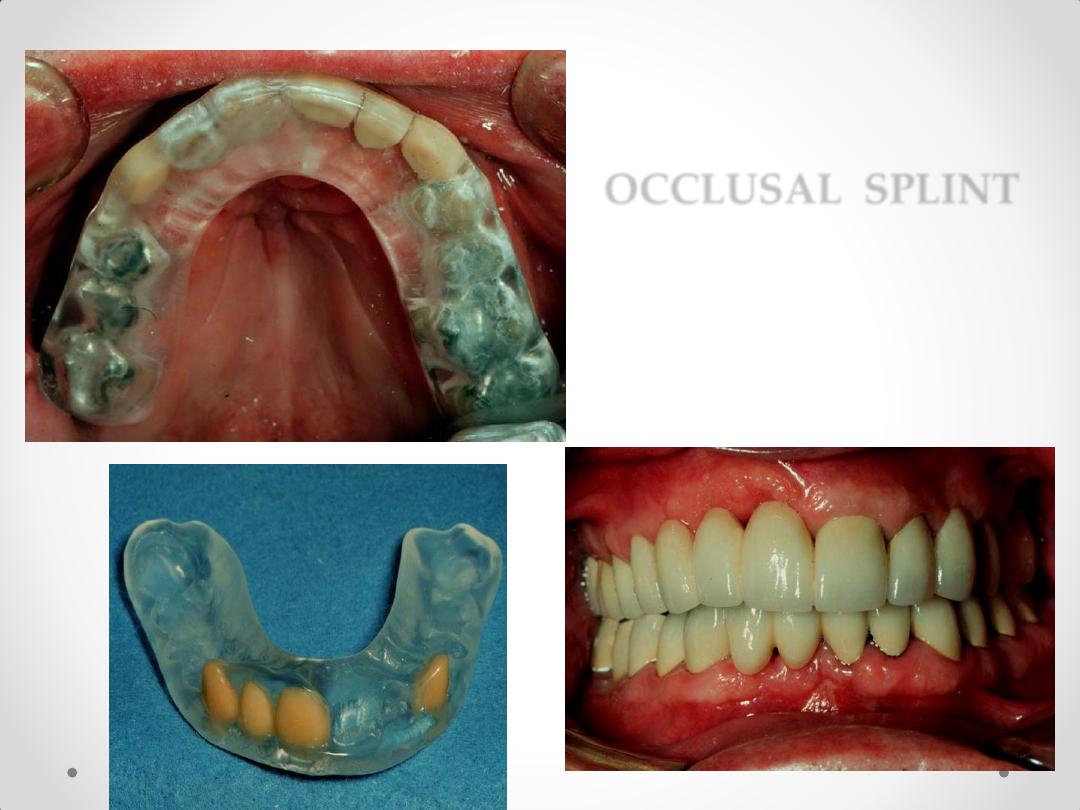
OCCLUSAL SPLINT
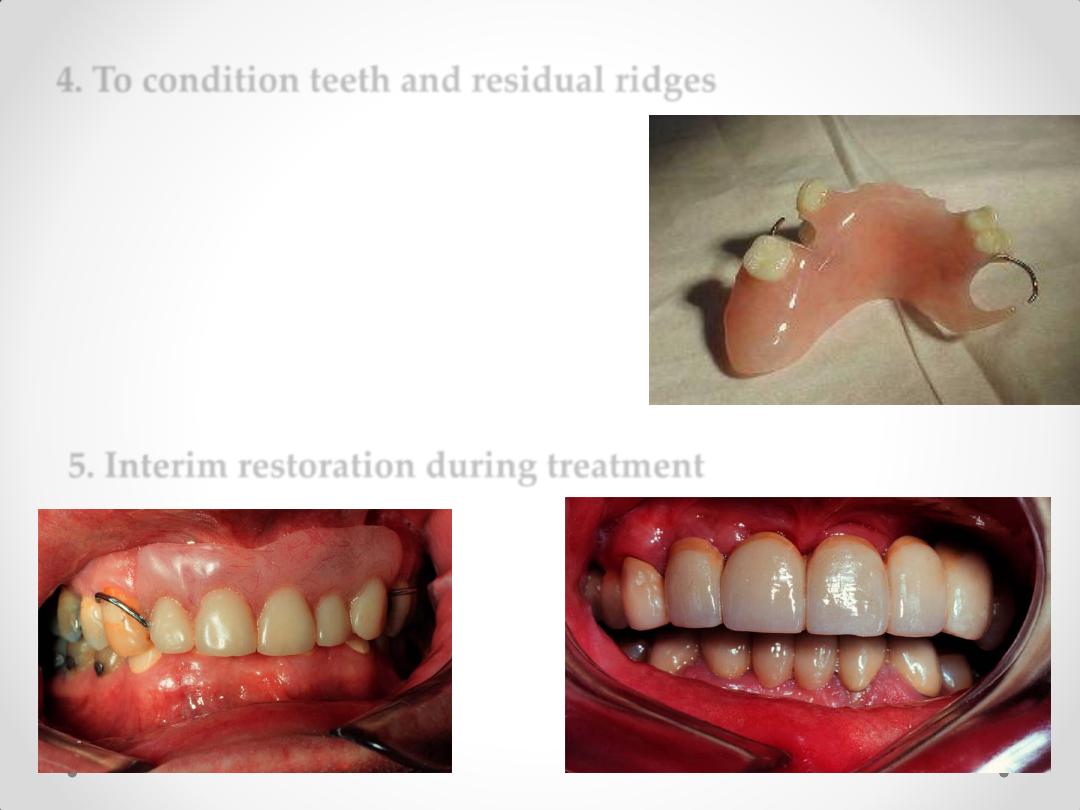
4. To condition teeth and residual ridges
5. Interim restoration during treatment
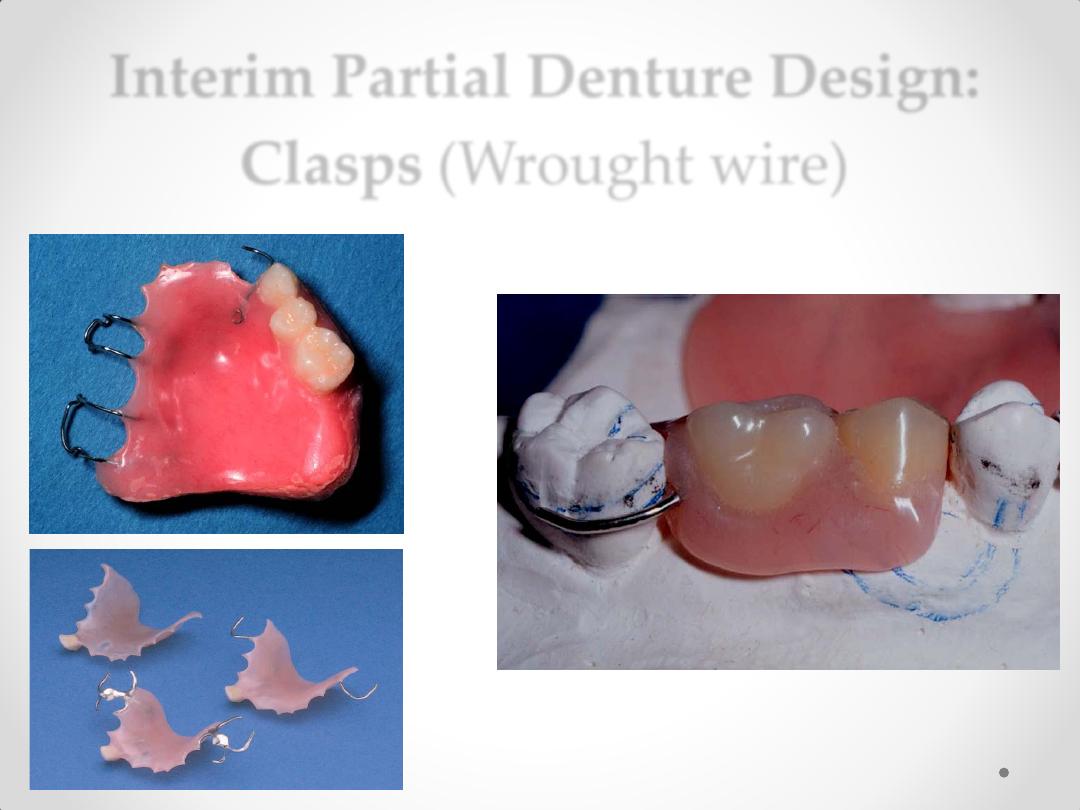
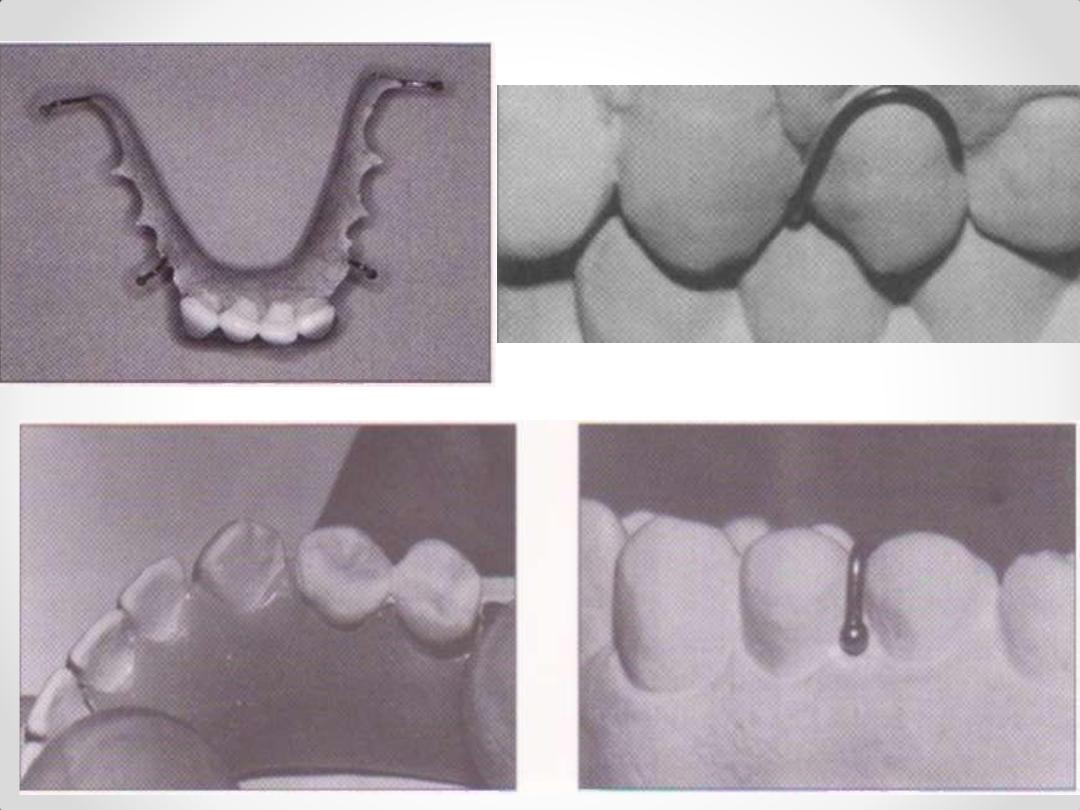
