PHYSICAL FACTORS &
THE SKIN
DR. HADAF ALJUNAIYEH
ASS. PROFESSOR DERMATOLOGY
COLLEGE OF MEDICINE/ THI QAR UNIVERSITY
2018/2019
OBJECTIVES
•
By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to:
•
Classify the main physical factors in the environment
•
Describe the skin changes induced by these factors
•
Recognize the main preventive measures for these conditions
& their best treatment modalities.
PHYSICAL FACTORS IN THE ENVIRONMENT
•
Heat
•
Cold
•
Sun
•
Physical pressure
•
Radiation
HEAT
•
Burn
•
Miliaria
•
Erythema ab igne

BURN
•
Thermal
Electrical
BURN
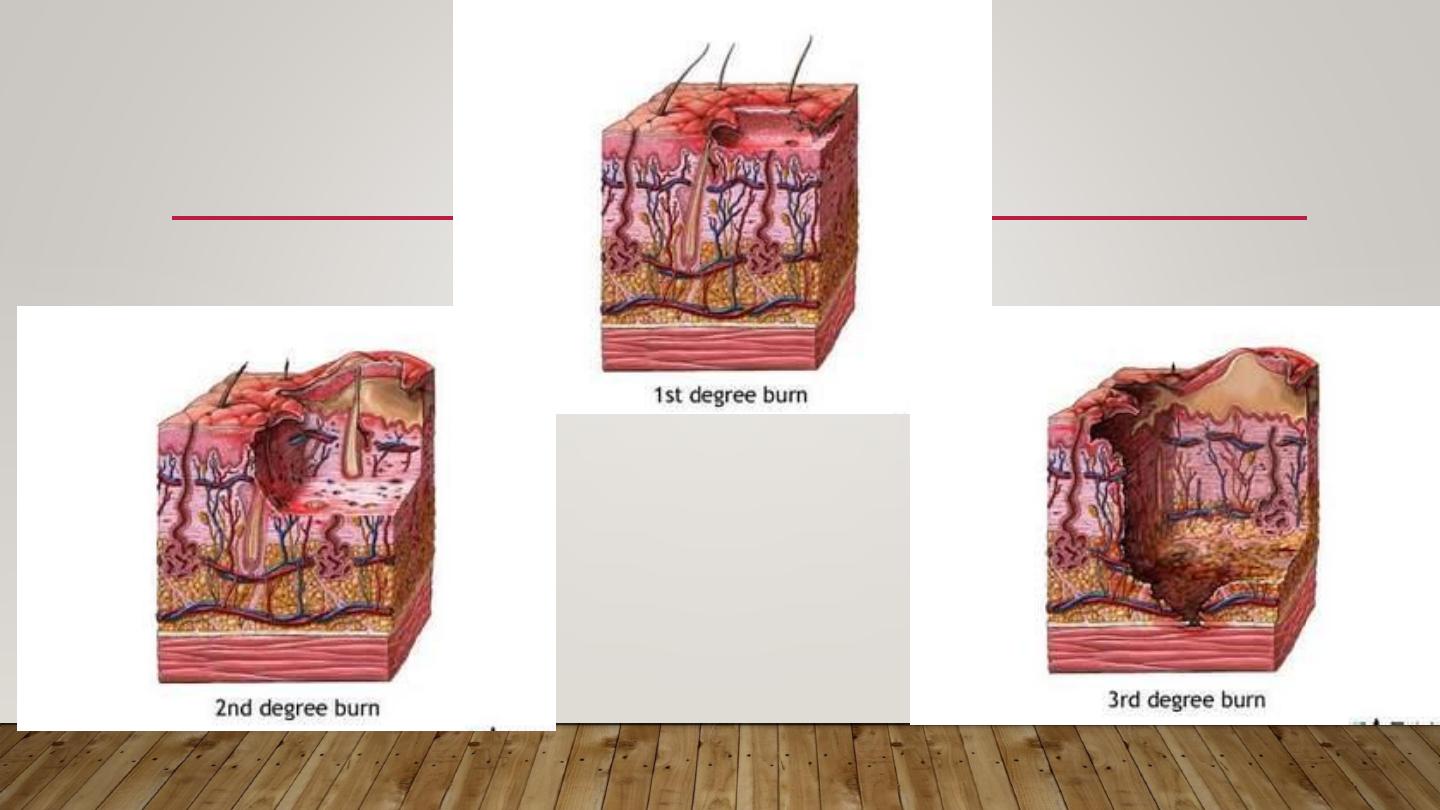
•
1
st
degree: only erythema + sometimes desquamation +
constitutional symptoms if a large area is involved
•
2
nd
degree: A- superficial B- deep
superficial deep
causing vesicles & bullae causing pallor
heal without scarring delayed healing with scarring
•
3
rd
degree: full thickness loss of tissue with scarring
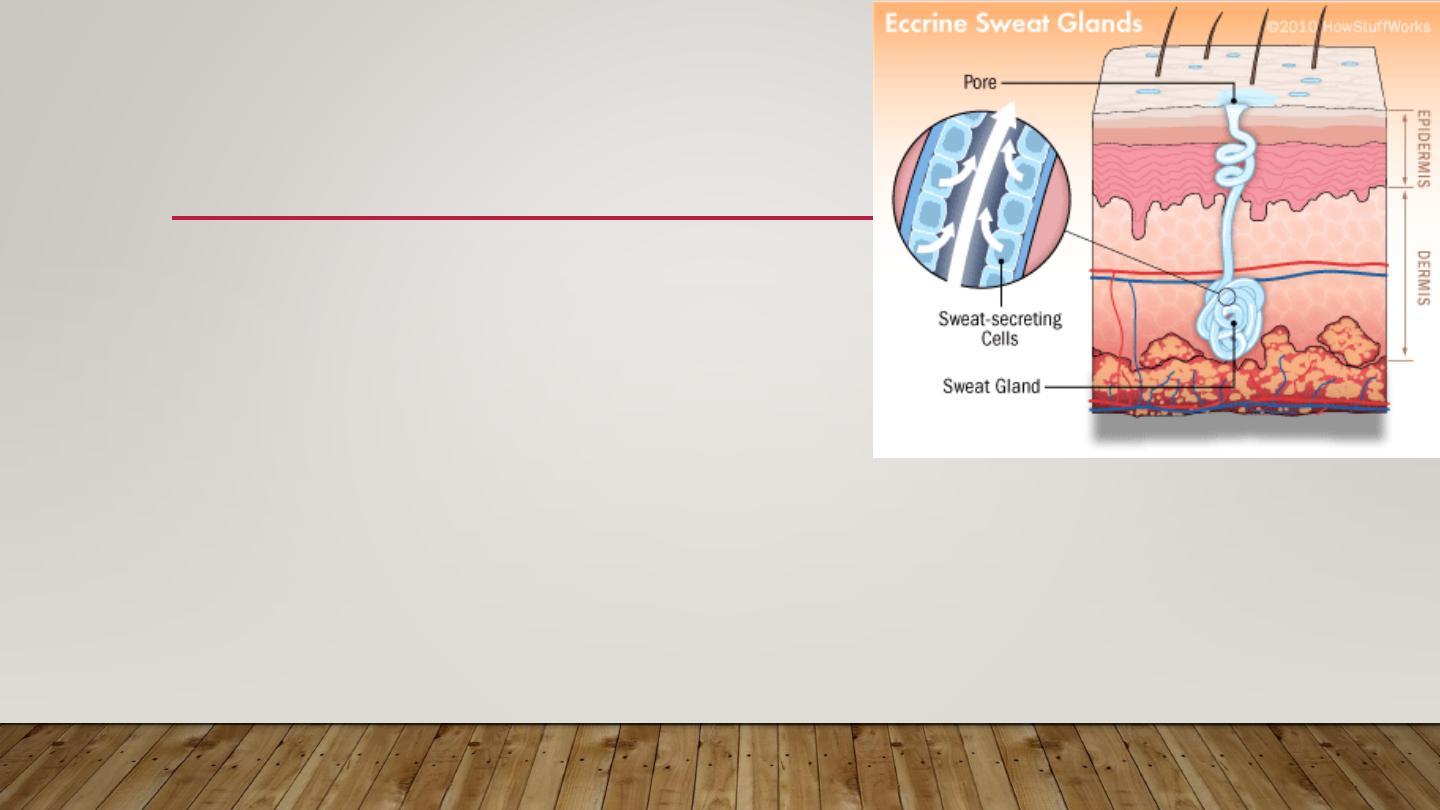
MILIARIA
•
Occlusion of eccrine sweat gland leads to sweat
retention & failure of delivery of sweat to skin surface.
