Practical respiratory
Systemطب الاسنان
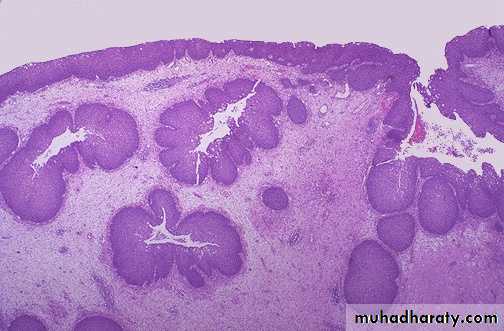
This inverted papilloma of the nose is a benign but locally aggressive neoplasm that can also occur in the paranasal sinuses. The proliferating squamous epithelium tends to "invert" inward into the stroma so that islands of squamous mucosa appear below the surface, as seen here
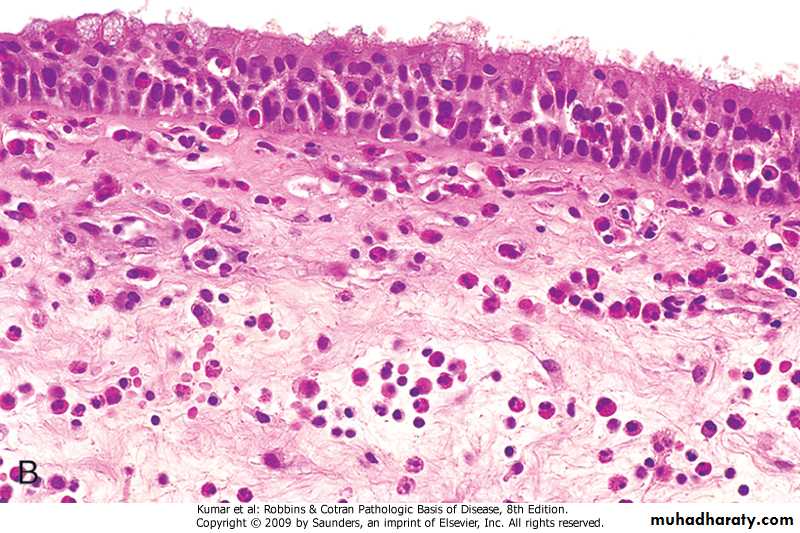
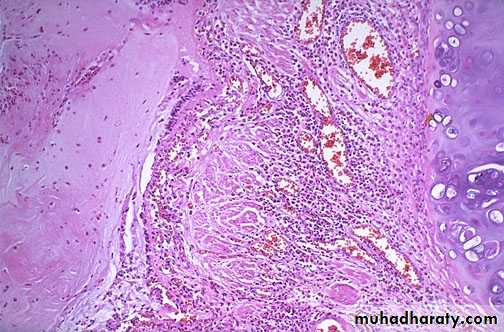