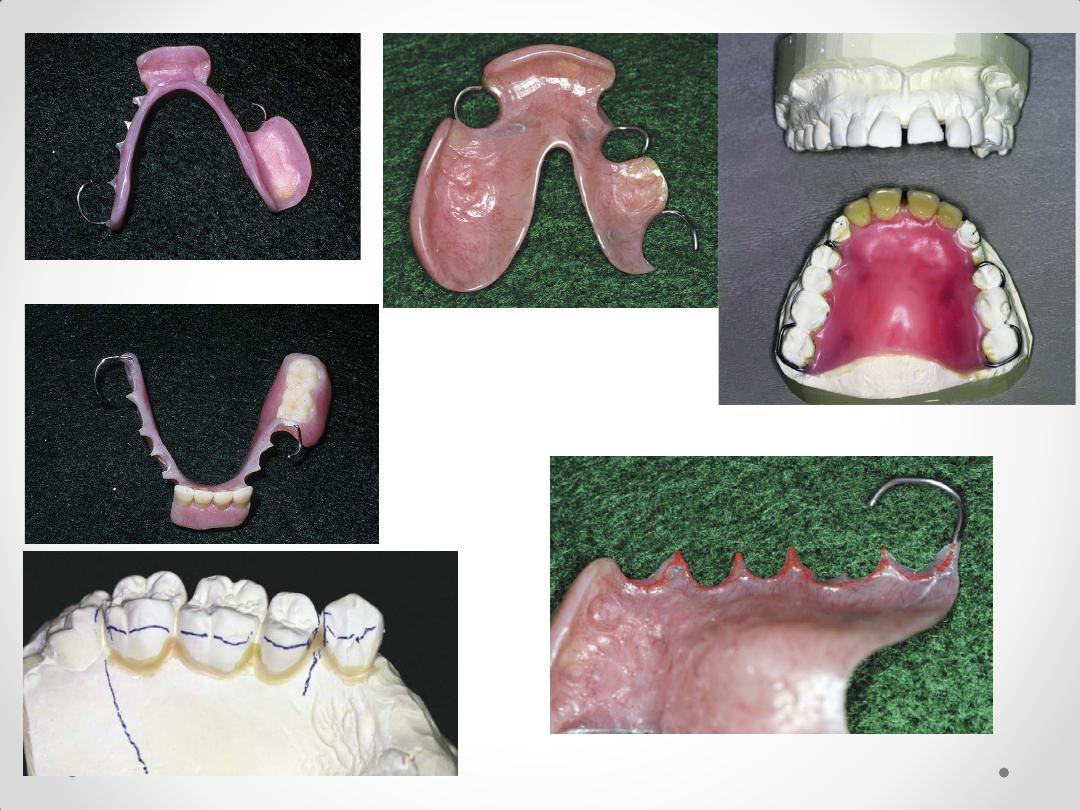
Interim Partial Denture Design:
Clasps (Wrought wire)
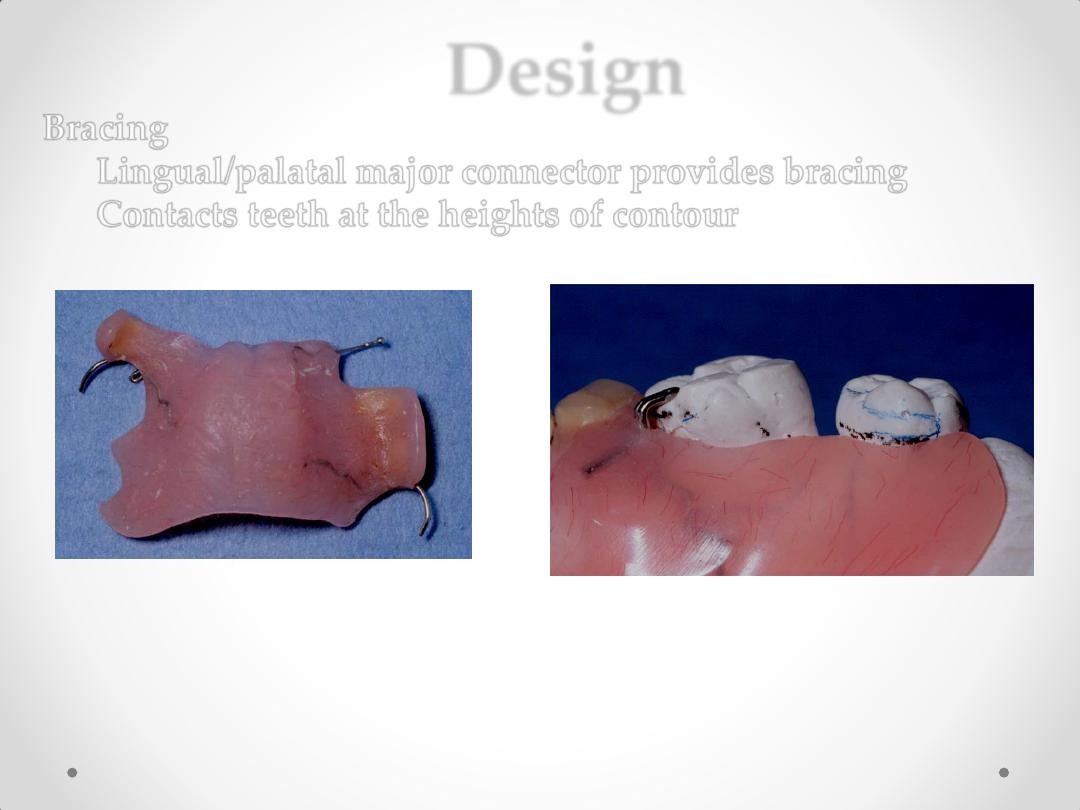
Design
Bracing
Lingual/palatal major connector provides bracing
Contacts teeth at the heights of contour
