Pharmacology lecture
CNS
3
rd
Stage
1
LOCAL ANESTHESIA AGENTS :-
Reversibly block impulses conduction along nerve axon & other excitable membrane
that utilize sodium channel as the primary means of action potential generation that
end in blocking pain sensation from sympathetic vasoconstriction impulses to specific
area of body . cocaine consider as the first agent within this group discover at 1860 ,
no ideal(of no toxicity ) available . consisting of the lipophilic group (aromatic ring
connecting by 1- amide to ionizable group[tertiary amine ] , 2- ester group . ) so local
anesthesia classified as ester & amide types as follows :-
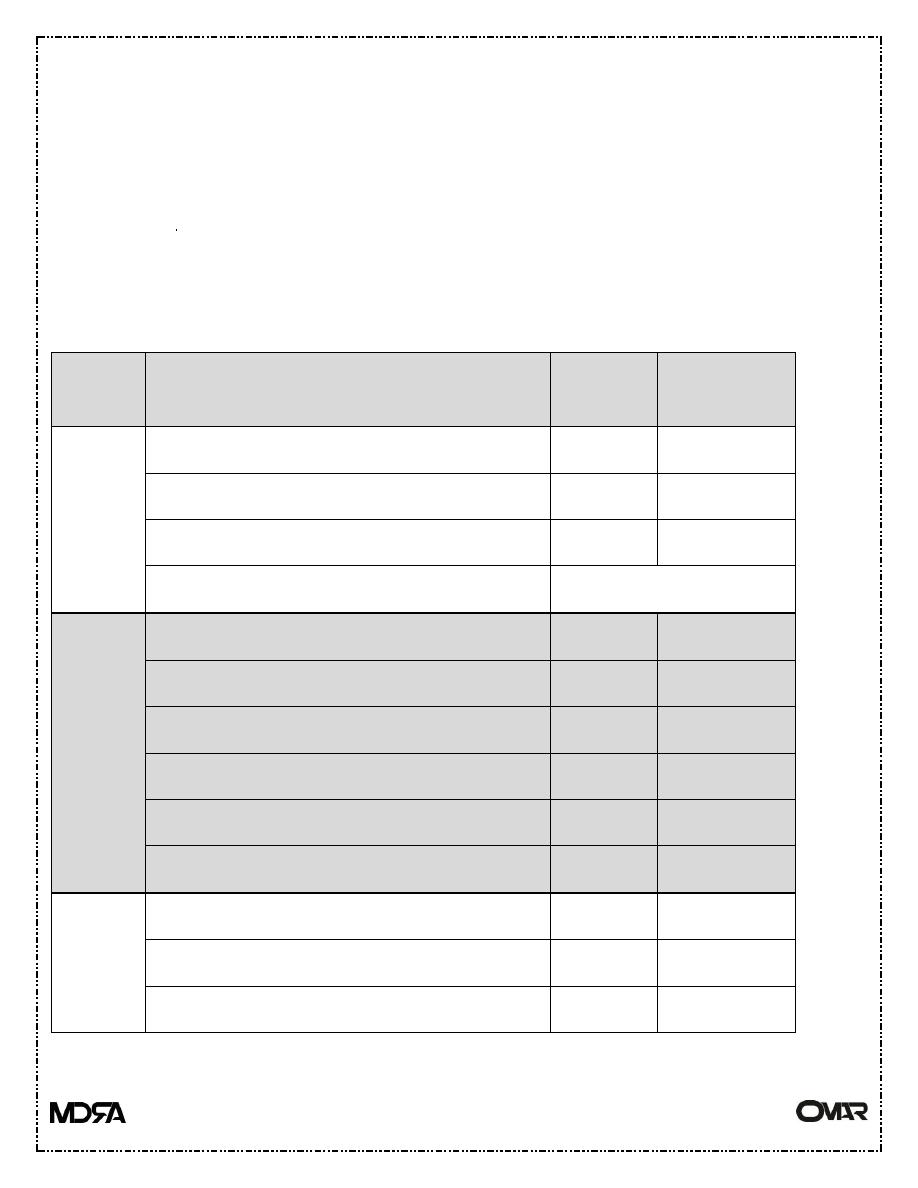
Type
Drug
Potency Duration of
action
Ester
Procaine
1(ideal ) Short
Cocaine
2
Medium
Tetracaine (pontocain)
16
Long
Benzocaine
Surface use only
Amides
Lidocaine(xylocaine)
4
Medium
Mepivacaine(carbocaine)(isocaine)
2
Medium
Prilocaine(citabest)
3
Medium
Bupivacaine
16
Ling
Etidocaine
16
Long
Ropivacaine
16
Long
Other
form of
L.A
Ether -like -pramoxine
Ketons –like - dyclonine
Phenetidin derivatives – phenacaine

Pharmacology lecture
CNS
3
rd
Stage
2
ESTER & AMIDE TYPE
Ester type of short duration of action & more prone to hydrolyze than amide type .