Nasal mass with edematous stroma with chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate ( mainly eosinophils) covered by ciliated columnar epitheliumallergic nasal polyp
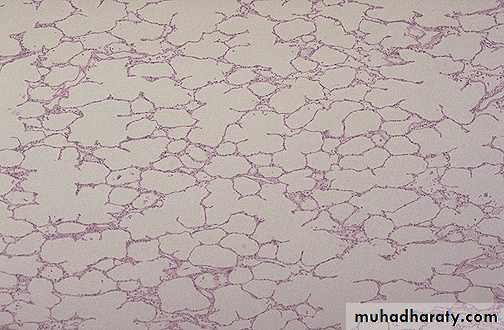
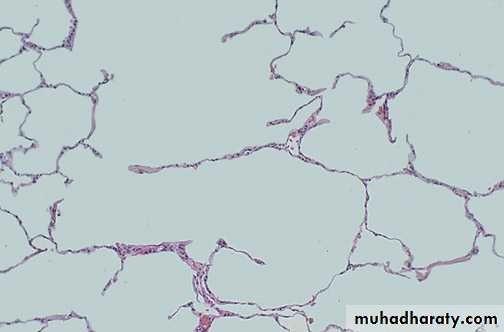
A normal lung microscopically
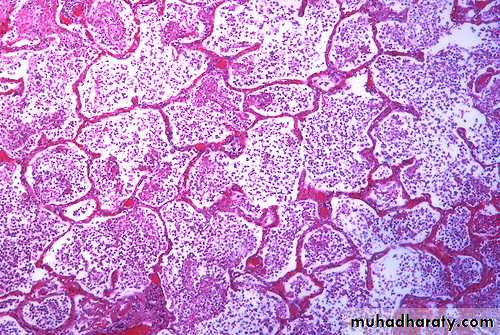
An example of bronchopneumonia with multiple areas of consolidation (lobular pneumonia)
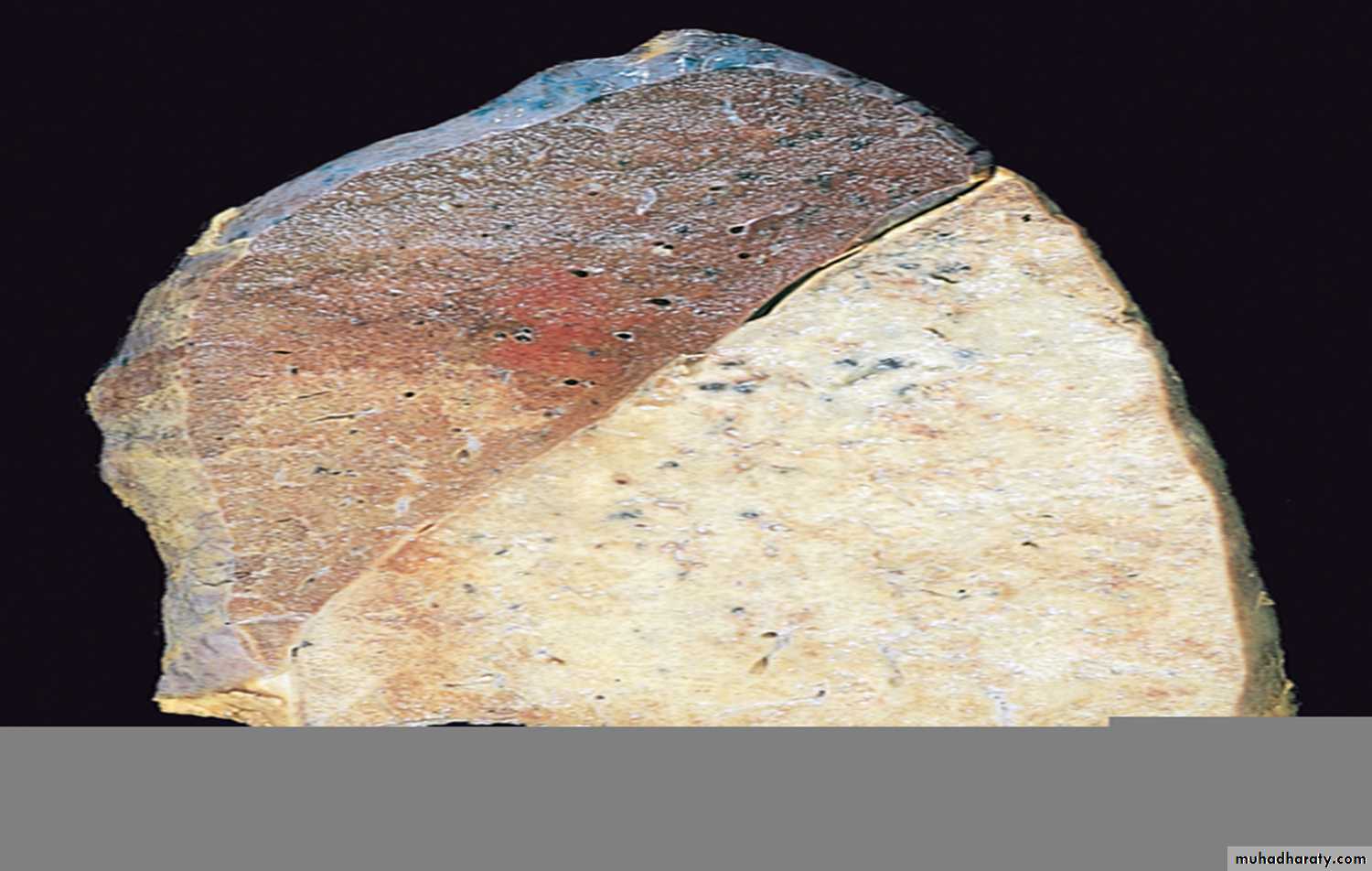
A lobar pneumonia with firm brownish-tan consolidation of the entire left upper lobe, which is confined by fissure line.
