Disorders of tongue
Dr. Lana Shabur Talabani


DISORDERS OF TONGUE IN DIFFERENT
CONDITIONS
ORAL LICHEN PLANUS
BLACK HAIRYTONGUE
STRAWBERRY TONGUE
RASPBERRY TONGUE
FISSURED TONGUE
ORAL HAIRY
LEUKOPLAKIA
MIGRATORY GLOSSITIS
ANKYLOGLOSSIA
MEDIAN RHOMBOID
GLOSSITIS
ORAL CANCER

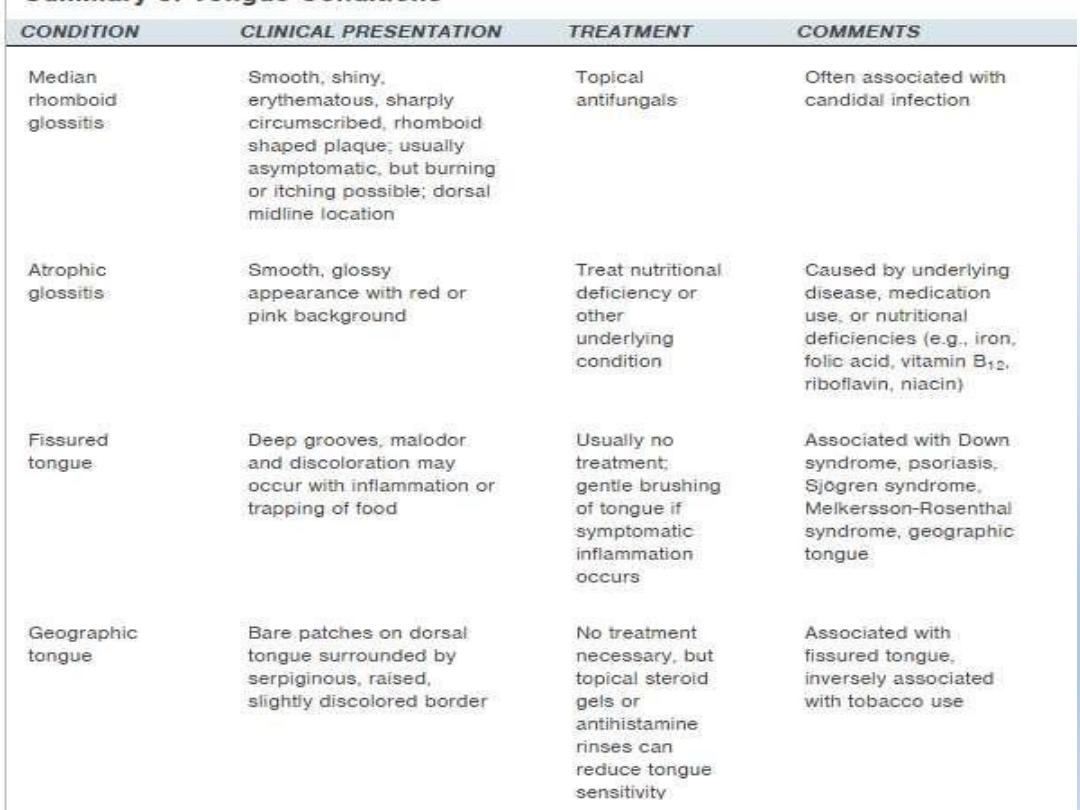
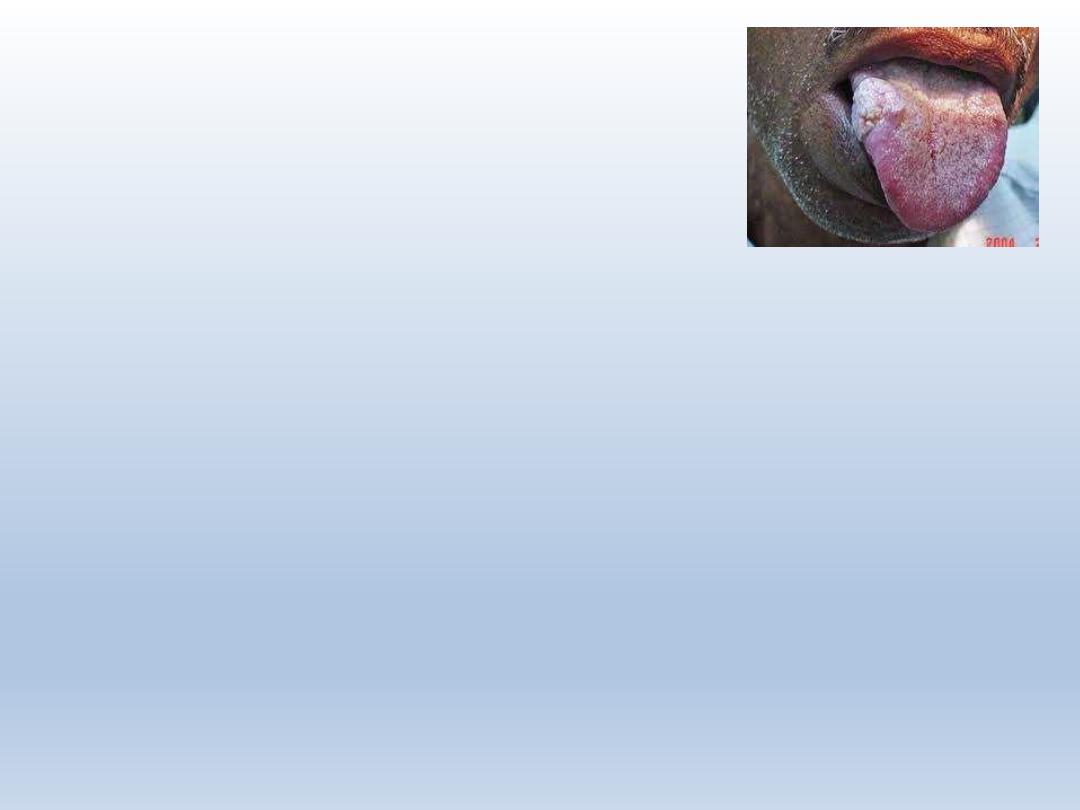
Oral hairy leukoplakia
OHL – corrugated white lesion seen on
ventral and lateral surfaces of tongue
Commonly associated with HIV
EBV – causative agent
Lesions are shaggy and frayed
Plaque like and often bilateral
Oral hairy leukoplakia
Shaggy corrugated
hyperkeratotic plaque

Treatment
N o treatment is rquired
Resolves with- zidovudine. Acyclovir, gancyclovir
Topically application of- podophyllin resin and tretinion
OHL is highly predictive of AIDS development

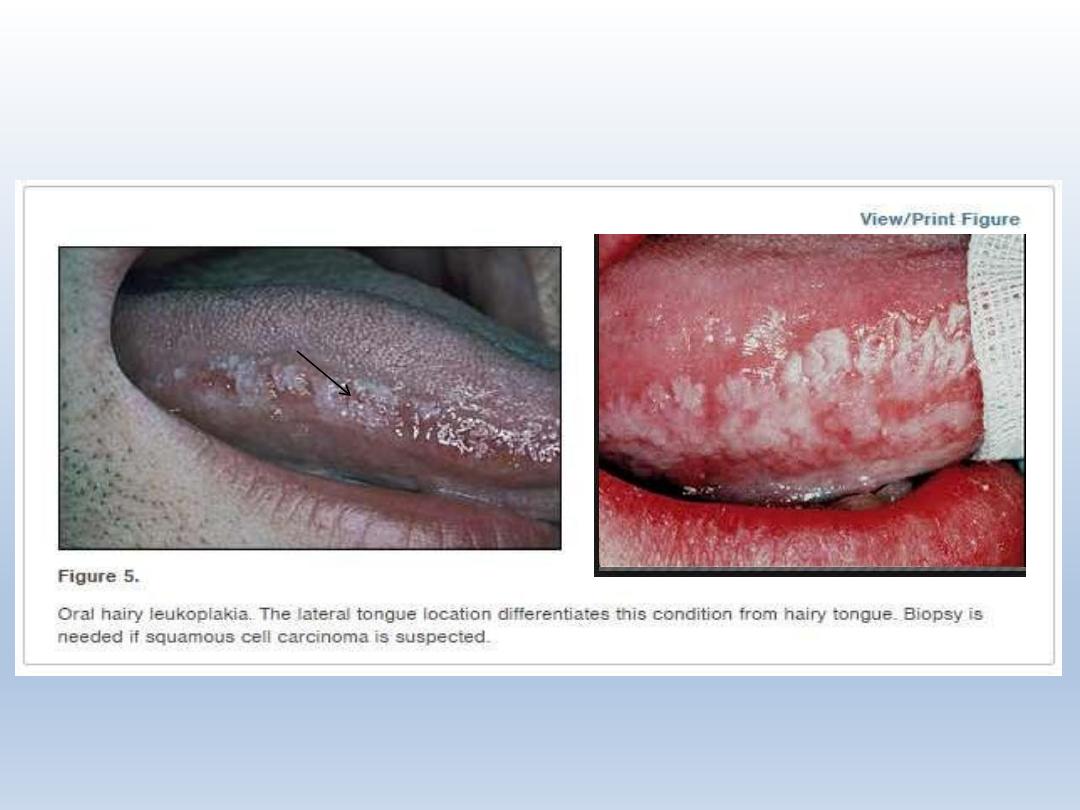
Hairy tongue/ lingua
villosa/Lingua nigra
Defective desquamation of filiform papillae
Accumulation of excess keratin on filiform papillae of the
