Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 2
P a g e
1
Imaging Technique
1 – Ba meal :
a - Double contrast Ba meal .
b – Single contrast Ba meal .
c – Biphasic Ba meal .
Indication of contrast radiography
1 - Assessment of duodenal stricture which cannot be overcome by endoscopy.
2 - Assessment of gastric emptying after surgery.
3 - To excludes or confirmed leak from anastomosis after gastric surgery by using water
soluble contrast.
Double contrast Ba meal technique :
a – Fasting 6 hours before examination .
b -Smooth muscle relaxant I.V 20 mg hyascine -N- butyl bromide ( Buscopan ) .
c - Distend stomach by gas producing agent .
d -Ba sulphate 200 ml .
e - Film taken in various positions to show each part of the stomach filled with Ba and
distended with air .
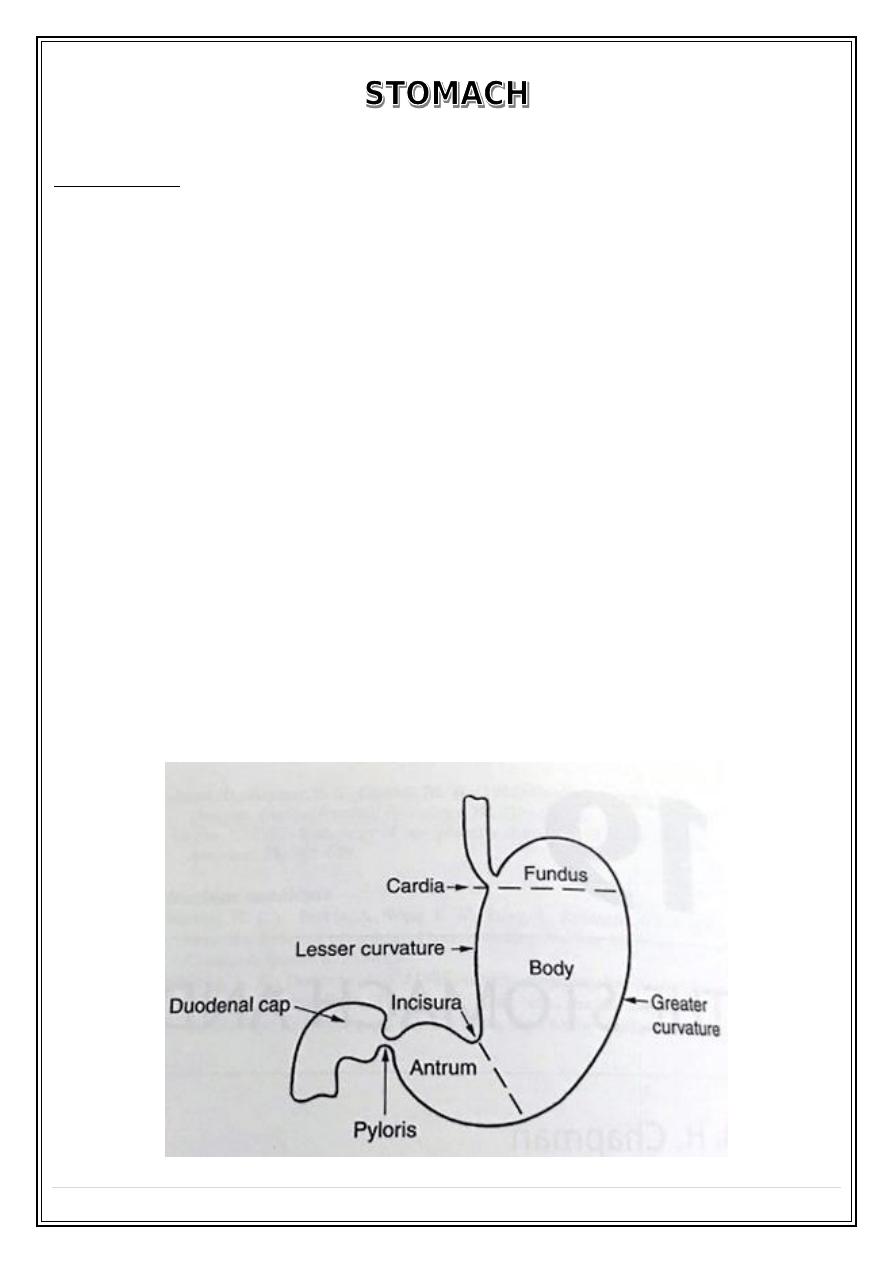
Anatomy of the stomach:
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
2
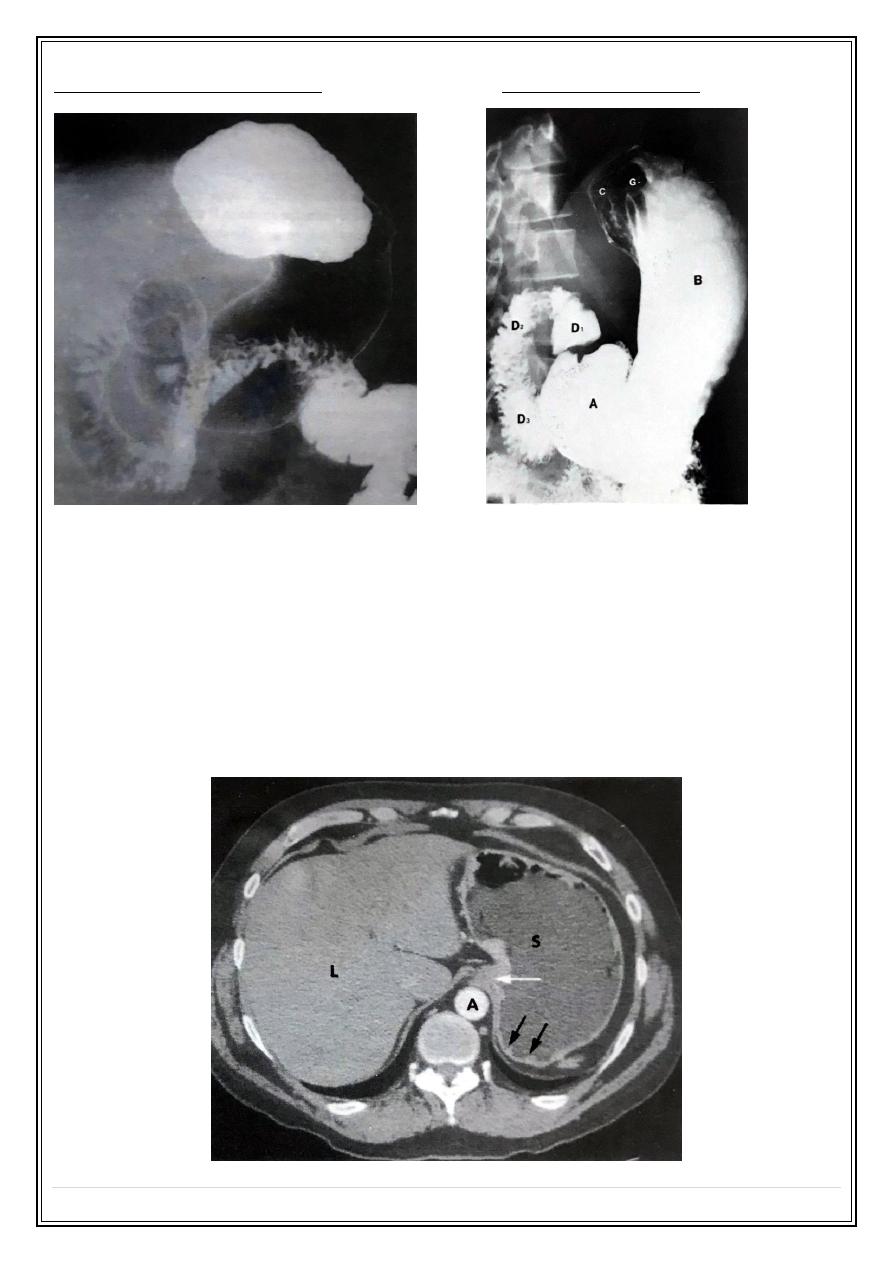
Normal double contrast Ba meal:
Single contrast Ba meal:
2-C.T stomach
Preparations :
1 - Fasting for 6 hours before examination .
2 - Smooth muscle relaxant 20 mg Buscopan I.V .
3 - Water ( 100 ml) for distention of the stomach .
4 – Intravenous contrast .