Major Connectors
Full palatal coverage increases strength & stability
Retentive clasps embedded into major connector
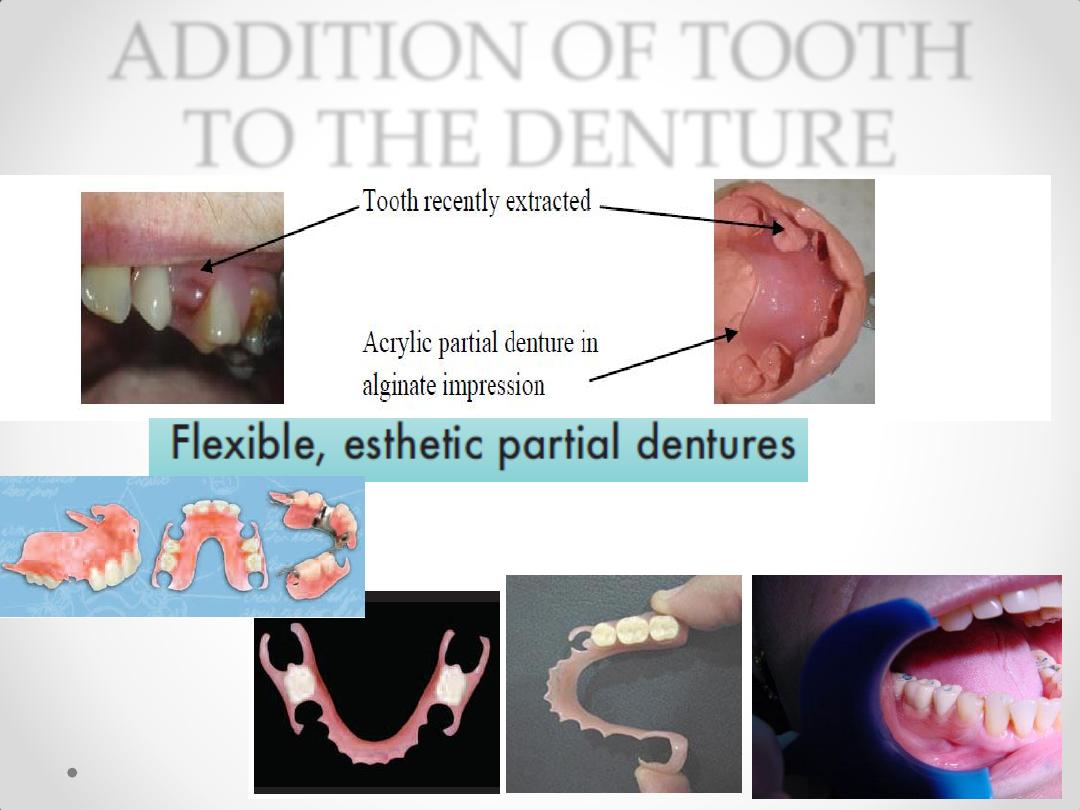
ADDITION OF TOOTH
TO THE DENTURE

FIXED VERSUS REMOVABLE
PARTIAL DENTURE