Local anesthesia less effective in infected tissues than health one because of the extra-
cellular pH that cause a very little amount of non-ionized local anesthetic agent to be
available for diffusion into the cells .
-absorption of local anesthesia their systemic absorption modified by the following
[dosage, site of injection , drug tissues binding , presence of vasoconstrictor agents ,
physiochemical properties of the drug (like adrenaline – epinephrine )] .
- their distribution the amide type of rapid distribution phase by highly perfuse organ
like liver –brain-heart –kidney & of slow distribution phase by moderately perfuse
organ like gut – muscles . while the ester type of short plasma half-life so not much
studied about their distribution .
their metabolism & excretion of local anesthesia :-
local anesthesia converted via liver or in the plasma into more water soluble
agent that excrete in the urine . the ester type hydrolyze very rapidly in the blood by
butyl-cholinesterase (pseudo cholinesterase ) make it of very short half-life about 1
min. for procaine & chloro-procaine . the amide form hydrolyze in the liver
microsomal cytochrome P450 in variable rate [prilocaine faster than etidocaine which
is faster than lidocaine which is faster than mepivacaine that faster than ropivacaine
that faster than bupivacaine which is the slowest one] so the toxicity may occur in
patients with liver diseases (lidocaine their half-life 1.8 hoyrs in normal person
increase up to 6 hours in patient with sever liver disease ) , also reduce blood flow to
the liver decrease the removal of local anesthesia ( lidocaine elimination by hepatic
system receiving halothane slower than that receive nitrous oxide or curare ) .
MODE of action of local anesthesia include that
---local anesthesia block voltage gated sodium channel by binding to their receptors
near intra-cellular part that increase threshold of excitation then slow the conduction
of impulses then decline rate of rise of action potential then decrease the amplitude
then abolish the ability to generate action potential , on increasing local anesthesia
concentration binding of local anesthesia be more & more to sodium channel ,
Pharmacology lecture
CNS
3
rd
Stage
3
---increase extra-cellular calcium increase surface potential on the membrane that
antagonist action of local anesthesia ,
--- increase extra-cellular potassium depolarize potential on the membrane so enhance
