LECTURE # 8 :
STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING
Repetition Statement ( for )
Content
for repetition statement
break and continue statements
Common errors
D. Abdalrahman R. Qubaa
First Class, System and Control Engineering Dep.

for
Repetition Statement
Provide counter-controlled repetition details in
a single statement
Syntax
for loop
repeats actions until condition becomes false
2
for (
initialization
;
condition
;
increment
)
{
action(s)
;
}
--------------------------------------------------------
for (
initialization
;
loop Continuation Condition
;
update
)
action1
;
---------------------------------------------------------
for (
initialization
;
loop Continuation Condition
;
update
)
{
action1
;
action2
;
… actionN
;
}

for
Repetition Statement
For Loop is probably the most popular looping instruction.
•
for
allows us to specify three things about a loop in a single line:
(a) Setting a loop counter to an initial value.
(b) testing the loop counter to detect whether its value reached the number of repetitions desired.
(c) increasing the value of loop counter each time the program segment within the loop has been
executed.

for (
init
;
condition
;
increment
)
{
action(s)
;
}
1/
The init. step is executed first, and does not repeat.
2/
Next, the condition is evaluated, and the body of the loop is executed if the
condition is true.
3/
In the next step, the increment statement updates the loop control variable.
4/
Then, the loop's body repeats itself, only stopping when the condition
becomes false.
remember that the
semicolons are mandatory.
for
Repetition Statement
Ex.: for (int x = 1; x < 10; x++)
{
// some code
}

•
Example
: Write a program that calculates and prints out the
Average grade for
6
students using
for
statement .
5
int grade=0, sum=0;
for (int counter =1 ; counter <=6 ; counter ++)
{
cout <<"Enter Grade \n";
cin>>grade;
sum += grade;
}
cout <<"
The Average grades is
“ << sum/6 <<"\n";
for
Repetition Statement
int counter = 1
;
int grade=0 , sum=0;
while (
counter <=6
)
{
cout <<"Enter grade for student \n“ ;
cin >>grade;
sum += grade;
counter ++;
}
cout <<"Average Grade is "<< sum/6
<<"\n";
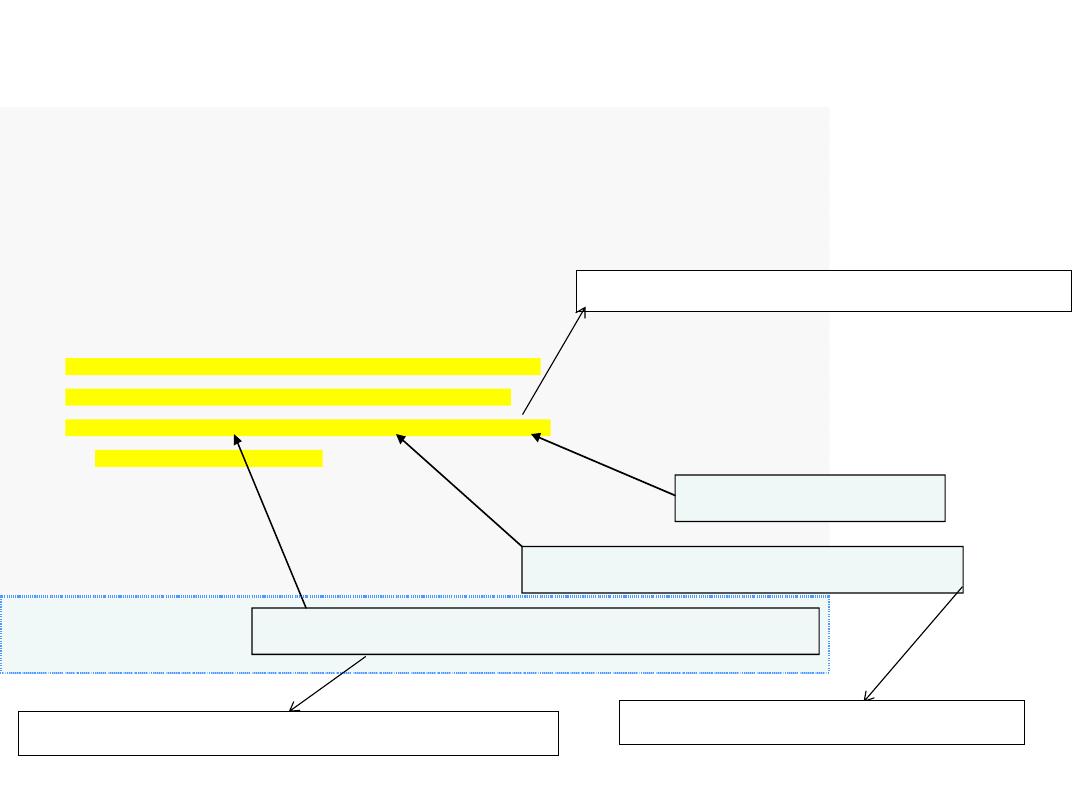
6
1
// Fig. 5.2: fig05_02.cpp
2
// Counter-controlled repetition with the for statement.
3
#include
<iostream>
4
using
std::cout;
5
using
std::endl;
6
7
int
main()
8
{
9
// for statement header includes initialization,
10
// loop-continuation condition and increment.
11
for
(
int
counter =
1
; counter <=
10
; counter++ )
12
cout << counter <<
" "
;
13
14
cout << endl;
// output a newline
15
return
0
;
// indicate successful termination
16
}
// end main
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Control-variable name is counter with initial value 1
Condition tests for counter’s final value
Increment for counter
اسم متغير السيطرة وهو عبارة عن عداد مع قيمة ابتدائية
=
1
شرط االستمرارية
(
أو شرط التوقف
)
للدارة
صيغة التحديث لمتغير السيطرة
(
لكي نصل إلى شرط التوقف
)
Example:
Write a C++ program to print numbers from 1 to 10 using
for
statement.