(comparison in preference)
•
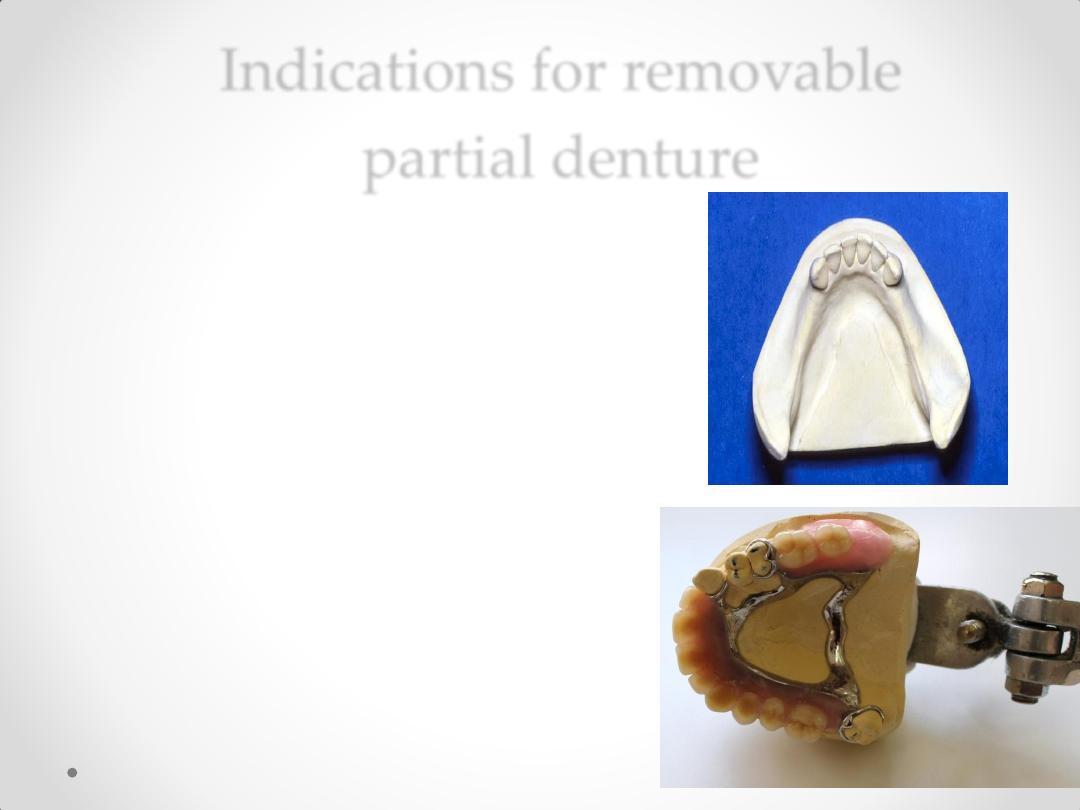
Indications for removable
partial denture
1-
Where vertical support from the
edentulous ridge is needed .
e.g. in the absence of a distal abutment.
e.g. to ensure stability with a