dorsal part of tongue
Dark color results from trapping of debris and bacteria
Use of broad spectrum antibiotics
Radiation therapy
Seen in smokers and persons with poor oral hygeine
Increased coffee and tea drinking
Treatment
No treatment is required
Gentle tongue scrapping and removal of etiology
Surgical removal of papillae- laser, electrodesication
Filiform papillae
attains 15 mm length
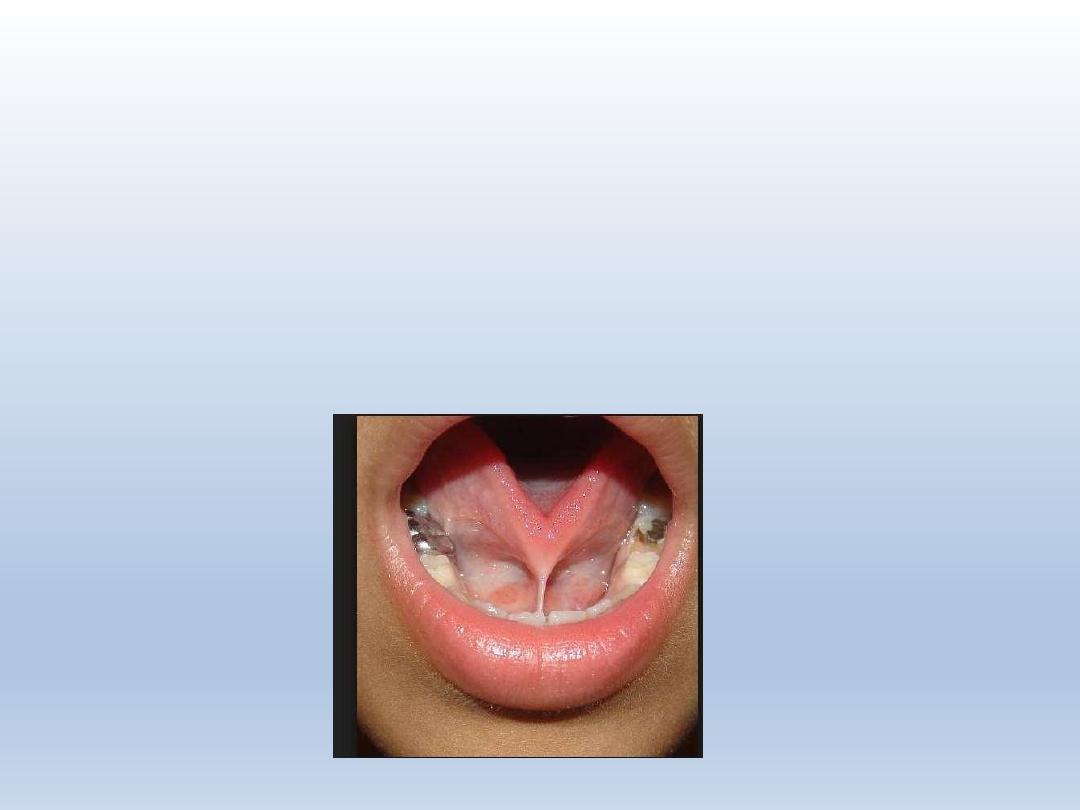
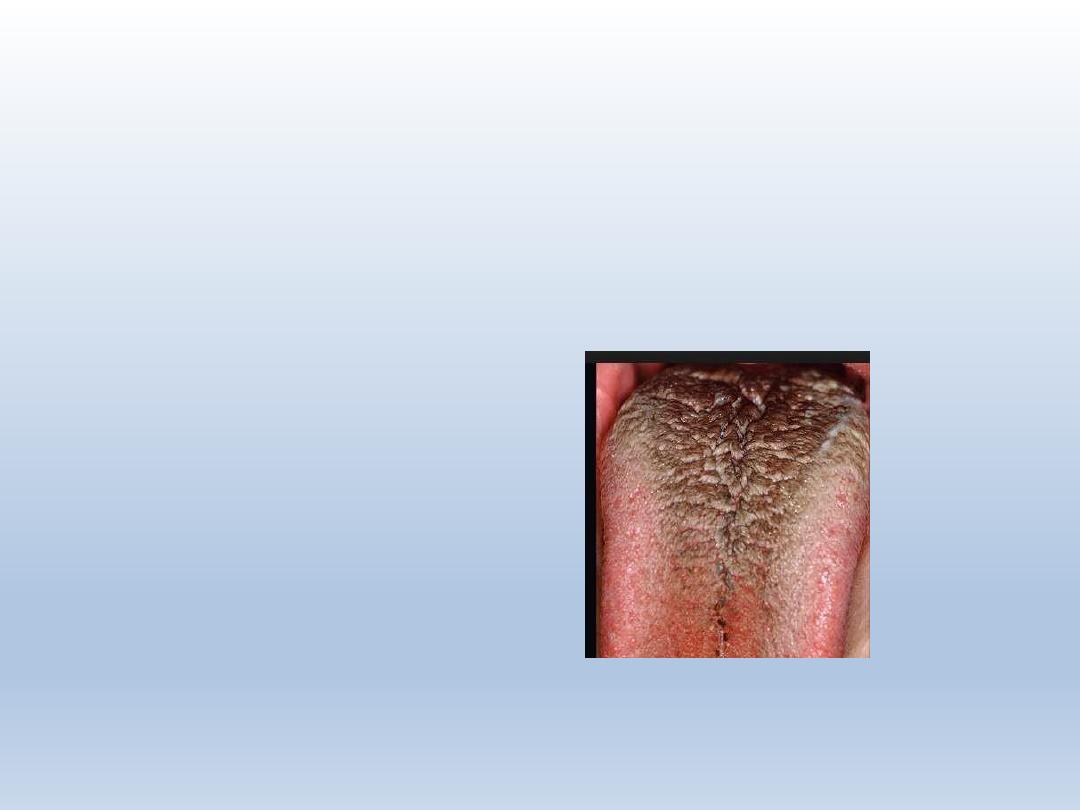
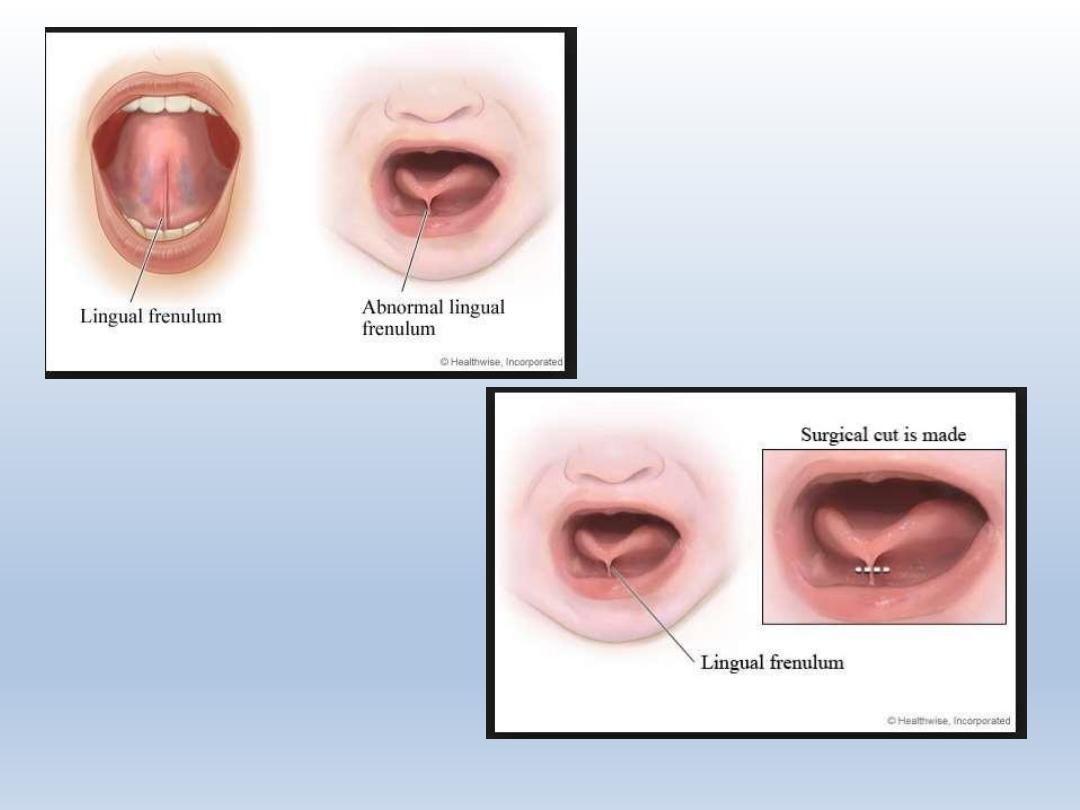
Ankyloglossia/ tongue tie
Inferior frenulum attaches to the bottom of tongue
Restricts free movement of tongue
Frenulectomy is recommended
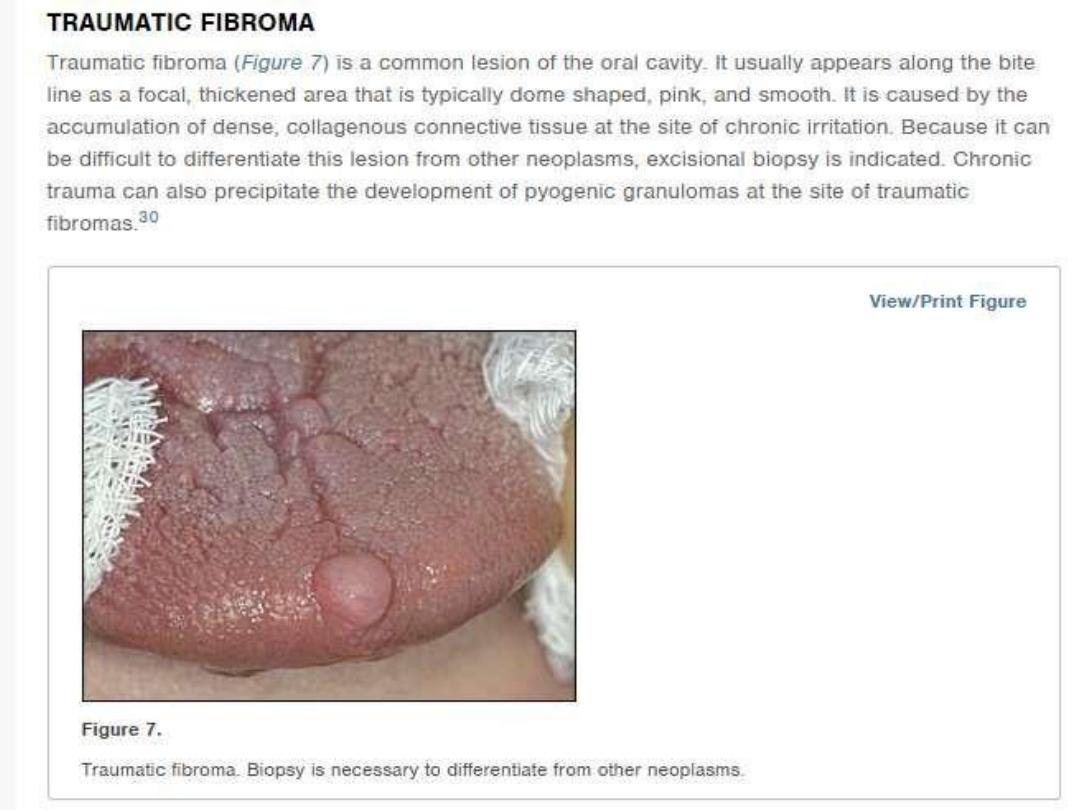

SCC of tongue
Smoking, alcohol abuse are risk factors for
SCC of tongue
HPV is implicated in tongue cancer
Seen in anterior two thirds of tongue
Usually painless
Presents as a non healing ulcer
Nodal metastasis is common due to
lymphatic drainage of tongue
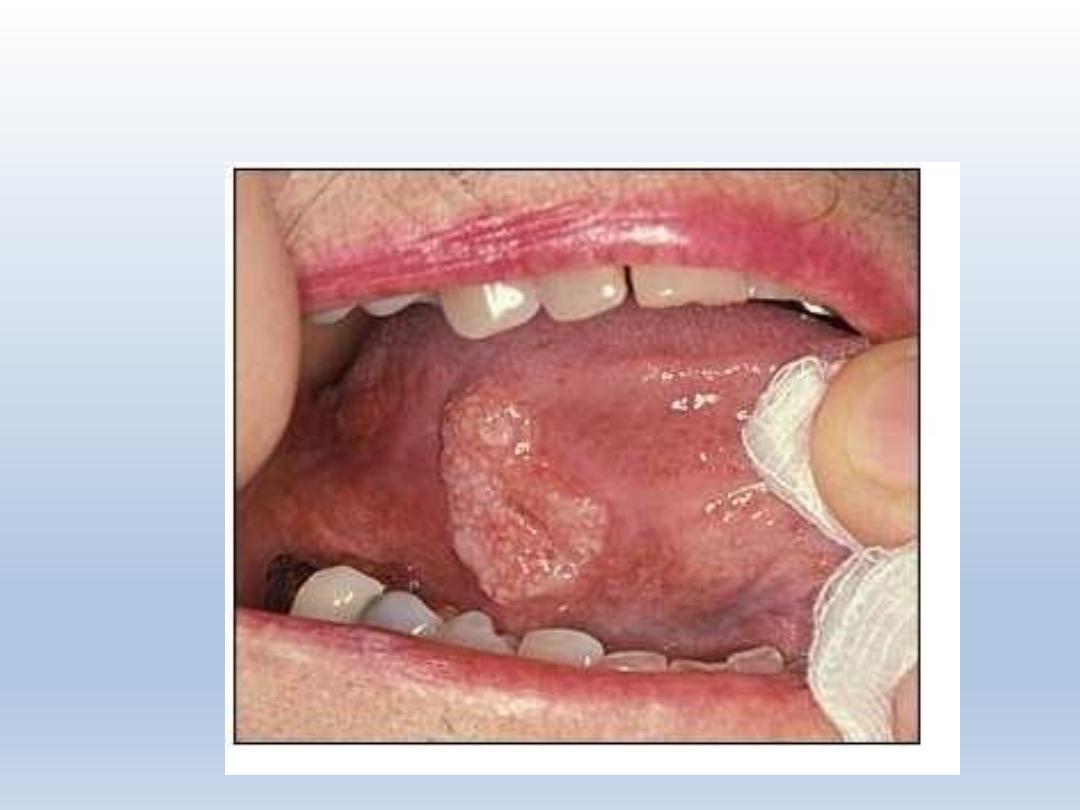
Squamous cell carcinoma of tongue
