Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Firas A. – Lecture 3
P a g e
1
Aims of our lecture:
Radiological signs of joint disease
Diagnosis of arthritis
Different types of arthritis
Other joint pathology
MRI of knee and shoulder
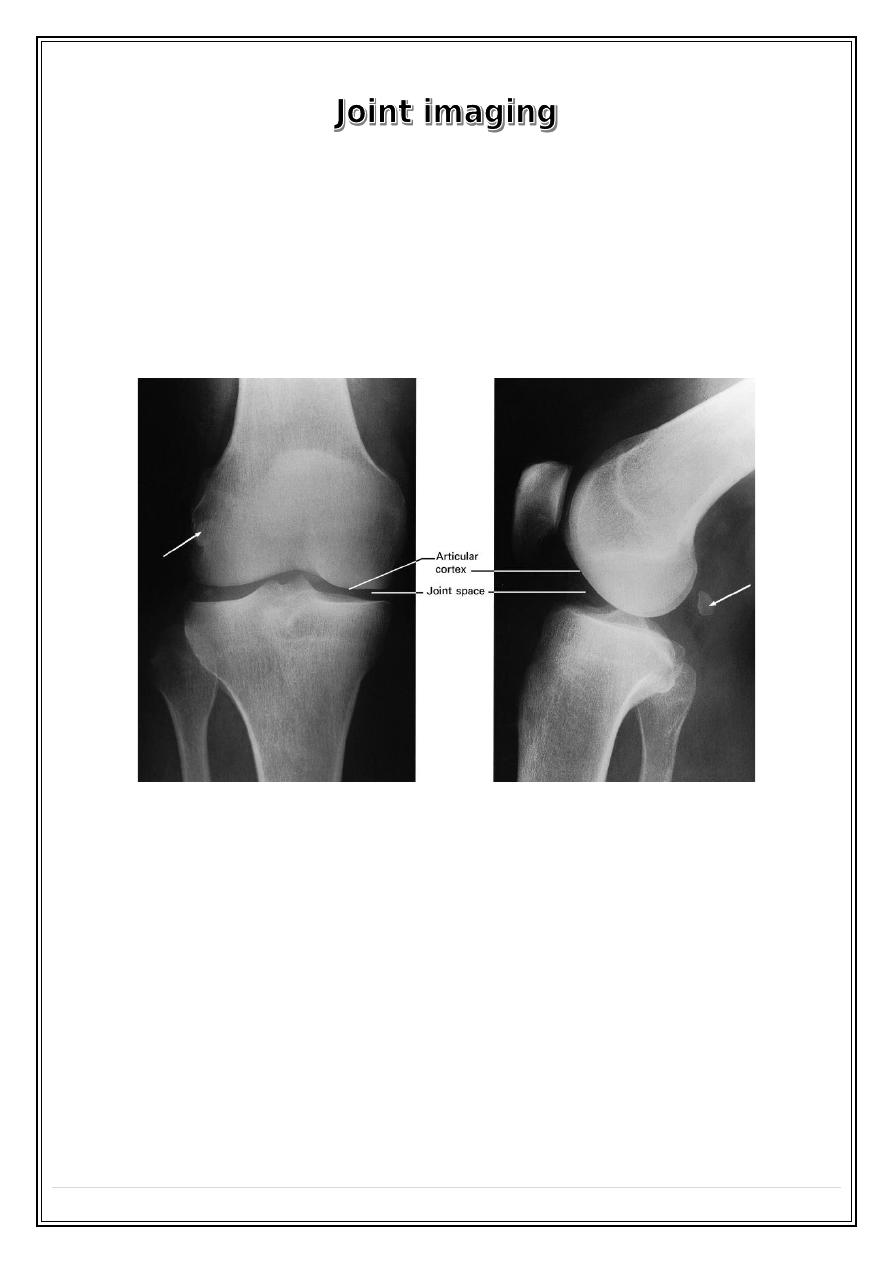
Plain film signs of joint disease
❖
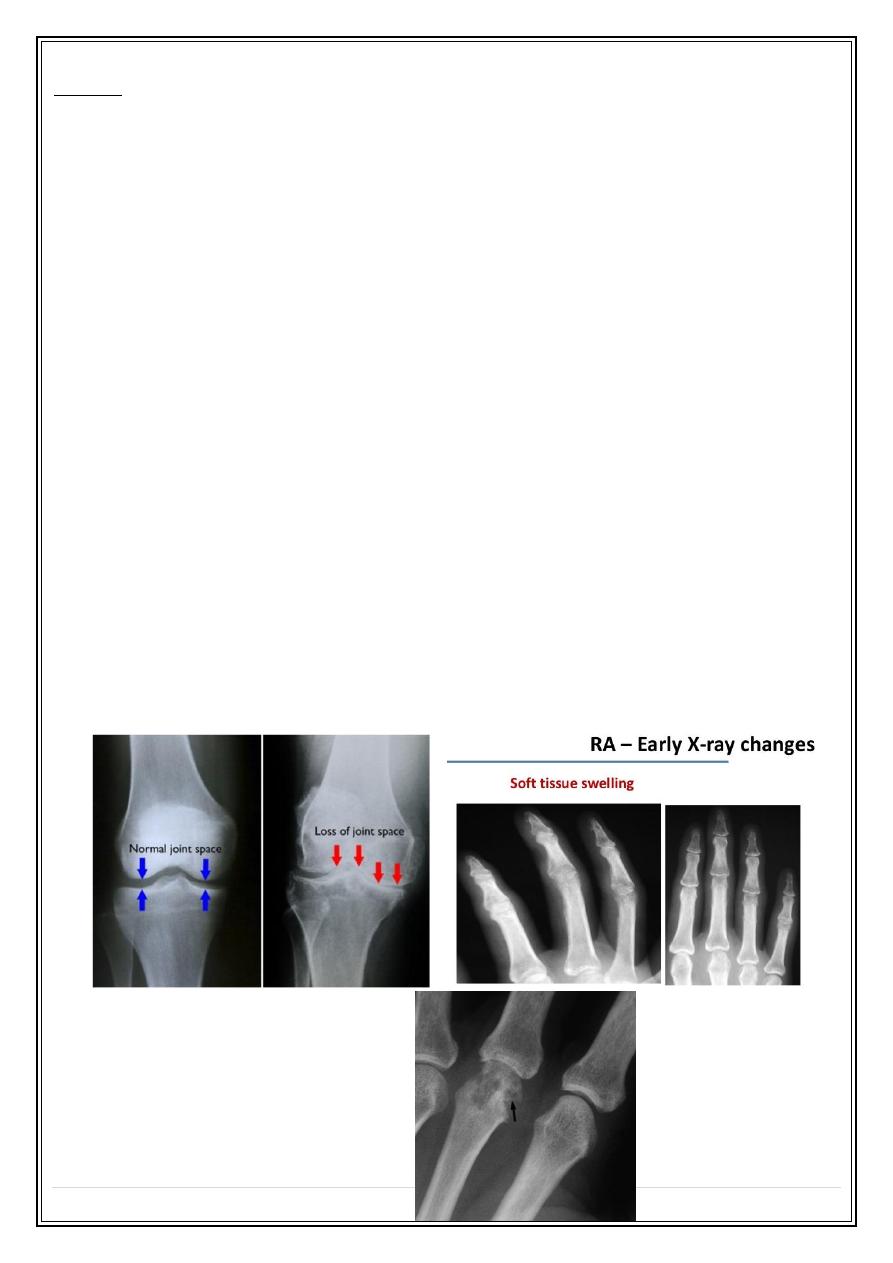
Joint space narrowing: due to destruction of articular cartilage. It occurs
in practically all forms of joint disease, except avascular necrosis.
❖
Soft tissue swelling: a feature of inflammatory, and particularly infective
arthritis. Also can be seen in gouty tophi.
❖
Osteoporosis: painful conditions and underuse of the bones. E.g.
rheumatoid and tuberculous arthritis.
❖
Articular erosions: destruction of the articular cortex and the adjacent
trabecular bone
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Firas A. – Lecture 3
P a g e
2
Causes:
1- Inflammatory overgrowth of the synovium (pannus)
•
Rheumatoid arthritis , commonest
•
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (Still’s disease)
•
Psoriasis
•
Reiter’s disease
•
Ankylosing spondylitis
•
Tuberculosis.
2- Deposition of urate crystals in gout.
3- Infection: pyogenic arthritis and tuberculosis.
4- Repeated hemorrhage in hemophilia
5- Neoplastic, e.g. synovial sarcoma.
❖
Osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis and cysts: Features of
osteoarthritis. A characteristic increase in the density of subchondral bone is
seen in avascular necrosis
❖
Alteration in the shape of the joint: slipped epiphysis, developmental
dysplasia of the hip, osteochondritis dissecans and avascular necrosis in its
later stages.
Joint erosion
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Firas A. – Lecture 3
P a g e
3
Diagnosis of arthritis
1. Whether one or more than one joint involved? e.g. rheumatoid
arthritis, infections and synovial tumours.
2. Which joints are involved?
Rheumatoid arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis
Gout characteristically
Osteoarthritis
Neuropathic arthritis
3. Is a known disease present? e.g. haemophilia or diabetes.
Rheumatoid arthritis
❖
A polyarthritis caused by inflammatory overgrowth of synovium known as
pannus.