•
Eventually backed-up pressure causes rupture of
sweat gland or duct at different levels & the escape
of sweat into adjacent tissue producing miliaria.
•
Common in hot, humid climates.
•
Different forms of miliaria occur depending on the level of injury to the sweat
gland.

1- MILIARIA CRYSTALLINA
1-Small, clear, superficial vesicles without inflammation.
2-In bedridden patients and bundled children.
3-Lesions are asymptomatic & rupture
at the slightest trauma.
4-Self-limited; requires no Rx
5- sweat duct is blocked at the
stratum corneum level
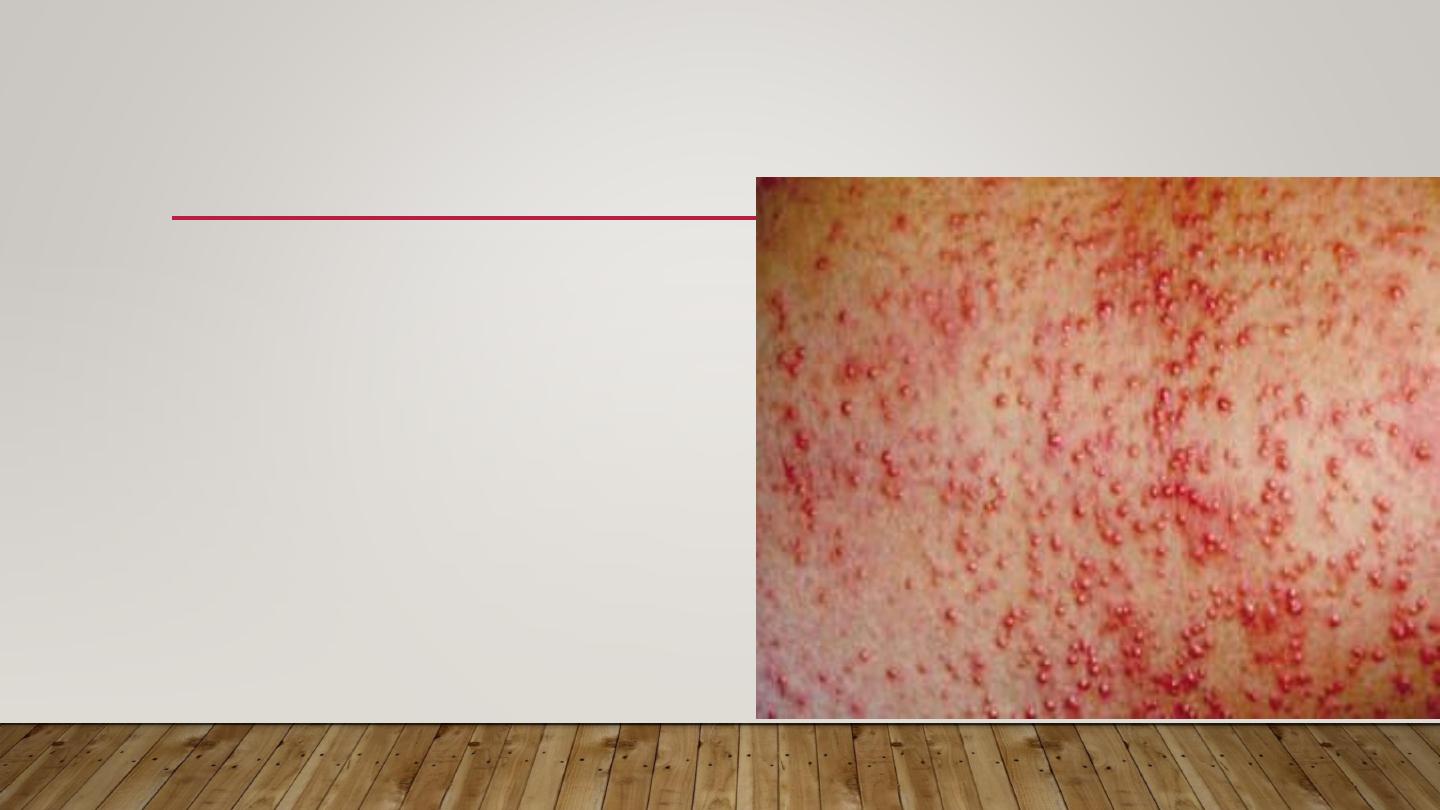
2-MILIARAI RUBRA ( PRICKLY HEAT)
•
Discrete, extremely pruritic,
erythematous papulovesicles with
sensation of prickling, burning,
or tingling.
•
Site of injury is prickle cell layer
•
Commonest type mostly in
Summer & jobs with excessive heat
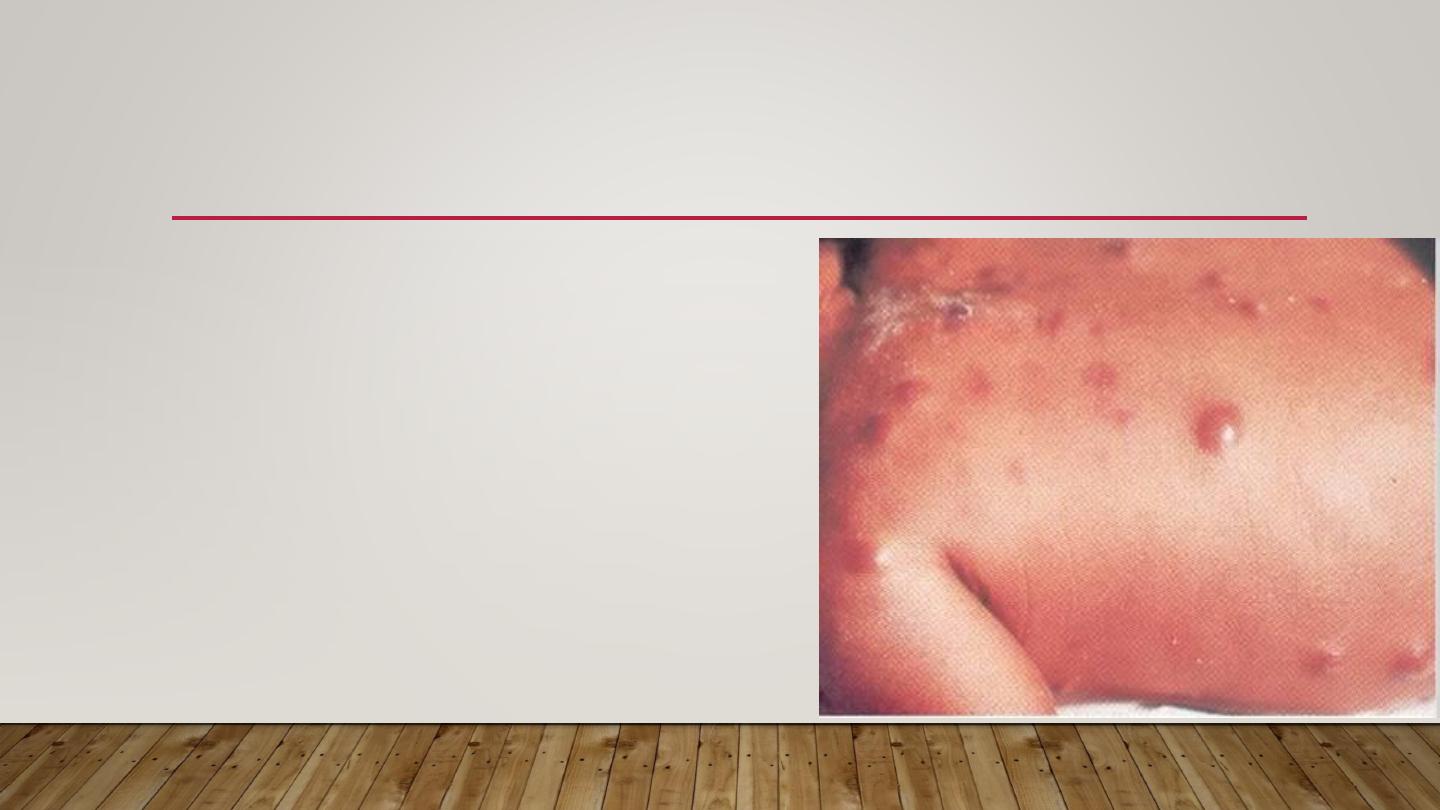
3-MILIARIA PROFUNDA
•
Occlusion is in the papillary dermis
•
Only seen in tropics
•
Rare in our country
•
Deep seated flesh colored papules
•
Asymptomatic

TREATMENT
•
Mild cases respond to cooling of skin
•