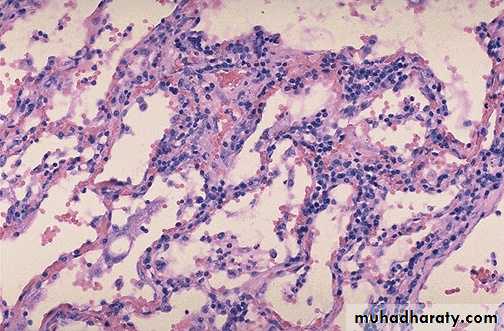
Bronchopneumonia with patchy area of alveoli filled with inflammatory cells with congestion of alveolar wall.
Viral pneumonia: Interstitial mononuclear cells mainly lymphocytic cells (interstitial pneumonia)
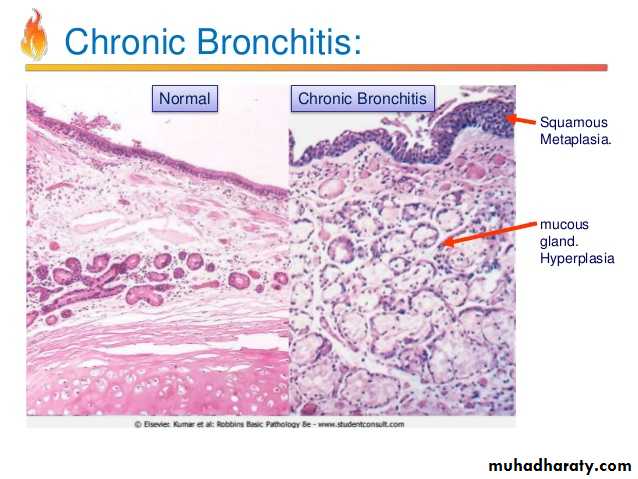
Bronchial asthma sub mucosal smooth muscle hypertrophy, basement membrane thickening, inflammatory cell infiltration rich in eosinophils with mucus collection in lumen, vascular congestion
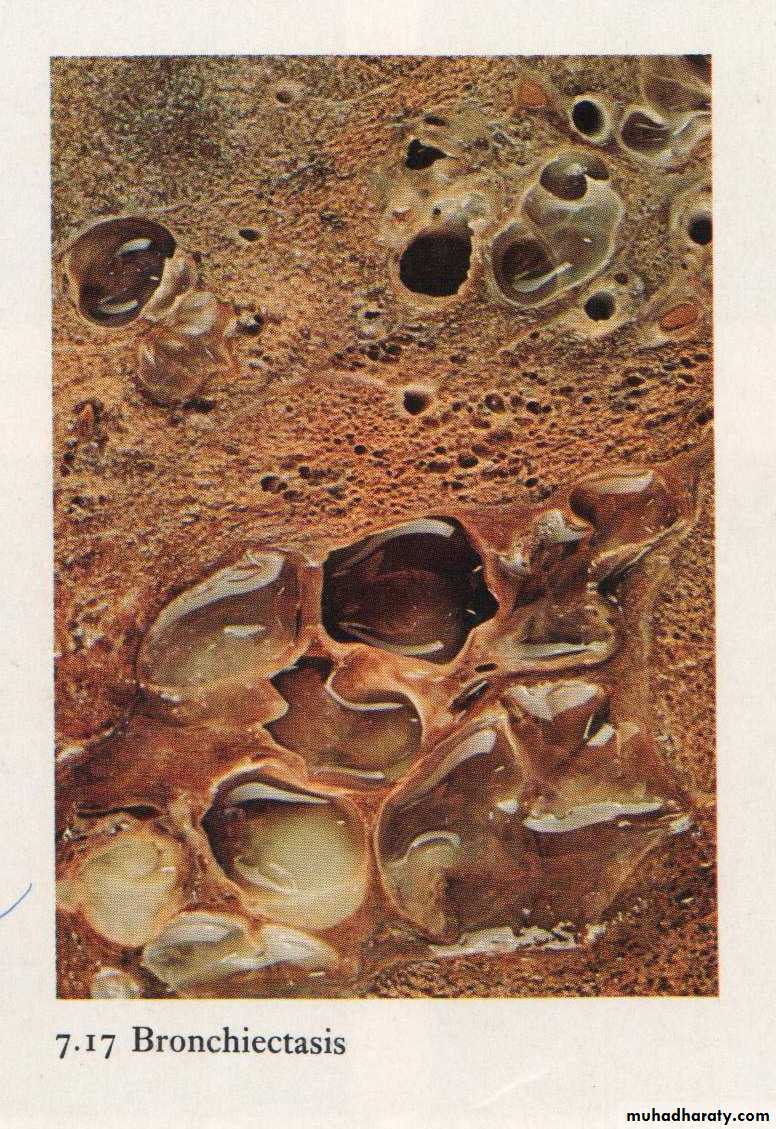
Destructed & dilated large airways form a honeycomb pattern in Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis: dilated bronchus with inflammation & destruction of the wall
