Dr.KHALID WISSAM
Lec 3Diseases of Respiratory System
Lung tumors
Primary tumors :Carcinoma(Bronchogenic carcinoma )90-95%
Carcinoid 5%
Sarcoma and others 2-5 %
Secondary tumors:
The lung is a common sites for metastatic tumors from many organs e.g. breast, GIT, ovaries,bone etc.
Bronchogenic carcinoma
A common cancer, In 2011 there was 221100 cases of brochogenic carcinoma in USA.It is more common in male.
Age incidence 50-70 Y
Present with cough ,sputum, haemoptysis .In late stages with metastasis.
abscess, bronchpneumonia, not responding to treatment
Chest x-ray show shadow in the lung.
Prognosis :Poor. The overall 5 year survival rate is 16%.
Bronchogenic carcinoma
The four major histologic types of carcinomas of the lung are
adenocarcinoma,
squamous cell carcinoma,
small cell carcinoma, and
large cell carcinoma.
Site:
Lung carcinomas may arise in the peripheral lung (more often adenocarcinomas) or in the central/hilar region (more often squamous cell carcinomas).
Etiology of bronchogenic carcinoma
Most lung cancer arises by stepwise accumulation of genetic abnormalities that transform benign bronchial epithelium to neoplastic tissue.inactivation of the tumor suppressor genes located on chromosome 3 (3p).
TP53 mutations.
activation of the KRAS oncogene.
activating mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in a subset of adenocarcinomas .
EML4-ALK tyrosine kinase fusion genes and c-MET tyrosine kinase gene amplifications in 4% to 6% of adenocarcinomas .
Etiology of bronchogenic carcinoma
Risk factors:1. Smoking: Smoker have 60 time greater risk than nonsmoker.
Among the major histologic subtypes of lung cancer, squamous and small-cell carcinomas show the strongest association with tobacco exposure.
2. Radioactive substances e.g. Radium.
3. Atmospheric pollution e.g.industrial fumes.
4. occupational hazards e.g. asbestos, workers exposed to dusts containing arsenic, chromium, uranium, nickel, vinyl chloride, and mustard gas.
Pathology of bronchogenic carcinoma (cont)
Histopathological classification:
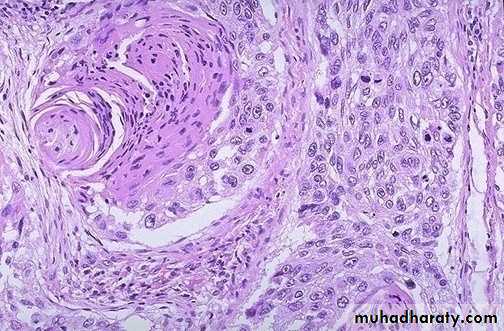
1. Squamous cell carcinoma ; arises from squamous metaplastic epithelium---dysplasia---carcinoma in situ---invasive carcinoma.
On histologic examination, these tumors range from well differentiated squamous cell carcinoma to poorly differentiated carcinoma.