the effect of local anesthesia .
local anesthesia more lipophilic & smaller molecules be more potent & of long
duration of action & faster rate of interaction with the sodium channel .
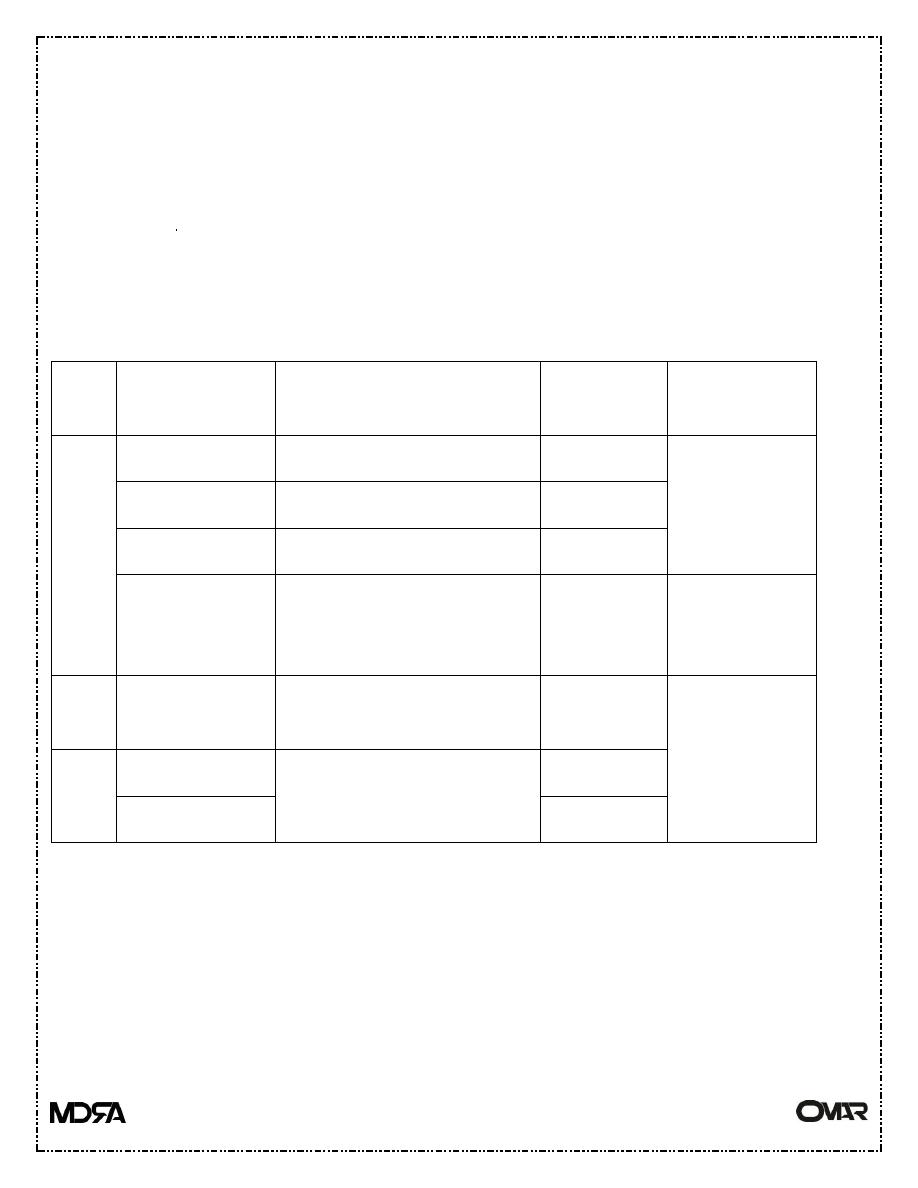
types of nerve fibers :-
Type Sub-type
Function
Sensitivity
to block
State of block
A
Alfa
Proprioception & motor
+
Block next
Beta
Touch & pressure
++
Gamma
Muscles spindle
++
Delta
Pain & temperature
+++
Small type A
fiber
block
next
B
Preganglionic
autonomic
++++
Smaller nerve
fiber
block
first
C
Dorsal root
Pain
++++
Postganglionic
++++
--Local anesthesia block all nerve fibers & not limited to loss of sensation .
Type C& B block first (fiber of pain) then block delta (small type A fiber- fiber of
sensation ) then block Alfa-beta –gamma (fiber of motor function) .
-- fiber of small diameter block firstly , non-myelinated fiber block after myelinated
one .

Pharmacology lecture
CNS
3
rd
Stage
4
Routes of administration of local anesthesia ;-
1- topically application route .
2-injection in the vicinity of the peripheral nerve ending & major nerve trunk
(infiltration)
3-instillatiuon within epidural or sub-arachenoid space surrounding spinal cord .
4-intravenously in case of anesthesia of arm (for less than 45 minutes) into distal vein+
block circulation of arm by tourniquet .
so their indication according to their duration of action can be classified into :-
1- short acting local anesthesia include procaine & chloro-procaine .
2-intermediate acting local anesthesia include lidocaine , mepivacaine , prilocaine .
3- long acting local anesthesia include tetracaine , bupivacaine , etidocaine ,
ropivacaine.
---- short & intermediate acting one can be prolong their duration of action by adding
vaso-constrictor agents like epinehprine or phenylephrine .
---- onset of action can be accelerated by using solution saturated with CO2 that
increase intracellular acidosis that increase intracellular accumulation of cationic local
anesthesia agent .
pregnancy increase susceptibility to local anesthesia . surface or topical local
anesthesia use foe eye , nose , throat , ear .
The toxicity of local anesthesia :- it occur when it absorbed into the circulation
including :-
1-CNS at low dose can cause sleepiness , light headache , visual & auditory
disturbance , restlessness . while on high dose cause nystagmus + muscle twitching .
