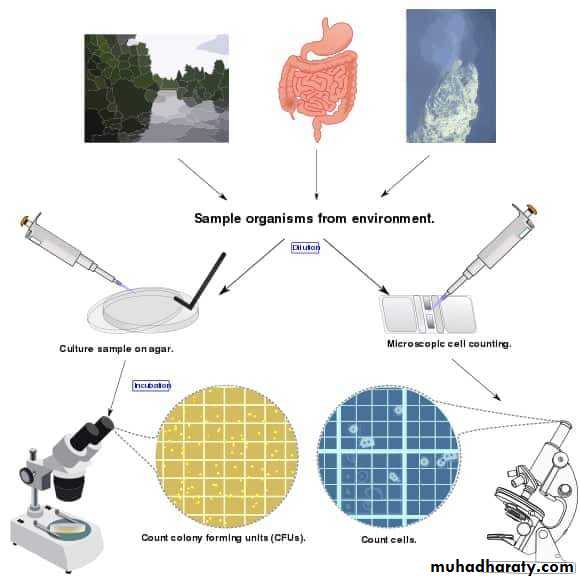
Culture of microorganisms from the environment
Microorganisms are found throughout the environment.
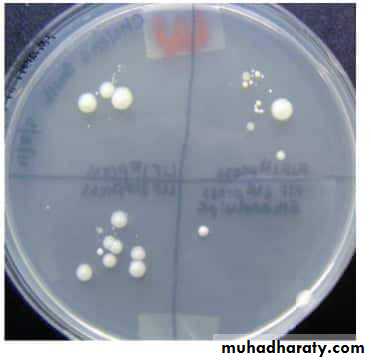
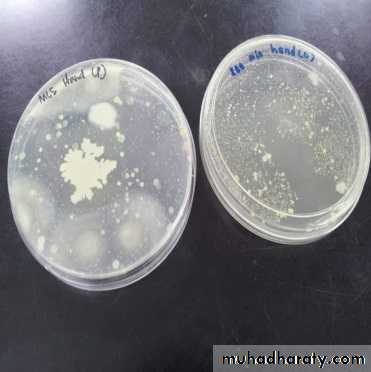
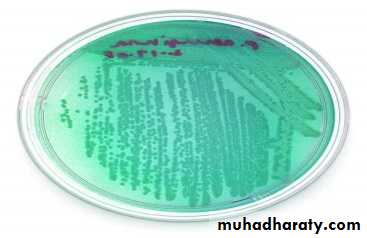
For better study of these microorganisms pure culture is need.Pure culture means a single kind of microorganisms growing alone in a protected environment.
To demonstrate the presence of m.o. in any environment, the media and the equipment to be used must be sterile and the technique must be aseptic to prevent contamination from sources other than the one being investigated.
Two methods are widely used for the preparation of pure cultures from laboratory specimens containing mixed m.o. :