Symptoms of tongue cancer
A red or white patch on the tongue, that will not
go away
sore throat
A sore spot (ulcer) or lump
Pain when swallowing
Numbness in the mouth
Unexplained bleeding from the tongue (that is
not caused by biting your tongue or other injury)
Pain in the ear (rare)
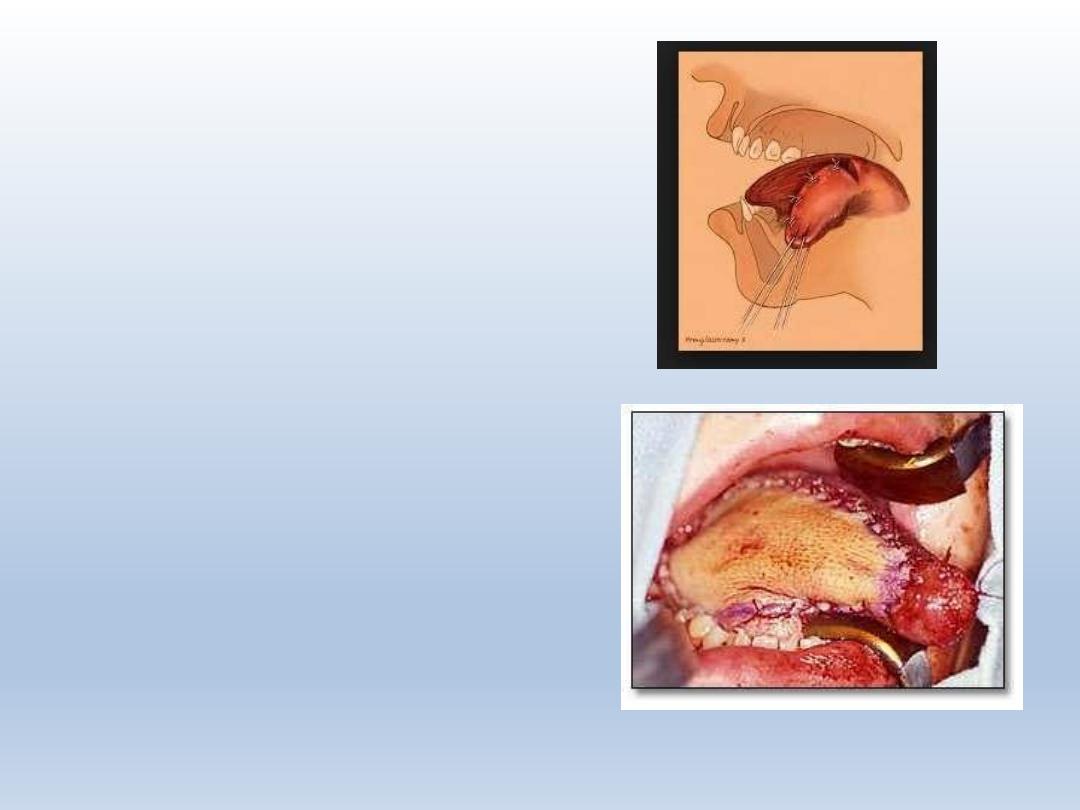
Treatment
Hemiglossectomy
Total glossectomy
Radiation therapy
Chemotherapy
Hemiglossectomy
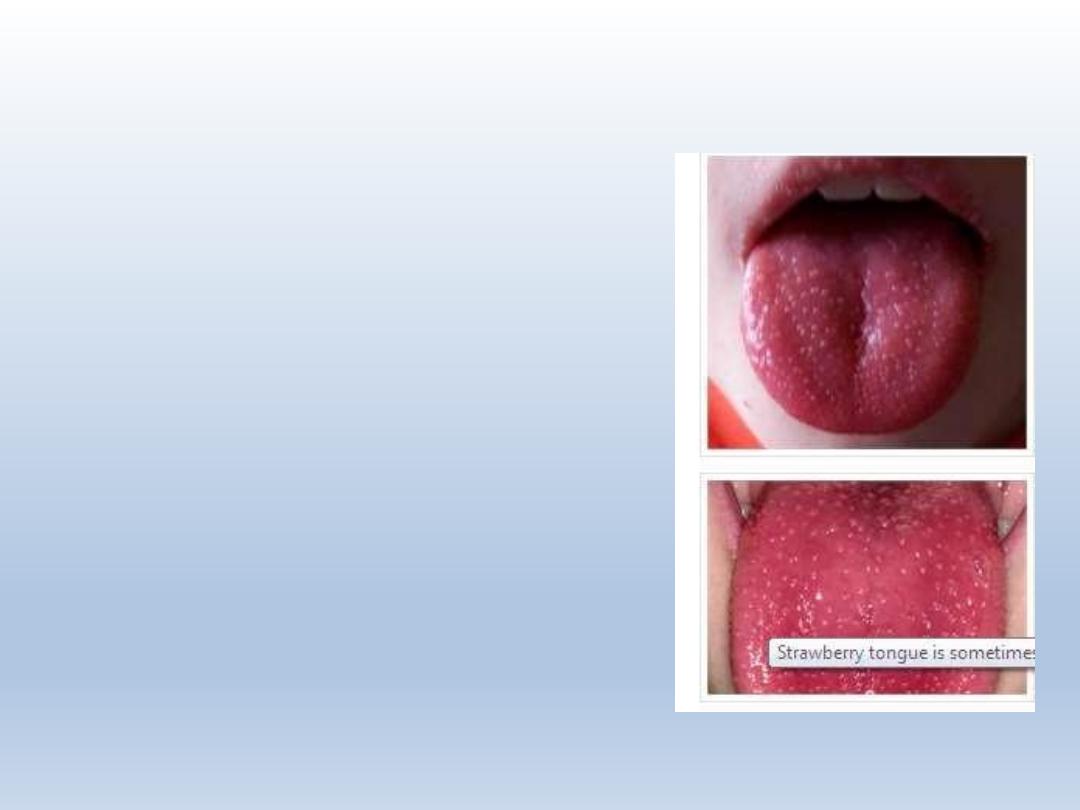
Strawberry tongue
tongue takes the
red
color
of
a
i.
In this the
distinctive
strawberry
ii.
This is different
inflammation
of
from general
the
tongue
,
glossitis, which often exhibits a
smooth shiny tongue.
iii.
This
is
characterized
by
enlargement of the fungiform
reddening of the tongue, it
papillae. Thus, along with the
is
dotted with raised papillae giving it
the look of a strawberry.
iv.
It can take two colors – white and
red. It is sometimes also referred
to as ‘raspberry tongue

Strawberry tongue
A strawberry tongue generally reflects a systemic disease rather than
oral disorder. Among the possible reasons are:
Scarlet Fever: This is a childhood disease which is caused by strep
infection. A tongue that looks like the surface of a strawberry is one of
the distinguishing features of this disease among other symptoms like
red rashes and fever. In the initial stage of the infection, the child
develops a white strawberry tongue which turns red after four to five
days.
Kawasaki disease: This is a rare disorder that occurs in small children. It is
characterized by fever, rashes and red mouth including the tongue. It
causes inflammation of blood vessels in the whole body. It needs to be
watched even after the child has recovered as it can sometimes have an
adverse effect on heart blood vessels. The cause for this disorder is not
known.
Toxic shock syndrome: This is characterized by fever, drop in blood
pressure, vomiting, rashes, red mouth and throat. It is caused by toxins
released by certain bacteria. This can quickly assume life threatening
proportions.