---Other tonic-clonic convulsion causing CNS depression causing death to prevent
such state of fit by give the patient adequate dose if high dose required pre-
medication with diazepam in dose 0.1-0.2 mg/kg IV or treat the fit with short acting

Pharmacology lecture
CNS
3
rd
Stage
5
barbiturate 1-2 mg/kg IV or diazepam 0.1-0.2 mg/kg IV , muscle manifestation
treated by short ating neuromuscular blocking agent like succinylcholine 0.5-1 mg/kg
IV .
2- peripheral neurons system(neurotoxicity ) if high dose of local anesthesia was give
, chloro-procaine more neurotoxicity than the others local anesthetic agents .
3-CVS directly effects via their effect on cardiac & smooth muscle membrane while
indirect effects via autonomic nerves .
local anesthesia block sodium channels to cause depress abnormal cardiac pacemaker
activity , hypotension either due to arteriolar dilatation or depress strength of cardiac
contraction , CV-collapse & death occasionally occur on high dose , cocaine block
nor-epinephrine receptors that cause vaso-constriction & hypertension + arrhythmia ,
bupivacaine more CVS toxicity especially if give as IV than other local anesthesia
that lead to CV-collapse while ropivacaine of less CV toxicity due to their low affinity
to cardiac sodium channels .
4- on blood on large dose more than 10 mg/kg of prilocaine cause accumulation of
toulidine (oxidizing agents ) that convert Hb in to met-Hb that cause cyanosis if be at
concentration of 3-5 mg /dL that can be treated with methylene blue or ascorbic acid
as IV ( both are reducing agents ) .
5-allergic reaction ester type metabolite into p-amino-benzoic acid (PABA) that may
cause allergic reaction in small % of the patients while amide type not metabolite into
PABA so rarely cause allergy .
=========================================================
DYCLONINE :- it is a topical local anesthetic agent used for oral - nasal - laryngeal
mucous membrane , respiratory mucosa , & for urinary tract , act by inhibiting the
conduction of the nerve impulses from sensory nerve , contra-indicated to be use for
eye , in case of sever shock . their adverse effects include cutaneous lesion , urticaria
, edema , contact dermatitis , anaphylactoid reaction , burning sting , tenderness ,
sloughing . their dose for oral mild & pharyngeal anesthesia in adult one 2mg or 3 mg
lozenge dissolved slowly in the mouth to be repeated every 2 hours if needed or as
0.1% solution ,sprayed into the mouth up to four times & swallowed or swished in
the mouth & expectorated . in child more than 3 years 1.2 mg lozenge dissolved slowly

Pharmacology lecture
CNS
3
rd
Stage
6
in the mouth to be repeated every 2 hours if needed or as 0.1% solution ,sprayed into
the mouth up to four times & swallowed or swished in the mouth & expectorated .
for mucous membrane anesthesia 0.5-1% solution applied topically to suppress the
gag reflex & to relief pain associated with the oral or anogenital lesion or applied to
provide anesthesia for endoscopic procedure of mouth , larynx ,trachea , esophagus ,
urethra , maximum dose 30 ml (300 mg ) .
========================================================== .
PRAMOXINE :- used together with the hydrocortisone as topical preparation to
treated inflamed & itching skin as in case of hemorrhoid irritation , the role of
pramoxine is to relief pain & itching , such combination use 3-4 times daily , available
in form of cream of 0.5, 1 or 2.5 % of hydrocortisone acetate + 1 % of pramoxine
hydrochloride .
============================================================
GENERAL ANESTHESIA :- which is attempt to suppress the pain of surgical
processes , include many stages from analgesia , amnesia , loss of consciousness ,
inhibit of sensory & autonomic reflexes & skeletal muscle relaxation .
Ideal properties of such agents are to be of smoothing –rapidly inducing agent , rapidly
recover , wide margin of safety , devoid adverse effects .
Their types include inhaled general anesthesia & intravenous general anesthesia .
INHALED GENERAL ANESTHESIA :-
Include two type :-
1-old inhaled anesthesia like a- ether b- cyclopropane no longer used nowadays
because of potential inflammability c- chloroform of organ toxicity .
2-newer inhaled anesthesia like nitric oxide(gaseous ) , [ halothane , enflurane ,
isoflurane , desflurane , sevoflurane , methoxyflurane ] as volatile liquids .
the depth of anesthesia directly related with their concentration of the agent in the
CNS . concentration of the agent in the brain depend on

Pharmacology lecture
CNS
3
rd
Stage
7
1-anesthetic agent solubility properties , it is important in transfer the agent between
lung & blood , increase solubility increase onset of induction of anesthesia .