long edentulous space
2-
Where resistance to lateral movement is
needed from contra-lateral teeth and soft
tissues.
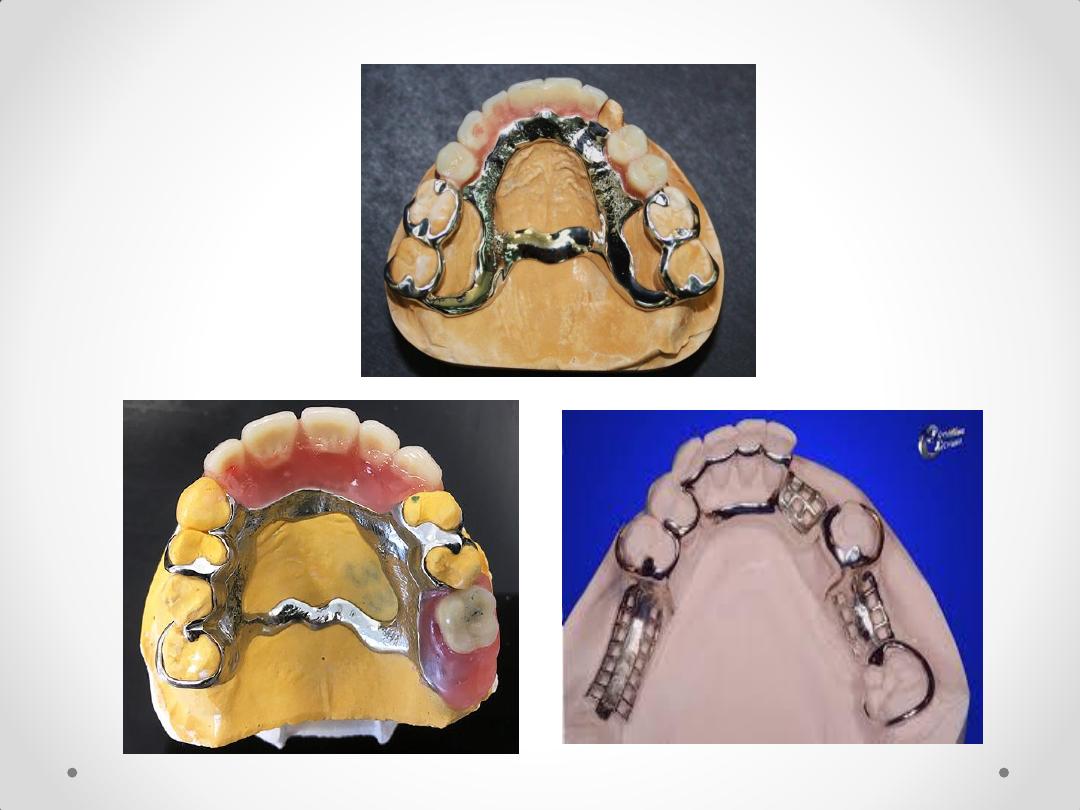
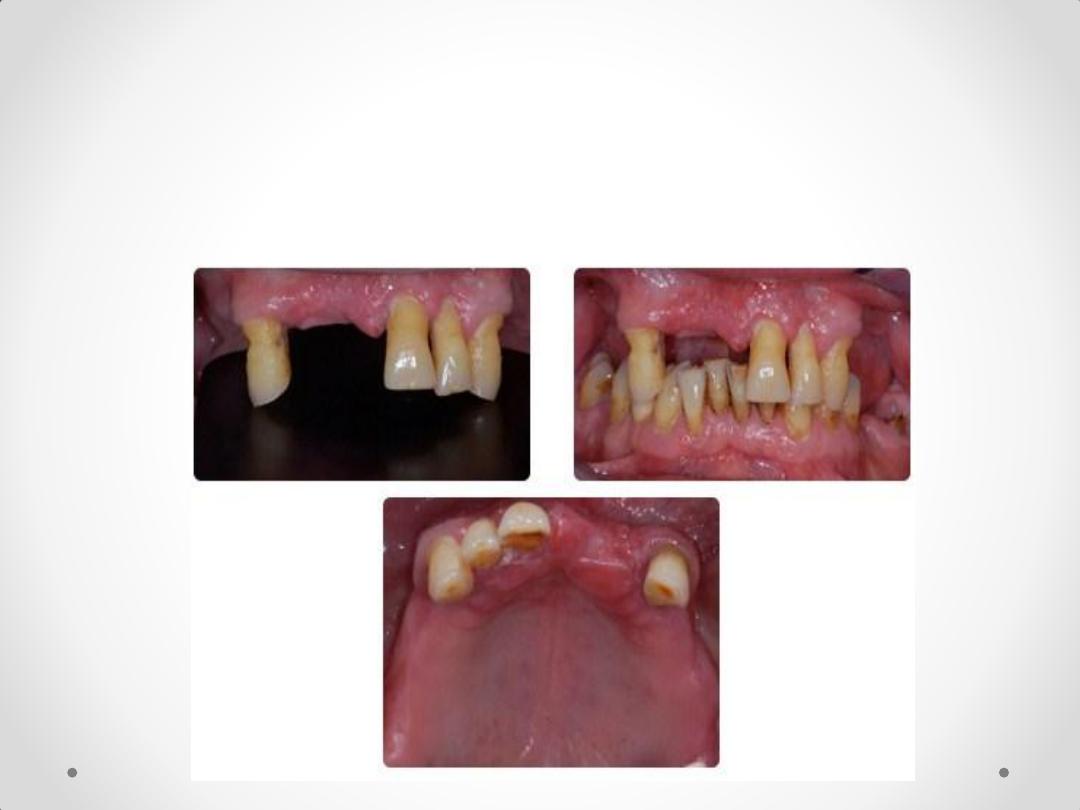
3-
Inadequate periodontal support