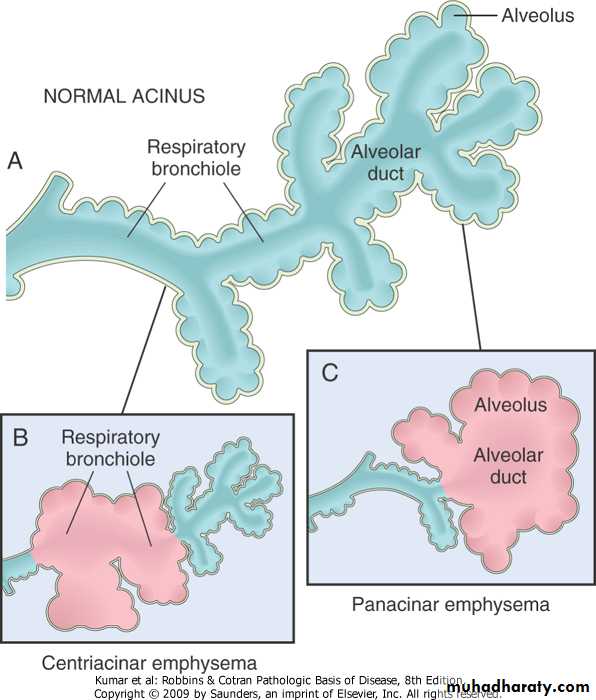
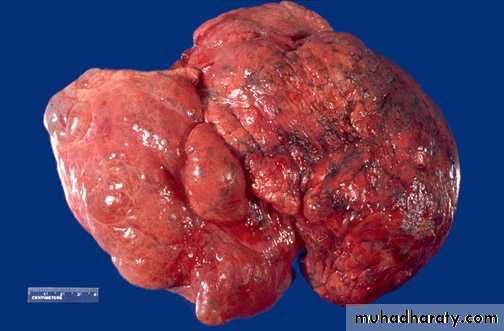
Bullous emphysema involving all lobes of the lung (panlobular emphysema). This carry risk of rupture & pneumothorax
Destruction of alveolar wall & dilatation of air spaces seen in emphysema
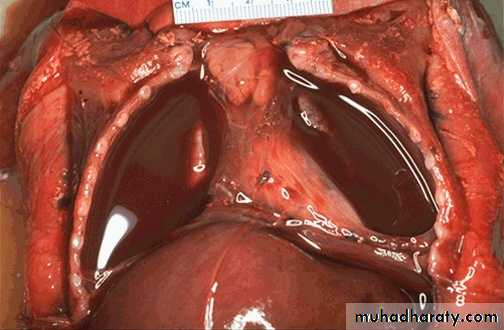
A pleural effusion ,the collected fluid within the pleural cavity is serosanguinous (serous & blood) with collapse of both lungs
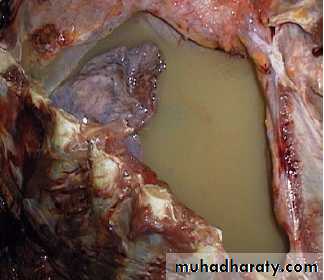
Yellowish tan fluid collected in the right pleural cavity it can be empyema or chylothorax.