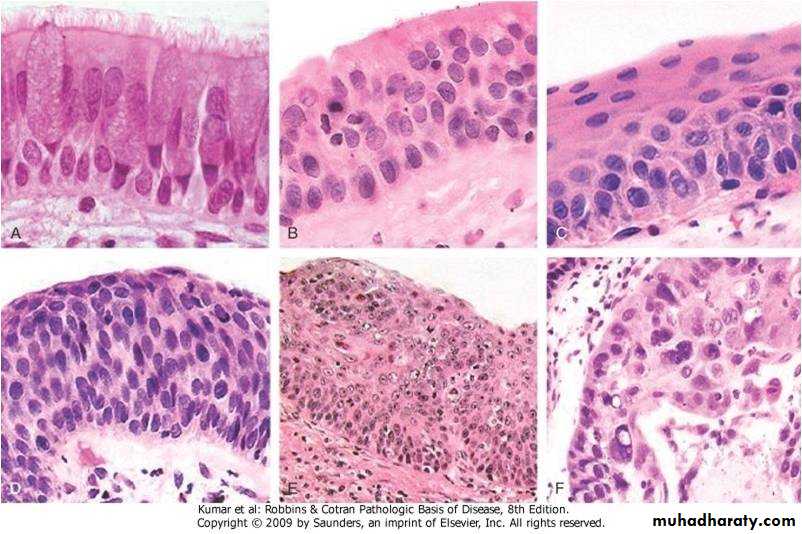
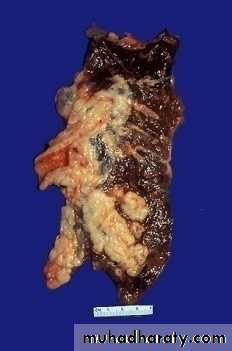
Bronchogenic carcinoma
Sequence of changes in bronchial epithelium
Squamous cell carcinoma of bronchus
Pathology of bronchogenic carcinoma (cont)
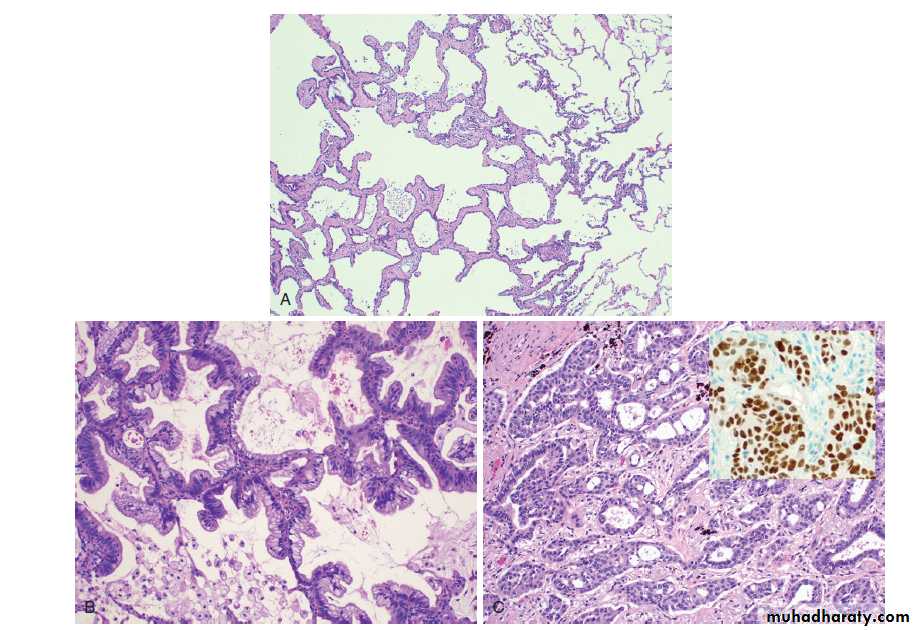
2. Adenocarcinoma : Arises from mucus gland in the bronchial mucosa, Consist of malignant glands with mucus secretion.The precursor of peripheral adenocarcinomas is thought to be atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) which progresses to adenocarcinoma in situ, minimally invasive adenocarcinoma and invasive adenocarcinoma.
Adenocarcinoma -Bronchus
(AAH) which progresses to adenocarcinoma in situ, and invasive adenocarcinoma.