The abutment teeth that exhibit reduced periodontal
support because of periodontal disease that would
benefit from cross-arch stabilization.
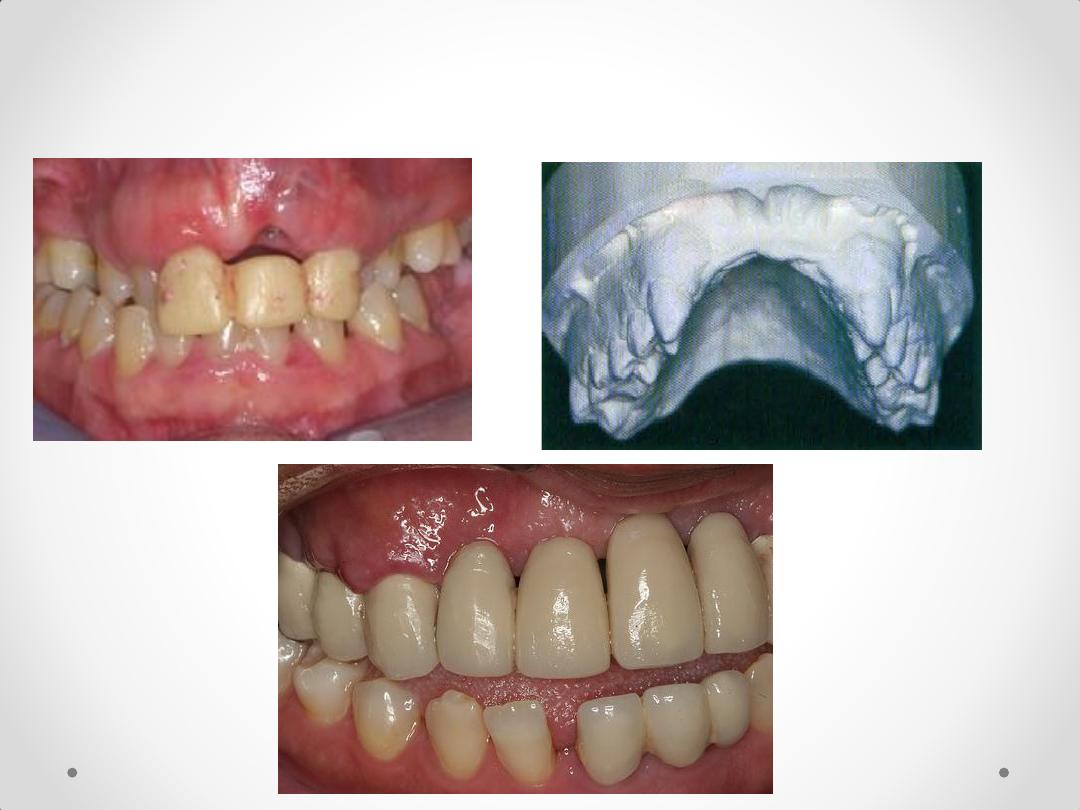
4-
considerable bone loss in the visible anterior
region.