2- its concentration in the inspire air increase the concentration increase onset of
anesthesia induction by increase transfer of agent into blood .
3- pulmonary ventilation rate , anesthetic gas tension in arterial blood directly related
with the rate & depth of ventilation , so increase ventilation significantly increase
agent gas tension in case of moderate & high solubility agent but only slightly
affecting low solubility agent .
4- pulmonary blood flow , increase pulmonary blood flow increase exposure of large
volume blood to the anesthetic agent that cause slow rate of rising of arterial tension
in moderate to high solubility , while decrease pulmonary blood flow increase rate of
rising of arterial tension , in shock state both decrease cardiac output + increase
ventilation that lead decrease pulmonary blood flow that end in acceleration in onset
of induction of anesthesia .
5- concentration gradient of anesthesia between arterial & mixed venous blood highly
solubility agent in tissues causing very low concentration in venous blood that cause
a slowly achieving arterial equilibrium .,
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- .
so agent of insolubility or low solubility in blood & brain causing faster rate of
removal than soluble one nitric oxide , desflurane , sevoflurane eliminate more than
halothane .
----duration of exposure to the anesthetic agent affecting recovery especially in
moderate to high solubility agents like methoxyflurane that accumulate in tissues like
skin, muscle , fat . while when the exposure is short make recovery rapid & vice versa
. lung is the main route of elimination of inhaled anesthesia & to less extend liver &
other organ via enzyme metabolism .
Oxidative metabolism of inhaled anesthesia include :-
Halothane into trifluoroacetic acid with the releasing of chloride ion & bromide ion
, but under low O2 into chlorotrihlouroethyle free radical that capable to react with
the hepatic component . isoflurane & desflurane least metabolites give trace amount

Pharmacology lecture
CNS
3
rd
Stage
8
of trifluoroacetic acid to appear in the urine ,. Enflurane & sevoflurane result in
formation of chloride ions , in addition sevoflurane by their react with CO2 that
absorbed via anesthetic machine to form compound A the last if absorbed in high
concentration may cause damage of kidney . 70 % of absorbed methoxyflurane result
in formation of fluoride ion that is nephrotoxic . .the extent of the metabolism of
inhaled anesthesia are methoxyflurane < halothane
< enflurane
< sevoflurane
<
isoflurane
< desflurane
< nitric oxide .
MECHANISM OF ACTION :-
1- directly activate GABA
A
receptor via binding to specific sites on the Trans-
membrane domains of both alfa & beta subunits .
2- it cause depress spontaneous & evoked activity of neurons by non-specific
interaction of these agents with the lipid matrix of nerve membrane that cause
secondary changes in ions flux that cause membrane hyper polarization (an inhibitors
action) , by activation of potassium channels( in the CNS it linked to several
neurotransmitter like Ach, dopamine , serotonin , nor-epinephrine ) + decrease
duration of opening of nicotinic receptors activated cation channels all decrease
excitatory effects of Ach at cholinergic synapses .
ORGAN SYSTEM EFFECTS :-
1-CVS effects :-
halothane , enflurane (both decrease blood pressure by decrease cardiac output eith
little changein peripheral resistance ), desflurane , sevoflurane , isoflurane ( all cause
decrease blood pressure by decrease peripheral resistance with little change in cardiac
output . halothane decrease heart rate via vagus stimulation , while enflurane +
isoflurane increase heart rate , methoxyflurane of little effect on heart rate .
2- respiratory system effects :-
all inhaled anesthesia except nitric oxide decrease tidal volume & increase
respiratory rate . all cause respiratory depressant especially enflurane & isoflurane .
all decrease mucocilliary function in airway causing pooling of mucus then cause
atelectasis & respiratory infection . . all are broncho-dilator used in treatment of status
asthmaticus . all cause airway irritation that cause provoke coughing or breath holding

Pharmacology lecture
CNS
3
rd
Stage
9
3- on the brain :-
cause a reduction in the metabolic rate & increase cerebral blood flow by decreasing
vascular resistance this is a critical in case of increasing intra-cranial pressure .