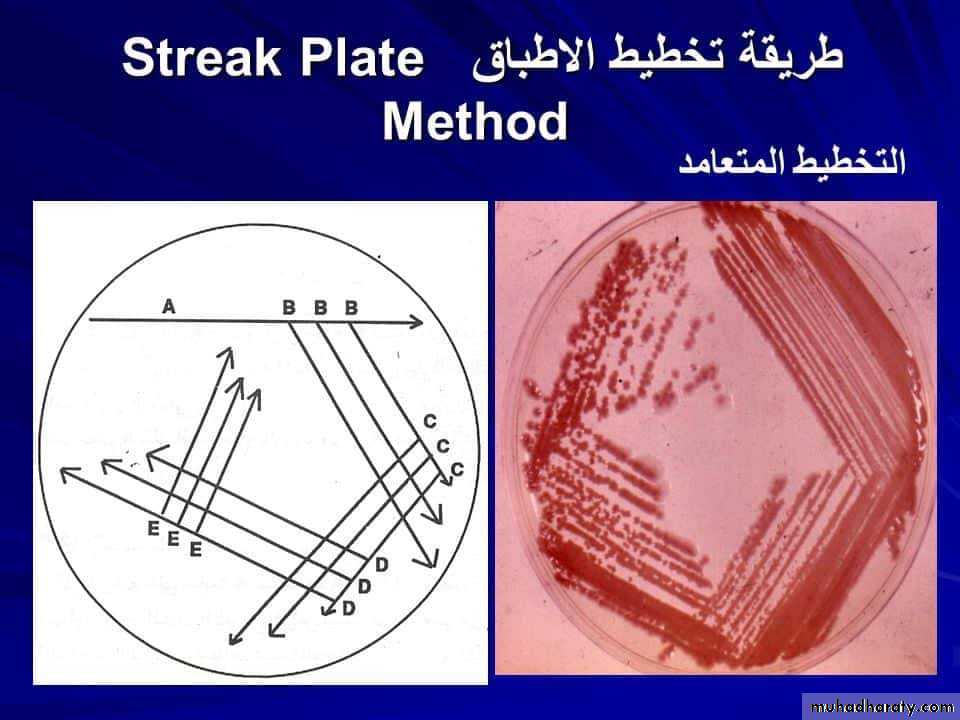
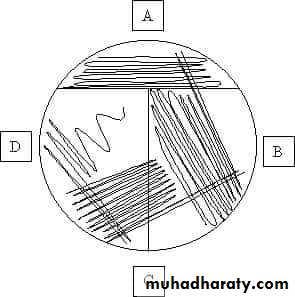
1. Streak plate method ( Quadrant method ).
2. Pour plate method.
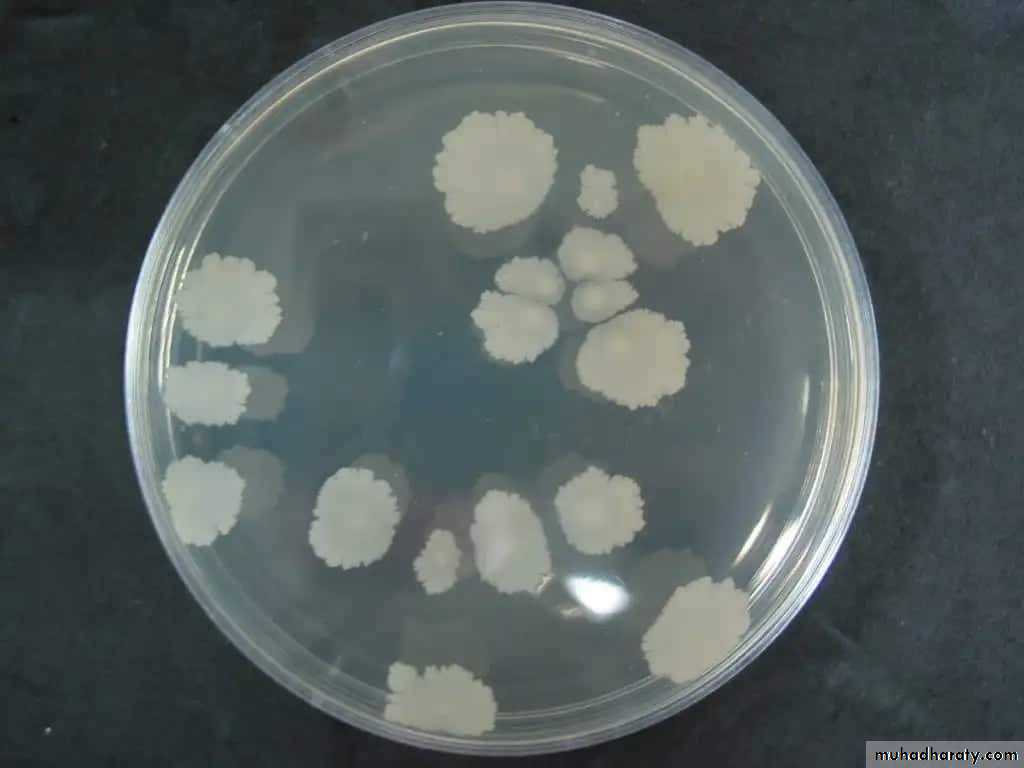
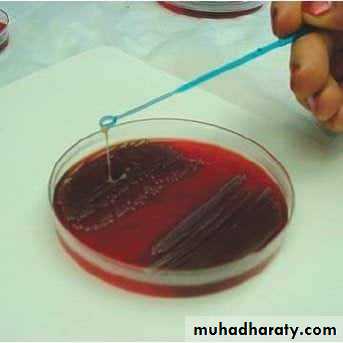
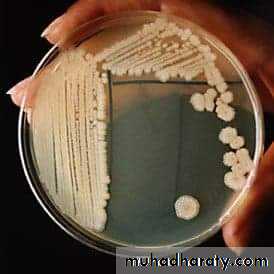
Streak plate method
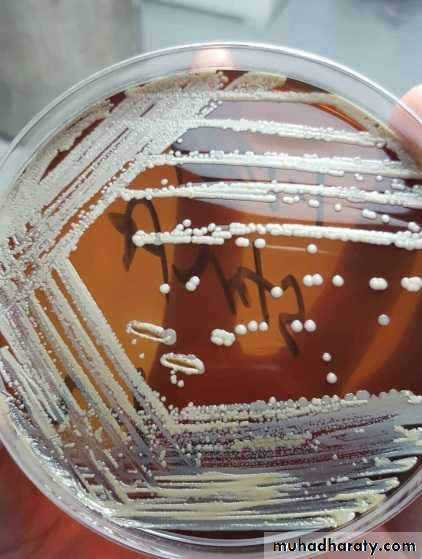
This method is employed for the isolation of pure culture of bacteria from mixed population, e.g., sputum, urine, stool, pus from infected wound and abscess.
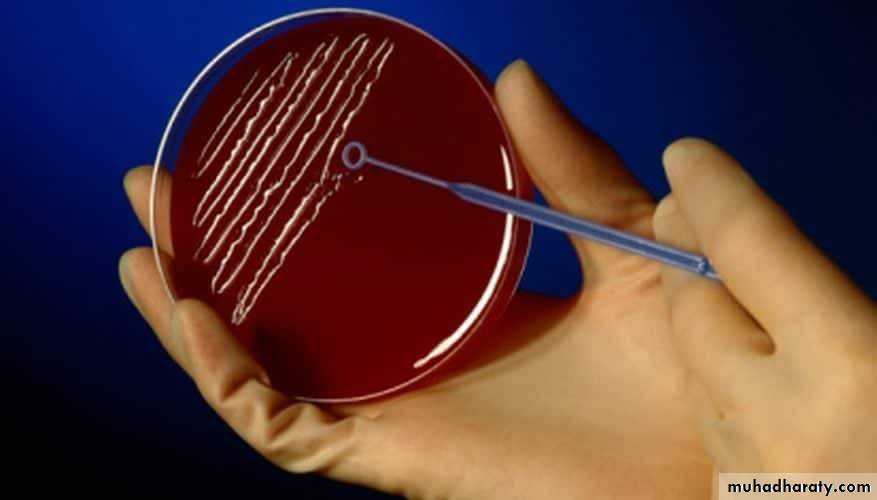