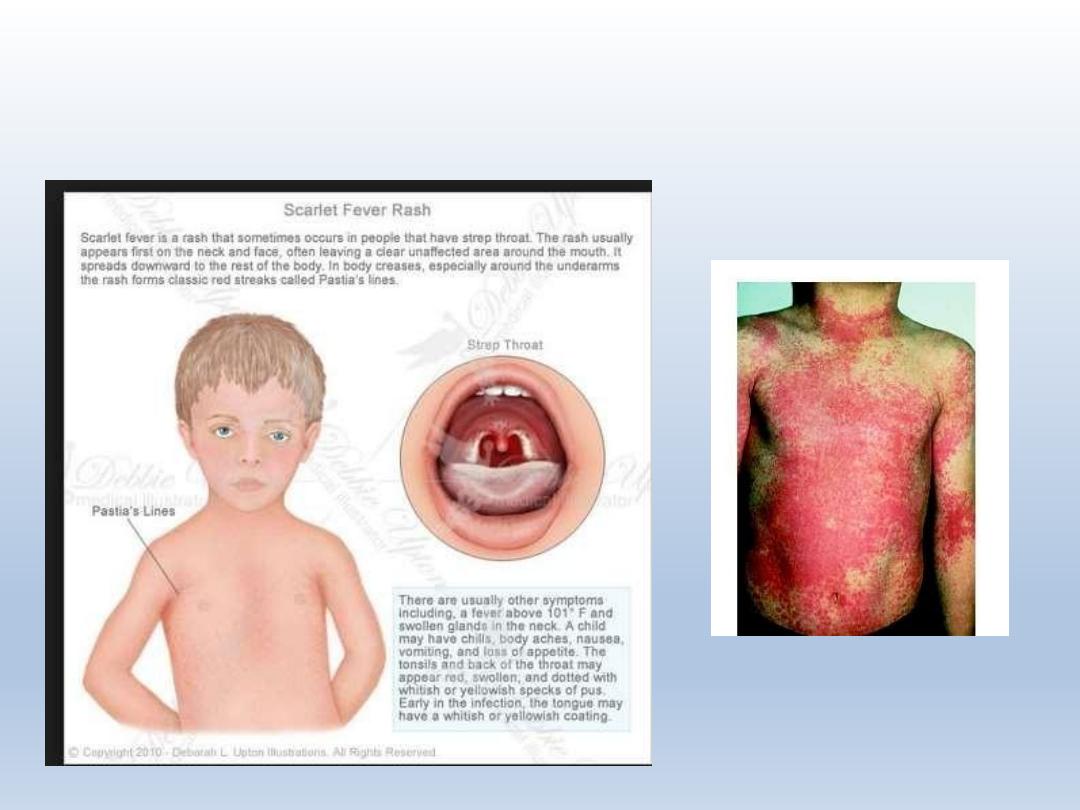
SCARLET FEVER
SAND PAPER
RASH ONSKIN
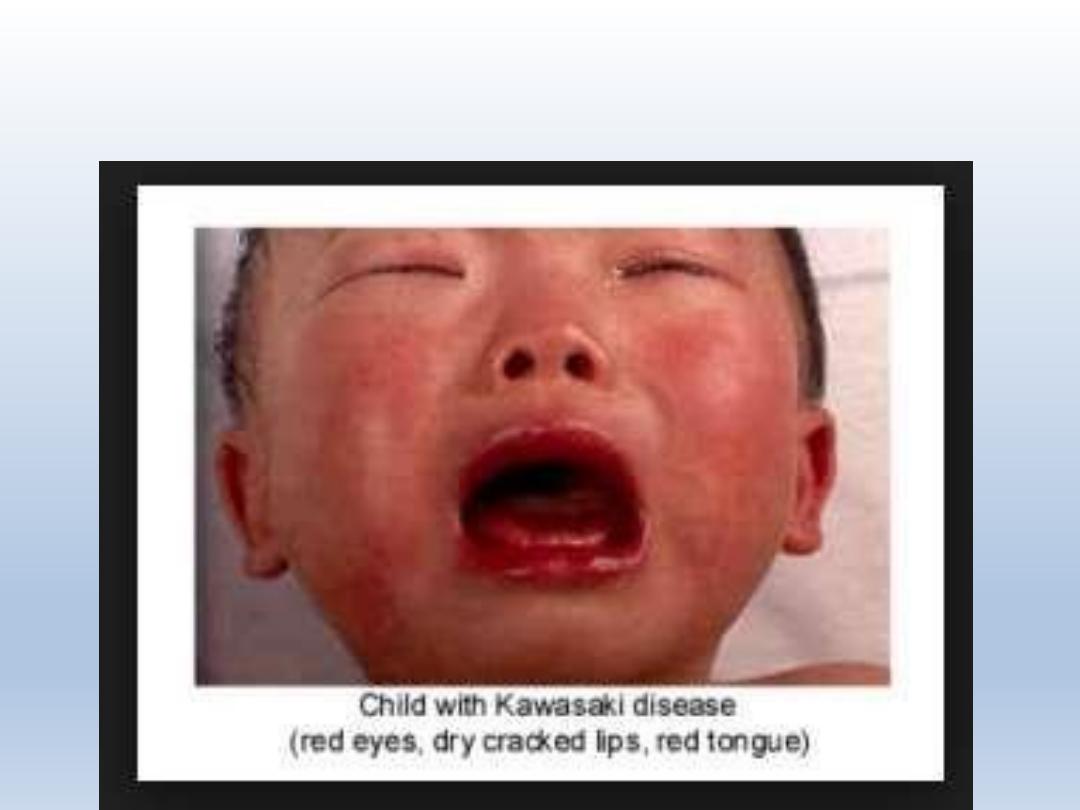
KAWASAKI DISEASE

PERNICIOUS ANEMIA
Chronic haematologic disease
Caused by Lack of intrinsic factor used for gastric
secretions
Traid of symptoms
1. generalized weakness
2. sore painful tongue
3. tingling of extremities
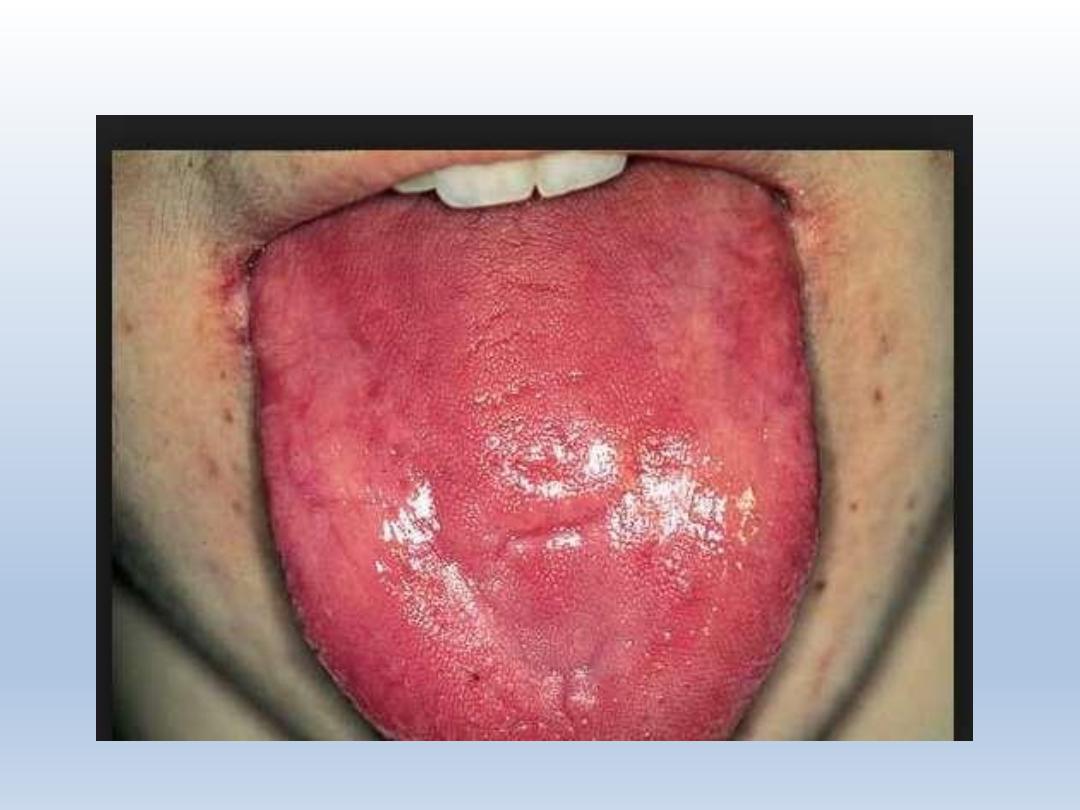
Red and beefy tongue in pernicious anemia
Glossitis
Glossodynia
Glossopyrosis leads
to bald tongue
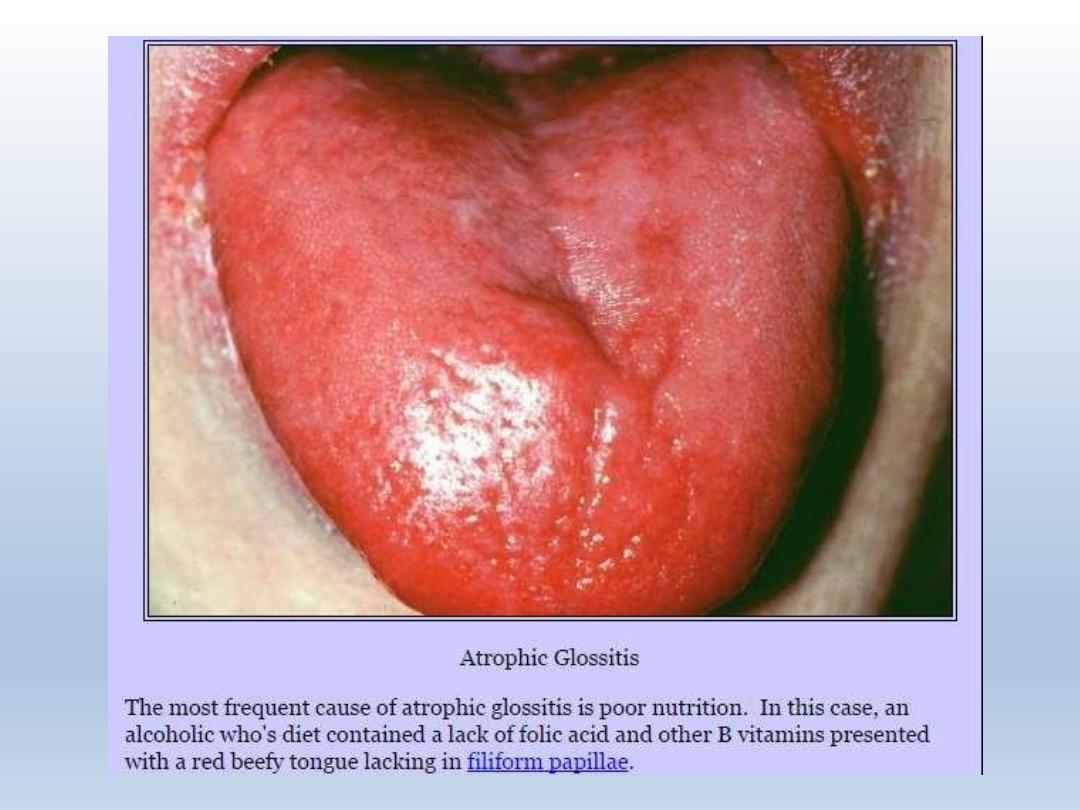

treatment
Administration of vit B12
Folic acid
Delayed treatment causes anemia,
neurological complications
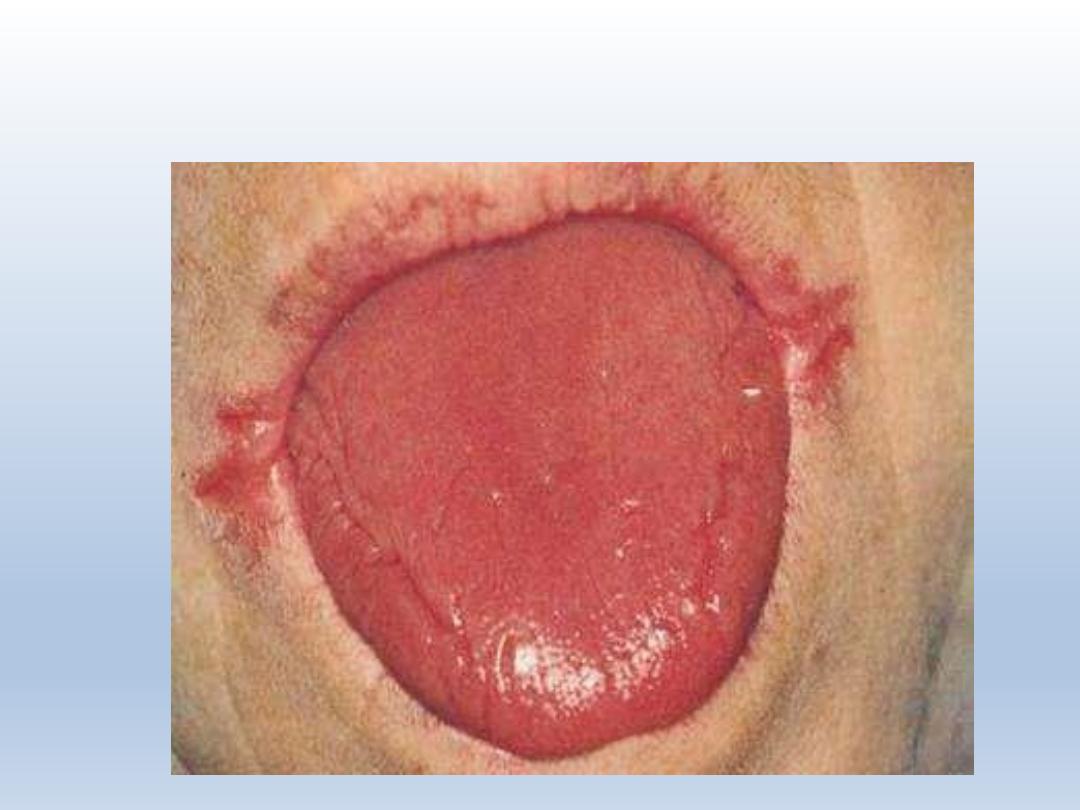
Iron deficiency anemia
Atrophic glossitis with
Angular chelitis
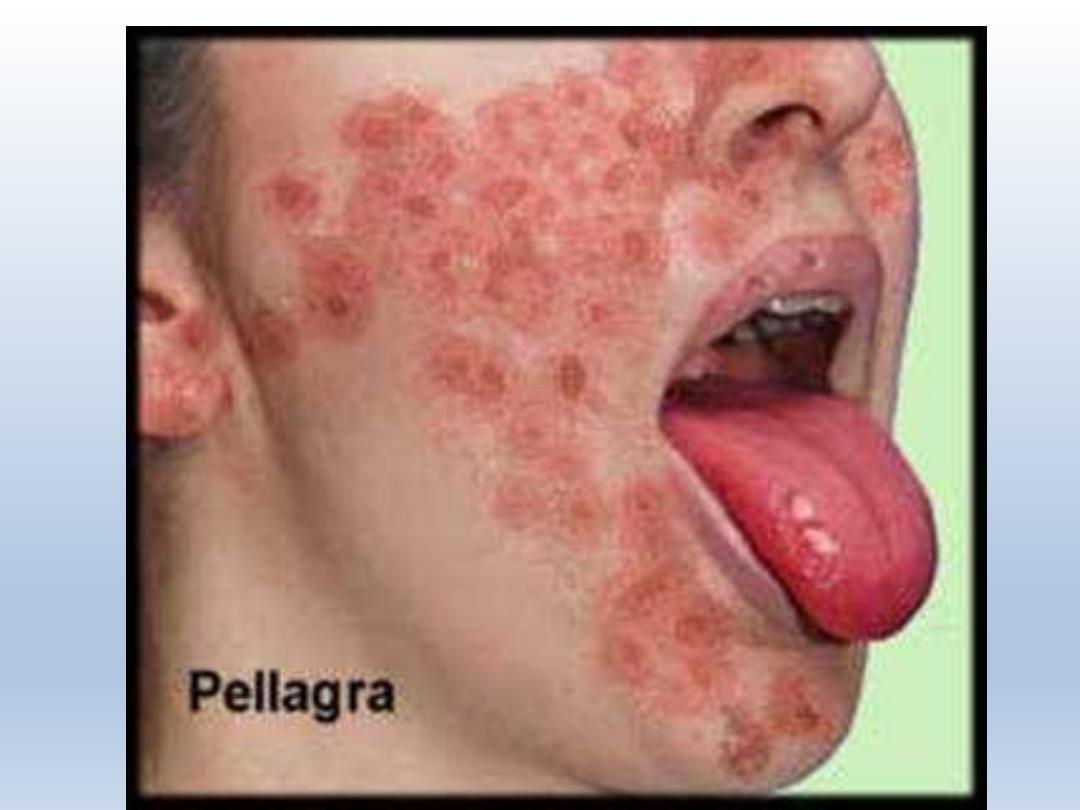
Red painful
tongue
Deficiency of niacin, VITB3