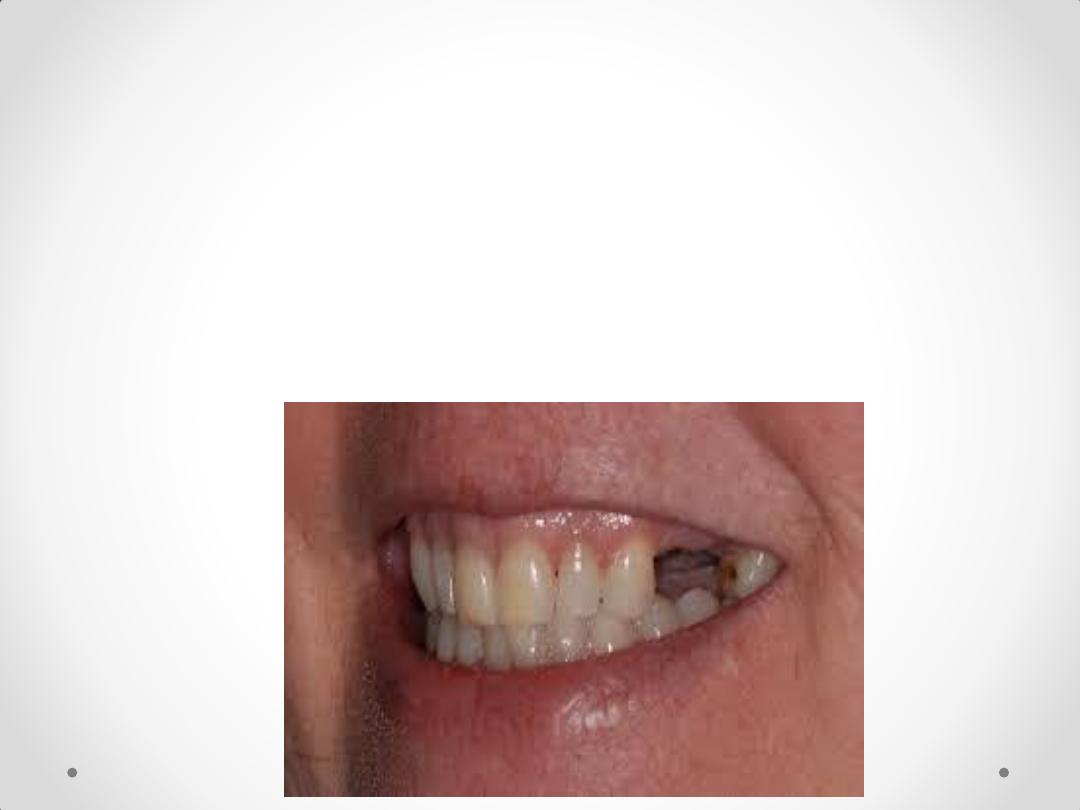
6-
Unusually Sound Abutment Teeth
• Sometimes the reasoning for making a
removable restoration is the desire to see
sound teeth preserved in their natural state
and not prepared for restorations.