Normal CT of the stomach:
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
3
. Peptic ulcer
•
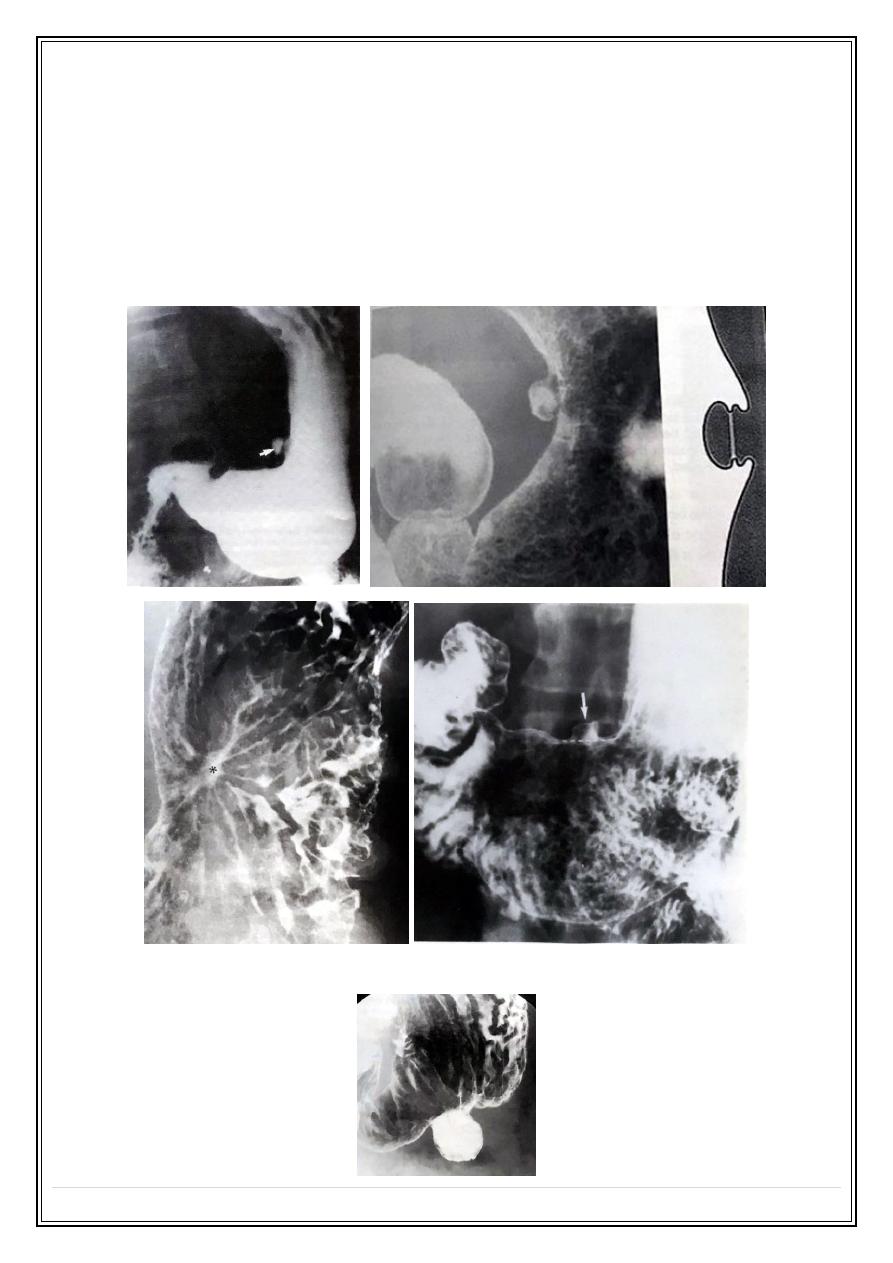
Gastric ulcer : is a breach of gastric mucosa contains Ba seen as outward
projection on profile view and appear round on enface view .
•
Benign ulcer most frequently occur along the lesser curvature of the stomach .
•