for
Repetition Statement
(cont.)
When loop counter is declared in initialization expression, it can
ONLY
be used inside
for
statement (
local variable
)
initialization and update expressions can be comma-separated lists
of expressions
7
for (
init.
;
Condition
;
update
)
action1
;
for
(
int
i=0
,
j=0
;
i<4 && j<8
;
i++
,
j++)
cout << “*”;

Examples Using for Statement
Write a program that prints out numbers from
0
to
10 in descending order
Write a program that prints out numbers from
7
to
77
in steps of
7
Write a program that prints out the sequence: 99, 88, 77, 66, 55, 44,
33, 22, 11, 0
// If we need the increments more than 1 we shod use counter
8
for
(
int
i = 10; i >= 1; i-- )
cout << i << "\n“;
for
(
int
i = 7; i <= 77; i += 7 )
cout << i << "\n“;
for
(
int
i = 99; i >= 0; i -= 11 )
cout << i << "\n“;

•
Example
: Write a program that calculates the Factorial for
any given positive number.
Ex
: Factorial (5) = 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1
9
int number, factorial=1;
cout <<"Enter a positive number\n";
cin >> number;
if (number < 0 )
cout <<" Enter Positive Numbers only\n";
else
for (int i= 1 ; I <=number ; i++)
factorial = factorial * i;
cout <<" Factorila = “ << factorial <<"\n";

Nested Loops
•
Example
: Write a program that calculates the Factorial for
numbers from
1
to
10
;
10
for ( int number=1; number<=10 ; number++)
{
for ( int i= 1 ; i <=number ; i++)
{
factorial = factorial * i ;
}
cout <<" Factorila of " << number <<"=" << factorial <<"\n";
}
Examples Using for Statement
(cont.)
Using a comma-separated list of expressions
Ex. Write a program to summation the even num. from 2 to 20.
can be written as
11
for
(
int
i = 2, total=0; i <= 20; total+= i
,
i+= 2 )
// total
and increment
int
total =0;
for
(
int
i = 2; i <= 20; i+= 2 )
total += i;

