
Removable partial denture are component of prosthodontic, consist of artificial teeth that
restore the function of missing teeth and craniofacial tissue in human arches, R.P.D should provide
comfort for the patient, maintenance of oral function and provide good appearance (esthetic). For all
of this, the partial denture should has a good RETENTION , SUPPORT and STABLITY.
Removable partial denture consist of main parts :
1- Direct retainer
2- Major connector
3- Minor connector
4- Indirect retainer
The Mechanical Consideration of Distal Extension Removable Partial Denture:
O Retention
O Support
O Stability
O Retention
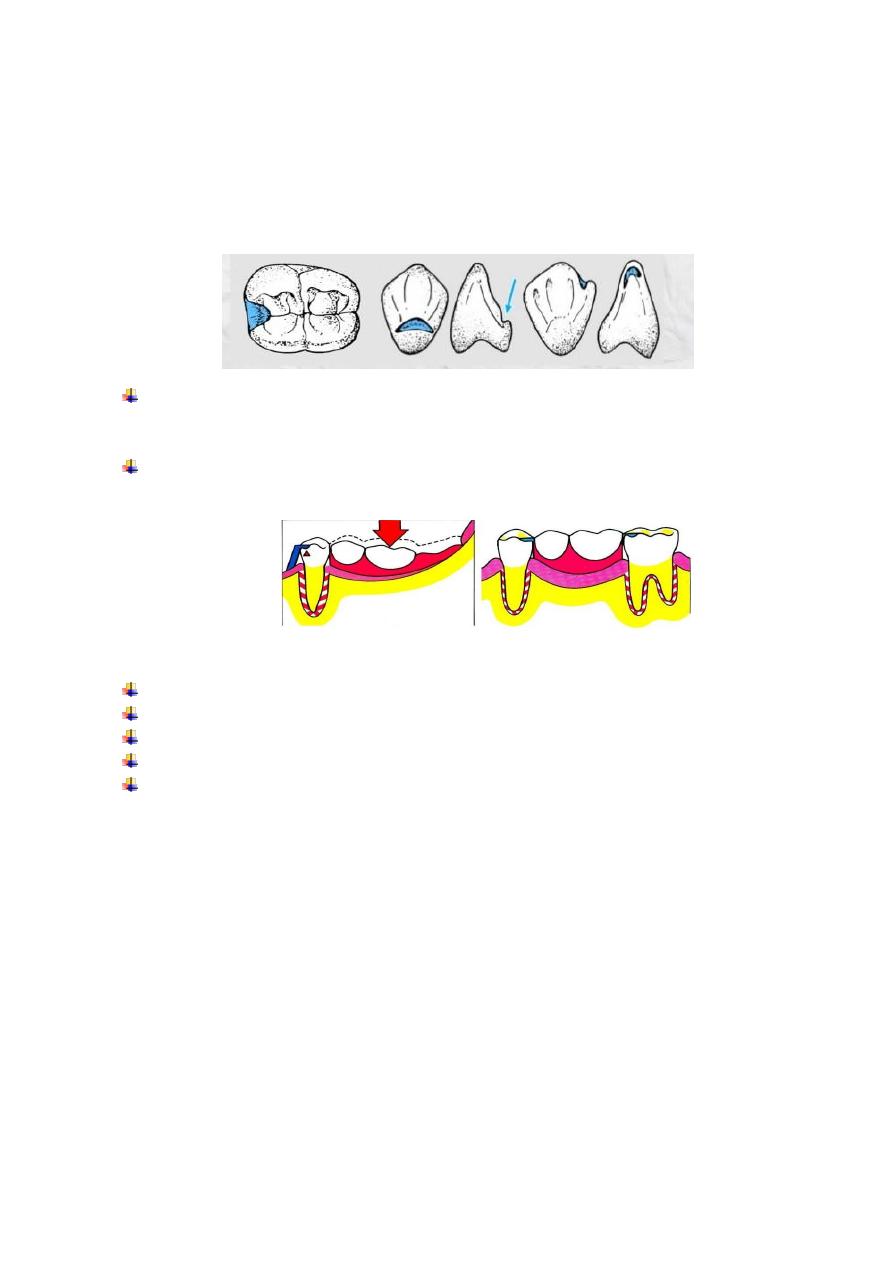
It is the quality of the clasp assembly that resists displacement of a prosthesis in an occlusal
direction, we gain retention from the retentive arm of the direct retainer that seat in the selected
undercut as show in figure (1).
Figure (1): Retentive parts of the clasp
Primary retention for removable partial denture : is accomplished mechanically by placing
retaining elements on the abutment teeth.
Secondary retention for removable partial denture : is provided by the intimate relationship
of denture bases and the major connector with the underlying tissues.
Retention of denture bases has been described as the result of the following forces:
1. Adhesion
2. Cohesion
3. Atmospheric pressure
4. Physiologic molding of the tissues around the polished surfaces of the denture and
5. The effects of gravity on the mandibular denture.