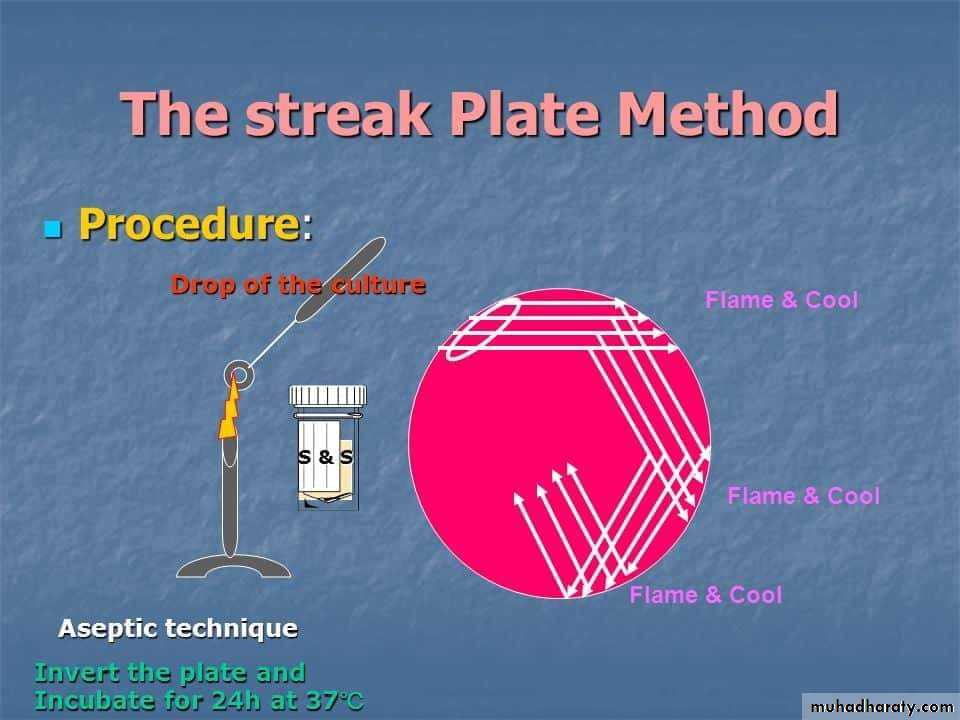
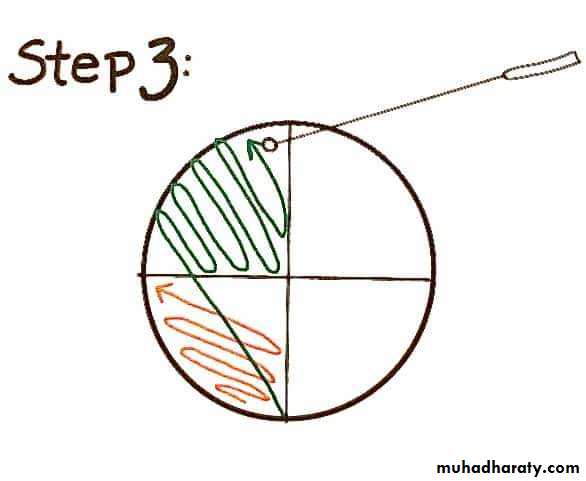
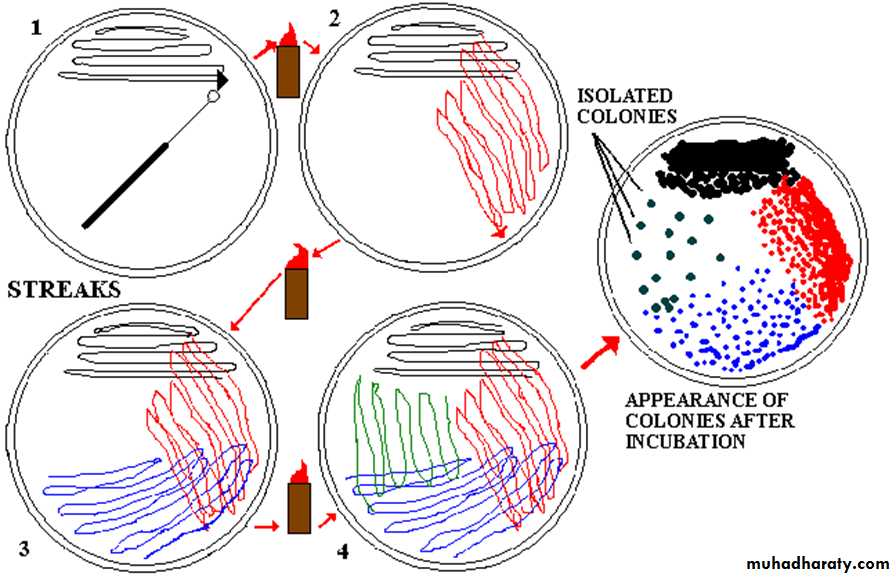
Technique of streak plate method
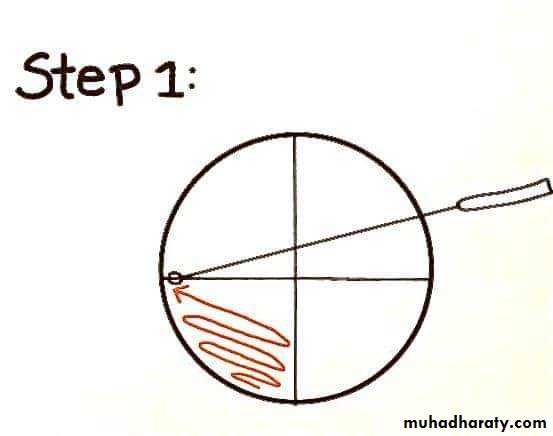
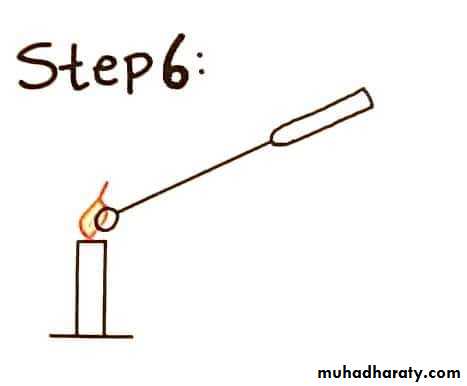
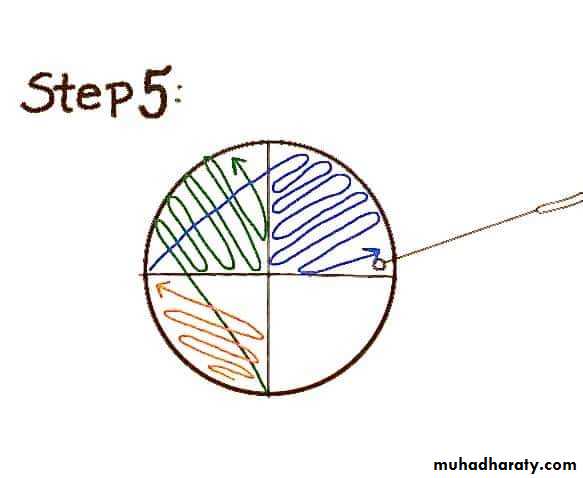
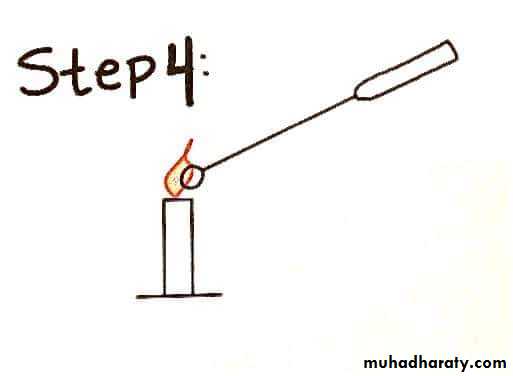
Sterilize the loop in a Bunsen flame, cool it and streak the specimen over an area – A.Re – sterilize the loop, cool it, then streak over an area – B from the distal part of area – A.