break
Statement
Alter flow of control
Causes immediate exit from control structure
Used with
while, for, do…while
or
switch
statements
Escape early from a loop (
while, for, do…while
)
Skip the remainder of
switch
12
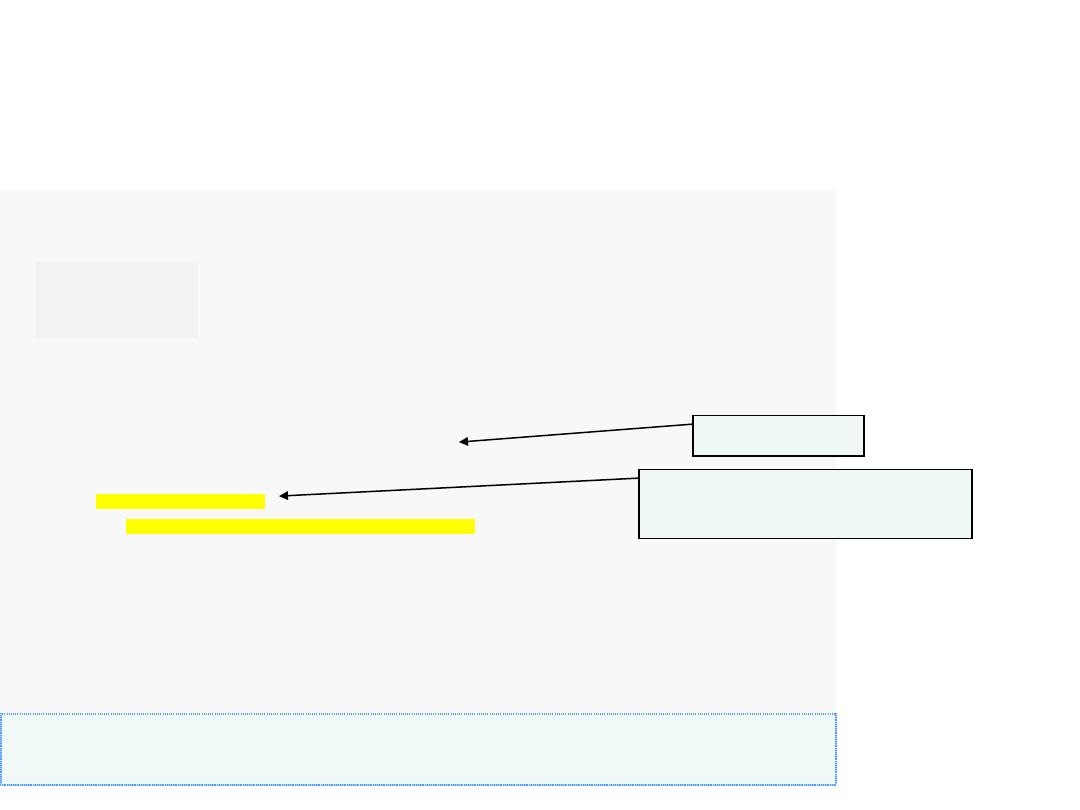
13
1
// Fig. 5.13: fig05_13.cpp
2
// break statement exiting a for statement.
3
#include
<iostream>
4
using
std::cout;
5
using
std::endl;
6
7
int
main()
8
{
9
int
count;
// control variable also used after loop terminates
10
11
for
( count =
1
; count <=
10
; count++ )
// loop 10 times
12
{
13
if
( count ==
5
)
14
break
;
// break loop only if x is 5
15
16
cout << count <<
" "
;
17
}
// end for
18
19
cout <<
"\nBroke out of loop at count = "
<< count << endl;
20
return
0
;
// indicate successful termination
21
}
// end main
1 2 3 4
Broke out of loop at count = 5
Loop 10 times
Exit for statement (with a
break) when count equals 5
Example:
Write a C++ program to print numbers from 1 to 10 using
for
statement and
broken the loop (stopping) at the 5.

continue
Statement
Used with
while, for
or
do…while
statements
Alter flow of control
Skips remainder of loop body of current iteration
Proceeds with next iteration of loop
With
while
and
do…while
statements
Loop-continuation test is evaluated immediately after continue statement
With
for
statement
Update expression is executed
Next, loop-continuation test is evaluated
14
15
1
// Fig. 5.14: fig05_14.cpp
2
// continue statement terminating an iteration of a for statement.
3
#include
<iostream>
4
using
std::cout;
5
using
std::endl;
6
7
int
main()
8
{
9
for
(
int
count =
1
; count <=
10
; count++ )
// loop 10 times
10
{
11
if
( count ==
5
)
// if count is 5,
12
continue
;
// skip remaining code in loop
13
14
cout << count <<
" "
;
15
}
// end for
16
17
cout <<
"\nUsed continue to skip printing 5"
<< endl;
18
return
0
;
// indicate successful termination
19
}
// end main
1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 10
Used continue to skip printing 5
Loop 10 times
Skip line 14 and proceed to
line 9 when count equals 5
Example:
Write a C++ program to print numbers from 1 to 10 and skip printing 5 (without 5)
using
for
statement.

Common Errors
Compilation errors
Using commas instead of the
two required
semicolons in a
for
header
Logic errors
Not initializing counters and totals
Placing semicolon immediately after
for
header
for (
init
;
condition
;
increment
)
{
action(s)
;
}
16

Home work:
1. Write C++ program to print numbers from 10 to 0
using (for) statement.
2. Write C++ program to find the summation of odd
numbers from 1 to 100 using (for) statement.
17