Aspirin and non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs cause ulcer in the greater
curvature .
Benign gastric ulcer:
Sump Ulcer:
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
4
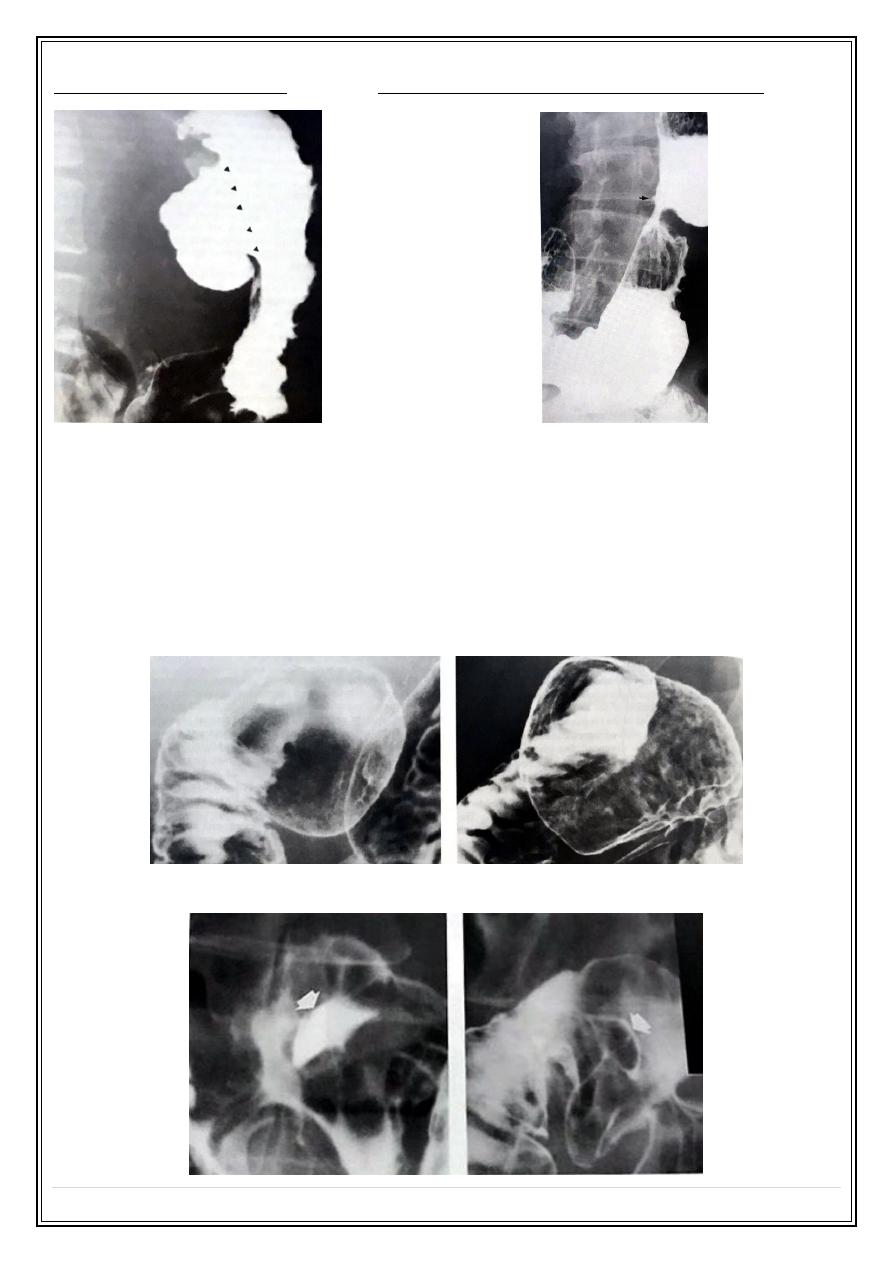
Giant benign gastric ulcer:
Hour-glass deformity of healed gastric ulcer:
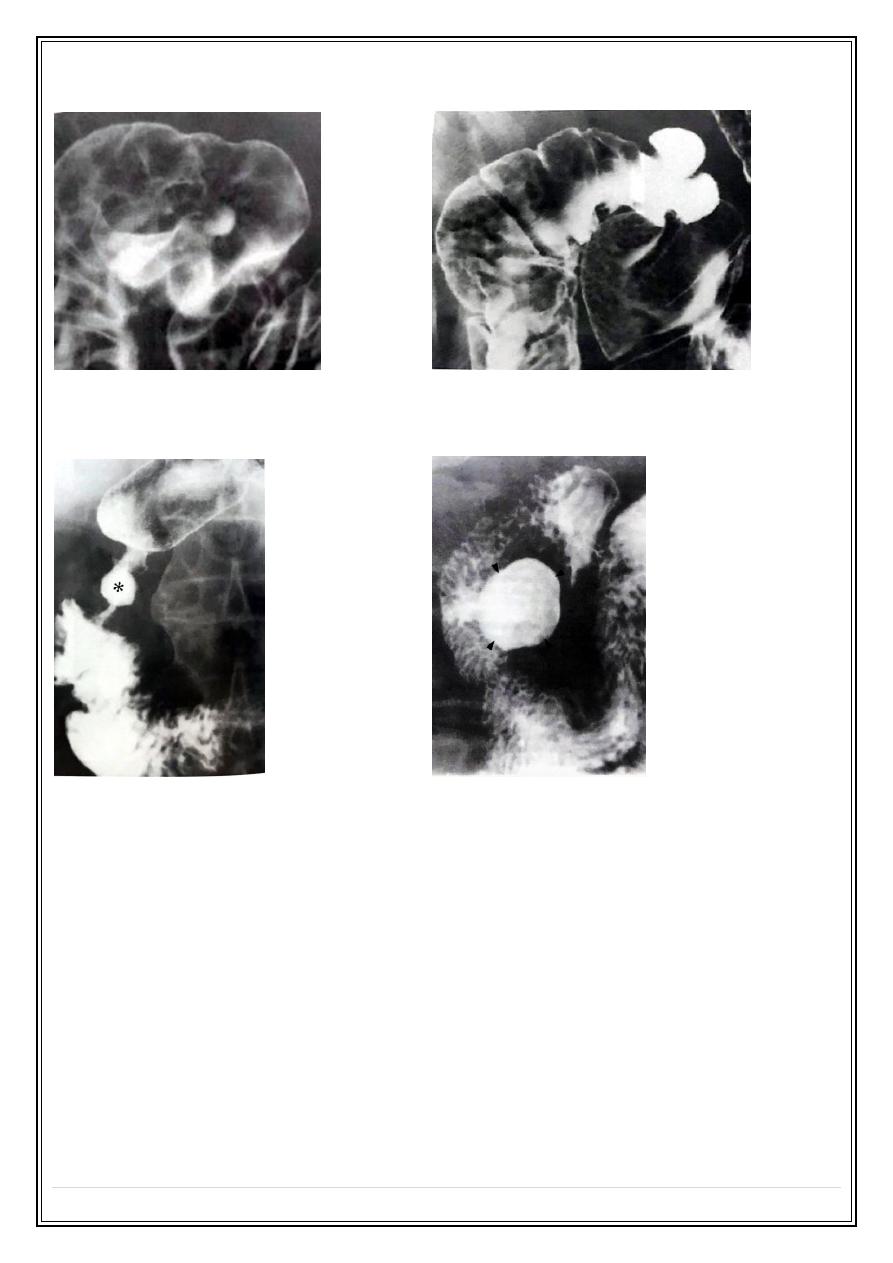
Duodenal ulcer:
* Duodenal ulcer are almost benign .