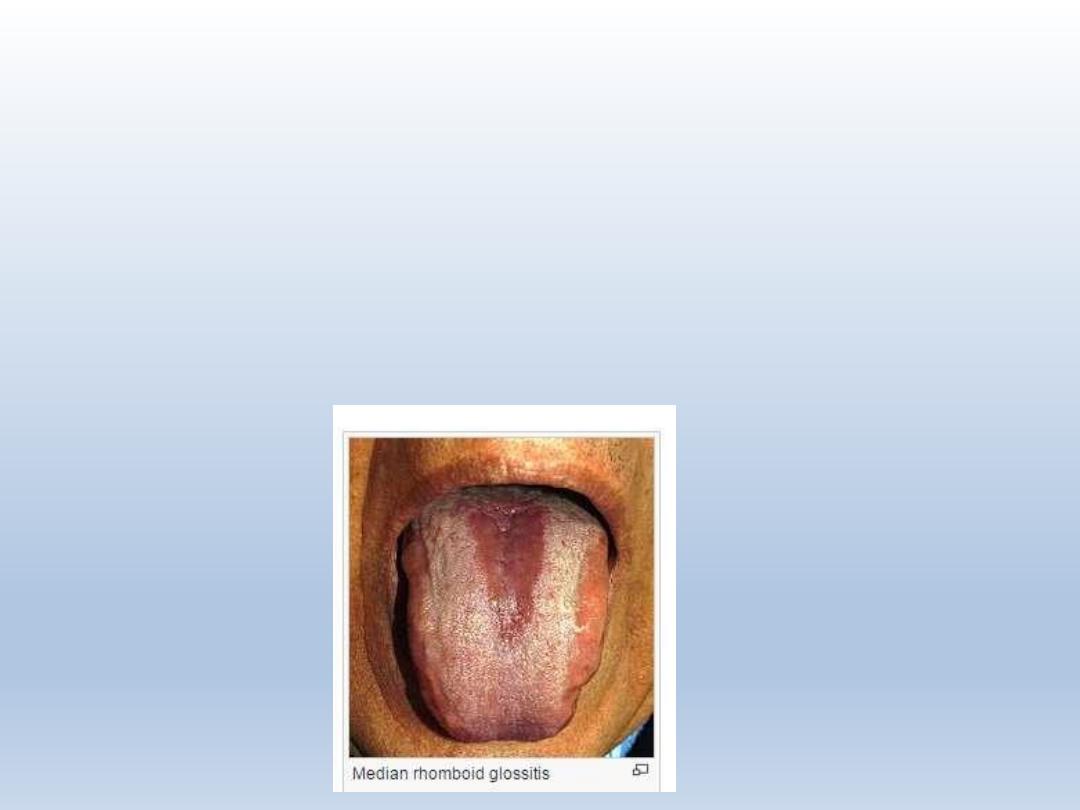
Median rhomboid glossitis
Central papillary atrophy of tongue- defective
fusion of lingual tubercles at the midline
Susceptibility for candidiasis
Absence of filiform papilllae
Presents – at posterior midline of dorsum of
tongue
soft palate eythema at the area of contact
with the underlying tongue- kissing lesion
Treatment
No treatment is necessary
Antifungal therapy- reduce clinical erythema
and inflammation in candida infection
Kissing lesion
Sharply circumscribed
Rhomboid in shape
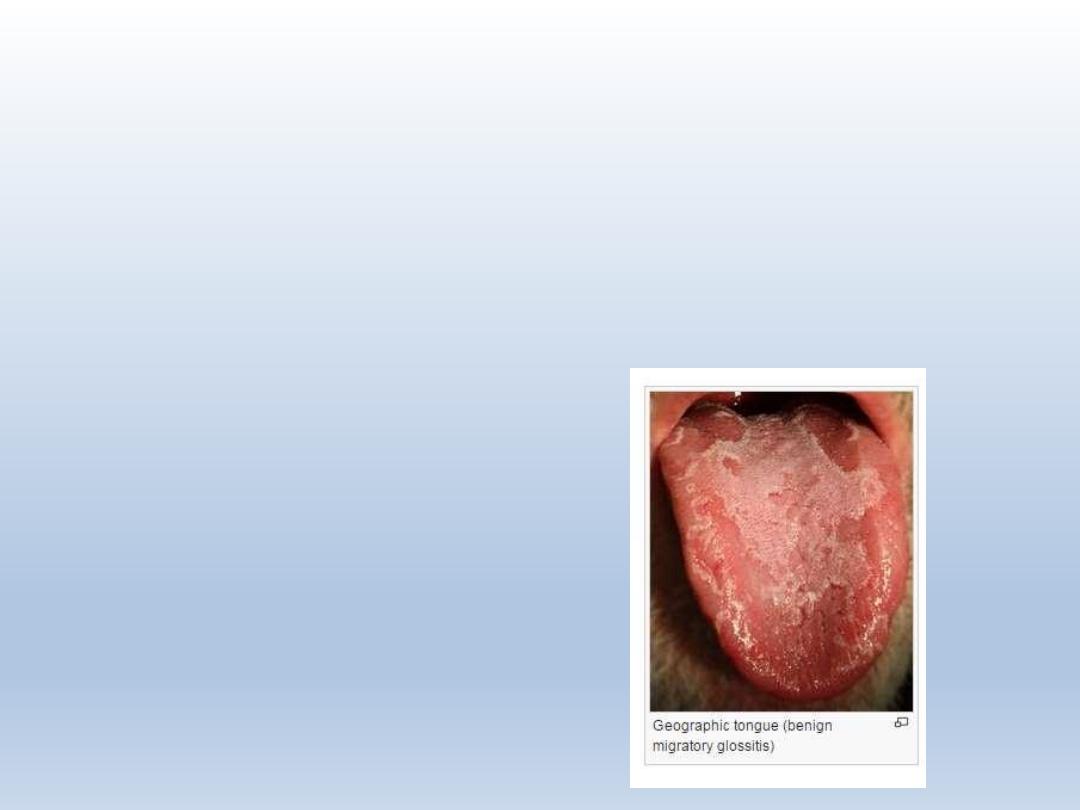
GEOGRAPHIC TONGUE
Benign migratory glossitis- psoriasiform mucositis in
dorsal part of tongue
Changing patterns of serpiginous white lines surrounded
by depapillated mucosa
Wandering rash of tongue
No treatment is necessary
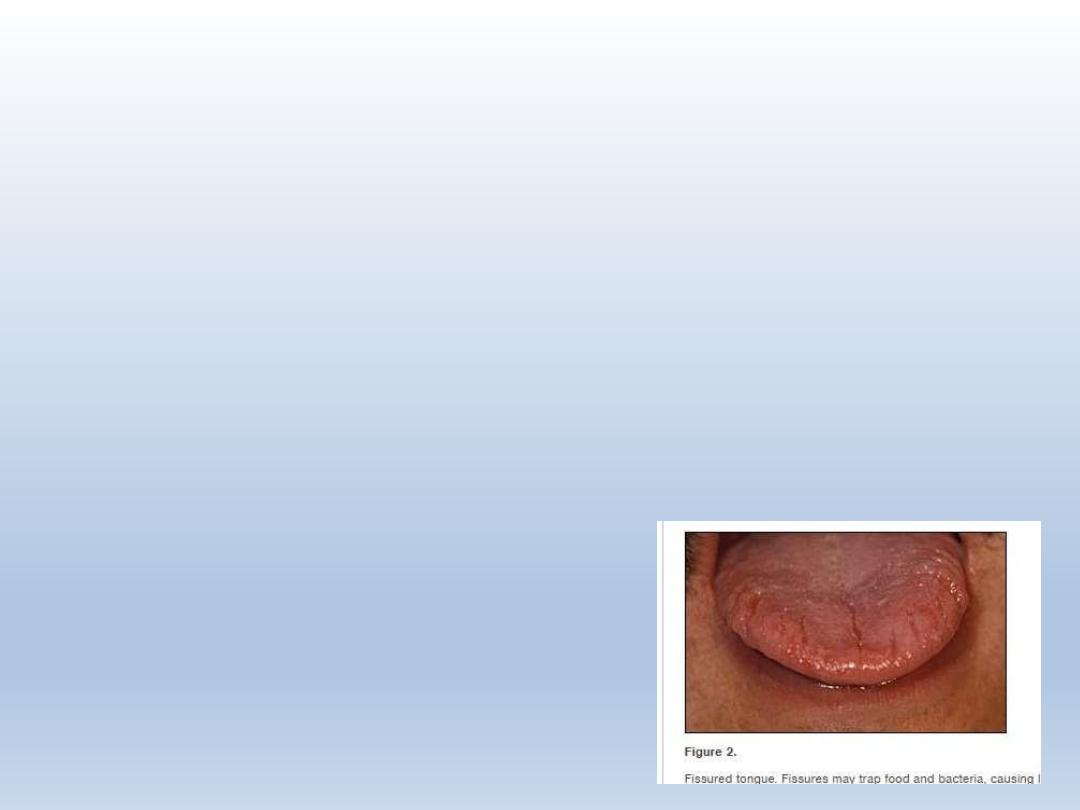
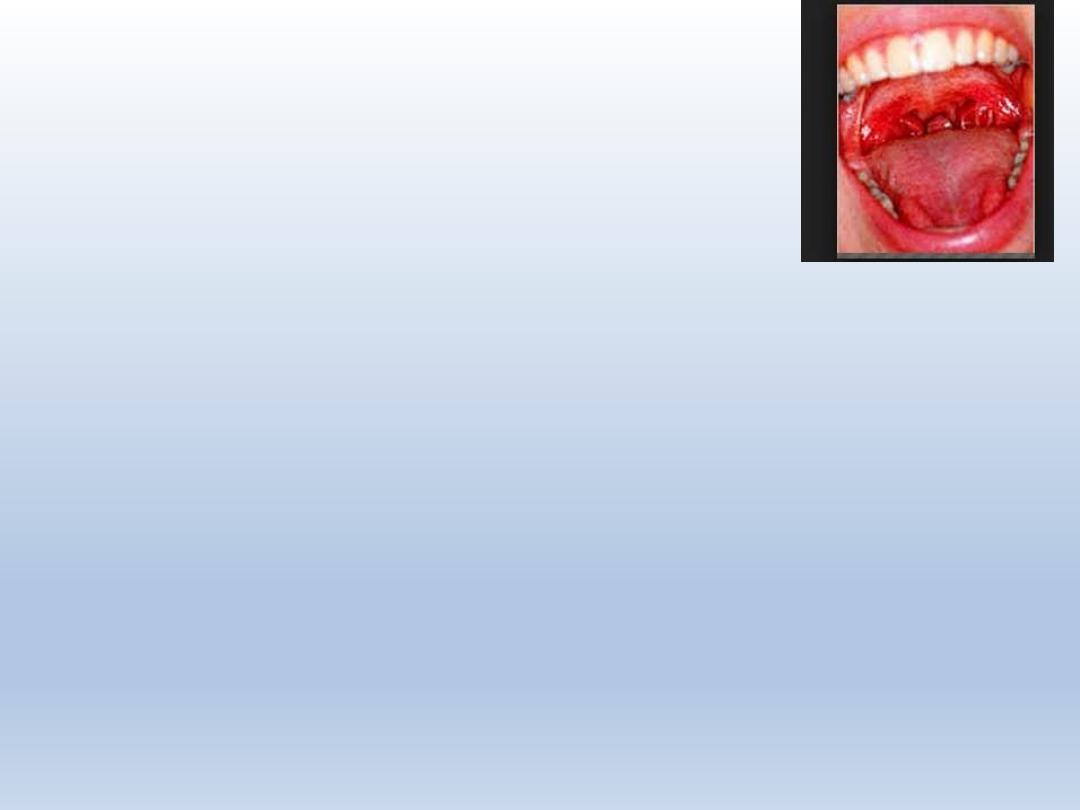