4- on kidney effect :-
decrease gromular filtration rate GFR , increase renal vascular resistance , all may
cause neohrotoxicity .
5- on liver :-
decrease hepatic blood flow + hepatotoxicity .
6- on uterine smooth muscles :-
cause relaxation of benefit for intra-uterine fetal manipulation at delivery .
THE TOXICITY of inhaled anesthesia :-
1- a- acute toxicity [ hepatotoxicity , nephrotoxicity , malignant hyperthermia ] , b-
chronic toxicity like [ mutagencity especially in the old form , carcinogenicity by
increase cancer rate in those work in operation room , on reproduction increase risk
of abortion , hematotoxicity that nitric oxide on prolong exposure decrease methionin
synthesis activity that cause megaloblastic anemia ] .
CLINICAL USES of inhaled anesthesia :-
Rarely use alone , use in combination with IV anesthesia to produce balance
anesthesia .
===========================================================
INTRAVENOUS INHALED ANESTHESIA :-
Such type either use alone or in combination with the other include :-
According to their types classified into :-
1-Barbiturate like thiopental or methohexital .
2-benzodiazepam like diazepam or midazolam .

Pharmacology lecture
CNS
3
rd
Stage
10
3-opioid analgesia like morphine , fentanyl , sulfentanil , alfentanil , remifentanil .
4-propofol .
5- ketamine that produce dissociation anesthesia .
6-miscellaneous include droperidol , etomidate , dexmetomidate .
according to their onset of action & recovery classified in to :-
1- slow onset of action + slow recovery like midazolam ?& fentanyl .
2- moderately of onset & recovery like ketamine .
3- rapid onset & recovery like propofol , etomidate , while thiopental only slow
recovery if give as infusion .
INTRAVENOUS ANESTHETIC AGENTS :-
1- ultra-short acting BARBITURATE :-
the most important example is thiopental for anesthetic induction in combination
with inhaled type . after IV given cause rapidly cross BBB within 1 minute cause
plasma brain equilibrium , because of high lipid solubility + rapidly diffuse out of the
brain & other high vascular tissues & redistribution into fat-muscles all make it of
short acting agent . it is metabolite in the liver , only 1 % excreted as unchanged in
the urine , on large dose decrease blood pressure , stoke volume & cardiac output . it
is respiratory depressant agent that decrease respiratory center sensitivity to CO2 ,
cause a reduction in both cerebral metabolism rate & their blood flow that apply
desirable effect to be use in patient with cerebral swelling than inhaled type , it cause
a reduction in hepatic blood flow & GFR .
2- benzodiazepines :-
sedative hypnotic agents like diazepam , lorazepam both lipid soluble , midazolam a
water soluble agent , all use in anesthetic procedure . , this form of slower induction
rate than barbiturate , IV benzodiazepnes cause prolong post-operative anesthetic
recovery period that is undesirable + it cause high incidence of amnesia which is
useful effect, midazolam IV 15-60 minutes before induction of anesthesia , useful as
pre-midication , & intra-operative sedation that cause balance anesthesia , their effect

Pharmacology lecture
CNS
3
rd
Stage
11
can be antagonist by using FLUMAZENIL that use for recovery from sedative effect
of IV benzodiazepines .
3- opioid analgesic anesthesia :-
used in high dose for either major operation or for cardiac surgery like morphine in
dose of 1-3 mg/kg IV or fentanyl 50-100 mg/kg IV . congeners of fentanyl like
sufentanil , alfentanil , remifentanil also used . IV opioid increase chest wall rigidity
so it impair ventilation . it is used as primary anesthetic agent or as pre-medication or
adjunct to inhaled anesthesia . alfentanil & remifentanil use as anesthetic induction
agents that is of rapid onset of action . remifentanil of short duration of action because
it rapidly metabolite via blood esterase in blood , muscles , it use in ambulatory
surgery . fentanyl + droperidol produce analgesia + amnesia . . may used as epidural
route .
4- propofol :-
an important IV anesthetic agent , of rapid onset of action & rapid recovery , patient
with it feel better post-operatively than other IV types , their post-operative vomiting
is uncommon , used for induction of anesthesia – maintenance of anesthesia .
extensively used since it not cause cumulative effects . it cause prolong sedative
effects . their half-life 2-8 minutes , rapidly metabolite in liver 10 times faster than
thiopental . it decrease blood pressure by decreasing peripheral resistance . apnea &
pain at site of injection may occur . it may cause tremor . it is very cost .