* It is four times more than gastric ulcer .
* In chronic duodenal ulcer the duodenal cap may be deformed.
Normal duodenal bulb:
Anteriorly located duodenal ulcer:
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
5
Posterior duodenal ulcer:
Deformed duodenum:
Postbulbar ulcer:
Duodenal Diverticulum:
Gastric tumors:
. Predisposing factors :
1 - Atrophic gastritis.
2 - Post H. Pylori infection .
3 - Adenomatous polyp .
4 - Pernicious anaemia .
5 - Partial gastrectomy .
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
6
Early gastric carcinoma
Confined to the mucosa and submucosa irrespective of regional L.N involvement, 5
years survival 90 % .
Advanced gastric carcinoma
The tumor invade the muscularis propria and May protrude into the stomach lumen and
can be polypoidal , fungating , ulcerated or infiltrative .
Spread of gastric tumors:
1 - Lymphatic .
2 - Peritoneal.
3 - Hematogenous mainly to the liver .
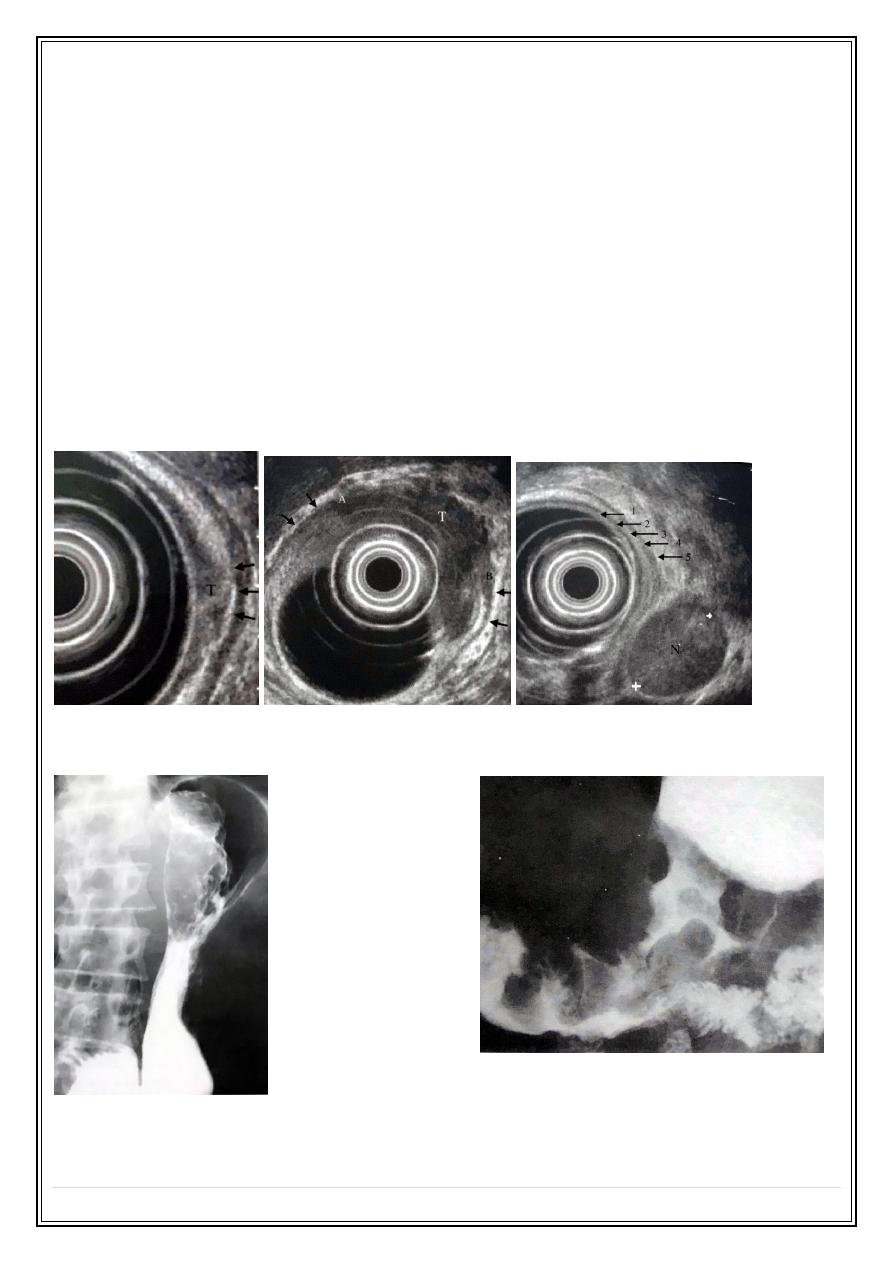
Endoscopic Ultrasound of gastric tumor:
Ba meal gastric tumors produce irregular filling
defect
with or without non projecting ulcer:
Gastric tumor:
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
7
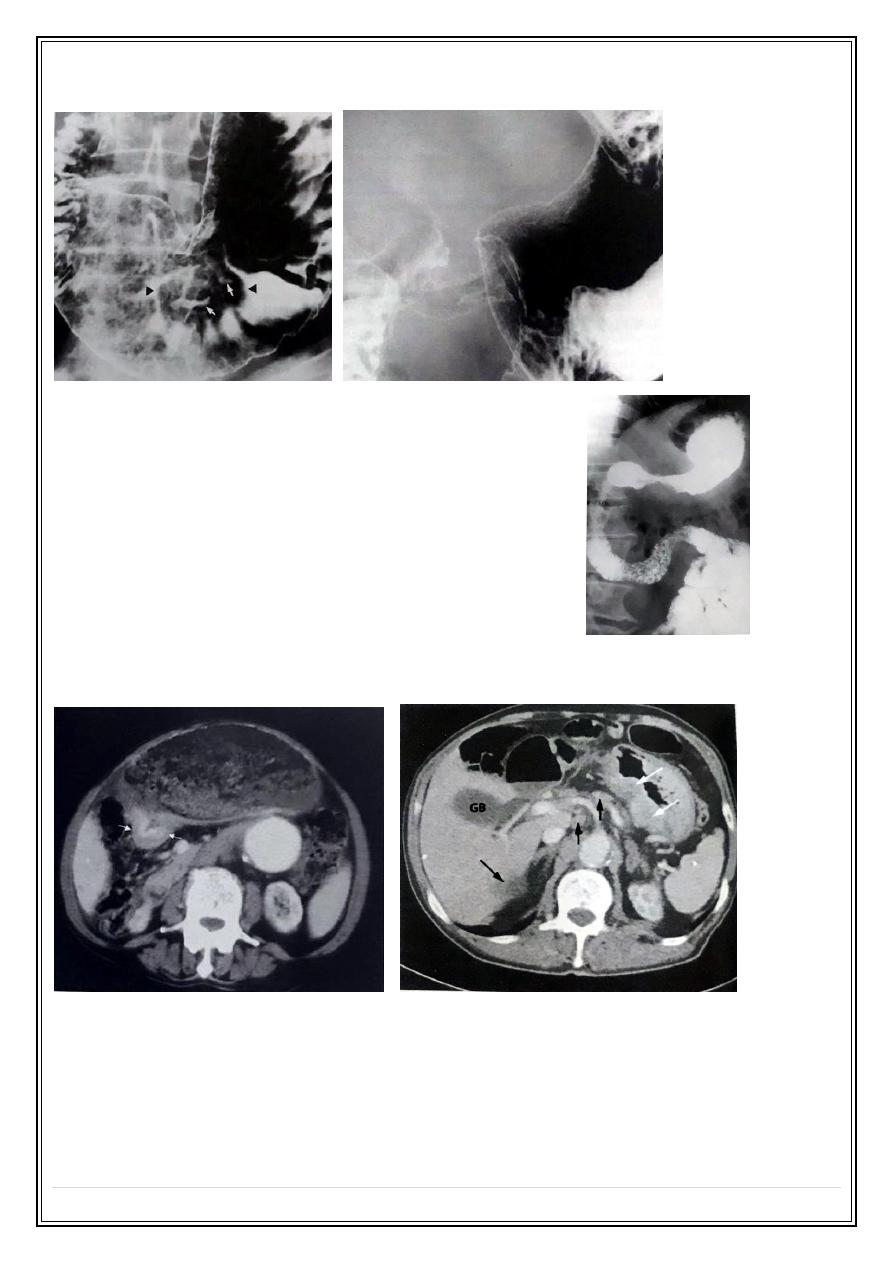
Stomach tumor with ulcers / narrowing in the gastric antrum:
In case of infiltrative gastric carcinoma the stomach
develops a leather bottle appearance ( linitis plastica ):