Centrally located irregular firm to solid whitish-gray mass compressing left bronchus with area of hemorrhage.
Diagnosis: bronchogenic carcinoma, mostly Squamous cell carcinoma
Tumor has a soft, lobulated, white to tan appearance, obstructing the main bronchus to left lung so that the distal lung is collapsed. Small cell carcinomas are very aggressive and often metastasize widely
Small cell carcinoma with small dark blue cells packet in sheets
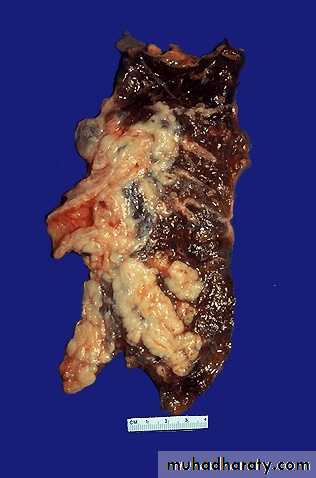
Solitary irregular yellowish-tan firm mass at periphery of lower left lung.
Diagnosis: Bronchogenic carcinoma, mostly adenocarcinomaPracticalLympho-Reticular System
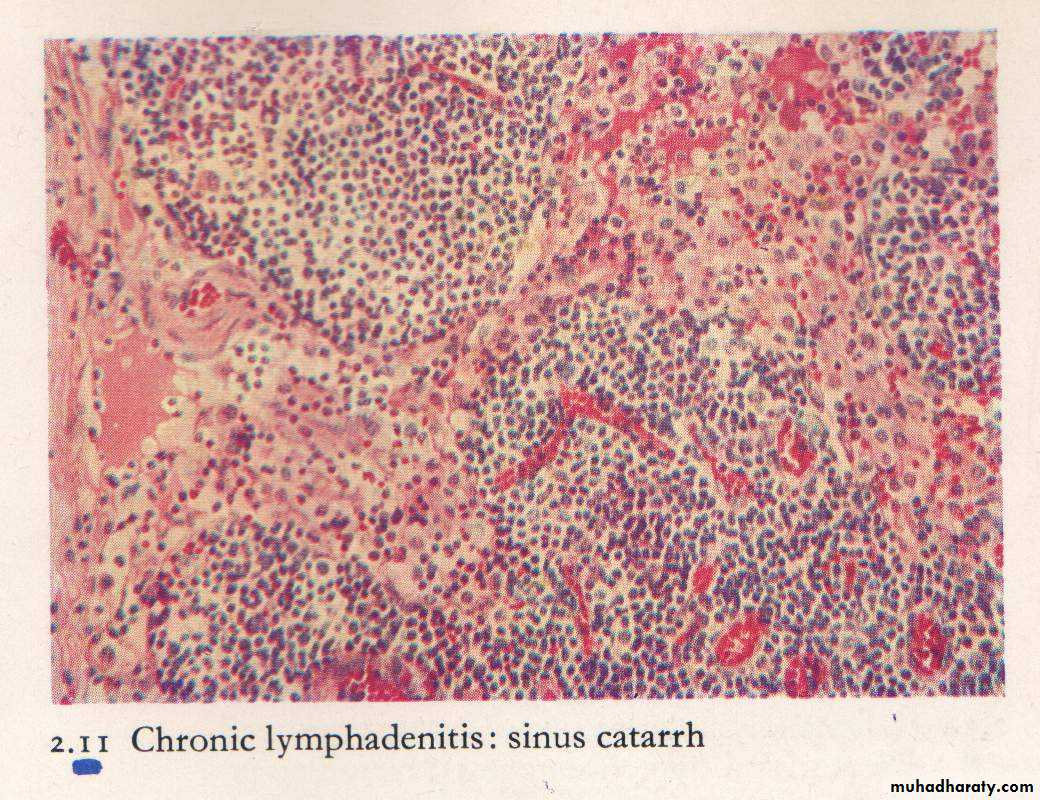
Non neoplastic lymphadenopathyLN is tender ,congested with sinus cattarh. Suppuration may occur.