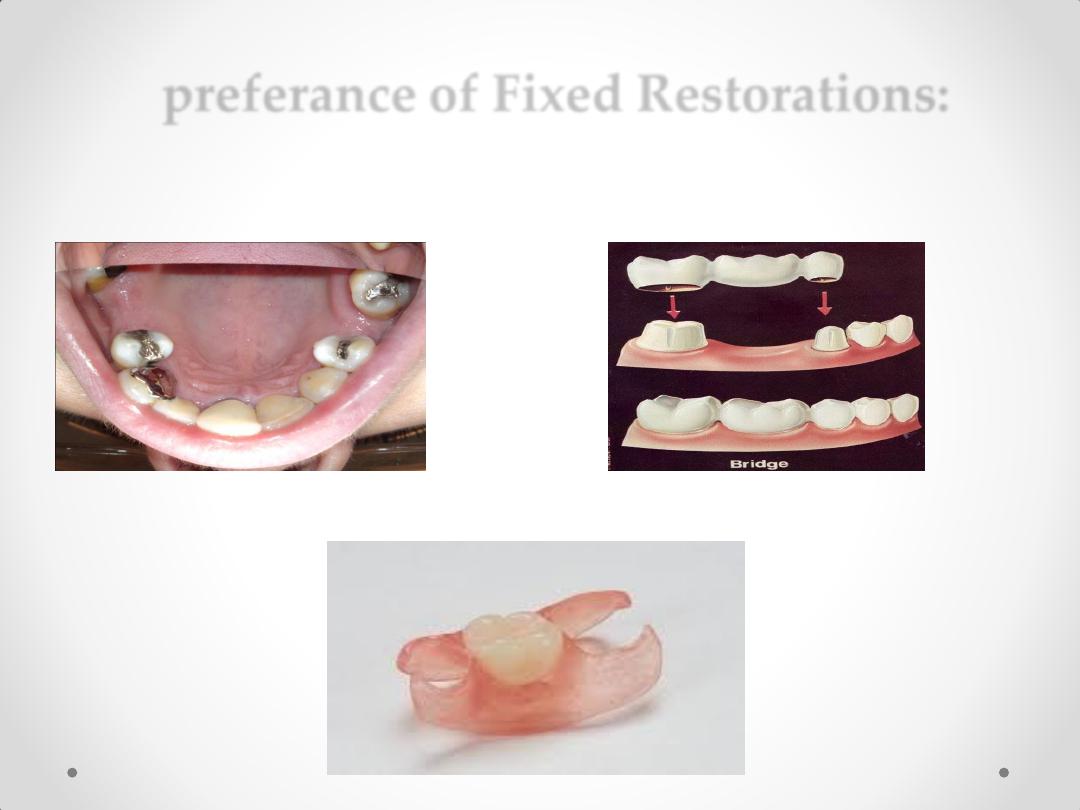
preferance of Fixed Restorations:
1-Tooth-Bounded Edentulous Regions
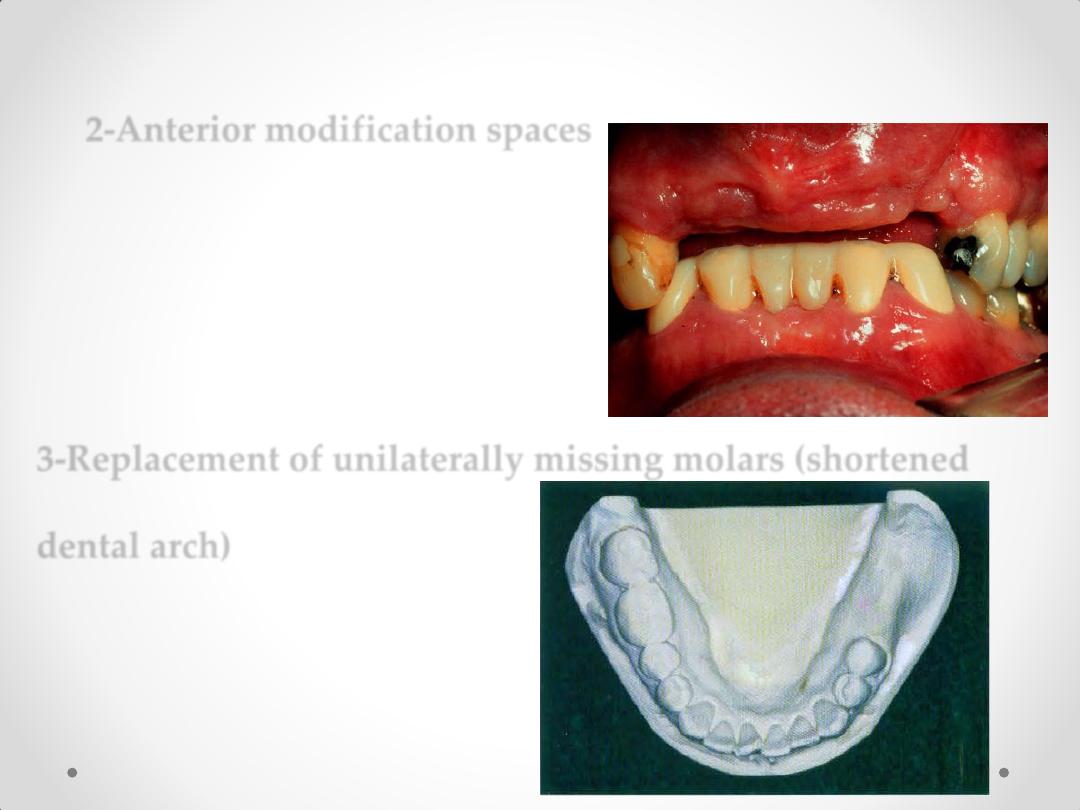
2-Anterior modification spaces
3-Replacement of unilaterally missing molars (shortened
dental arch)

•
ال تنسونا بدعائكم بالنجاح