❖
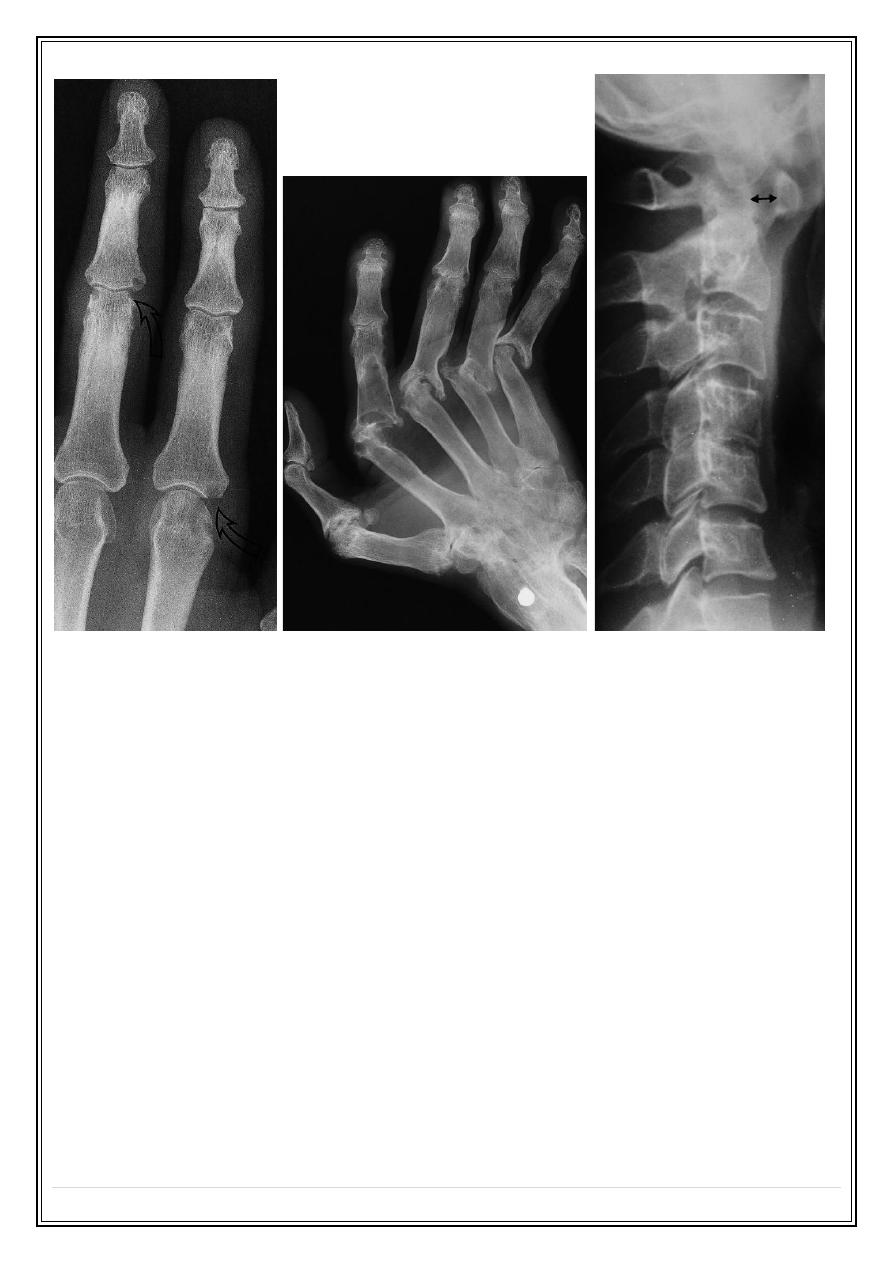
The earliest change is periarticular soft tissue swelling and osteoporosis.
❖
Joint space narrowing.
❖
Initially small bony erosions, at the joint margins. Later, extensive erosions
❖
Metatarso- or metacarpophalangeal joints, proximal interphalangeal joints
and on the styloid process of the ulna.
❖
Advance changes: Ulnar deviation. Arthritis mutilans.
❖
With severe disease, there may be subluxation at the atlantoaxial joint,
possibility of neurological symptoms from compression of the spinal cord by
the odontoid process
❖
A widespread erosive arthropathy is almost diagnostic of rheumatoid
arthritis.