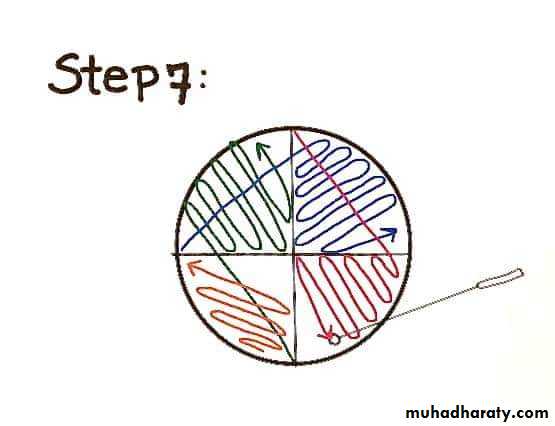
Continue the streak in the same manner to areas C and D.
Incubate the plates at 37º C for 24 hours.
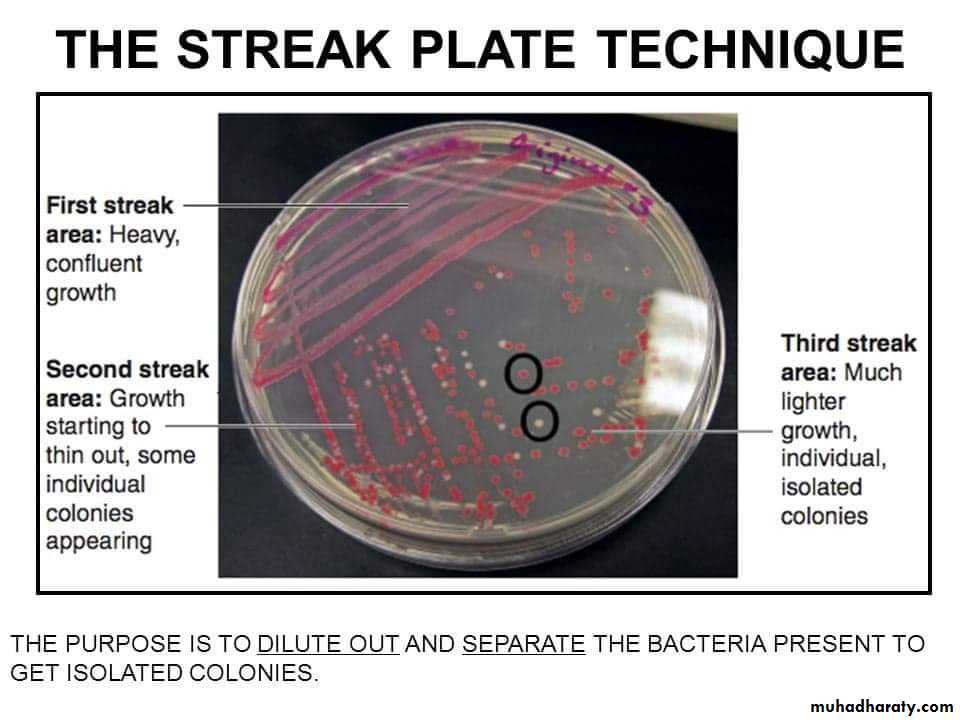
A subculture is done after 24 hours incubation from one of the colonies, needed for study on to a sterile medium following the same technique mentioned above, the culture produced is a pure one.
Pour plate method
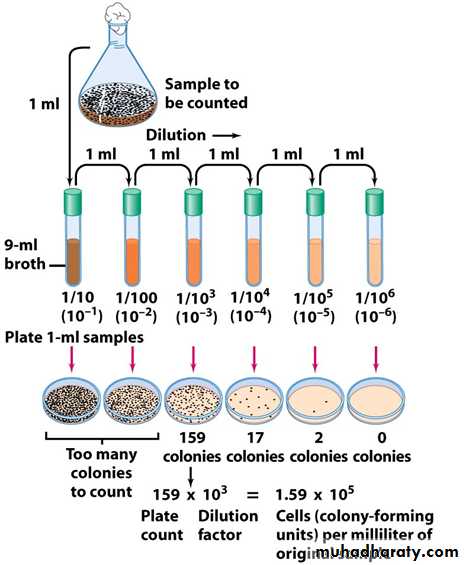
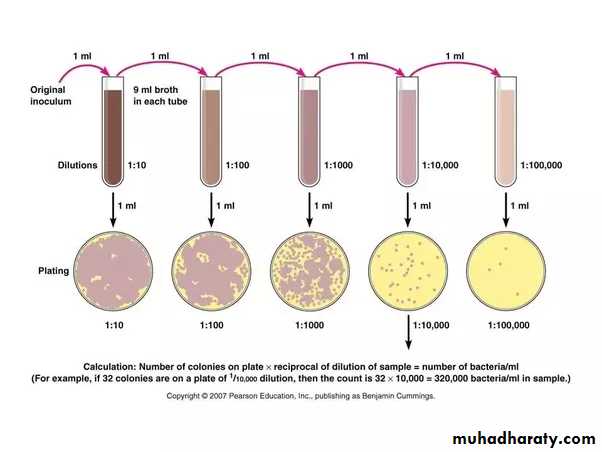
This technique deals with the isolation of pure cultures from a mixed bacterial suspension by serial dilution and plating.Technique of Pour Plate Method :
Make serial dilutions of the specimen, e.g., food, stuff, water, …… etc.
Mix the dilutions of the specimens with melted media in tubes.
Quickly pour the content of each tube into sterilized plates, this is called plating.
Incubate at 37º C after solidification of the melted media.