Fissured tongue/ scrotal
tongue/ lingua plicata
Characterized by grooves that vary in depth
Seen on dorsal and lateral aspects of tongue
Seen in melkersson rosenthal syndrome and downs
syndrome
Debris can be trapped in the fissure
Depth of fissure varies about – 6mm
No treatment is required
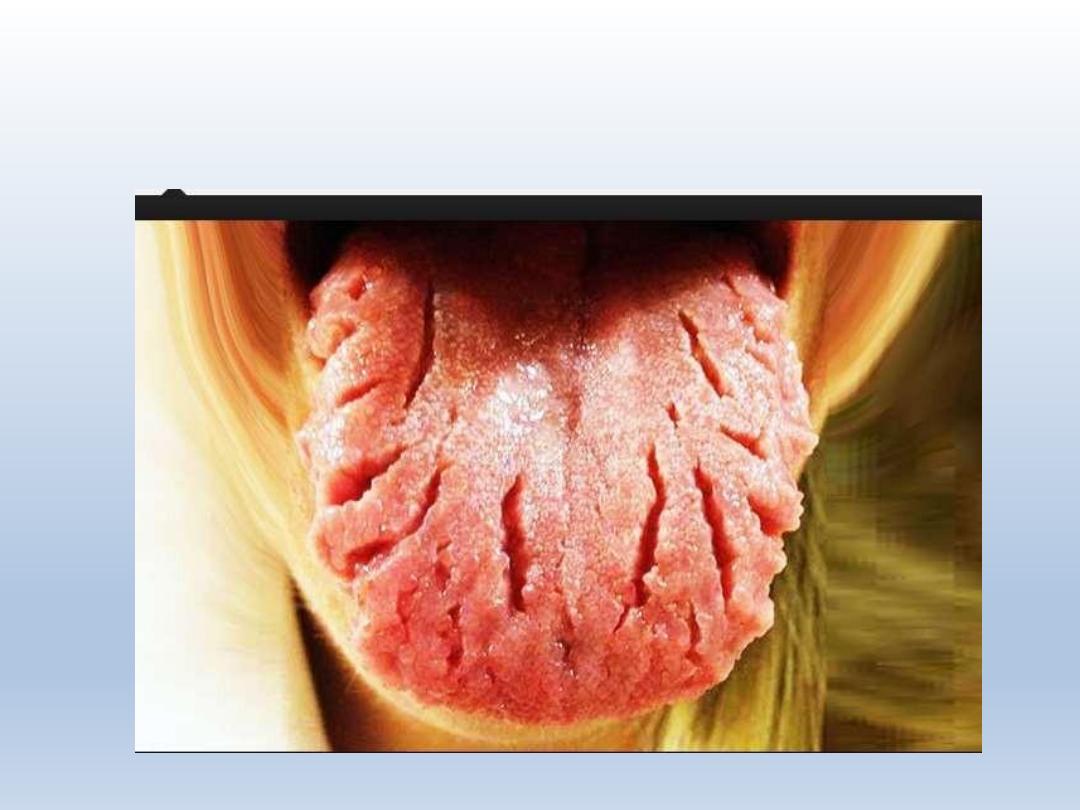
Scrotal tongue
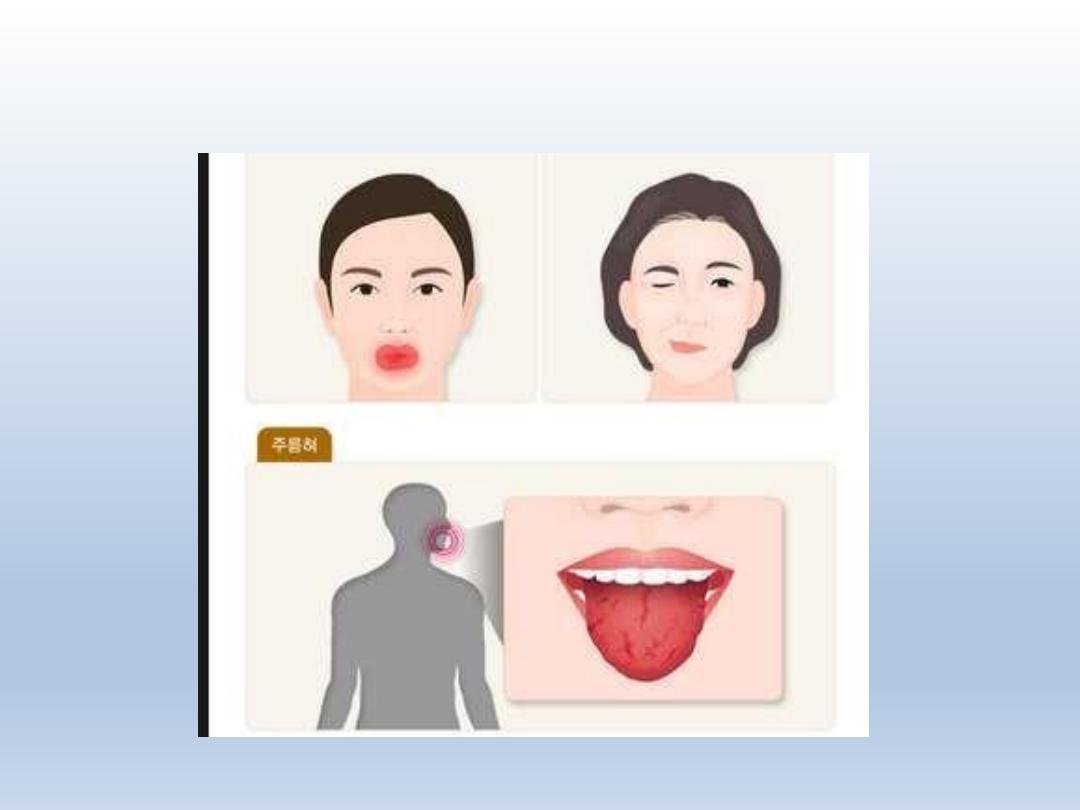
Melketsson Rosenthal Syndrome
Lip swelling
Facial palsy
Fissured tongue
BMS
Burning Mouth Syndrome
Burning mouth syndrome (also called oral dysesthesia) occurs most
commonly in women after menopause.
The most commonly affected part of the mouth is the tongue (pain
in the tongue is termed glossodynia)
. A painful burning sensation may affect the entire mouth
(particularly the tongue, lips, and roof of the mouth [palate]) or just
the tongue
The sensation may be continuous or intermittent and may gradually
increase throughout the day.
Symptoms that commonly accompany the burning sensation
include a dry mouth, thirst, and altered taste
Possible consequences include changes in eating habits, irritability,
depression, and avoidance of other people.

Burning mouth syndrome is not the same as the
temporary discomfort that many people experience
after eating irritating or acidic foods. Burning mouth
syndrome is poorly understood. It probably
represents a number of different conditions with
different causes but a common symptom.
A common cause is the use of antibiotics, which
alters the balance of bacteria in the mouth, leading
to an overgrowth of the fungus Candida (a condition
called thrush). Ill-fitting dentures and allergies to
dental materials may be causes as well.