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Firas A. – Lecture 3
P a g e
4
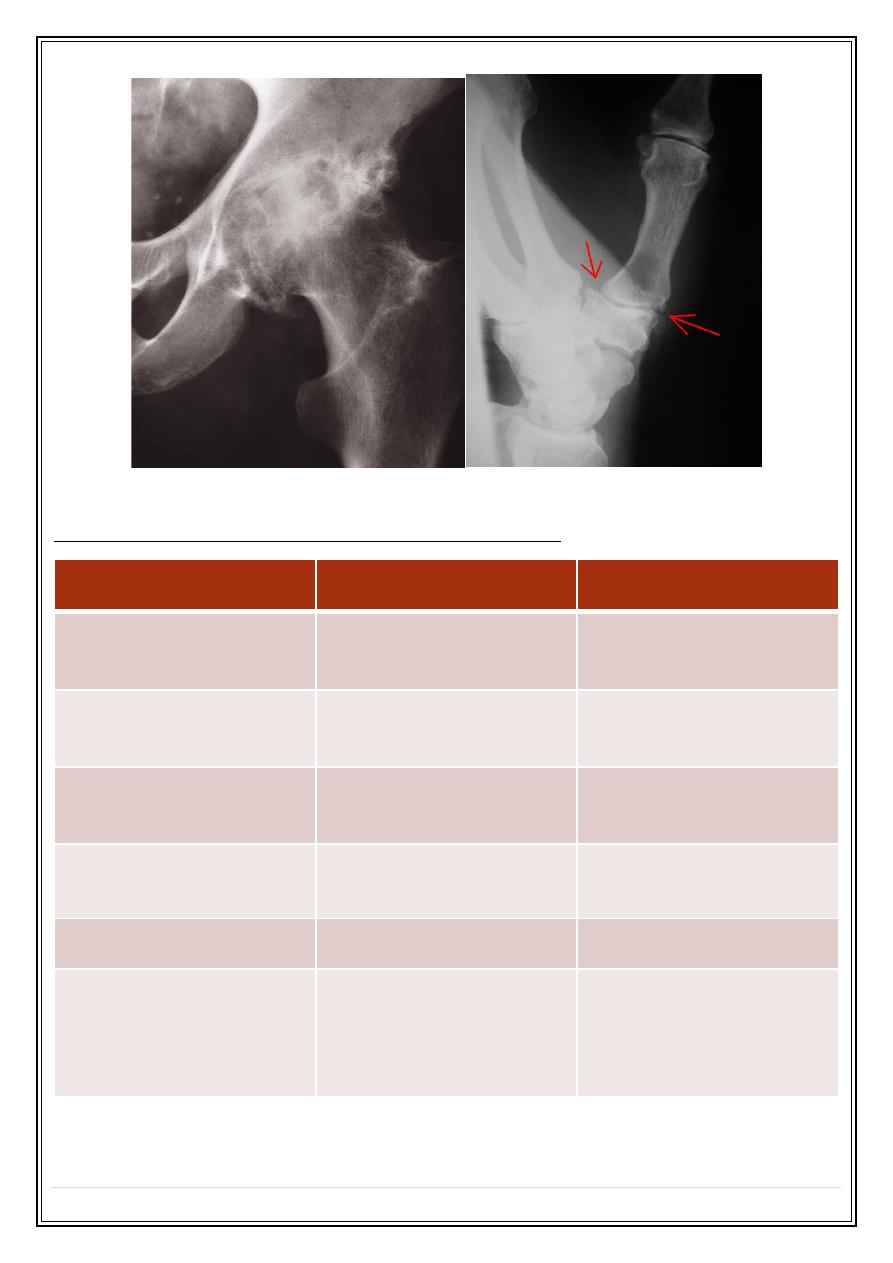
Osteoarthritis
❖
commonest form of arthritis.
❖
The hip and the knee are frequently involved, the ankle elbow are
infrequently affected.
❖
The wrist, joints of the hand and the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big
toe are also frequently involved.
❖
Radiological features:
Joint space narrowing.
Osteophytes
Subchondral sclerosis
Subchondral cysts
Loose bodies
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Firas A. – Lecture 3
P a g e
5
Comparison of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
Radiological feature
Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Joint space narrowing Maximal at weight-