Pathology of bronchogenic carcinoma (cont)
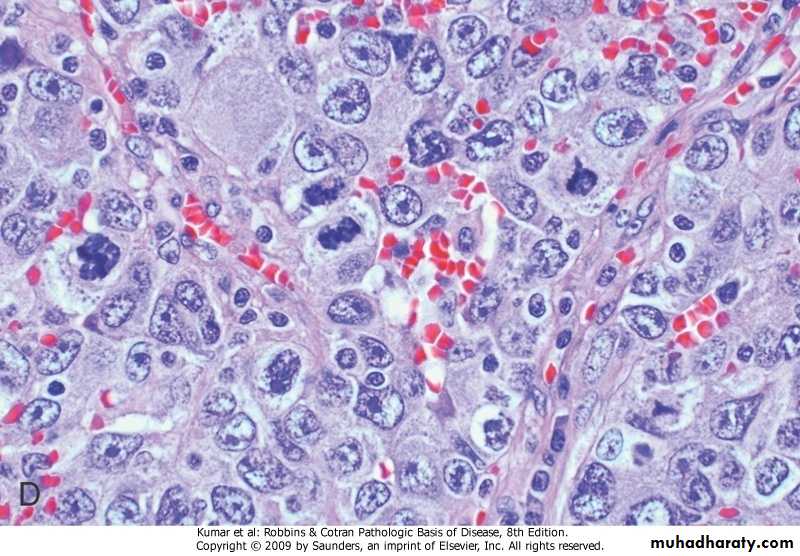
3.Large cell carcinoma: Undifferentiated carcinoma consist of large hyperchromatic cells with some giant malignant cells.It is probably of squamous or adenocarcinoma that is so undifferentiated to know the histogenesisLarge Cell Carcinoma of Bronchus
Pathology of bronchogenic carcinoma (cont)
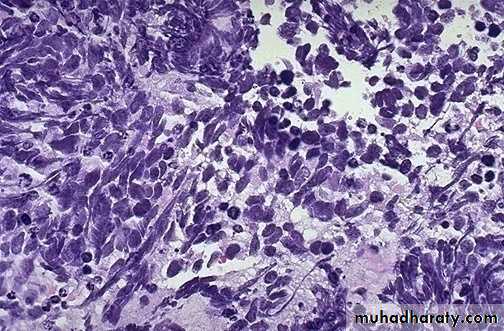
4. Small cell carcinoma : Arises from neuroendocrine cells in the bronchial mucosa.By E/M the cells contain neurosecretory granules
These cancers are composed of tumor cells with a round to fusiform shape, scant cytoplasm, and finely granular chromatin. Mitotic figures frequently are seen.
Small cell carcinoma -Bronchus
Small cell carcinoma -Bronchus
Spread of bronchogenic carcinoma
1.Direct spread: to pleura, pericardium,Esophagus, left recurrent laryngeal nerve.
Tumor at the apex may involve brachial plexus causing pain and muscle atrophy and Involving the cervical sympathetic chain leading to Horner syndrome ( contracted pupil , ptoses & ipsilateral facial anhydrosis), Such apical neoplasms sometimes are called Pancoast tumors.
Spread of bronchogenic carcinoma (cont)
2. Lymphatic spread: To the hilar trachiobronchial , mediastinal ,supraclavicular lymph node leading to enlargement of the lymph node ( lymphadenopathy).3.Blood spread: to the liver .bone. Adrenal brain etc.
Paraneoplastic syndrome in bronchogenic carcinoma (cont)
Effects ocure in patients with bronchogenic carcinoma which is neither due to the primary tumour nor to secondary metastasis. But probably due to substances secreted by the tumorIt may be:
1.Endocrine syndrome
2.Neurological syndrome
Paraneoplastic syndrome in bronchogenic carcinoma (cont)
1.Endocrine syndrome :
a. Cushing syndrome: small cell carcinoma secrete ACTH.
b. Secretion of ADH by small cell lead to water retention and brain edema.
c. Hypercalcaemia due to secretion of parathyroid like hormone by squamus cell carcinoma.
Paraneoplastic syndrome in bronchogenic carcinoma (cont)
2.Neurological syndrome:a. peripheral neuropathy,
b. encephalopathy
c. myopathy
3. Dermatomyocytis
4. Pulmonary osteoarthropathy with clubbing of fingers
Diagnosis of bronchogenic carcinoma
History, Clinical examinationSputum cytology
Bronchoscopic biopsy
Percutaneous fine needle aspiration
Open biopsy
Scalene lymph node aspiration & biopsy
Secondary tumors in the lung
The lung is the most common site of metastatic neoplasms. due to the high blood supply.
Both carcinomas and sarcomas arising anywhere in the body may spread to the lungs via the blood or lymphatics or by direct continuity.
The pattern of metastatic growth within the lungs is quite variable.
In the usual case, multiple discrete nodules (cannonball lesions) are scattered throughout all lobes, more being at the periphery.