NOTE :
In both methods ( No. 1 & 2 ) it is essential that the medium surface is dry to obtain discrete colonies.
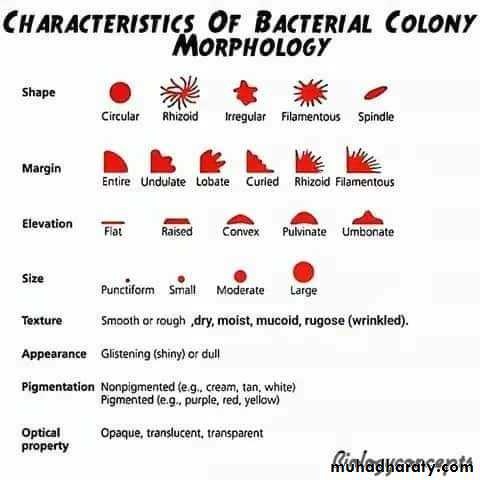
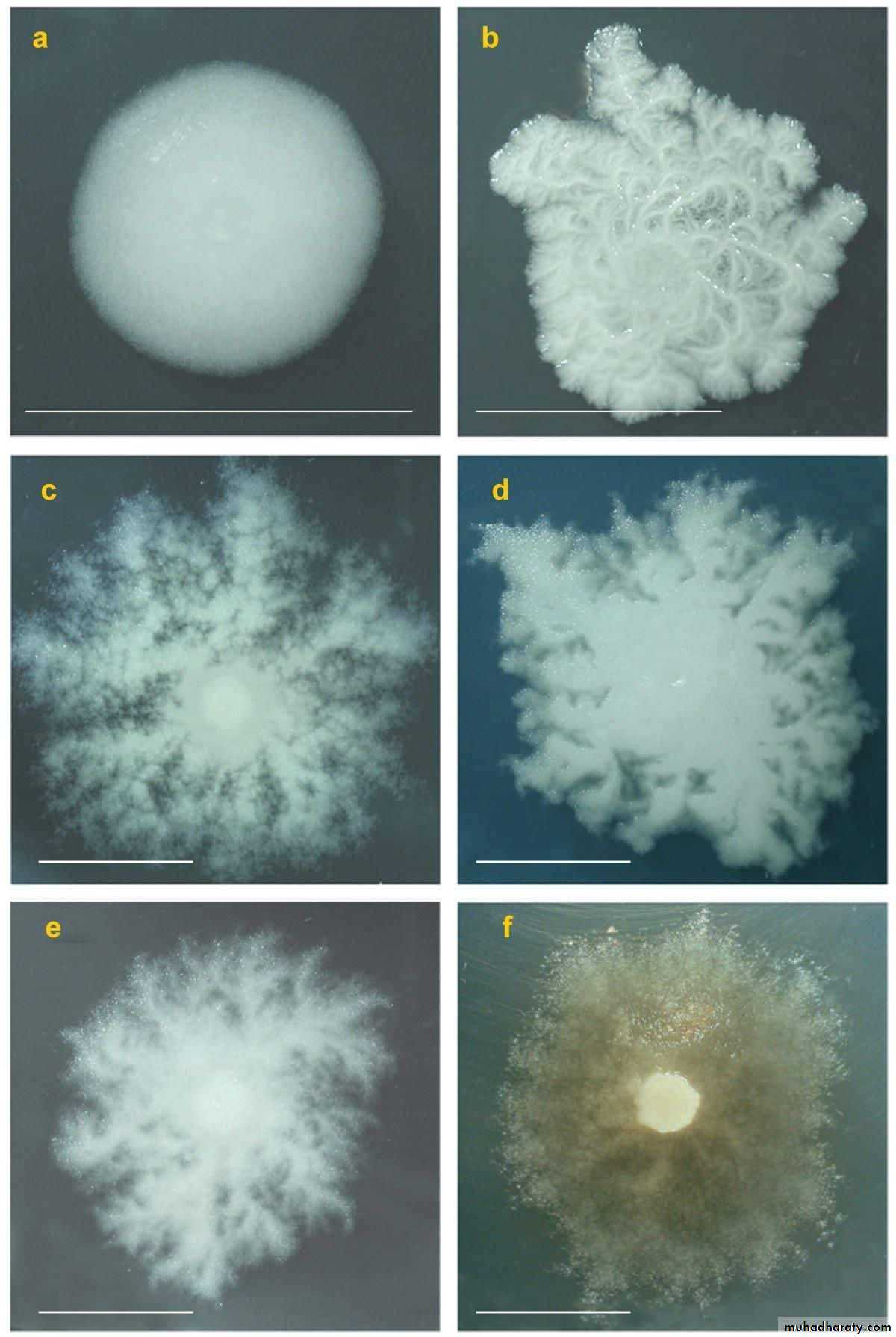
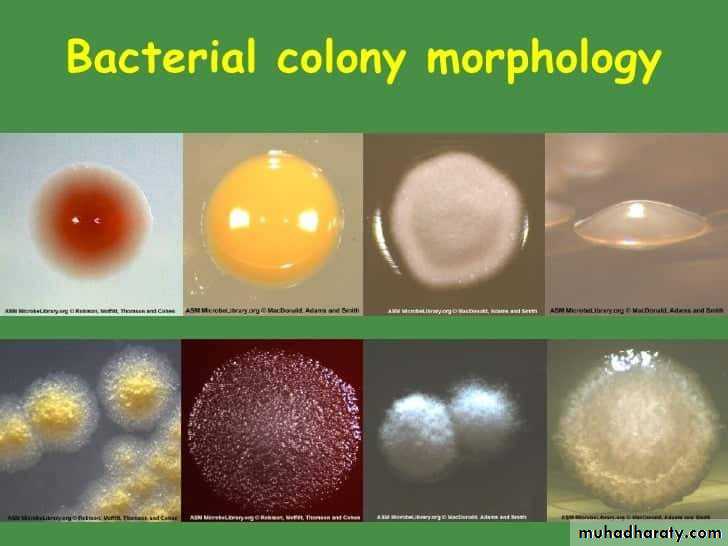
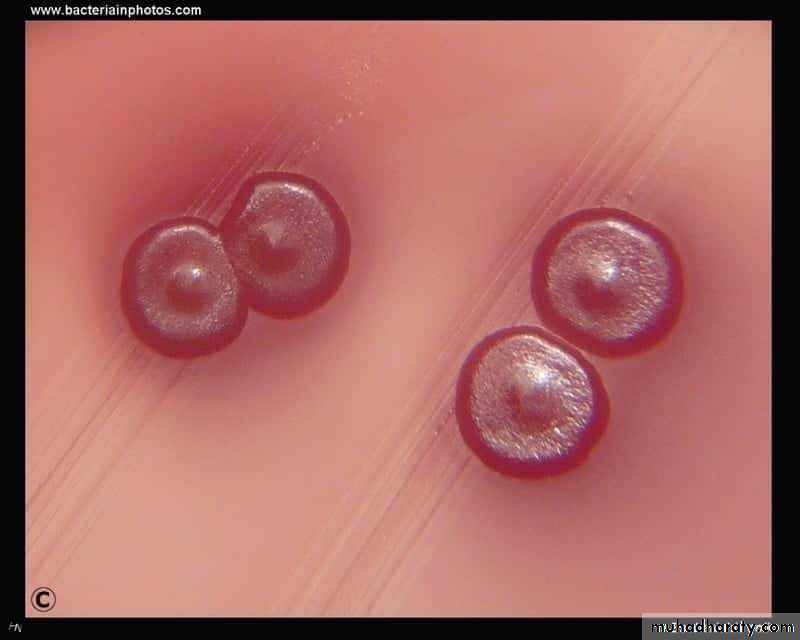
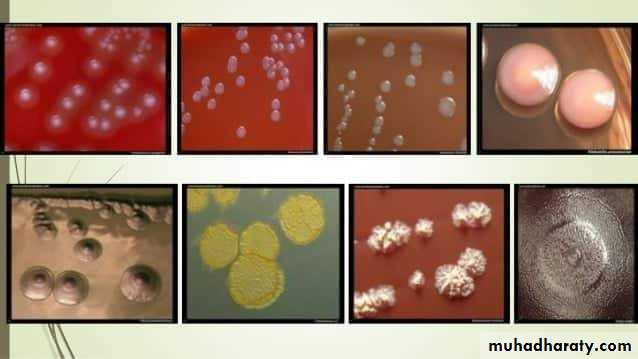
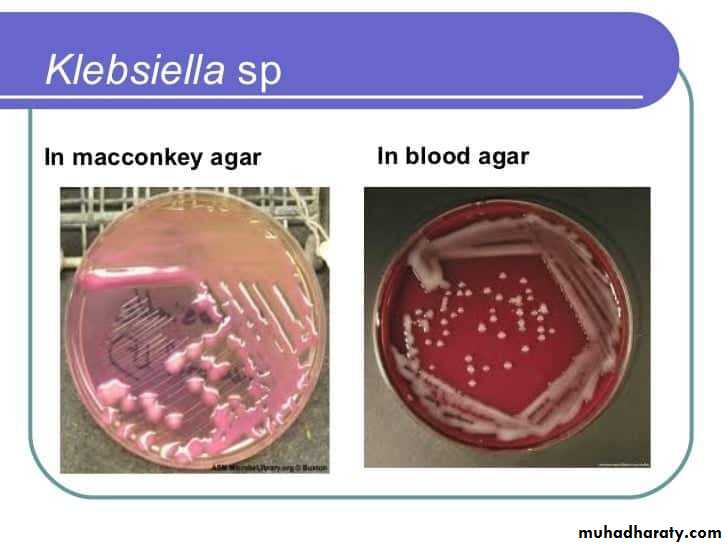
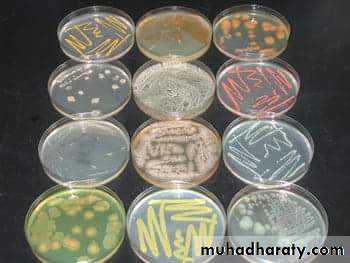
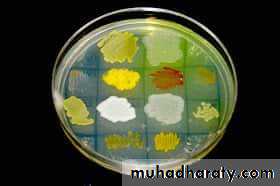