Place patient in a cool environment
•
Use dusting powder as talcum
•
Cooling baths of menthol & corn starch
•
Emollients & steroid ointment to dissolve keratin
Plugs & restore sweating

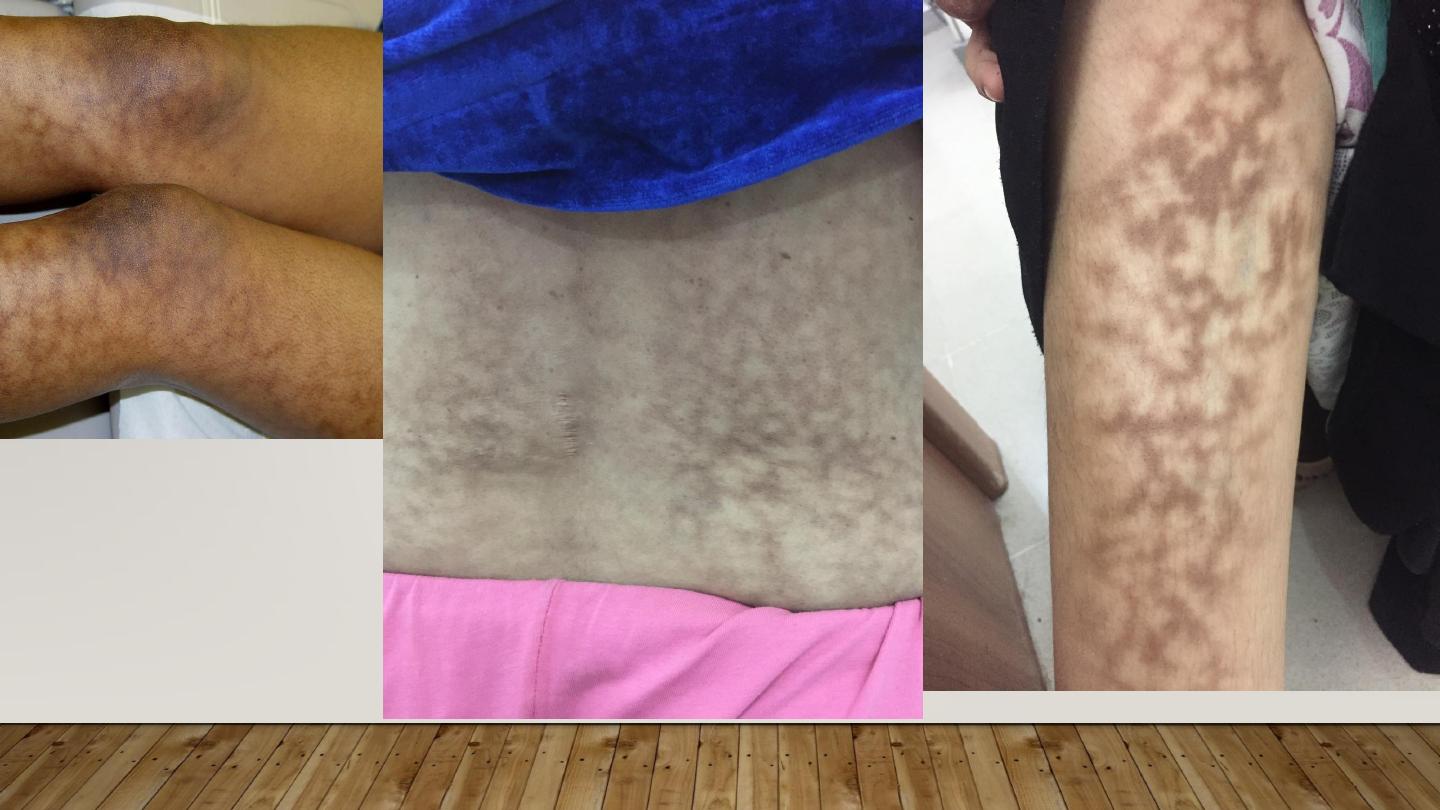
ERYTHEMA AB IGNE
1- Persistent erythema or the coarsely reticulated
residual pigmentation resulting from it, due to long
exposure to excessive heat without burn.
2- First transient, then permanent
3- Mostly on the legs of women
May cause epithelial atypia, rarely Bowen’s disease or squamous cell
carcinoma.

COLD INJURY

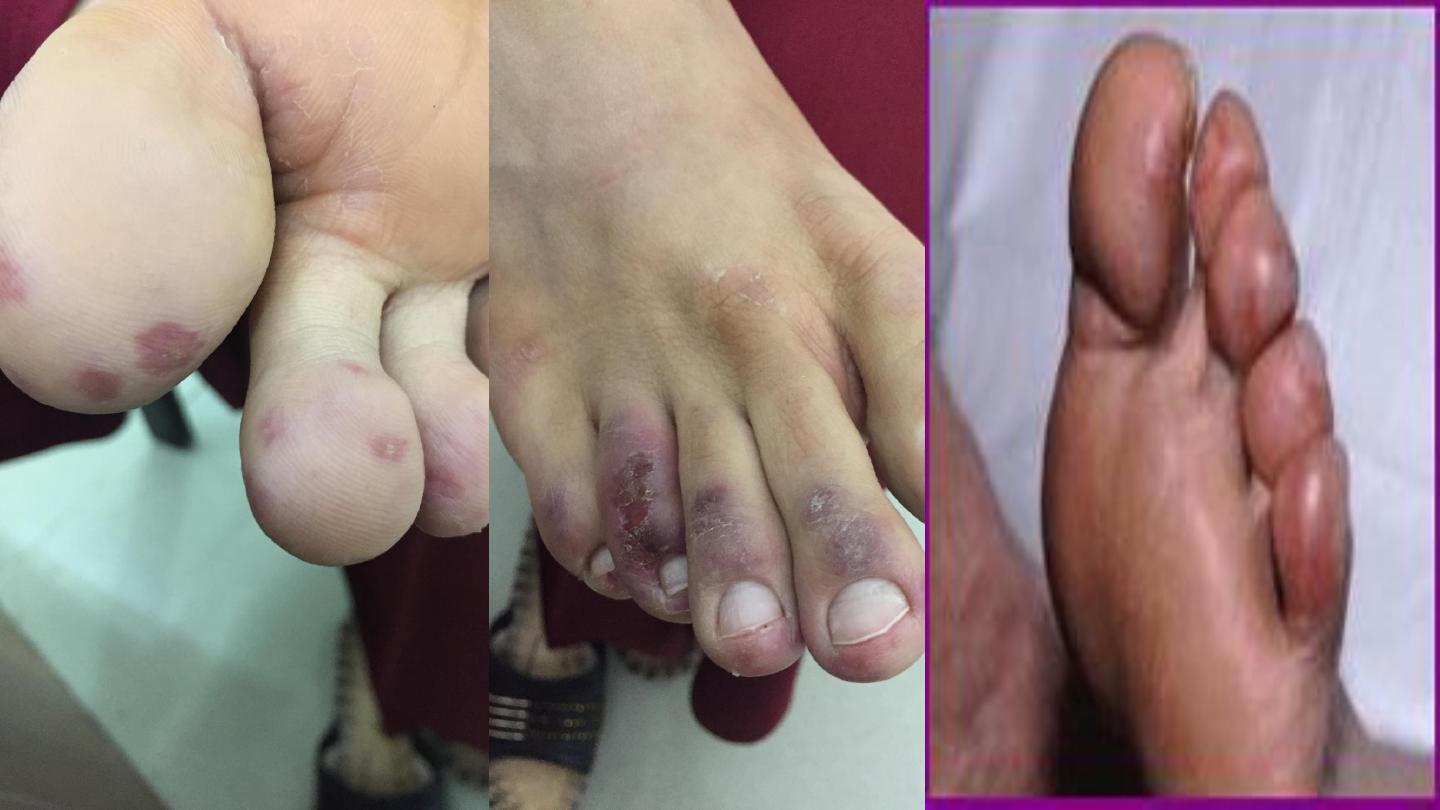
PERNIOSIS(=CHILL BLAINS)
•
Cold hypersensitivity
•
Erythema & swelling (purple pink) of
exposed parts mainly fingers, toes, nose & ears
•
Can lead to blistering or ulceration
•
Pain, itching & burning
•
Cool to touch, onset enhanced by dampness
IMG_9356.JPG
•
IMG_9356.JPG

TREATMENT
•
•
Protection & prophylaxis of cold Quit smoking
•
Topical steroids & systemic antihistamines
•
Nifidipine 20 mg t.d.s., vasodilators (nicotinamide, dipyridamole)
•
Spontaneous resolution occur in 1-3 weeks

FROST BITE.