bearing site
Uniform
Erosions
Not occur
Is a characteristic
feature
Subchondral sclerosis
and cysts
Seen
Not a feature
Sclerosis
Prominent feature
Not a feature
Osteoporosis
Not occur
Often present
Joint involved
Knee, hip
Metacarpophalangeal
Distal interphalangeal
Metacarpophalangeal
Proximal interphalangeal
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Firas A. – Lecture 3
P a g e
6
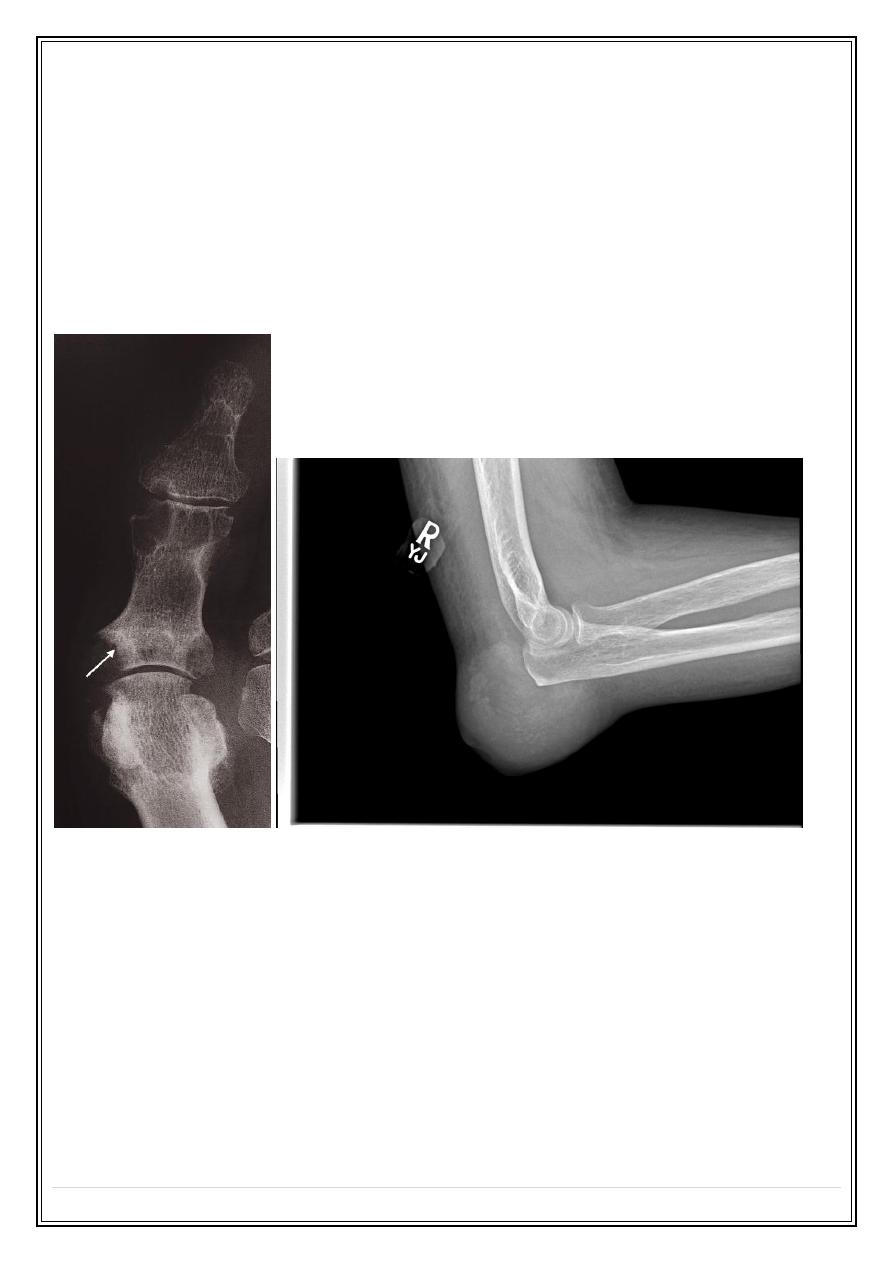
Gouty Arthritis
❖
Most commonly affects the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe.
❖
The earliest change is soft tissue swelling
❖
Erosions have a well-defined, often sclerotic overhanging edge
❖
Usually no osteoporosis
❖
Localized soft tissue lumps, known as tophi, may occur in the periarticular