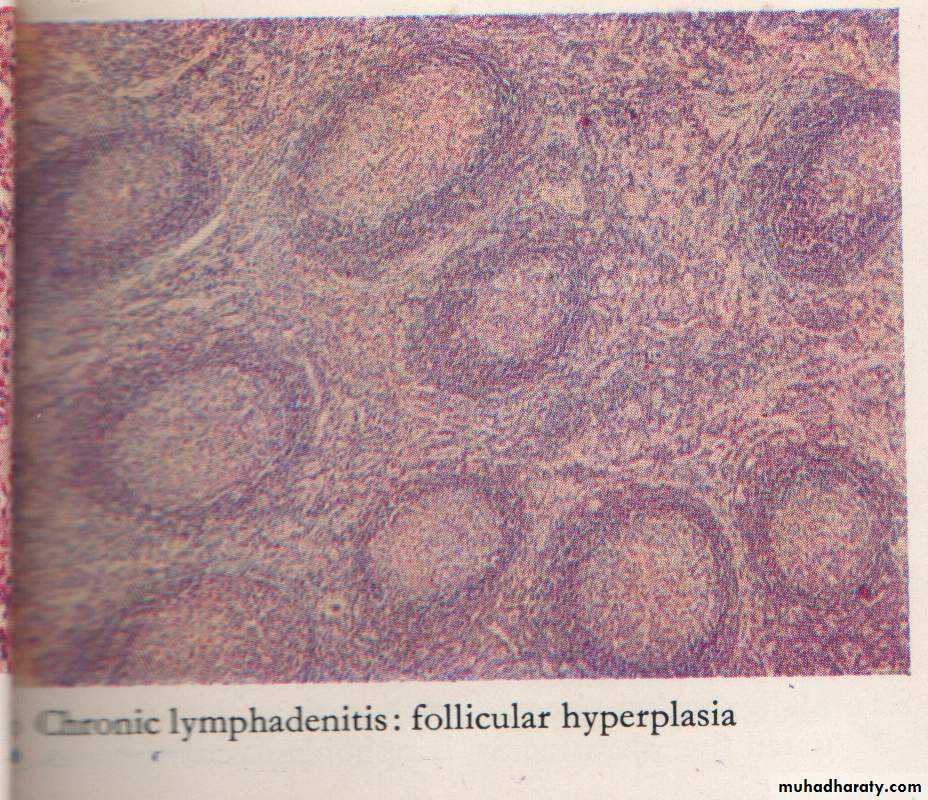
Chronic Lymphadenitis (Reactive hyperplasia) follicles of different size & shapes with prominent germinal center & prominent mantle zone( B-zone)
