Staphylococci
Genus staphylococciIncludes more than 35 species, the most three important are:
Staphylococcus aureus (pyogenes)
Staphylococcus epidermidis (albus)
Staphylococcus saprophyticus (citreus)
General characteristics
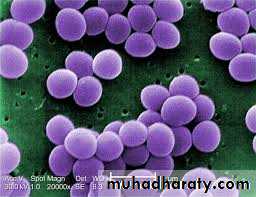
Gram positive cocci, grow in grape-like clustersNon-motile
Non-spore former
Aerobic & facultatively anaerobic
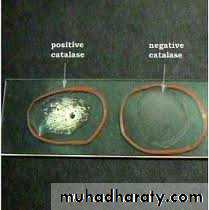
Catalase test: Positive
Usually uncapsulated
Some are members of the normal flora of skin & mucus membrane of humans
The pathogenic spp. Produce a variety of enzymes & toxins
Staph aureus is coagulase test : POSITIVE
Staph epidermidis is coagulase test : NEGATIVE
Staph saprophyticus is coagulase test : NEGATIVE
Coagulas negative Staphylococci are normal flora but sometimes can cause infections.
Nasal carriage of Staph aureus is 20-50 % of humans.
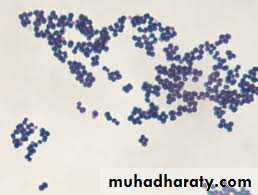
Microscopical appearance
Gram positive cocci arranged in irregular clusters.
Spherical, non-capsulated
Non-motile & non-spore forming.
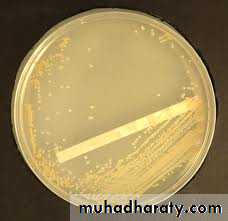
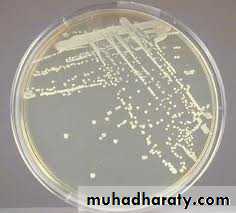
Cultural characteristics
Aerobic and facultatively anaerobic.Can grow on simple medium like nutrient agar
2-3 mm after 24 hrs incubation at 24hrs.
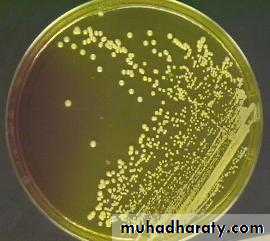
Circular, convex, opaque, smooth, moist with entire edge and pigmented.
Selective medium for growth of Staph aureus is manitol salt agar ( with NaCl conc. Of 7.5-10%).
Genus staphylococci
Staphylococcus aureus (pyogenes)Golden –yellow colonies
Cont,
Staphylococcus epidermidis (albus)White colonies
Cont,
Staphylococcus saprophyticus (citreus)Lemon or yellow colonies
Biochemical tests
Catalase testAll staphylococci are catalase test POSTIVE
All streptococci are catalase test NEGATIVE
Staphylococcus aureus
Is the major pathogen oneDiseases caused by Staph aureus
Boils, furuncle, styes, impetigo & pyoderma.
It may cause more serious infection such as pneumonia, deep abscesses, osteomylitis, endocarditis, phlebitis, mastitis, meningitis & suppuration of any organ.
Pathogenesis of Staph aureus infection
It has many virulence factors such asAdherence:
Express on their surface proteins that promote attachment to host proteins such as laminin & fibronectin that form part of the normal extracellular matrix.
This fibronectin is present on endothelial cells .
These strains are associated with osteomylitis & septic arthritis.
Cont ,
Avoidance of host defenseProtein A :
Is a surface protein that can bind IgG by the FC region this will disrupt opsonization & phagocyotosis.
Alpha-toxin
Platelets & monocytes are sensitive to this toxin .
This allow toxin to bind to these cells with secondary reactions causing release of inflammatory mediators that may lead to septic shock.
Cont,
γ- toxin & leukocidin
These two components cause damage of the membrane of susceptible cells
May cause necrotizing skin infections
Superantigens ( enterotoxin & toxic shock syndrome toxins
Enterotoxins cause food poisoning
Toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 when released systemically .e.g: tampon –associated TSS is caused by growth of Staph aureus on the tampon and the release of the toxin, its absorption into the blood circulation.
Cont,
Epidermolytic exfoliative toxin ( ET)This toxin cause scalded skin syndrome in neonates.
This toxin has protease activity .
Coagulase
Is an extra-cellular protein that binds to prothrombin in the host to form a complex called staphylothrombin resulting in the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin. This allow bacteria to avoid host defense by causing localized clotting.
Cont,
It can express lipase, deoxyribonuclease & protease that are important in forming abscessesStaphylokinase resulting in fibrinolysis.
Β-lactamase
Staph epidermidis
It lack virulence factors & toxins compared to Staph aureus.Major cause of infections associated with prosthetics valves & catheters
Can cause peritonitis in patients receiving peritonial dialysis, endocarditis in patients with prosthetic valves.
These infections are often chronic.
Pathogeneis of Staph epidermidis
Adhesion is the 1st step in infection
An interaction between the Staph epidermidis & plastic material.
This bacteria will form a biofilm on the surface of a prosthetic device.
Is a common cause of infections associated with indwelling devices such as joint prostheses, cardiovascular devices.
Staph saprophyticus
Cause urinary tract infection in young womenIs novobiocin –resistant.
Lab diagnosis
Clinical specimen: swab from pus, blood, CSF, urine.Direct Gram stain
Culture
Only Staph aureus can grow on manitol salt agar.
Catalase test : to differentiate it from streptococci
Coagulase test: only Stahph aureus gives +ve test
Antimicrobial drugs
Staph aureusRapidly acquire resistance to antibiotics by plasmid, transposon or by mutation in chromosomal genes.
Penicillin resistant Staph aureus produce penicillinas
β-lactamase production is common, under plasmid control, makes the organism resistant to many penicillins .
Staph aureus is susceptible to B-lactamase resistant penicillin, cephalosporin or vancomycin and methicillin.
Cont,
Resistance to nafcillin, methicillin and oxacillin, is independent of β- lactamase production.
It is under chromosomal control through special gene known as mec A gene which resides on bacterial chromosome. The resistance is related to the lack of certain penicillin binding proteins (PBPs) in the organisms.
Cont,
New vancomycin-resistance Staph isolated due to presence of Van resistance gene that was acquired from enterococci.Plasmid-mediated resistance to tetracyclines & erythromycins.
Staph aureus also express resistance to antiseptics & disinfectant that allows its survival in hospitals.