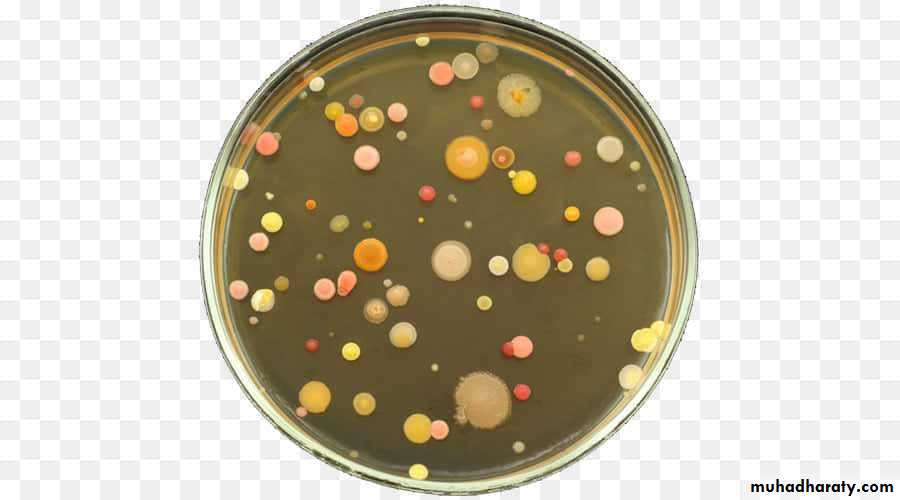
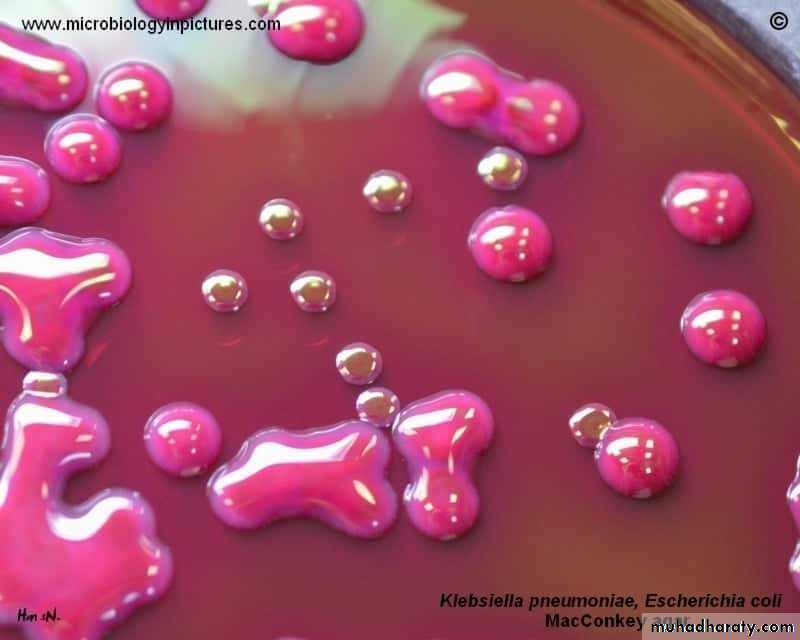
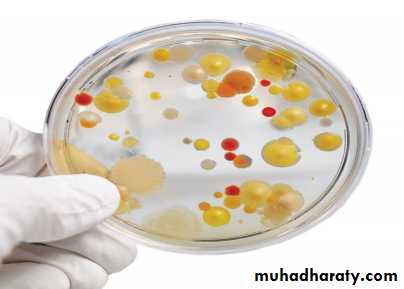
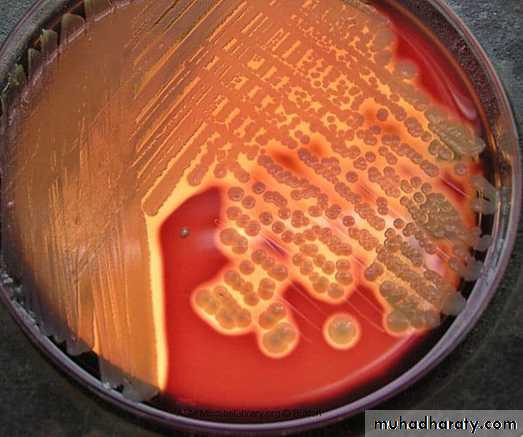
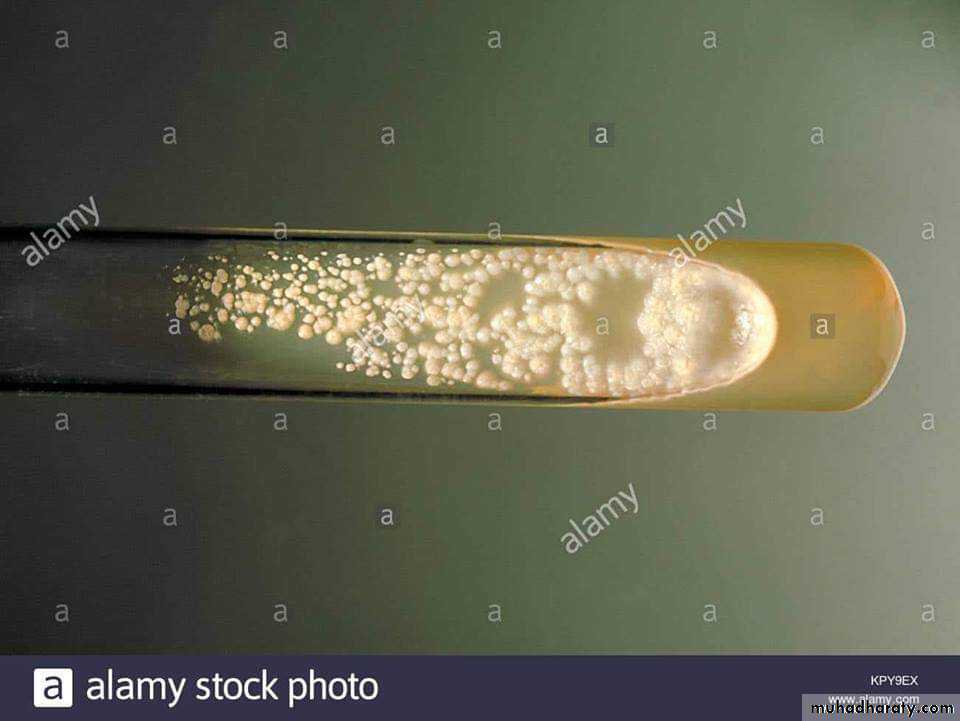
Cultural characteristics :
To study the macroscopic characteristics of a pure culture on a solid medium, the following points have to be considered in describing a colony :Size : measured in m.m.
Shape : punctiform, circular, rhizoid, irregular, filamentous, spindle.