•
Cold toxicity due to exposure to extremely
low temperatures with freezing of tissue
•
Affected part is pale, waxy, painless
•
Different degrees of tissue damage from erythema to
deep gangrene similar to burn
•
Degree of damage depends on temperature & duration

TREATMENT
•
Rapid rewarming in hot water bath
•
Analgesia: counteract thawing pain
•
Supportive measures:
Bed rest
High protein/calorie diet
Wound care
Avoidance of trauma
SOLAR INJURY
The sunlight spectrum is divided into
Visible light
400 to 760 nm, has little biologic activity,
except for stimulating the retina
Infrared radiation
beyond 760 nm, experienced as radiant heat.
Below 400 nm is the
ultraviolet
spectrum, divided into three bands:
-UVA, 320 to 400 nm
-UVB, 290 to 320 nm
-UVC, 200 to 290 nm
Virtually no UVC reaches the earth’s surface, because it is absorbed by the ozone
layer.
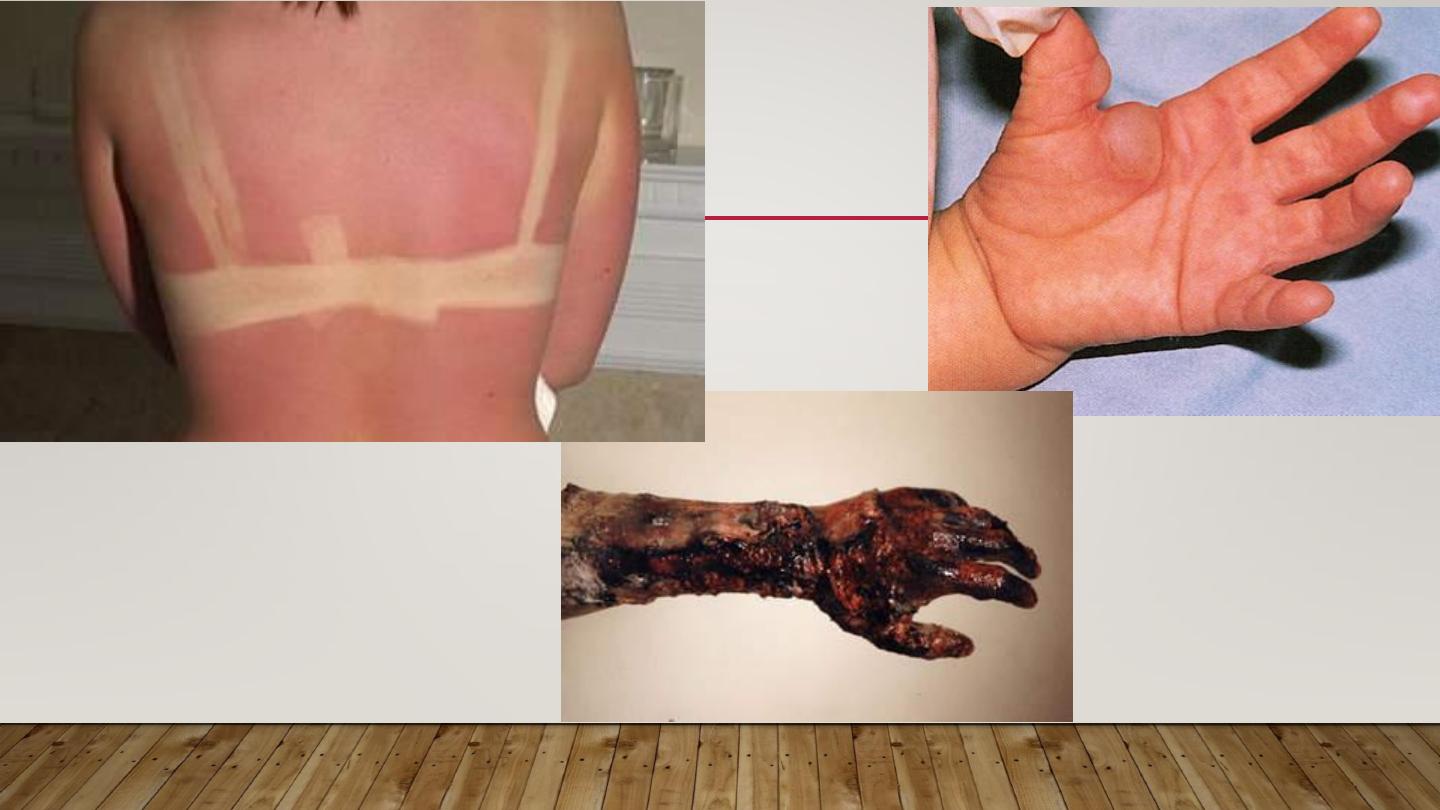
SUN BURN
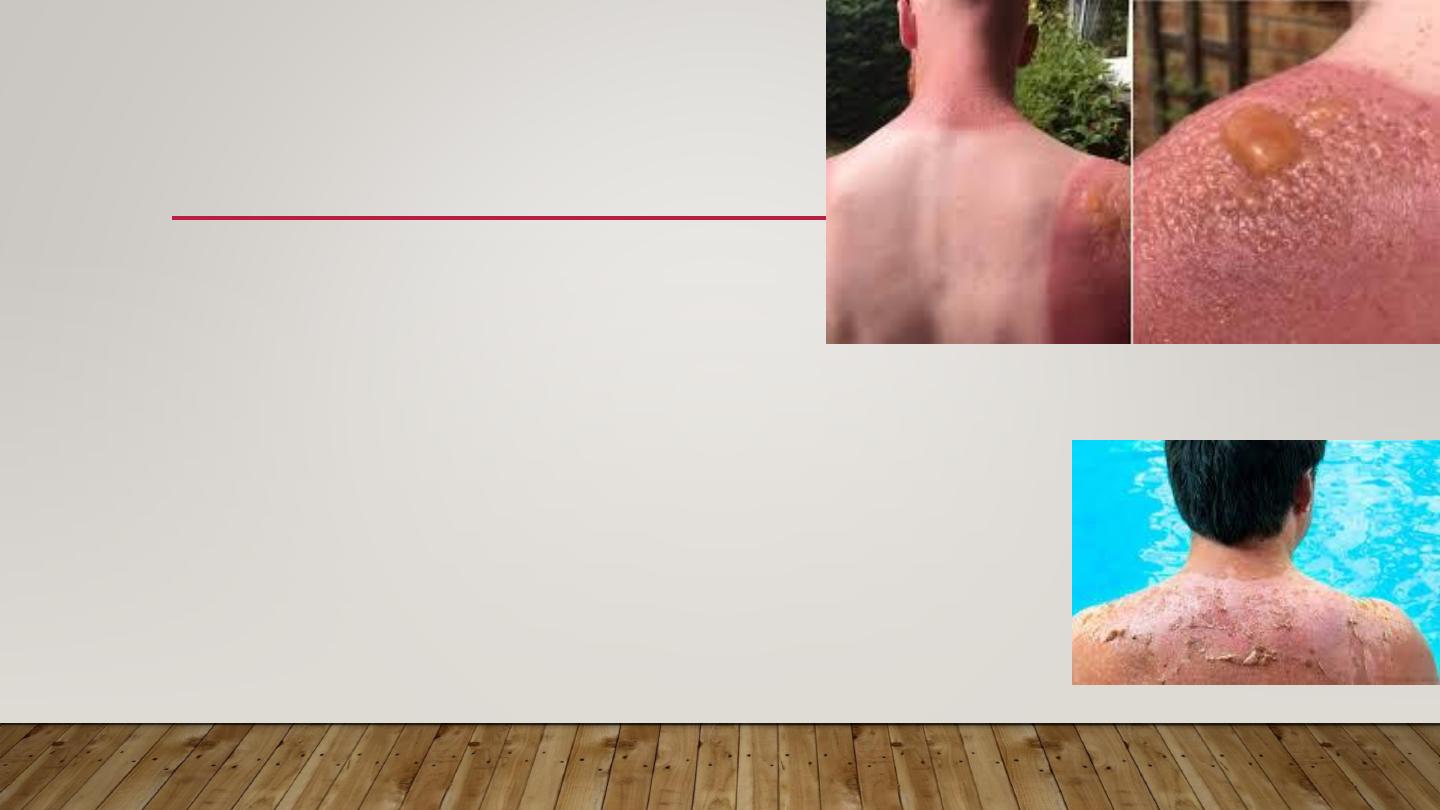
•
Normal reaction of skin to sunlight in
excess of erythema dose
•
Erythema, edema, sometimes blistering on sun exposed skin
•
Desquamation follows within a week
•
If severe may be accompanied by fever, chills, nausea
& hypotension
•
Treatment by analgesics, cool compresses, topical steroids
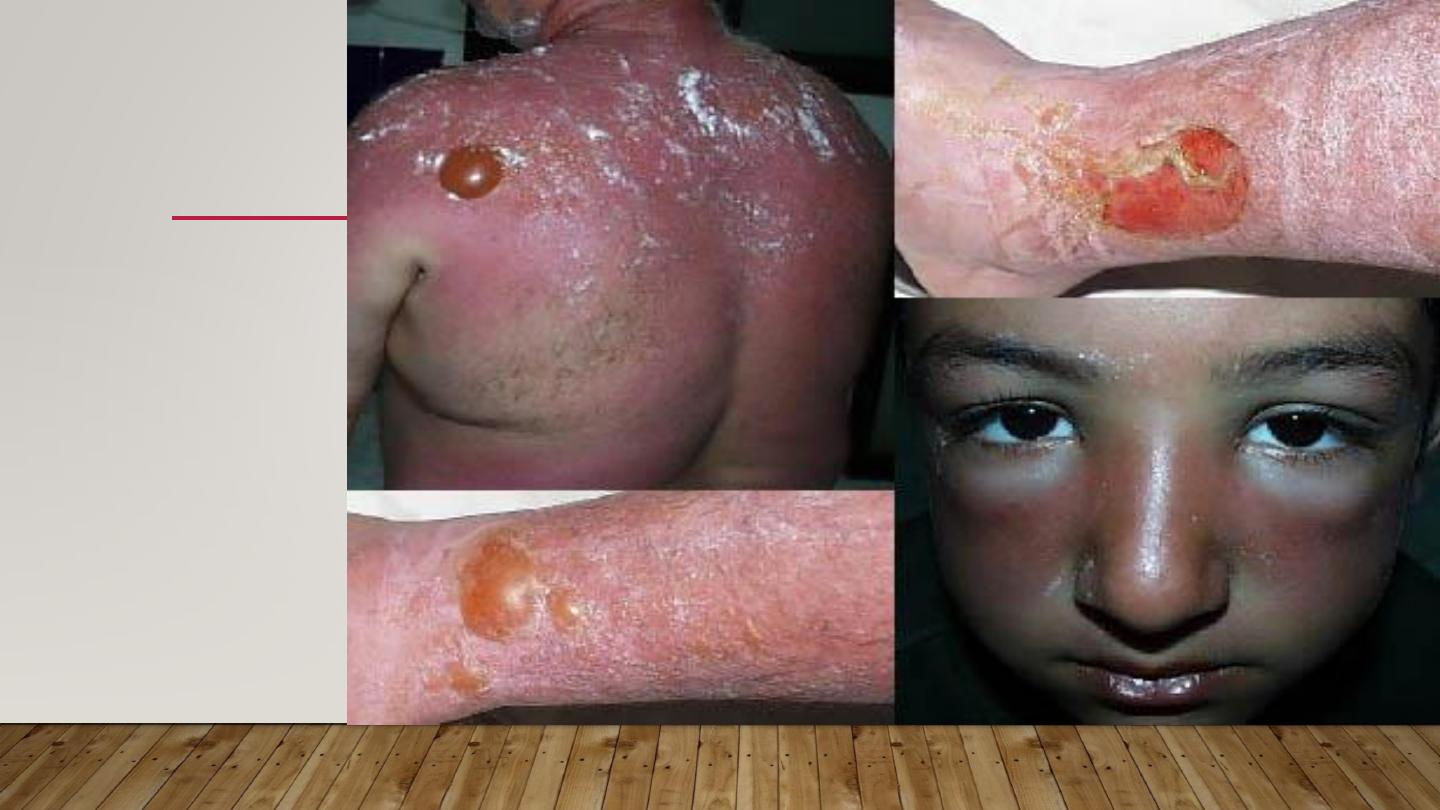
ERYTHEMA,
EDEMA,
BLISTERING
DESQUAMATION

TREATMENT
COOL COMPRESSES
PHOTOSENSITIVITY
Abnormal reaction to normal amount of sunlight
Can be either:
1- chemical photosensitivity: phototoxic & photo allergic photosensitizers
2- metabolic disorders
3- light exacerbated disorders
4- idiopathic phtosensitivity
CHEMICAL PHOTOSENSITIVITY
•
Photosensitizers
are substances that may induce an abnormal
reaction in skin exposed to sunlight or its equivalent.