and occasionally show calcification.
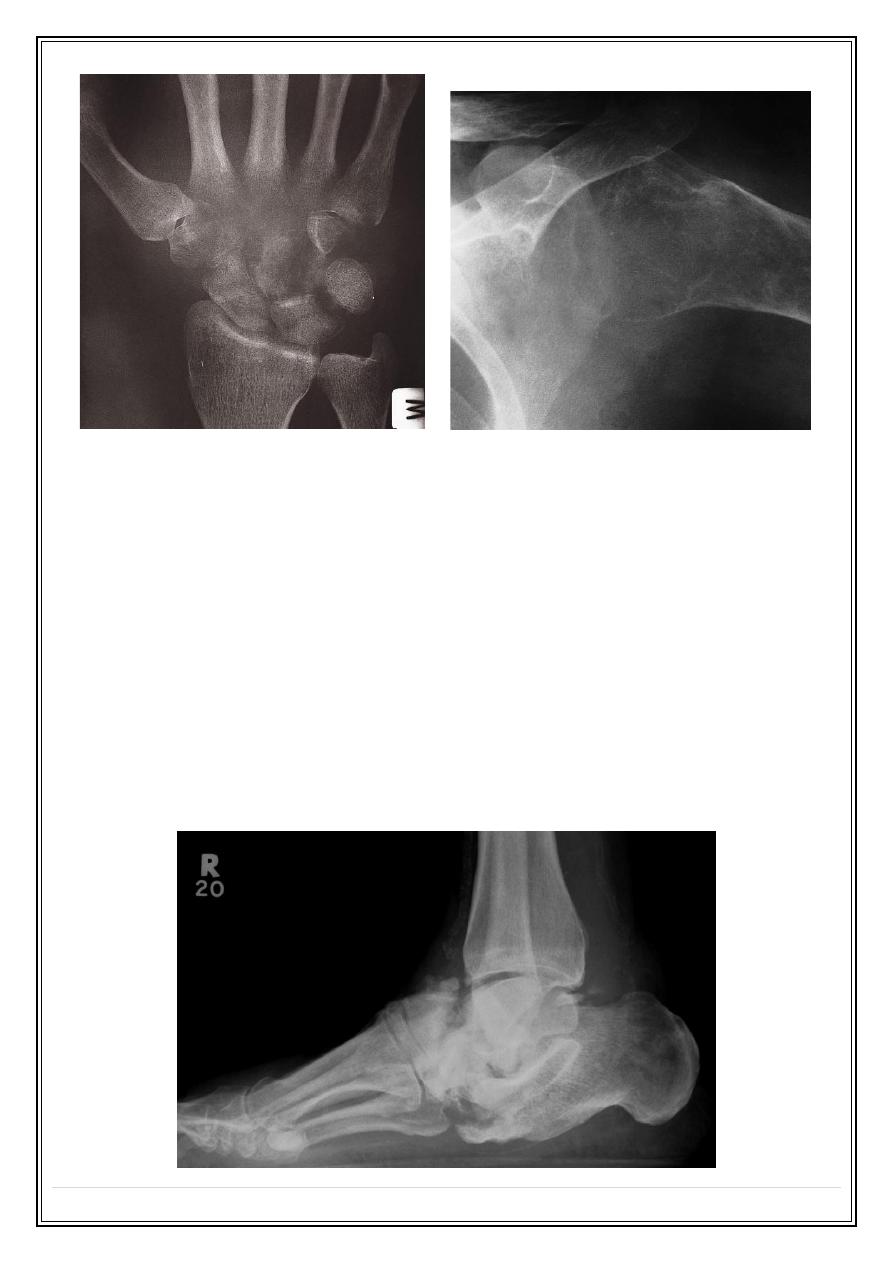
Joint Infection
❖
Pyogenic bacterial infection or tuberculosis
❖
In pyogenic arthritis, Staphylococcus aureus, there is rapid destruction of
the articular cartilage & subchondral bone and a soft tissue swelling. A joint
effusion is the earliest finding
❖
TB arthritis, The hip and knee are the most commonly affected. Joint space
narrowing and erosions, articular cortex destruction, and striking
osteoporosis,
Tophi
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Firas A. – Lecture 3
P a g e
7
pyogenic arthritis
TB arthritis
Neuropathic joint (Charcot joint)
6 Ds of Charcot joint:
Increased Density (subchondral sclerosis)