Hodgkin`s lymphoma
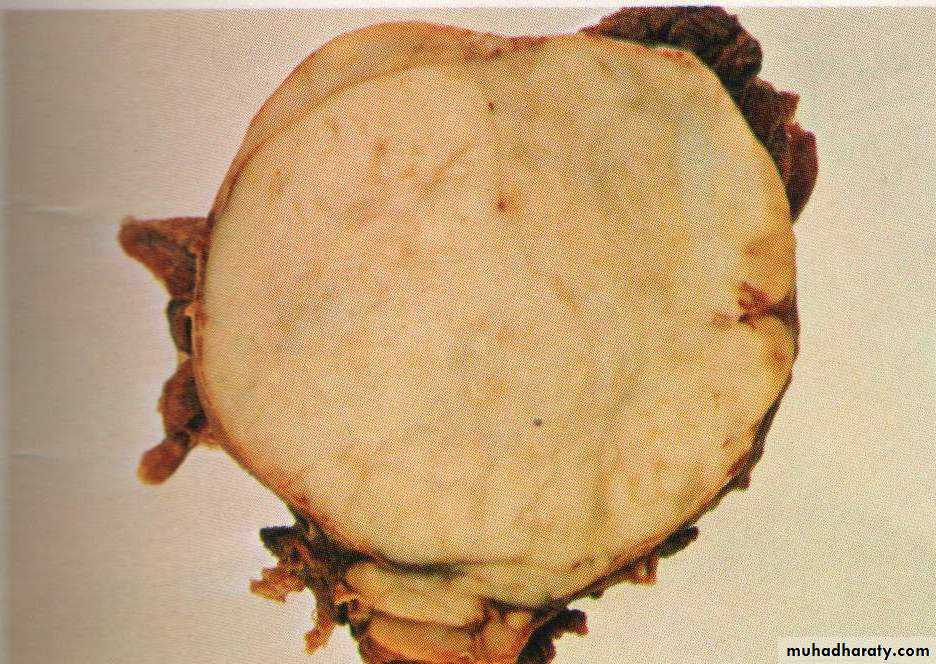
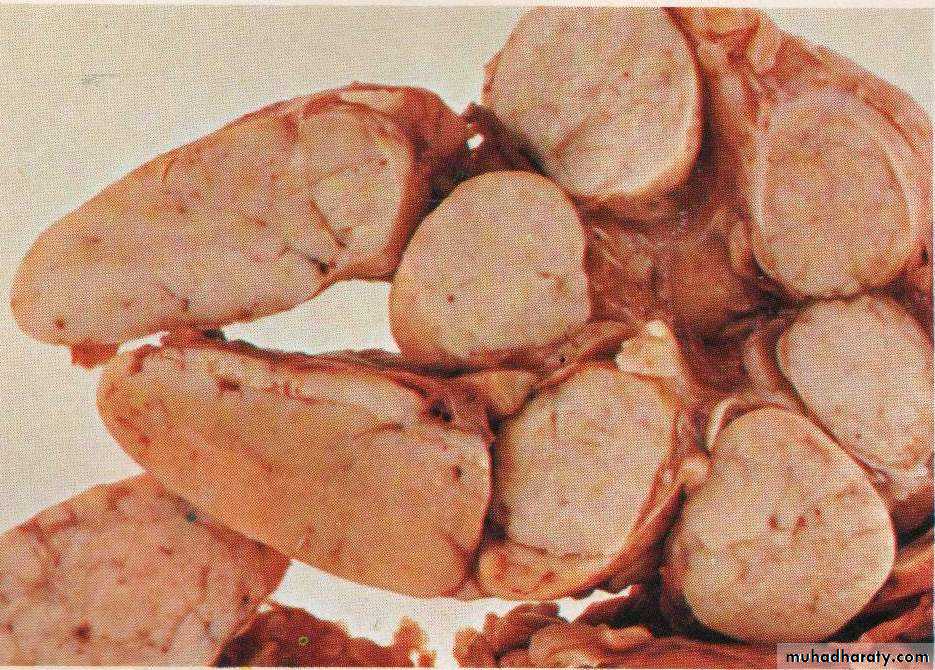
Grossly : lymph node is enlarged, firm discrete with homogenous ,potato- like cut surface.