•
Substances may be delivered externally or internally.
•
Increased sunburn response without prior allergic sensitization is
called
phototoxicity.
Phototoxicity may occur from both externally
applied
phytophotodermatitis
or internally administered chemicals
phototoxic drug reaction.
•
Photo allergy:
needs prior exposure to the substance (sensitization)
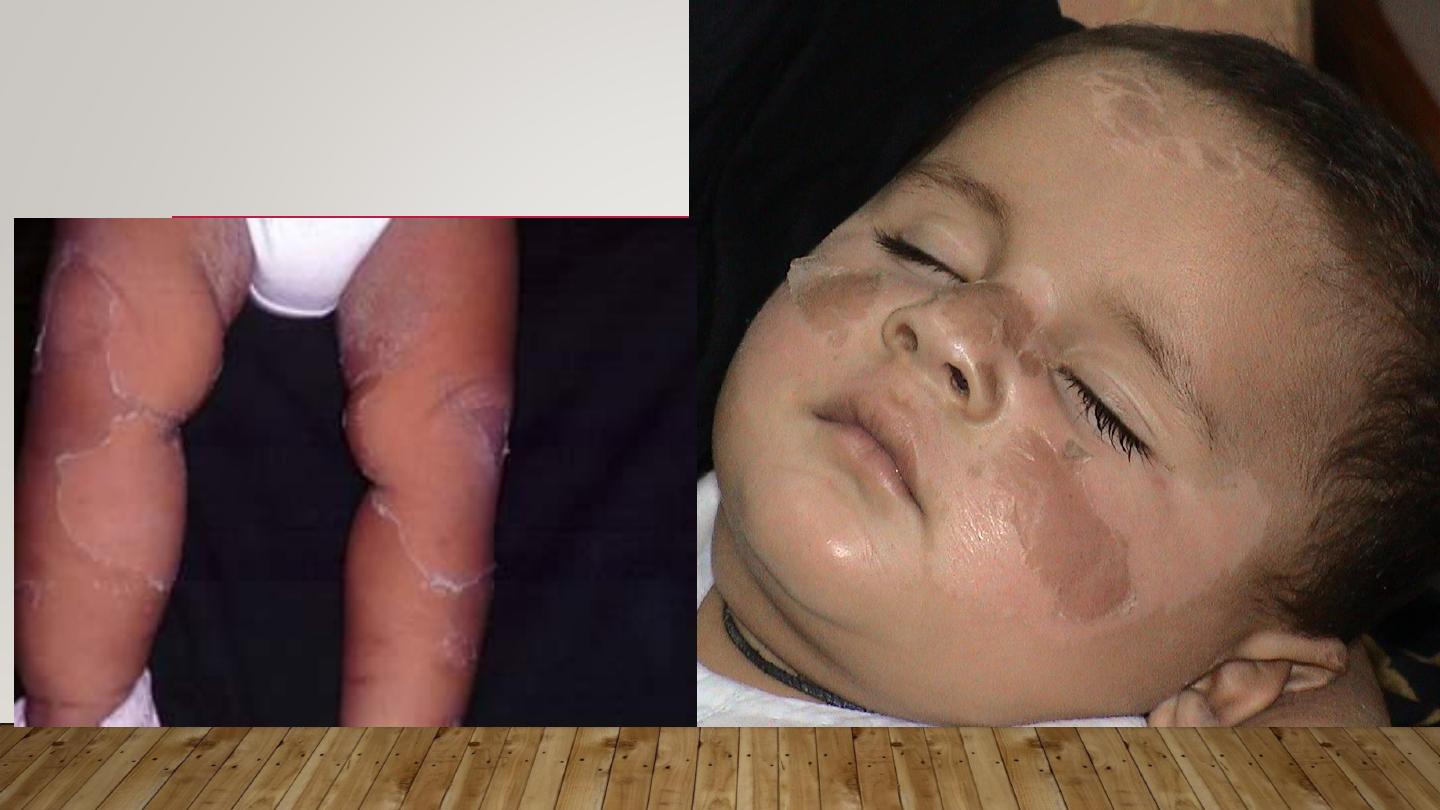
PHYTOPHOTODERMATITIS
•
Contact between certain plants containing a substance called
furocumarine with moist skin & then exposed to long wave UV
(UVA)
•
A dermatitis develops followed by intense pigmentation that
can last wk.s or m.s
•
More in women & children dealing with citrus fruits, & on
exposed skin (face & hands)
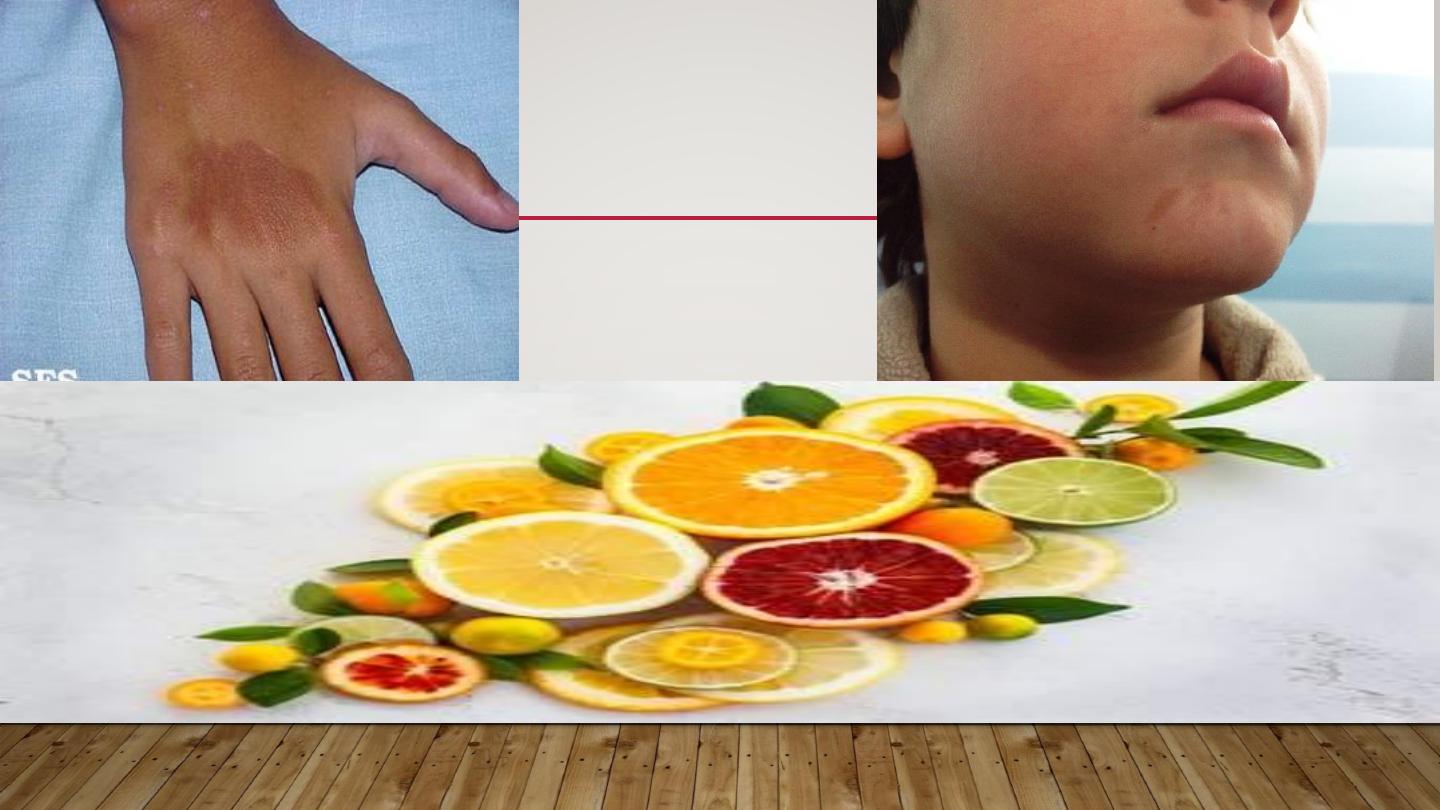
PHYTO-PHOTO
DERMATITIS
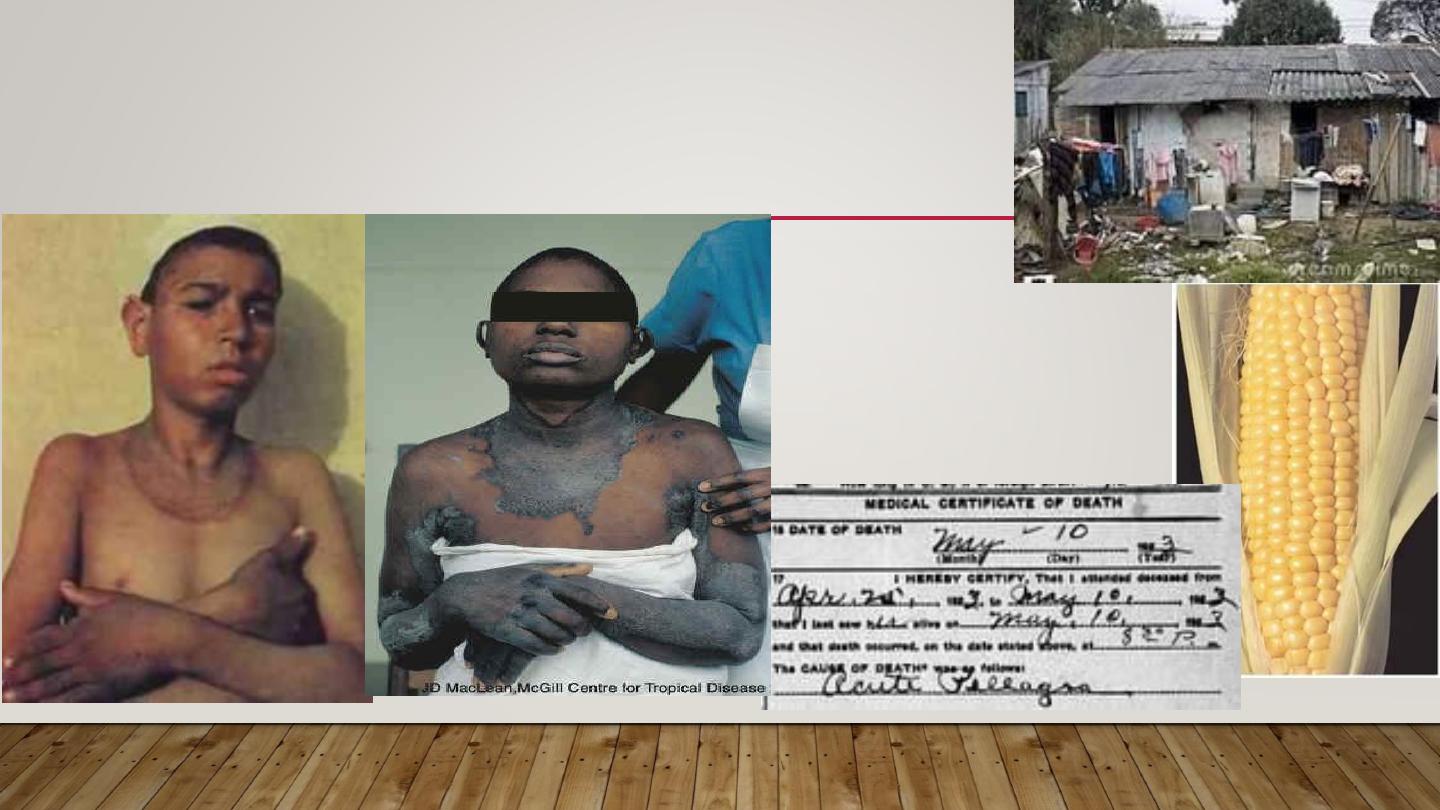