Elevation: flat, raised, convex, umbonate.
Margin : entire, lobate, filamentous.
Cultural characteristics :
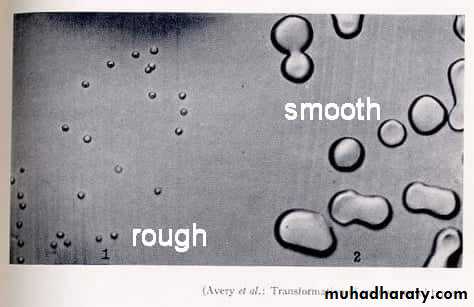
Consistency : dry, mucoid.Surface texture : smooth, rough.
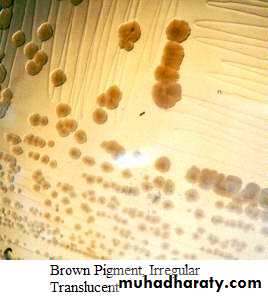
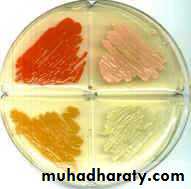
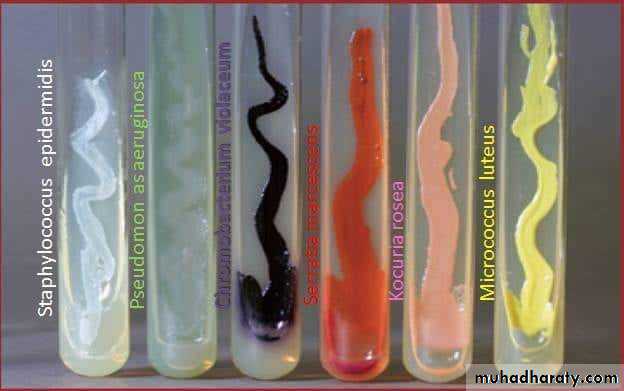
Colour or pigmentation : white, cream, yellow, green, pink, red, purple, ….. etc.