Destruction
Debris (intra-articular loose bodies)
Dislocation
Distention
Disorganisation
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Firas A. – Lecture 3
P a g e
8
Avascular (aseptic) necrosis
❖
Causes:
➢
steroid therapy
➢
Collagen vascular diseases
➢
Radiation therapy
➢
Sickle cell anemia
➢
Exposure to high pressure environments
➢
Fractures.
❖
The radiographic features:
➢
Increased density of the subchondral bone with irregularity of the
articular contour or fragmentation of the bone
➢
A characteristic crescentic lucent line just beneath the articular cortex.
➢
The cartilage space is preserved until secondary degenerative changes
supervene.
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Firas A. – Lecture 3
P a g e
9
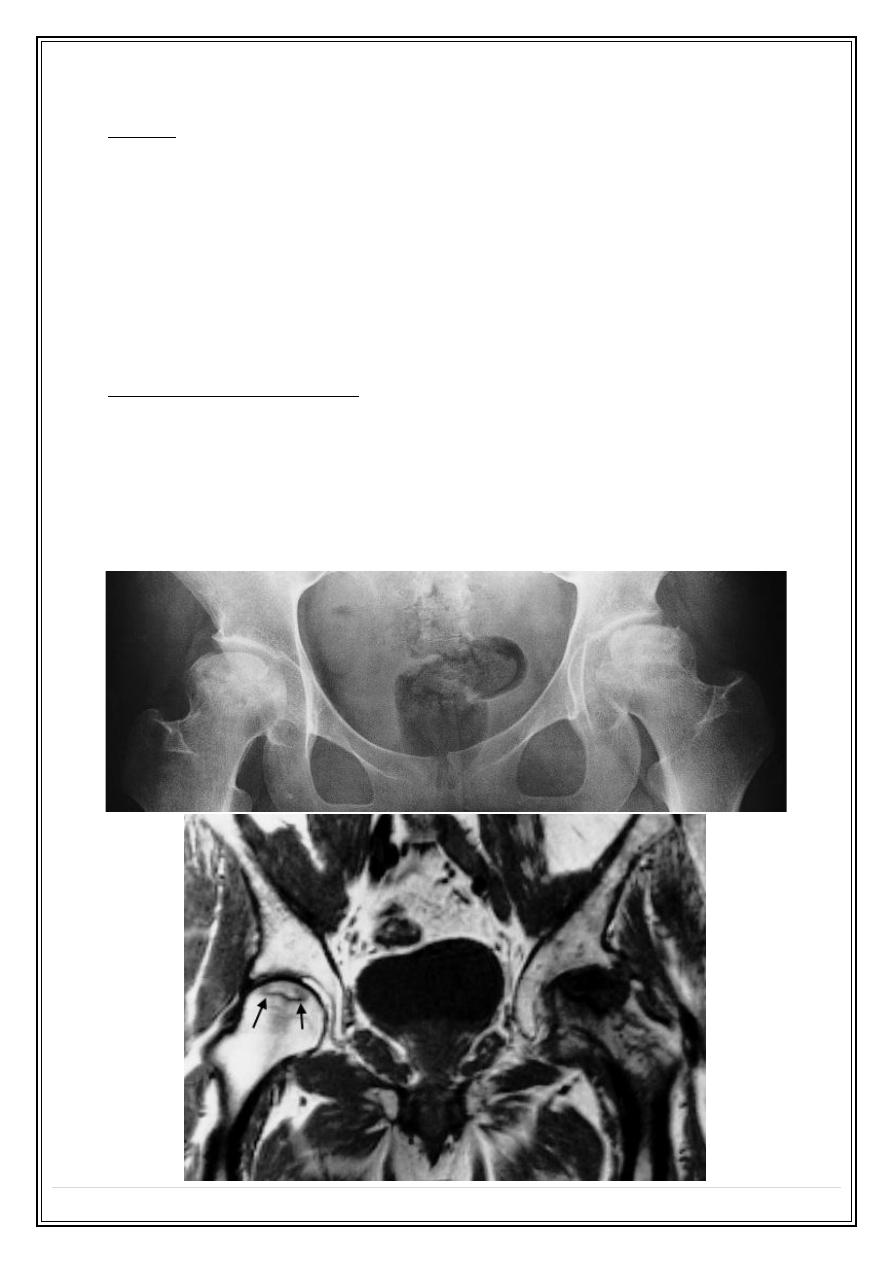
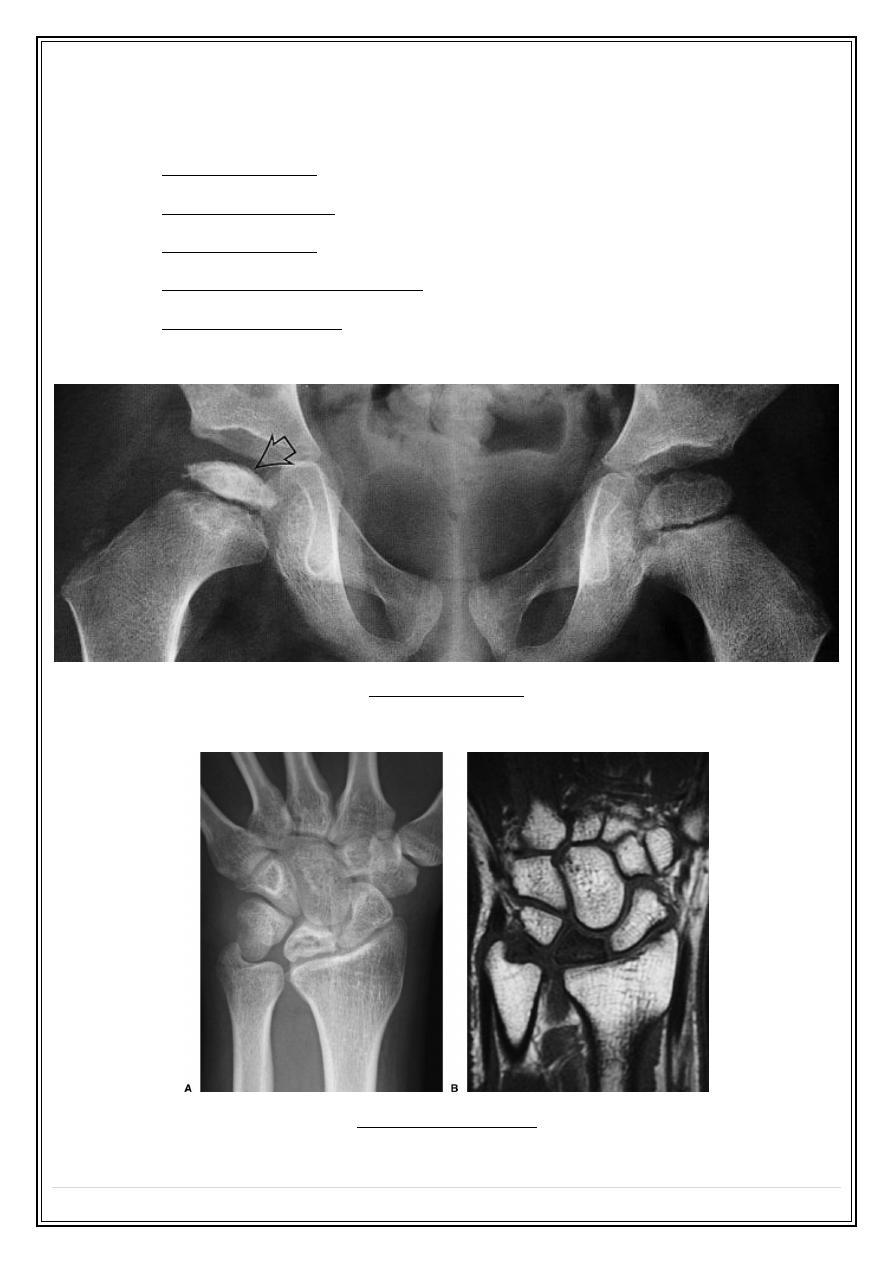
Osteochondritis
❖
Avascular necrosis, but with unknown cause
➢
Perthe's disease: femora head
➢
Freiberg’s disease: metatarsal heads
➢
Kohler’s disease: navicular bone of the foot
➢
Osgood–Schlatter’s disease: tibial tuberosity
➢
Kienböck’s disease: lunate bone in the wrist
Perthe's disease
Kienböck’s disease
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Firas A. – Lecture 3
P a g e
10
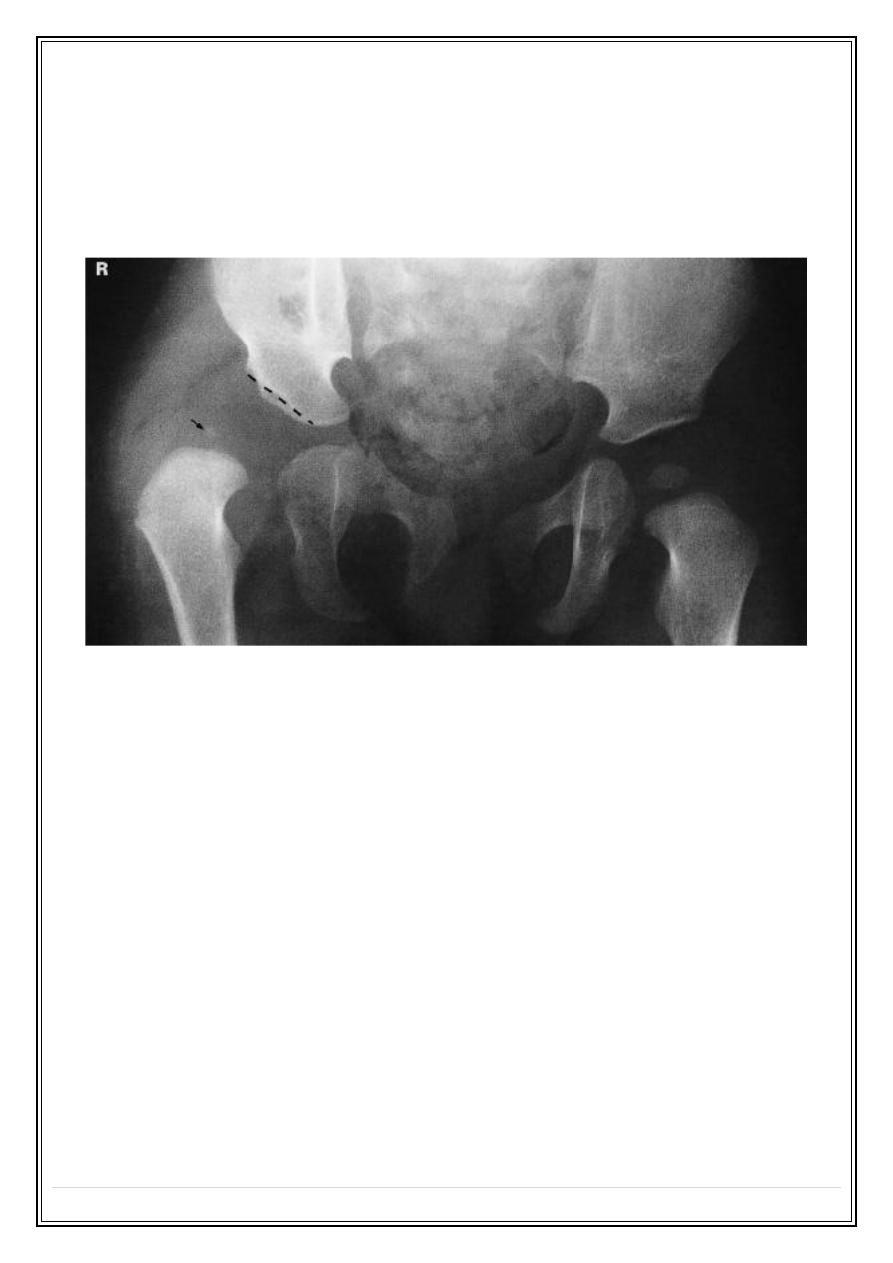
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)
❖
Ultrasound at early infancy
❖
X ray later in life
❖
The features: lateral and upper displacement of the head of the femur.
Increased slope to the acetabular roof
Thank you,,,