2- METABOLIC PHOTOSENSITIVITY
PELLAGRA & PORPHYRIA
Pellagra
Niacin deficiency
4 D’s disease
•
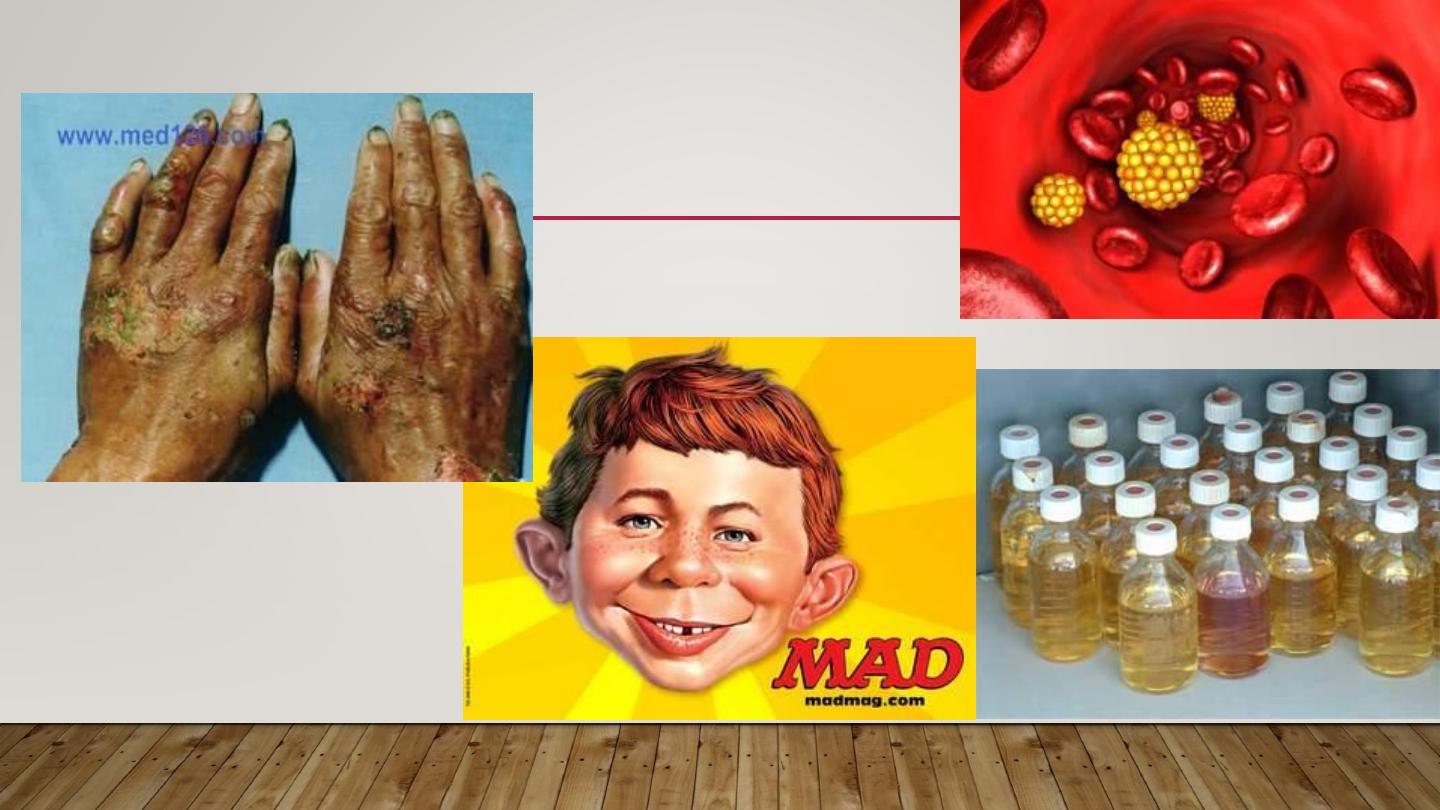
METABOLIC PHOTOSENSITIVITY
porphyria
Defect in heam
synthesis
3- LIGHT EXACERBATED DISORDERS
(DISEASES AGGRAVATED BY SUN LIGHT EXPOSURE)
•
1-genetic: xeroderma pigmentosum
•
2- acquired: SLE, Darier’s, vitiligo, acne, small % of
psoriasis, dermatomyositis, lichen planus actinicus, &
chloasma.
4- IDIOPATHIC PHOTOSENSITIVITY
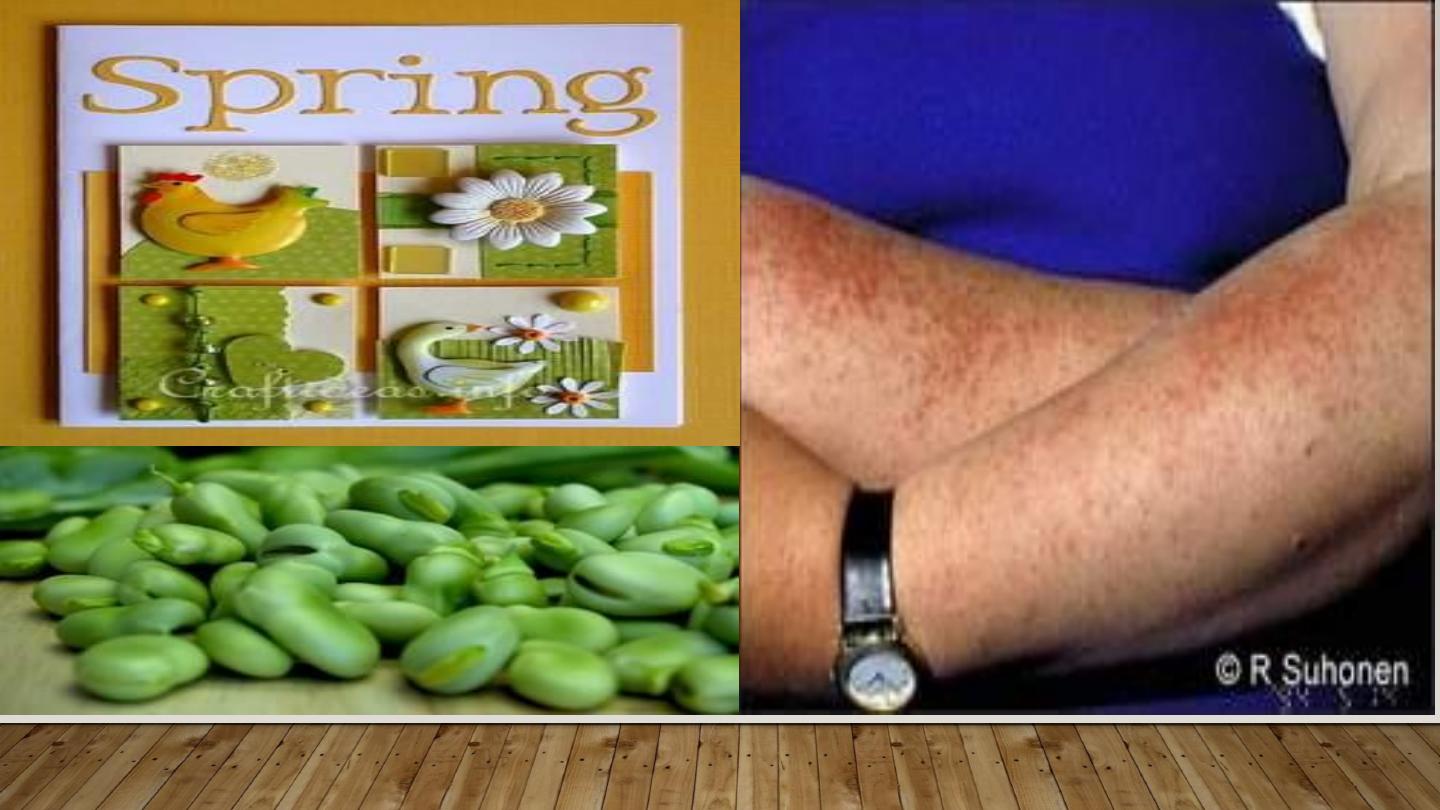
PLE (POLYMORPHIC LIGHT ERUPTION)
•
Different morphologies in different people
•
Constant morphology in the same patient
•
More in young adults, more in females
•
Mostly erythematous papular rash on exposed skin
•
Starts in spring & improves in summer

TREATMENT
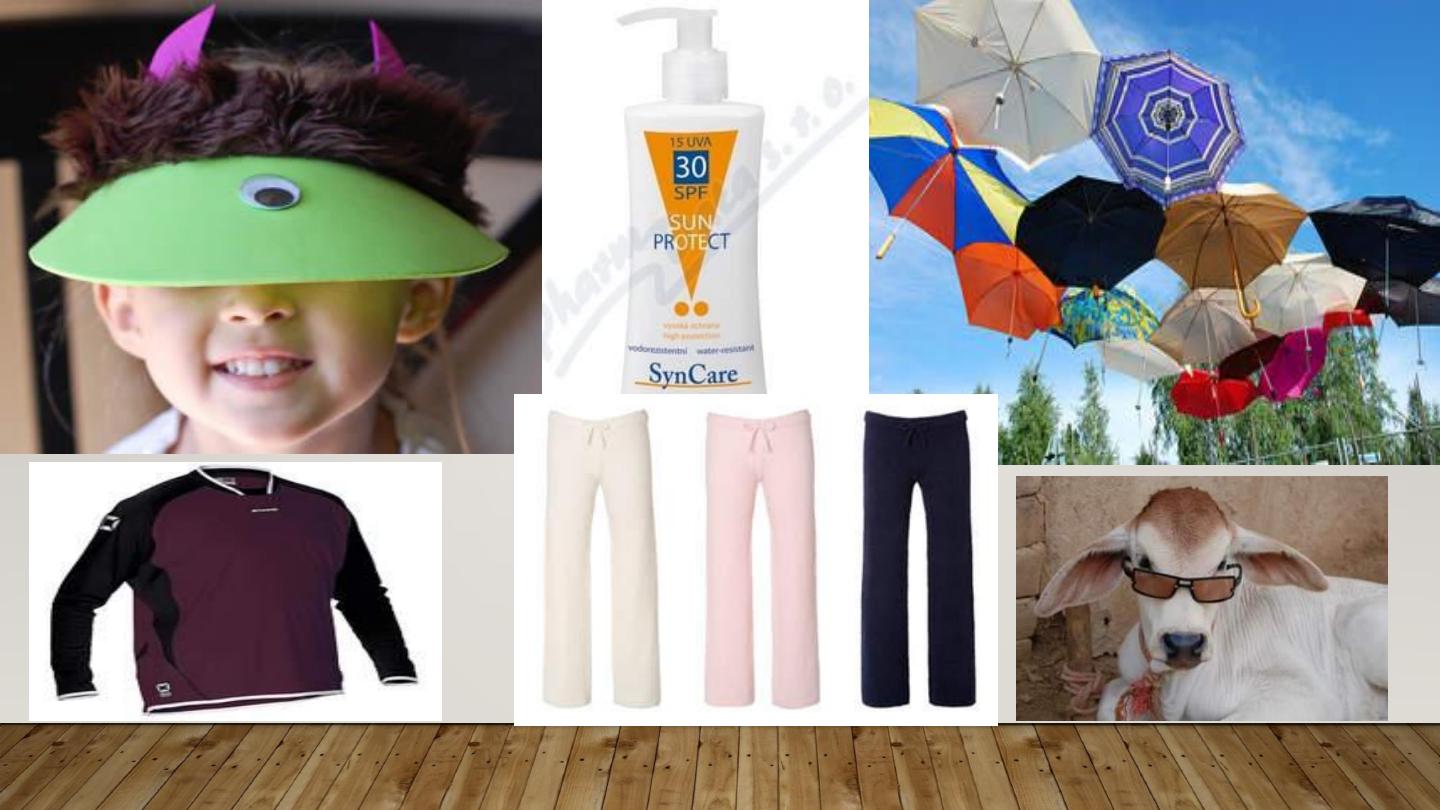
•
Prophylaxis:
•
-Avoid sun exposure between 10 am and 2 pm.