C.T used for preoperative staging as it can shows the extent of the primary tumor, L.N
enlargement and liver metastasis:

Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
8
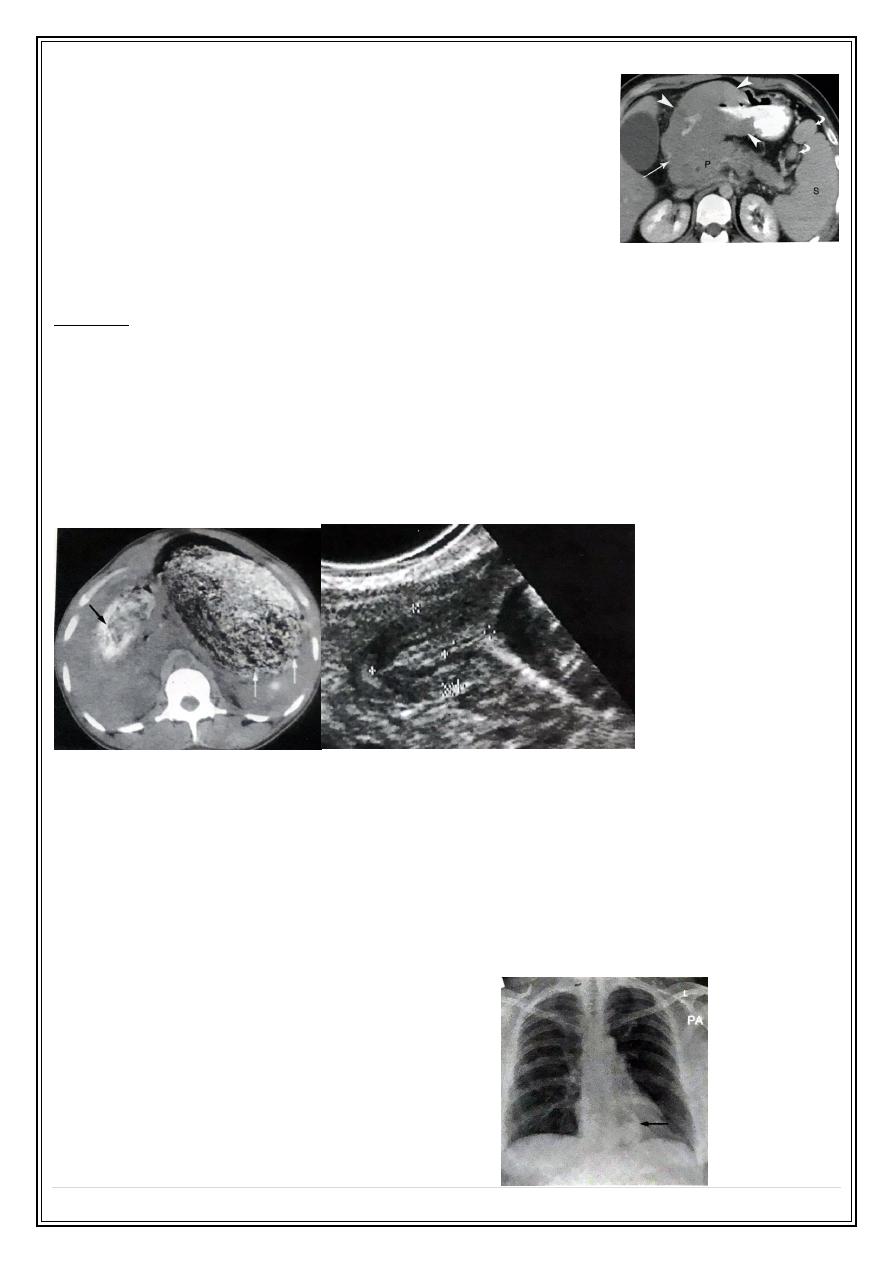
Advance gastric tumor with vascular encasement:
Gastrointestinal stromal cell tumors
Usually benign and well differentiated stromal cell tumors occur any where in GIT ,
about 60-70% seen in the stomach wall as smooth, rounded submucosal filling defect
which may ulcerate e.g. Leiomyoma .
Leomyoma:
Neuroendicrine tumors of the stomach and duodenum include carcinoid and gastrinoma
which secret hormones and causes severe symptoms when it small in size.
