Uses of laser
in dentistry1
Laser irradiation can be a useful tool for many procedures in medicine, dentistry, biology, physiotherapy, and other life sciences.
The clinical use of laser irradiation is based on a wide range of physical phenomena of light interaction with biological tissues, cells, and fluids.
2
What is laser?
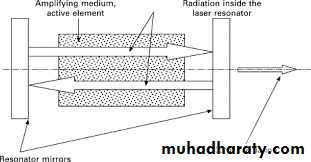
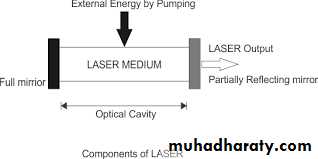
The acronym 'LASER' stands for 'Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.' Lasers work as a result of resonant effects.They produce heat by converting electromagnetic energy into thermal energy.
Their working principle is generation of monochromatic, coherent and collimated radiation by suitable laser medium in an optical resonator.
.
3
Properties of laser :
monochromatic, (emitted only one wavelength)coherent (all in same face, improve focusing)
collimated radiation (one direction, non spreading)
5
Laser emission modes play an important role in increasing the tissues temperature
The thermal effect of laser energy on tissues primarily involves the water content of tissues and the temperature rise of tissues.The thermal effects are necessary for clinical procedures such as cutting, coagulation, vaporization, and ablation of biological tissues,
These lasers increase tissue temperature by 1 °C or more
6Lasers available for utilization in dentistry with high power include:
CO2 (carbon dioxide 9300nm or 10600nm),
Er:YAG (Erbium 2940nm),
Ho:YAG (Holmium Yttrium Aluminum Garnet 2100nm),
Nd:YAG (Neodymium Yttrium Aluminum Garnet 1064nm) and
argon lasers (488nm or 514nm) and other types of laser.
Laser is used in almost all the specialties of dentistry.
7More recently, researchers reported the use of other type of laser systems in dentistry, in which non-linear interactions with biological tissues take place.
These systems have extremely short pulse lengths (femtoseconds, fs) and are called ultra short pulsed lasers (USPLs).
8
Laser effects on tissues:
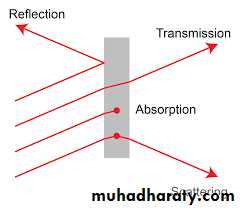
Depending on the optical properties of the tissues,the light energy from a laser may have four different interactions with the target tissues, as follows:
Reflection.
Transmission.Scattering.
Absorption.
9
Each of these processes of laser interaction depends on the characteristics of the laser system, such as
wavelength, pulse duration, pulse energy, delivery method, laser beam characteristics and optical properties of tissue.
10
Role of laser in preventive dentistry
Action of preventive techniques likes fluoride applications, pit and fissure sealants etc. have more uccessful results after combining them with lasers.11
Roles of laser in prevention of dental caries:
Enhancement of enamel resistance to caries have reportedCO2 lasers were the first to be investigated in the reduction of acid dissolution of enamel.
Other lasers have been investigated as Nd:YAG, Er:YAG, argon laser and others.
12
To prevent dental caries,
the energy of the lasers absorbed by the dental substrates converted into thermal energy, which canmodify the structure and chemical composition of these substrates to promote increased acid resistance.
A greater selectivity of wavelengths in the removal of the carbonate group from enamel mineral molecule results in an increased acid-resistant compound.
Also, the altered mineral has greater uptake of topically applied fluoride.
13
The change in the solubility of heated apatite as less soluble compounds are formed.
The analysis of irradiated surfaces revealed:the presence of calcium oxide phosphate, which is less soluble than the group of phosphate minerals commonly present in enamel.
Reduction of carbonate content is usual in irradiated enamel
14
CO2 laser can be used safely to:
alter the enamel surface and make it more resistant to caries, without causing dental pulp damage.
enhancing fluoride uptake into the crystalline structure of the tooth in the form of firmly bound fluoride.
15
Argon laser:
The mechanism for the protective effect of argon laser against both caries initiation and progression is
alteration of the characteristics of the enamel surface by creating microspaces that trap calcium, phosphate, and fluoride ions during an acid challenge.
The ions are incorporated into the enamel surface.
Thus, the surface has an increased affinity for calcium, phosphate, and fluoride ions.
The use of argon lasers with and without fluoride may be a simple technique to reduce the caries susceptibility of enamel.
16
Nd:YAG laser: Similar mechanisms to CO2 lasers have been suggested for Nd:YAG laser in caries prevention.
However, unlike the CO2 laser, the Nd:YAG laser is not effectively absorbed by human enamel.
Thus, its efficient use in this substrate depends on the application of a photosensitizer.
17
Ruby laser is less effective in decreasing subsurface demineralization during caries process.
The extensive heating generated by this type of laser resulted in structural damage of tooth.
Erbium lasers: used in caries prevention as greatly increased acid resistant of enamel.
18Benefits of dental lasers
- The main benefit is the ability to interact selectively and precisely with diseased tissues.
- Reduce the amount of bacteria
- The cavity preparation by laser has been disinfectant because of the bactericidal nature of laser energy.
19
Drawbacks of dental lasers
- The relatively high cost and the required training.- The inability of erbium laser to remove metallic restorations.
- No single wavelength will optimally treat all dental tissues.
20
Laser Safety:
- All laser devices have complete instructions on the safe use of the machine.- Protective eyewear must be worn by the patient and dental team.
- Masks must be of appropriate filtering capacity.
21
Laser Safety Officer (LSO) duties are as follows:
Understandable the operational characteristics of laser.
Knows output limitations of the device.
Supervises staff education and training.
Oversees personal protective wear.
Knows the potential hazard of the laser.
22