5-etomidate :-
it is a carboxylated imidazole derivative that use for balance anesthesia & for
induction of anesthesia . it consider as the least one causing CV & respiratory
depression effects than other types . cause loss of conscious within seconds . it cause
slight hypotension . pre-medication with opioid should done because it is of no
analgesic effect . their recovery times between 3-5 minutes . on prolong use may cause
oliguria , hypotension , electrolytes imbalance . hydrolyze in both liver & plasma into
inactive metabolites . it cause high incidence of [nausea , vomiting , pain at site of
injection , myoclonus , adrenocortical suppression ] . it is of biphasic distribution
curve at 3 minute & 29 minutes to redistribution from the brain into other highly blood
perfusion tissues that make it of short duration of action .

Pharmacology lecture
CNS
3
rd
Stage
12
6- ketamine :-
Produce what called DISSCIATION anesthesia [ amnesia , analgesia , but no loss of
consciousness ] . it is arylcyclohexylamine . it is of psychoactive property . act via
blockade of membrane effect of excitatory neuro- transmitter glutamic acid at
NMDA(N-methyl-D- Aspartate ) receptor subtype . it is highly lipophilic agent of
rapidly distribution into highly vascular organ . it is of both urinary & biliary excretion
. their metabolism in the liver . it is the only one within the all that cause CV
stimulation that increase heart rate , cardiac output & blood pressure . within 2-4
minutes after IV injection , their stimulation via 1- causing excitation of central
sympathetic nervous system , / 2- inhibit reuptake of epinephrine & nor-epinephrine
at sympathetic nerve terminal . it cause increasing of cerebral blood floe , increase O2
consumption , increase intra-cranial pressure all make it not to be use in patient with
elevated intra-cranial pressure like inhaled anesthesia . following anesthesia it cause
emergency phenomena [disorientation , sensory+ perception illusions , vivid dreams
] . such can be reduce by IV 0.2-0.3 mg/kg diazepam before injection of ketamine .
used in shock patients since it cause CV stimulation . used also for out patients &
children undergo painful procedure like change of dressing .
7-droperidol :-
it is a parenteral sedative hypnotic agent .it is a butyrophenone derivatives structurally
similar to haloperidol . it is used as an induction agent & as adjunct medication during
general anesthesia . also it provides neuroleptanalgesia when combine with opiate
analgesia . it is also of anti-emetic property make it useful in treatment of nausea &
vomiting induce by either anesthetic agents or anti-neoplastic agent like cisplatin .
------It mode of action include a simillsr effect to that of phenothiazine , it antagonist
dopamine mediated neuro-transmission at the synapse as well as block postsynaptic
dopamine receptor sites , it is of extra-pyramidal effect , it also antagonist alfa-
adrenergic receptors that decrease the sensitivity to epinephrine .
their effects is seen within 3-10 minutes after IV or IM injection their sedative &
tranquilizing effect last for 2-4 hours while alteration of consciousness persist up to
12 hours . it cross BBB , appear in CSF , cross placenta . it metabolize in the liver to
4- fluorophenylacetic acid that conjugated with glycine other metabolite include 4-

Pharmacology lecture
CNS
3
rd
Stage
13
hydroxypiperidine + benzimidazolone . the drug & their metabolites excreted in both
urine & feces , 10 % of administrated drug excreted unchanged in the urine .
------their indication in anesthesia include [induction of anesthesia(in a dose 0.25 mg
/kg IV ) , regional anesthesia(in a dose 2.5-5 mg IV ) , general anesthesia
maintenance(in a dose 1.25-2.5 mg IV ) ] in addition it indicated for treatment of
nausea , vomiting , anxiety & agitation in a dose of 2.5-10 mg IM 30-60 minutes
before induction of anesthesia in adult , in children 0.088-0.165 mg /kg IM or IV .
----it is contraindicated in [breast feeding , cardiac disease , children , elderly , renal
impairment , prostatic hypertrophy , spinal anesthesia , seizure disorder , hepatic
disease , hypotension , pregnancy , glaucoma] .
----their adverse effects [ akathisia , bronchospasm , delirium , hallucination ,
hypotension , laryngospasm , tremor , sinus tachycardia , parkinsonism , depression ,
dizziness , dystonia , drowsiness ] .