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
9
Gastric lymphoma
The stomach is the most common site involved by lymphoma,
seen as area of diffuse thickening of the stomach wall with or
without L.N enlargement, it may mimic gastric carcinoma.
Gastric outlet obstruction
Dilated stomach contains food residue with delay emptying time.
Causes :
1 - Chronic duodenal ulcer.
2 - Gastric antrum tumor .
3 - Periampullery tumors.
4 - Pancreatitis.
5 - Infantile hypertonic pyloric stenosis.
Hiatus hernia
Herniation part of the stomach into the mediastinum through diaphragm hiatus .
1 - Sliding H.H is the commoner type in which gastro-Esophageal junction and part of the
stomach located above diaphragm, usually associated with gastro-Esophageal reflux
disease .
2 - Rolling ( para-Esophageal) hernia in which gastric fundus herniated into the
mediastinum with gastro-Esophageal junction still below the diaphragm, it is rarely seen
Mass with air fluid level through the heart:
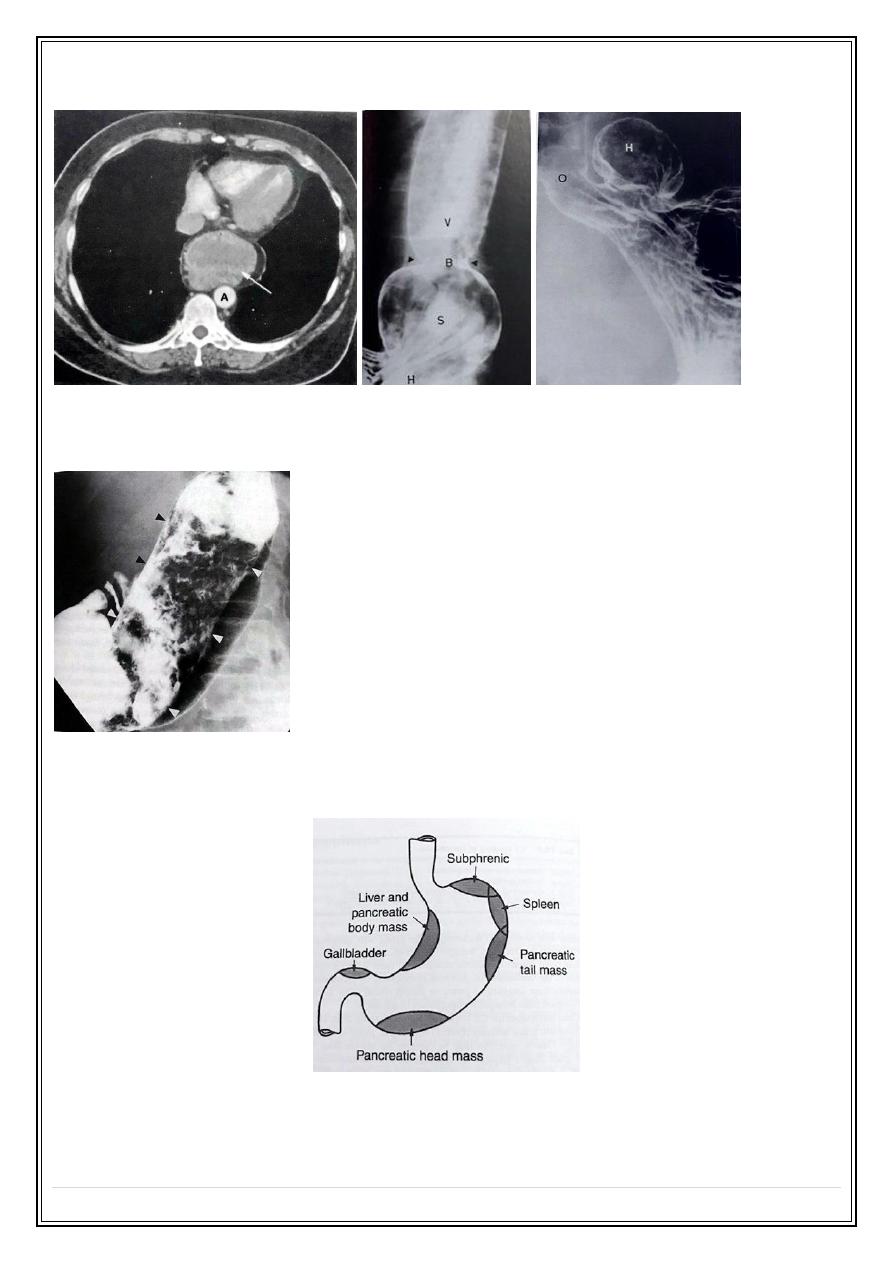
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
10
CT H.H:
Bizora:
Sites of extrinsic gastric compression:
Thank you,,,