1
Direct Retainers for Distal Extension Partial Denture
Retainers for distal extension partial dentures, while retaining the prosthesis, must be also able
to flex or disengage when the denture base moves tissue-ward. Thus the retainer may act as a stress-
breaker. Mechanical stress breakers accomplish the same thing, but they do so at the expense of
horizontal stabilization. When some kinds of mechanical stress breaker is used, the denture flange
must be able to prevent horizontal movement. Clasps design that allow flexing of the retentive clasp
arm my accomplish the same purpose as that of mechanical stress breaker, without sacrificing
horizontal stabilization and with less complicated techniques.
In evaluating the ability of a clasp arm to act as a stress breaker, one must realize that flexing
in one plane is not enough. The clasp arm must be freely flexible in any direction as dictated by
stresses applied. In evaluating the ability of a clasp arm to act as a stress breaker, one must realize
that flexing in one plane is not enough. The clasp arm must be freely flexible in any direction as
dictated by stresses applied. Bulky, half round clasp arm cannot do this, and neither can a bar clasp
engaging an undercut on the side of the tooth away from the denture base. Round, tapered clasp
forms offer the advantages of greater and more universal flexibility, less tooth contact, and better
esthetics
Either the combination, circumferential clasp with it is tapered wrought wire retentive arm or
the carefully located and properly designed circumferential or bar clasp can be considered for use
on all abutment teeth adjacent to extension denture bases if the abutment teeth have been properly
prepared and tissue support effectively achieved, and if the patient exercises good oral hygiene.
Indirect Retainers for Distal Extension Partial Denture
The effect achieved by one or more indirect retainers of a removable partial denture prosthesis
that reduces the tendency for a denture base to move in an occlusal direction or rotate about the
fulcrum line.
Indirect retainers are defined as the component of removable dental prosthesis that assist the
direct retainers in preventing displacement of distal extension denture base by functioning through
lever action on the opposite side of fulcrum line when the denture base moves away from the tissues
in pure rotation around the fulcrum line.
Functions of Indirect Retainers:
1) It resist rotation of the prosthesis around fulcrum line under masticatory stresses
2) It aids in additional support and stability to the prosthesis
3) It helps in accurate repositioning of the prosthesis during relining or rebasing procedure as is
act as a third point of tooth contact
4) Major connector such as lingual plate supported on both the ends with rests can provide
effective indirect retention
5) Contact of its minor connector with the axial tooth surface help in providing stabilization
against horizontal movement of the prosthesis
Indirect Retainers in Distal Extension Cases:
• In kennedy class I arch , the fulcrum line passes through the most posterior abutments, provided
some of the rigid components of the framework are located occlusal to the abutments' height of
contour.
2
• In kennedy class II arch , the fulcrum line is diagonal passing through abutment on the distal
extension side and the most posterior abutment on the opposite side.
O Support
Can say the support for the distal extension partial denture, is the clasp assembly that resists
displacement of a prosthesis in an apical direction as shown in figure below, it is gain by the rest of
the clasp.
The distal extension removable partial denture does not have the advantage of total tooth
support because one or more bases are extensions covering the residual ridge distal to the
last abutment.
It therefore is dependent on the residual ridge for a portion of its support, as shown in figure
below.
›
The abutment selected for the support has to be evaluated for
Periodontal health.
Crown- root ratio.
Crown-root morphology.
Location of the tooth in the arch.
The opposing dentition.
Factors Influencing Support of a Distal Extension Base
Contour and quality of the residual ridge.
Extent of residual ridge coverage by the denture base.
Type and accuracy of the impression registration.
Accuracy of the fit of the denture base.
Design of the removable partial denture framework.
Total occlusal load applied.
› Snowshoe principle
Snowshoe principle which suggests that the broader coverage (large area) for denture base
provides the best support with least load per unit area which consider the principle of choice for
providing maximum support under physiologic limits.

3
Why snowshoe principle considers important ?
Firstly, because support should be the primary consideration in selecting, designing and
fabricating a distal extension partial denture base rather than other important considerations for
example esthetics, stimulation of underlying tissue and oral cleanliness.
Secondly, it decreases tissue displacement and denture base movement.
Greater coverage
1) Force distributed
2) Less load applied
3) Maximum support
Lesser coverage
1) Force concentrated
2) More load applied
3) Less support
O Stability
It is the quality of the clasp assembly that resists displacement of a prosthesis in a horizontal
direction, we gain stability by the reciprocal arm and the minor connector of the direct retainer.
The stabilization derived from
The reciprocal arm.
The minor connector.
The rigid portion of the retentive arm.
lingual plate.
Denture base.
Major connector.
CROSS-ARCH STABILITY
Resistance against dislodging or rotational forces obtained by using a partial removable
dental prosthesis design that uses natural teeth on the opposite side of the dental arch from the
edentulous space to assist in stabilization.
Need for cross-arch stabilization: When stabilization of the remaining teeth is needed to
balance mediolateral and anteroposterior forces (e.g, after treatment of advanced periodontal
disease), cross arch stabilization frequently is required.
The reciprocal arm
It should be rigid different from retentive arm which it should be flexible.
It diameter should be greater than retentive arm.
To optimize reciprocation, the axial surface of an abutment should be prepared parallel to
the path of insertion and removal.
It should be place above the height of contour.

4
To provide true reciprocation, the reciprocal clasp arm must be in contact during the entire
period of retentive clasp deformation.
The minor connectors that join the rests and the clasp assemblies to the major connector
serve as stabilizing.
All minor connectors that contact vertical tooth surfaces (and all reciprocal clasp arms) act
as stabilizing components
It is necessary that minor connectors have sufficient bulk to be rigid and yet present as little
bulk to the tongue as possible. This means that they should be confined to interdental
embrasures whenever possible. When minor connectors are located on vertical tooth
surfaces, it is best that these surfaces be parallel to the path of placement.
Major Connecter and Stability
A major connector is the component of the partial denture that connects the parts of the
prosthesis located on one side of the arch with those on the opposite side. It is that unit of the partial
denture to which all other parts are directly or indirectly attached. This component also provides
cross-arch stability to help resist displacement by functional stresses.