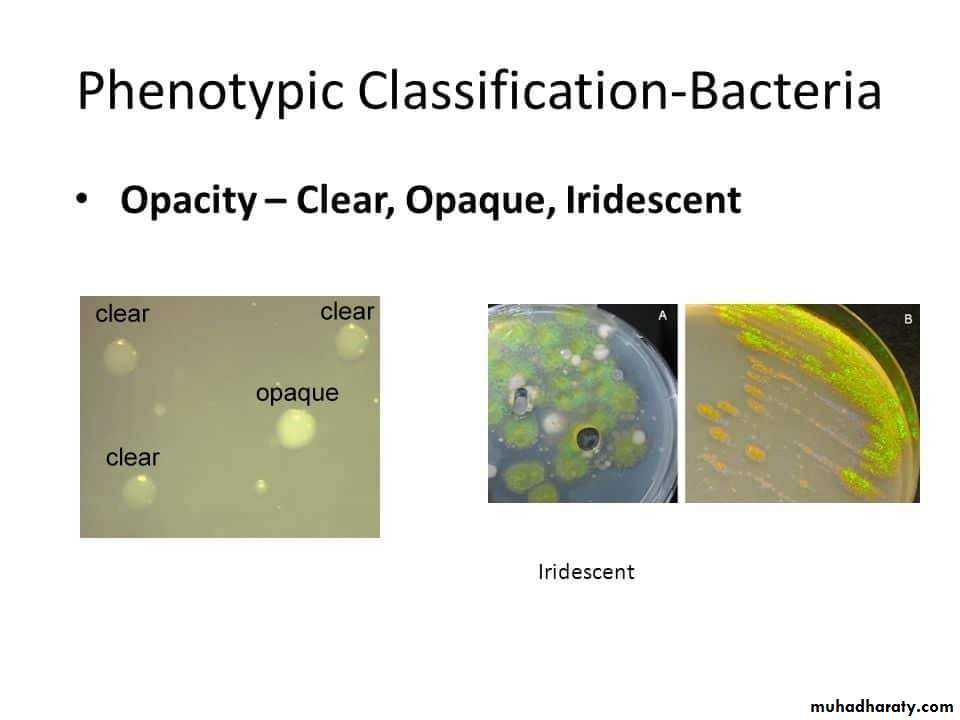
Optical density : opaque, translucent, glistening.
Cultural characteristics :
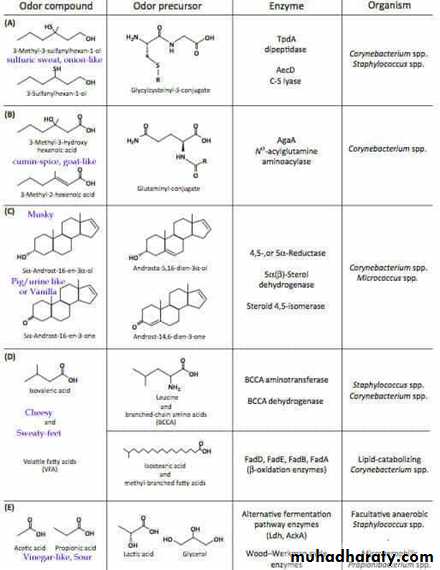
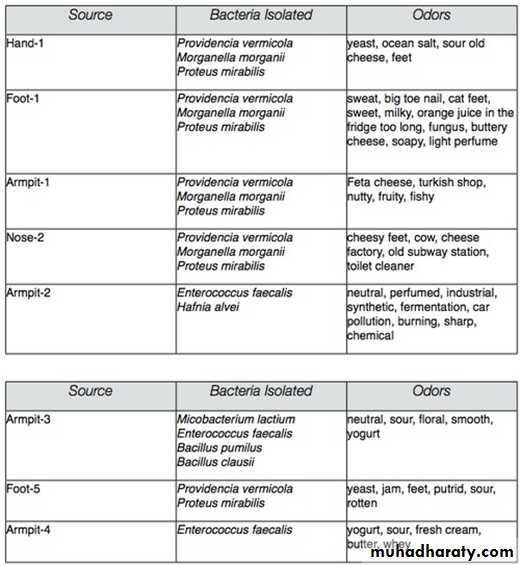
Odour : bad odour, sweat musty odour.
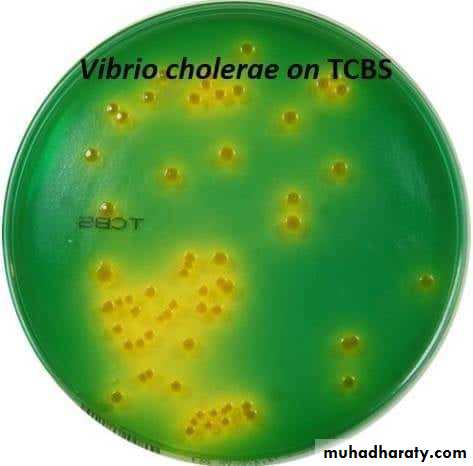
Changes in the inoculated medium: hemolysis, bile precipitation,e.g.
TCBS agar.
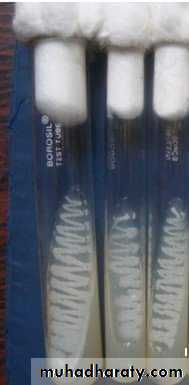
Stock culture :
Stock culture means the preservation of a microorganism in a culture medium for future study, it can be kept usually for about one month at 4º C.Technique of stock culture :
Use a universal bottle containing medium in a slanted position ( to prevent a wide surface for inoculation and good nutrition ).
Using a sterile loop inoculate the surface of medium with on or few colonies of a pure culture.
Incubate the inoculated medium at 37º C for 24 hours, then store at 4º C.