•
-Barrier protection with hats and clothing.
•
-Sunscreen agents include UV-absorbing chemicals
(chemical sunscreens:, and UV-scattering or blocking
agents (physical sunscreens).
1- Avoidance: sunscreens with SPF more than 30 with physical &
chemical properties
2- Topical steroids: usually potent
3- Systemic antihistamines: to control itching
4-Systemic steroids: in severe cases
5- Antimalarial: as chloroquine
6- Light therapy as PUVA or UVB to induce hardening of the skin
7- Immunosuppressant only in recalcitrant cases: azathioprine &
cyclosporin


MECHANICAL TRAUMA
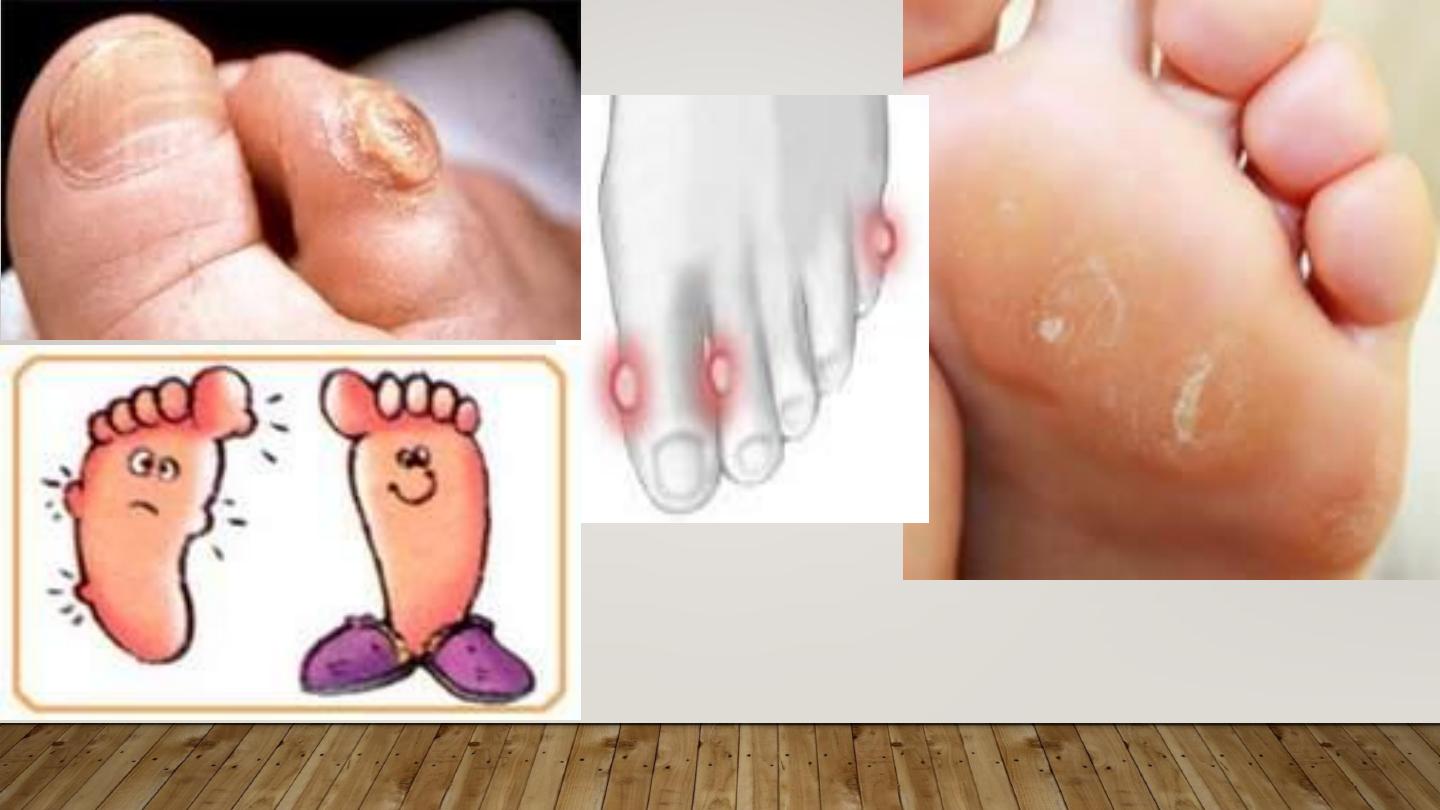
CALLUS:
circumscribed hyperkeratosis induced by
pressure, diffuse with no central core.
CLAVUS:
(corn): circumscribed conical thickenning with
base on surface & apex down pressing on subjacent
structures, of 2 types: Soft corns & hard corn