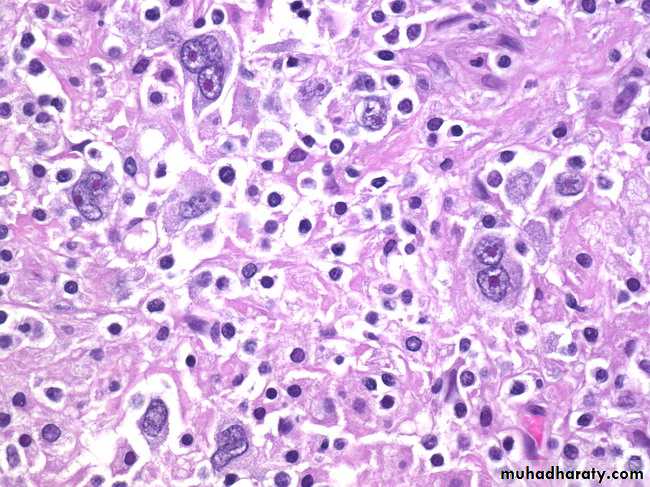
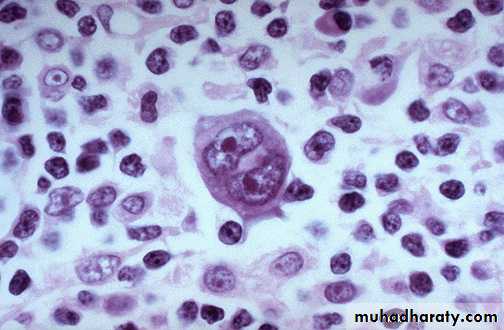
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, Reed-Sternberg Cells: The conventional definition of Hodgkin’s lymphoma requires the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells (many are seen in this image) in a characteristic background infiltrate composed of eosinophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and histiocytes. It lacks the monomorphic appearance of non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas
Hodgkin lymphoma, Reed-Sternberg cell, (Large cell with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, large bilobated, or binucleated vesicular nuclei, & prominent eosinophilic large nucleoli (mirror-image or owl-eye apopearance) present in a reactive background
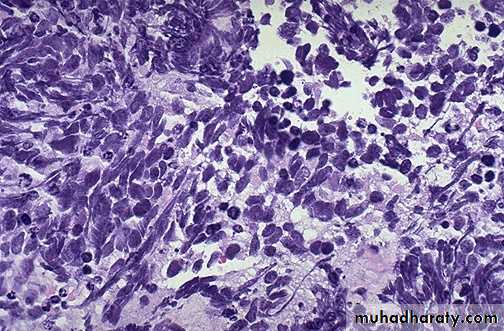
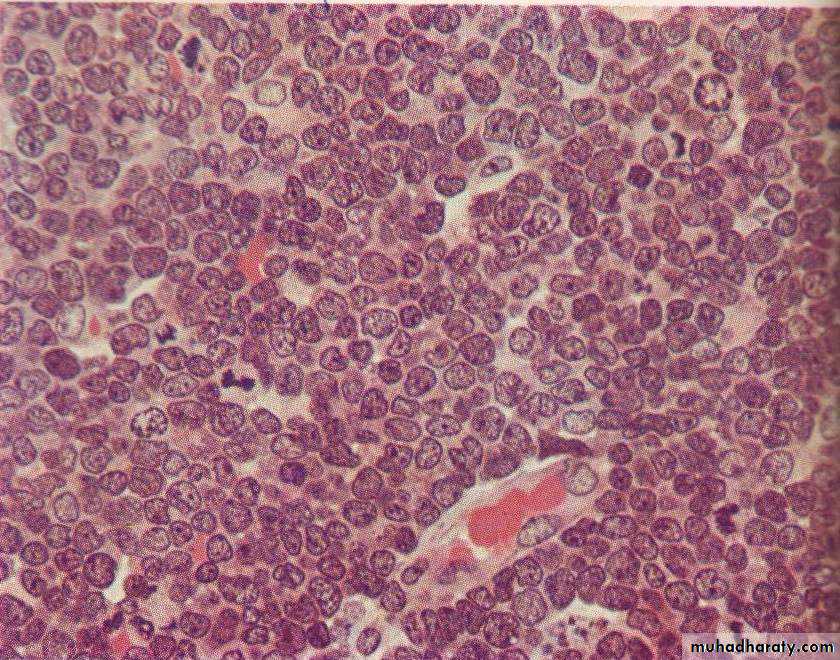
Non hodgkin lymphoma , loss of lymph node architecture, with monotonous diffuse proliferation of lymphoid cells with prominent mitotic figures